Walleye larva (8741578944).jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the yellow pike or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern United States. It is a North American close relative of the European
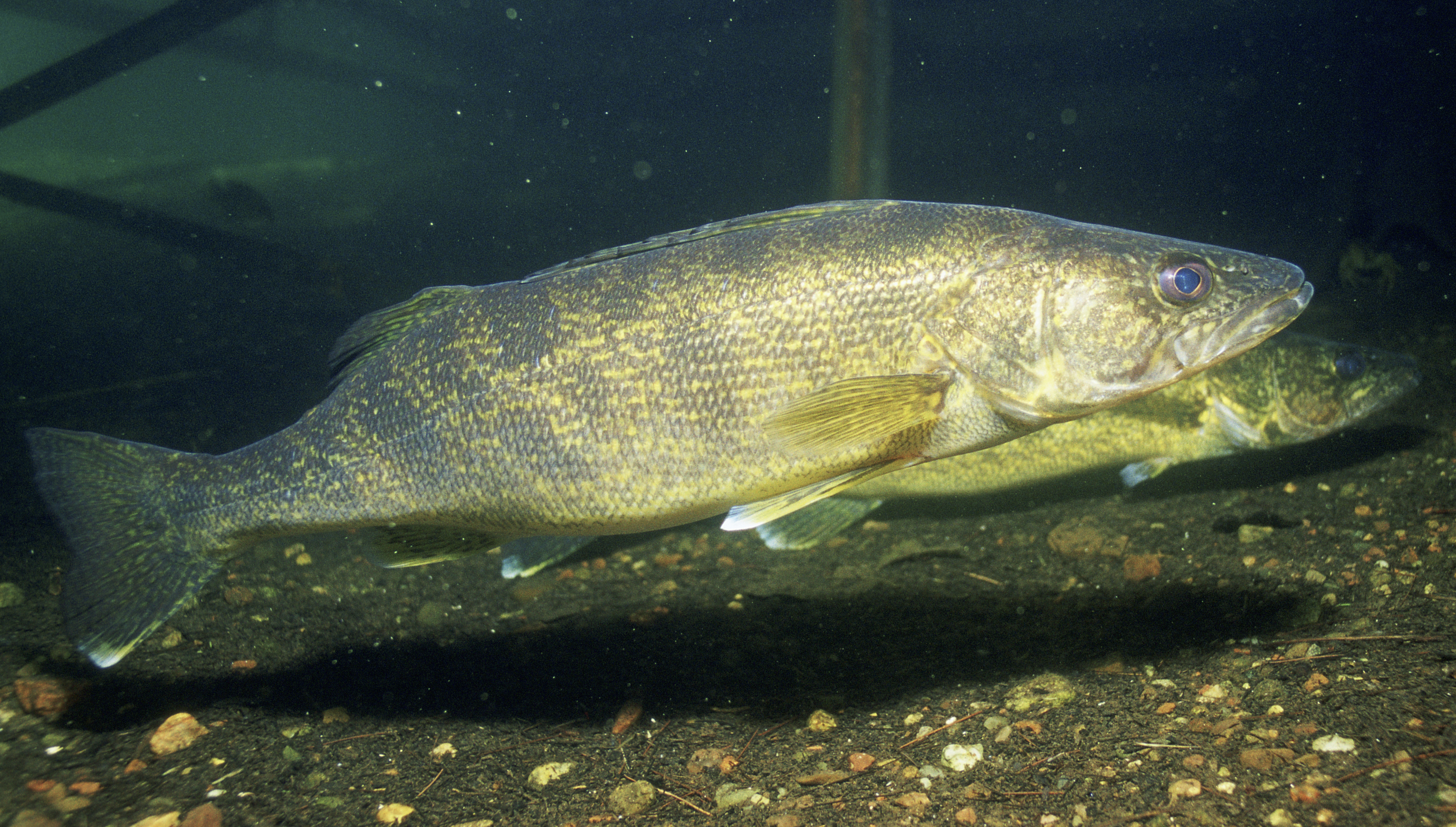 The name "walleye" comes from its pearlescent eyes caused by the reflective
The name "walleye" comes from its pearlescent eyes caused by the reflective
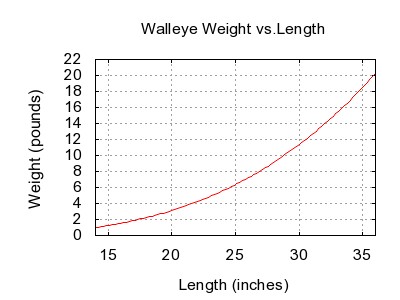 Walleyes grow to about in length, and weigh up to about . The maximum recorded size for the fish is in length and in weight. The rate depends partly on where in their range they occur, with southern populations often growing faster and larger. In general, females grow larger than males. Walleyes may live for decades; the maximum recorded age is 29 years. In heavily fished populations, however, few walleye older than five or six years of age are encountered. In North America, where they are highly prized, their typical size when caught is on the order of , substantially below their potential size.
As walleye grow longer, they increase in weight. The relationship between total length (''L'') and total weight (''W'') for nearly all species of fish can be expressed by an equation of the form
:
Invariably, ''b'' is close to 3.0 for all species, and ''c'' is a constant that varies among species. For walleye, ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000228 (with units in inches and pounds) or ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000005337 (with units in cm and kg).
This relationship suggests a walleye will weigh about , while a walleye will likely weigh about .
Walleyes grow to about in length, and weigh up to about . The maximum recorded size for the fish is in length and in weight. The rate depends partly on where in their range they occur, with southern populations often growing faster and larger. In general, females grow larger than males. Walleyes may live for decades; the maximum recorded age is 29 years. In heavily fished populations, however, few walleye older than five or six years of age are encountered. In North America, where they are highly prized, their typical size when caught is on the order of , substantially below their potential size.
As walleye grow longer, they increase in weight. The relationship between total length (''L'') and total weight (''W'') for nearly all species of fish can be expressed by an equation of the form
:
Invariably, ''b'' is close to 3.0 for all species, and ''c'' is a constant that varies among species. For walleye, ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000228 (with units in inches and pounds) or ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000005337 (with units in cm and kg).
This relationship suggests a walleye will weigh about , while a walleye will likely weigh about .
 In most of the species' range, male walleyes mature sexually between three and four years of age. Females normally mature about a year later. Adults migrate to tributary streams in late winter or early spring to lay eggs over gravel and rock, although open-water
In most of the species' range, male walleyes mature sexually between three and four years of age. Females normally mature about a year later. Adults migrate to tributary streams in late winter or early spring to lay eggs over gravel and rock, although open-water
 The walleye is considered to be a quite palatable freshwater fish, and consequently, is fished recreationally and commercially for food. Because of its nocturnal feeding habits, it is most easily caught at night using live minnows or lures that mimic small fish. Most commercial fisheries for walleye are situated in the Canadian waters of the
The walleye is considered to be a quite palatable freshwater fish, and consequently, is fished recreationally and commercially for food. Because of its nocturnal feeding habits, it is most easily caught at night using live minnows or lures that mimic small fish. Most commercial fisheries for walleye are situated in the Canadian waters of the
 Walleye is a culturally significant food in the
Walleye is a culturally significant food in the
Why walleye? How this flaky fish became a South Dakota food favorite
''Argus Leader'' (August 28, 2019). Walleye is popular in Minnesota; the Minnesota Legislature declared walleye the official state fish in 1965. Three towns—
Small 2010 Lake Erie walleye hatch predicted
{{Authority control Sander (fish) Fish described in 1818 Taxa named by Samuel L. Mitchill Commercial fish Sport fish Freshwater fish of North America Fish of Canada Fish of the United States Fish of the Great Lakes Symbols of Vermont Symbols of Minnesota Symbols of South Dakota Cuisine of Minnesota Cuisine of Manitoba
zander
The zander (''Sander lucioperca''), sander or pikeperch, is a species of ray-finned fish from the family Percidae, which includes the perches, ruffes and darters. It is found in freshwater and brackish habitats in western Eurasia. It is a popul ...
, also known as the pikeperch. The walleye is sometimes called the yellow walleye to distinguish it from the blue walleye
The blue walleye (''Sander vitreus'' var. ''glaucus''), also called the blue pike, was a unique color morph (formerly considered a subspecies) of walleye which was endemic to the Great Lakes of North America. Morphometric studies led biologists t ...
, which is a color morph that was once found in the southern Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
regions, but is now presumed extinct. However, recent genetic analysis of a preserved (frozen) 'blue walleye' sample suggests that the blue and yellow walleye were simply phenotypes
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or phenotypic trait, traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (biology), morphology or physical form and structure, its Developmental biology, dev ...
within the same species and do not merit separate taxonomic classification.
In parts of its range in English-speaking Canada, the walleye is known as a pickerel, though the fish is not related to the true pickerels, which are members of the family ''Esocidae
Esocidae is a family of fish in the order Esociformes, which contains pike, pickerel, and mudminnows. While the family traditionally only contained the genus ''Esox'', recent genetic and paleontological research have recovered ''Novumbra'' and ' ...
''.
Walleyes show a fair amount of variation across watersheds. In general, fish within a watershed are quite similar and are genetically distinct from those of nearby watersheds. The species has been artificially propagated for over a century and has been planted on top of existing populations or introduced into waters naturally devoid of the species, sometimes reducing the overall genetic distinctiveness of populations.
Etymology
 The name "walleye" comes from its pearlescent eyes caused by the reflective
The name "walleye" comes from its pearlescent eyes caused by the reflective tapetum lucidum
The ''tapetum lucidum'' ( ; ; ) is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrates and some other animals. Lying immediately behind the retina, it is a retroreflector. It reflects visible light back through the retina, increasing the light a ...
which, in addition to allowing the fish to see well in low-light conditions, gives its eyes an opaque appearance. Their vision affects their behavior. They avoid bright light and feed in low light on fish that cannot see as well as they do. Many anglers look for walleyes at night since this is when major feeding efforts occur. The fish's eyes also allow them to see well in turbid waters (stained or rough, breaking waters), which gives them an advantage over their prey. Thus, walleye anglers commonly look for locations where a good "walleye chop" (i.e., rough water) occurs. Their vision also allows the fish to populate the deeper regions in a lake, and they can often be found in deeper water, particularly during the warmest part of the summer and at night.
Description
Walleyes are largely olive and gold in color (hence the French common name: ''doré''—golden). The dorsal side of a walleye is olive, grading into a golden hue on the flanks. The olive/gold pattern is broken up by five darker saddles that extend to the upper sides. The color shades to white on the belly. The mouth of a walleye is large and is armed with many sharp teeth. The first dorsal and anal fins are spinous, as is the operculum. Walleyes are distinguished from their close relative thesauger
The sauger (''Sander canadensis'') is a freshwater perciform fish of the family Percidae that resembles its close relative, the walleye. The species is a member of the largest vertebrate order, the Perciformes.Jaeger, Matthew. 2004. Montana's ...
by the white coloration on the lower lobe of the caudal fin, which is absent on the sauger. In addition, the two dorsals and the caudal fin of the sauger are marked with distinctive rows of black dots which are absent from or indistinct on the same fins of walleyes.
Length and weight
 Walleyes grow to about in length, and weigh up to about . The maximum recorded size for the fish is in length and in weight. The rate depends partly on where in their range they occur, with southern populations often growing faster and larger. In general, females grow larger than males. Walleyes may live for decades; the maximum recorded age is 29 years. In heavily fished populations, however, few walleye older than five or six years of age are encountered. In North America, where they are highly prized, their typical size when caught is on the order of , substantially below their potential size.
As walleye grow longer, they increase in weight. The relationship between total length (''L'') and total weight (''W'') for nearly all species of fish can be expressed by an equation of the form
:
Invariably, ''b'' is close to 3.0 for all species, and ''c'' is a constant that varies among species. For walleye, ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000228 (with units in inches and pounds) or ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000005337 (with units in cm and kg).
This relationship suggests a walleye will weigh about , while a walleye will likely weigh about .
Walleyes grow to about in length, and weigh up to about . The maximum recorded size for the fish is in length and in weight. The rate depends partly on where in their range they occur, with southern populations often growing faster and larger. In general, females grow larger than males. Walleyes may live for decades; the maximum recorded age is 29 years. In heavily fished populations, however, few walleye older than five or six years of age are encountered. In North America, where they are highly prized, their typical size when caught is on the order of , substantially below their potential size.
As walleye grow longer, they increase in weight. The relationship between total length (''L'') and total weight (''W'') for nearly all species of fish can be expressed by an equation of the form
:
Invariably, ''b'' is close to 3.0 for all species, and ''c'' is a constant that varies among species. For walleye, ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000228 (with units in inches and pounds) or ''b'' = 3.180 and ''c'' = 0.000005337 (with units in cm and kg).
This relationship suggests a walleye will weigh about , while a walleye will likely weigh about .
Population dynamics
TheGarrison Dam National Fish Hatchery
A garrison (from the French language, French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that c ...
at Garrison Dam, North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, So ...
, is the largest walleye hatchery in the world. Although they are in high demand for fishing and consumption in North Dakota, elsewhere they are considered a nuisance. For that reason GDNFH is also researching hormonal population control to provide control options to other areas.
Reproduction
 In most of the species' range, male walleyes mature sexually between three and four years of age. Females normally mature about a year later. Adults migrate to tributary streams in late winter or early spring to lay eggs over gravel and rock, although open-water
In most of the species' range, male walleyes mature sexually between three and four years of age. Females normally mature about a year later. Adults migrate to tributary streams in late winter or early spring to lay eggs over gravel and rock, although open-water reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processes— deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock o ...
or shoal-spawning strains are seen, as well. Some populations are known to spawn on sand or vegetation. Spawning occurs at water temperatures of . A large female can lay up to 500,000 eggs, and no care is given by the parents to the eggs or fry. The eggs are slightly adhesive and fall into spaces between rocks. The incubation period for the embryos is temperature-dependent, but generally lasts from 12 to 30 days. After hatching, the free-swimming embryos spend about a week absorbing a relatively small amount of yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example ...
. Once the yolk has been fully absorbed, the young walleyes begin to feed on invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s, such as fly larvæ and zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
. After 40 to 60 days, juvenile walleyes become piscivorous
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equivalent to the Greek-derived word ichthyophage, both of which mean "fish eater". Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evoluti ...
. Thenceforth, both juvenile and adult walleyes eat fish almost exclusively, frequently yellow perch
The yellow perch (''Perca flavescens''), commonly referred to as perch, striped perch, American perch, American river perch or preacher is a freshwater perciform fish native to much of North America. The yellow perch was described in 1814 by Sam ...
or ciscoes
The ciscoes (or ''ciscos'') are salmonid fish that differ from other members of the genus in having upper and lower jaws of approximately equal length and high gill raker counts. These species have been the focus of much study recently, as rese ...
, moving onto bars and shoals at night to feed. Walleye also feed heavily on crayfish, minnows, and leeches.
Taxonomy
The walleye is part of the North American clade within the genus ''Sander
A sander is a power tool used to smooth surfaces by abrasion with sandpaper. Sanders have a means to attach the sandpaper and a mechanism to move it rapidly contained within a housing with means to hand-hold it or fix it to a workbench. Woodw ...
'', alongside the sauger
The sauger (''Sander canadensis'') is a freshwater perciform fish of the family Percidae that resembles its close relative, the walleye. The species is a member of the largest vertebrate order, the Perciformes.Jaeger, Matthew. 2004. Montana's ...
(''S. canadensis''). Hubbs described a taxon called the blue walleye
The blue walleye (''Sander vitreus'' var. ''glaucus''), also called the blue pike, was a unique color morph (formerly considered a subspecies) of walleye which was endemic to the Great Lakes of North America. Morphometric studies led biologists t ...
(''S. glaucus'') from the Great Lakes but subsequent taxonomic work showed no consistent differences between this form and the "yellow" walleye and the blue walleye is now considered to be a synonym and color variant of the walleye. The walleye was first formally described by the American naturalist Samuel Latham Mitchill (1764-1831) with the type locality given as Cayuga Lake
Cayuga Lake (,,) is the longest of central New York's glacial Finger Lakes, and is the second largest in surface area (marginally smaller than Seneca Lake) and second largest in volume. It is just under long. Its average width is , and it is ...
near Ithaca, New York
Ithaca is a city in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. Situated on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake, Ithaca is the seat of Tompkins County and the largest community in the Ithaca metropolitan statistical area. It is named ...
.
As food
 The walleye is considered to be a quite palatable freshwater fish, and consequently, is fished recreationally and commercially for food. Because of its nocturnal feeding habits, it is most easily caught at night using live minnows or lures that mimic small fish. Most commercial fisheries for walleye are situated in the Canadian waters of the
The walleye is considered to be a quite palatable freshwater fish, and consequently, is fished recreationally and commercially for food. Because of its nocturnal feeding habits, it is most easily caught at night using live minnows or lures that mimic small fish. Most commercial fisheries for walleye are situated in the Canadian waters of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
, and fried walleye is considered a staple of Canadian cuisine
Canadian cuisine consists of the cooking traditions and practices of Canada, with regional variances around the country. First Nations and Inuit have practiced their own culinary traditions in what is now Canada since time immemorial. The adve ...
. In Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
, the walleye is often fished for in the late afternoon on windy days (known as a "walleye chop") or at night. Often served as a sandwich in Minnesota's pubs where the fish is very popular, deep fried walleye on a stick is a Minnesota State Fair
The Minnesota State Fair is the state fair of the U.S. state of Minnesota. Also known by its slogan, "The Great Minnesota Get-Together", it is the largest state fair in the United States by average daily attendance and the second-largest state f ...
food.
Fishing
Because walleyes are popular with anglers,fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
for walleyes is regulated by most natural resource agencies. Management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a Government agency, government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includ ...
may include the use of quotas and length limits to ensure that populations are not overexploited
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to replenish. The term ap ...
. For example, in Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
, walleyes shorter than may not be legally kept.
Since walleyes have excellent visual acuity under low illumination levels, they tend to feed more extensively at dawn and dusk, on cloudy or overcast days, and under choppy conditions when light penetration into the water column is disrupted. Although anglers interpret this as light avoidance, it is merely an expression of the walleyes' competitive advantage over their prey under those conditions. Similarly, in darkly stained or turbid
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids can ...
waters, walleyes tend to feed throughout the day. In the spring and fall, walleyes are located near the shallower areas due to the spawning grounds, and they are most often located in shallower areas during higher winds due to the murkier, higher oxygenated water at around six feet deep. On calm spring days, walleyes are more often located at the deep side of the shoreline drop-off and around shore slopes around or deeper than 10 feet.
As a result of their widespread presence in Canada and the northern United States, walleyes are frequently caught while ice fishing
Ice fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities.
Shelters
Longe ...
, a popular winter pastime throughout those regions.
"Walleye chop" is a term used by walleye anglers for rough water typically with winds of , and is one of the indicators for good walleye fishing due to the walleyes' increased feeding activity during such conditions. In addition to fishing this chop, night fishing with live bait can be very effective.
The current all-tackle world record for a walleye is held by Mabry Harper, who caught an 11.34-kg (25-lb) walleye in Old Hickory Lake in Tennessee on 2 August 1960.
Cultural aspects
 Walleye is a culturally significant food in the
Walleye is a culturally significant food in the Upper Midwest
The Upper Midwest is a region in the northern portion of the U.S. Census Bureau's Midwestern United States. It is largely a sub-region of the Midwest. Although the exact boundaries are not uniformly agreed-upon, the region is defined as referring ...
.Makenzie HuberWhy walleye? How this flaky fish became a South Dakota food favorite
''Argus Leader'' (August 28, 2019). Walleye is popular in Minnesota; the Minnesota Legislature declared walleye the official state fish in 1965. Three towns—
Garrison, Minnesota
Garrison is a city in Crow Wing County, Minnesota, United States, along Mille Lacs Lake. The population was 210 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Brainerd Micropolitan Statistical Area. U.S. Highway 169 and Minnesota State Highway 18 are ...
, Baudette, Minnesota, and Garrison, North Dakota
Garrison is a city in McLean County, North Dakota, United States. The population was 1,462 at the 2020 census.
History
Garrison was laid out in 1905 when the Soo Line Railroad was extended to that point. The town took its name from Garrison C ...
s—each claim to be the "Walleye Capital of the World" and a large statue of the fish is erected in each town. Walleye pike was declared the official "state warm water fish" of Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
in 2012. (Vermont's official "state cold water fish" is the brook trout, ''salvelinus fontinalis''.)
South Dakota designated the walleye as its official state fish in 1982. Although the fish is native to South Dakota, living in Missouri River reservoirs and eastern glacial lakes of the state, it only became a popular food in South Dakota in 1970s and 1980s, when the fishing tournament circuit promoted the fish and operated walleye fishing contests in the state.
The walleye is the official provincial fish of Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
. Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
, Manitoba, considers the walleye (referred to locally as "pickerel") its most important local fish. Icelandic fishermen in Lake Winnipeg traditionally supplied the Winnipeg market. The walleye is also the provincial fish of Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dak ...
, which declared the species its official fish in 2015 after it won a fish emblem contest. Walleye is the most popular fish for sport fishing
Recreational fishing, also called sport fishing or game fishing, is fishing for leisure, exercise or competition. It can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is professional fishing for profit (economics), profit; or subsistence fishing ...
in Saskatchewan, and can be caught in many rivers, reservoirs, and lakes.Michael Snook, ''Fishing Saskatchewan: An Angler's Guide to Provincial Waters'' (University of Regina Press: 2004), pp. 101-03. The International Underwater Spearfishing Association record for largest spearfishing
Spearfishing is a method of fishing that involves impaling the fish with a straight pointed object such as a spear, gig or harpoon. It has been deployed in artisanal fishing throughout the world for millennia. Early civilisations were familia ...
-caught walleye is held by a 13.3-pound walleye caught in 2014 on the South Saskatchewan River
The South Saskatchewan River is a major river in Canada that flows through the provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan.
For the first half of the 20th century, the South Saskatchewan would completely freeze over during winter, creating spectacular ...
north of Lake Diefenbaker
Lake Diefenbaker is a reservoir and bifurcation lake in Southern Saskatchewan, Canada. It was formed by the construction of Gardiner Dam and the Qu'Appelle River Dam across the South Saskatchewan and Qu'Appelle Rivers respectively. Construc ...
.
See also
* Wisconsin Walleye WarReferences
Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
Small 2010 Lake Erie walleye hatch predicted
{{Authority control Sander (fish) Fish described in 1818 Taxa named by Samuel L. Mitchill Commercial fish Sport fish Freshwater fish of North America Fish of Canada Fish of the United States Fish of the Great Lakes Symbols of Vermont Symbols of Minnesota Symbols of South Dakota Cuisine of Minnesota Cuisine of Manitoba