Zhejiang Expwy S8 sign no name.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an
 After the collapse of the Tang dynasty in 907, the entire area of what is now Zhejiang fell under the control of the kingdom Wuyue established by King Qian Liu, who selected
After the collapse of the Tang dynasty in 907, the entire area of what is now Zhejiang fell under the control of the kingdom Wuyue established by King Qian Liu, who selected
 The Song dynasty re-established unity around 960. Under the Song, the prosperity of South China began to overtake that of North China. After the north was lost to the Jurchen people, Jurchen Jurchen Jin, Jin dynasty in 1127 following the Jingkang Incident, Hangzhou became the capital of the Song dynasty under the name Hangzhou, Lin'an, which was renowned for its prosperity and beauty, it was suspected to have been the largest city in the world at the time.
From then on, northern Zhejiang and neighboring southern Jiangsu have been synonymous with luxury and opulence in Chinese culture. The Mongols, Mongol conquest and the establishment of the Yuan dynasty in 1279 ended Hangzhou's political clout, but its economy continued to prosper. The famous traveler Marco Polo visited the city, which he called "Kinsay" (after the Chinese ''Jingshi'', meaning "Capital City") claiming it was "the finest and noblest city in the world."
Greenware ceramics made from celadon had been made in the area since the 3rd-century Sima Jin, Jin dynasty, but it returned to prominence—particularly in Longquan—during the Southern Song and Yuan. Longquan greenware is characterized by a thick unctuous glaze of a particular bluish-green tint over an otherwise undecorated light-grey porcellaneous body that is delicately potted. Yuan Longquan celadons feature a thinner, greener glaze on larger vessels with decoration and shapes derived from Middle Eastern ceramic and metalwares. These were produced in large quantities for the Chinese export trade to Southeast Asia, the Middle East and (during the Ming dynasty, Ming) Europe. By the Ming, however, production was notably deficient in quality. It is in this period that the Longquan kilns declined, to be eventually replaced in popularity and ceramic production by the kilns of Jingdezhen in
The Song dynasty re-established unity around 960. Under the Song, the prosperity of South China began to overtake that of North China. After the north was lost to the Jurchen people, Jurchen Jurchen Jin, Jin dynasty in 1127 following the Jingkang Incident, Hangzhou became the capital of the Song dynasty under the name Hangzhou, Lin'an, which was renowned for its prosperity and beauty, it was suspected to have been the largest city in the world at the time.
From then on, northern Zhejiang and neighboring southern Jiangsu have been synonymous with luxury and opulence in Chinese culture. The Mongols, Mongol conquest and the establishment of the Yuan dynasty in 1279 ended Hangzhou's political clout, but its economy continued to prosper. The famous traveler Marco Polo visited the city, which he called "Kinsay" (after the Chinese ''Jingshi'', meaning "Capital City") claiming it was "the finest and noblest city in the world."
Greenware ceramics made from celadon had been made in the area since the 3rd-century Sima Jin, Jin dynasty, but it returned to prominence—particularly in Longquan—during the Southern Song and Yuan. Longquan greenware is characterized by a thick unctuous glaze of a particular bluish-green tint over an otherwise undecorated light-grey porcellaneous body that is delicately potted. Yuan Longquan celadons feature a thinner, greener glaze on larger vessels with decoration and shapes derived from Middle Eastern ceramic and metalwares. These were produced in large quantities for the Chinese export trade to Southeast Asia, the Middle East and (during the Ming dynasty, Ming) Europe. By the Ming, however, production was notably deficient in quality. It is in this period that the Longquan kilns declined, to be eventually replaced in popularity and ceramic production by the kilns of Jingdezhen in
 Zhejiang was finally Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty, conquered by the Mongols in the late 13th century who later established the short lived Yuan dynasty. Zhejiang became part of the much larger Jiangzhe Province.
The
Zhejiang was finally Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty, conquered by the Mongols in the late 13th century who later established the short lived Yuan dynasty. Zhejiang became part of the much larger Jiangzhe Province.
The
 "In 1727 the to-min or 'idle people' of Cheh Kiang province (a Ningbo, Ningpo name still existing), the yoh-hu or 'music people' of Shanxi, Shanxi province, the si-min or 'small people' of Kiang Su (Jiangsu) province and the Tanka people or 'egg-people' of Guangdong, Canton (to this day the boat population there), were all freed from their social disabilities and allowed to count as free men." "Cheh Kiang" is another romanization for Zhejiang. The Duomin () are a caste of Untouchability, outcasts in this province.
During the First Opium War, the British navy defeated Eight Banners forces at
"In 1727 the to-min or 'idle people' of Cheh Kiang province (a Ningbo, Ningpo name still existing), the yoh-hu or 'music people' of Shanxi, Shanxi province, the si-min or 'small people' of Kiang Su (Jiangsu) province and the Tanka people or 'egg-people' of Guangdong, Canton (to this day the boat population there), were all freed from their social disabilities and allowed to count as free men." "Cheh Kiang" is another romanization for Zhejiang. The Duomin () are a caste of Untouchability, outcasts in this province.
During the First Opium War, the British navy defeated Eight Banners forces at


 Zhejiang is one of the richest and most developed provinces in China. As of 2020, Zhejiang's nominal GDP was United States dollar, US$1.01 trillion, ranking between the Netherlands and Indonesia with a GDP of US$ 913 billion and US$ 1.06 trillion respectively, the List of countries by GDP (nominal), 16th and 17th larges
Zhejiang is one of the richest and most developed provinces in China. As of 2020, Zhejiang's nominal GDP was United States dollar, US$1.01 trillion, ranking between the Netherlands and Indonesia with a GDP of US$ 913 billion and US$ 1.06 trillion respectively, the List of countries by GDP (nominal), 16th and 17th larges
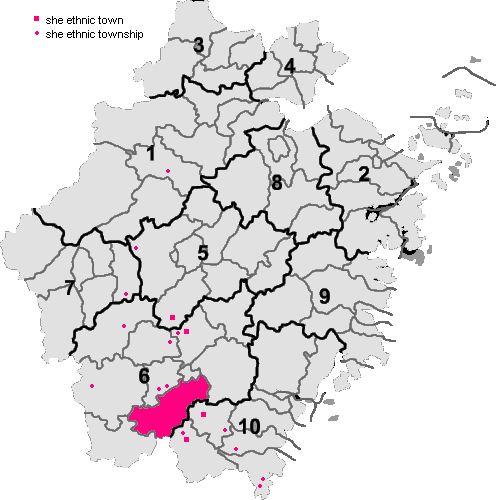 Han Chinese make up the vast majority of the population and the largest Han subgroup are the Wuyue people, speakers of Wu varieties of Chinese. There are also 400,000 members of List of Chinese ethnic groups, ethnic minorities, including approximately 200,000 She people and approximately 20,000 Hui Chinese. Jingning She Autonomous County in Lishui, Zhejiang, Lishui is the only She autonomous county in China.
Han Chinese make up the vast majority of the population and the largest Han subgroup are the Wuyue people, speakers of Wu varieties of Chinese. There are also 400,000 members of List of Chinese ethnic groups, ethnic minorities, including approximately 200,000 She people and approximately 20,000 Hui Chinese. Jingning She Autonomous County in Lishui, Zhejiang, Lishui is the only She autonomous county in China.

 Longjing tea (also called dragon well tea), originating in Hangzhou, is one of the most prestigious, if not ''the'' most prestigious Chinese tea. Hangzhou is also renowned for its silk umbrellas and hand fans. Zhejiang cuisine (itself subdivided into many traditions, including Hangzhou cuisine) is one of the eight great traditions of Chinese cuisine.
Longjing tea (also called dragon well tea), originating in Hangzhou, is one of the most prestigious, if not ''the'' most prestigious Chinese tea. Hangzhou is also renowned for its silk umbrellas and hand fans. Zhejiang cuisine (itself subdivided into many traditions, including Hangzhou cuisine) is one of the eight great traditions of Chinese cuisine.
 Tourist destinations in Zhejiang include:
* Baoguo Temple (Ningbo), Baoguo Temple, one of the oldest intact wooden structures in Southern China, north of Ningbo.
* Mount Putuo, one of the most noted Buddhist mountains in China. Chinese Buddhists associate it with Guan Yin.
* Qita Temple, Ningbo.
* Shaoxing, site of the Tomb of Yu the Great, Wuzhen and other waterway towns.
* The ancient capital of Hangzhou.
* Tiantai Mountain, Mount Tiantai, a mountain important to Zen Buddhism.
* West Lake, in Hangzhou.
* Yandangshan, a mountainous scenic area near Wenzhou.
* Qiandao Lake, lit. ''Thousand-island lake''.
* Guoqing Temple, founded in the Sui dynasty, the founding location of Tiantai Buddhism
* Mount Mogan, a scenic mountain an hour from Hangzhou with many pre-World War II villas built by foreigners, along with one of Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang compounds
* Zhejiang Museum of Natural History, in Hangzhou.
Tourist destinations in Zhejiang include:
* Baoguo Temple (Ningbo), Baoguo Temple, one of the oldest intact wooden structures in Southern China, north of Ningbo.
* Mount Putuo, one of the most noted Buddhist mountains in China. Chinese Buddhists associate it with Guan Yin.
* Qita Temple, Ningbo.
* Shaoxing, site of the Tomb of Yu the Great, Wuzhen and other waterway towns.
* The ancient capital of Hangzhou.
* Tiantai Mountain, Mount Tiantai, a mountain important to Zen Buddhism.
* West Lake, in Hangzhou.
* Yandangshan, a mountainous scenic area near Wenzhou.
* Qiandao Lake, lit. ''Thousand-island lake''.
* Guoqing Temple, founded in the Sui dynasty, the founding location of Tiantai Buddhism
* Mount Mogan, a scenic mountain an hour from Hangzhou with many pre-World War II villas built by foreigners, along with one of Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang compounds
* Zhejiang Museum of Natural History, in Hangzhou.
Economic profile of Zhejiang
at Hong Kong Trade Development Council, HKTDC
Zhejiang Government website
*
Complete Map of the Seven Coastal Provinces
from 1821 to 1850 * {{Authority control Zhejiang, Provinces of the People's Republic of China East China Yangtze River Delta Wu (region) States and territories established in 1368
eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
, coastal province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
, and other notable cities include Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
and Wenzhou
Wenzhou (pronounced ; Wenzhounese: Yuziou �y33–11 tɕiɤu33–32 ), historically known as Wenchow is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Zhejiang province in the People's Republic of China. Wenzhou is located at the extreme south east ...
. Zhejiang is bordered by Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its ca ...
and Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
to the north, Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River ...
to the northwest, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
to the west and Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
to the south. To the east is the East China Sea, beyond which lies the Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ōsumi, Tokara, Amami, Okinawa, and Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), with Yona ...
. The population of Zhejiang stands at 64.6 million, the 8th highest among China. It has been called 'the backbone of China' due to being a major driving force in the Chinese economy and being the birthplace of several notable persons, including the Chinese Nationalist leader Chiang Kai-shek and entrepreneur Jack Ma
Jack Ma Yun (; born 10 September 1964) is a Chinese business magnate, investor and philanthropist. He is the co-founder and former executive chairman of Alibaba Group, a multinational technology conglomerate. In addition, he co-founded Yunfen ...
. Zhejiang consists of 90 counties (incl. county-level cities and districts).
The area of Zhejiang was controlled by the Kingdom of Yue during the Spring and Autumn period. The Qin Empire
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), the ...
later annexed it in 222 BC. Under the late Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
and the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
that followed it, Zhejiang's ports became important centers of international trade. It was occupied by the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of Japan, 1947 constitu ...
during the Second Sino-Japanese war
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Th ...
and placed under the control of the Japanese puppet state known as the Reorganized National Government of China
The Wang Jingwei regime or the Wang Ching-wei regime is the common name of the Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China ( zh , t = 中華民國國民政府 , p = Zhōnghuá Mínguó Guómín Zhèngfǔ ), the government of the pup ...
. After Japan's defeat, Zhejiang's economy became stagnant under Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
's policies.
Nevertheless, after China's economic reform, Zhejiang has grown to be considered one of China's wealthiest provinces, ranking fourth in GDP nationally and fifth by GDP per capita, with a nominal GDP of United States dollar, US$1.01 trillion as of 2020, ranking between the Netherlands and Indonesia with a GDP of US$ 913 billion and US$ 1.06 trillion respectively, the List of countries by GDP (nominal), 16th and 17th largesHangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
marks the end of the Grand Canal (China), Grand Canal and lies on Hangzhou Bay on the north of Zhejiang, which separates Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
and Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
. The bay contains many small islands collectively called the Zhoushan Islands.
Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
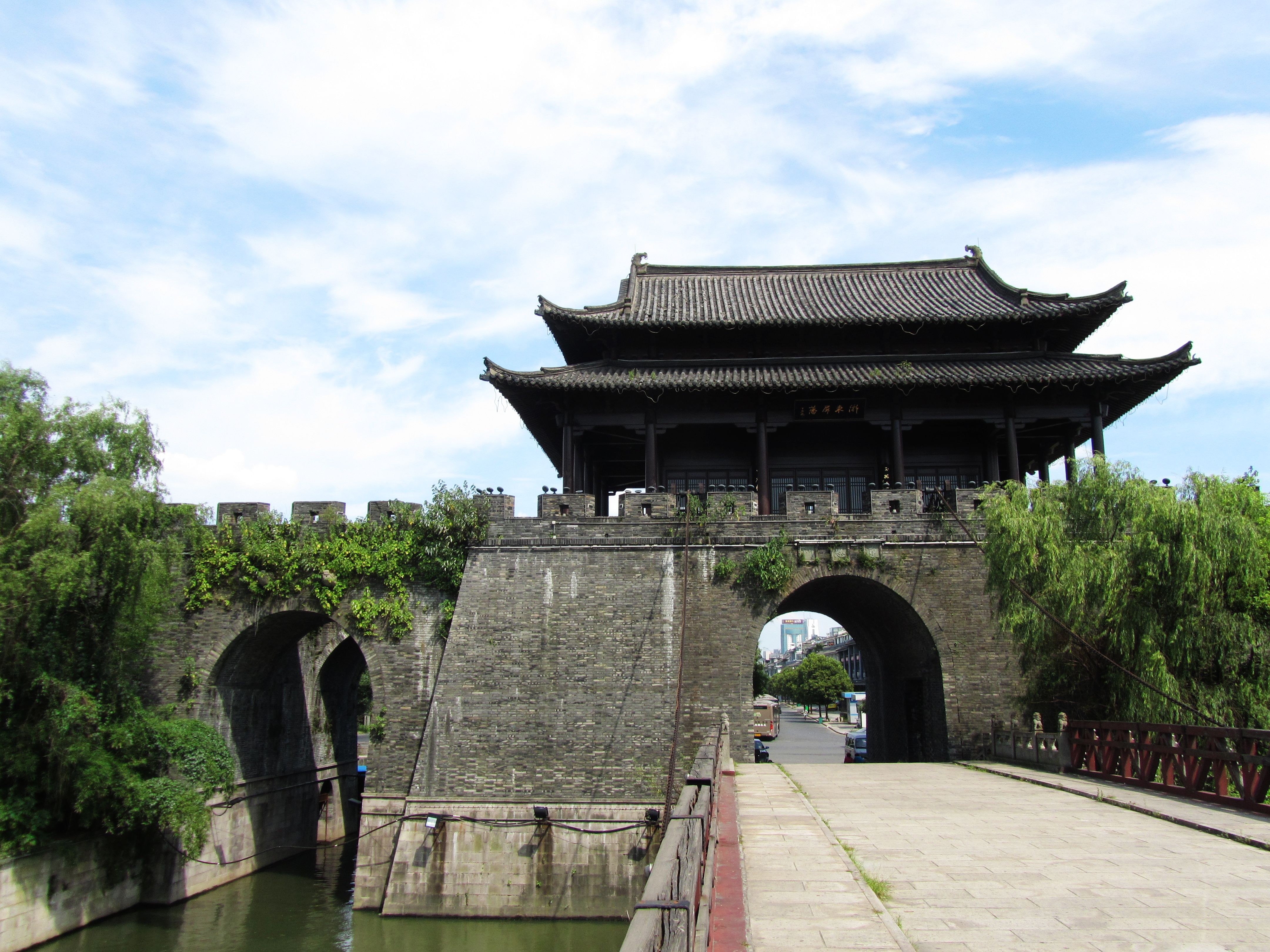
is a historically important city of China and is considered a Global city, World City with a "Beta+" classification according to Globalization and World Cities Research Network, GaWC. It includes the notable West Lake. Various varieties of Chinese are spoken in Zhejiang, the most prominent being Wu Chinese. Zhejiang is also one of China's leading provinces in research and education. As of 2022, two major cities in Zhejiang ranked in the world's top 200 cities (Hangzhou 19th and Ningbo 170th) by scientific research output, as tracked by Nature Index.
Etymology
The province's name derives from the Zhe River (), the former name of the Qiantang River which flows pastHangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
and whose mouth forms Hangzhou Bay. It is usually understood as meaning "Crooked" or "Bent River," from the meaning of Chinese language, Chinese , but is more likely a phono-semantic compound formed from adding (the "water" Chinese radical, radical used for river names) to phonetic (Pinyin ''zhé'' but reconstructed Old Chinese *''tet''), preserving a proto-Wu name of the local Yue (state), Yue, similar to Yuhang District, Yuhang, Mount Xianglu, Kuaiji and Yangtze, Jiang.
History
Prehistory
Kuahuqiao site, Kuahuqiao culture was an early Neolithic culture that flourished in theHangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
area in 6,000-5,000 BC.
Zhejiang was the site of the Chinese Neolithic, Neolithic cultures of the Hemudu culture, Hemudu (starting in 5500 BC) and Liangzhu culture, Liangzhu (starting in 3400 BC).
Ancient history
The area of modern Zhejiang was outside the major sphere of influence of Shang dynasty, Shang civilization during the second millennium BC. Instead, this area was populated by peoples collectively known as Dongyue. The Yue (state), kingdom of Yue began to appear in the chronicles and records written during the Spring and Autumn period. According to the chronicles, the kingdom of Yue was in Northern Zhejiang. Shiji claims that its leaders were descended from the Xia dynasty, Xia founder Yu the Great. The "Song of the Yue Boatman" () was transliterated into Chinese and recorded by authors in North China or inland China of Hebei and Henan around 528 BC. The song shows that the Yue people spoke Old Yue language, a language that was mutually unintelligible with the dialects spoken in north and inland China. The Sword of Goujian bears bird-worm seal script. Yuenü () was a swordswoman from the state of Yue. To check the growth of the Wu (state), kingdom of Wu, Chu (state), Chu pursued a policy of strengthening Yue. Under Goujian, King Goujian, Yue recovered from its early reverses and fully annexed the lands of its rival in . The Yue kings then moved their capital center from their original home around Mount Kuaiji in present-day Shaoxing to the former Wu capital at present-day Suzhou. With no southern power to turn against Yue, Chu opposed it directly and, in 333 BC, succeeded in destroying it. Yue's former lands were annexed by the Qin Empire in 222 BC and organized into a commandery (China), commandery named for Kuaiji in Zhejiang but initially headquartered in Wu County, Wu inJiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its ca ...
.
Han and the Three Kingdoms
Kuaiji Commandery was the initial power base for Xiang Liang and Xiang Yu's rebellion against the Qin Empire which initially succeeded in restoring the kingdom of Chu but Chu-Han contention, eventually fell to the Han dynasty, Han. Under the Eastern Han, Later Han, control of the area returned to the settlement below Mount Kuaiji but authority over the Minyue hinterland was nominal at best and its Yue inhabitants largely retained their own political and social structures. At the beginning of the Three Kingdoms era (220–280 CE), Zhejiang was home to the warlords Yan Baihu and Wang Lang (Cao Wei), Wang Lang prior to their defeat by Sun Ce and Sun Quan, who eventually established the Eastern Wu, Kingdom of Wu. Despite the removal of their court from Kuaiji to Jiankang, Jianye (present-day Nanjing) and they continued development of the region and benefitted from influxes of refugees fleeing the turmoil in northern China. Industrial kilns were established and trade reached as far as Manchuria and Kingdom of Funan, Funan (South Vietnam). Zhejiang was part of the Eastern Wu, Wu during the Three Kingdoms. Wu (229–280), commonly known as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu, had been the economically most developed state among the Three Kingdoms (220–280 CE). The historical novel Romance of the Three Kingdoms records that Zhejiang had the best-equipped, strong navy force. The story depicts how the states of Wei (state), Wei () and Shu (state), Shu (), lack of material resources, avoided direct confrontation with the Wu. In armed military conflicts with Wu, the two states relied intensively on tactics of camouflage and deception to steal Wu's military resources including arrows and bows.Six Dynasties
Despite the continuing prominence of Nanjing (then known as Jiankang), the settlement of Qiantang, the former name ofHangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
, remained one of the three major metropolitan centers in the south to provide major tax revenue to the imperial centers in the north China. The other two centers in the south were Jiankang and Chengdu. In 589, Qiantang was raised in status and renamed Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
.
Following the fall of Eastern Wu, Wu and the turmoil of the Wu Hu uprising against the Jin dynasty (266–420), most of elite Chinese families had collaborated with the non-Chinese rulers and military conquerors in the north. Some may have lost social privilege and took refuge in areas south of the Yangtze River. Some of the Chinese refugees from North China might have resided in areas near Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
. For example, the clan of Zhuge Liang (181–234), a chancellor of the state of Shu Han from Central Plain (China), Central Plain in north China during the Three Kingdoms period, gathered together at the suburb of Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
, forming an exclusive, closed village Zhuge Village (Zhege Cun), consisting of villagers all with family name "Zhuge." The village has intentionally isolated itself from the surrounding communities for centuries to this day and only recently came to be known in public. It suggests that a small number of powerful, elite Chinese refugees from the Central Plain (China), Central Plain might have taken refuge south of the Yangtze River. However, considering the mountainous geography and relative lack of agrarian lands in Zhejiang, most of these refugees might have resided in some areas in South China beyond Zhejiang, where fertile agrarian lands and metropolitan resources were available, mainly Southern Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its ca ...
, Eastern Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
, Hunan, Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River ...
and provinces where less cohesive, organized regional governments had been in place. Metropolitan areas of Sichuan was another hub for refugees, given that the state of Shu (state), Shu had long been founded and ruled by political and military elites from the Central Plain and North China. Some refugees from North China might have found residence in South China depending on their social status and military power in the north. The Eastern Jin, rump Jin state or the Southern dynasties vied against some elite Chinese from the Central Plain (China), Central Plain and south of the Yangtze River.
Sui and Tang eras
Zhejiang, as the heartland of the Jiangnan (Yangtze River Delta), remained the wealthiest area during the Six Dynasties (220 or 222–589), Sui and Tang. After being incorporated into the Sui dynasty, its economic richness was used for the Sui dynasty's ambitions to expand north and south, particularly into Goguryeo–Sui War, Korea and Vietnam. The plan led the Sui dynasty to restore and expand the network which became the Grand Canal of China. The Canal regularly transported grains and resources from Zhejiang, through its metropolitan center Hangzhou (and its hinterland along both the Zhe River and the shores of Hangzhou Bay) and from Suzhou and thence to the North China Plain. The débâcle of the Korean war led to Sui's overthrow by the Tang dynasty, Tang, who then presided over a centuries-long golden age for the country. Zhejiang was an important economic center of the empire's Jiangnan East Circuit and was considered particularly prosperous. Throughout the Tang dynasty, The Grand Canal had remained effective, transporting grains and material resources to North China plain and metropolitan centers of the empire. As the Tang dynasty disintegrated, Zhejiang constituted most of the territory of the regional kingdom of Wuyue.Wuyue era
 After the collapse of the Tang dynasty in 907, the entire area of what is now Zhejiang fell under the control of the kingdom Wuyue established by King Qian Liu, who selected
After the collapse of the Tang dynasty in 907, the entire area of what is now Zhejiang fell under the control of the kingdom Wuyue established by King Qian Liu, who selected Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
(a city in the modern day area of Zhejiang) as his kingdom's capital. Despite being under Wuyue rule for a relatively short period of time, Zhejiang underwent a long period of financial and cultural prosperity which continued even after the kingdom fell.
After Wuyue was conquered during the reunification of China, many shrines were erected across the former territories of Wuyue, mainly in Zhejiang, where the kings of Wuyue were memorialised, and sometimes, worshipped as being able to dictate weather and agriculture. Many of these shrines, known as "Shrine of the Qian King" or "Temple to the Qian King," still remain today, with the most popularly visited example being that near West Lake in Hangzhou.
China's province of Zhejiang during the 940s was also the place of origin of the Hu (surname), Hú family (Hồ in Vietnamese) from which the founder of the Hồ Dynasty who ruled Vietnam, Emperor Hồ Quý Ly, came from.
Song era
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
.
Yuan and Ming eras
 Zhejiang was finally Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty, conquered by the Mongols in the late 13th century who later established the short lived Yuan dynasty. Zhejiang became part of the much larger Jiangzhe Province.
The
Zhejiang was finally Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty, conquered by the Mongols in the late 13th century who later established the short lived Yuan dynasty. Zhejiang became part of the much larger Jiangzhe Province.
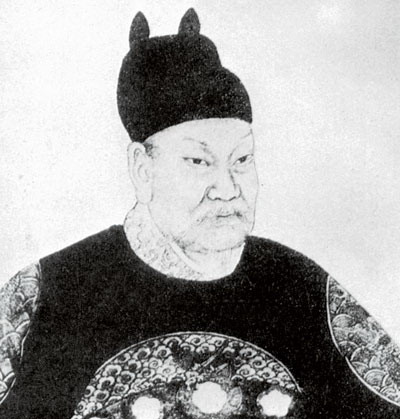
The Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
, which drove out the Mongols in 1368, finally established the present day province of Zhejiang with its borders having little changes since this establishment.
As in other coastal provinces, number of fortresses were constructed along the Zhejiang coast during the early Ming to defend the land against wokou, pirate incursions. Some of them have been preserved or restored, such as Pucheng in the south of the province (Cangnan County).
Qing era
Under the late Ming dynasty and theQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
that followed it, Zhejiang's ports were important centers of international trade.
Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
and Dinghai. Under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking, signed in 1843, Ningbo became one of the five Chinese treaty ports opened to virtually unrestricted foreign trade. Much of Zhejiang came under the control of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom during the Taiping Rebellion, which resulted in a considerable loss of life in the north-western and central parts of the province, sparing the rest of Zhejiang from the disastrous depopulation that occurred. In 1876, Wenzhou
Wenzhou (pronounced ; Wenzhounese: Yuziou �y33–11 tɕiɤu33–32 ), historically known as Wenchow is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Zhejiang province in the People's Republic of China. Wenzhou is located at the extreme south east ...
became Zhejiang's second treaty port. Lower Yangtze Mandarin, Jianghuai Mandarin speakers later came to settle in these depopulated regions of northern Zhejiang.
Republican era
During the Second Sino-Japanese War, which led into World War II, much of Zhejiang was occupied by Japan and placed under the control of the Japanese puppet state known as the Reorganized National Government of China. Following the Doolittle Raid, most of the B-25 American crews that came down in China eventually made it to safety with the help of Chinese civilians and soldiers. The Chinese people who helped them, however, paid dearly for sheltering the Americans. The Imperial Japanese Army began the Zhejiang-Jiangxi campaign, Zhejiang-Jiangxi Campaign to intimidate the Chinese out of helping downed American airmen. Imperial Japanese forces killed an estimated 250,000 Chinese civilians from the area of Hangzhou to Nanchang and also Zhuzhou while searching for Doolittle's men.People's Republic era
After the People's Republic of China took control of Mainland China in 1949, the Taiwan, Republic of China government based in Taiwan continued to control the Dachen Islands off the coast of Zhejiang until 1955, even establishing a rival Zhejiang provincial government there. During the Cultural Revolution (1966–76), Zhejiang was in chaos and disunity and its economy was stagnant, especially during the high tide (1966–69) of the revolution. The agricultural policy favoring grain production at the expense of industrial and cash crops intensified economic hardships in the province. Mao's self-reliance policy and the reduction in maritime trade cut off the lifelines of the port cities of Ningbo and Wenzhou. While Mao invested heavily in railroads in interior China, no major railroads were built in South Zhejiang, where transportation remained poor. Zhejiang benefited less from central government investment than some other provinces due to its lack of natural resources, a location vulnerable to potential flooding from the sea and an economic base at the national average. Zhejiang, however, has been an epicenter of capitalist development in China and has led the nation in the development of a market economy and private enterprises. Northeast Zhejiang, as part of the Yangtze Delta, is flat, more developed and industrial.Geography
Zhejiang consists mostly of hills, which account for about 70% of its total area. Altitudes tend to be the highest to the south and west and the highest peak of the province, Huangmaojian Peak (), is located there. Other prominent mountains include Mount Yandang, Mounts Yandang, Mount Tianmu, Tianmu, Mount Tiantai (Zhejiang), Tiantai and Mount Mogan, Mogan, which reach altitudes of . Valleys and plains are found along the coastline and rivers. The north of the province lies just south of the Yangtze Delta and consists of plains around the cities of Hangzhou, Jiaxing and Huzhou, where the Grand Canal of China enters from the northern border to end at Hangzhou. Another relatively flat area is found along the Qu River around the cities of Quzhou and Jinhua. Major rivers include the Qiantang River, Qiangtang and Ou River, China, Ou Rivers. Most rivers carve out valleys in the highlands, with plenty of rapids and other features associated with such topography. Well-known lakes include the West Lake of Hangzhou and the South Lake, Jiaxing, South Lake of Jiaxing. There are over three thousand islands along the rugged coastline of Zhejiang. The largest, Zhoushan Island, is Mainland China's third largest island, after Hainan and Chongming Island, Chongming. There are also many bays, of which Hangzhou Bay is the largest. Zhejiang has a humid subtropical climate with four distinct seasons. Spring starts in March and is rainy with changeable weather. Summer, from June to September is long, hot, rainy and humid. Fall is generally dry, warm and sunny. Winters are short but cold except in the far south. Average annual temperature is around , average January temperature is around and average July temperature is around . Annual precipitation is about . There is plenty of rainfall in early summer and by late summer Zhejiang is directly threatened by typhoons forming in the Pacific.Administrative divisions
Zhejiang is divided into eleven Administrative divisions of China, prefecture-level divisions: all Prefecture-level city, prefecture-level cities (including two Sub-provincial division, sub-provincial cities): The eleven prefecture-level divisions of Zhejiang are subdivided into 90 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#County level (3rd), county-level divisions (36 District of China, districts, 20 county-level cities, 33 County (People's Republic of China), counties, and one autonomous county). Those are in turn divided into 1,570 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Township level, township-level divisions (761 town of China, towns, 505 Township (Republic of China), townships, 14 ethnic townships, and 290 Subdistricts of China, subdistricts). Hengdian belongs to Jinhua, which is the largest base of shooting films and TV dramas in China. Hengdian World Studios is called "China's Hollywood." At the year end of 2017, the total population is 56.57 million.Urban areas
Politics
The politics of Zhejiang is structured in a dual party-government system like all other governing institutions in Mainland China. The Governor of Zhejiang is the highest-ranking official in the People's Government of Zhejiang. However, in the province's dual party-government governing system, the Governor is subordinate to the Zhejiang Chinese Communist Party (CCP) Provincial Committee Secretary, colloquially termed the "Zhejiang Chinese Communist Party Committee Secretary, CCP Party Chief." Several political figures who served as Zhejiang's top political office of Communist Party Secretary have played key roles in various events in PRC history. Tan Zhenlin (term 1949–1952), the inaugural Party Secretary, was one of the leading voices against Mao's Cultural Revolution during the so-called February Countercurrent of 1967. Jiang Hua (term 1956–1968), was the "chief justice" on the Special Court in the case against the Gang of Four in 1980. Three provincial Party Secretaries since the 1990s have gone onto prominence at the national level. They include CPC General Secretary and President Xi Jinping (term 2002–2007), National People's Congress Chairman and former Vice-Premier Zhang Dejiang (term 1998–2002), and Zhao Hongzhu (term 2007–2012), the Deputy Secretary of the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection, China's top anti-corruption body. Of Zhejiang's fourteen Party Secretaries since 1949, none were native to the province. Zhejiang was home to Chiang Kai-shek and many high-ranking officials in the Kuomintang, who fled to Taiwan in 1949 after losing the Civil War.Economy

Economic and Technological Development Zones
* Huzhou Economic Development Zone * Dinghai Industrial Park * Hangzhou Economic & Technological Developing Area * Hangzhou New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone * Hangzhou Export Processing Zone * Hangzhou Zhijiang National Tourist Holiday Resort * Jiaxing Export Processing Zone * Ningbo Economic and Technical Development Zone * Ningbo Daxie Island Development Zone * Ningbo Free Trade Zone * Ningbo Export Processing Zone * Quzhou Industrial Park * Shenjia Economic and Technological Development Zone * Wenzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone * Xiaoshan Economic and Technological Development Zone * Zhejiang Quzhou Hi-Tech Park * Zhejiang Zhoushan Economic Development Zone * Zhejiang Donggang Economic Development ZoneEconomic and technological development concerns
Waste disposal
On Thursday, September 15, 2011, more than 500 people from Hongxiao Village protested over the large-scale water pollution in China, death of fish in a nearby river. Angry protesters stormed the Zhejiang Jinko Solar Company factory compound, overturned eight company vehicles, and destroyed the offices before police came to disperse the crowd. Protests continued on the two following nights with reports of scuffles, officials said. Chen Hongming, a deputy head of Haining City, Haining's environmental protection bureau, said the factory's waste disposal had failed pollution tests since April. The environmental watchdog had warned the factory, but it had not effectively controlled the pollution, Chen added.Demographics
 Han Chinese make up the vast majority of the population and the largest Han subgroup are the Wuyue people, speakers of Wu varieties of Chinese. There are also 400,000 members of List of Chinese ethnic groups, ethnic minorities, including approximately 200,000 She people and approximately 20,000 Hui Chinese. Jingning She Autonomous County in Lishui, Zhejiang, Lishui is the only She autonomous county in China.
Han Chinese make up the vast majority of the population and the largest Han subgroup are the Wuyue people, speakers of Wu varieties of Chinese. There are also 400,000 members of List of Chinese ethnic groups, ethnic minorities, including approximately 200,000 She people and approximately 20,000 Hui Chinese. Jingning She Autonomous County in Lishui, Zhejiang, Lishui is the only She autonomous county in China.
Religion
The predominant religions in Zhejiang are Chinese folk religions, Taoism, Taoist traditions and Chinese Buddhism. According to surveys conducted in 2007 and 2009, 23.02% of the population believes and is involved in Chinese ancestral religion, ancestor veneration, while 2.62% of the population identifies as Christian, decreasing from 3.92% in 2004. The reports didn't give figures for other types of religion; 74.36% of the population may be either irreligious or involved in Chinese folk religion, worship of nature deities, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Chinese salvationist religions, folk religious sects. As of the mid-2010s, Zhejiang has 34,880 registered folk religious temples greater than 20 sqm and 10,000 registered places of worship of the religion in China, five doctrines (Buddhism, Taoism, Catholicism, Protestantism, Islam). In mid-2015 the government of Zhejiang recognised folk religion as "civil religion" beginning the formal registration of the province's folk religious temples under the aegis of the provincial Bureau of Folk Faith. Buddhism has an important presence since its arrival in Zhejiang 1,800 years ago. Catholicism arrived 400 years ago in the province and Protestantism 150 years ago. Zhejiang is one of the provinces of China with the largest concentrations of Protestants, especially notable in the city ofWenzhou
Wenzhou (pronounced ; Wenzhounese: Yuziou �y33–11 tɕiɤu33–32 ), historically known as Wenchow is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Zhejiang province in the People's Republic of China. Wenzhou is located at the extreme south east ...
. In 1999, Zhejiang's Protestant population comprised 2.8% of the provincial population, a small percentage but higher than the national average.
The rapid development of religions in Zhejiang has driven the local committee of ethnic and religious affairs to enact policies to rationalise them in 2014, variously named "Three Remodelings and One Demolition" operations or "Special Treatment Work on Illegally Constructed Sites of Religious and Folk Religion Activities" according to the locality. These regulations have led to cases of demolition of churches and folk religion temples or the removal of crosses from churches' roofs and spires. An exemplary case was that of the Sanjiang Church. Despite English-language media focused on Christian churches, only 2.3% of the buildings affected by the regulations were Christian churches; most of them were folk religious temples.
Islam arrived 1,400 years ago in Zhejiang. Today Islam is practiced by a small number of people including virtually all the Hui people, Hui Chinese living in Zhejiang. In 2020, there are 117,000 Muslims in Zhejiang. Another religion present in the province is She people, She shamanism (practiced by She people, She ethnic minority).
Media
The Zhejiang Radio & Television, Hangzhou Radio & Television Group, Ningbo Radio & Television Group are the local broadcasters in Zhejiang Province.Culture

Languages
Zhejiang is mountainous and has therefore fostered the development of many distinct local cultures. Linguistically speaking, Zhejiang is extremely diverse. Most inhabitants of Zhejiang speak varieties of Wu Chinese, Wu, but those Wu dialects are very diverse, especially in the south, where one valley may speak a dialect completely unintelligible to the next valley a few kilometers away. Other varieties of Chinese are spoken as well, mostly along the borders; Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin and Huizhou Chinese, Huizhou dialects are spoken on the border with Anhui, while Min Chinese, Min dialects are spoken on the border with Fujian. (See Hangzhou dialect, Shaoxing dialect, Ningbo dialect, Wenzhou dialect, Taizhou dialect, Jinhua dialect and Quzhou dialect for more information) Throughout history there have been a series of ''lingua francas'' in the area to allow for better communication. The dialects spoken in Hangzhou, Shaoxing and Ningbo have taken on this role historically. Since the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949, Standard Chinese, Mandarin, which is not mutually intelligible with any of the Wu dialects, has been promoted as the standard language of communication throughout China. As a result, most of the population now can, to some degree, speak and comprehend Mandarin and can Code-switching, code-switch when necessary. A majority of the population educated since 1978 can speak some Mandarin. Urban residents tend to be more fluent in Mandarin than rural people. Nevertheless, a Zhejiang accent is detectable in almost everyone from the area communicating in Mandarin and the home dialect remains an important part of the everyday lives and cultural identities of most Zhejiang residents.Music
Zhejiang is the home of Yue opera, one of the most prominent forms of Chinese opera. ''Yueju'' originated in Shengzhou and is traditionally performed by actresses only, in both male and female roles. Other important opera traditions include Yongju (of Ningbo), Shao opera (of Shaoxing), Ouju (of Wenzhou), Wuju (of Jinhua), Taizhou Luantan (of Taizhou) and Zhuji Luantan (of Zhuji).Cuisine
Place names
Since ancient times, north Zhejiang and neighbouring south Jiangsu have been famed for their prosperity and opulence and simply inserting north Zhejiang place names (Hangzhou, Jiaxing, etc.) into poetry gave an effect of dreaminess, a practice followed by many noted poets. In particular, the fame of Hangzhou (as well as Suzhou in neighbouring Jiangsu province) has led to the popular saying: "Above there is heaven; below there is Suzhou and Hangzhou" (), a saying that continues to be a source of pride for the people of these two still prosperous cities.Tourism
 Tourist destinations in Zhejiang include:
* Baoguo Temple (Ningbo), Baoguo Temple, one of the oldest intact wooden structures in Southern China, north of Ningbo.
* Mount Putuo, one of the most noted Buddhist mountains in China. Chinese Buddhists associate it with Guan Yin.
* Qita Temple, Ningbo.
* Shaoxing, site of the Tomb of Yu the Great, Wuzhen and other waterway towns.
* The ancient capital of Hangzhou.
* Tiantai Mountain, Mount Tiantai, a mountain important to Zen Buddhism.
* West Lake, in Hangzhou.
* Yandangshan, a mountainous scenic area near Wenzhou.
* Qiandao Lake, lit. ''Thousand-island lake''.
* Guoqing Temple, founded in the Sui dynasty, the founding location of Tiantai Buddhism
* Mount Mogan, a scenic mountain an hour from Hangzhou with many pre-World War II villas built by foreigners, along with one of Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang compounds
* Zhejiang Museum of Natural History, in Hangzhou.
Tourist destinations in Zhejiang include:
* Baoguo Temple (Ningbo), Baoguo Temple, one of the oldest intact wooden structures in Southern China, north of Ningbo.
* Mount Putuo, one of the most noted Buddhist mountains in China. Chinese Buddhists associate it with Guan Yin.
* Qita Temple, Ningbo.
* Shaoxing, site of the Tomb of Yu the Great, Wuzhen and other waterway towns.
* The ancient capital of Hangzhou.
* Tiantai Mountain, Mount Tiantai, a mountain important to Zen Buddhism.
* West Lake, in Hangzhou.
* Yandangshan, a mountainous scenic area near Wenzhou.
* Qiandao Lake, lit. ''Thousand-island lake''.
* Guoqing Temple, founded in the Sui dynasty, the founding location of Tiantai Buddhism
* Mount Mogan, a scenic mountain an hour from Hangzhou with many pre-World War II villas built by foreigners, along with one of Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang compounds
* Zhejiang Museum of Natural History, in Hangzhou.
Sports
Professional sports teams based in Zhejiang include: * Chinese Basketball Association ** Zhejiang Golden Bulls ** Bayi Rockets (in Ningbo) * China League One ** Zhejiang Greentown F.C.Education and research
Zhejiang is one of China's leading provinces in research and education. As of 2022, two major cities in Zhejiang ranked in the world's top 200 cities (Hangzhou 19th and Ningbo 170th) by scientific research output, as tracked by Nature Index.Colleges and universities
* Zhejiang University (; Hangzhou) * Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (; Hangzhou) * China Academy of Art (; Hangzhou) * Hangzhou Dianzi University (; Hangzhou) * China Jiliang University (; Hangzhou) * Hangzhou Normal University (; Hangzhou) * Ningbo University (; Ningbo) * University of Nottingham Ningbo China (; Ningbo) * Zhejiang A & F University (; Hangzhou) * Zhejiang University of Technology (; Hangzhou) * Zhejiang Medical University * Zhejiang Normal University (; Jinhua) * Zhejiang University of Finance and Economics (; Hangzhou) * Zhejiang Gongshang University (; Hangzhou) * Shaoxing University (; Shaoxing) * Wenzhou Medical University (; Wenzhou) * Wenzhou Teachers College * Wenzhou-Kean University * Shaoxing College of Arts and Science * Zhejiang Institute of Education * Hangzhou Institute of Electronic Engineering * Hangzhou University of Commerce * Hangzhou Institute of Financial ManagersNotable people
* Wang Yangming: Ming dynasty philosopher * Su Shi: Poet and writer from the Song era, also known as a government official who contributed to the maintenance of West Lake.See also
* List of railway stations in ZhejiangNotes
References
Citations
Sources
Economic profile of Zhejiang
at Hong Kong Trade Development Council, HKTDC
External links
Zhejiang Government website
*
Complete Map of the Seven Coastal Provinces
from 1821 to 1850 * {{Authority control Zhejiang, Provinces of the People's Republic of China East China Yangtze River Delta Wu (region) States and territories established in 1368