Volyn oblast detail map.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in
 Geographically it occupies northern areas of the
Geographically it occupies northern areas of the

 After the disintegration of the Grand Duchy of Halych-Volhynia circa 1340, the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania divided the region between them, Poland taking Western Volhynia and Lithuania taking Eastern Volhynia (1352–1366). After 1569, Volhynia was organized as a province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During this period many
After the disintegration of the Grand Duchy of Halych-Volhynia circa 1340, the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania divided the region between them, Poland taking Western Volhynia and Lithuania taking Eastern Volhynia (1352–1366). After 1569, Volhynia was organized as a province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During this period many
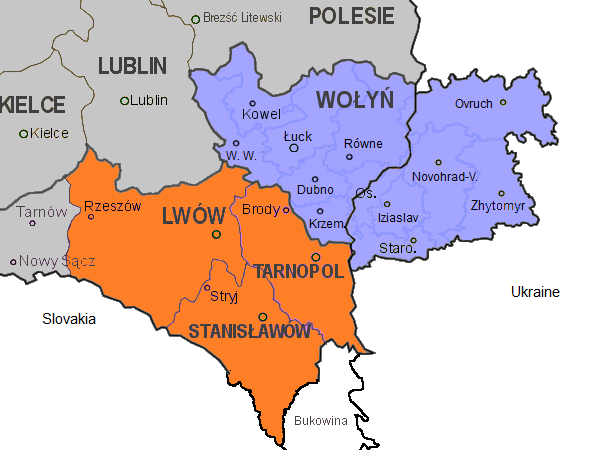
 In 1921, after the end of the Polish–Soviet War, the treaty known as the Peace of Riga divided the Volhynian Governorate between Poland and the Soviet Union. Poland took the larger part and established Volhynian Voivodeship.
Most of eastern Volhynian Governorate became part of the Ukrainian SSR, eventually being split into smaller districts. During that period, a number of national districts were formed within the Soviet Ukraine as part of cultural liberalization. The policies of Polonization in Poland led to formations of various resistance movements in West Ukraine and
In 1921, after the end of the Polish–Soviet War, the treaty known as the Peace of Riga divided the Volhynian Governorate between Poland and the Soviet Union. Poland took the larger part and established Volhynian Voivodeship.
Most of eastern Volhynian Governorate became part of the Ukrainian SSR, eventually being split into smaller districts. During that period, a number of national districts were formed within the Soviet Ukraine as part of cultural liberalization. The policies of Polonization in Poland led to formations of various resistance movements in West Ukraine and
''[Essay on the History of Volyn land]''
at Runivers.ru in
at Polona. Saint Petersburg: Imperial Academy of Sciences.
American Historical Society of Germans from Russia
in Lincoln, Nebraska
* , from the Roll "Fame" Family Genealogy website
The Journey to Trochenbrod and Lozisht Aug 2006
The Society for German Genealogy in Eastern Europe
The Swiss Mennonite Cultural & Historical Association
Volhynia.com
wolhynien.de
{{Authority control . Historical regions in Poland Historical regions in Ukraine Historical regions in Lithuania Historical regions
Central and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term encompassing the countries in the Baltics, Central Europe, Eastern Europe and Southeast Europe (mostly the Balkans), usually meaning former communist states from the Eastern Bloc and Warsaw Pact in Europe. ...
, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but the territory that still carries the name is Volyn Oblast, in western Ukraine
Western Ukraine or West Ukraine ( uk, Західна Україна, Zakhidna Ukraina or , ) is the territory of Ukraine linked to the former Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, which was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Austria ...
. Volhynia has changed hands numerous times throughout history and been divided among competing powers. For centuries it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Russian annexation, all of Volhynia was part of the Pale of Settlement designated by Imperial Russia on its south-western-most border.
Important cities include Lutsk, Rivne, Volodymyr, Ostroh, Ustyluh, Iziaslav, Peresopnytsia, and Novohrad-Volynskyi
Zviahel (, ; translit. ''Zvil'') is a city in the Zhytomyr Oblast (province) of northern Ukraine. Originally known as ''Zviahel'', the city was renamed to ''Novohrad-Volynskyi'' () in 1795 after annexation of territories of Polish–Lithuanian ...
(Zviahel). After the annexation of Volhynia by the Russian Empire as part of the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
, it also included the cities of Zhytomyr
Zhytomyr ( uk, Жито́мир, translit=Zhytomyr ; russian: Жито́мир, Zhitomir ; pl, Żytomierz ; yi, זשיטאָמיר, Zhitomir; german: Schytomyr ) is a city in the north of the western half of Ukraine. It is the Capital city, a ...
, Ovruch, Korosten. The city of Zviahel was renamed Novograd-Volynsky, and Volodymyr became Vladimir-Volinski.
Names and etymology
* uk, Волинь, Volyn'; * pl, Wołyń; * lt, Voluinė or ; * cs, Volyň; * hu, Volhínia; * german: Wolhynien or (both ); Volhynian German: , , or (all ); * yi, װאָהלין, translit=Vohlin. The alternative name for the region is Lodomeria after the city of Volodymyr, which was once a political capital of the medieval Volhynian Principality. According to some historians, the region is named after a semi-legendary city of ''Volin'' or ''Velin'', said to have been located on theSouthern Bug
, ''Pivdennyi Buh''
, name_etymology =
, image = Sunset S Bug Vinnitsa 2007 G1.jpg
, image_size = 270
, image_caption = Southern Bug River in the vicinity of Vinnytsia, Ukraine
, map = PietinisBug ...
River, whose name may come from the Proto-Slavic root 'wet'. In other versions, the city was located over to the west of Volodymyr near the mouth of the River, a tributary of the Western Bug
uk, Західний Буг be, Захо́дні Буг
, name_etymology =
, image = Wyszkow_Bug.jpg
, image_size = 250
, image_caption = Bug River in the vicinity of Wyszków, Poland
, map = Vi ...
.
Geography
 Geographically it occupies northern areas of the
Geographically it occupies northern areas of the Volhynian-Podolian Upland
Volhynian-Podolian Upland ( uk, Волинсько-Поділська височина) is a system of uplands in West Ukraine and Right-bank Ukraine.
The upland includes such features:
* Podillia Upland
**Opillia Upland
**Lviv Plateau
**Holohor ...
and western areas of Polesian Lowland along the Prypyat valley as part of the vast East European Plain, between the Western Bug
uk, Західний Буг be, Захо́дні Буг
, name_etymology =
, image = Wyszkow_Bug.jpg
, image_size = 250
, image_caption = Bug River in the vicinity of Wyszków, Poland
, map = Vi ...
in the west and upper streams of Uzh
The Uzh ( uk, Уж; translit. ''Uzh''; sk, Uh; hu, Ung, pl, Uż) is a river in Ukraine and Slovakia. Its name comes from the ancient west Slavic dialect word ''už'', meaning "Snake", (lat. "Serpentes").
The Uzh is a tributary of the Labore ...
and Teteriv
The Teteriv () is a right tributary of the Dnieper River in Ukraine. It has a length of 365 km and a drainage basin of 15,300 km².
In the underflow the valley of the Teteriv in Polissia on up to 4 km, the width of the river widens ...
rivers. Before the partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
, the eastern edge stretched a little west along the right-banks of the Sluch River or just east of it. Within the territory of Volhynia is located Little Polisie, a lowland that actually divides the Volhynian-Podolian Upland into separate Volhynian Upland and northern outskirts of Podolian Upland, the so-called Kremenets Hills. Volhynia is located in the basins of the Western Bug and Prypyat, therefore most of its rivers flow either in a northern or a western direction.
Relative to other historical regions, it is northeast of Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, east of Lesser Poland and northwest of Podolia. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, and it is often considered to overlap a number of other regions, among which are Polesia and Podlasie
Podlachia, or Podlasie, ( pl, Podlasie, , be, Падляшша, translit=Padliašša, uk, Підляшшя, translit=Pidliashshia) is a historical region in the north-eastern part of Poland. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the c ...
.
The territories of historical Volhynia are now part of the Volyn, Rivne and parts of the Zhytomyr
Zhytomyr ( uk, Жито́мир, translit=Zhytomyr ; russian: Жито́мир, Zhitomir ; pl, Żytomierz ; yi, זשיטאָמיר, Zhitomir; german: Schytomyr ) is a city in the north of the western half of Ukraine. It is the Capital city, a ...
, Ternopil and Khmelnytskyi Oblast
Khmelnytskyi Oblast ( uk, Хмельни́цька о́бласть, translit=Khmelnytska oblast; also referred to as Khmelnychchyna — uk, Хмельни́ччина) is an oblast (province) of western Ukraine covering portions of the histo ...
s of Ukraine, as well as parts of Poland (see Chełm). Major cities include Lutsk, Rivne, Kovel
Kovel (, ; pl, Kowel; yi, קאוולע / קאוולי ) is a city in Volyn Oblast (province), in northwestern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Kovel Raion (district). Population:
Kovel gives its name to one of the oldest runi ...
, Volodymyr, Kremenets (Ternopil Oblast) and Starokostiantyniv (Khmelnytskyi Oblast). Before World War II, many Jewish '' shtetls'' (small towns), such as Trochenbrod
Trochenbrod or Trohinbrod, also in Polish: ''Zofiówka'', or in russian: Софиевка (Sofievka), in uk, Трохимбрід (Trokhymbrid), he, טרוכנברוד, was an exclusively Jewish shtetl – a small town, with an area of – loc ...
and Lozisht
Ignatówka, also Lozisht, was a Jewish shtetl (village) located in what is now western Ukraine but which used to be part of the Second Polish Republic before the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland in 1939. Ignatówka was bordering a Jewish shtetl in Z ...
, were an integral part of the region. At one time all of Volhynia was part of the Pale of Settlement designated by Imperial Russia on its southwesternmost border.
History
The first records can be traced to the Ruthenian chronicles, such as the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
,'' which mentions tribes of the Dulebes
The Dulebes, Dulebs, Dudlebi or Dulibyh ( uk, Дуліби) were one of the tribal unions of Early Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries. According to medieval sources they lived in Western Volhynia, as well as southern parts of the Duchy o ...
, Buzhans and Volhynians. The land was mentioned in the works of Al-Masudi and Abraham ben Jacob that in ancient times the ''Walitābā'' and king ''Mājik'', which some read as ''Walīnānā'' and identified with the Volhynians, were "the original, pure-blooded Saqaliba, the most highly honoured" and dominated the rest of the Slavic tribes, but due to "dissent" their "original organization was destroyed" and "the people divided into factions, each of them ruled by their own king", implying existence of a Slavic federation which perished after the attack of the Pannonian Avars.
Volhynia may have been included in (or was in the sphere of influence of) the Grand Duchy of Kyiv (Ruthenia) as early as the tenth century. At that time Princess Olga
Olga may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Olga (name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters named Olga or Olha
* Michael Algar (born 1962), English singer also known as "Olga"
Places
Russia
* Olga, Russia, ...
sent a punitive raid against the Drevlians to avenge the death of her husband Grand Prince Igor
Igor may refer to:
People
* Igor (given name), an East Slavic given name and a list of people with the name
* Mighty Igor (1931–2002), former American professional wrestler
* Igor Volkoff, a professional wrestler from NWA All-Star Wrestling
* ...
(Ingvar Röreksson); she later established pogost
''Pogost'' (russian: погост, from Old East Slavic: погостъ) is a historical term with several meanings in the Russian language. It has also been borrowed into Latgalian (''pogosts''), Finnish (''pogosta'') and Latvian (''pagasts'') ...
s along the Luha River
The Luha ( uk, Луга, pl, Ług) is a river in Ukraine and a right tributary of the Bug. Its source is located near village Kolpytiv located at the Horokhiv Upland and in its upper reaches the Luha runs mainly in western, northwestern direct ...
. In the opinion of the Ukrainian historian Yuriy Dyba, the chronicle phrase «и оустави по мьстѣ. погосты и дань. и по лузѣ погосты и дань и ѡброкы» (and established in place pogosts and tribute along Luha), the path of pogosts and tribute reflects the actual route of Olga's raid against the Drevlians further to the west, up to the Western Bug
uk, Західний Буг be, Захо́дні Буг
, name_etymology =
, image = Wyszkow_Bug.jpg
, image_size = 250
, image_caption = Bug River in the vicinity of Wyszków, Poland
, map = Vi ...
's right tributary Luha River
The Luha ( uk, Луга, pl, Ług) is a river in Ukraine and a right tributary of the Bug. Its source is located near village Kolpytiv located at the Horokhiv Upland and in its upper reaches the Luha runs mainly in western, northwestern direct ...
.
As early as 983, Vladimir the Great appointed his son Vsevolod as the ruler of the Volhynian Principality. In 988, he established the city of Volodymer (''Володимѣръ'').
Volhynia's early history coincides with that of the duchies or principalities of Halych and Volhynia. These two successor states of the Kyivan Rus formed Halych-Volhynia between the 12th and the 14th centuries.

 After the disintegration of the Grand Duchy of Halych-Volhynia circa 1340, the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania divided the region between them, Poland taking Western Volhynia and Lithuania taking Eastern Volhynia (1352–1366). After 1569, Volhynia was organized as a province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During this period many
After the disintegration of the Grand Duchy of Halych-Volhynia circa 1340, the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania divided the region between them, Poland taking Western Volhynia and Lithuania taking Eastern Volhynia (1352–1366). After 1569, Volhynia was organized as a province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During this period many Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
and Jews settled in the area. The Roman and Greek Catholic churches became established in the province. In 1375, a Roman Catholic Diocese of Lodomeria was established, but it was suppressed in 1425. Many Orthodox churches joined the latter organization in order to benefit from a more attractive legal status. Records of the first agricultural colonies of Mennonites, Protestants from Germany, date from 1783.
After the Third partition of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795, Volhynia was annexed as the Volhynian Governorate of the Russian Empire. It covered an area of 71,852.7 square kilometres. Following this annexation, the Russian government greatly changed the religious make-up of the area: it forcibly liquidated the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church, transferring all of its buildings to the ownership and control of the Russian Orthodox Church. Many Roman Catholic church buildings were also given to the Russian Church. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Lutsk was suppressed by order of Empress Catherine II.
In 1897, the population amounted to 2,989,482 people (41.7 per square kilometre). It consisted of 73.7 percent East Slavs (predominantly Ukrainians), 13.2 percent Jews, 6.2 percent Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
, and 5.7 percent Germans. Most of the German settlers had immigrated from Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It w ...
. A small number of Czech settlers also had migrated here. Although economically the area was developing rather quickly, upon the eve of the First World War it was still the most rural province in Western Russia.
Ukrainian People's Republic
After theFebruary Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and somet ...
and the formation of the Russian Provisional Government, Ukrainian nationalists declared the autonomous Ukrainian People's Republic. The territory of Volhynia was split in half by a frontline just west of the city of Lutsk. Due to an invasion of the Bolsheviks, the government of Ukraine was forced to retreat to Volhynia after the sack of Kyiv. Military aid from the Central Powers as a result of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk brought peace in the region and some degree of stability. Until the end of the war, the area saw a revival of Ukrainian culture after years of Russian oppression and the denial of Ukrainian traditions. After German troops were withdrawn, the whole region was engulfed by a new wave of military actions by Poles and Russians competing for control of the territory. The Ukrainian People's Army was forced to fight on three fronts: Bolsheviks, Poles and a Volunteer Army of Imperial Russia.
Interwar period

 In 1921, after the end of the Polish–Soviet War, the treaty known as the Peace of Riga divided the Volhynian Governorate between Poland and the Soviet Union. Poland took the larger part and established Volhynian Voivodeship.
Most of eastern Volhynian Governorate became part of the Ukrainian SSR, eventually being split into smaller districts. During that period, a number of national districts were formed within the Soviet Ukraine as part of cultural liberalization. The policies of Polonization in Poland led to formations of various resistance movements in West Ukraine and
In 1921, after the end of the Polish–Soviet War, the treaty known as the Peace of Riga divided the Volhynian Governorate between Poland and the Soviet Union. Poland took the larger part and established Volhynian Voivodeship.
Most of eastern Volhynian Governorate became part of the Ukrainian SSR, eventually being split into smaller districts. During that period, a number of national districts were formed within the Soviet Ukraine as part of cultural liberalization. The policies of Polonization in Poland led to formations of various resistance movements in West Ukraine and West Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus ( be, Заходняя Беларусь, translit=Zachodniaja Bielaruś; pl, Zachodnia Białoruś; russian: Западная Белоруссия, translit=Zapadnaya Belorussiya) is a historical region of mod ...
, including Volhynia. In 1931, the Vatican of the Roman Catholic Church established a Ukrainian Catholic Apostolic Exarchate of Volhynia, Polesia and Pidliashia (''Wolhynien, Polissia und Pidliashia'' in German), where the congregation practiced the Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
Th ...
in Ukrainian language.
From 1935 to 1938, the government of the Soviet Union deported numerous nationals from Volhynia in a population transfer to Siberia and Central Asia, as part of the dekulakization
Dekulakization (russian: раскулачивание, ''raskulachivanie''; uk, розкуркулення, ''rozkurkulennia'') was the Soviet campaign of political repressions, including arrests, deportations, or executions of millions of kulak ...
, an effort to suppress peasant farmers in the region. These people included Poles of Eastern Volhynia (see Population transfer in the Soviet Union
From 1930 to 1952, the government of the Soviet Union, on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin under the direction of the NKVD official Lavrentiy Beria, forcibly transferred populations of various groups. These actions may be classified ...
).
World War II
Following the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact in 1939, and the subsequent invasion and division of Polish territories between the Reich and the USSR, the Soviet Union invaded and occupied the Polish part of Volhynia. In the course of theNazi–Soviet population transfers
The Nazi–Soviet population transfers were population transfers of ethnic Germans, ethnic Poles, and some ethnic East Slavs that took place from 1939 to 1941. These transfers were part of the German '' Heim ins Reich'' policy in accordance with ...
which followed this (temporary) German-Soviet alliance, most of the ethnic German-minority population of Volhynia were transferred to those Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany. Following the mass deportations and arrests carried out by the NKVD, and repressive actions against Poles taken by Germany, including deportation to the Reich to forced labour camps, arrests, detention in camps and mass executions, by 1943 ethnic Poles constituted only 10–12% of the entire population of Volhynia.
During the German invasion, around 50,000–100,000 Polish people (mostly women and children) in Volhynia were massacred by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army. The number of Ukrainian victims of Polish retaliatory attacks until the spring of 1945 is estimated at approx. 2,000−3,000 in Volhynia. In 1945, Soviet Ukraine expelled ethnic Germans from Volhynia following the end of the war, claiming that Nazi Germany had used ethnic Germans in eastern Europe as part of an alleged Generalplan Ost. The expulsion of Germans from eastern Europe was part of broader mass population transfers after the war.
The Soviet Union annexed Volhynia to Ukraine after the end of World War II. In 1944, the communists in Volyhnia suppressed the Ukrainian Catholic Apostolic Exarchate. Most of the remaining ethnic Polish population were expelled to Poland in 1945. Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
in the 1990s, Volhynia has been an integral part of Ukraine.
Important relics
*Peresopnytsia Gospel
The Peresopnytsia Gospel ( uk, Пересопницьке Євангеліє, ''Peresopnytske Yevanheliie''), dating from the 16th century, is one of the most intricate surviving East Slavic manuscripts. It was made between 15 August 1556 and 29 ...
Famous personalities
* Dov Ber of Mezeritch, rabbi * Hayim Nahman Bialik, literary figure * Shlomo Flam, rabbi *Moisey Kasyanik
Moisey Davidovich Kasyanik (russian: Моисе́й Дави́дович Касья́ник, also "Moisei and Moysey" and "Kas'ianik, Kosyanik, or Kosianiki"; born January 1, 1911 – 1988) was a Soviet weightlifter.
He was Jewish, and was born i ...
, weightlifter
* Sergei Korolev (1907–1966), Soviet rocket engineer and spacecraft designer.
* Malbim, rabbi
See also
*Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia
, conventional_long_name = Principality of Galicia–VolhyniaKingdom of Galicia–Volhynia
, common_name = Galicia–Volhynia
, status = Vassal state of the Golden Horde (from 1246)
, era = Middle Ages
, year_start = 1199
, year_end = 1349
, ...
* Galicia (Eastern Europe)
* Massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia
* Historiography of the Volyn tragedy
* Polish Autonomous District
Polish National Districts (called in Russian "полрайоны", ''polrajony'', an abbreviation for "польские национальные районы", "Polish national raions") were in the interbellum period possessing some form of a na ...
* Kresy Wschodnie
References
Literature
* Andriyashev, Alexander (1887)''[Essay on the History of Volyn land]''
at Runivers.ru in
Djvu
DjVu ( , like French "déjà vu") is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as ima ...
and PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
formats. Kyiv: Imperial University of Saint Vladimir.
*
* .
* Merten, Ulrich (2015). ''Voices from the Gulag: Oppression of the German Minority in the Soviet Union''. Lincoln, NE: American Historical Society of Germans from Russia.
* Potocki, Jan (1805)at Polona. Saint Petersburg: Imperial Academy of Sciences.
External links
American Historical Society of Germans from Russia
in Lincoln, Nebraska
* , from the Roll "Fame" Family Genealogy website
The Journey to Trochenbrod and Lozisht Aug 2006
The Society for German Genealogy in Eastern Europe
The Swiss Mennonite Cultural & Historical Association
Volhynia.com
wolhynien.de
{{Authority control . Historical regions in Poland Historical regions in Ukraine Historical regions in Lithuania Historical regions