Tibet Expwy S1 sign no name.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in
 The Tibetan name for their land, ''Bod'' (), means 'Tibet' or '
The Tibetan name for their land, ''Bod'' (), means 'Tibet' or '
 The language has numerous regional dialects which are generally not mutually intelligible. It is employed throughout the Tibetan plateau and
The language has numerous regional dialects which are generally not mutually intelligible. It is employed throughout the Tibetan plateau and
 The history of a unified Tibet begins with the rule of
The history of a unified Tibet begins with the rule of  The Kingdom of Nanzhao (in
The Kingdom of Nanzhao (in
 The Mongol Yuan dynasty, through the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan, ruled Tibet through a top-level administrative department. One of the department's purposes was to select a ''dpon-chen'' ("great administrator"), usually appointed by the lama and confirmed by the Mongol emperor in Beijing.Dawa Norbu.
The Mongol Yuan dynasty, through the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan, ruled Tibet through a top-level administrative department. One of the department's purposes was to select a ''dpon-chen'' ("great administrator"), usually appointed by the lama and confirmed by the Mongol emperor in Beijing.Dawa Norbu.
China's Tibet Policy
'', p. 139. Psychology Press. The Sakya (tribe), Sakya lama retained a degree of autonomy, acting as the political authority of the region, while the ''dpon-chen'' held administrative and military power. Mongol rule of Tibet remained separate from the main provinces of China, but the region existed Tibet under Yuan rule, under the administration of the Yuan dynasty. If the Sakya lama ever came into conflict with the ''dpon-chen'', the ''dpon-chen'' had the authority to send Chinese troops into the region. Tibet retained nominal power over religious and regional political affairs, while the Mongols managed a structural and administrative rule over the region, reinforced by the rare military intervention. This existed as a "diarchy, diarchic structure" under the Yuan emperor, with power primarily in favor of the Mongols. Mongolian prince Khuden gained temporal power in Tibet in the 1240s and sponsored Sakya Pandita, whose seat became the capital of Tibet. Drogön Chögyal Phagpa, Sakya Pandita's nephew became Imperial Preceptor of Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty. Yuan control over the region ended with the Ming overthrow of the Yuan and Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen's revolt against the Mongols.Rossabi 1983, p. 194 Following the uprising, Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen founded the Phagmodrupa Dynasty, and sought to reduce Yuan influences over Tibetan culture and politics.
 Between 1346 and 1354, Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen toppled the Sakya and founded the Phagmodrupa Dynasty. The following 80 years saw the founding of the Gelug school (also known as Yellow Hats) by the disciples of Je Tsongkhapa, and the founding of the important Ganden Monastery, Ganden, Drepung Monastery, Drepung and Sera Monastery, Sera monasteries near Lhasa. However, internal strife within the dynasty and the strong localism of the various fiefs and political-religious factions led to a long series of internal conflicts. The minister family Rinpungpa, based in Tsang (West Central Tibet), dominated politics after 1435. In 1565 they were overthrown by the Tsangpa Dynasty of
Between 1346 and 1354, Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen toppled the Sakya and founded the Phagmodrupa Dynasty. The following 80 years saw the founding of the Gelug school (also known as Yellow Hats) by the disciples of Je Tsongkhapa, and the founding of the important Ganden Monastery, Ganden, Drepung Monastery, Drepung and Sera Monastery, Sera monasteries near Lhasa. However, internal strife within the dynasty and the strong localism of the various fiefs and political-religious factions led to a long series of internal conflicts. The minister family Rinpungpa, based in Tsang (West Central Tibet), dominated politics after 1435. In 1565 they were overthrown by the Tsangpa Dynasty of

 As the Qing dynasty weakened, its authority over Tibet also gradually declined, and by the mid-19th century, its influence was minuscule. Qing authority over Tibet had become more symbolic than real by the late 19th century, although in the 1860s, the Tibetans still chose for reasons of their own to emphasize the empire's symbolic authority and make it seem substantial.
In 1774, a Scottish people, Scottish Peerage of Scotland, nobleman, George Bogle (diplomat), George Bogle, travelled to
As the Qing dynasty weakened, its authority over Tibet also gradually declined, and by the mid-19th century, its influence was minuscule. Qing authority over Tibet had become more symbolic than real by the late 19th century, although in the 1860s, the Tibetans still chose for reasons of their own to emphasize the empire's symbolic authority and make it seem substantial.
In 1774, a Scottish people, Scottish Peerage of Scotland, nobleman, George Bogle (diplomat), George Bogle, travelled to

 After the
After the
 Emerging with control over most of mainland China after the Chinese Civil War, the
Emerging with control over most of mainland China after the Chinese Civil War, the

 All of modern China, including Tibet, is considered a part of East Asia. Historically, some European sources also considered parts of Tibet to lie in Central Asia. Tibet is west of the Central Plain (China), Central China plain. In China, Tibet is regarded as part of (), a term usually translated by Chinese media as "the Western section", meaning "Western China".
All of modern China, including Tibet, is considered a part of East Asia. Historically, some European sources also considered parts of Tibet to lie in Central Asia. Tibet is west of the Central Plain (China), Central China plain. In China, Tibet is regarded as part of (), a term usually translated by Chinese media as "the Western section", meaning "Western China".
 Tibet has some of the world's tallest mountains, with several of them making the top ten list.
Tibet has some of the world's tallest mountains, with several of them making the top ten list.  The Indus and Brahmaputra rivers originate from the vicinities of Lake Mapam Yumco in Western Tibet, near Mount Kailash. The mountain is a holy pilgrimage site for both Hindus and Tibetans. The Hindus consider the mountain to be the abode of Lord Shiva. The Tibetan name for Mount Kailash is Khang Rinpoche. Tibet has numerous high-altitude lakes referred to in Tibetan as ''tso'' or ''co''. These include
The Indus and Brahmaputra rivers originate from the vicinities of Lake Mapam Yumco in Western Tibet, near Mount Kailash. The mountain is a holy pilgrimage site for both Hindus and Tibetans. The Hindus consider the mountain to be the abode of Lord Shiva. The Tibetan name for Mount Kailash is Khang Rinpoche. Tibet has numerous high-altitude lakes referred to in Tibetan as ''tso'' or ''co''. These include
 Cultural Tibet consists of several regions. These include Amdo (''A mdo'') in the northeast, which is administratively part of the provinces of Qinghai, Gansu, and Sichuan. Kham (''Khams'') in the southeast encompasses parts of western Sichuan, northern
Cultural Tibet consists of several regions. These include Amdo (''A mdo'') in the northeast, which is administratively part of the provinces of Qinghai, Gansu, and Sichuan. Kham (''Khams'') in the southeast encompasses parts of western Sichuan, northern
 The Tibetan economy is dominated by subsistence agriculture. Due to limited arable land, the primary occupation of the Tibetan Plateau is raising livestock, such as Domestic sheep, sheep, cattle, Domestic goat, goats, camels, yaks, dzo, and horses.
The main crops grown are
The Tibetan economy is dominated by subsistence agriculture. Due to limited arable land, the primary occupation of the Tibetan Plateau is raising livestock, such as Domestic sheep, sheep, cattle, Domestic goat, goats, camels, yaks, dzo, and horses.
The main crops grown are  Forty percent of the rural cash income in the Tibet Autonomous Region is derived from the harvesting of the fungus ''Ophiocordyceps sinensis'' (formerly ''Cordyceps sinensis''); contributing at least 1.8 billion yuan, (US$225 million) to the region's GDP.
Forty percent of the rural cash income in the Tibet Autonomous Region is derived from the harvesting of the fungus ''Ophiocordyceps sinensis'' (formerly ''Cordyceps sinensis''); contributing at least 1.8 billion yuan, (US$225 million) to the region's GDP.
 The Qingzang railway linking the
The Qingzang railway linking the
 Historically, the population of Tibet consisted of primarily ethnic Tibetan people, Tibetans and some other ethnic groups. According to tradition the original ancestors of the Tibetan people, as represented by the six red bands in the Tibetan flag, are: the Se, Mu, Dong, Tong, Dru and Ra. Other traditional ethnic groups with significant population or with the majority of the ethnic group residing in Tibet (excluding a Sino-Indian War, disputed area with India) include Bai people, Blang people, Blang, Bonans, Bonan, Dongxiang people, Dongxiang, Han Chinese, Han, Hui people, Lhoba, Lisu people, Miao people, Miao, Mongols, Monguor people, Monguor (Tu people), Monpa people, Menba (Monpa), Mosuo, Nakhi, Qiang, Nu people, Pumi people, Pumi, Salar people, Salar, and Yi people.
The proportion of the non-Tibetan population in Tibet is disputed. On the one hand, the Central Tibetan Administration of the Dalai Lama accuses China of actively swamping Tibet with Chinese settlements in Tibet, migrants in order to alter Tibet's demographic makeup. On the other hand, according to the Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, 2010 Chinese census ethnic Tibetans comprise 90% of a total population of 3 million in the
Historically, the population of Tibet consisted of primarily ethnic Tibetan people, Tibetans and some other ethnic groups. According to tradition the original ancestors of the Tibetan people, as represented by the six red bands in the Tibetan flag, are: the Se, Mu, Dong, Tong, Dru and Ra. Other traditional ethnic groups with significant population or with the majority of the ethnic group residing in Tibet (excluding a Sino-Indian War, disputed area with India) include Bai people, Blang people, Blang, Bonans, Bonan, Dongxiang people, Dongxiang, Han Chinese, Han, Hui people, Lhoba, Lisu people, Miao people, Miao, Mongols, Monguor people, Monguor (Tu people), Monpa people, Menba (Monpa), Mosuo, Nakhi, Qiang, Nu people, Pumi people, Pumi, Salar people, Salar, and Yi people.
The proportion of the non-Tibetan population in Tibet is disputed. On the one hand, the Central Tibetan Administration of the Dalai Lama accuses China of actively swamping Tibet with Chinese settlements in Tibet, migrants in order to alter Tibet's demographic makeup. On the other hand, according to the Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, 2010 Chinese census ethnic Tibetans comprise 90% of a total population of 3 million in the



 Religion is extremely important to the Tibetans and has a strong influence over all aspects of their lives. Bön is the indigenous religion of Tibet, but has been almost eclipsed by Tibetan Buddhism, a distinctive form of Mahayana and Vajrayana, which was introduced into Tibet from the Sanskrit Buddhist tradition of northern India. Tibetan Buddhism is practiced not only in Tibet but also in Mongolia, parts of northern India, the Buryat Republic, the Tuva Republic, and in the Republic of Kalmykia and some other parts of China. During China's Cultural Revolution, nearly all Tibet's List of Tibetan monasteries, monasteries were ransacked and destroyed by the Red Guards (China), Red Guards.Tibetan monks: A controlled life
Religion is extremely important to the Tibetans and has a strong influence over all aspects of their lives. Bön is the indigenous religion of Tibet, but has been almost eclipsed by Tibetan Buddhism, a distinctive form of Mahayana and Vajrayana, which was introduced into Tibet from the Sanskrit Buddhist tradition of northern India. Tibetan Buddhism is practiced not only in Tibet but also in Mongolia, parts of northern India, the Buryat Republic, the Tuva Republic, and in the Republic of Kalmykia and some other parts of China. During China's Cultural Revolution, nearly all Tibet's List of Tibetan monasteries, monasteries were ransacked and destroyed by the Red Guards (China), Red Guards.Tibetan monks: A controlled life
. BBC News. March 20, 2008. A few monasteries have begun to rebuild since the 1980s (with limited support from the Chinese government) and greater religious freedom has been granted – although it is still limited. Monks returned to monasteries across Tibet and monastic education resumed even though the number of monks imposed is strictly limited. Before the 1950s, between 10 and 20% of males in Tibet were monks. Tibetan Buddhism has five main traditions (the suffix ''pa'' is comparable to "er" in English): * Gelug, Gelug(pa), ''Way of Virtue'', also known casually as ''Yellow Hat'', whose spiritual head is the Ganden Tripa and whose temporal head is the Dalai Lama. Successive Dalai Lamas ruled Tibet from the mid-17th to mid-20th centuries. This order was founded in the 14th to 15th centuries by Je Tsongkhapa, based on the foundations of the Kadampa tradition. Tsongkhapa was renowned for both his scholasticism and his virtue. The Dalai Lama belongs to the Gelugpa school, and is regarded as the embodiment of the Bodhisattva of Compassion. * Kagyu, Kagyu(pa), ''Oral Lineage''. This contains one major subsect and one minor subsect. The first, the Dagpo Kagyu, encompasses those Kagyu schools that trace back to Gampopa. In turn, the Dagpo Kagyu consists of four major sub-sects: the Karma Kagyu, headed by a Karmapa, the Tsalpa Kagyu, the Barom Kagyu, and Pagtru Kagyu. The once-obscure Shangpa Kagyu, which was famously represented by the 20th-century teacher Kalu Rinpoche, traces its history back to the Indian master Niguma, sister of Kagyu lineage holder Naropa. This is an oral tradition which is very much concerned with the experiential dimension of meditation. Its most famous exponent was Milarepa, an 11th-century mystic. * Nyingma, Nyingma(pa), ''The Ancient Ones''. This is the oldest, the original order founded by Padmasambhava. * Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist school), Sakya(pa), ''Grey Earth'', headed by the Sakya Trizin, founded by Khon Konchog Gyalpo, a disciple of the great translator Drokmi Lotsawa. Sakya Pandita 1182–1251 CE was the great-grandson of Khon Konchog Gyalpo. This school emphasizes scholarship. * Jonang, Jonang(pa) Its origins in Tibet can be traced to early 12th century master Yumo Mikyo Dorje, but became much wider known with the help of Dolpopa Sherab Gyaltsen, a monk originally trained in the Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist school), Sakya school. The Jonang school was widely thought to have become extinct in the late 17th century at the hands of the 5th Dalai Lama, who forcibly annexed the Jonang monasteries to his Gelug school, declaring them heretical. Thus, Tibetology, Tibetologists were astonished when fieldwork turned up several active Jonangpa monasteries, including the main monastery, Tsangwa, located in Zamtang County, Sichuan. Almost 40 monasteries, comprising about 5000 monks, have subsequently been found, including some in the Amdo Tibetan and Qiang people, rGyalgrong areas of
 Muslims have been living in Tibet since as early as the 8th or 9th century. In Tibetan cities, there are small communities of Tibetan Muslim, Muslims, known as Kachee (Kache), who trace their origin to immigrants from three main regions: Kashmir (Kachee Yul in ancient Tibetan), Ladakh and the Central Asian Turkic countries. Islamic influence in Tibet also came from Persia. A Muslim Sufi Ali Hamadani, Syed Ali Hamdani preached to the people of Baltistan, then known as little Tibet. After 1959, a group of Tibetan Muslims made a case for Indian nationality based on their historic roots to Kashmir and the Indian government declared all Tibetan Muslims Indian citizens later on that year. Other Muslim ethnic groups who have long inhabited Tibet include
Muslims have been living in Tibet since as early as the 8th or 9th century. In Tibetan cities, there are small communities of Tibetan Muslim, Muslims, known as Kachee (Kache), who trace their origin to immigrants from three main regions: Kashmir (Kachee Yul in ancient Tibetan), Ladakh and the Central Asian Turkic countries. Islamic influence in Tibet also came from Persia. A Muslim Sufi Ali Hamadani, Syed Ali Hamdani preached to the people of Baltistan, then known as little Tibet. After 1959, a group of Tibetan Muslims made a case for Indian nationality based on their historic roots to Kashmir and the Indian government declared all Tibetan Muslims Indian citizens later on that year. Other Muslim ethnic groups who have long inhabited Tibet include

File:thanka.jpg, A thangka painting in
 Tibet has various festivals, many for worshipping the Buddha, that take place throughout the year. Losar is the Tibetan New Year Festival. Preparations for the festive event are manifested by special offerings to family shrine deities, painted doors with religious symbols, and other painstaking jobs done to prepare for the event. Tibetans eat ''Guthuk'' (barley noodle soup with filling) on New Year's Eve with their families. The Monlam Prayer Festival follows it in the first month of the Tibetan calendar, falling between the fourth and the eleventh days of the first Tibetan month. It involves dancing and participating in sports events, as well as sharing picnics. The event was established in 1049 by Tsong Khapa, the founder of the Dalai Lama and the Panchen Lama's order.
Tibet has various festivals, many for worshipping the Buddha, that take place throughout the year. Losar is the Tibetan New Year Festival. Preparations for the festive event are manifested by special offerings to family shrine deities, painted doors with religious symbols, and other painstaking jobs done to prepare for the event. Tibetans eat ''Guthuk'' (barley noodle soup with filling) on New Year's Eve with their families. The Monlam Prayer Festival follows it in the first month of the Tibetan calendar, falling between the fourth and the eleventh days of the first Tibetan month. It involves dancing and participating in sports events, as well as sharing picnics. The event was established in 1049 by Tsong Khapa, the founder of the Dalai Lama and the Panchen Lama's order.

A History of Modern Tibet, 1913–1951: The Demise of the Lamaist State
' (1989) University of California Press. *Melvyn Goldstein, Goldstein, Melvyn C. ''A History of Modern Tibet, 1913–1951: The Demise of the Lamaist State'' (1989), first Indian edition (1993) Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers, New Delhi, Pagination is identical to University of California edition. *Goldstein, Melvyn C. ''The Snow Lion and the Dragon: China, Tibet, and the Dalai Lama'' (1997) University of California Press. *A. Tom Grunfeld, Grunfeld, Tom (1996). ''The Making of Modern Tibet.'' . *Peter Hopkirk, Hopkirk, Peter
''Trespassers on the Roof of the World: The Secret Exploration of Tibet''
(1983) J. P. Tarcher. *Matthew Kapstein, Kapstein, Matthew T. ''The Tibetans'' (2006) Blackwell Publishing. *Laird, Thomas. ''The Story of Tibet: Conversations with the Dalai Lama'' (2006) Grove Press. *Glenn H. Mullin, Mullin, Glenn H.''The Fourteen Dalai Lamas: A Sacred Legacy of Reincarnations'' (2001) Clear Light Publishers. *Powers, John. ''History as Propaganda: Tibetan Exiles versus the People's Republic of China'' (2004) Oxford University Press. *Hugh Edward Richardson, Richardson, Hugh E. ''Tibet and its History'' Second Edition, Revised and Updated (1984) Shambhala. *Tsering Shakya, Shakya, Tsering. ''The Dragon In The Land Of Snows'' (1999) Columbia University Press. *Rolf Stein, Stein, R. ''Tibetan Civilization'' (1972) Stanford University Press. *Teltscher, Kate. ''The High Road to China (book), The High Road to China: George Bogle, the Panchen Lama and the First British Expedition to Tibet'' (2006) Bloomsbury UK.
Tibet wasn't always ours, says Chinese scholar
by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, February 22, 2007 * Wylie, Turrell V. "The First Mongol Conquest of Tibet Reinterpreted", ''Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies'' (Volume 37, Number 1, June 1977) *
from Columbia University Libraries
British photographs of Tibet 1920–1950
released by the Information Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China June 22
Historical maps and images of Tibet
presented by University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Libraries Digital Collections
The Tibetan & Himalayan Library (THL)
* {{Authority control Tibet, Former countries in East Asia Central Asia East Asia Inner Asia Regions of China Western China Cultural regions Historical regions
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans l ...
. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Tamang
The Tamang (; Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāṅ'') are an Tibeto-Burmese ethnic group of Nepal. In Nepal Tamang/Moormi people constitute 5.6% of the Nepalese population at over 1.3 million in 2001, increasing to 1,539,830 as of the 2011 ...
, Qiang, Sherpa Sherpa may refer to:
Ethnography
* Sherpa people, an ethnic group in north eastern Nepal
* Sherpa language
Organizations and companies
* Sherpa (association), a French network of jurists dedicated to promoting corporate social responsibility
* ...
and Lhoba people
Lhoba (English translation: ; ; bo, ལྷོ་པ།) is any of a diverse amalgamation of Sino-Tibetan-speaking tribespeople living in and around Pemako, a region in southeastern Tibet including Mainling, Medog and Zayü counties of Nying ...
s and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
and Hui
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
settlers. Since 1951
Events
January
* January 4 – Korean War: Third Battle of Seoul – Chinese and North Korean forces capture Seoul for the second time (having lost the Second Battle of Seoul in September 1950).
* January 9 – The Government of the United ...
, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
, and other portions in the Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
and Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
provinces.
Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest
Mount Everest (; Tibetic languages, Tibetan: ''Chomolungma'' ; ) is List of highest mountains on Earth, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border ru ...
, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level.
The Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the 3 ...
emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the 3 ...
extended far beyond the Tibetan Plateau, from Central Asian's Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
and the Pamirs
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world ...
in the west to Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
and Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
in the southeast. But once the process of fragmentation began, the empire divided into a variety of territories. The bulk of western and central Tibet (Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered ...
) was often at least nominally unified under a series of Tibetan governments in Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Region in Southwest China. The inner urban area of Lhas ...
, Shigatse
Shigatse, officially known as Xigazê (; Nepali: ''सिगात्से''), is a prefecture-level city of the Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Its area of jurisdiction, with an area of , corresponds to the histor ...
, or nearby locations. The eastern regions of Kham and Amdo
Amdo ( �am˥˥.to˥˥ ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being U-Tsang in the west and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Amdo is also the ...
often maintained a more decentralized indigenous political structure, being divided among a number of small principalities and tribal groups, while also often falling more directly under Chinese rule; most of this area was eventually annexed into the Chinese provinces of Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
and Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
. The current borders of Tibet were generally established in the 18th century.
Following the Xinhai Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a ...
against the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
in 1912, Qing soldiers were disarmed and escorted out of Tibet Area (Ü-Tsang). The region subsequently declared its independence in 1913 without recognition and permission by the subsequent Chinese Republican government. Later, Lhasa took control of the western part of Xikang
Xikang (also Sikang or Hsikang) was a nominal province
formed by the Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and continued by the early People's Republic of China. Thei idea was to form a single unif ...
. The region maintained its autonomy until 1951 when, following the Battle of Chamdo
The Battle of Chamdo (or Qamdo; ) occurred from 6 to 24 October 1950. It was a military campaign by the People's Republic of China (PRC) to take the Chamdo Region from a ''de facto'' independent Tibetan state.Shakya 1999 pp.28–32. The campa ...
, Tibet was occupied and annexed into the People's Republic of China, and the previous Tibetan government was abolished in 1959 after a failed uprising. Today, China governs western and central Tibet as the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
while the eastern areas are now mostly ethnic autonomous prefectures within Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
, Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
and other neighbouring provinces. There are tensions regarding Tibet's political status and dissident groups that are active in exile.
Tibetan activists in Tibet have reportedly been arrested or tortured.
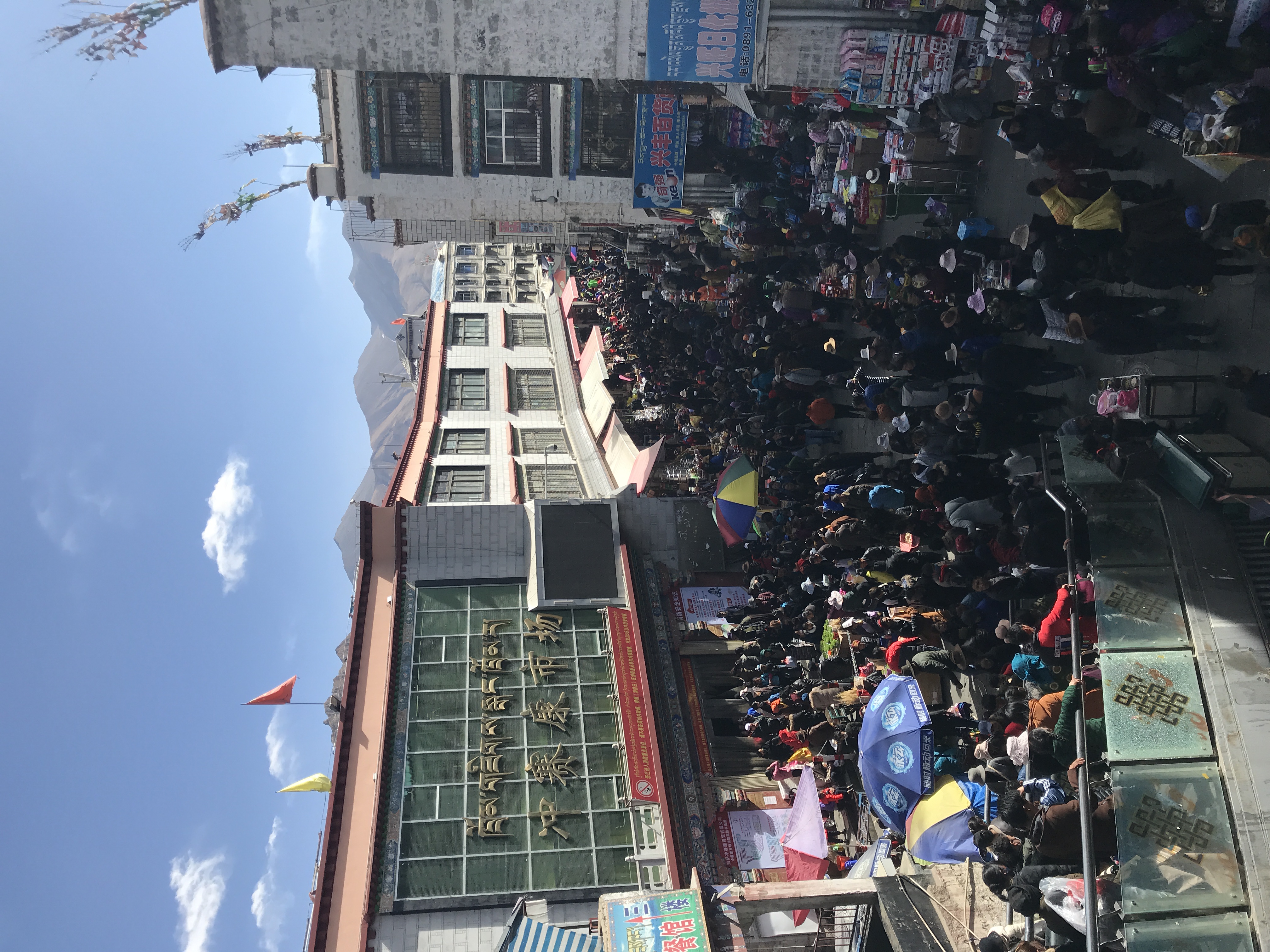
With the growth of tourism in recent years, the service sector has become the largest sector in Tibet, accounting for 50.1% of the local GDP in 2020. The dominant religion in Tibet is Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
; other religions include Bön, an indigenous religion similar to Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan Muslims
Tibetan Muslims, also known as the Kachee (; ; also spelled Kache), form a small minority in Tibet. Despite being Muslim, they are officially recognized as Tibetans by the government of the People's Republic of China, unlike the Hui Muslims, ...
, and Christian minorities. Tibetan Buddhism is a primary influence on the art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
, and festivals
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, mela, or eid. A festival c ...
of the region. Tibetan architecture reflects Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
and Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
influences. Staple foods in Tibet are roasted barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
, yak meat, and butter tea
Butter tea, also known as ''po cha'' (, "Tibetan tea"), ''cha süma'' (, "churned tea"), Mandarin Chinese: ''sūyóu chá'' ( 酥 油 茶) or ''gur gur cha'' in the Ladakhi language, is a drink of the people in the Himalayan regions of Nepal, Bhut ...
.
Names
 The Tibetan name for their land, ''Bod'' (), means 'Tibet' or '
The Tibetan name for their land, ''Bod'' (), means 'Tibet' or 'Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
', although it originally meant the central region around Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Region in Southwest China. The inner urban area of Lhas ...
, now known in Tibetan as ''Ü'' (). The Standard Tibetan pronunciation of ''Bod'' () is transcribed as: ''Bhö'' in Tournadre Phonetic Transcription; ''Bö'' in the THL Simplified Phonetic Transcription
The THL Simplified Phonetic Transcription of Standard Tibetan (or ''THL Phonetic Transcription'' for short) is a system for the phonetic rendering of the Tibetan language.
It was created by David Germano and Nicolas Tournadre and was published on ...
; and ''Poi'' in Tibetan pinyin. Some scholars believe the first written reference to ''Bod'' ('Tibet') was the ancient Bautai people recorded in the Egyptian-Greek works ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
'' (1st century CE) and ''Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
'' (Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
, 2nd century CE), itself from the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
form ''Bhauṭṭa'' of the Indian geographical tradition.
The modern Standard Chinese exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
for the ethnic Tibetan region is ''Zangqu'' (), which derives by metonymy from the Tsang region around Shigatse
Shigatse, officially known as Xigazê (; Nepali: ''सिगात्से''), is a prefecture-level city of the Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Its area of jurisdiction, with an area of , corresponds to the histor ...
plus the addition of a Chinese suffix (), which means 'area, district, region, ward'. Tibetan people, language, and culture, regardless of where they are from, are referred to as ''Zang'' (), although the geographical term is often limited to the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
. The term ''Xīzàng'' was coined during the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
in the reign of the Jiaqing Emperor
The Jiaqing Emperor (13 November 1760 – 2 September 1820), also known by his temple name Emperor Renzong of Qing, born Yongyan, was the sixth emperor of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and the fifth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, from ...
(1796–1820) through the addition of the prefix (, 'west') to ''Zang''.
The best-known medieval Chinese name for Tibet is ''Tubo'' (; or , or , ). This name first appears in Chinese characters as in the 7th century ( Li Tai) and as in the 10th-century ('' Old Book of Tang'', describing 608–609 emissaries from Tibetan King Namri Songtsen
Namri Songtsen (), also known as "Namri Löntsen" () (died 618) was according to tradition, the 32nd King of Tibet of the Yarlung Dynasty. (Reign: 570 – 618) During his 48 years of reign, he expanded his kingdom to rule the central part of the ...
to Emperor Yang of Sui). In the Middle-Chinese language spoken during that period, as reconstructed by William H. Baxter
William Hubbard Baxter III (born March 3, 1949) is an American linguistics, linguist specializing in the history of the Chinese language and best known for Baxter's transcription for Middle Chinese, his work on the reconstruction on Old Chinese.
...
, was pronounced ''thu-phjon'', and was pronounced ''thu-pjon'' (with the ' representing a '' shang'' tone).
Other pre-modern Chinese names for Tibet include:
* ''Wusiguo'' (; cf.
The abbreviation ''cf.'' (short for the la, confer/conferatur, both meaning "compare") is used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. Style guides recommend that ''cf.'' be used onl ...
Tibetan: ''dbus'', Ü, );
* ''Wusizang'' (, cf. Tibetan: ''dbus-gtsang'', Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered ...
);
* ''Tubote'' (); and
* ''Tanggute'' (, cf. Tangut).
American Tibetologist
Tibetology () refers to the study of things related to Tibet, including its history, religion, language, culture, politics and the collection of Tibetan articles of historical, cultural and religious significance. The last may mean a collection of ...
Elliot Sperling
Elliot Sperling (January 4, 1951 – January 29, 2017) was one of the world's leading historians of Tibet and Tibetan- Chinese relations, and a MacArthur Fellow. He spent most of his scholarly career as an associate professor at Indiana Universi ...
has argued in favor of a recent tendency by some authors writing in Chinese to revive the term ''Tubote'' () for modern use in place of ''Xizang'', on the grounds that ''Tubote'' more clearly includes the entire Tibetan plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
rather than simply the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
.
The English word ''Tibet'' or ''Thibet'' dates back to the 18th century. Historical linguists generally agree that "Tibet" names in European languages are loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
s from Semitic or ( ar, طيبة، توبات; he, טובּה, טובּת), itself deriving from Turkic ' (plural of ), literally 'The Heights'.
Language
Linguists generally classify theTibetan language Tibetan language may refer to:
* Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
* Lhasa Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dialect
* Any of the other Tibetic languages
See also
* Old Tibetan, the languag ...
as a Tibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spea ...
language of the Sino-Tibetan language
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
family although the boundaries between 'Tibetan' and certain other Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
n languages can be unclear. According to Matthew Kapstein
Matthew T. Kapstein is a scholar of Tibetan religions, Buddhism, and the cultural effects of the Chinese occupation of Tibet. He is Numata Visiting Professor of Buddhist Studies at the University of Chicago Divinity School, and Director of Tibetan ...
:From the perspective of historical linguistics, Tibetan most closely resembles Burmese among the major languages of Asia. Grouping these two together with other apparently related languages spoken in theHimalaya The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...n lands, as well as in the highlands of Southeast Asia and the Sino-Tibetan frontier regions, linguists have generally concluded that there exists a Tibeto-Burman family of languages. More controversial is the theory that the Tibeto-Burman family is itself part of a larger language family, calledSino-Tibetan Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ..., and that through it Tibetan and Burmese are distant cousins of Chinese.
 The language has numerous regional dialects which are generally not mutually intelligible. It is employed throughout the Tibetan plateau and
The language has numerous regional dialects which are generally not mutually intelligible. It is employed throughout the Tibetan plateau and Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
and is also spoken in parts of Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
and northern India, such as Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Silig ...
. In general, the dialects of central Tibet (including Lhasa), Kham, Amdo
Amdo ( �am˥˥.to˥˥ ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being U-Tsang in the west and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Amdo is also the ...
and some smaller nearby areas are considered Tibetan dialects. Other forms, particularly Dzongkha, Sikkimese, Sherpa Sherpa may refer to:
Ethnography
* Sherpa people, an ethnic group in north eastern Nepal
* Sherpa language
Organizations and companies
* Sherpa (association), a French network of jurists dedicated to promoting corporate social responsibility
* ...
, and Ladakhi, are considered by their speakers, largely for political reasons, to be separate languages. However, if the latter group of Tibetan-type languages are included in the calculation, then 'greater Tibetan' is spoken by approximately 6 million people across the Tibetan Plateau. Tibetan is also spoken by approximately 150,000 exile speakers who have fled from modern-day Tibet to India and other countries.
Although spoken Tibetan varies according to the region, the written language, based on Classical Tibetan
Classical Tibetan refers to the language of any text written in Tibetic after the Old Tibetan period. Though it extends from the 12th century until the modern day, it particularly refers to the language of early canonical texts translated from ot ...
, is consistent throughout. This is probably due to the long-standing influence of the Tibetan empire, whose rule embraced (and extended at times far beyond) the present Tibetan linguistic area, which runs from Gilgit Baltistan
Gilgit (; Shina: ; ur, ) is the capital city of Gilgit–Baltistan, Pakistan. The city is located in a broad valley near the confluence of the Gilgit River and the Hunza River. It is a major tourist destination in Pakistan, serving as a h ...
in the west to Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
and Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
in the east, and from north of Qinghai Lake
Qinghai Lake or Ch'inghai Lake, also known by other names, is the largest lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline salt lake. The lake has fluctuate ...
south as far as Bhutan. The Tibetan language has its own script which it shares with Ladakhi and Dzongkha, and which is derived from the ancient Indian Brāhmī script.
Starting in 2001, the local deaf sign language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign l ...
s of Tibet were standardized, and Tibetan Sign Language
Tibetan Sign Language is the recently established deaf sign language of Tibet.
Tibetan Sign is the first recognized sign language for a minority in China. The Tibetan Sign Language Project, staffed by members of the local deaf club, was set up ...
is now being promoted across the country.
The first Tibetan-English dictionary and grammar book was written by Alexander Csoma de Kőrös in 1834.
History
Early history
Humans inhabited the Tibetan Plateau at least 21,000 years ago. This population was largely replaced around 3,000 BP byNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
immigrants from northern China, but there is a partial genetic continuity between the Paleolithic inhabitants and contemporary Tibetan populations.
The earliest Tibetan historical texts identify the Zhang Zhung culture as a people who migrated from the Amdo region into what is now the region of Guge in western Tibet.Norbu 1989, pp. 127–128 Zhang Zhung is considered to be the original home of the Bön religion.Helmut Hoffman in McKay 2003 vol. 1, pp. 45–68 By the 1st century BCE, a neighboring kingdom arose in the Yarlung valley
The Yarlung Valley is formed by Yarlung Chu, a tributary of the Tsangpo River in the Shannan Prefecture in the Tibet region of China. It refers especially to the district where Yarlung Chu joins with the Chongye River, and broadens out into a la ...
, and the Yarlung king, Drigum Tsenpo Drigum Tsenpo was an emperor of Tibet. According to Tibetan mythology, he was the first king of Tibet to lose his immortality when he angered his stable master, Lo-ngam. Legend states that rulers of Tibet descended from heaven to earth on a cord ...
, attempted to remove the influence of the Zhang Zhung by expelling the Zhang's Bön priests from Yarlung. He was assassinated and Zhang Zhung continued its dominance of the region until it was annexed by Songtsen Gampo in the 7th century. Prior to Songtsen Gampo
Songtsen Gampo (; 569–649? 650), also Songzan Ganbu (), was the 33rd Tibetan king and founder of the Tibetan Empire, and is traditionally credited with the introduction of Buddhism to Tibet, influenced by his Nepali consort Bhrikuti, of Nepa ...
, the kings of Tibet were more mythological than factual, and there is insufficient evidence of their existence.
Tibetan Empire
 The history of a unified Tibet begins with the rule of
The history of a unified Tibet begins with the rule of Songtsen Gampo
Songtsen Gampo (; 569–649? 650), also Songzan Ganbu (), was the 33rd Tibetan king and founder of the Tibetan Empire, and is traditionally credited with the introduction of Buddhism to Tibet, influenced by his Nepali consort Bhrikuti, of Nepa ...
(604–650CE), who united parts of the Yarlung River Valley and founded the Tibetan Empire. He also brought in many reforms, and Tibetan power spread rapidly, creating a large and powerful empire. It is traditionally considered that his first wife was the Princess of Nepal, Bhrikuti
Princess Bhrikuti Devi ( sa, भृकुटी, known to Tibetans as Bal-mo-bza' Khri-btsun, Bhelsa Tritsun (Nepal ), or simply, Khri bTsun ()) of Licchavi is traditionally considered to have been the first wife and queen of the earliest emperor ...
, and that she played a great role in the establishment of Buddhism in Tibet. In 640, he married Princess Wencheng
Princess Wencheng (; ) was a member of a minor branch of the royal clan of the Tang Dynasty who married King Songtsen Gampo of the Tibetan Empire in 641. She is also known by the name Gyasa or "Chinese wife" in Tibet. Some Tibetan historians cons ...
, the niece of the Chinese emperor Emperor Taizong of Tang, Taizong of Tang China.
Under the next few Tibetan kings, Buddhism became established as the state religion and Tibetan power increased even further over large areas of Central Asia, while major inroads were made into Chinese territory, even reaching the Tang dynasty, Tang's capital Chang'an (modern Xi'an) in late 763. However, the Tibetan occupation of Chang'an only lasted for fifteen days, after which they were defeated by Tang and its ally, the Turkic Uyghur Khaganate.
 The Kingdom of Nanzhao (in
The Kingdom of Nanzhao (in Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
and neighbouring regions) remained under Tibetan control from 750 to 794, when they turned on their Tibetan overlords and helped the Chinese inflict a serious defeat on the Tibetans.
In 747, the hold of Tibet was loosened by the campaign of general Gao Xianzhi, who tried to re-open the direct communications between Central Asia and Kashmir. By 750, the Tibetans had lost almost all of their central Asian possessions to the Tang dynasty, Chinese. However, after Gao Xianzhi's defeat by the Abbasid Caliphate, Arabs and Karluks, Qarluqs at the Battle of Talas (751) and the subsequent civil war known as the An Lushan Rebellion (755), Chinese influence decreased rapidly and Tibetan influence resumed.
At its height in the 780s to 790s, the Tibetan Empire reached its highest glory when it ruled and controlled a territory stretching from modern day Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Burma, China, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan.
In 821/822CE, Tibet and China signed a peace treaty. A bilingual account of this treaty, including details of the borders between the two countries, is inscribed on a stone pillar which stands outside the Jokhang temple in Lhasa. Tibet continued as a Central Asian empire until the mid-9th century, when a civil war over succession led to the collapse of imperial Tibet. The period that followed is known traditionally as the ''Era of Fragmentation'', when political control over Tibet became divided between regional warlords and tribes with no dominant centralized authority. An Tibetan Expedition of Islamic Bengal, Islamic invasion from Bengal took place in 1206.
Yuan dynasty
 The Mongol Yuan dynasty, through the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan, ruled Tibet through a top-level administrative department. One of the department's purposes was to select a ''dpon-chen'' ("great administrator"), usually appointed by the lama and confirmed by the Mongol emperor in Beijing.Dawa Norbu.
The Mongol Yuan dynasty, through the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan, ruled Tibet through a top-level administrative department. One of the department's purposes was to select a ''dpon-chen'' ("great administrator"), usually appointed by the lama and confirmed by the Mongol emperor in Beijing.Dawa Norbu. China's Tibet Policy
'', p. 139. Psychology Press. The Sakya (tribe), Sakya lama retained a degree of autonomy, acting as the political authority of the region, while the ''dpon-chen'' held administrative and military power. Mongol rule of Tibet remained separate from the main provinces of China, but the region existed Tibet under Yuan rule, under the administration of the Yuan dynasty. If the Sakya lama ever came into conflict with the ''dpon-chen'', the ''dpon-chen'' had the authority to send Chinese troops into the region. Tibet retained nominal power over religious and regional political affairs, while the Mongols managed a structural and administrative rule over the region, reinforced by the rare military intervention. This existed as a "diarchy, diarchic structure" under the Yuan emperor, with power primarily in favor of the Mongols. Mongolian prince Khuden gained temporal power in Tibet in the 1240s and sponsored Sakya Pandita, whose seat became the capital of Tibet. Drogön Chögyal Phagpa, Sakya Pandita's nephew became Imperial Preceptor of Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty. Yuan control over the region ended with the Ming overthrow of the Yuan and Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen's revolt against the Mongols.Rossabi 1983, p. 194 Following the uprising, Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen founded the Phagmodrupa Dynasty, and sought to reduce Yuan influences over Tibetan culture and politics.
Phagmodrupa, Rinpungpa and Tsangpa Dynasties
 Between 1346 and 1354, Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen toppled the Sakya and founded the Phagmodrupa Dynasty. The following 80 years saw the founding of the Gelug school (also known as Yellow Hats) by the disciples of Je Tsongkhapa, and the founding of the important Ganden Monastery, Ganden, Drepung Monastery, Drepung and Sera Monastery, Sera monasteries near Lhasa. However, internal strife within the dynasty and the strong localism of the various fiefs and political-religious factions led to a long series of internal conflicts. The minister family Rinpungpa, based in Tsang (West Central Tibet), dominated politics after 1435. In 1565 they were overthrown by the Tsangpa Dynasty of
Between 1346 and 1354, Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen toppled the Sakya and founded the Phagmodrupa Dynasty. The following 80 years saw the founding of the Gelug school (also known as Yellow Hats) by the disciples of Je Tsongkhapa, and the founding of the important Ganden Monastery, Ganden, Drepung Monastery, Drepung and Sera Monastery, Sera monasteries near Lhasa. However, internal strife within the dynasty and the strong localism of the various fiefs and political-religious factions led to a long series of internal conflicts. The minister family Rinpungpa, based in Tsang (West Central Tibet), dominated politics after 1435. In 1565 they were overthrown by the Tsangpa Dynasty of Shigatse
Shigatse, officially known as Xigazê (; Nepali: ''सिगात्से''), is a prefecture-level city of the Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Its area of jurisdiction, with an area of , corresponds to the histor ...
which expanded its power in different directions of Tibet in the following decades and favoured the Karma Kagyu sect.
Rise of Ganden Phodrang
In 1578, Altan Khan of the Tümed Mongols gave 3rd Dalai Lama, Sonam Gyatso, a high lama of the Gelugpa school, the name ''Dalai Lama'', ''Dalai'' being the Mongolian translation of the Tibetan name ''Gyatso'' "Ocean".Unified heartland under Buddhist Gelug school
The 5th Dalai Lama (1617-1682) is known for unifying the Tibetan heartland under the control of the Gelug school ofTibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
, after defeating the rival Kagyu and Jonang sects and the secular ruler, the Tsangpa prince, in a prolonged civil war. His efforts were successful in part because of aid from Güshi Khan, the Oirats, Oirat leader of the Khoshut Khanate. With Güshi Khan as a largely uninvolved overlord, the 5th Dalai Lama and his intimates established a civil administration which is referred to by historians as the ''Lhasa state''. This Tibetan regime or government is also referred to as the Ganden Phodrang.
Qing dynasty

Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
rule in Tibet began with their Chinese expedition to Tibet (1720), 1720 expedition to the country when they expelled the invading Dzungar Khanate, Dzungars. Amdo
Amdo ( �am˥˥.to˥˥ ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being U-Tsang in the west and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Amdo is also the ...
came under Qing control in 1724, and eastern Kham was incorporated into neighbouring Chinese provinces in 1728.Wang Jiawei, "The Historical Status of China's Tibet", 2000, pp. 162–6. Meanwhile, the Qing government sent resident commissioners called ''Ambans'' to Lhasa. In 1750, the Ambans and the majority of the Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
and Manchus living in Lhasa were killed in Lhasa riot of 1750, a riot, and Qing troops arrived quickly and suppressed the rebels in the next year. Like the preceding Yuan dynasty, the Manchus of the Qing dynasty exerted military and administrative control of the region, while granting it a degree of political autonomy. The Qing commander publicly executed a number of supporters of the rebels and, as in 1723 and 1728, made changes in the political structure and drew up a formal organization plan. The Qing now restored the Dalai Lama as ruler, leading the governing council called ''Kashag'', but elevated the role of ''Ambans'' to include more direct involvement in Tibetan internal affairs. At the same time, the Qing took steps to counterbalance the power of the aristocracy by adding officials recruited from the clergy to key posts.
For several decades, peace reigned in Tibet, but in 1792, the Qing Qianlong Emperor sent Sino-Nepalese War, a large Chinese army into Tibet to push the invading Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
ese out. This prompted yet another Qing reorganization of the Tibetan government, this time through a written plan called the "Twenty-Nine Regulations for Better Government in Tibet". Qing military garrisons staffed with Qing troops were now also established near the Nepalese border. Tibet was dominated by the Manchus in various stages in the 18th century, and the years immediately following the 1792 regulations were the peak of the Qing imperial commissioners' authority; but there was no attempt to make Tibet a Chinese province.
In 1834, the Sikh Empire invaded and annexed Ladakh, a culturally Tibetan region that was an independent kingdom at the time. Seven years later, a Sikh army led by General Zorawar Singh invaded western Tibet from Ladakh, starting the Sino-Sikh War. A Qing-Tibetan army repelled the invaders but was in turn defeated when it chased the Sikhs into Ladakh. The war ended with the signing of the Treaty of Chushul between the Chinese and Sikh empires.
 As the Qing dynasty weakened, its authority over Tibet also gradually declined, and by the mid-19th century, its influence was minuscule. Qing authority over Tibet had become more symbolic than real by the late 19th century, although in the 1860s, the Tibetans still chose for reasons of their own to emphasize the empire's symbolic authority and make it seem substantial.
In 1774, a Scottish people, Scottish Peerage of Scotland, nobleman, George Bogle (diplomat), George Bogle, travelled to
As the Qing dynasty weakened, its authority over Tibet also gradually declined, and by the mid-19th century, its influence was minuscule. Qing authority over Tibet had become more symbolic than real by the late 19th century, although in the 1860s, the Tibetans still chose for reasons of their own to emphasize the empire's symbolic authority and make it seem substantial.
In 1774, a Scottish people, Scottish Peerage of Scotland, nobleman, George Bogle (diplomat), George Bogle, travelled to Shigatse
Shigatse, officially known as Xigazê (; Nepali: ''सिगात्से''), is a prefecture-level city of the Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Its area of jurisdiction, with an area of , corresponds to the histor ...
to investigate prospects of trade for the East India Company. His efforts, while largely unsuccessful, established permanent contact between Tibet and the Western world. However, in the 19th century, tensions between foreign powers and Tibet increased. The British Empire was expanding its British Raj, territories in India into the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
, while the Emirate of Afghanistan and the Russian Empire were both doing likewise in Central Asia.
In 1904, a British expedition to Tibet, spurred in part by a fear that Russian Empire, Russia was extending its power into Tibet as part of the Great Game, was launched. Although the expedition initially set out with the stated purpose of resolving border disputes between Tibet and Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Silig ...
, it quickly turned into a military invasion. The British expeditionary force, consisting of British Indian Army, mostly Indian troops, quickly invaded and captured Lhasa, with the 13th Dalai Lama, Dalai Lama fleeing to the countryside.Smith 1996, pp. 154–6 Afterwards, the leader of the expedition, Francis Younghusband, Sir Francis Younghusband, negotiated the Treaty of Lhasa, Convention Between Great Britain and Tibet with the Tibetans, which guaranteed the British great economic influence but ensured the region Tibet under Qing rule, remained under Chinese control. The Qing imperial resident, known as the Amban, publicly repudiated the treaty, while the British government, eager for friendly relations with China, negotiated a new treaty two years later known as the Convention Between Great Britain and China Respecting Tibet. The British agreed not to annex or interfere in Tibet in return for an indemnity from the Chinese government, while China agreed not to permit any other foreign state to interfere with the territory or internal administration of Tibet.
In 1910, the Qing government sent Chinese expedition to Tibet (1910), a military expedition of its own under Zhao Erfeng to establish direct Manchu-Chinese rule and, in an imperial edict, deposed the Dalai Lama, who fled to British India. Zhao Erfeng defeated the Tibetan military conclusively and expelled the Dalai Lama's forces from the province. His actions were unpopular, and there was much animosity against him for his mistreatment of civilians and disregard for local culture.
Post-Qing period

 After the
After the Xinhai Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a ...
(1911–12) toppled the Qing dynasty and the last Qing troops were escorted out of Tibet, the new Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China apologized for the actions of the Qing and offered to restore the Dalai Lama's title. The Dalai Lama refused any Chinese title and declared himself ruler of an Tibet (1912–51), independent Tibet.Shakya 1999, pg. 5 In 1913, Tibet and Mongolia (1911–24), Mongolia concluded Treaty of friendship and alliance between the Government of Mongolia and Tibet, a treaty of mutual recognition. For the next 36 years, the 13th Dalai Lama and the politics in Tibet, regents who succeeded him governed Tibet. During this time, Tibet fought Chinese warlords for control of the ethnically Tibetan areas in Xikang
Xikang (also Sikang or Hsikang) was a nominal province
formed by the Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and continued by the early People's Republic of China. Thei idea was to form a single unif ...
and Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
(parts of Kham and Amdo) along the upper reaches of the Yangtze River.Wang Jiawei, "The Historical Status of China's Tibet", 2000, p. 150. In 1914, the Tibetan government signed the Simla Convention with Britain, which recognized Chinese suzerainty over Tibet in return for a border settlement. China refused to sign the Convention and lost its suzerain rights.
When in the 1930s and 1940s the regents displayed negligence in affairs, the Kuomintang Government of the Republic of China took advantage of this to expand its reach into the territory. On December 20, 1941, Kuomingtang leader Chiang Kai-shek, Chiang Kai-Shek noted in his diary that Tibet would be among the territories which he would demand as restitution for China following the conclusion of World War II.
From 1950 to present
 Emerging with control over most of mainland China after the Chinese Civil War, the
Emerging with control over most of mainland China after the Chinese Civil War, the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
Incorporation of Tibet into the People's Republic of China, annexed Tibet in 1950 and negotiated the Seventeen Point Agreement for the Peaceful Liberation of Tibet, Seventeen Point Agreement with the newly enthroned 14th Dalai Lama's government, affirming the People's Republic of China's sovereignty but granting the area autonomy. Subsequently, on his journey into exile, the 14th Dalai Lama completely repudiated the agreement, which he has repeated on many occasions. According to the Central Intelligence Agency, CIA, the Chinese used the Dalai Lama to gain control of the military's training and actions.
The Dalai Lama had a strong following as many people from Tibet looked at him not just as their political leader, but as their spiritual leader. After the Dalai Lama's government fled to Dharamsala, Himachal Pradesh, Dharamsala, India, during the 1959 Tibetan Rebellion, it established a Central Tibetan Administration, rival government-in-exile. Afterwards, the Central People's Government in Beijing renounced the agreement and began implementation of the halted social and political reforms. During the Great Leap Forward, between 200,000 and 1,000,000 Tibetans may have died and approximately 6,000 monasteries were destroyed during the Cultural Revolution—destroying the vast majority of historic Tibetan architecture.
In 1980, General Secretary and reformist Hu Yaobang visited Tibet and ushered in a period of social, political, and economic liberalization. At the end of the decade, however, before the Tiananmen Square protests of 1989, monks in the Drepung Monastery, Drepung and Sera Monastery, Sera monasteries started protesting for independence. The government halted reforms and started an anti-separatist campaign. Human rights organisations have been critical of the Beijing and Lhasa governments' approach to Human rights in Tibet, human rights in the region when cracking down on separatist convulsions that have occurred around monasteries and cities, most recently in the 2008 Tibetan unrest.
Geography

 All of modern China, including Tibet, is considered a part of East Asia. Historically, some European sources also considered parts of Tibet to lie in Central Asia. Tibet is west of the Central Plain (China), Central China plain. In China, Tibet is regarded as part of (), a term usually translated by Chinese media as "the Western section", meaning "Western China".
All of modern China, including Tibet, is considered a part of East Asia. Historically, some European sources also considered parts of Tibet to lie in Central Asia. Tibet is west of the Central Plain (China), Central China plain. In China, Tibet is regarded as part of (), a term usually translated by Chinese media as "the Western section", meaning "Western China".
Mountains and rivers

 Tibet has some of the world's tallest mountains, with several of them making the top ten list.
Tibet has some of the world's tallest mountains, with several of them making the top ten list. Mount Everest
Mount Everest (; Tibetic languages, Tibetan: ''Chomolungma'' ; ) is List of highest mountains on Earth, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border ru ...
, located on the border with Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
, is, at , the List of highest mountains, highest mountain on earth. Several major rivers have their source in the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
(mostly in present-day Qinghai Province). These include the Yangtze River, Yangtze, Yellow River, Indus River, Mekong, Ganges, Salween River, Salween and the Yarlung Tsangpo River (Brahmaputra River). The Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon, along the Yarlung Tsangpo River, is among the deepest and longest canyons in the world.
Tibet has been called the "Water Tower" of Asia, and China is investing heavily in water projects in Tibet.
 The Indus and Brahmaputra rivers originate from the vicinities of Lake Mapam Yumco in Western Tibet, near Mount Kailash. The mountain is a holy pilgrimage site for both Hindus and Tibetans. The Hindus consider the mountain to be the abode of Lord Shiva. The Tibetan name for Mount Kailash is Khang Rinpoche. Tibet has numerous high-altitude lakes referred to in Tibetan as ''tso'' or ''co''. These include
The Indus and Brahmaputra rivers originate from the vicinities of Lake Mapam Yumco in Western Tibet, near Mount Kailash. The mountain is a holy pilgrimage site for both Hindus and Tibetans. The Hindus consider the mountain to be the abode of Lord Shiva. The Tibetan name for Mount Kailash is Khang Rinpoche. Tibet has numerous high-altitude lakes referred to in Tibetan as ''tso'' or ''co''. These include Qinghai Lake
Qinghai Lake or Ch'inghai Lake, also known by other names, is the largest lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline salt lake. The lake has fluctuate ...
, Lake Manasarovar, Namtso, Pangong Tso, Yamdrok Lake, Siling Co, Lhamo La-tso, Lumajangdong Co, Lake Puma Yumco, Lake Paiku, Como Chamling, Lake Rakshastal, Dagze Co and Dong Co. The Qinghai Lake (Koko Nor) is the largest lake in the People's Republic of China.
Climate
The climate is severely dry nine months of the year, and average annual snowfall is only , due to the rain shadow, rain shadow effect. Western passes receive small amounts of fresh snow each year but remain traversible all year round. Low temperatures are prevalent throughout these western regions, where bleak desolation is unrelieved by any vegetation bigger than a low bush, and where the wind sweeps unchecked across vast expanses of arid plain. The Indian monsoon exerts some influence on eastern Tibet. Northern Tibet is subject to high temperatures in the summer and intense cold in the winter.Regions
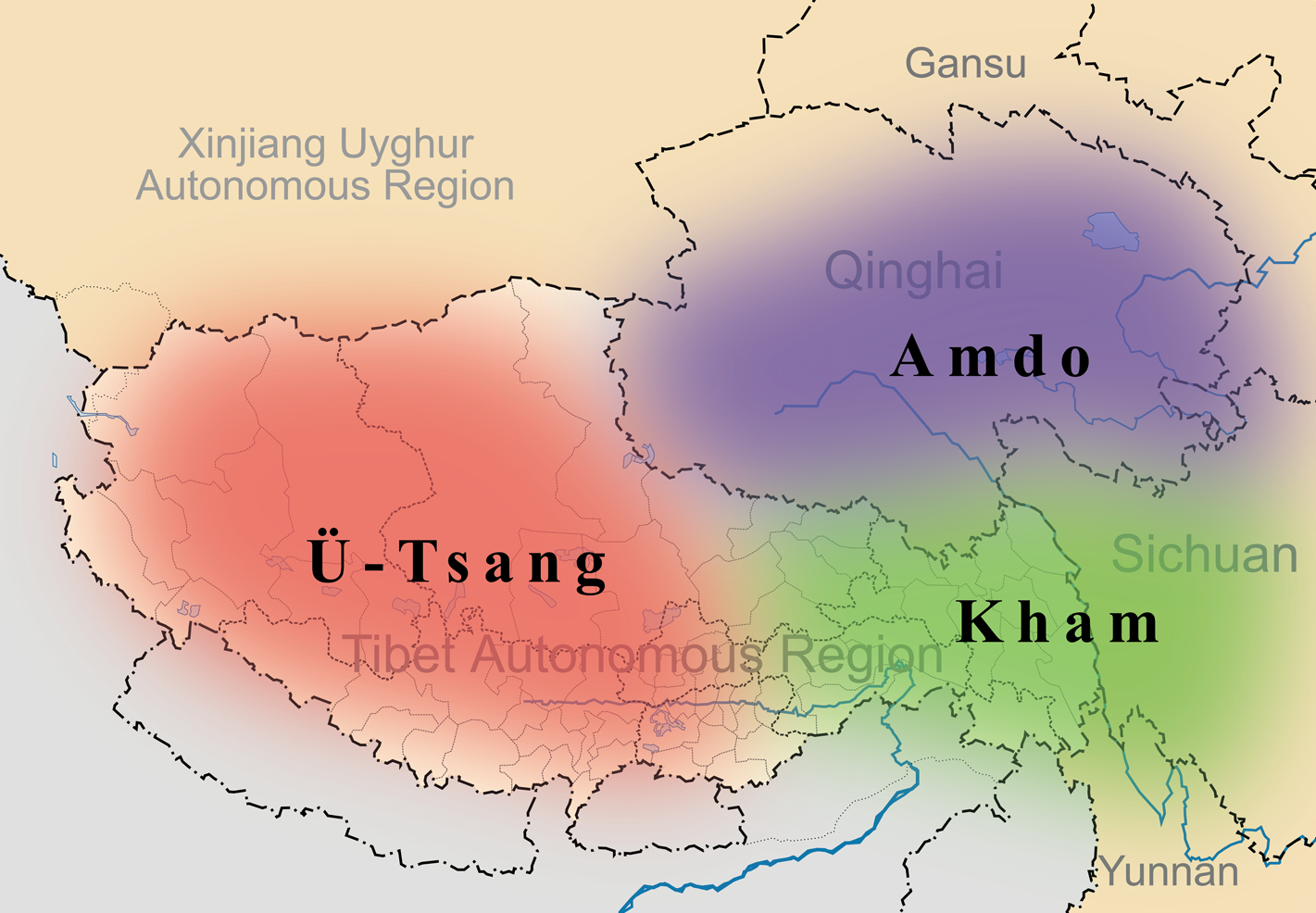
 Cultural Tibet consists of several regions. These include Amdo (''A mdo'') in the northeast, which is administratively part of the provinces of Qinghai, Gansu, and Sichuan. Kham (''Khams'') in the southeast encompasses parts of western Sichuan, northern
Cultural Tibet consists of several regions. These include Amdo (''A mdo'') in the northeast, which is administratively part of the provinces of Qinghai, Gansu, and Sichuan. Kham (''Khams'') in the southeast encompasses parts of western Sichuan, northern Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, southern Qinghai, and the eastern part of the Tibet Autonomous Region. Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered ...
(''dBus gTsang'') (Ü in the center, Tsang in the center-west, and Ngari (''mNga' ris'') in the far west) covered the central and western portion of Tibet Autonomous Region.
Tibetan cultural influences extend to the neighboring states of Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
, Nepal, regions of India such as Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Silig ...
, Ladakh, Lahaul, and Spiti, Northern Pakistan Baltistan or Balti-yul in addition to designated Tibetan autonomous areas in adjacent Chinese provinces.
Cities, towns and villages
There are over 800 settlements in Tibet. Lhasa is Tibet's traditional capital and the capital of Tibet Autonomous Region. It contains two world heritage sites – the Potala Palace and Norbulingka, which were the residences of the Dalai Lama. Lhasa contains a number of significant temples and monasteries, including Jokhang and Ramoche Temple.Shigatse
Shigatse, officially known as Xigazê (; Nepali: ''सिगात्से''), is a prefecture-level city of the Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Its area of jurisdiction, with an area of , corresponds to the histor ...
is the second largest city in the Tibet AR, west of Lhasa. Gyantse and Qamdo are also amongst the largest.
Other cities and towns in cultural Tibet include Shiquanhe (Gar), Nagchu Town, Nagchu, Bamda, Rutog Town, Rutog, Nyingchi, Shannan, Tibet, Nedong, Coqên (village), Coqên, Barkam Town, Barkam, Sagya, Gêrzê County, Gertse, Pelbar, Lhatse, and Tingri Town, Tingri; in Sichuan, Kangding (Dartsedo); in Qinghai, Jyekundo (Yushu), Maqên County, Machen, and Golmud; in India, Tawang, Leh, and Gangtok, and in Pakistan, Skardu, Kharmang Valley, Kharmang, and Khaplu.
Wildlife
''Sus scrofa'' expanded from its origin in southeast Asia into the Plateau, acquiring and fixation (population genetics), fixing adaptive alleles for the high-altitude environment. The forests of Tibet are home to black bears, red pandas, musk deer, barking deer, and squirrels. Monkeys such as rhesus macaques and Colobinae, langurs live in the warmer forest zones. Tibetan antelopes, gazelles, and kiangs gaze on the grasslands of the Tibetan plateau. There are more than 500 bird species in Tibet. Because of the high altitude and harsh climate, there are few insects in Tibet. Snow leopards are hunted for their fur and the eggs of black-necked cranes have been collected as a delicacy food.Government
The central region of Tibet is an autonomous administrative divisions of China, autonomous region within China, theTibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
. The Tibet Autonomous Region is a province-level entity of the People's Republic of China. It is governed by a People's Government, led by a chairman. In practice, however, the chairman is subordinate to the branch secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). As a matter of convention, the chairman has almost always been an ethnic Tibetan, while the party secretary has always been ethnically non-Tibetan.
Economy
 The Tibetan economy is dominated by subsistence agriculture. Due to limited arable land, the primary occupation of the Tibetan Plateau is raising livestock, such as Domestic sheep, sheep, cattle, Domestic goat, goats, camels, yaks, dzo, and horses.
The main crops grown are
The Tibetan economy is dominated by subsistence agriculture. Due to limited arable land, the primary occupation of the Tibetan Plateau is raising livestock, such as Domestic sheep, sheep, cattle, Domestic goat, goats, camels, yaks, dzo, and horses.
The main crops grown are barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
, wheat, buckwheat, rye, potatoes, and assorted fruits and vegetables. Tibet is ranked the lowest among China's 31 provinces on the Human Development Index according to UN Development Programme data. In recent years, due to increased interest in Tibetan Buddhism, tourism has become an increasingly important sector, and is actively promoted by the authorities. Tourism brings in the most income from the sale of handicrafts. These include Tibetan hats, jewelry (silver and gold), wooden items, clothing, quilts, fabrics, Tibetan rugs and carpets. The Central People's Government exempts Tibet from all taxation and provides 90% of Tibet's government expenditures. However most of this investment goes to pay migrant workers who do not settle in Tibet and send much of their income home to other provinces.
 Forty percent of the rural cash income in the Tibet Autonomous Region is derived from the harvesting of the fungus ''Ophiocordyceps sinensis'' (formerly ''Cordyceps sinensis''); contributing at least 1.8 billion yuan, (US$225 million) to the region's GDP.
Forty percent of the rural cash income in the Tibet Autonomous Region is derived from the harvesting of the fungus ''Ophiocordyceps sinensis'' (formerly ''Cordyceps sinensis''); contributing at least 1.8 billion yuan, (US$225 million) to the region's GDP.
 The Qingzang railway linking the
The Qingzang railway linking the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
to Qinghai, Qinghai Province was opened in 2006, but it was controversial.
In January 2007, the Chinese government issued a report outlining the discovery of a large mineral deposit under the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
. The deposit has an estimated value of $128 billion and may double Chinese reserves of zinc, copper, and lead. The Chinese government sees this as a way to alleviate the nation's dependence on foreign mineral imports for its growing economy. However, critics worry that mining these vast resources will harm Tibet's fragile ecosystem and undermine Tibetan culture.
On January 15, 2009, China announced the construction of Tibet's first expressway, the Lhasa Airport Expressway, a stretch of controlled-access highway in southwestern Lhasa. The project will cost 1.55 billion Chinese yuan, yuan (US$227 million).
From January 18–20, 2010, a national conference on Tibet and areas inhabited by Tibetans in Sichuan, Yunnan, Gansu and Qinghai was held in China and a plan to improve development of the areas was announced. The conference was attended by General secretary Hu Jintao, Wu Bangguo, Wen Jiabao, Jia Qinglin, Li Changchun, Xi Jinping, Li Keqiang, He Guoqiang and Zhou Yongkang, all members of Politburo Standing Committee of the Chinese Communist Party. The plan called for improvement of rural Tibetan income to national standards by 2020 and free education for all rural Tibetan children. China has invested 310 billion yuan (about 45.6 billion U.S. dollars) in Tibet since 2001.
Development zone
The State Council approved Tibet Lhasa Economic and Technological Development Zone as a state-level development zone in 2001. It is located in the western suburbs of Lhasa, the capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region. It is away from the Gonggar Airport, and away from Lhasa Railway Station and away from 318 national highway. The zone has a planned area of and is divided into two zones. Zone A developed a land area of for construction purposes. It is a flat zone, and has the natural conditions for good drainage.Demographics
 Historically, the population of Tibet consisted of primarily ethnic Tibetan people, Tibetans and some other ethnic groups. According to tradition the original ancestors of the Tibetan people, as represented by the six red bands in the Tibetan flag, are: the Se, Mu, Dong, Tong, Dru and Ra. Other traditional ethnic groups with significant population or with the majority of the ethnic group residing in Tibet (excluding a Sino-Indian War, disputed area with India) include Bai people, Blang people, Blang, Bonans, Bonan, Dongxiang people, Dongxiang, Han Chinese, Han, Hui people, Lhoba, Lisu people, Miao people, Miao, Mongols, Monguor people, Monguor (Tu people), Monpa people, Menba (Monpa), Mosuo, Nakhi, Qiang, Nu people, Pumi people, Pumi, Salar people, Salar, and Yi people.
The proportion of the non-Tibetan population in Tibet is disputed. On the one hand, the Central Tibetan Administration of the Dalai Lama accuses China of actively swamping Tibet with Chinese settlements in Tibet, migrants in order to alter Tibet's demographic makeup. On the other hand, according to the Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, 2010 Chinese census ethnic Tibetans comprise 90% of a total population of 3 million in the
Historically, the population of Tibet consisted of primarily ethnic Tibetan people, Tibetans and some other ethnic groups. According to tradition the original ancestors of the Tibetan people, as represented by the six red bands in the Tibetan flag, are: the Se, Mu, Dong, Tong, Dru and Ra. Other traditional ethnic groups with significant population or with the majority of the ethnic group residing in Tibet (excluding a Sino-Indian War, disputed area with India) include Bai people, Blang people, Blang, Bonans, Bonan, Dongxiang people, Dongxiang, Han Chinese, Han, Hui people, Lhoba, Lisu people, Miao people, Miao, Mongols, Monguor people, Monguor (Tu people), Monpa people, Menba (Monpa), Mosuo, Nakhi, Qiang, Nu people, Pumi people, Pumi, Salar people, Salar, and Yi people.
The proportion of the non-Tibetan population in Tibet is disputed. On the one hand, the Central Tibetan Administration of the Dalai Lama accuses China of actively swamping Tibet with Chinese settlements in Tibet, migrants in order to alter Tibet's demographic makeup. On the other hand, according to the Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, 2010 Chinese census ethnic Tibetans comprise 90% of a total population of 3 million in the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
.
Culture

Religion
Buddhism


 Religion is extremely important to the Tibetans and has a strong influence over all aspects of their lives. Bön is the indigenous religion of Tibet, but has been almost eclipsed by Tibetan Buddhism, a distinctive form of Mahayana and Vajrayana, which was introduced into Tibet from the Sanskrit Buddhist tradition of northern India. Tibetan Buddhism is practiced not only in Tibet but also in Mongolia, parts of northern India, the Buryat Republic, the Tuva Republic, and in the Republic of Kalmykia and some other parts of China. During China's Cultural Revolution, nearly all Tibet's List of Tibetan monasteries, monasteries were ransacked and destroyed by the Red Guards (China), Red Guards.Tibetan monks: A controlled life
Religion is extremely important to the Tibetans and has a strong influence over all aspects of their lives. Bön is the indigenous religion of Tibet, but has been almost eclipsed by Tibetan Buddhism, a distinctive form of Mahayana and Vajrayana, which was introduced into Tibet from the Sanskrit Buddhist tradition of northern India. Tibetan Buddhism is practiced not only in Tibet but also in Mongolia, parts of northern India, the Buryat Republic, the Tuva Republic, and in the Republic of Kalmykia and some other parts of China. During China's Cultural Revolution, nearly all Tibet's List of Tibetan monasteries, monasteries were ransacked and destroyed by the Red Guards (China), Red Guards.Tibetan monks: A controlled life. BBC News. March 20, 2008. A few monasteries have begun to rebuild since the 1980s (with limited support from the Chinese government) and greater religious freedom has been granted – although it is still limited. Monks returned to monasteries across Tibet and monastic education resumed even though the number of monks imposed is strictly limited. Before the 1950s, between 10 and 20% of males in Tibet were monks. Tibetan Buddhism has five main traditions (the suffix ''pa'' is comparable to "er" in English): * Gelug, Gelug(pa), ''Way of Virtue'', also known casually as ''Yellow Hat'', whose spiritual head is the Ganden Tripa and whose temporal head is the Dalai Lama. Successive Dalai Lamas ruled Tibet from the mid-17th to mid-20th centuries. This order was founded in the 14th to 15th centuries by Je Tsongkhapa, based on the foundations of the Kadampa tradition. Tsongkhapa was renowned for both his scholasticism and his virtue. The Dalai Lama belongs to the Gelugpa school, and is regarded as the embodiment of the Bodhisattva of Compassion. * Kagyu, Kagyu(pa), ''Oral Lineage''. This contains one major subsect and one minor subsect. The first, the Dagpo Kagyu, encompasses those Kagyu schools that trace back to Gampopa. In turn, the Dagpo Kagyu consists of four major sub-sects: the Karma Kagyu, headed by a Karmapa, the Tsalpa Kagyu, the Barom Kagyu, and Pagtru Kagyu. The once-obscure Shangpa Kagyu, which was famously represented by the 20th-century teacher Kalu Rinpoche, traces its history back to the Indian master Niguma, sister of Kagyu lineage holder Naropa. This is an oral tradition which is very much concerned with the experiential dimension of meditation. Its most famous exponent was Milarepa, an 11th-century mystic. * Nyingma, Nyingma(pa), ''The Ancient Ones''. This is the oldest, the original order founded by Padmasambhava. * Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist school), Sakya(pa), ''Grey Earth'', headed by the Sakya Trizin, founded by Khon Konchog Gyalpo, a disciple of the great translator Drokmi Lotsawa. Sakya Pandita 1182–1251 CE was the great-grandson of Khon Konchog Gyalpo. This school emphasizes scholarship. * Jonang, Jonang(pa) Its origins in Tibet can be traced to early 12th century master Yumo Mikyo Dorje, but became much wider known with the help of Dolpopa Sherab Gyaltsen, a monk originally trained in the Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist school), Sakya school. The Jonang school was widely thought to have become extinct in the late 17th century at the hands of the 5th Dalai Lama, who forcibly annexed the Jonang monasteries to his Gelug school, declaring them heretical. Thus, Tibetology, Tibetologists were astonished when fieldwork turned up several active Jonangpa monasteries, including the main monastery, Tsangwa, located in Zamtang County, Sichuan. Almost 40 monasteries, comprising about 5000 monks, have subsequently been found, including some in the Amdo Tibetan and Qiang people, rGyalgrong areas of
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
, Sichuan and Tibet. One of the primary supporters of the Jonang lineage in exile has been the 14th Dalai Lama of the Gelugpa lineage. The Jonang tradition has recently officially registered with the Central Tibetan Administration, Tibetan Government in exile to be recognized as the fifth living Buddhist tradition of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
. The 14th Dalai Lama assigned Jebtsundamba Khutuktu of Mongolia (who is considered to be an incarnation of Taranatha) as the leader of the Jonang tradition.
The Chinese government continued to pursue a strategy of forced assimilation and suppression of Tibetan Buddhism, as demonstrated by the laws designed to control the next reincarnation of the Dalai Lama and those of other Tibetan eminent lamas. Monks and nuns who refused to denounce the Dalai Lama have been expelled from their monasteries, imprisoned, and tortured.
It was reported in June 2021 that amidst the 2020–2022 China–India skirmishes, the People's Liberation Army had been forming a new unit for Tibetans who would be taken to Buddhist monks for religious blessings after completing their training.
Christianity
The first Christians documented to have reached Tibet were the Nestorian Christians, Nestorians, of whom various remains and inscriptions have been found in Tibet. They were also present at the imperial camp of Möngke Khan at Shira Ordo, where they debated in 1256 with Karma Pakshi (1204/6-83), head of the Karma Kagyu order. Desideri, who reached Lhasa in 1716, encountered Armenian and Russian merchants. Roman Catholic Jesuits and Order of Friars Minor Capuchin, Capuchins arrived from Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries. Portuguese missionaries Jesuit Father António de Andrade and Brother Manuel Marques first reached the kingdom of Gelu, Nepal, Gelu in western Tibet in 1624 and was welcomed by the royal family who allowed them to build a church later on. By 1627, there were about a hundred local converts in the Guge kingdom. Later on, Christianity was introduced to Rudok, Ladakh and Tsang and was welcomed by the ruler of the Ü-Tsang, Tsang kingdom, where Andrade and his fellows established a Jesuit outpost at Shigatse in 1626. In 1661 another Jesuit, Johann Grueber, crossed Tibet from Sining to Lhasa (where he spent a month), before heading on to Nepal. He was followed by others who actually built a church in Lhasa. These included the Jesuit Father Ippolito Desideri, 1716–1721, who gained a deep knowledge of Tibetan culture, language and Buddhism, and various Capuchins in 1707–1711, 1716–1733 and 1741–1745,Stein 1972, p. 85. Christianity was used by some Tibetan monarchs and their courts and the Karmapa sect lamas to counterbalance the influence of the Gelugpa sect in the 17th century until in 1745 when all the missionaries were expelled at the lama's insistence. In 1877, the Protestantism, Protestant James Cameron (China Inland Mission), James Cameron from the China Inland Mission walked from Chongqing to Batang County, Batang in Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan province, and "brought the Gospel to the Tibetan people." Beginning in the 20th century, in Dêqên Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Yunnan, a large number of Lisu people and some Yi and Nu people converted to Christianity. Famous earlier missionaries include James O. Fraser, Alfred James Broomhall and Isobel Kuhn of the China Inland Mission, among others who were active in this area. Proselytising has been illegal in China since 1949. But , many Christian missionaries were reported to be active in Tibet with the tacit approval of Chinese authorities, who view the missionaries as a counterforce to Tibetan Buddhism or as a boon to the local economy.Islam
 Muslims have been living in Tibet since as early as the 8th or 9th century. In Tibetan cities, there are small communities of Tibetan Muslim, Muslims, known as Kachee (Kache), who trace their origin to immigrants from three main regions: Kashmir (Kachee Yul in ancient Tibetan), Ladakh and the Central Asian Turkic countries. Islamic influence in Tibet also came from Persia. A Muslim Sufi Ali Hamadani, Syed Ali Hamdani preached to the people of Baltistan, then known as little Tibet. After 1959, a group of Tibetan Muslims made a case for Indian nationality based on their historic roots to Kashmir and the Indian government declared all Tibetan Muslims Indian citizens later on that year. Other Muslim ethnic groups who have long inhabited Tibet include
Muslims have been living in Tibet since as early as the 8th or 9th century. In Tibetan cities, there are small communities of Tibetan Muslim, Muslims, known as Kachee (Kache), who trace their origin to immigrants from three main regions: Kashmir (Kachee Yul in ancient Tibetan), Ladakh and the Central Asian Turkic countries. Islamic influence in Tibet also came from Persia. A Muslim Sufi Ali Hamadani, Syed Ali Hamdani preached to the people of Baltistan, then known as little Tibet. After 1959, a group of Tibetan Muslims made a case for Indian nationality based on their historic roots to Kashmir and the Indian government declared all Tibetan Muslims Indian citizens later on that year. Other Muslim ethnic groups who have long inhabited Tibet include Hui
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
, Salar people, Salar, Dongxiang people, Dongxiang and Bonans, Bonan. There is also a well established Chinese Muslim community (gya kachee), which traces its ancestry back to the Hui
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
ethnic group of China.
Tibetan art
Tibetan representations of art are intrinsically bound withTibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
and commonly depict deities or variations of Gautama Buddha, Buddha in various forms from bronze Buddhist statues and shrines, to highly colorful thangka paintings and mandalas. Thangkas are Tibet's traditional cloth paintings. Rendered on cotton cloth with a thin rod at the top, they portray Buddhist deities or themes in color and detail.

Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Silig ...
File:Tibetan - A Ritual Box - Walters 572299 - Reverse.jpg, A ritual box
Architecture
Tibetan architecture contains Chinese and Indian influences, and reflects a deeply Buddhist approach. The Dharmacakra, Buddhist wheel, along with two dragons, can be seen on nearly every Gompa in Tibet. The design of the Tibetan Chörtens can vary, from roundish walls in Kham to squarish, four-sided walls in Ladakh. The most distinctive feature of Tibetan architecture is that many of the houses and monasteries are built on elevated, sunny sites facing the south, and are often made out of a mixture of rocks, wood, cement and earth. Little fuel is available for heat or lighting, so flat roofs are built to conserve heat, and multiple windows are constructed to let in sunlight. Walls are usually sloped inwards at 10 degrees as a precaution against the frequent earthquakes in this mountainous area. Standing at in height and in width, the Potala Palace is the most important example of Tibetan architecture. Formerly the residence of the Dalai Lama, it contains over one thousand rooms within thirteen stories, and houses portraits of the past Dalai Lamas and statues of the Buddha. It is divided between the outer White Palace, which serves as the administrative quarters, and the inner Red Quarters, which houses the assembly hall of the Lamas, chapels, 10,000 shrines, and a vast library of Buddhist scriptures. The Potala Palace is a World Heritage Site, as is Norbulingka, the former summer residence of the Dalai Lama.Music
The music of Tibet reflects the cultural heritage of the trans-Himalayan region, centered in Tibet but also known wherever ethnic Tibetan people, Tibetan groups are found in India,Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
, Nepal and further abroad. First and foremost Tibetan music is religious music, reflecting the profound influence of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
on the culture.
Tibetan music often involves chanting in Tibetan or Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
, as an integral part of the religion. These chants are complex, often recitations of sacred texts or in celebration of various festivals. Yin and yang, Yang chanting, performed without metrical timing, is accompanied by resonant drums and low, sustained syllables. Other styles include those unique to the various schools of Tibetan Buddhism, such as the classical music of the popular Gelugpa school, and the romantic music of the Nyingmapa, Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist school), Sakyapa and Kagyupa schools.
Nangma dance music is especially popular in the karaoke bars of the urban center of Tibet, Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Region in Southwest China. The inner urban area of Lhas ...
. Another form of popular music is the classical gar (music), gar style, which is performed at rituals and ceremonies. Lu (music), Lu are a type of songs that feature glottal vibrations and high pitches. There are also epic bards who sing of Gesar, who is a hero to ethnic Tibetans.
Festivals
 Tibet has various festivals, many for worshipping the Buddha, that take place throughout the year. Losar is the Tibetan New Year Festival. Preparations for the festive event are manifested by special offerings to family shrine deities, painted doors with religious symbols, and other painstaking jobs done to prepare for the event. Tibetans eat ''Guthuk'' (barley noodle soup with filling) on New Year's Eve with their families. The Monlam Prayer Festival follows it in the first month of the Tibetan calendar, falling between the fourth and the eleventh days of the first Tibetan month. It involves dancing and participating in sports events, as well as sharing picnics. The event was established in 1049 by Tsong Khapa, the founder of the Dalai Lama and the Panchen Lama's order.
Tibet has various festivals, many for worshipping the Buddha, that take place throughout the year. Losar is the Tibetan New Year Festival. Preparations for the festive event are manifested by special offerings to family shrine deities, painted doors with religious symbols, and other painstaking jobs done to prepare for the event. Tibetans eat ''Guthuk'' (barley noodle soup with filling) on New Year's Eve with their families. The Monlam Prayer Festival follows it in the first month of the Tibetan calendar, falling between the fourth and the eleventh days of the first Tibetan month. It involves dancing and participating in sports events, as well as sharing picnics. The event was established in 1049 by Tsong Khapa, the founder of the Dalai Lama and the Panchen Lama's order.
Cuisine
The most important crop in Tibet isbarley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
, and dough made from barley flour—called tsampa—is the staple food of Tibet. This is either rolled into noodles or made into steamed dumplings called momo (food), momos. Meat dishes are likely to be yak, goat, or Lamb (food), mutton, often dried, or cooked into a spicy stew with potatoes. Mustard seed is cultivated in Tibet, and therefore features heavily in its cuisine. Yak yogurt, butter and cheese are frequently eaten, and well-prepared yogurt is considered something of a prestige item. Butter tea is a very popular drink.
See also
* Index of Tibet-related articles * List of Major National Historical and Cultural Sites in Tibet * Outline of Tibet * Sinicization of Tibet * Chinese settlements in Tibet, Chinese Settlements in Tibet * Free TibetReferences
Citations
Sources
*Christopher I. Beckwith, Beckwith, Christopher I. ''The Tibetan Empire in Central Asia: A History of the Struggle for Great Power among Tibetans, Turks, Arabs, and Chinese during the Early Middle Ages (1987) Princeton University Press. *Melvyn Goldstein, Goldstein, Melvyn C.A History of Modern Tibet, 1913–1951: The Demise of the Lamaist State
' (1989) University of California Press. *Melvyn Goldstein, Goldstein, Melvyn C. ''A History of Modern Tibet, 1913–1951: The Demise of the Lamaist State'' (1989), first Indian edition (1993) Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers, New Delhi, Pagination is identical to University of California edition. *Goldstein, Melvyn C. ''The Snow Lion and the Dragon: China, Tibet, and the Dalai Lama'' (1997) University of California Press. *A. Tom Grunfeld, Grunfeld, Tom (1996). ''The Making of Modern Tibet.'' . *Peter Hopkirk, Hopkirk, Peter
''Trespassers on the Roof of the World: The Secret Exploration of Tibet''
(1983) J. P. Tarcher. *Matthew Kapstein, Kapstein, Matthew T. ''The Tibetans'' (2006) Blackwell Publishing. *Laird, Thomas. ''The Story of Tibet: Conversations with the Dalai Lama'' (2006) Grove Press. *Glenn H. Mullin, Mullin, Glenn H.''The Fourteen Dalai Lamas: A Sacred Legacy of Reincarnations'' (2001) Clear Light Publishers. *Powers, John. ''History as Propaganda: Tibetan Exiles versus the People's Republic of China'' (2004) Oxford University Press. *Hugh Edward Richardson, Richardson, Hugh E. ''Tibet and its History'' Second Edition, Revised and Updated (1984) Shambhala. *Tsering Shakya, Shakya, Tsering. ''The Dragon In The Land Of Snows'' (1999) Columbia University Press. *Rolf Stein, Stein, R. ''Tibetan Civilization'' (1972) Stanford University Press. *Teltscher, Kate. ''The High Road to China (book), The High Road to China: George Bogle, the Panchen Lama and the First British Expedition to Tibet'' (2006) Bloomsbury UK.
Further reading
* Charles Allen (writer), Allen, Charles (2004). ''Duel in the Snows: The True Story of the Younghusband Mission to Lhasa.'' London: John Murray. . * Bell, Charles (1924). ''Tibet: Past & Present.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. * Dowman, Keith (1988). ''The Power-Places of Central Tibet: The Pilgrim's Guide.'' Routledge & Kegan Paul. London, . New York, . * Feigon, Lee. (1998). ''Demystifying Tibet: unlocking the secrets of the land of the snows.'' Chicago: Ivan R. Dee. . 1996 hardback, * Gyatso, Palden (1997). ''The Autobiography of a Tibetan Monk.'' Grove Press. NY, NY. * Human Rights in China: ''China, Minority Exclusion, Marginalization and Rising Tensions'', London, Minority Rights Group International, 2007 * Le Sueur, Alec (2013). ''The Hotel on the Roof of the World – Five Years in Tibet.'' Chichester: Summersdale. . Oakland: RDR Books. * McKay, Alex (1997). ''Tibet and the British Raj: The Frontier Cadre 1904–1947.'' London: Curzon. . * Norbu, Thubten Jigme; Turnbull, Colin (1968). ''Tibet: Its History, Religion and People.'' Reprint: Penguin Books (1987). * Pachen, Ani; Donnely, Adelaide (2000). ''Sorrow Mountain: The Journey of a Tibetan Warrior Nun.'' Kodansha America, Inc. . * Petech, Luciano (1997). ''China and Tibet in the Early XVIIIth Century: History of the Establishment of Chinese Protectorate in Tibet.'' T'oung Pao Monographies, Brill Academic Publishers, . * * Samuel, Geoffrey (1993). ''Civilized Shamans: Buddhism in Tibetan Societies.'' Smithsonian . * Schell, Orville (2000). ''Virtual Tibet: Searching for Shangri-La from the Himalayas to Hollywood.'' Henry Holt. . * * * * – (online version) * Thurman, Robert (2002). ''Robert Thurman on Tibet.'' DVD. ASIN B00005Y722. * Van Walt van Praag, Michael C. (1987). ''The Status of Tibet: History, Rights, and Prospects in International Law.'' Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press. * Wilby, Sorrel (1988). ''Journey Across Tibet: A Young Woman's Trek Across the Rooftop of the World.'' Contemporary Books. . * Wilson, Brandon (2004). ''Yak Butter Blues: A Tibetan Trek of Faith.'' Pilgrim's Tales. , . (second edition 2005) * Wang Jiawei (2000). ''The Historical Status of China's Tibet.'' .Tibet wasn't always ours, says Chinese scholar
by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, February 22, 2007 * Wylie, Turrell V. "The First Mongol Conquest of Tibet Reinterpreted", ''Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies'' (Volume 37, Number 1, June 1977) *
External links
from Columbia University Libraries
British photographs of Tibet 1920–1950
released by the Information Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China June 22
Historical maps and images of Tibet
presented by University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Libraries Digital Collections
The Tibetan & Himalayan Library (THL)
* {{Authority control Tibet, Former countries in East Asia Central Asia East Asia Inner Asia Regions of China Western China Cultural regions Historical regions