Western Asia (orthographic projection).svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, Armenian Highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and partly the Caucasus, Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Western Asia covers an area of , with a population of around 313 million. Out of the 20 UN member countries located fully or partly within the region, 13 are a part of the Arab world. The most populous countries in Western Asia are Iran, Turkey, Iraq, Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
In the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD), Western Asia excludes the Arabian Peninsula.

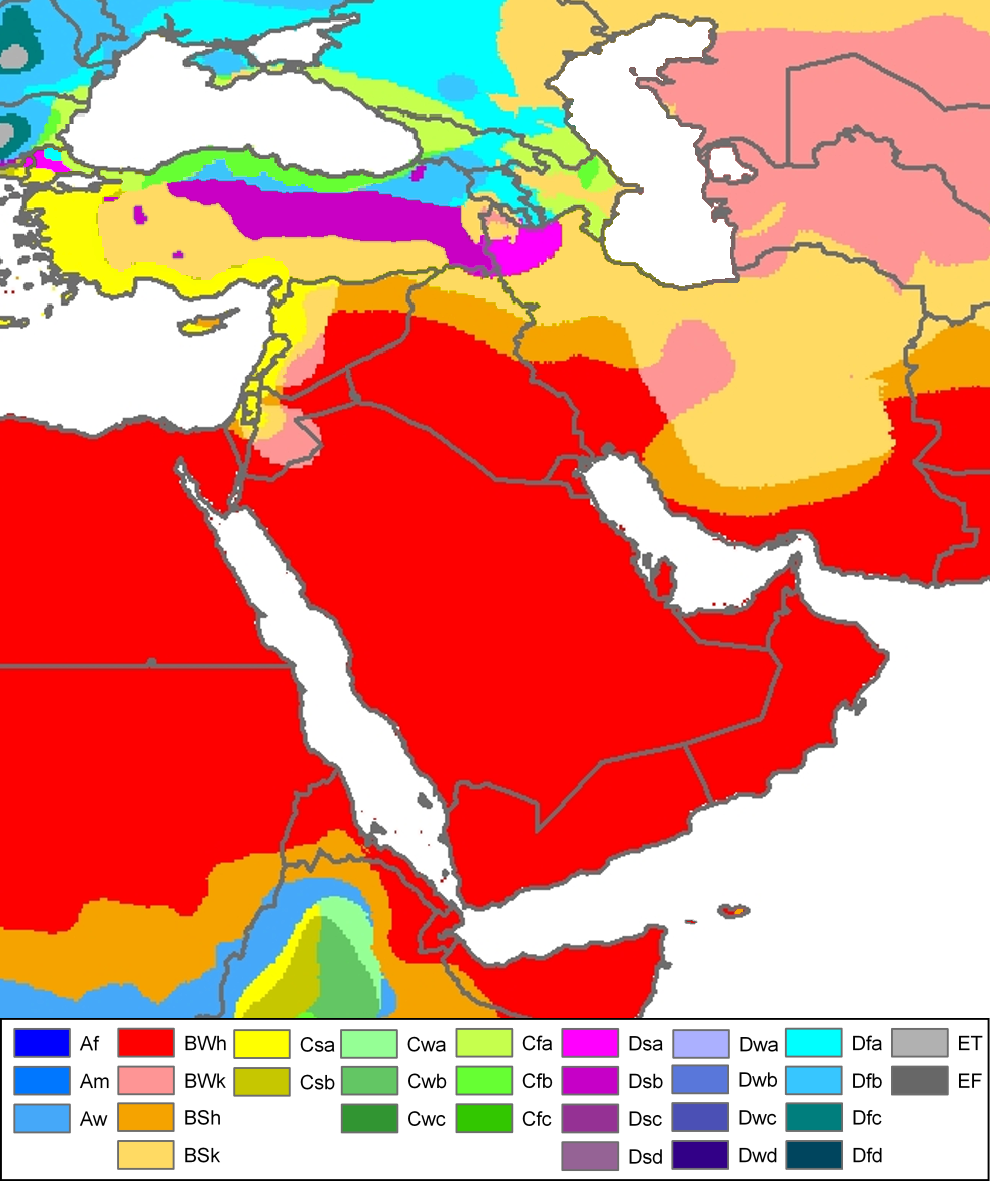 Western Asia is primarily arid climate, arid and semi-arid, and can be subject to drought, but it also contains vast expanses of forest and fertile valleys. The region consists of grasslands, rangelands, deserts, and mountains. Water shortages are a problem in many parts of West Asia, with rapidly growing populations increasing demands for water, while salinity, salinization and pollution threaten water supplies. Major rivers, including the Tigris and Euphrates River, Euphrates, provide sources for irrigation water to support agriculture.
There are two wind phenomena in Western Asia: the ''sharqi'' and the ''shamal (wind), shamal''. The ''sharqi'' (or ''sharki'') is a wind that comes from the south and southeast. It is seasonal, lasting from April to early June, and comes again between late September and November. The winds are dry and dusty, with occasional gusts up to 80 kilometres per hour (50 miles per hour) and often kick up violent sand and dust storms that can carry sand a few thousand meters high, and can close down airports for short periods of time. These winds can last for a full day at the beginning and end of the season, and for several days during the middle of the season. The ''shamal'' is a summer northwesterly wind blowing over Iraq and the Persian Gulf states (including Saudi Arabia and Kuwait), often strong during the day, but decreasing at night. This weather effect occurs anywhere from once to several times a year.
Western Asia is primarily arid climate, arid and semi-arid, and can be subject to drought, but it also contains vast expanses of forest and fertile valleys. The region consists of grasslands, rangelands, deserts, and mountains. Water shortages are a problem in many parts of West Asia, with rapidly growing populations increasing demands for water, while salinity, salinization and pollution threaten water supplies. Major rivers, including the Tigris and Euphrates River, Euphrates, provide sources for irrigation water to support agriculture.
There are two wind phenomena in Western Asia: the ''sharqi'' and the ''shamal (wind), shamal''. The ''sharqi'' (or ''sharki'') is a wind that comes from the south and southeast. It is seasonal, lasting from April to early June, and comes again between late September and November. The winds are dry and dusty, with occasional gusts up to 80 kilometres per hour (50 miles per hour) and often kick up violent sand and dust storms that can carry sand a few thousand meters high, and can close down airports for short periods of time. These winds can last for a full day at the beginning and end of the season, and for several days during the middle of the season. The ''shamal'' is a summer northwesterly wind blowing over Iraq and the Persian Gulf states (including Saudi Arabia and Kuwait), often strong during the day, but decreasing at night. This weather effect occurs anywhere from once to several times a year.
File:Kaaba mirror edit jj.jpg, Pilgrims in the annual Hajj at the Kaabah in Mecca.
File:Saint Elijah Maronite Cathedral, Aleppo (4).jpg, Cathedral of Saint Elijah, Aleppo.
File:Western Wall, Jerusalem, (16037897867).jpg, Jews Praying at the Western Wall.
Image:Flickr - Government Press Office (GPO) - Nebi Shueib Festival.jpg, Israeli Druze, Druze dignitaries celebrating the Ziyarat al-Nabi Shu'ayb festival at the tomb of the prophet in Hittin
File:Pilgrims and festival at Lalish on the day of the Yezidi New Year in 2017 06 (cropped).jpg, Yazidi pilgrims celebrating the Yazidi new year festival at the ancient holy temple of Lalish, Iraq
2 The area and population figures for Egypt only include the Sinai Peninsula.
3 Ramallah is the actual location of the government, whereas the proclaimed capital of Palestine is Jerusalem, which is Positions on Jerusalem, disputed.
4 Jerusalem is the Jerusalem Law, proclaimed capital of Israel and the actual location of the Knesset, Israeli Supreme Court, etc. Due to its Positions on Jerusalem, disputed status, most embassies are in Tel Aviv.
5 List of states with limited recognition, Unrecognised state
6 UN observer state
7 British Overseas Territory
Definition
The term ''West Asia'' is used pragmatically and has no "correct" or generally agreed-upon definition. Its typical definitions overlap substantially, but not entirely, with definitions of the terms Middle East, Eastern Mediterranean, and Near East (which is historically familiar but is widely deprecated today). The ''National Geographic Society, National Geographic Style Manual'' as well as Angus Maddison, Maddison's ''The World Economy: Historical Statistics'' (2003) by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) only includes Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, Palestine (called West Bank and Gaza in the latter), Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, UAE, and Yemen as West Asian countries. In contrast to this definition, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) in its 2015 yearbook also includes Armenia and Azerbaijan, and excludes Israel (as Other) and Turkey (as Europe). Unlike the UNIDO, the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) excludes Iran from Western Asia and includes Turkey, Georgia, and Cyprus in the region. In the United Nations geopolitical United Nations Regional Groups, Eastern European Group, Armenia and Georgia are included in Eastern Europe, whereas Cyprus and East Thracian Turkey are in Southern Europe. These three nations are listed in the European category of the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO). National members of Western Asian sports governing bodies are limited to Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Syria, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. The Olympic Council of Asia's multi-sport event West Asian Games are contested by athletes representing these thirteen countries. Among the region's sports organisations are the West Asia Basketball Association, West Asian Billiards & Snooker Federation, West Asian Billiards and Snooker Federation, West Asian Football Federation, and the West Asian Tennis Federation.History
"Western Asia" was in use as a geographical term in the early 19th century, before "Near East" became current as a geopolitical concept. In the context of the history of classical antiquity, "Western Asia" could mean the part of Asia known in classical antiquity, as opposed to the reaches of "interior Asia", i.e. Scythia, and "Eastern Asia" the easternmost reaches of geographical knowledge in classical authors, i.e. Transoxania and Indus valley, India. In the 20th century, "Western Asia" was used to denote a rough geographical era in the fields of archaeology and ancient history, especially as a shorthand for "the Fertile Crescent excluding Ancient Egypt" for the purposes of comparing the early civilizations of Egypt and the former. Use of the term in the context of contemporary geopolitics or world economy appears to date from at least the mid-1960s.Geography
The region is surrounded by eight major seas; the Aegean Sea, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea. To the northwest and north, the region is delimited from Europe by the Turkish Straits and drainage divide of the Greater Caucasus, to the southwest, it is delimited from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez, while to the northeast and east, the region adjoins Central Asia and South Asia. The region is located east of Southern Europe and south of Eastern Europe. The Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut deserts in eastern Iran naturally delimit the region from Balochistan and South Asia.Geology
Plate tectonics
Three major plate tectonics, tectonic plates converge on Western Asia, including the African Plate, African, Eurasian Plate, Eurasian, and Arabian Plate, Arabian plates. The boundaries between the tectonic plates make up the Azores–Gibraltar Transform Fault, Azores-Gibraltar Ridge, extending across North Africa, the Red Sea, and into Iran.Beaumont (1988), p. 22 The Arabian Plate is moving northward into the Anatolian Plate, Anatolian plate (Turkey) at the East Anatolian Fault, and the boundary between the Aegean Sea Plate, Aegean and Anatolian plate in eastern Turkey is also seismically active.Water resources
Several major aquifers provide water to large portions of Western Asia. In Saudi Arabia, two large aquifers of Palaeozoic and Triassic origins are located beneath the Jabal Tuwayq mountains and areas west to the Red Sea.Beaumont (1988), p. 86 Cretaceous and Eocene-origin aquifers are located beneath large portions of central and eastern Saudi Arabia, including Wasia and Biyadh which contain amounts of both fresh water and saline water. Flood or furrow irrigation, as well as sprinkler methods, are extensively used for irrigation, covering nearly across Western Asia for agriculture. Also, the Tigris and Euphrates rivers contribute very well.Climate

 Western Asia is primarily arid climate, arid and semi-arid, and can be subject to drought, but it also contains vast expanses of forest and fertile valleys. The region consists of grasslands, rangelands, deserts, and mountains. Water shortages are a problem in many parts of West Asia, with rapidly growing populations increasing demands for water, while salinity, salinization and pollution threaten water supplies. Major rivers, including the Tigris and Euphrates River, Euphrates, provide sources for irrigation water to support agriculture.
There are two wind phenomena in Western Asia: the ''sharqi'' and the ''shamal (wind), shamal''. The ''sharqi'' (or ''sharki'') is a wind that comes from the south and southeast. It is seasonal, lasting from April to early June, and comes again between late September and November. The winds are dry and dusty, with occasional gusts up to 80 kilometres per hour (50 miles per hour) and often kick up violent sand and dust storms that can carry sand a few thousand meters high, and can close down airports for short periods of time. These winds can last for a full day at the beginning and end of the season, and for several days during the middle of the season. The ''shamal'' is a summer northwesterly wind blowing over Iraq and the Persian Gulf states (including Saudi Arabia and Kuwait), often strong during the day, but decreasing at night. This weather effect occurs anywhere from once to several times a year.
Western Asia is primarily arid climate, arid and semi-arid, and can be subject to drought, but it also contains vast expanses of forest and fertile valleys. The region consists of grasslands, rangelands, deserts, and mountains. Water shortages are a problem in many parts of West Asia, with rapidly growing populations increasing demands for water, while salinity, salinization and pollution threaten water supplies. Major rivers, including the Tigris and Euphrates River, Euphrates, provide sources for irrigation water to support agriculture.
There are two wind phenomena in Western Asia: the ''sharqi'' and the ''shamal (wind), shamal''. The ''sharqi'' (or ''sharki'') is a wind that comes from the south and southeast. It is seasonal, lasting from April to early June, and comes again between late September and November. The winds are dry and dusty, with occasional gusts up to 80 kilometres per hour (50 miles per hour) and often kick up violent sand and dust storms that can carry sand a few thousand meters high, and can close down airports for short periods of time. These winds can last for a full day at the beginning and end of the season, and for several days during the middle of the season. The ''shamal'' is a summer northwesterly wind blowing over Iraq and the Persian Gulf states (including Saudi Arabia and Kuwait), often strong during the day, but decreasing at night. This weather effect occurs anywhere from once to several times a year.
Topography
Western Asia contains large areas of mountainous terrain. The Anatolian Plateau is sandwiched between the Pontus Mountains and Taurus Mountains in Turkey. Mount Ararat in Turkey rises to 5,137 meters. The Zagros Mountains are located in Iran, in areas along its border with Iraq. The Central Plateau of Iran is divided into two drainage basins. The northern basin is Dasht-e Kavir (Great Salt Desert), and Dasht-e-Lut is the southern basin. In Yemen, elevations exceed 3,700 meters in many areas, and Highland (geography), highland areas extend north along the Red Sea coast and north into Lebanon. A Geologic fault, fault-zone also exists along the Red Sea, with continental rifting creating Trough (geology), trough-like topography with areas located well-below sea level. The Dead Sea, located on the border between the West Bank, Israel, and Jordan, is situated at 418 m (1371 ft) below sea level, making it the Extremes on Earth, lowest point on the surface of the Earth. Rub' al Khali, one of the world's largest sand deserts, spans the southern third of the Arabian Peninsula in Saudi Arabia, parts of Oman, the United Arab Emirates and Yemen. Jebel Akhdar (Oman), Jebel al Akhdar is a small range of mountains located in northeastern Oman, bordering the Gulf of Oman.Demographics
The population of Western Asia was estimated at 272 million as of 2008, projected to reach 370 million by 2030 by Maddison (2007; the estimate excludes the Caucasus and Cyprus). This corresponds to an annual growth rate of 1.4% (or a doubling time of 50 years), well above the world population estimates, world average of 0.9% (doubling time 75 years). The population of Western Asia is estimated at about 4% of world population, up from about 39 million at the beginning of the 20th century, or about 2% of world population at the time. The most populous countries in the region are Turkey and Iran, each with around 79 million people, followed by Iraq and Saudi Arabia with around 33 million people each, and Yemen with around 29 million people. Numerically, Western Asia is predominantly Arabs, Arab, Persians, Persian, Turkish people, Turkish, and the dominating languages are correspondingly Arabic language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian and Turkish language, Turkish, each with of the order of 70 million speakers, followed by smaller communities of Kurdish Language, Kurdish, Azerbaijani Language, Azerbaijani, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Armenian Language, Armenian and Neo-Aramaic. The dominance of Arabic and Turkish is the result of the medieval Islamic conquests, Arab and Turkic expansion, Turkic invasions beginning with the Islamic conquests of the 7th century AD, which displaced the formerly dominant Aramaic language, Aramaic in the Syria (region), region of Syria, and Greek language, Greek in Anatolia, although Hebrew became the dominant language in Israel in the second half of the 20th century, and Neo-Aramaic (spoken by modern Modern Arameans, Arameans, Modern Assyrians, Assyrians, and Modern Chaldeans, Chaldeans) and Greek language, Greek both remain present in their respective territories as minority languages. Significant native minorities include, in alphabetical order: Modern Arameans, Arameans, Modern Assyrians, Assyrians, Modern Chaldeans, Chaldeans, Druze, Jews, Lurs, Mandeans, Maronites, Shabaks and Yezidis.Religion
Four major religious groups (i.e. the two largest religions in the world: Christianity and Islam, plus Judaism and Druze faith) originated in Western Asia. Islam is the largest religion in Western Asia, but other faiths that originated there, such as Judaism and Christianity, are also well represented. In Christianity in Armenia, Armenia and Christianity in Georgia (country), Georgia, Eastern Orthodoxy is the predominant religion, and there are still different ancient communities of Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christians in Christianity in Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan. There are still large ancient communities of Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christians (such as Assyrian people, Assyrians, Christianity in the Middle East, Middle Eastern Christians and Arab Christians) in Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanon, Christianity in Iraq, Iraq, Christianity in Iran, Iran, Turkey, Syria, Christianity in Jordan, Jordan, Christianity in Israel, Israel and Palestinian Christians, Palestine numbering more than 3 million in West Asia. There are also a large populations of expatriate workers which include a sizeable Christian communities live in Arabian Peninsula numbering more than 3 million. Christianity in the Middle East, Christian communities have Role of Christianity in civilization, played a vital role in Western Asia. Judaism is the predominant religion in Israel, and there are small ancient Jewish communities in Western Asia such as in History of the Jews in Turkey, Turkey (17,400), History of the Jews in Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan (9,100), and Persian Jews#Iran, Iran (8,756). The Druze Faith or Druzism originated in Western Asia. It is a monotheistic religion based on the teachings of figures like Hamza ibn-'Ali ibn-Ahmad and Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah and Greek philosophy, philosophers such as Plato and Aristotle. The number of Druze people worldwide is around one million, with about 45% to 50% living in Syria, 35% to 40% living in Lebanon, and less than 10% living in Israel; recently there has been a growing Druze diaspora. There are also important minority religions like the Baháʼí Faith, Yarsanism, Yazidism, Zoroastrianism, Mandaeism, and Shabak people#Religious beliefs, Shabakism.Economy
The economy of Western Asia is diverse and the region experiences high economic growth. Turkey has the largest economy in the region, followed by Saudi Arabia and Iran. Petroleum is the major Petroleum industry, industry in the regional economy, as more than half of the world's oil reserves and around 40 percent of the world's natural gas List of countries by natural gas proven reserves, reserves are located in the region.Statistical data
Notes: 1 The figures for Turkey includes East Thrace, which is not a part of Anatolia.2 The area and population figures for Egypt only include the Sinai Peninsula.
3 Ramallah is the actual location of the government, whereas the proclaimed capital of Palestine is Jerusalem, which is Positions on Jerusalem, disputed.
4 Jerusalem is the Jerusalem Law, proclaimed capital of Israel and the actual location of the Knesset, Israeli Supreme Court, etc. Due to its Positions on Jerusalem, disputed status, most embassies are in Tel Aviv.
5 List of states with limited recognition, Unrecognised state
6 UN observer state
7 British Overseas Territory
Sports
*The West Asian Tennis Federation regulates the championships and leagues in the region. *The West Asian Billiards & Snooker Federation regulates the championships related to billiards and snooker, amongst which an annual tournament. *The West Asian Games have been held in 1997, 2002 and 2005. *The West Asian Football Federation was founded in 2001 and is one of the regional federations of the Asian Football Federation. They organize the WAFF Championship. *The West Asia Basketball Association organizes the WABA Championship since 1999.Map
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
*Further reading
{{Authority control Western Asia, Regions of Asia Geography of Western Asia,