Walrus scrimshaw.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered
 The origin of the word ''walrus'' derives from a
The origin of the word ''walrus'' derives from a
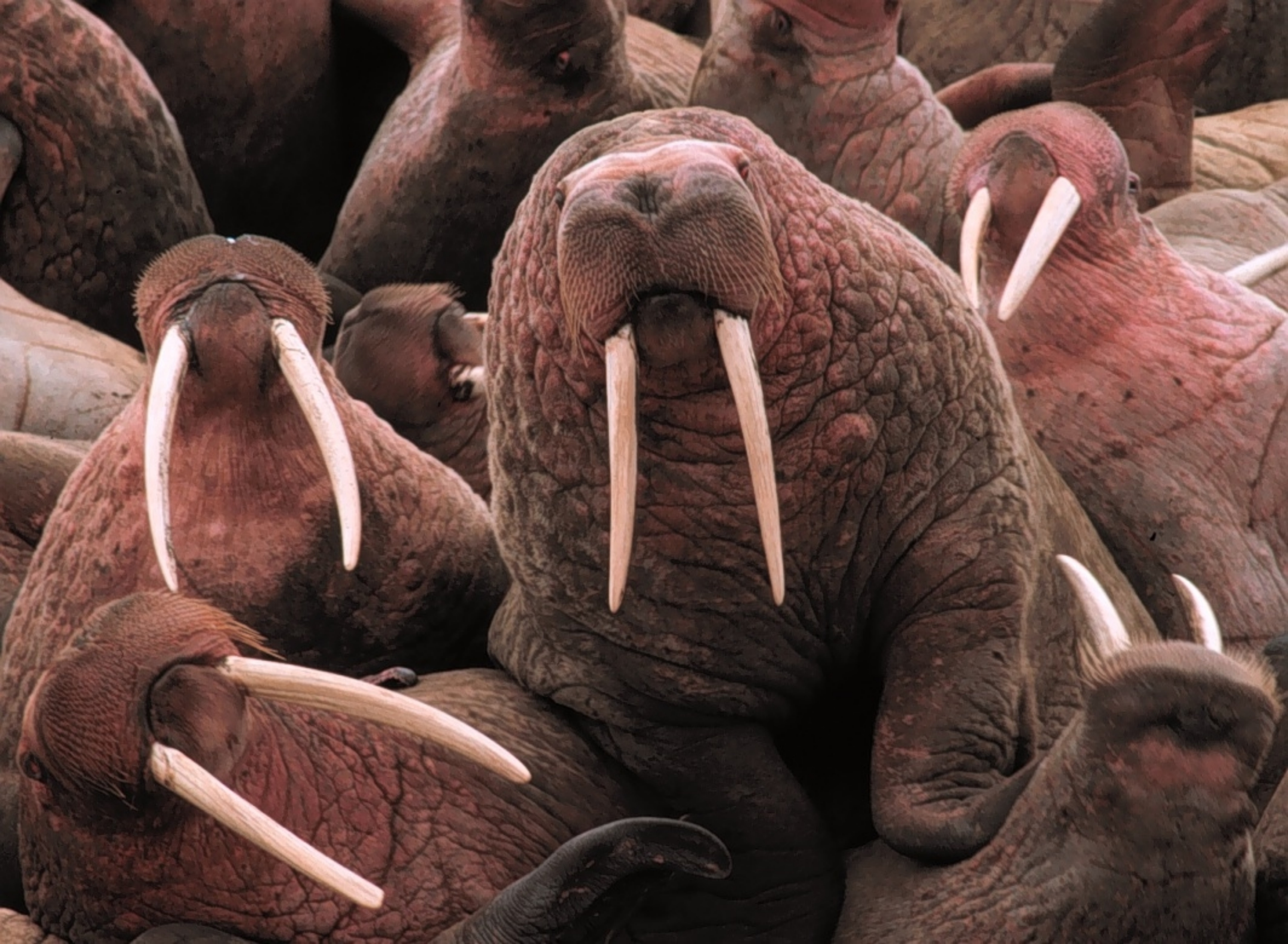
 While some outsized Pacific males can weigh as much as , most weigh between . An occasional male of the Pacific subspecies far exceeds normal dimensions. In 1909, a walrus hide weighing was collected from an enormous bull in
While some outsized Pacific males can weigh as much as , most weigh between . An occasional male of the Pacific subspecies far exceeds normal dimensions. In 1909, a walrus hide weighing was collected from an enormous bull in

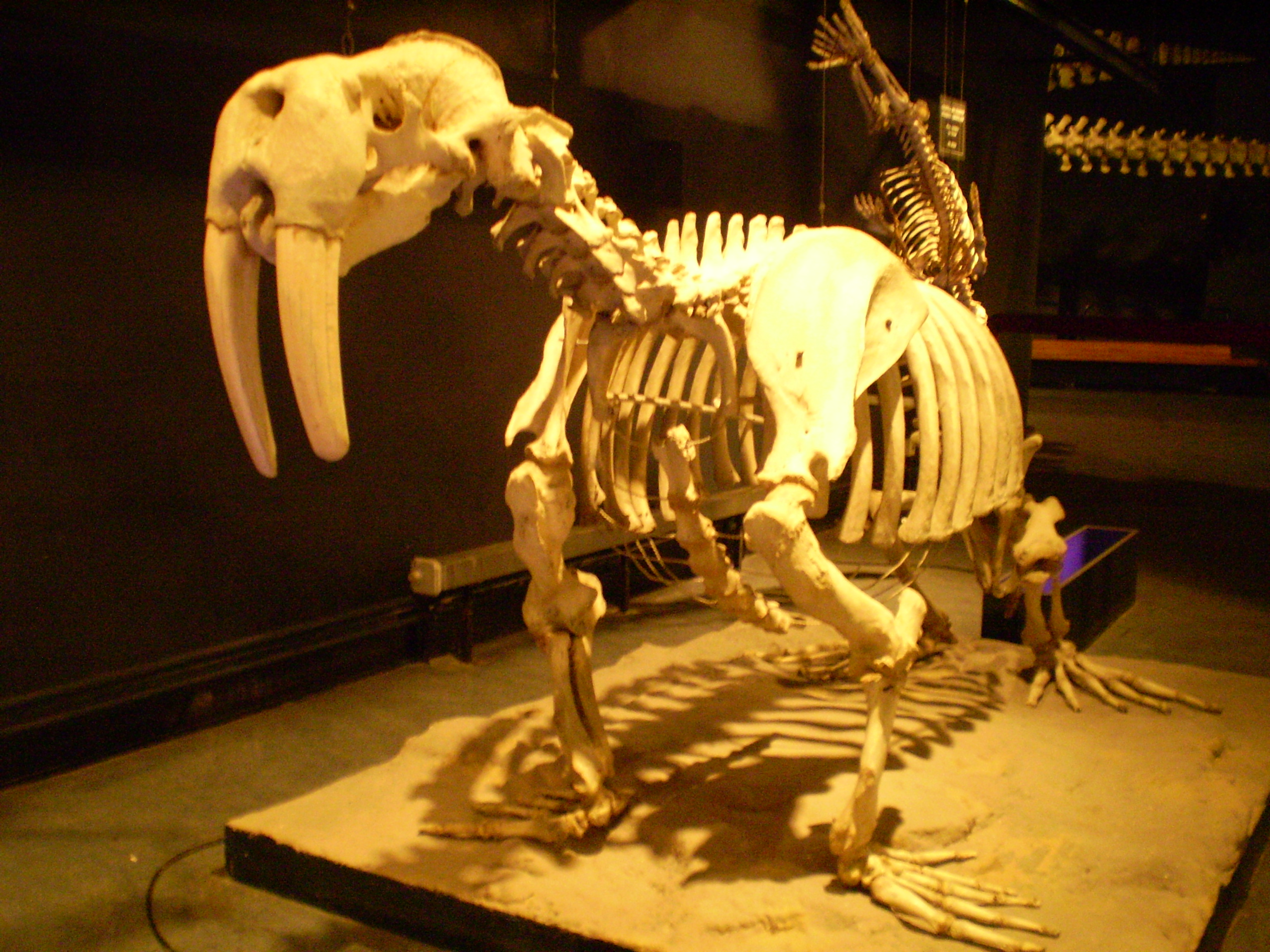
 While this was not true of all extinct walruses, the most prominent feature of the living species is its long tusks. These are elongated
While this was not true of all extinct walruses, the most prominent feature of the living species is its long tusks. These are elongated
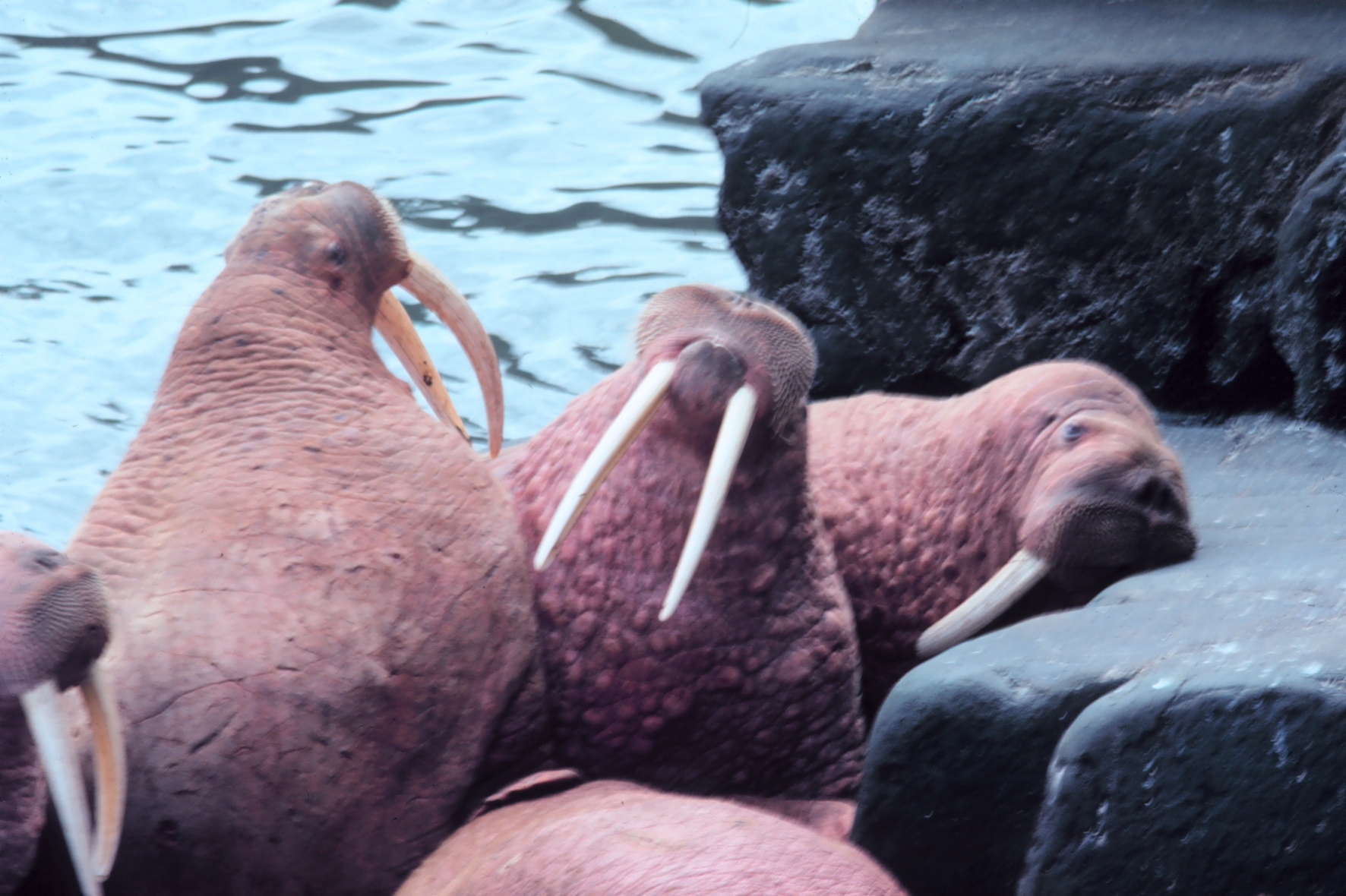
 The walrus has an air sac under its throat which acts like a flotation bubble and allows it to bob vertically in the water and sleep. The males possess a large baculum (penis bone), up to in length, the largest of any land mammal, both in absolute size and relative to body size.
The walrus has an air sac under its throat which acts like a flotation bubble and allows it to bob vertically in the water and sleep. The males possess a large baculum (penis bone), up to in length, the largest of any land mammal, both in absolute size and relative to body size.
 Gestation lasts 15 to 16 months. The first three to four months are spent with the
Gestation lasts 15 to 16 months. The first three to four months are spent with the

 Walruses prefer shallow shelf regions and forage primarily on the sea floor, often from sea ice platforms. They are not particularly deep divers compared to other pinnipeds; the deepest dives in a study of Atlantic walrus near Svalbard were only 31±17 m (102 ft) but a more recent study recorded dives exceeding 500 m (1640 ft) in Smith Sound, between NW Greenland and Arctic Canada - in general peak dive depth can be expected to depend on prey distribution and seabed depth.
The walrus has a diverse and opportunistic diet, feeding on more than 60 genera of marine organisms, including shrimp, crabs, tube worms, soft
Walruses prefer shallow shelf regions and forage primarily on the sea floor, often from sea ice platforms. They are not particularly deep divers compared to other pinnipeds; the deepest dives in a study of Atlantic walrus near Svalbard were only 31±17 m (102 ft) but a more recent study recorded dives exceeding 500 m (1640 ft) in Smith Sound, between NW Greenland and Arctic Canada - in general peak dive depth can be expected to depend on prey distribution and seabed depth.
The walrus has a diverse and opportunistic diet, feeding on more than 60 genera of marine organisms, including shrimp, crabs, tube worms, soft
 The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their ...
with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
in the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Odobenidae
Odobenidae is a family of pinnipeds. The only living species is the walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus''). In the past, however, the group was much more diverse, and includes more than a dozen fossil genera.
Taxonomy
All genera, except ''Odobenus'', ...
and genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Odobenus''. This species is subdivided into two subspecies: the Atlantic walrus (''O. r. rosmarus''), which lives in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, and the Pacific walrus (''O. r. divergens''), which lives in the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
.
Adult walrus are characterised by prominent tusk
Tusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canine teeth, as with pigs and walruses, or, in the case of elephants, elongated incisors. Tusks share ...
s and whiskers
Vibrissae (; singular: vibrissa; ), more generally called Whiskers, are a type of stiff, functional hair used by mammals to sense their environment. These hairs are finely specialised for this purpose, whereas other types of hair are coarse ...
, and their considerable bulk: adult males in the Pacific can weigh more than and, among pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammal, marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant family (biology ...
s, are exceeded in size only by the two species of elephant seal
Elephant seals are very large, oceangoing earless seals in the genus ''Mirounga''. Both species, the northern elephant seal (''M. angustirostris'') and the southern elephant seal (''M. leonina''), were hunted to the brink of extinction for oi ...
s. Walruses live mostly in shallow waters above the continental shelves, spending significant amounts of their lives on the sea ice looking for benthic bivalve mollusks to eat. Walruses are relatively long-lived, social animals, and they are considered to be a " keystone species" in the Arctic marine regions.
The walrus has played a prominent role in the cultures of many indigenous Arctic peoples
Circumpolar peoples and Arctic peoples are umbrella terms for the various Indigenous peoples of the Arctic.
Prehistory
The earliest inhabitants of North America's central and eastern Arctic are referred to as the Arctic small tool tradition (AST) ...
, who have hunted the walrus for its meat, fat, skin, tusks, and bone. During the 19th century and the early 20th century, walruses were widely hunted and killed for their blubber, walrus ivory
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
, and meat. The population of walruses dropped rapidly all around the Arctic region. Their population has rebounded somewhat since then, though the populations of Atlantic and Laptev walruses remain fragmented and at low levels compared with the time before human interference.
Etymology
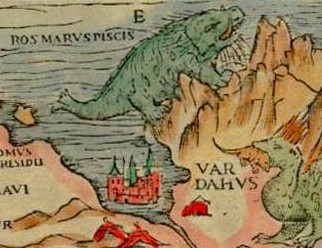
 The origin of the word ''walrus'' derives from a
The origin of the word ''walrus'' derives from a Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, E ...
, and it has been attributed largely to either the Dutch language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-Europea ...
or Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlemen ...
. Its first part is thought to derive from a word such as Old Norse ('whale') and the second part has been hypothesized to come from the Old Norse word ('horse'). For example, the Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlemen ...
word means 'horse-whale' and is thought to have been passed in an inverted form to both Dutch and the dialects of northern Germany as and . An alternative theory is that it comes from the Dutch words 'shore' and 'giant'.
The species name ''rosmarus'' is Scandinavian. The Norwegian manuscript ''Konungs skuggsjá
''Konungs skuggsjá'' (Old Norse for "King's mirror"; Latin: ''Speculum regale'', modern Norwegian: ''Kongsspegelen'' (Nynorsk) or ''Kongespeilet'' (Bokmål)) is a Norwegian didactic text in Old Norse from around 1250, an example of speculum lite ...
'', thought to date from around AD 1240, refers to the walrus as in Iceland and in Greenland (walruses were by now extinct in Iceland and Norway, while the word evolved in Greenland). Several place names in Iceland, Greenland and Norway may originate from walrus sites: Hvalfjord, Hvallatrar and Hvalsnes to name some, all being typical walrus breeding grounds.
The archaic English word for walrus—''morse''—is widely thought to have come from the Slavic languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the ...
, which in turn borrowed it from Finno-Ugric languages, and ultimately (according to Ante Aikio
Ante Aikio (Sámi: Luobbal Sámmol Sámmol Ánte; born 1977) is a Finnish linguist of Sámi origin who has been a professor of Sámi languages at the Sámi University of Applied Sciences in Kautokeino, Norway since 2015. Prior to this he has been a ...
) from an unknown Pre-Finno-Ugric substrate
Pre-Finno-Ugric substrate refers to substratum loanwords from unidentified non-Indo-European and non-Uralic languages that are found in various Finno-Ugric languages, most notably Sami. The presence of Pre-Finno-Ugric substrate in Sami language ...
language of Northern Europe. Compare () in Russian, in Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
, in Northern Saami, and in French. Olaus Magnus
Olaus Magnus (October 1490 – 1 August 1557) was a Swedish writer, cartographer, and Catholic ecclesiastic.
Biography
Olaus Magnus (a Latin translation of his birth name Olof Månsson) was born in Linköping in October 1490. Like his elder ...
, who depicted the walrus in the ''Carta Marina
''Carta marina et descriptio septentrionalium terrarum'' (Latin for ''Marine map and description of the Northern lands''; commonly abbreviated ''Carta marina'') is the first map of the Nordic countries to give details and place names, created by S ...
'' in 1539, first referred to the walrus as the , probably a Latinization of , and this was adopted by Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
in his binomial nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
.
The coincidental similarity between ''morse'' and the Latin word ('a bite') supposedly contributed to the walrus's reputation as a "terrible monster".
The compound ''Odobenus'' comes from ' (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
for 'teeth') and ' (Greek for 'walk'), based on observations of walruses using their tusks to pull themselves out of the water. The term in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
means 'turning apart', referring to their tusks.
Taxonomy and evolution
The walrus is a mammal in the order Carnivora. It is the sole surviving member of thefamily
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Odobenidae, one of three lineages in the suborder Pinnipedia
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant families Odobenidae (whose only living member is the wal ...
along with true seals ( Phocidae) and eared seals ( Otariidae). While there has been some debate as to whether all three lineages are monophyletic, i.e. descended from a single ancestor, or diphyletic, recent genetic evidence suggests all three descended from a caniform
Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs (wolves, foxes, etc.), bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia (seals, walruses and sea lions) are also assigned to this group. ...
ancestor most closely related to modern bears. Recent multigene analysis indicates the odobenids and otariids diverged from the phocids about 20–26 million years ago, while the odobenids and the otariids separated 15–20 million years ago. Odobenidae was once a highly diverse and widespread family, including at least twenty species in the subfamilies Imagotariinae, Dusignathinae and Odobeninae. The key distinguishing feature was the development of a squirt/suction feeding mechanism; tusks are a later feature specific to Odobeninae, of which the modern walrus is the last remaining (relict
A relict is a surviving remnant of a natural phenomenon.
Biology
A relict (or relic) is an organism that at an earlier time was abundant in a large area but now occurs at only one or a few small areas.
Geology and geomorphology
In geology, a r ...
) species.
Two subspecies of walrus are widely recognized: the Atlantic walrus, ''O. r. rosmarus'' (Linnaeus, 1758) and the Pacific walrus, ''O. r. divergens'' (Illiger, 1815). Fixed genetic differences between the Atlantic and Pacific subspecies indicate very restricted gene flow, but relatively recent separation, estimated at 500,000 and 785,000 years ago. These dates coincide with the hypothesis derived from fossils that the walrus evolved from a tropical or subtropical ancestor that became isolated in the Atlantic Ocean and gradually adapted to colder conditions in the Arctic. From there, it presumably recolonized the North Pacific Ocean
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' i ...
during high glaciation periods in the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
via the Central American Seaway.
An isolated population in the Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, t ...
was considered by some authorities, including many Russian biologists and the canonical ''Mammal Species of the World'', to be a third subspecies, ''O. r. laptevi'' (Chapskii, 1940), but has since been determined to be of Pacific walrus origin.
Anatomy

Franz Josef Land
Franz Josef Land, Frantz Iosef Land, Franz Joseph Land or Francis Joseph's Land ( rus, Земля́ Фра́нца-Ио́сифа, r=Zemlya Frantsa-Iosifa, no, Fridtjof Nansen Land) is a Russian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. It is inhabited on ...
, while in August 1910, Jack Woodson shot a walrus, harvesting its hide. Since a walrus's hide usually accounts for about 20% of its body weight, the total body mass of these two giants is estimated to have been at least . The Atlantic subspecies weighs about 10–20% less than the Pacific subspecies. Male Atlantic walrus weigh an average of . The Atlantic walrus also tends to have relatively shorter tusks and somewhat more flattened snout. Females weigh about two-thirds as much as males, with the Atlantic females averaging , sometimes weighing as little as , and the Pacific female averaging . Length typically ranges from . Newborn walruses are already quite large, averaging in weight and in length across both sexes and subspecies. All told, the walrus is the third largest pinniped species, after the two elephant seals
Elephant seals are very large, oceangoing earless seals in the genus ''Mirounga''. Both species, the northern elephant seal (''M. angustirostris'') and the southern elephant seal (''M. leonina''), were hunted to the brink of extinction for oil ...
. Walruses maintain such a high body weight because of the blubber stored underneath their skin. This blubber keeps them warm and the fat provides energy to the walrus.
The walrus's body shape shares features with both sea lions (eared seal
An eared seal or otariid or otary is any member of the marine mammal family Otariidae, one of three groupings of pinnipeds. They comprise 15 extant species in seven genera (another species became extinct in the 1950s) and are commonly known eith ...
s: Otariidae) and seals (true seals
The earless seals, phocids or true seals are one of the three main groups of mammals within the seal lineage, Pinnipedia. All true seals are members of the family Phocidae (). They are sometimes called crawling seals to distinguish them from th ...
: Phocidae). As with otariids, it can turn its rear flippers forward and move on all fours; however, its swimming technique is more like that of true seals, relying less on flippers and more on sinuous whole body movements. Also like phocids, it lacks external ears.
The extraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles (extrinsic ocular muscles), are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the othe ...
of the walrus are well-developed. This and its lack of orbital roof allow it to protrude its eyes and see in both a frontal and dorsal direction. However, vision in this species appears to be more suited for short-range.
Tusks and dentition

 While this was not true of all extinct walruses, the most prominent feature of the living species is its long tusks. These are elongated
While this was not true of all extinct walruses, the most prominent feature of the living species is its long tusks. These are elongated canines
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* a dog-like Canid animal in the subfamily Caninae
** ''Canis'', a genus including dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Dog, the domestic dog
* Canine tooth, in mammalian oral anatomy
People with the surn ...
, which are present in both male and female walruses and can reach a length of 1 m (3 ft 3 in) and weigh up to 5.4 kg (12 lb). Tusks are slightly longer and thicker among males, which use them for fighting, dominance and display; the strongest males with the largest tusks typically dominate social groups. Tusks are also used to form and maintain holes in the ice and aid the walrus in climbing out of water onto ice. Tusks were once thought to be used to dig out prey from the seabed, but analyses of abrasion patterns on the tusks indicate they are dragged through the sediment while the upper edge of the snout is used for digging. While the dentition of walruses is highly variable, they generally have relatively few teeth other than the tusks. The maximal number of teeth is 38 with dentition formula: , but over half of the teeth are rudimentary and occur with less than 50% frequency, such that a typical dentition includes only 18 teeth
Vibrissae (whiskers)
Surrounding the tusks is a broad mat of stiff bristles ("mystacialvibrissae
Vibrissae (; singular: vibrissa; ), more generally called Whiskers, are a type of stiff, functional hair used by mammals to sense their environment. These hairs are finely specialised for this purpose, whereas other types of hair are coarser ...
"), giving the walrus a characteristic whiskered appearance. There can be 400 to 700 vibrissae in 13 to 15 rows reaching 30 cm (12 in) in length, though in the wild they are often worn to much shorter lengths due to constant use in foraging. The vibrissae are attached to muscles and are supplied with blood and nerves, making them highly sensitive organs capable of differentiating shapes thick and wide.
Skin
Aside from the vibrissae, the walrus is sparsely covered with fur and appears bald. Its skin is highly wrinkled and thick, up to around the neck and shoulders of males. The blubber layer beneath is up to thick. Young walruses are deep brown and grow paler and more cinnamon-colored as they age. Old males, in particular, become nearly pink. Because skin blood vessels constrict in cold water, the walrus can appear almost white when swimming. As asecondary sexual characteristic
Secondary sex characteristics are features that appear during puberty in humans, and at sexual maturity in other animals. These characteristics are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a s ...
, males also acquire significant nodules, called "bosses", particularly around the neck and shoulders.
 The walrus has an air sac under its throat which acts like a flotation bubble and allows it to bob vertically in the water and sleep. The males possess a large baculum (penis bone), up to in length, the largest of any land mammal, both in absolute size and relative to body size.
The walrus has an air sac under its throat which acts like a flotation bubble and allows it to bob vertically in the water and sleep. The males possess a large baculum (penis bone), up to in length, the largest of any land mammal, both in absolute size and relative to body size.
Life history

Reproduction
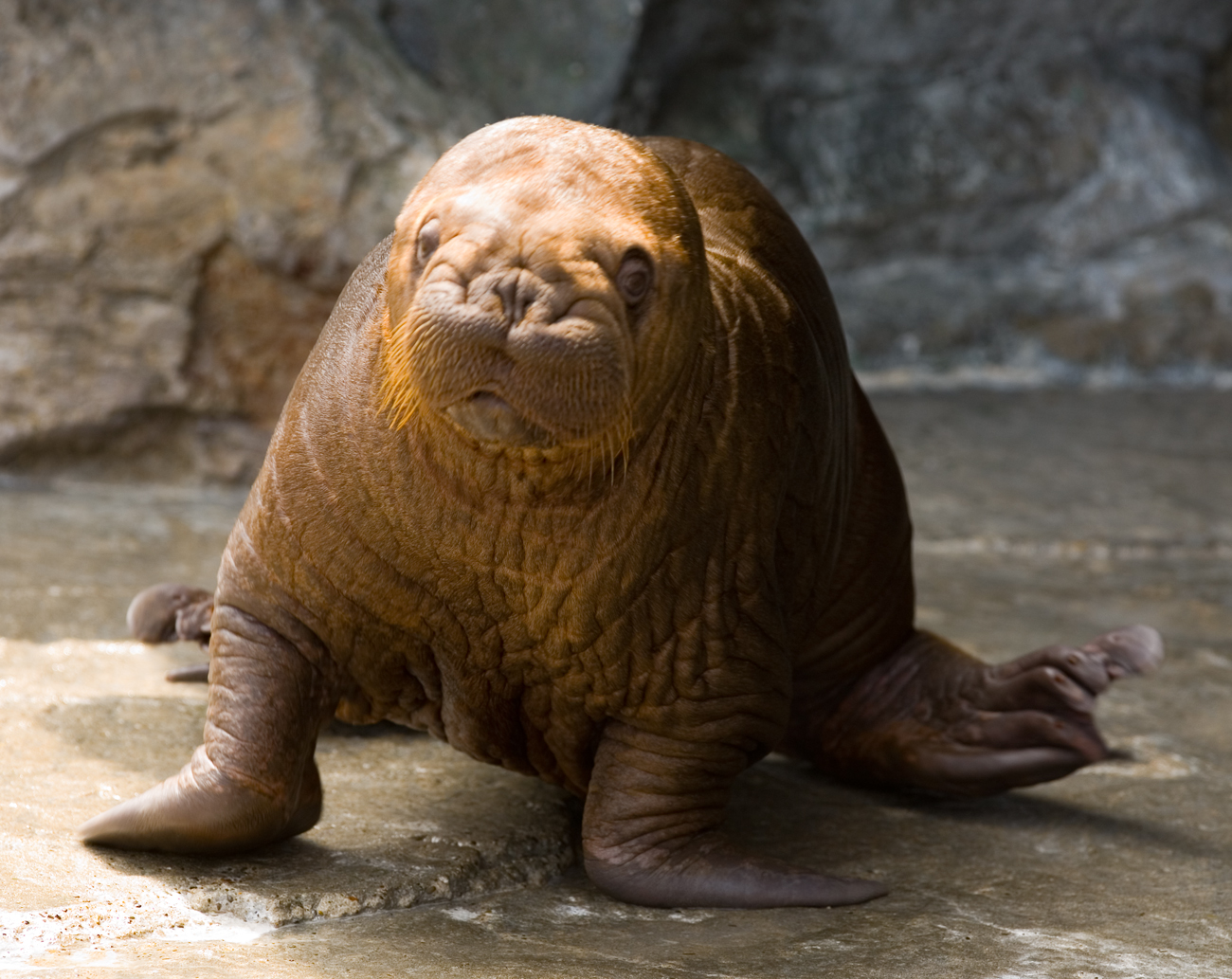
Walruses live to about 20–30 years old in the wild. The males reach sexual maturity as early as seven years, but do not typically mate until fully developed at around 15 years of age. They rut from January through April, decreasing their food intake dramatically. The females begin ovulating as soon as four to six years old. The females are diestrous, coming into heat in late summer and also around February, yet the males are fertile only around February; the potential fertility of this second period is unknown. Breeding occurs from January to March, peaking in February. Males aggregate in the water around ice-bound groups of estrous females and engage in competitive vocal displays. The females join them and copulate in the water. Gestation lasts 15 to 16 months. The first three to four months are spent with the
Gestation lasts 15 to 16 months. The first three to four months are spent with the blastula
Blastulation is the stage in early animal embryonic development that produces the blastula. In mammalian development the blastula develops into the blastocyst with a differentiated inner cell mass and an outer trophectoderm. The blastula (f ...
in suspended development before it implants itself in the uterus. This strategy of delayed implantation, common among pinnipeds, presumably evolved to optimize both the mating season and the birthing season, determined by ecological conditions that promote newborn survival. Calves are born during the spring migration, from April to June. They weigh at birth and are able to swim. The mothers nurse for over a year before weaning, but the young can spend up to five years with the mothers. Walrus milk contains higher amounts of fats and protein compared to land animals but lower compared to phocid seals. This lower fat content in turn causes a slower growth rate among calves and a longer nursing investment for their mothers. Because ovulation is suppressed until the calf is weaned, females give birth at most every two years, leaving the walrus with the lowest reproductive rate of any pinniped.
Migration
The rest of the year (late summer and fall), walruses tend to form massive aggregations of tens of thousands of individuals on rocky beaches or outcrops. The migration between the ice and the beach can be long-distance and dramatic. In late spring and summer, for example, several hundred thousand Pacific walruses migrate from the Bering Sea into the Chukchi Sea through the relatively narrow Bering Strait.Ecology
Range and habitat
The majority of the population of the Pacific walrus spends its summers north of the Bering Strait in the Chukchi Sea of the Arctic Ocean along the northern coast of easternSiberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
, around Wrangel Island
Wrangel Island ( rus, О́стров Вра́нгеля, r=Ostrov Vrangelya, p=ˈostrəf ˈvrangʲɪlʲə; ckt, Умӄиԓир, translit=Umqiḷir) is an island of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. It is the 91st largest island in the w ...
, in the Beaufort Sea along the northern shore of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
south to Unimak Island
Unimak Island ( ale, Unimax, russian: Унимак) is the largest island in the Aleutian Islands chain of the U.S. state of Alaska.
Geography
It is the easternmost island in the Aleutians and, with an area of , the ninth largest island in the ...
, and in the waters between those locations. Smaller numbers of males summer in the Gulf of Anadyr
The Gulf of Anadyr, or Anadyr Bay (russian: Анадырский залив), is a large bay on the Bering Sea in far northeast Siberia. It has a total surface area of
Location
The bay is roughly rectangular and opens to the southeast. The corn ...
on the southern coast of the Siberian Chukchi Peninsula
The Chukchi Peninsula (also Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula; russian: Чуко́тский полуо́стров, ''Chukotskiy poluostrov'', short form russian: Чуко́тка, ''Chukotka''), at about 66° N 172° W, is the eastern ...
, and in Bristol Bay off the southern coast of Alaska, west of the Alaska Peninsula. In the spring and fall, walruses congregate throughout the Bering Strait, reaching from the western coast of Alaska to the Gulf of Anadyr. They winter over in the Bering Sea along the eastern coast of Siberia south to the northern part of the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and w ...
, and along the southern coast of Alaska. A 28,000-year-old fossil walrus was dredged up from the bottom of San Francisco Bay, indicating that Pacific walruses ranged that far south during the last Ice Age.
Commercial harvesting reduced the population of the Pacific walrus to between 50,000 and 100,000 in the 1950s-1960s. Limits on commercial hunting allowed the population to increase to a peak in the 1970s-1980s, but subsequently, walrus numbers have again declined. Early aerial censuses of Pacific walrus conducted at five-year intervals between 1975 and 1985 estimated populations of above 220,000 in each of the three surveys.
In 2006, the population of the Pacific walrus was estimated to be around 129,000 on the basis of an aerial census combined with satellite tracking. There were roughly 200,000 Pacific walruses in 1990.
The much smaller population of Atlantic walruses ranges from the Canadian Arctic, across Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
, Svalbard, and the western part of Arctic Russia. There are eight hypothetical subpopulations of Atlantic walruses, based largely on their geographical distribution and movements: five west of Greenland and three east of Greenland. The Atlantic walrus once ranged south to Sable Island
Sable Island (french: île de Sable, literally "island of sand") is a small Canadian island situated southeast of Halifax, Nova Scotia, and about southeast of the closest point of mainland Nova Scotia in the North Atlantic Ocean. The island ...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, and as late as the 18th century was found in large numbers in the Greater Gulf of St. Lawrence region, sometimes in colonies of up to 7,000 to 8,000 individuals. This population was nearly eradicated by commercial harvest; their current numbers, though difficult to estimate, probably remain below 20,000. In April 2006, the Canadian Species at Risk Act listed the population of the northwestern Atlantic walrus in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, Newfoundland and Labrador as having been eradicated in Canada. A genetically distinct population existed in Iceland that was wiped out after Norse settlement around 1213–1330 AD.
The isolated population of Laptev Sea walruses is confined year-round to the central and western regions of the Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, t ...
, the eastmost regions of the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. ...
, and the westmost regions of the East Siberian Sea. The current population of these walruses has been estimated to be between 5,000 and 10,000.
Even though walruses can dive to depths beyond 500 meters, they spend most of their time in shallow waters (and the nearby ice floes) hunting for food.
In March 2021, a single walrus, nicknamed Wally the Walrus
Wally the Walrus, also known as Wally the Wandering Walrus, is a male arctic walrus who attracted much media attention for appearing, and hauling out, during 2021 in several locations across the coast of western Europe, mainly Ireland and Brit ...
, was sighted at Valentia Island
Valentia Island () is one of Ireland's most westerly points. It lies off the Iveragh Peninsula in the southwest of County Kerry. It is linked to the mainland by the Maurice O'Neill Memorial Bridge at Portmagee. A car ferry also departs from ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, far south of its typical range, potentially due to having fallen asleep on an iceberg that then drifted south towards Ireland. Days later, a walrus, thought to be the same animal, was spotted on the Pembrokeshire coast, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
.
In June 2022, a single walrus was sighted on the shores of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
- at Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
Island, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Mielno
Mielno (german: Groß Möllen or ) is a resort town in Koszalin County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Mielno. It lies approximately north-west of Koszali ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and Skälder Bay
Skälder Bay ( sv, Skälderviken) is a bay in Skåne County, Sweden. It is an inlet of the Kattegat on the western coast of Scania, located between the Bjäre Peninsula to the north (which separates it from Laholm Bay) and the Kullen Peninsula ...
, Sweden. In July 2022, there was a report of a lost, starving walrus (nicknamed as Stena) in the coastal waters of the towns of Hamina and Kotka
Kotka (; ; la, Aquilopolis) is a city in the southern part of the Kymenlaakso province on the Gulf of Finland. Kotka is a major port and industrial city and also a diverse school and cultural city, which was formerly part of the old Kymi parish ...
in Kymenlaakso
Kymenlaakso ( sv, Kymmenedalen; " Kymi/Kymmene Valley") is a region in Finland. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Päijät-Häme, South Savo and South Karelia and Russia (Leningrad Oblast). Its name means literally ''The Valley of River Kym ...
, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, that, despite rescue attempts, died of starvation when the rescuers tried to transport it to the Korkeasaari Zoo for treatment.
Diet

 Walruses prefer shallow shelf regions and forage primarily on the sea floor, often from sea ice platforms. They are not particularly deep divers compared to other pinnipeds; the deepest dives in a study of Atlantic walrus near Svalbard were only 31±17 m (102 ft) but a more recent study recorded dives exceeding 500 m (1640 ft) in Smith Sound, between NW Greenland and Arctic Canada - in general peak dive depth can be expected to depend on prey distribution and seabed depth.
The walrus has a diverse and opportunistic diet, feeding on more than 60 genera of marine organisms, including shrimp, crabs, tube worms, soft
Walruses prefer shallow shelf regions and forage primarily on the sea floor, often from sea ice platforms. They are not particularly deep divers compared to other pinnipeds; the deepest dives in a study of Atlantic walrus near Svalbard were only 31±17 m (102 ft) but a more recent study recorded dives exceeding 500 m (1640 ft) in Smith Sound, between NW Greenland and Arctic Canada - in general peak dive depth can be expected to depend on prey distribution and seabed depth.
The walrus has a diverse and opportunistic diet, feeding on more than 60 genera of marine organisms, including shrimp, crabs, tube worms, soft coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and ...
s, tunicate
A tunicate is a marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata (). It is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time ...
s, sea cucumbers, various mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is e ...
s (such as snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class G ...
s, octopuses, and squid), some types of slow-moving fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
, and even parts of other pinnipeds. However, it prefers benthic bivalve mollusks, especially clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve molluscs. The word is often applied only to those that are edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the seafloor or riverbeds. Clams have two shel ...
s, for which it forages by grazing along the sea bottom, searching and identifying prey with its sensitive vibrissae
Vibrissae (; singular: vibrissa; ), more generally called Whiskers, are a type of stiff, functional hair used by mammals to sense their environment. These hairs are finely specialised for this purpose, whereas other types of hair are coarser ...
and clearing the murky bottoms with jets of water and active flipper movements. The walrus sucks the meat out by sealing its powerful lips to the organism and withdrawing its piston-like tongue rapidly into its mouth, creating a vacuum. The walrus palate is uniquely vaulted, enabling effective suction. The diet of the Pacific walrus consist almost exclusively of benthic invertebrates (97 percent).
Aside from the large numbers of organisms actually consumed by the walrus, its foraging has a large peripheral impact on benthic communities. It disturbs ( bioturbates) the sea floor, releasing nutrients into the water column, encouraging mixing and movement of many organisms and increasing the patchiness of the benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.
Seal tissue has been observed in a fairly significant proportion of walrus stomachs in the Pacific, but the importance of seals in the walrus diet is under debate. There have been isolated observations of walruses preying on seals up to the size of a bearded seal. Rarely, incidents of walruses preying on seabirds, particularly the
File:Walrus hunter 1911.jpg, Hunter sitting on dozens of walruses killed for their tusks, 1911
File:PolarBearWalrusTuskCarving.jpg, alt=Photo of section of tusk, Walrus tusk
Walrus hunts are regulated by resource managers in
File:Ivorymasks.jpg, alt=Photo of two masks: In the center is the image of a face, surrounded by a ring, in turn surrounded by eight white rectangular pieces., Walrus ivory masks made by
Most of the distinctive 12th-century Lewis Chessmen from northern Europe are carved from walrus ivory, though a few have been found to be made of whales' teeth.
Biologist Tracks Walruses Forced Ashore As Ice Melts
– audio report by ''
Thousands Of Walruses Crowd Ashore Due To Melting Sea Ice
– video by '' National Geographic''
Voices in the Sea – Sounds of the Walrus
{{good article Pinnipeds of the Arctic Ocean Mammals described in 1758 Mammals of Asia Mammals of Canada Mammals of Greenland Mammals of North America Mammals of Russia Mammals of the United States Mammals of Europe Marine mammals Pinnipeds of North America Odobenids Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Holarctic fauna
Brünnich's guillemot
The thick-billed murre or Brünnich's guillemot (''Uria lomvia'') is a bird in the auk family (Alcidae). This bird is named after the Danish zoologist Morten Thrane Brünnich. The very deeply black North Pacific subspecies ''Uria lomvia arra'' i ...
(''Uria lomvia''), have been documented. Walruses may occasionally prey on ice-entrapped narwhals and scavenge on whale carcasses but there is little evidence to prove this.
Predators
Due to its great size and tusks, the walrus has only two natural predators: theorca
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
and the polar bear. The walrus does not, however, comprise a significant component of either of these predators' diets. Both the orca and the polar bear are also most likely to prey on walrus calves. The polar bear often hunts the walrus by rushing at beached aggregations and consuming the individuals crushed or wounded in the sudden exodus, typically younger or infirm animals. The bears also isolate walruses when they overwinter
Overwintering is the process by which some organisms pass through or wait out the winter season, or pass through that period of the year when "winter" conditions (cold or sub-zero temperatures, ice, snow, limited food supplies) make normal acti ...
and are unable to escape a charging bear due to inaccessible diving holes in the ice. However, even an injured walrus is a formidable opponent for a polar bear, and direct attacks are rare. Armed with its ivory tusks, walruses have been known to fatally injure polar bears in battles if the latter follows the other into the water, where the bear is at a disadvantage. Polar bear–walrus battles are often extremely protracted and exhausting, and bears have been known to break away from the attack after injuring a walrus. Orcas regularly attack walruses, although walruses are believed to have successfully defended themselves via counterattack against the larger cetacean. However, orcas have been observed successfully attacking walruses with few or no injuries.
Relationship with humans
Conservation
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the walrus was heavily exploited by American and Europeansealers Sealer may refer either to a person or ship engaged in seal hunting, or to a sealant; associated terms include:
Seal hunting
* Sealer Hill, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica
* Sealers' Oven, bread oven of mud and stone built by sealers around 18 ...
and whalers, leading to the near-extirpation
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
of the Atlantic subspecies. As early as 1871 traditional hunters were expressing concern about the numbers of walrus being hunted by whaling fleets. Commercial walrus harvesting is now outlawed throughout its range, although Chukchi, Yupik Yupik may refer to:
* Yupik peoples, a group of indigenous peoples of Alaska and the Russian Far East
* Yupik languages, a group of Eskimo-Aleut languages
Yupꞌik (with the apostrophe) may refer to:
* Yup'ik people
The Yup'ik or Yupiaq (sg ...
and Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
peoples are permitted to kill small numbers towards the end of each summer.
Traditional hunters used all parts of the walrus. The meat, often preserved, is an important winter nutrition source; the flippers are fermented and stored as a delicacy until spring; tusks and bone were historically used for tools, as well as material for handicrafts; the oil was rendered for warmth and light; the tough hide made rope and house and boat coverings; and the intestines and gut linings made waterproof parkas. While some of these uses have faded with access to alternative technologies, walrus meat remains an important part of local diets, and tusk carving and engraving remain a vital art form.
According to Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld
Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld (18 November 183212 August 1901) was a Finland-Swedish aristocrat, geologist, mineralogist and Arctic explorer. He was a member of the Fenno-Swedish Nordenskiöld family of scientists and held the title of a friher ...
, European hunters and Arctic explorers found walrus meat not particularly tasty, and only ate it in case of necessity; however walrus tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
was a delicacy.
scrimshaw
Scrimshaw is scrollwork, engravings, and carvings done in bone or ivory. Typically it refers to the artwork created by whalers, engraved on the byproducts of whales, such as bones or cartilage. It is most commonly made out of the bones and teeth ...
made by Chukchi artisans depicting polar bears attacking walruses, on display in the Magadan Regional Museum, Magadan, Russia
File:Walrus in Marineland, Ontario, Canada - 2017 (37223504105).jpg, Trained walrus in captivity at Marineland
File:Valrossarna på Skansen matas av djurskötare och herre i paletå och hög hatt - Nordiska Museet - NMA.0048348.jpg, Walrus being fed at Skansen
Skansen (; "the Sconce") is the oldest open-air museum and zoo in Sweden located on the island Djurgården in Stockholm, Sweden. It was opened on 11 October 1891 by Artur Hazelius (1833–1901) to show the way of life in the different parts ...
in Stockholm, Sweden, 1908
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, the United States, Canada, and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
(self-governing country in the Kingdom of Denmark), and representatives of the respective hunting communities. An estimated four to seven thousand Pacific walruses are harvested in Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
and in Russia, including a significant portion (about 42%) of struck and lost animals. Several hundred are removed annually around Greenland. The sustainability of these levels of harvest is difficult to determine given uncertain population estimates and parameters such as fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the natural capability to pr ...
and mortality. The ''Boone and Crockett Big Game Record'' book has entries for Atlantic and Pacific walrus. The recorded largest tusks are just over 30 inches and 37 inches long respectively.
The effects of global climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
are another element of concern. The extent and thickness of the pack ice has reached unusually low levels in several recent years. The walrus relies on this ice while giving birth and aggregating in the reproductive period. Thinner pack ice over the Bering Sea has reduced the amount of resting habitat near optimal feeding grounds. This more widely separates lactating females from their calves, increasing nutritional stress for the young and lower reproductive rates. Reduced coastal sea ice has also been implicated in the increase of stampeding deaths crowding the shorelines of the Chukchi Sea between eastern Russia and western Alaska. Analysis of trends in ice cover published in 2012 indicate that Pacific walrus populations are likely to continue to decline for the foreseeable future, and shift further north, but that careful conservation management might be able to limit these effects.
Currently, two of the three walrus subspecies are listed as "least-concern" by the IUCN, while the third is "data deficient". The Pacific walrus is not listed as "depleted" according to the Marine Mammal Protection Act
The Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA) was the first act of the United States Congress to call specifically for an ecosystem approach to wildlife management.
Authority
MMPA was signed into law on October 21, 1972, by President Richard Nixon ...
nor as "threatened" or "endangered" under the Endangered Species Act. The Russian Atlantic and Laptev Sea populations are classified as Category 2 (decreasing) and Category 3 (rare) in the Russian Red Book. Global trade in walrus ivory
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
is restricted according to a CITES
CITES (shorter name for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of interna ...
Appendix 3 listing. In October 2017, the Center for Biological Diversity
The Center for Biological Diversity is a nonprofit membership organization known for its work protecting endangered species through legal action, scientific petitions, creative media and grassroots activism. It was founded in 1989 by Kieran Suckl ...
announced they would sue the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
to force it to classify the Pacific Walrus as a threatened or endangered species.
In 1952, walruses in Svalbard were nearly gone due to ivory hunting over a 300 years period, but the Norwegian government banned their commercial hunting and the walruses began to rebound in 2006, making their population increase to 2,629.
Culture
Folklore
The walrus plays an important role in the religion andfolklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
of many Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
peoples. Skin and bone are used in some ceremonies, and the animal appears frequently in legends. For example, in a Chukchi version of the widespread myth of the Raven, in which Raven recovers the sun and the moon from an evil spirit by seducing his daughter, the angry father throws the daughter from a high cliff and, as she drops into the water, she turns into a walrus – possibly the original walrus. According to various legends, the tusks are formed either by the trails of mucus from the weeping girl or her long braids. This myth is possibly related to the Chukchi myth of the old walrus-headed woman who rules the bottom of the sea, who is in turn linked to the Inuit goddess Sedna. Both in Chukotka and Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
, the aurora borealis
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
is believed to be a special world inhabited by those who died by violence, the changing rays representing deceased souls playing ball with a walrus head.
Yupik Yupik may refer to:
* Yupik peoples, a group of indigenous peoples of Alaska and the Russian Far East
* Yupik languages, a group of Eskimo-Aleut languages
Yupꞌik (with the apostrophe) may refer to:
* Yup'ik people
The Yup'ik or Yupiaq (sg ...
in Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
File:Briny Beach.jpg, alt=Drawing of walrus, and square-headed men, both perched on rocks, with ocean and cliffs in background, John Tenniel
Sir John Tenniel (; 28 February 182025 February 1914)Johnson, Lewis (2003), "Tenniel, John", ''Grove Art Online, Oxford Art Online'', Oxford University Press. Web. Retrieved 12 December 2016. was an English illustrator, graphic humorist and poli ...
's illustration for Lewis Carroll
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (; 27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet and mathematician. His most notable works are '' Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865) and its sequ ...
's poem "The Walrus and the Carpenter
"The Walrus and the Carpenter" is a narrative poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in his book ''Through the Looking-Glass'', published in December 1871. The poem is recited in chapter four, by Tweedledum and Tweedledee to Alice. The poem is co ...
"
File:Hugo-de-Groot-Nederlandtsche-jaerboeken MG 0188.tif, Dutch explorers fight a walrus on the coast of Novaya Zemlya, 1596
Literature
Because of its distinctive appearance, great bulk, and immediately recognizable whiskers and tusks, the walrus also appears in the popular cultures of peoples with little direct experience with the animal, particularly in English children's literature. Perhaps its best-known appearance is inLewis Carroll
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (; 27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet and mathematician. His most notable works are '' Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865) and its sequ ...
's whimsical poem "The Walrus and the Carpenter
"The Walrus and the Carpenter" is a narrative poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in his book ''Through the Looking-Glass'', published in December 1871. The poem is recited in chapter four, by Tweedledum and Tweedledee to Alice. The poem is co ...
" that appears in his 1871 book ''Through the Looking-Glass
''Through the Looking-Glass, and What Alice Found There'' (also known as ''Alice Through the Looking-Glass'' or simply ''Through the Looking-Glass'') is a novel published on 27 December 1871 (though indicated as 1872) by Lewis Carroll and the ...
''. In the poem, the eponymous
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
antiheroes use trickery to consume a great number of oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not ...
s. Although Carroll accurately portrays the biological walrus's appetite for bivalve mollusks, oysters, primarily nearshore and intertidal
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species ...
inhabitants, these organisms in fact comprise an insignificant portion of its diet in captivity.
The "walrus" in the cryptic Beatles song "I Am the Walrus
"I Am the Walrus" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles from their 1967 television film ''Magical Mystery Tour''. Written by John Lennon and credited to Lennon–McCartney, it was released as the B-side to the single "Hello, Goodbye" a ...
" is a reference to the Lewis Carroll poem.
Another appearance of the walrus in literature is in the story "The White Seal" in Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
's ''The Jungle Book
''The Jungle Book'' (1894) is a collection of stories by the English author Rudyard Kipling. Most of the characters are animals such as Shere Khan the tiger and Baloo the bear, though a principal character is the boy or "man-cub" Mowgli, w ...
'', where it is the "old Sea Vitch—the big, ugly, bloated, pimpled, fat-necked, long-tusked walrus of the North Pacific, who has no manners except when he is asleep".
See also
*Elephant seal
Elephant seals are very large, oceangoing earless seals in the genus ''Mirounga''. Both species, the northern elephant seal (''M. angustirostris'') and the southern elephant seal (''M. leonina''), were hunted to the brink of extinction for oi ...
References
Further reading
*External links
* *Biologist Tracks Walruses Forced Ashore As Ice Melts
– audio report by ''
NPR
National Public Radio (NPR, stylized in all lowercase) is an American privately and state funded nonprofit media organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It differs from other ...
''Thousands Of Walruses Crowd Ashore Due To Melting Sea Ice
– video by '' National Geographic''
Voices in the Sea – Sounds of the Walrus
{{good article Pinnipeds of the Arctic Ocean Mammals described in 1758 Mammals of Asia Mammals of Canada Mammals of Greenland Mammals of North America Mammals of Russia Mammals of the United States Mammals of Europe Marine mammals Pinnipeds of North America Odobenids Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Holarctic fauna