Viet Nam Export Treemap.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Vietnamese people ( vi, người Việt, lit=Viet people) or Kinh people ( vi, người Kinh) are a
"Shang Dynasty - Political History"
in ''ChinaKnowledge.de - An Encyclopaedia on Chinese History, Literature and Art''. quote: "Enemies of the Shang state were called fang 方 "regions", like the Tufang 土方, which roamed the northern region of Shanxi, the Guifang 鬼方 and Gongfang 𢀛方 in the northwest, the Qiangfang 羌方, Suifang 繐方, Yuefang 戉方, Xuanfang 亘方 and Zhoufang 周方 in the west, as well as the Yifang 夷方 and Renfang 人方 in the southeast." In the early 8th century BC, a tribe on the middle
Waterworld: lexical evidence for aquatic subsistence strategies in Austroasiatic
In ''Papers from the Seventh International Conference on Austroasiatic Linguistics'', 174-193. Journal of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society Special Publication No. 3. University of Hawaii Press.Blench, Roger. 2017.
Waterworld: lexical evidence for aquatic subsistence strategies in Austroasiatic
'. Presented at ICAAL 7, Kiel, Germany.Sidwell, Paul. 2015b. ''Phylogeny, innovations, and correlations in the prehistory of Austroasiatic''. Paper presented at the workshop ''Integrating inferences about our past: new findings and current issues in the peopling of the Pacific and South East Asia'', 22–23 June 2015, Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, Jena, Germany. Some linguists (James Chamberlain, Joachim Schliesinger) suggested that the Vietic-speaking people migrated from North Central Region to the
 The earliest reference of the proto-Vietnamese in Chinese annals was the ''Lạc'' (Chinese: Luo), ''
The earliest reference of the proto-Vietnamese in Chinese annals was the ''Lạc'' (Chinese: Luo), ''
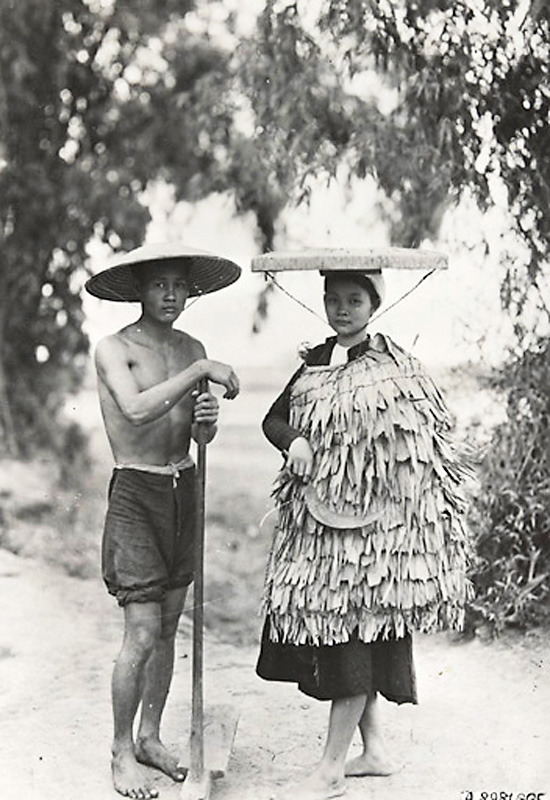




 With the death of Thánh Tông in 1497, the Đại Việt kingdom swiftly declined. Climate extremes, failing crops, regionalism and factionism tore the Vietnamese apart. From 1533 to 1790s, four powerful Vietnamese families: Mạc, Lê, Trịnh and Nguyễn, each ruled on their own domains. In northern Vietnam (Đàng Ngoài–outer realm), the Lê Emperors barely sat on the throne while the Trịnh lords held power of the court. The Mạc controlled northeast Vietnam. The Nguyễn lords ruled the southern polity of Đàng Trong (inner realm). Thousands of ethnic Vietnamese migrated south, settled on the old Cham lands. European missionaries and traders from the sixteenth century brought new religion, ideas and crops to the Vietnamese (Annamese). By 1639, there were 82,500 Catholic converts throughout Vietnam. In 1651,
With the death of Thánh Tông in 1497, the Đại Việt kingdom swiftly declined. Climate extremes, failing crops, regionalism and factionism tore the Vietnamese apart. From 1533 to 1790s, four powerful Vietnamese families: Mạc, Lê, Trịnh and Nguyễn, each ruled on their own domains. In northern Vietnam (Đàng Ngoài–outer realm), the Lê Emperors barely sat on the throne while the Trịnh lords held power of the court. The Mạc controlled northeast Vietnam. The Nguyễn lords ruled the southern polity of Đàng Trong (inner realm). Thousands of ethnic Vietnamese migrated south, settled on the old Cham lands. European missionaries and traders from the sixteenth century brought new religion, ideas and crops to the Vietnamese (Annamese). By 1639, there were 82,500 Catholic converts throughout Vietnam. In 1651,  Despite having a long recorded history of the Vietnamese language and people, the identification and distinction of 'ethnic Vietnamese' or ethnic Kinh, as well as other ethnic groups in Vietnam, were only begun by colonial administration in the late 19th and early 20th century. Following colonial government's efforts of ethnic classificating, nationalism, especially ethnic nationalism, ethnonationalism and eugenic Social Darwinism were encouraged among the new Vietnamese intelligentsias discourse. Ethnic tensions sparked by Vietnamese ethnonationalism peaked during the late 1940s at the beginning phase of the First Indochina War (1946–1954), which resulted in violences between Khmer and Vietnamese in the Mekong Delta. Further North Vietnam's Soviet-style social integrational and ethnic classification, tried to build an image of Diversity under the harmony of Socialism, promoting the idea of the Vietnamese nation as a 'great single family' comprised by many different ethnic groups, and Vietnamese ethnic chauvinism was officially discouraged.
Despite having a long recorded history of the Vietnamese language and people, the identification and distinction of 'ethnic Vietnamese' or ethnic Kinh, as well as other ethnic groups in Vietnam, were only begun by colonial administration in the late 19th and early 20th century. Following colonial government's efforts of ethnic classificating, nationalism, especially ethnic nationalism, ethnonationalism and eugenic Social Darwinism were encouraged among the new Vietnamese intelligentsias discourse. Ethnic tensions sparked by Vietnamese ethnonationalism peaked during the late 1940s at the beginning phase of the First Indochina War (1946–1954), which resulted in violences between Khmer and Vietnamese in the Mekong Delta. Further North Vietnam's Soviet-style social integrational and ethnic classification, tried to build an image of Diversity under the harmony of Socialism, promoting the idea of the Vietnamese nation as a 'great single family' comprised by many different ethnic groups, and Vietnamese ethnic chauvinism was officially discouraged.

 Originally from northern Vietnam and southern China, the Vietnamese have expanded south and conquered much of the land belonging to the former Champa Kingdom and Khmer Empire over the centuries. They are the dominant ethnic group in most provinces of Vietnam, and constitute a small percentage of the population in neighbouring Cambodia.
Beginning around the sixteenth century, groups of Vietnamese migrated to Cambodia and China for commerce and political purposes. Descendants of Vietnamese migrants in China form the Gin ethnic group in the country and primarily reside in and around Guangxi Province. Vietnamese form the largest ethnic minority group in Cambodia, at 5% of the population. Under the Khmer Rouge, they were heavily persecuted and survivors of the regime largely fled to Vietnam.
During French Indochina, French colonialism, Vietnam was regarded as the most important colony in Asia by the French colonial powers, and the Vietnamese had a higher social standing than other ethnic groups in French Indochina. As a result, educated Vietnamese were often trained to be placed in colonial government positions in the other Asian French colonies of Laos and Cambodia rather than locals of the respective colonies. There was also a significant representation of Vietnamese students in France during this period, primarily consisting of members of the elite class. A large number of Vietnamese also migrated to France as workers, especially during World War I and World War II, when France recruited soldiers and locals of its colonies to help with war efforts in Metropolitan France. The wave of migrants to France during World War I formed the first major presence of Vietnamese people in France and the Western world.La Diaspora Vietnamienne en France un cas particulier
Originally from northern Vietnam and southern China, the Vietnamese have expanded south and conquered much of the land belonging to the former Champa Kingdom and Khmer Empire over the centuries. They are the dominant ethnic group in most provinces of Vietnam, and constitute a small percentage of the population in neighbouring Cambodia.
Beginning around the sixteenth century, groups of Vietnamese migrated to Cambodia and China for commerce and political purposes. Descendants of Vietnamese migrants in China form the Gin ethnic group in the country and primarily reside in and around Guangxi Province. Vietnamese form the largest ethnic minority group in Cambodia, at 5% of the population. Under the Khmer Rouge, they were heavily persecuted and survivors of the regime largely fled to Vietnam.
During French Indochina, French colonialism, Vietnam was regarded as the most important colony in Asia by the French colonial powers, and the Vietnamese had a higher social standing than other ethnic groups in French Indochina. As a result, educated Vietnamese were often trained to be placed in colonial government positions in the other Asian French colonies of Laos and Cambodia rather than locals of the respective colonies. There was also a significant representation of Vietnamese students in France during this period, primarily consisting of members of the elite class. A large number of Vietnamese also migrated to France as workers, especially during World War I and World War II, when France recruited soldiers and locals of its colonies to help with war efforts in Metropolitan France. The wave of migrants to France during World War I formed the first major presence of Vietnamese people in France and the Western world.La Diaspora Vietnamienne en France un cas particulier
(in French) When Vietnam gained its independence from France in 1954, a number of Vietnamese loyal to the colonial government also migrated to France. During the partition of Vietnam into North Vietnam, North and South Vietnam, South, a number of South Vietnamese students also arrived to study in France, along with individuals involved in commerce for trade with France, which was a principal economic partner with South Vietnam.
When Vietnam gained its independence from France in 1954, a number of Vietnamese loyal to the colonial government also migrated to France. During the partition of Vietnam into North Vietnam, North and South Vietnam, South, a number of South Vietnamese students also arrived to study in France, along with individuals involved in commerce for trade with France, which was a principal economic partner with South Vietnam.
 Forced repatriation in 1970 and deaths during the Khmer Rouge era reduced the Vietnamese Cambodian, Vietnamese population in Cambodia from between 250,000 and 300,000 in 1969 to a reported 56,000 in 1984.
The Fall of Saigon and end of the Vietnam War prompted the start of the Vietnamese diaspora, which saw millions of Vietnamese fleeing the country from the new communist regime. Recognizing an international humanitarian crisis, many countries accepted Vietnamese refugees, primarily the United States, France, Australia and Canada. Meanwhile, under the new communist regime, tens of thousands of Vietnamese were sent to work or study in Eastern Bloc countries of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe as development aid to the Vietnamese government and for migrants to acquire skills that were to be brought home to help with development. However, after the fall of the Berlin Wall, a vast majority of these overseas Vietnamese decided to remain in their host nations.
Forced repatriation in 1970 and deaths during the Khmer Rouge era reduced the Vietnamese Cambodian, Vietnamese population in Cambodia from between 250,000 and 300,000 in 1969 to a reported 56,000 in 1984.
The Fall of Saigon and end of the Vietnam War prompted the start of the Vietnamese diaspora, which saw millions of Vietnamese fleeing the country from the new communist regime. Recognizing an international humanitarian crisis, many countries accepted Vietnamese refugees, primarily the United States, France, Australia and Canada. Meanwhile, under the new communist regime, tens of thousands of Vietnamese were sent to work or study in Eastern Bloc countries of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe as development aid to the Vietnamese government and for migrants to acquire skills that were to be brought home to help with development. However, after the fall of the Berlin Wall, a vast majority of these overseas Vietnamese decided to remain in their host nations.
link to the article's abstract.
/ref> Kim Wook et al. (2000) said that, genetically, Vietnamese people more probably clustered with East Asians of which the study analyzed DNA samples of Chinese people, Chinese, Japanese people, Japanese, Koreans and Mongols, Mongolians rather than with Southeast Asians of which the study analyzed DNA samples of Indonesians, Filipinos, Thai people, Thais and Vietnamese. The study said that Vietnamese people were the only population in the study's Phylogenetics, phylogenetic analysis that did not reflect a sizable genetic difference between East Asian and Southeast Asian populations. The study said that the likely reason for Vietnamese people more probably clustering with East Asians was genetic drift and distinct Founder effect, founder populations. The study said that the alternative reason for Vietnamese people more probably clustering with East Asians is a recent Colonisation (biology), range expansion from South China. The study mentioned that the majority of its Vietnamese DNA samples were from
link.
/ref> Jung Jongsun et al. (2010) said that genetic structure analysis found significant admixture in "''Vietnamese (or Khmer people, Cambodian) with unknown Southern original settlers.''" The study said that it used Cambodians and Vietnamese to represent "Southern people," and the study used Cambodia ( Khmer) and
link.
A 2015 study revealed that Vietnamese (Kinh) test subjects showed more genetic variants in common with Chinese compared to Japanese. Sara Pischedda et al. (2017) stated that modern Vietnamese have a major component of their ethnic origin coming from the now-called southern China region and a minor component from a Thai-Indonesian composite. The study said that admixture analysis indicates that Vietnamese Kinh have a major part which is most common in Han Chinese, Chinese and two minor parts which have the highest prevalence in the Bidayuh of Malaysia and the Proto-Malay. The study said that multidimensional scaling analysis indicates that Vietnamese Kinh have a closeness to Malay people, Thai and Chinese, and the study said that Malays and Thai are the samples which could be admixed with Chinese in the Vietnamese gene pool. The study said that Vietnamese Human mitochondrial genetics, mtDNA genetic variation matches well with the pattern seen in Southeast Asia, and the study said that most Vietnamese people had mtDNA haplotypes that clustered in clades Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M7 (20%) and Haplogroup R (mtDNA), R9’F (27%) which are clades that also dominate maternal lineages in Southeast Asia more generally.Pischedda, S. et al. (2017). Phylogeographic and genome-wide investigations of Vietnam ethnic groups reveal signatures of complex historical demographic movements. ''Scientific Reports, 7''(1). Pages 4, 6, 11, 13, & 14. Digital object identifier, doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12813-6 Retrieved January 6, 2018, fro
link.
/ref>
link to the article.
/ref> However, such a theory is not within the mainstream genetic study of most historians and scholars due to the lack of evidence of any such migration path ever occurring.
''The Making of South East Asia''
(illustrated, reprint ed.). University of California Press. . Retrieved 7 August 2013. * * * * *Contributor: Far-Eastern Prehistory Associatio
''Asian Perspectives, Volume 28, Issue 1''
(1990) University Press of Hawaii. Retrieved 7 August 2013. * *Hall, Kenneth R., ed. (2008)
''Secondary Cities and Urban Networking in the Indian Ocean Realm, C. 1400–1800''
Volume 1 of Comparative urban studies. Lexington Books. . Retrieved 7 August 2013. * * * * * * * * * * *Marr, David G. (2010). Vietnamese, Chinese, and Overseas Chinese during the Chinese Occupation of Northern Indochina (1945-1946), ''Chinese Southern Diaspora Studies'', Vol. 4: 129–139. * * * * * * * *Ungar, E. S. (1988). The Struggle Over the Chinese Community in Vietnam, 1946–1986, ''Pacific Affairs'', Vol. 60, Issue 4: 596–614. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
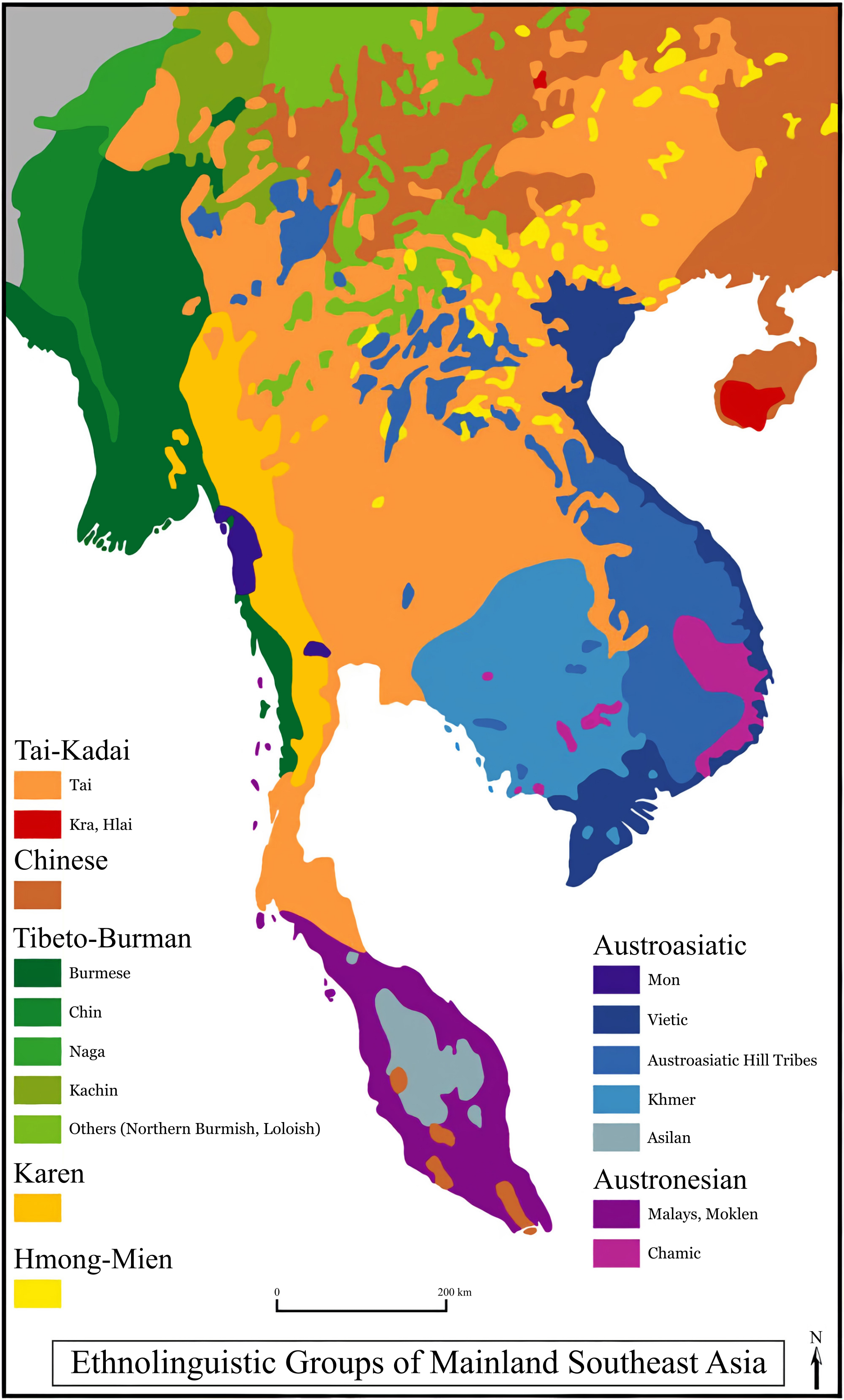
n ethnic group native to modern-day Northern Vietnam
Northern Vietnam ( vi, Bắc Bộ) is one of three geographical regions within Vietnam. It consists of three administrative regions: the Northwest (Vùng Tây Bắc), the Northeast (Vùng Đông Bắc), and the Red River Delta (Đồng Bằng S ...
and Southern China (Jing Islands, Dongxing, Guangxi). The native language is Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
, the most widely spoken Austroasiatic language
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are t ...
.
Vietnamese Kinh people account for just over 85.32% of the population of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
in the 2019 census, and are officially known as Kinh people () to distinguish them from the other minority group
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
s residing in the country such as the Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related to ...
, Cham
Cham or CHAM may refer to:
Ethnicities and languages
*Chams, people in Vietnam and Cambodia
**Cham language, the language of the Cham people
***Cham script
*** Cham (Unicode block), a block of Unicode characters of the Cham script
*Cham Albania ...
, or Mường. The Vietnamese are one of the four main groups of Vietic
The Vietic languages are a branch of the Austroasiatic language family, spoken by the Vietic peoples in Laos and Vietnam. The branch was once referred to by the terms ''Việt–Mường'', ''Annamese–Muong'', and ''Vietnamuong''; the term '' ...
speakers in Vietnam, the others being the Mường, Thổ, and Chứt people
The Chut (Vietnamese: ''Người Chứt'', Rục language: ''Cheut'' /rocky mountain) are a small ethnic group located in the Minh Hóa and Tuyên Hóa districts of Quảng Bình Province, in Vietnam's North Central Coast.
''Chut'' is not a d ...
. They are related to the Gin people, a Vietnamese ethnic group in China.
Terminology
According to Churchman (2010), all endonyms and exonyms referring to the Vietnamese such as ''Viet'' (related to ancient Chinese geographical imagination), ''Kinh'' (related to medieval administrative designation), or ''Keeu'' and ''Kæw'' (derived from Jiāo 交, ancient Chinese toponym for Northern Vietnam,Old Chinese
Old Chinese, also called Archaic Chinese in older works, is the oldest attested stage of Chinese, and the ancestor of all modern varieties of Chinese. The earliest examples of Chinese are divinatory inscriptions on oracle bones from around 1250 ...
''*kraw'') by Kra-Dai speaking peoples, are related to political structures or have common origins in ancient Chinese geographical imagination. Most of the time, the Austroasiatic-speaking ancestors of the modern Kinh under one single ruler might have assumed for themselves a similar or identical social self-designation inherent in the modern Vietnamese first-person pronoun ''ta'' (us, we, I) to differentiate themselves with other groups. In the older colloquial usage, ''ta'' corresponded to "ours" as opposed to "theirs", and during colonial time they were "''nước ta''" (our country) and "''tiếng ta''" (our language) in contrast to "''nước tây''" (western countries) and "''tiếng tây''" (western languages).
Việt
The term "" (Yue) () inEarly Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the ''Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The S ...
was first written using the logograph
In a written language, a logogram, logograph, or lexigraph is a written character that represents a word or morpheme. Chinese characters (pronounced '' hanzi'' in Mandarin, ''kanji'' in Japanese, ''hanja'' in Korean) are generally logograms, ...
"戉" for an axe (a homophone), in oracle bone
Oracle bones () are pieces of ox scapula and turtle plastron, which were used for pyromancy – a form of divination – in ancient China, mainly during the late Shang dynasty. '' Scapulimancy'' is the correct term if ox scapulae were used for ...
and bronze inscriptions of the late Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and ...
( BC), and later as "越". At that time it referred to a people or chieftain to the northwest of the Shang.Theobald, Ulrich (2018"Shang Dynasty - Political History"
in ''ChinaKnowledge.de - An Encyclopaedia on Chinese History, Literature and Art''. quote: "Enemies of the Shang state were called fang 方 "regions", like the Tufang 土方, which roamed the northern region of Shanxi, the Guifang 鬼方 and Gongfang 𢀛方 in the northwest, the Qiangfang 羌方, Suifang 繐方, Yuefang 戉方, Xuanfang 亘方 and Zhoufang 周方 in the west, as well as the Yifang 夷方 and Renfang 人方 in the southeast." In the early 8th century BC, a tribe on the middle
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
were called the Yangyue The Yangyue () were a tribe of the Yue people, one of the ancient peoples of South China. In Chinese historical books, the earliest description about the Yangyue appeared during the Warring States period. The commonly accepted hypothesis is that ...
, a term later used for peoples further south. Between the 7th and 4th centuries BC Yue/Việt referred to the State of Yue
Yue (, Old Chinese: ''*''), also known as Yuyue (), was a state in ancient China which existed during the first millennium BC the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods of China's Zhou dynasty in the modern provinces of Zhejiang, Sha ...
in the lower Yangtze basin and its people. From the 3rd century BC the term was used for the non-Chinese populations of south and southwest China and northern Vietnam, with particular ethnic groups called Minyue
Minyue () was an ancient kingdom in what is now the Fujian province in southern China. It was a contemporary of the Han dynasty, and was later annexed by the Han empire as the dynasty expanded southward. The kingdom existed approximately from ...
, Ouyue (Vietnamese: Âu Việt The Âu Việt or Ouyue () were an ancient conglomeration of Baiyue tribes living in what is today the mountainous regions of northernmost Vietnam, western Guangdong, and northern Guangxi, China, since at least the third century BCE. They were belie ...
), Luoyue (Vietnamese: Lạc Việt
The Lạc Việt or Luoyue ( or ; pinyin: ''Luòyuè'' ← Middle Chinese: *''lɑk̚-ɦʉɐt̚'' ← Old Chinese *''râk-wat'') was a group of multilinguistic, specifically Kra-Dai and Austroasiatic, tribal peoples that inhabited ancient northe ...
), etc., collectively called the Baiyue
The Baiyue (, ), Hundred Yue, or simply Yue (; ), were various ethnic groups who inhabited the regions of East China, South China and Northern Vietnam during the 1st millennium BC and 1st millennium AD. They were known for their short hair, b ...
(Bách Việt, ; ). The term Baiyue/Bách Việt first appeared in the book ''Lüshi Chunqiu
The ''Lüshi Chunqiu'', also known in English as ''Master Lü's Spring and Autumn Annals'', is an encyclopedic Chinese classic text compiled around 239 BC under the patronage of the Qin Dynasty Chancellor Lü Buwei. In the evaluation of Micha ...
'' compiled around 239 BC. According to Ye Wenxian (1990), apud Wan (2013), the ethnonym of the Yuefang in northwestern China is not associated with that of the Baiyue in southeastern China.
The late medieval period saw the rise of Vietnamese elites identified themselves with the ancient Yue in order to incline with 'an ancient origin', and that identity might have born by constructing traditions. By the 17th and 18th centuries AD, educated Vietnamese apparently referred to themselves as ''người Việt'' 𠊛越 (Viet people) or ''người Nam'' 𠊛南 (southern people).
Kinh
Beginning in the 10th and 11th centuries, a strand of Viet-Muong (northern Vietic language) with influence from a hypothetic Chinese dialect in northern Vietnam, dubbed as Annamese Middle Chinese, started to become what is now theVietnamese language
Vietnamese ( vi, tiếng Việt, links=no) is an Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic language originating from Vietnam where it is the national language, national and official language. Vietnamese is spoken natively by over 70 million people, ...
. Its speakers called themselves the "Kinh" people, meaning people of the "metropolitan" centered around the Red River Delta with Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is ...
as its capital. Historic and modern Chữ Nôm scripture classically uses the Han character '京', pronounced "Jīng" in Mandarin, and "Kinh" with Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation. Other variants of Proto-Viet-Muong were driven from the lowlands by the Kinh and were called ''Trại'' (寨 Mandarin: ''Zhài''), or "outpost" people," by the 13th century. These became the modern Mường people. According to Victor Lieberman, ''người Kinh'' (Chữ Nôm
Chữ Nôm (, ; ) is a logographic writing system formerly used to write the Vietnamese language. It uses Chinese characters ('' Chữ Hán'') to represent Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary and some native Vietnamese words, with other words represent ...
: 𠊛京) may be a colonial-era term for Vietnamese speakers inserted anachronistically into translations of pre-colonial documents, but literature on 18th century ethnic formation is lacking.
History
Origins and pre-history
The forerunners of the ethnic Vietnamese were Proto-Vietic people who descended fromProto-Austroasiatic
Proto-Austroasiatic is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austroasiatic languages. Proto-Mon–Khmer (i.e., all Austroasiatic branches except for Munda) has been reconstructed in Harry L. Shorto's ''Mon–Khmer Comparative Dictionary'', while a ...
people who may have originated from somewhere in Southern China, Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, the Lingnan, or the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
, or mainland Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, together with the Monic, who settled further to the west and the Khmeric migrated further south. Most archaeologists and linguists, and other specialists like Sinologists and crop experts, believe that they arrived no later than 2000 BC bringing with them the practice of riverine agriculture and in particular the cultivation of wet rice.Blench, Roger. 2018Waterworld: lexical evidence for aquatic subsistence strategies in Austroasiatic
In ''Papers from the Seventh International Conference on Austroasiatic Linguistics'', 174-193. Journal of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society Special Publication No. 3. University of Hawaii Press.Blench, Roger. 2017.
Waterworld: lexical evidence for aquatic subsistence strategies in Austroasiatic
'. Presented at ICAAL 7, Kiel, Germany.Sidwell, Paul. 2015b. ''Phylogeny, innovations, and correlations in the prehistory of Austroasiatic''. Paper presented at the workshop ''Integrating inferences about our past: new findings and current issues in the peopling of the Pacific and South East Asia'', 22–23 June 2015, Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, Jena, Germany. Some linguists (James Chamberlain, Joachim Schliesinger) suggested that the Vietic-speaking people migrated from North Central Region to the
Red River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
, which had originally been inhabited by Tai
Tai or TAI may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*Tai (comics) a fictional Marvel Comics supervillain
*Tai Fraiser, a fictional character in the 1995 film ''Clueless''
*Tai Kamiya, a fictional character in ''Digimon''
Businesses and organisations ...
-speakers
Speaker may refer to:
Society and politics
* Speaker (politics), the presiding officer in a legislative assembly
* Public speaker, one who gives a speech or lecture
* A person producing speech: the producer of a given utterance, especially:
** I ...
. However, Michael Churchman found no records of population shifts in Jiaozhi
Jiaozhi (standard Chinese, pinyin: ''Jiāozhǐ''), or Giao Chỉ (Vietnamese), was a historical region ruled by various Chinese dynasties, corresponding to present-day northern Vietnam. The kingdom of Nanyue (204–111 BC) set up the Jiaozhi Co ...
(centered around the Red River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
) in Chinese sources, indicating that a fairly stable population of Austroasiatic speakers, ancestral to modern Vietnamese, inhabited in the delta during the Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
-Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) b ...
periods. Other proposes that Northern Vietnam and Southern China were never homogeneous in term of ethnicity and languages, but peoples shared some customs. These ancient tribes did not have any kind of defined ethnic boundary and could not be described as "Vietnamese" (Kinh) in any satisfactory sense. Any attempt of identify an ethnic group in ancient Vietnam is problematized inaccurate.
Another theory, based on linguistic diversity, locates the most probable homeland of the Vietic languages in modern-day Bolikhamsai Province and Khammouane Province in Laos as well as parts of Nghệ An Province and Quảng Bình Province in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
. In the 1930s, clusters of Vietic-speaking communities were discovered in the hills of eastern Laos, are believed to be the earliest inhabitants of that region. Archaeogenetics demonstrated that before the Dong Son period, the Red River Delta's inhabitants were predominantly Austroasiatic: genetic data from Phùng Nguyên culture
The Phùng Nguyên culture of Vietnam (c. 2,000 – 1,500 BC) is a name given to a culture of the Bronze Age in Vietnam which takes its name from an archeological site in Phùng Nguyên, east of Việt Trì discovered in 1958. It was during this p ...
's Mán Bạc
Mán Bạc is a Neolithic archaeological site located in Yên Mô District, Ninh Bình Province, Vietnam, dated from around 1,850–1,650 BC. Mán Bạc is associated with the Phùng Nguyên culture. With 95 burials found at the site, Mán Bạ ...
burial site (dated 1,800 BC) have close proximity to modern Austroasiatic speakers such as the Khmer and Mlabri Mlabri can refer to:
* Mlabri people
The Mlabri ( Thai: มลาบรี) or Mrabri are an ethnic group of Thailand and Laos, and have been called "the most interesting and least understood people in Southeast Asia". Only about 400 or fewer Mlab ...
; meanwhile, "mixed genetics" from Đông Sơn culture
The Dong Son culture or the Lạc Việt culture (named for modern village Đông Sơn, a village in Thanh Hóa, Vietnam) was a Bronze Age culture in ancient Vietnam centred at the Red River Valley of northern Vietnam from 1000 BC until the ...
's Núi Nấp site showed affinity to " Dai from China, Tai-Kadai speakers from Thailand, and Austroasiatic speakers from Vietnam, including the Kinh
The Vietnamese people ( vi, người Việt, lit=Viet people) or Kinh people ( vi, người Kinh) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to modern-day Northern Vietnam and Southern China (Jing Islands, Dongxing, Guangxi). The native lang ...
".
According to Vietnamese legend ''The Tale the Hồng Bàng Clan'' (''Hồng Bàng'' thị truyện) written in the 15th century, the first Vietnamese descended from the dragon lord Lạc Long Quân and the fairy Âu Cơ. They married and had one hundred eggs, from which hatched one hundred children. Their eldest son ruled as the Hùng king
Hùng king (c. 2524 BC – ?; Chữ Hán: 雄王; vi, Hùng Vương (雄王) or ''vua Hùng'' (𤤰雄); ''Vương'' means "king" and ''vua'' means "monarch; could mean emperor or king") is the title given to the ancient Vietnamese rulers of the ...
. The Hùng king
Hùng king (c. 2524 BC – ?; Chữ Hán: 雄王; vi, Hùng Vương (雄王) or ''vua Hùng'' (𤤰雄); ''Vương'' means "king" and ''vua'' means "monarch; could mean emperor or king") is the title given to the ancient Vietnamese rulers of the ...
s were claimed to be descended from the mythical figure Shen Nong.
Early history and Chinese rule
 The earliest reference of the proto-Vietnamese in Chinese annals was the ''Lạc'' (Chinese: Luo), ''
The earliest reference of the proto-Vietnamese in Chinese annals was the ''Lạc'' (Chinese: Luo), ''Lạc Việt
The Lạc Việt or Luoyue ( or ; pinyin: ''Luòyuè'' ← Middle Chinese: *''lɑk̚-ɦʉɐt̚'' ← Old Chinese *''râk-wat'') was a group of multilinguistic, specifically Kra-Dai and Austroasiatic, tribal peoples that inhabited ancient northe ...
'', or the Dongsonian, an ancient tribal confederacy of perhaps polyglot Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
and Kra-Dai speakers occupied the Red River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
. The Lạc developed the metallurgical Đông Sơn Culture
The Dong Son culture or the Lạc Việt culture (named for modern village Đông Sơn, a village in Thanh Hóa, Vietnam) was a Bronze Age culture in ancient Vietnam centred at the Red River Valley of northern Vietnam from 1000 BC until the ...
and the Văn Lang chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
, ruled by the semi-mythical Hùng king
Hùng king (c. 2524 BC – ?; Chữ Hán: 雄王; vi, Hùng Vương (雄王) or ''vua Hùng'' (𤤰雄); ''Vương'' means "king" and ''vua'' means "monarch; could mean emperor or king") is the title given to the ancient Vietnamese rulers of the ...
s. To the south of the Dongsonians was the Sa Huỳnh Culture
The Sa Huỳnh culture was a culture in modern-day central and southern Vietnam that flourished between 1000 BC and 200 AD. Archaeological sites from the culture have been discovered from the Mekong Delta to Quang Binh province in central Vietna ...
of the Austronesian Chamic people. Around 400–200 BC, the Lạc came to contact with the Âu Việt The Âu Việt or Ouyue () were an ancient conglomeration of Baiyue tribes living in what is today the mountainous regions of northernmost Vietnam, western Guangdong, and northern Guangxi, China, since at least the third century BCE. They were belie ...
(a splinter group of Tai people
Tai peoples are the populations who speak (or formerly spoke) the Tai languages. There are a total of about 93 million people of Tai ancestry worldwide, with the largest ethnic groups being Dai, Thais, Isan, Tai Yai (Shan), Lao, Tai Ahom, a ...
) and the Sinitic
The Sinitic languages (漢語族/汉语族), often synonymous with "Chinese languages", are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is ...
people from the north. According to a late third or early fourth century AD Chinese chronicle, the leader of the Âu Việt, Thục Phán, conquered Văn Lang and deposed the last Hùng king
Hùng king (c. 2524 BC – ?; Chữ Hán: 雄王; vi, Hùng Vương (雄王) or ''vua Hùng'' (𤤰雄); ''Vương'' means "king" and ''vua'' means "monarch; could mean emperor or king") is the title given to the ancient Vietnamese rulers of the ...
. Having submissions of Lạc lords, Thục Phán proclaimed himself King An Dương of Âu Lạc
Âu Lạc ( Hán tự: 甌貉 (Peripheral Records/Volume 1:6a): "王既併文郎國,改國號曰甌貉國。""The King then annexed the Văn Lang nation, changed the nation's name to Âu Lạc nation."/甌駱; (Volume 113): "且南方卑濕, ...
kingdom.
In 179 BC, Zhao Tuo, a Chinese general who has established the Nanyue
Nanyue (), was an ancient kingdom ruled by Chinese monarchs of the Zhao family that covered the modern Chinese subdivisions of Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong, Macau, southern Fujian and central to northern Vietnam. Nanyue was establis ...
state in modern-day Southern China, annexed Âu Lạc, and began the Sino-Vietic interaction that lasted in a millennium. In 111 BC, the Han Empire
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
conquered Nanyue, brought the Northern Vietnam region under Han rule.
By the 7th century to 9th century AD, as the Tang Empire
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingd ...
ruled over the region, historians such as Henri Maspero
Henri Paul Gaston Maspero (15 December 188317 March 1945) was a French sinologist and professor who contributed to a variety of topics relating to East Asia. Maspero is best known for his pioneering studies of Daoism. He was imprisoned by the Naz ...
proposed that Vietnamese-speaking people became separated from other Vietic groups such as the Mường and Chứt due to heavier Chinese influences on the Vietnamese. Other argue that a Vietic migration from north central Vietnam to the Red River Delta in the seventh century replaced the original Tai-speaking inhabitants. In the mid-9th century, local rebels aided by Nanzhao
Nanzhao (, also spelled Nanchao, ) was a dynastic kingdom that flourished in what is now southern China and northern Southeast Asia during the 8th and 9th centuries. It was centered on present-day Yunnan in China.
History
Origins
Nanzh ...
tore the Tang Chinese rule to nearly collapse. The Tang reconquered the region in 866, causing half of the local rebels to flee into the mountains, which historians believe that was the separation between the Mường and the Vietnamese took at the end of Tang rule in Vietnam. In 938, the Vietnamese leader Ngô Quyền
Ngô Quyền ( vi-hantu, 吳權) (April 17, 898 – February 14, 944), often referred to as Tiền Ngô Vương (前吳王; "First King of Ngô"), was a warlord who later became the founding king of the Ngô dynasty of Vietnam. He reigned from ...
who was a native of Thanh Hóa
Thanh Hóa () is the capital of Thanh Hóa Province. The city is situated in the east of the province on the Ma River (Sông Mã), about 150 kilometers (93 miles) south of Hanoi and 1560 kilometers (969 miles) north of Ho Chi Minh City. Thanh ...
, led Viet forces defeated the Chinese Southern Han
Southern Han (; 917–971), officially Han (), originally Yue (), was one of the ten kingdoms that existed during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was located on China's southern coast, controlling modern Guangdong and Guangxi. The ...
armada at Bạch Đằng River The Bạch Đằng River ( vi, Sông Bạch Đằng, ), also called Bạch Đằng Giang (from ), ''white wisteria river'', is a river in northern Vietnam, located near Hạ Long Bay. It flows through the Yên Hưng District of Quảng Ninh Provin ...
and proclaimed himself king, became the first Viet king of polity that now could be perceived as "Vietnamese".
Medieval and early modern period

Ngô Quyền
Ngô Quyền ( vi-hantu, 吳權) (April 17, 898 – February 14, 944), often referred to as Tiền Ngô Vương (前吳王; "First King of Ngô"), was a warlord who later became the founding king of the Ngô dynasty of Vietnam. He reigned from ...
died in 944 and his kingdom collapsed into chaos and disturbances between twelve warlords and chiefs. In 968, a leader named Đinh Bộ Lĩnh united them and established the Đại Việt (Great Việt) kingdom. With assistance of powerful Buddhist monks, Đinh Bộ Lĩnh chose Hoa Lư in the southern edge of the Red River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
as the capital instead of Tang-era Đại La, adopted Chinese-style imperial titles, coinage, and ceremonies and tried to preserve the Chinese administrative framework. The independence of Đại Việt, according to Andrew Chittick, allows it "to develop its own distinctive political culture and ethnic consciousness." In 979 Dinh Bo Linh was assassinated, and Queen Duong Van Nga married with Dinh's general Le Hoan, appointed him as king. Disturbances in Đại Việt attracted attentions from neighbouring Chinese Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
and Champa Kingdom, but they were defeated by Lê Hoàn. A Khmer inscription dated 987 records the arrival of Vietnamese merchants (Yuon) in Angkor
Angkor ( km, អង្គរ , 'Capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura ( km, យសោធរបុរៈ; sa, यशोधरपुर),Headly, Robert K.; Chhor, Kylin; Lim, Lam Kheng; Kheang, Lim Hak; Chun, Chen. 1977. ''Cambodian-Engl ...
. Chinese writers, Song Hao, Fan Chengda Fan Chengda (, 1126–1193), courtesy name Zhineng (), was a Chinese geographer, poet, and politician. Known as one of the best-known Chinese poets of the Song Dynasty, he served as a government official, and was an academic authority in geograph ...
and Zhou Qufei, both reported that the inhabitants of Đại Việt "tattooed their foreheads, crossed feet, black teeth, bare feet and blacken clothing." The early 11th century Cham
Cham or CHAM may refer to:
Ethnicities and languages
*Chams, people in Vietnam and Cambodia
**Cham language, the language of the Cham people
***Cham script
*** Cham (Unicode block), a block of Unicode characters of the Cham script
*Cham Albania ...
inscription of Chiên Đàn, My Son
My or MY may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* My (radio station), a Malaysian radio station
* Little My, a fictional character in the Moomins universe
* ''My'' (album), by Edyta Górniak
* ''My'' (EP), by Cho Mi-yeon
Business
* Mar ...
, erected by king of Champa Harivarman IV (r. 1074–1080), mentions that he had offered Khmer (Kmīra/Kmir) and Viet (Yvan) prisoners as slaves to various local gods and temples of the citadel of Tralauṅ Svon.
Successive Vietnamese royal families from the Đinh, Lê, Lý dynasties and ( Hoa)/Chinese ancestry Trần and Hồ dynasties ruled the kingdom peacefully from 968 to 1407. Emperor Lý Thái Tổ
Lý Thái Tổ ( vi-hantu, , 8 March 974 – 31 March 1028), Vietnamese name, personal name Lý Công Uẩn, temple name Thái Tổ, was a Vietnamese people, Vietnamese emperor, the founder of the Lý dynasty of Vietnam and the 6th ruler of ...
(r. 1009–1028) relocated the Vietnamese capital from Hoa Lư to Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is ...
, the center of the Red River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
in 1010. They practiced elitist marriage alliances between clans and nobles in the country. Mahayana Buddhism became state religion, Vietnamese music instruments, dancing and religious worshipping were influenced by both Cham, Indian and Chinese styles, while Confucianism slowly gained attention and influence. The earliest surviving corpus and text in Vietnamese language
Vietnamese ( vi, tiếng Việt, links=no) is an Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic language originating from Vietnam where it is the national language, national and official language. Vietnamese is spoken natively by over 70 million people, ...
dated early 12th century, and surviving ''chữ nôm
Chữ Nôm (, ; ) is a logographic writing system formerly used to write the Vietnamese language. It uses Chinese characters ('' Chữ Hán'') to represent Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary and some native Vietnamese words, with other words represent ...
'' script inscriptions dated early 13th century, showcasing enormous influences of Chinese culture among the early Vietnamese elites.
The Mongol Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fift ...
unsuccessful invaded Đại Việt in the 1250s and 1280s, though they sacked Hanoi. The Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
of China conquered Đại Việt in 1406, brought the Vietnamese under Chinese rule for 20 years, before they were driven out by Vietnamese leader Lê Lợi
Lê Lợi (, Chữ Hán: 黎利; c. 10 September 1384/1385 – 5 October 1433), also known by his temple name as Lê Thái Tổ (黎太祖) and by his pre-imperial title Bình Định vương (平定王; "Prince of Pacification"), was a Vietnam ...
. The fourth grandson of Lê Lợi, king Lê Thánh Tông (r. 1460–1497), is considered one of the greatest monarchs in Vietnamese history. His reign is recognized for the extensive administrative, military, education, and fiscal reforms he instituted, and a cultural revolution that replaced the old traditional aristocracy with a generation of literati scholars, adopted Confucianism, and transformed a Đại Việt from a Southeast Asian style polity to a bureaucratic state, and flourished. Thánh Tông's forces, armed with gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
weapons, overwhelmed the long-term rival Champa in 1471, then launched an unsuccessful invasion against the Laotian and Lan Na kingdoms in the 1480s.
16th century – Modern period




 With the death of Thánh Tông in 1497, the Đại Việt kingdom swiftly declined. Climate extremes, failing crops, regionalism and factionism tore the Vietnamese apart. From 1533 to 1790s, four powerful Vietnamese families: Mạc, Lê, Trịnh and Nguyễn, each ruled on their own domains. In northern Vietnam (Đàng Ngoài–outer realm), the Lê Emperors barely sat on the throne while the Trịnh lords held power of the court. The Mạc controlled northeast Vietnam. The Nguyễn lords ruled the southern polity of Đàng Trong (inner realm). Thousands of ethnic Vietnamese migrated south, settled on the old Cham lands. European missionaries and traders from the sixteenth century brought new religion, ideas and crops to the Vietnamese (Annamese). By 1639, there were 82,500 Catholic converts throughout Vietnam. In 1651,
With the death of Thánh Tông in 1497, the Đại Việt kingdom swiftly declined. Climate extremes, failing crops, regionalism and factionism tore the Vietnamese apart. From 1533 to 1790s, four powerful Vietnamese families: Mạc, Lê, Trịnh and Nguyễn, each ruled on their own domains. In northern Vietnam (Đàng Ngoài–outer realm), the Lê Emperors barely sat on the throne while the Trịnh lords held power of the court. The Mạc controlled northeast Vietnam. The Nguyễn lords ruled the southern polity of Đàng Trong (inner realm). Thousands of ethnic Vietnamese migrated south, settled on the old Cham lands. European missionaries and traders from the sixteenth century brought new religion, ideas and crops to the Vietnamese (Annamese). By 1639, there were 82,500 Catholic converts throughout Vietnam. In 1651, Alexandre de Rhodes
Alexandre de Rhodes (15 March 1593 – 5 November 1660) was an Avignonese Jesuit missionary and lexicographer who had a lasting impact on Christianity in Vietnam. He wrote the '' Dictionarium Annamiticum Lusitanum et Latinum'', the first triling ...
published a 300-pages catechism in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and romanized-Vietnamese (''chữ Quốc Ngữ'') or the Vietnamese alphabet
The Vietnamese alphabet ( vi, chữ Quốc ngữ, lit=script of the National language) is the modern Latin writing script or writing system for Vietnamese. It uses the Latin script based on Romance languages originally developed by Portuguese m ...
.
The Vietnamese Fragmentation period ended in 1802 as Emperor Gia Long, who was aided by French mercenaries defeated the Tay Son dynasty, Tay Son kingdoms and reunited Vietnam. Through assimilation and brutal subjugation in the 1830s by Minh Mang, a large chunk of indigenous Cham people, Cham had been assimilated into Vietnamese. By 1847, the Vietnamese state under Emperor Thieu Tri, Thiệu Trị, people that identified them as "người Việt Nam" accounted for nearly 80 percent of the country's population. This demographic model continues to persist through the French Indochina, French Indochina in World War II, Japanese occupation and modern day.
Between 1862 and 1867, the southern third of the country became the French Cochinchina, French colony of Cochinchina. By 1884, the entire country had come under French rule, with the central and northern parts of Vietnam separated into the two protectorates of Annam (French protectorate), Annam and Tonkin (French protectorate), Tonkin. The three Vietnamese entities were formally integrated into the union of French Indochina in 1887. The French administration imposed significant political and cultural changes on Vietnamese society. A Western-style system of modern education introduced new humanism, humanist values into Vietnam.
 Despite having a long recorded history of the Vietnamese language and people, the identification and distinction of 'ethnic Vietnamese' or ethnic Kinh, as well as other ethnic groups in Vietnam, were only begun by colonial administration in the late 19th and early 20th century. Following colonial government's efforts of ethnic classificating, nationalism, especially ethnic nationalism, ethnonationalism and eugenic Social Darwinism were encouraged among the new Vietnamese intelligentsias discourse. Ethnic tensions sparked by Vietnamese ethnonationalism peaked during the late 1940s at the beginning phase of the First Indochina War (1946–1954), which resulted in violences between Khmer and Vietnamese in the Mekong Delta. Further North Vietnam's Soviet-style social integrational and ethnic classification, tried to build an image of Diversity under the harmony of Socialism, promoting the idea of the Vietnamese nation as a 'great single family' comprised by many different ethnic groups, and Vietnamese ethnic chauvinism was officially discouraged.
Despite having a long recorded history of the Vietnamese language and people, the identification and distinction of 'ethnic Vietnamese' or ethnic Kinh, as well as other ethnic groups in Vietnam, were only begun by colonial administration in the late 19th and early 20th century. Following colonial government's efforts of ethnic classificating, nationalism, especially ethnic nationalism, ethnonationalism and eugenic Social Darwinism were encouraged among the new Vietnamese intelligentsias discourse. Ethnic tensions sparked by Vietnamese ethnonationalism peaked during the late 1940s at the beginning phase of the First Indochina War (1946–1954), which resulted in violences between Khmer and Vietnamese in the Mekong Delta. Further North Vietnam's Soviet-style social integrational and ethnic classification, tried to build an image of Diversity under the harmony of Socialism, promoting the idea of the Vietnamese nation as a 'great single family' comprised by many different ethnic groups, and Vietnamese ethnic chauvinism was officially discouraged.
Religions
According to the 2019 Census, the religious demographics of Vietnam are as follows: *86.32% Vietnamese folk religion or non religious *6.1% Catholic Church in Vietnam, Catholicism *4.79% Buddhism (mainly Mahayana) *1.02% Hòa Hảo, Hoahaoism *1% Protestantism *<1% Caodaism *0.77 Others It is worth noting here that the data is highly skewered, as a large majority of Vietnamese may declare themselves atheist, yet practice forms of traditional folk religion or Mahayana Buddhism. Estimates for the year 2010 published by the Pew Research Center: *Vietnamese folk religion, 45.3% *Unaffiliated, 29.6% *Buddhism, 16.4% *Christianity, 8.2% *Other, 0.5%Diaspora
 Originally from northern Vietnam and southern China, the Vietnamese have expanded south and conquered much of the land belonging to the former Champa Kingdom and Khmer Empire over the centuries. They are the dominant ethnic group in most provinces of Vietnam, and constitute a small percentage of the population in neighbouring Cambodia.
Beginning around the sixteenth century, groups of Vietnamese migrated to Cambodia and China for commerce and political purposes. Descendants of Vietnamese migrants in China form the Gin ethnic group in the country and primarily reside in and around Guangxi Province. Vietnamese form the largest ethnic minority group in Cambodia, at 5% of the population. Under the Khmer Rouge, they were heavily persecuted and survivors of the regime largely fled to Vietnam.
During French Indochina, French colonialism, Vietnam was regarded as the most important colony in Asia by the French colonial powers, and the Vietnamese had a higher social standing than other ethnic groups in French Indochina. As a result, educated Vietnamese were often trained to be placed in colonial government positions in the other Asian French colonies of Laos and Cambodia rather than locals of the respective colonies. There was also a significant representation of Vietnamese students in France during this period, primarily consisting of members of the elite class. A large number of Vietnamese also migrated to France as workers, especially during World War I and World War II, when France recruited soldiers and locals of its colonies to help with war efforts in Metropolitan France. The wave of migrants to France during World War I formed the first major presence of Vietnamese people in France and the Western world.La Diaspora Vietnamienne en France un cas particulier
Originally from northern Vietnam and southern China, the Vietnamese have expanded south and conquered much of the land belonging to the former Champa Kingdom and Khmer Empire over the centuries. They are the dominant ethnic group in most provinces of Vietnam, and constitute a small percentage of the population in neighbouring Cambodia.
Beginning around the sixteenth century, groups of Vietnamese migrated to Cambodia and China for commerce and political purposes. Descendants of Vietnamese migrants in China form the Gin ethnic group in the country and primarily reside in and around Guangxi Province. Vietnamese form the largest ethnic minority group in Cambodia, at 5% of the population. Under the Khmer Rouge, they were heavily persecuted and survivors of the regime largely fled to Vietnam.
During French Indochina, French colonialism, Vietnam was regarded as the most important colony in Asia by the French colonial powers, and the Vietnamese had a higher social standing than other ethnic groups in French Indochina. As a result, educated Vietnamese were often trained to be placed in colonial government positions in the other Asian French colonies of Laos and Cambodia rather than locals of the respective colonies. There was also a significant representation of Vietnamese students in France during this period, primarily consisting of members of the elite class. A large number of Vietnamese also migrated to France as workers, especially during World War I and World War II, when France recruited soldiers and locals of its colonies to help with war efforts in Metropolitan France. The wave of migrants to France during World War I formed the first major presence of Vietnamese people in France and the Western world.La Diaspora Vietnamienne en France un cas particulier(in French)
 When Vietnam gained its independence from France in 1954, a number of Vietnamese loyal to the colonial government also migrated to France. During the partition of Vietnam into North Vietnam, North and South Vietnam, South, a number of South Vietnamese students also arrived to study in France, along with individuals involved in commerce for trade with France, which was a principal economic partner with South Vietnam.
When Vietnam gained its independence from France in 1954, a number of Vietnamese loyal to the colonial government also migrated to France. During the partition of Vietnam into North Vietnam, North and South Vietnam, South, a number of South Vietnamese students also arrived to study in France, along with individuals involved in commerce for trade with France, which was a principal economic partner with South Vietnam.
 Forced repatriation in 1970 and deaths during the Khmer Rouge era reduced the Vietnamese Cambodian, Vietnamese population in Cambodia from between 250,000 and 300,000 in 1969 to a reported 56,000 in 1984.
The Fall of Saigon and end of the Vietnam War prompted the start of the Vietnamese diaspora, which saw millions of Vietnamese fleeing the country from the new communist regime. Recognizing an international humanitarian crisis, many countries accepted Vietnamese refugees, primarily the United States, France, Australia and Canada. Meanwhile, under the new communist regime, tens of thousands of Vietnamese were sent to work or study in Eastern Bloc countries of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe as development aid to the Vietnamese government and for migrants to acquire skills that were to be brought home to help with development. However, after the fall of the Berlin Wall, a vast majority of these overseas Vietnamese decided to remain in their host nations.
Forced repatriation in 1970 and deaths during the Khmer Rouge era reduced the Vietnamese Cambodian, Vietnamese population in Cambodia from between 250,000 and 300,000 in 1969 to a reported 56,000 in 1984.
The Fall of Saigon and end of the Vietnam War prompted the start of the Vietnamese diaspora, which saw millions of Vietnamese fleeing the country from the new communist regime. Recognizing an international humanitarian crisis, many countries accepted Vietnamese refugees, primarily the United States, France, Australia and Canada. Meanwhile, under the new communist regime, tens of thousands of Vietnamese were sent to work or study in Eastern Bloc countries of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe as development aid to the Vietnamese government and for migrants to acquire skills that were to be brought home to help with development. However, after the fall of the Berlin Wall, a vast majority of these overseas Vietnamese decided to remain in their host nations.
DNA and genetics analysis
Anthropometry
Stephen Pheasant (1986), who taught anatomy, biomechanics and Human factors and ergonomics, ergonomics at the Royal Free Hospital and the University College London, University College, London, said that East Asians, East Asian and Southeast Asian people have proportionately shorter lower limbs than White people, European and black people, black African people. Pheasant said that the proportionately short lower limbs of East Asian and Southeast Asian people is a difference that is most characterized in Japanese people, less characterized in Koreans, Korean and Han Chinese, Chinese people, and least characterized in Vietnamese and Thai people. Nguyen Manh Lien (1998) of the Vietnam Atomic Energy Commission indicated the average sitting height to body height ratios of Vietnamese 17-19 year olds to be 52.59% for males and 52.57% for females. Neville Moray (2005) indicated that modifications in basic cockpit geometry are required to accommodate Genetic and anthropometric studies on Japanese people, Japanese and Vietnamese Aircraft pilot, pilots. Moray said that the Japanese have longer torsos and a higher shoulder point than the Vietnamese, but the Japanese have about similar arm lengths to the Vietnamese, so the Aircraft flight control system, control stick would have to be moved 8 cm closer to the pilot for the Japanese and 7 cm closer to the pilot for the Vietnamese. Moray said that, due to having shorter legs than Americans (of European Americans, European and African Americans, African descent), Aircraft flight control system, rudder pedals must be moved closer to the pilot by 10 cm for the Japanese and 12 cm for the Vietnamese.Craniometry
Ann Kumar (1998) said that Michael Pietrusewsky (1992) said that, in a craniometric study, Borneo,Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, Sulu, Java, and Sulawesi are closer to Japan, in that order, than Mongols, Mongolian and Han Chinese, Chinese populations are close to Japan. In the craniometric study, Michael Pietrusewsky (1992) said that, even though Japanese people Cluster analysis, cluster with Mongolians, Chinese and Southeast Asians in a larger Asian cluster, Japanese people are more closely aligned with several Mainland Southeast Asia, mainland and Maritime Southeast Asia, island Southeast Asian samples than with Mongolians and Chinese.
Hirofumi Matsumura et al. (2001) and Hideo Matsumoto et al. (2009) said that the Japanese people, Japanese and Vietnamese people are regarded to be a mix of Northeast Asians and Southeast Asians who are related to today Austronesian peoples. But the amount of northern genetics is higher in Japanese people compared to Vietnamese who are closer to other Southeast Asians (Thai people, Thai or Bamar people).
Bradley J. Adams, a forensic anthropology, forensic anthropologist in the Office of Chief Medical Examiner of the City of New York, said that Vietnamese people could be classified as Mongoloid.
A 2009 book about forensic anthropology said that Vietnamese skulls are more Gracility, gracile and less Sexual dimorphism, sexually dimorphic than the skulls of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans.
Matsumura and Hudson (2005) said that a broad comparison of dental traits indicated that modern Vietnamese and other modern Southeast Asians derive from a northern source, supporting the Two layer hypothesis, immigration hypothesis, instead of regional continuity hypothesis, as the model for the origins of modern Southeast Asians.
Genetics
Vietnamese show a close genetic relationship with other Southeast Asians. The reference population for Vietnamese (Kinh) used in the Genographic Project#Geno 2.0 Next Generation, Geno 2.0 Next Generation is 83% Southeast Asia & Oceania, 12% Eastern Asia and 3% Southern Asia. Jin Han-jun et al. (1999) said that the Human mitochondrial genetics, mtDNA 9‐Base pair, bp deletion frequencies in the wikt:intergenic, intergenic ''Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II, COII/Transfer RNA, tRNALysine, Lys'' region for Vietnamese (23.2%) and Indonesians (25.0%), which are the two populations constituting Southeast Asians in the study, are relatively high frequencies when compared to the 9-bp deletion frequencies for Mongols, Mongolians (5.1%), Han Chinese, Chinese (14.2%), Japanese people, Japanese (14.3%) and Koreans (15.5%), which are the four populations constituting East Asians in the study. The study said that these 9-bp deletion frequencies are consistent with earlier surveys which showed that 9-bp deletion frequencies increase going from Japan to mainland Asia to the Malay Peninsula, which is supported by the following studies: Horai et al. (1987); Hertzberg et al. (1989); Stoneking & Wilson (1989); Horai (1991); Ballinger et al. (1992); Hanihara et al. (1992); and Chen et al. (1995). The Genetic distance#Cavalli-Sforza chord distance, Cavalli-Sforza's chord genetic distance (4D), from Cavalli-Sforza & Bodmer (1971), which is based on the allele frequencies of the intergenic ''COII/tRNALys'' region, between Vietnamese and other East Asian populations in the study, from least to greatest, are as follows: Vietnamese to Indonesians, Indonesian (0.0004), Vietnamese to Han Chinese, Chinese (0.0135), Vietnamese to Japanese people, Japanese (0.0153), Vietnamese to Koreans, Korean (0.0265) and Vietnamese to Mongols, Mongolian (0.0750).Jin, Han-jun et al. (1999). Distribution of length variation of the mtDNA 9‐bp motif in the intergenic COII/tRNALys region in East Asian populations. ''Korean Journal of Biological Sciences 3''(4). Pages 395 & 396. Retrieved March 2, 2018, frolink to the article's abstract.
/ref> Kim Wook et al. (2000) said that, genetically, Vietnamese people more probably clustered with East Asians of which the study analyzed DNA samples of Chinese people, Chinese, Japanese people, Japanese, Koreans and Mongols, Mongolians rather than with Southeast Asians of which the study analyzed DNA samples of Indonesians, Filipinos, Thai people, Thais and Vietnamese. The study said that Vietnamese people were the only population in the study's Phylogenetics, phylogenetic analysis that did not reflect a sizable genetic difference between East Asian and Southeast Asian populations. The study said that the likely reason for Vietnamese people more probably clustering with East Asians was genetic drift and distinct Founder effect, founder populations. The study said that the alternative reason for Vietnamese people more probably clustering with East Asians is a recent Colonisation (biology), range expansion from South China. The study mentioned that the majority of its Vietnamese DNA samples were from
Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is ...
which is the closest region to South China.
Schurr & Wallace (2002) said that Vietnamese people display genetic similarities with certain peoples from Malaysia. The study said that the aboriginal groups from Malaysia, the Orang Asli, are somewhat genetically intermediate between Malay people and Vietnamese. The study said that Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, mtDNA haplogroup Haplogroup F (mtDNA), F is present at its highest frequency in Vietnamese and a high frequency of this haplogroup is also present in the Orang Asli, a people with whom Vietnamese have a linguistic connection (Austroasiatic languages).Schurr, Theodore G. & Wallace, Douglas C. (2002). Mitochondrial DNA Diversity in Southeast Asian Populations. ''Human Biology (journal), Human Biology, 74''(3). Pages 433, 439, 446, 447 & 448. Retrieved January 7, 2018,
frolink.
/ref> Jung Jongsun et al. (2010) said that genetic structure analysis found significant admixture in "''Vietnamese (or Khmer people, Cambodian) with unknown Southern original settlers.''" The study said that it used Cambodians and Vietnamese to represent "Southern people," and the study used Cambodia ( Khmer) and
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
(Kinh) as its populations for "South Asia." The study said that Chinese people are located between Koreans, Korean and Vietnamese people in the study's Gene mapping, genome map. The study also said that Vietnamese people are located between Chinese and Cambodian people in the study's genome map.
He Jun-dong et al. (2012) did a principal component analysis using the Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, NRY haplogroup distribution frequencies of 45 populations, and the second principal component showed a close affinity between Kinh and Vietnamese who were most likely Kinh with populations from mainland South China, southern China because of the high frequency of NRY haplogroup Haplogroup O-K18, O-M88. The study said that Kinh often have NRY haplogroup Haplogroup O-M122, O-M7 which is the characteristic Chinese haplogroup. Out of the study's Sample (statistics), sample of seventy-six Kinh NRY haplogroups, twenty-three haplogroups (30.26%) were O-M88 and eight haplogroups (10.53%) were O-M7. The study said that, in ancient northern Vietnam, it is suggested that there has been considerable assimilation of inhabitants from present-day southern China through immigration into the Kinh people.He, Jun-dong et al. (2012). Patrilineal Perspective on the Austronesian Diffusion in Mainland Southeast Asia. In ''PLOS One, PLoS 7''(5), Page 7. Retrieved December 14, 2017, frolink.
A 2015 study revealed that Vietnamese (Kinh) test subjects showed more genetic variants in common with Chinese compared to Japanese. Sara Pischedda et al. (2017) stated that modern Vietnamese have a major component of their ethnic origin coming from the now-called southern China region and a minor component from a Thai-Indonesian composite. The study said that admixture analysis indicates that Vietnamese Kinh have a major part which is most common in Han Chinese, Chinese and two minor parts which have the highest prevalence in the Bidayuh of Malaysia and the Proto-Malay. The study said that multidimensional scaling analysis indicates that Vietnamese Kinh have a closeness to Malay people, Thai and Chinese, and the study said that Malays and Thai are the samples which could be admixed with Chinese in the Vietnamese gene pool. The study said that Vietnamese Human mitochondrial genetics, mtDNA genetic variation matches well with the pattern seen in Southeast Asia, and the study said that most Vietnamese people had mtDNA haplotypes that clustered in clades Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M7 (20%) and Haplogroup R (mtDNA), R9’F (27%) which are clades that also dominate maternal lineages in Southeast Asia more generally.Pischedda, S. et al. (2017). Phylogeographic and genome-wide investigations of Vietnam ethnic groups reveal signatures of complex historical demographic movements. ''Scientific Reports, 7''(1). Pages 4, 6, 11, 13, & 14. Digital object identifier, doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12813-6 Retrieved January 6, 2018, fro
link.
/ref>
Genome sequencing by Vietnamese researchers
Vinh S. Le et al. (2019) elucidated that Kinh and present‐day Southeast Asian (SEA) populations mainly originated from SEA ancestries, while Southern Han Chinese (CHS) and Northern Han Chinese (CHB) populations were mixed from both Southeast Asian and East Asian ancestries. The results are generally compatible with that from the 1 kg project (2015 Genomes Project Consortium et al., 2015) and the HUGO Pan‐Asian SNP Consortium (Abdulla et al., 2009). The results from both phylogenetic tree reconstruction and PCA also reinforce the hypothesis that a population migration from Africa to Asia following the South‐to‐North route (Abdulla et al., 2009; Chu et al., 1998). Interestingly, it was discovered that Kinh and Thai people "had similar genomic structures and close evolutionary relationships".Y-chromosome DNA
Kayser ''et al.'' (2006) found four members of haplogroup O-M95, O-M95, four members of haplogroup O-M122, O-M122(xM134), one member of haplogroup C-M217, C-M217, and one member of haplogroup O-M119, O-M119 in a sample of ten individuals from Vietnam. He Jun-dong ''et al.'' (2012) found that the human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, NRY haplogroup profile for a Sample (statistics), sample of 76 Kinh in Hanoi, Vietnam was as follows: twenty-three (30.26%) belonged to Haplogroup O-K18, O-M88, nine (11.84%) belonged to Haplogroup O-K18, O-M95*(xM88), nine (11.84%) belonged to Haplogroup C-M217, C-M217, eight (10.53%) belonged to Haplogroup O-M122, O-M7, seven (9.21%) belonged to Haplogroup O-M122, O-M134, seven (9.21%) belonged to Haplogroup O-M122, O-P200*(xM121, M164, P201, 002611), five (6.58%) belonged to Haplogroup O-M119, O-P203, two (2.63%) belonged to Haplogroup N-M231, N-M231, two (2.63%) belonged to Haplogroup O-M122, O-002611, two (2.63%) belonged to Haplogroup O-M122, O-P201*(xM7, M134), one (1.32%) belonged to Haplogroup K-M9, K-P131*(xN-M231, O-P191, Q-P36, R-M207), and one (1.32%) belonged to Haplogroup R1a, R-M17. Having analyzed the Y-DNA of another sample of 24 males from Hanoi, Vietnam, Trejaut ''et al.'' (2014) found that six (25.0%) belonged to haplogroup O-M95, O-M88, three (12.5%) belonged to haplogroup O-M122, O-M7, three (12.5%) belonged to haplogroup O-M122, O-M134(xM133), two (8.3%) belonged to haplogroup O-M95, O-M95(xM88), two (8.3%) belonged to haplogroup C-M217, C-M217, two (8.3%) belonged to haplogroup N-M231, N-LLY22g(xM128, M178), one (4.2%) belonged to haplogroup O-K18, O-PK4(xM95), one (4.2%) belonged to haplogroup O-M122, O-JST002611, one (4.2%) belonged to haplogroup O-M117, O-M133, one (4.2%) belonged to haplogroup O-M122, O-M159, one (4.2%) belonged to haplogroup O-M119, O-M119(xP203, M50), and one (4.2%) belonged to haplogroup D-M15, D-M15. A study published in 2010 reported the following data obtained through analysis of the Y-DNA of a sample from Vietnam (more precisely, Austroasiatic languages, Austro-Asiatic speakers from Southern Vietnam according to He Jun-dong ''et al.''): 20.0% (14/70) haplogroup O-M95, O-M111, 15.7% (11/70) haplogroup O-M122, O-M134, 14.3% (10/70) haplogroup O-M122, O-JST002611, 7.1% (5/70) haplogroup O-M95, O-M95(xM111), 7.1% (5/70) haplogroup Q-M242, Q-P36(xM346), 5.7% (4/70) haplogroup O-M122, O-M7, 5.7% (4/70) haplogroup O-M119, O-P203, 4.3% (3/70) haplogroup C-M217, C-M217, 2.9% (2/70) haplogroup D-M15, D-M15, 2.9% (2/70) haplogroup N-M231, N-LLY22g(xM178, M128), 2.9% (2/70) haplogroup O-M122, O-P197*(xJST002611, P201), 2.9% (2/70) haplogroup O-M176, O-47z, 1.4% (1/70) haplogroup J-M172, J2-M172, 1.4% (1/70) haplogroup J-M304, J-M304(xM172), 1.4% (1/70) haplogroup O-M122, O-P201(xM7, M134), 1.4% (1/70) haplogroup O-P31, O-P31(xM176, M95), 1.4% (1/70) haplogroup O-M176, O-M176(x47z), 1.4% (1/70) haplogroup R-M17, R-M17. The individuals who comprise the KHV (Kinh in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam) sample of the 1000 Genomes Project have been found to belong to the following Y-DNA haplogroups: 26.1% (12/46) haplogroup O-M95, O-M88/M111, 13.0% (6/46) haplogroup O-M122, O-M7, 8.7% (4/46) haplogroup O-M122, O-JST002611, 8.7% (4/46) haplogroup O-M122, O-F444 (= O-M134(xM117)), 8.7% (4/46) haplogroup O-M117, O-M133, 6.5% (3/46) haplogroup O-M95, O-M95(xM88/M111), 4.3% (2/46) haplogroup O-M119, O-P203.1, 4.3% (2/46) haplogroup O-M122, O-F2159 (= O-KL2(xJST002611)), 4.3% (2/46) haplogroup Q-M242, Q-Y529, 2.2% (1/46) haplogroup O-K18, O-CTS9996 (= O-K18(xM95)), 2.2% (1/46) haplogroup O-M122, O-CTS1754 (= O-M122(xM324)), 2.2% (1/46) haplogroup O-M122, O-F4124 (= O-N6 or O-P164(xM134)), 2.2% (1/46) haplogroup C-M217, C-F845, 2.2% (1/46) haplogroup F-M89, F-Y27277(xM427, M428), 2.2% (1/46) haplogroup N-M231, N1b2a-M1811, 2.2% (1/46) haplogroup N-M231, N1a2a-M128. Macholdt ''et al.'' (2020) tested a sample of Kinh (''n''=50, including 42 fromHanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is ...
, three from Nam Trực District, two from Yên Phong District, one from Ngô Quyền District, one from Bắc Hà District, and one from Nghĩa Hưng District) and found that they belonged to the following Y-DNA haplogroups: 44% haplogroup O-M95, haplogroup O1b1a1a-M95, 30% haplogroup O-M122, haplogroup O2a-M324, 10% haplogroup C-M217, haplogroup C2c1-F2613, 4% haplogroup O-M119, haplogroup O1a1a-M307.1, 4% haplogroup N-M231, haplogroup N1-M2291, 4% haplogroup Q-M242, haplogroup Q1a1a1-M120, 2% haplogroup O-K18, haplogroup O1b1a2a1-F1759, and 2% haplogroup H (Y-DNA), haplogroup H1a2a-Z4487.Enrico Macholdt, Leonardo Arias, Nguyen Thuy Duong, ''et al.'', "The paternal and maternal genetic history of Vietnamese populations." ''European Journal of Human Genetics'' (2020) 28:636–645. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-019-0557-4
Mitochondrial DNA
Schurr & Wallace (2002) displayed the Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, mtDNA haplogroup profile for a Sample (statistics), sample of 28 Vietnamese as follows: 17.9% belonged to Haplogroup B (mtDNA), B/B*, 32.1% belonged to Haplogroup F (mtDNA), F, 32.1% belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M and 17.9% belonged to other haplogroups. He Jun-dong et al. (2012) found that the Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, mtDNA haplogroup profile for a Sample (statistics), sample of 139 Kinh was as follows: twenty-four (17.27%) belonged to Haplogroup B (mtDNA), B4, nineteen (13.67%) belonged to Haplogroup B (mtDNA), B5, one (0.72%) belonged to Haplogroup B (mtDNA), B6, four (2.88%) belonged to Haplogroup D (mtDNA), D, twenty-nine (20.86%) belonged to Haplogroup F (mtDNA), F, one (0.72%) belonged to Haplogroup G (mtDNA), G, seven (5.04%) belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M*, twenty-one (15.11%) belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M7, twelve (8.63%) belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M8, four (2.88%) belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M9a'b, one (0.72%) belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M10, two (1.44%) belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M12, one (0.72%) belonged to Haplogroup N (mtDNA), N*, two (1.44%) belonged to Haplogroup N (mtDNA), N9a, ten (7.19%) belonged to Haplogroup R (mtDNA), R9 and one (0.72%) belonged to Haplogroup W (mtDNA), W4. Sara Pischedda et al. (2017) found that the Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, mtDNA haplogroup profile for a Sample (statistics), sample of 399 Kinh was as follows: 1% belonged to Haplogroup A (mtDNA), A, 23% belonged to Haplogroup B (mtDNA), B, 2% belonged to Haplogroup C (mtDNA), C, 4% belonged to Haplogroup D (mtDNA), D, 35% belonged to Haplogroup M (mtDNA), M (xD,C), 8% belonged to Haplogroup N (mtDNA), N(xB,R9'F,A) and 27% belonged to Haplogroup R (mtDNA), R9'F.Genetic contribution theories
Bhak Jong-hwa, a professor in the biomedical engineering department at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), claimed that the ancient Vietnamese was a population that flourished with rapid agricultural development after 8th millennium BC, 8,000 BC, slowly travelled north to ancient civilizations in the Korean Peninsula and the Russian Far East. Bhak claimed that the Koreans, Korean people were formed from the admixture of "agricultural Southern Mongoloids" from Vietnam who went through China as well as "hunter-gatherer Northern Mongoloids" in the Korean Peninsula and another group of Southern Mongoloids. Bhak added, "''We believe the number of ancient dwellers who migrated north from Vietnam far exceeds the number of those occupying the peninsula''," making Koreans inherit more of their DNA from southerners.Jang, Lina. (2017). Genome Research Finds Roots of Korean Ancestry in Vietnam. The Korea Bizwire. Retrieved February 22, 2018, frolink to the article.
/ref> However, such a theory is not within the mainstream genetic study of most historians and scholars due to the lack of evidence of any such migration path ever occurring.
See also
Notes
References
Bibliography
Books
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Journal articles and theses
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Web sources
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * *Amer, Ramses (1996). Vietnam's Policies and Ethnic Chinese since 1975, ''Sojourn'', Vol. 11, Issue 1: 76–104. * * * *Cœdès, George. (1966)''The Making of South East Asia''
(illustrated, reprint ed.). University of California Press. . Retrieved 7 August 2013. * * * * *Contributor: Far-Eastern Prehistory Associatio
''Asian Perspectives, Volume 28, Issue 1''
(1990) University Press of Hawaii. Retrieved 7 August 2013. * *Hall, Kenneth R., ed. (2008)
''Secondary Cities and Urban Networking in the Indian Ocean Realm, C. 1400–1800''
Volume 1 of Comparative urban studies. Lexington Books. . Retrieved 7 August 2013. * * * * * * * * * * *Marr, David G. (2010). Vietnamese, Chinese, and Overseas Chinese during the Chinese Occupation of Northern Indochina (1945-1946), ''Chinese Southern Diaspora Studies'', Vol. 4: 129–139. * * * * * * * *Ungar, E. S. (1988). The Struggle Over the Chinese Community in Vietnam, 1946–1986, ''Pacific Affairs'', Vol. 60, Issue 4: 596–614. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Vietnamese People Vietnamese people, Ethnic groups in Vietnam