Thüringen Kreise (nummeriert).svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a
 The name ''Thuringia'' or ''Thüringen'' derives from the Germanic tribe
The name ''Thuringia'' or ''Thüringen'' derives from the Germanic tribe
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of central Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
, Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
and Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
, Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
, Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
, and Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale (german: Sächsische Saale) and Thuringian Saale (german: Thüringische Saale), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale ...
drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
, a left-bank tributary of the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
.
Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking trail
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or small road usually passing through a natural area. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. The ...
. Its winter resort of Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports
Winter sports or winter activities are competitive sports or non-competitive recreational activities which are played on snow or ice. Most are variations of skiing, ice skating and sledding. Traditionally, such games were only played in cold are ...
destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympic
The Winter Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'hiver) is a major international multi-sport event held once every four years for sports practiced on snow and ice. The first Winter Olympic Games, the 1924 Winter Olympics, were hel ...
gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectuals and leaders in the arts: Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the '' Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard wo ...
, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as t ...
, and Friedrich Schiller. The state has the University of Jena
The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (german: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany.
The un ...
, the Ilmenau University of Technology
Ilmenau () is a town in Thuringia, central Germany. It is the largest town within the Ilm district with a population of 38,600, while the district capital is Arnstadt. Ilmenau is located approximately south of Erfurt and north of Nuremberg wi ...
, the University of Erfurt
The University of Erfurt (german: Universität Erfurt) is a public university located in Erfurt, the capital city of the German state of Thuringia. It was founded in 1379, and closed in 1816. It was re-established in 1994, three years after Germ ...
, and the Bauhaus University of Weimar.
Thuringia had an earlier existence as the Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
Duchy of Thuringia
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogas ...
, established around 631 AD by King Dagobert I. The state was established in 1920 as a state of the Weimar Republic from a merger of the Ernestine duchies
The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine appanage duchies of Weissenfels, Merseburg and Zeitz were also "Saxon duchies" and adjacent to several Ernestine ones), were a group of small states whose num ...
, save for Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany.
History
Ernestine Line
When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of th ...
. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Thuringia came under the Soviet occupation zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a ...
in Allied-occupied Germany
Germany was already de facto occupied by the Allies from the real fall of Nazi Germany in World War II on 8 May 1945 to the establishment of the East Germany on 7 October 1949. The Allies (United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and Franc ...
, and its borders were reformed, to become contiguous
Contiguity or contiguous may refer to:
*Contiguous data storage, in computer science
*Contiguity (probability theory)
*Contiguity (psychology)
*Contiguous distribution of species, in biogeography
*Geographic contiguity of territorial land
*Contigu ...
. Thuringia became part of the German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
in 1949 but was dissolved in 1952 during administrative reforms, to be divided into the Districts of Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
, Suhl
Suhl () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located SW of Erfurt, NE of Würzburg and N of Nuremberg. With its 37,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest of the six urban districts within Thuringia. Together with its northern neighbour-town Zella- ...
and Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
. Thuringia was re-established in 1990 following German reunification, slightly re-drawn, and became one of the new states of the Federal Republic of Germany.
Etymology and symbols
 The name ''Thuringia'' or ''Thüringen'' derives from the Germanic tribe
The name ''Thuringia'' or ''Thüringen'' derives from the Germanic tribe Thuringii
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into co ...
, who emerged during the Migration Period. Their origin is largely unknown. An older theory claims that they were successors of the Hermunduri, but later research rejected the idea. Other historians argue that the Thuringians were allies of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, came to central Europe together with them, and lived before in what is Galicia today. Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus first mentioned the Thuringii around 400; during that period, the Thuringii were famous for their excellent horses.
The Thuringian Realm existed until after 531, the Landgraviate of Thuringia
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogastis ...
was the largest state in the region, persisting between 1131 and 1247. Afterwards the state known as Thuringia ceased to exist; nevertheless the term commonly described the region between the Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
mountains in the north, the White Elster
The White Elster
Accessed on 16 Jan 2011. (, ) is a long river in central
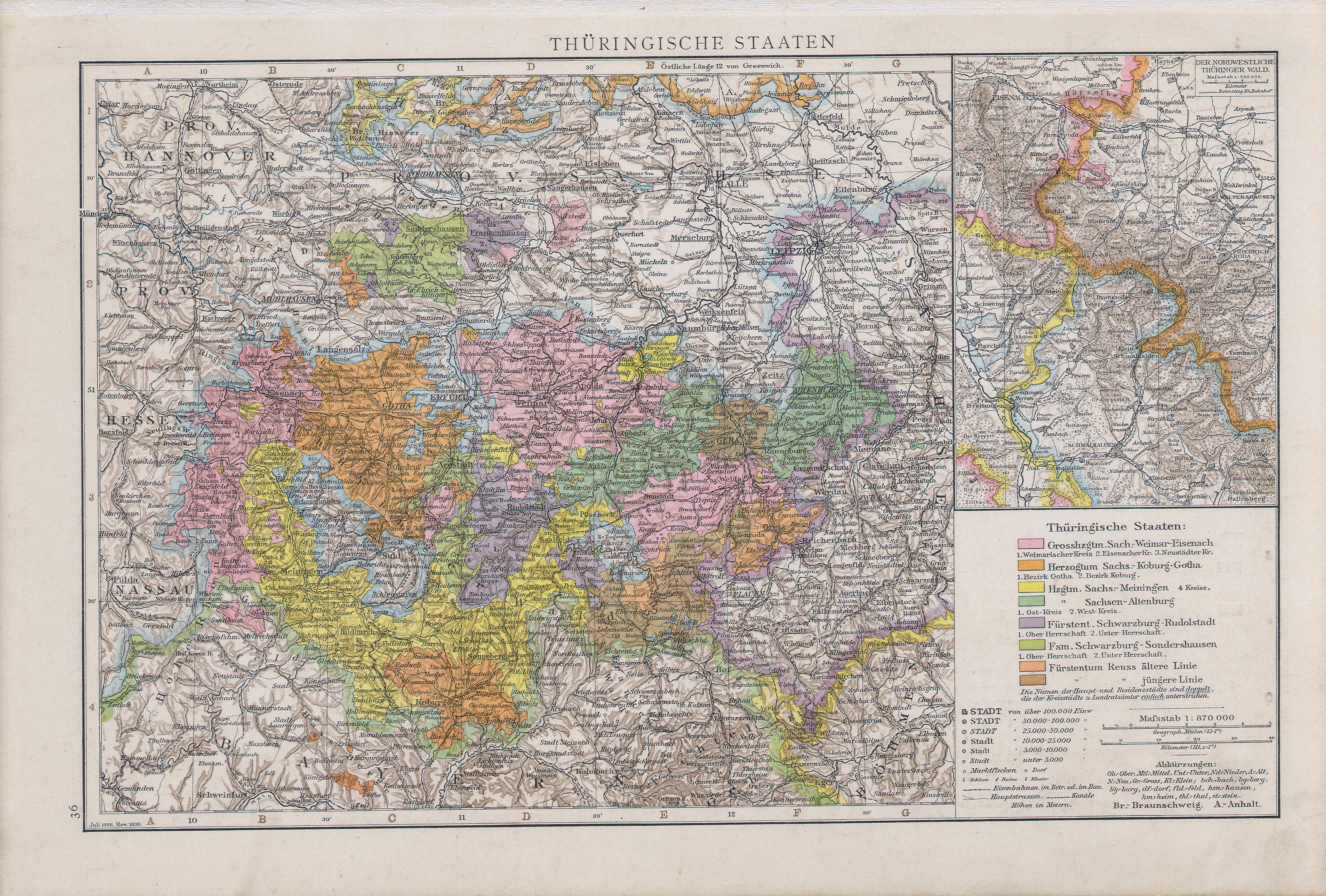 Some reordering of the Thuringian states occurred during the
Some reordering of the Thuringian states occurred during the
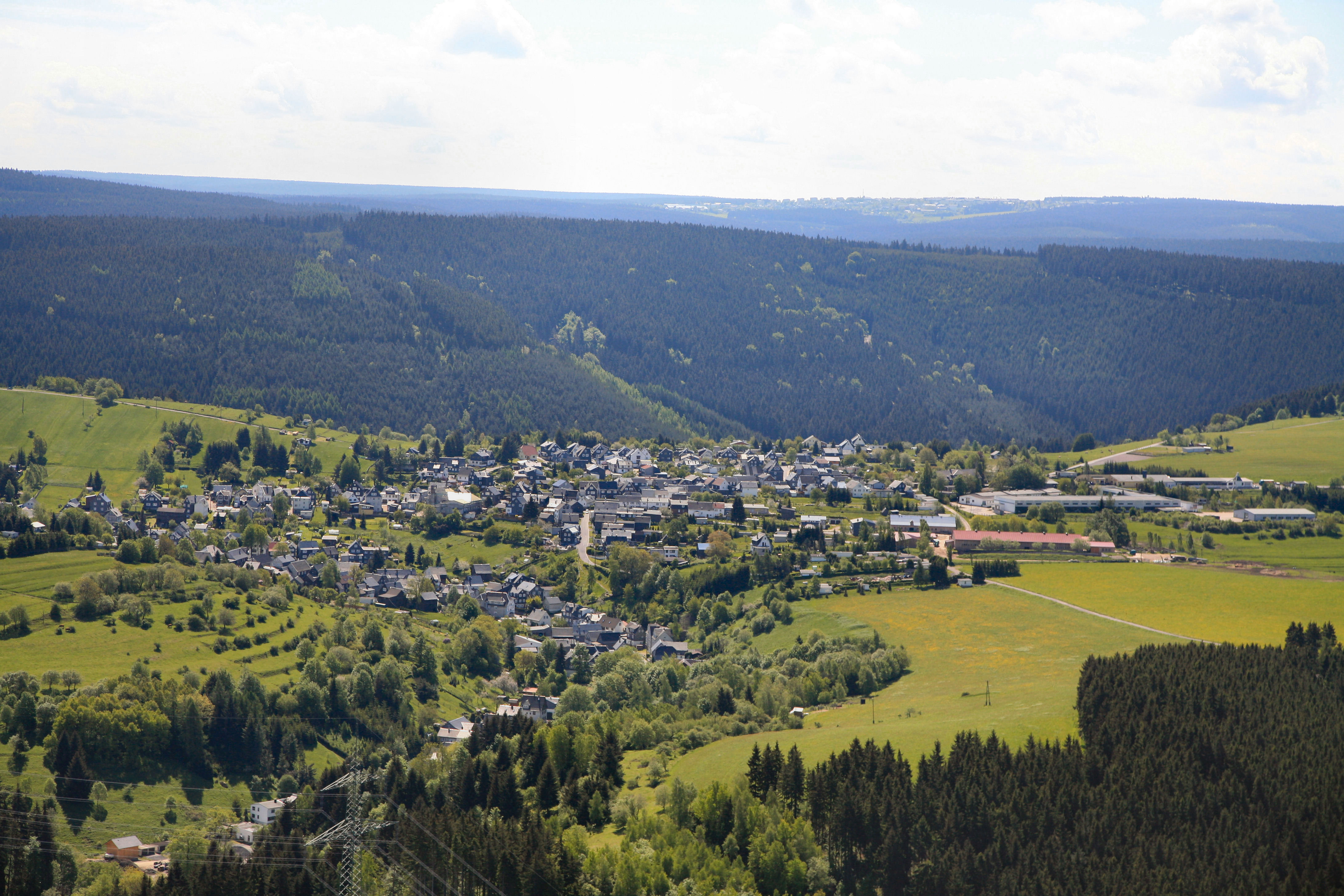 The landscapes of Thuringia are quite diverse. The far north is occupied by the
The landscapes of Thuringia are quite diverse. The far north is occupied by the

 Due to many centuries of intensive settlement, most of the area is shaped by human influence. The original natural vegetation of Thuringia is forest with beech as its predominant species, as can still be found in the
Due to many centuries of intensive settlement, most of the area is shaped by human influence. The original natural vegetation of Thuringia is forest with beech as its predominant species, as can still be found in the
* Average annual change in percent within the last three years (13 December 2009 to 31 December 2012), adjusted from incorporations and the 2011 Census results.
File:Evangelisch Thüringen.png, EKD Protestant membership in 2011 (municipalities)
File:Katholisch Thüringen.png, Catholic membership in 2011 (municipalities)
 , -
! colspan="2" , Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
! Seats %
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , The Left (Germany), The Left (Die Linke)
, align="right" , 343,780
, align="right" , 31.0
, align="right" , 2.8
, align="right" , 29
, align="right" , 1
, align="right" , 32.2
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Alternative for Germany (AfD)
, align="right" , 259,382
, align="right" , 23.4
, align="right" , 12.8
, align="right" , 22
, align="right" , 11
, align="right" , 24.4
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Christian Democratic Union of Germany, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, align="right" , 241,049
, align="right" , 21.7
, align="right" , 11.8
, align="right" , 21
, align="right" , 13
, align="right" , 23.3
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD)
, align="right" , 90,987
, align="right" , 8.2
, align="right" , 4.2
, align="right" , 8
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 8.9
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Alliance 90/The Greens (Grünen)
, align="right" , 57,474
, align="right" , 5.2
, align="right" , 0.5
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 1
, align="right" , 5.6
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Free Democratic Party (Germany), Free Democratic Party (FDP)
, align="right" , 55,493
, align="right" , 5.0
, align="right" , 2.5
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 5.6
, -
! colspan=8,
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , National Democratic Party of Germany
, align="right" , 6,044
, align="right" , 0.5
, align="right" , 3.1
, align="right" , 0
, align="right" , ±0
, align="right" , 0
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Others
, align="right" , 54,179
, align="right" , 4.9
, align="right" , 1.4
, align="right" , 0
, align="right" , ±0
, align="right" , 0
, -
! align="right" colspan=2, Valid votes
! align="right" , 1,108,388
! align="right" , 98.8
! align="right" , 0.2
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
, -
! align="right" colspan=2, Blank and invalid votes
! align="right" , 13,426
! align="right" , 1.2
! align="right" , 0.2
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
, -
! align="right" colspan=2, Total
! align="right" , 1,121,814
! align="right" , 100.0
! align="right" ,
! align="right" , 90
! align="right" , 1
! align="right" ,
, -
! colspan="2" , Electorate / voter turnout
!1,729,242
!64.9
!12.2
!
!
!
, -
, colspan=9 align=left , Source
, -
! colspan="2" , Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
! Seats %
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , The Left (Germany), The Left (Die Linke)
, align="right" , 343,780
, align="right" , 31.0
, align="right" , 2.8
, align="right" , 29
, align="right" , 1
, align="right" , 32.2
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Alternative for Germany (AfD)
, align="right" , 259,382
, align="right" , 23.4
, align="right" , 12.8
, align="right" , 22
, align="right" , 11
, align="right" , 24.4
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Christian Democratic Union of Germany, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, align="right" , 241,049
, align="right" , 21.7
, align="right" , 11.8
, align="right" , 21
, align="right" , 13
, align="right" , 23.3
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD)
, align="right" , 90,987
, align="right" , 8.2
, align="right" , 4.2
, align="right" , 8
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 8.9
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Alliance 90/The Greens (Grünen)
, align="right" , 57,474
, align="right" , 5.2
, align="right" , 0.5
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 1
, align="right" , 5.6
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Free Democratic Party (Germany), Free Democratic Party (FDP)
, align="right" , 55,493
, align="right" , 5.0
, align="right" , 2.5
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 5
, align="right" , 5.6
, -
! colspan=8,
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , National Democratic Party of Germany
, align="right" , 6,044
, align="right" , 0.5
, align="right" , 3.1
, align="right" , 0
, align="right" , ±0
, align="right" , 0
, -
, style="width: 1px" bgcolor= align="center" ,
, align="left" , Others
, align="right" , 54,179
, align="right" , 4.9
, align="right" , 1.4
, align="right" , 0
, align="right" , ±0
, align="right" , 0
, -
! align="right" colspan=2, Valid votes
! align="right" , 1,108,388
! align="right" , 98.8
! align="right" , 0.2
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
, -
! align="right" colspan=2, Blank and invalid votes
! align="right" , 13,426
! align="right" , 1.2
! align="right" , 0.2
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
! align="right" ,
, -
! align="right" colspan=2, Total
! align="right" , 1,121,814
! align="right" , 100.0
! align="right" ,
! align="right" , 90
! align="right" , 1
! align="right" ,
, -
! colspan="2" , Electorate / voter turnout
!1,729,242
!64.9
!12.2
!
!
!
, -
, colspan=9 align=left , Source
Thüringer Landesamt für Statistik
 Furthermore, there are five urban districts:
*
Furthermore, there are five urban districts:
*

 Thuringia's economy is marked by the economic transition that happened after the German reunification and led to the closure of most of the factories within the Land. The unemployment rate reached a peak in 2005. Since that year, the economy has seen an upturn and the general economic situation has improved.
Thuringia's economy is marked by the economic transition that happened after the German reunification and led to the closure of most of the factories within the Land. The unemployment rate reached a peak in 2005. Since that year, the economy has seen an upturn and the general economic situation has improved.
File:Wartburg Eisenach DSCN3512.jpg, Wartburg
File:Goethe Schiller Weimar.jpg, Goethe–Schiller Monument in
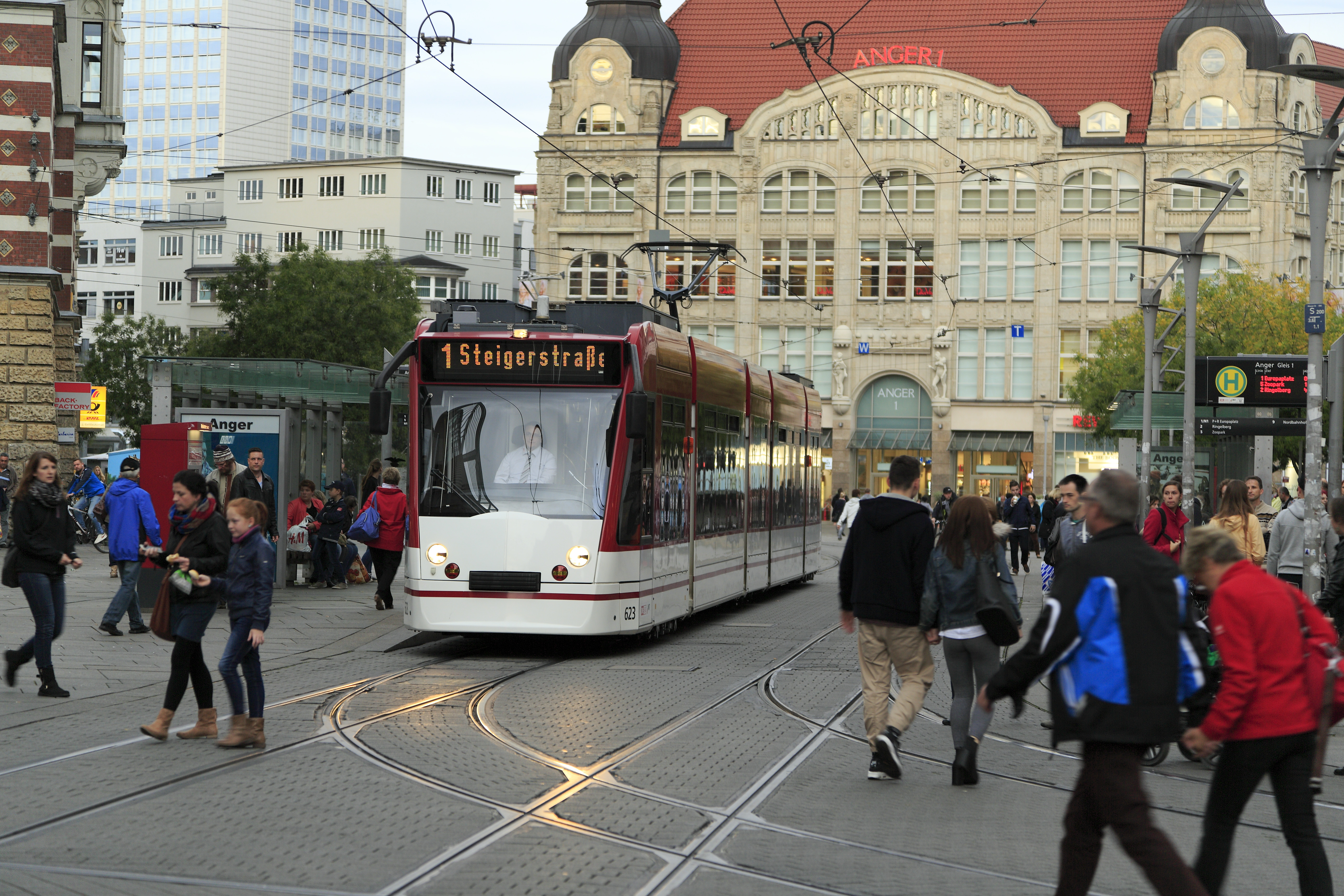

 As Germany's most central state, Thuringia is an important hub of transit traffic. The transportation infrastructure was in very poor condition after the GDR period. Since 1990, many billions of Euros have been invested to improve the condition of roads and railways within Thuringia.
During the 1930s, the first two Autobahn, motorways were built across the Land, the Bundesautobahn 4, A4 motorway as an important east–west connection in central Germany and the main link between Berlin and south-west Germany, and the Bundesautobahn 9, A9 motorway as the main north–south route in eastern Germany, connecting Berlin with Munich. The A4 runs from Frankfurt in
As Germany's most central state, Thuringia is an important hub of transit traffic. The transportation infrastructure was in very poor condition after the GDR period. Since 1990, many billions of Euros have been invested to improve the condition of roads and railways within Thuringia.
During the 1930s, the first two Autobahn, motorways were built across the Land, the Bundesautobahn 4, A4 motorway as an important east–west connection in central Germany and the main link between Berlin and south-west Germany, and the Bundesautobahn 9, A9 motorway as the main north–south route in eastern Germany, connecting Berlin with Munich. The A4 runs from Frankfurt in
 The German higher education system comprises two forms of academic institutions: university, universities and polytechnics (Fachhochschule). The
The German higher education system comprises two forms of academic institutions: university, universities and polytechnics (Fachhochschule). The
Official government siteTourist website for Thuringia
Official Directory
* *Thuringian flags at *# *# * {{Authority control Thuringia, States of the Weimar Republic NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1920 1952 disestablishments in East Germany States and territories established in 1990 States of Germany Former republics
Accessed on 16 Jan 2011. (, ) is a long river in central
Franconian Forest
View to Döbraberg
The Franconian Forest''Franconian Forest''
at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
in the south and the at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
Werra
The Werra (), a river in central Germany, is the right-bank headwater of the Weser. "Weser" is a synonym in an old dialect of German. The Werra has its source near Eisfeld in southern Thuringia. After the Werra joins the river Fulda in the ...
river in the west. After the Treaty of Leipzig
The Treaty of Leipzig or Partition of Leipzig (German ''Leipziger Teilung'') was signed on 11 November 1485 between Elector Ernest of Saxony and his younger brother Albert III, the sons of Elector Frederick II of Saxony from the House of Wettin ...
, Thuringia had its own dynasty again, the Ernestine Wettins. Their various lands formed the Free State of Thuringia, founded in 1920, together with some other small principalities. The Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n territories around Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
, Mühlhausen and Nordhausen joined Thuringia in 1945.
The coat of arms of Thuringia
The coat of arms German state Thuringia
was introduced in 1990. Like the 1949 coat of arms of Hesse it is based on the Ludovingian ''lion barry'', also known as the "lion of Hesse", with the addition of eight mullets.
Description
The coat of ...
shows the lion of the Ludowingian Landgraves of 12th-century origin. The eight stars around it represent the eight former states which formed Thuringia. The flag of Thuringia is a white-red bicolor, derived from the white and red stripes of the Ludowingian lion. The coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
and flag of Hesse
The civil flag of Hesse consists of a bicolor of a red top and a bottom white stripe, in the proportion 3:5. The state flag is similar, except it is emblazoned with the state coat of arms in the centre, and may only be used by government departm ...
are quite similar to the Thuringian ones, since they are also derived from the Ludowingian symbols.
Symbols of Thuringia in popular culture are the ''Bratwurst
Bratwurst () is a type of German sausage made from pork or, less commonly, beef or veal. The name is derived from the Old High German ''Brätwurst'', from ''brät-'', finely chopped meat, and ''Wurst'', sausage, although in modern German it is o ...
'' and the Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
, because a large amount of the territory is forested.
History
Named after theThuringii
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into co ...
Germanic tribe who occupied it around AD 300, Thuringia came under Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
domination in the 6th century.
Thuringia became a landgraviate
Landgrave (german: Landgraf, nl, landgraaf, sv, lantgreve, french: landgrave; la, comes magnus, ', ', ', ', ') was a noble title used in the Holy Roman Empire, and later on in its former territories. The German titles of ', ' ("margrave"), a ...
in 1130 AD. After the extinction of the reigning Ludowingian line of counts and landgraves in 1247 and the War of the Thuringian Succession
The War of the Thuringian Succession (German: ''Thüringisch-hessischer Erbfolgekrieg'') (1247–1264) was a military conflict over a successor to the last Landgrave of Thuringia for control of the state of Thuringia (now in modern-day Germany).
...
(1247–1264), the western half became independent under the name of "Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
", never to become a part of Thuringia again. Most of the remaining Thuringia came under the rule of the Wettin dynasty
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its orig ...
of the nearby Margraviate of Meissen, the nucleus of the later Electorate
Electorate may refer to:
* The people who are eligible to vote in an election, especially their number e.g. the term ''size of (the) electorate''
* The dominion of a Prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, ...
and Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony (german: Königreich Sachsen), lasting from 1806 to 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. The kingdom was formed from the Electorate of Saxo ...
. With the division of the house of Wettin in 1485, Thuringia went to the senior Ernestine Ernestine is a feminine given name. Ernest is the male counterpart of this name. Notable people with the name include:
* Ernestine Anderson (1928–2016), American jazz and blues singer
* Ernestine Bayer (1909–2006), American athlete
* Ernestine ...
branch of the family, which subsequently subdivided the area into a number of smaller states, according to the Saxon tradition of dividing inheritance amongst male heirs. These were the "Saxon duchies
The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine appanage duchies of Weissenfels, Merseburg and Zeitz were also "Saxon duchies" and adjacent to several Ernestine ones), were a group of small states whose numb ...
", consisting, among others, of the states of Saxe-Weimar, Saxe-Eisenach
Saxe-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Eisenach) was an Ernestine duchy ruled by the Saxon House of Wettin. The state intermittently existed at three different times in the Thuringian region of the Holy Roman Empire. The chief town and capital of all t ...
, Saxe-Jena
The Duchy of Saxe-Jena was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1672 for Bernhard, fourth son of Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Saxe-Jena was reincorporated into Saxe-Weimar on the extinction ...
, Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernest ...
, Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete ...
, Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany.
History
Ernestine Line
When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of th ...
, and Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Gotha) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha.
History
The duchy was established in 1640, wh ...
.
Thuringia generally accepted the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
, and Roman Catholicism was suppressed as early as 1520; priests who remained loyal to it were driven away and churches and monasteries were largely destroyed, especially during the German Peasants' War of 1525. In Mühlhausen and elsewhere, the Anabaptists
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
found many adherents. Thomas Müntzer
Thomas Müntzer ( – 27 May 1525) was a German preacher and theologian of the early Reformation whose opposition to both Martin Luther and the Roman Catholic Church led to his open defiance of late-feudal authority in central Germany. Müntzer w ...
, a leader of some non-peaceful groups of this sect, was active in this city. Within the borders of modern Thuringia the Roman Catholic faith only survived in the Eichsfeld district, which was ruled by the Archbishop of Mainz, and to a small degree in Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
and its immediate vicinity.
Early modern period
The modern German black-red-gold tricolour flag's first appearance anywhere in a German-ethnicitysovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined te ...
, within what today comprises Germany, occurred in 1778 as the state flag of the Principality of Reuss-Greiz
The Principality of Reuss-Greiz (german: Fürstentum Reuß-Greiz), called the Principality of the Reuss Elder Line (german: Fürstentum Reuß älterer Linie) after 1848, was a sovereign state in modern Germany, ruled by members of the House of ...
, a defunct principality in the modern state's borders.
 Some reordering of the Thuringian states occurred during the
Some reordering of the Thuringian states occurred during the German Mediatisation
German mediatisation (; german: deutsche Mediatisierung) was the major territorial restructuring that took place between 1802 and 1814 in Germany and the surrounding region by means of the mass mediatisation and secularisation of a large number ...
from 1795 to 1814, and the territory was included within the Napoleonic Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria an ...
organized in 1806. The 1815 Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
confirmed these changes and the Thuringian states' inclusion in the German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, w ...
; the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
also acquired some Thuringian territory and administered it within the Province of Saxony. The Thuringian duchies which became part of the German Empire in 1871 during the Prussian-led unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of t ...
were Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) was a historical German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was ra ...
, Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernest ...
, Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete ...
, Saxe-Coburg-Gotha
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha), or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg-Gotha, links=no ), was an Ernestine, Thuringian duchy ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present- ...
, Schwarzburg-Sondershausen
Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was a small principality in Germany, in the present day state of Thuringia, with its capital at Sondershausen.
History
Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was a county until 1697. In that year, it became a principality, which la ...
, Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt
Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was a small historic state in present-day Thuringia, Germany, with its capital at Rudolstadt.
History
Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was established in 1599 in the course of a resettlement of Schwarzburg dynasty lands. Since t ...
and the two principalities of Reuss Elder Line
The Principality of Reuss-Greiz (german: Fürstentum Reuß-Greiz), called the Principality of the Reuss Elder Line (german: Fürstentum Reuß älterer Linie) after 1848, was a sovereign state in modern Germany, ruled by members of the House of ...
and Reuss Younger Line
The Principality of Reuss-Gera (german: Fürstentum Reuß-Gera), called the Principality of the Reuss Junior Line (german: Fürstentum Reuß jüngerer Linie) after 1848, was a sovereign state in modern Germany, ruled by members of the House of Re ...
.
Free State of Thuringia
In 1920, afterWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, these small states merged into one state, called Thuringia; only Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany.
History
Ernestine Line
When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of th ...
voted to join Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
instead. Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
became the new capital of Thuringia. The coat of arms of this new state was simpler than those of its predecessors.
In 1930, Thuringia was one of the free states where the Nazis gained real political power. Wilhelm Frick was appointed Minister of the Interior for the state of Thuringia after the Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
won six delegates to the Thuringia Diet. In this position he removed from the Thuringia police force anyone he suspected of being a republican and replaced them with men who were favourable towards the Nazi Party. He also ensured that whenever an important position came up within Thuringia, he used his power to ensure that a Nazi was given that post.
After being controlled briefly by the US, from July 1945, the state of Thuringia came under the Soviet occupation zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a ...
, and was expanded to include parts of Prussian Saxony, such as the areas around Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
, Mühlhausen, and Nordhausen. Erfurt became the new capital of Thuringia. Ostheim
Ostheim vor der Rhön is a town in Northern Bavaria in the district of Rhön-Grabfeld in Franconia. Though politically part of Bavaria since 1947, it was historically a part of Thuringia, and remains religiously, architecturally, and to some exten ...
, an exclave of ''Landkreis
In all German states, except for the three city states, the primary administrative subdivision higher than a '' Gemeinde'' (municipality) is the (official term in all but two states) or (official term in the states of North Rhine-Westphalia ...
'' Eisenach, was ceded to Bavaria.
In 1952, the German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
dissolved its states, and created districts () instead. The three districts that shared the former territory of Thuringia were Erfurt, Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
and Suhl
Suhl () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located SW of Erfurt, NE of Würzburg and N of Nuremberg. With its 37,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest of the six urban districts within Thuringia. Together with its northern neighbour-town Zella- ...
. Altenburg Kreis was part of Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
Bezirk.
The State of Thuringia was recreated with slightly altered borders during German reunification in 1990.
Geography
Topography
From the northwest going clockwise; Thuringia borders on the German states ofLower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
and Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
.
Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
mountains, followed by the Goldene Aue The Goldene Aue (German: "golden lowland", also " ... bottom" or " ... meadow" / " ... pasture", with "Au referring to a low-lying area, often a wetland) is a valley in eastern Germany, in the states Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt. It is situated betw ...
, a fertile floodplain around Nordhausen with the Helme
The Helme is river in central Germany that is about long and which forms a left-hand, western tributary of the Unstrut in the states of Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt.
Course
The river rises in Thuringia south of the Harz mountains in the dis ...
as most important river. The north-west includes the Eichsfeld, a hilly and sometimes forested region, where the Leine
The Leine (; Old Saxon ''Lagina'') is a river in Thuringia and Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Aller and the Weser and is long.
The river's source is located close to the town of Leinefelde in Thuringia. About downriver, ...
river emanates. The central and northern part of Thuringia is defined by the wide Thuringian Basin
The Thuringian Basin (german: Thüringer Becken) is a depression in the central and northwest part of Thuringia in Germany which is crossed by several rivers, the longest of which is the Unstrut. It stretches about from north to south and around ...
, a very fertile and flat area around the Unstrut
The Unstrut () is a river in Germany and a left tributary of the Saale.
The Unstrut originates in northern Thuringia near Dingelstädt (west of Kefferhausen in the Eichsfeld area) and its catchment area is the whole of the Thuringian Basin. ...
river and completely surrounded by the following hill chains (clockwise from the north-west): Dün, Hainleite
The Hainleite is a Muschelkalk ridge of hills up to in northern Thuringia, Germany.
Geography
This heavily wooded landscape lies between Bleicherode in Nordhausen district, Sondershausen in Kyffhäuser district, Bad Frankenhausen, Dingelst� ...
, Windleite, Kyffhäuser
The Kyffhäuser (,''Duden - Das Aussprachewörterbuch, 7. Auflage (German)'', Dudenverlag, sometimes also referred to as ''Kyffhäusergebirge'', is a hill range in Central Germany, shared by Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, southeast of the Harz mou ...
, Hohe Schrecke, Schmücke, Finne, Ettersberg, Steigerwald
The Steigerwald is a hill region up to in the Bavarian-Franconian part of the South German Scarplands between Würzburg and Nuremberg. It is part of the Keuper Uplands, and within it, it is continued to the north-northeast and right of the river ...
, Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side i ...
, Hörselberge and Hainich
Hainich is a forested hill chain in the state of Thuringia in Germany, between the towns of Eisenach, Mühlhausen and Bad Langensalza. Hainich covers an area of around 160 km² (61,8 sq mi), of which, since 31 December 1997, half has be ...
. Within the Basin the smaller hill chains Fahner Höhe and Heilinger Höhen. South of the Thuringian Basin is the state's largest mountain range, marked by the Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side i ...
in the north-west, the Thuringian Highland
The Thuringian Highland, Thuringian Highlands or Thuringian-Vogtlandian Slate MountainsKohl, Horst; Marcinek, Joachim and Nitz, Bernhard (1986). ''Geography of the German Democratic Republic'', VEB Hermann Haack, Gotha, p. 7 ff. . (german: Thüring ...
in the middle and the Franconian Forest
View to Döbraberg
The Franconian Forest''Franconian Forest''
at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
in the south-east. Most of this range is forested and the at www.britannica.com. Acce ...
Großer Beerberg
The Großer Beerberg is a mountain, , whose summit is the highest point in the Thuringian Forest and the state of Thuringia. It is located between the three villages of Heidersbach, Goldlauter and Gehlberg in the borough of Suhl. The mountain is ...
(983 m) is Thuringia's highest mountain. To the south-west, the Forest is followed up by Werra
The Werra (), a river in central Germany, is the right-bank headwater of the Weser. "Weser" is a synonym in an old dialect of German. The Werra has its source near Eisfeld in southern Thuringia. After the Werra joins the river Fulda in the ...
river valley, dividing it from the Rhön Mountains in the west and the Grabfeld
The Grabfeld is a region in Germany, on the border between Bavaria and Thuringia. It is situated southeast of the Rhön Mountains. Its highest elevation is 679 metres high in the little Gleichberge mountain range. The Grabfeld gave its name to t ...
plain in the south. Eastern Thuringia, commonly described as the area east of Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale (german: Sächsische Saale) and Thuringian Saale (german: Thüringische Saale), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale ...
and Loquitz
The Loquitz is a river in Bavaria and Thuringia, Germany. It flows into the Saale in Kaulsdorf (Saale).
See also
*List of rivers of Bavaria
A list of rivers of Bavaria, Germany:
A
* Aalbach
* Abens
* Ach
* Afferbach
*Affinger Bach
*Ailsbach
...
valley, is marked by a hilly landscape, rising slowly from the flat north to the mountainous south. The Saale in the west and the White Elster in the east are the two big rivers running from south to north and forming densely settled valleys in this area. Between them lies the flat and forested Holzland in the north, the flat and fertile Orlasenke in the middle and the Vogtland
Vogtland (; cz, Fojtsko) is a region spanning the German states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and north-western Bohemia in the Czech Republic. It overlaps with and is largely contained within Euregio Egrensis. The name alludes to the former ...
, a hilly but in most parts non-forested region in the south. The far eastern region (east of White Elster) is the Osterland or Altenburger Land
Altenburger Land is a district in Thuringia, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the district of Greiz, the Burgenlandkreis (Saxony-Anhalt), and the districts Leipzig, Mittelsachsen and Zwickau in Saxony. The district is a mem ...
along Pleiße river, a flat, fertile and densely settled agricultural area.
There are two large rivers in Thuringia. The Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale (german: Sächsische Saale) and Thuringian Saale (german: Thüringische Saale), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale ...
, a tributary of the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
, with its tributaries the Unstrut
The Unstrut () is a river in Germany and a left tributary of the Saale.
The Unstrut originates in northern Thuringia near Dingelstädt (west of Kefferhausen in the Eichsfeld area) and its catchment area is the whole of the Thuringian Basin. ...
, Ilm Ilm or ILM may refer to:
Acronyms
* Identity Lifecycle Manager, a Microsoft Server Product
* '' I Love Money,'' a TV show on VH1
* Independent Loading Mechanism, a mounting system for CPU sockets
* Industrial Light & Magic, an American motion ...
and White Elster, drains the most part of Thuringia. The Werra
The Werra (), a river in central Germany, is the right-bank headwater of the Weser. "Weser" is a synonym in an old dialect of German. The Werra has its source near Eisfeld in southern Thuringia. After the Werra joins the river Fulda in the ...
– the headwater of the Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
– drains the south-west and west of the state. Furthermore, some small areas on the southern border are drained by tributaries of the Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
, itself a tributary of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
. There are no large natural lakes in Thuringia, but it does have some of Germany's biggest dams, including the Bleiloch Dam and the Hohenwarte Dam on the River Saale, as well as the Leibis-Lichte Dam
The Leibis-Lichte Dam (german: Talsperre Leibis –Lichte) is a dam in the German state of Thuringia in the Thuringian Highland. The dam was completed in 2005 to impound the River Lichte, between the Lichte municipality section Geiersthal and ...
and the Goldisthal Pumped Storage Station
The Goldisthal Pumped Storage Station is a pumped-storage power station in the Thüringer Mountains at the upper run of the river Schwarza in Goldisthal, Germany. It was constructed between 1997 and 2004. It has an installed capacity of , the la ...
in the Thuringian Highlands. Thuringia is Germany's only state with no connection to navigable waterways.
The geographic centre
In geography, the centroid of the two-dimensional shape of a region of the Earth's surface (projected radially to sea level or onto a geoid surface) is known as its geographic centre or geographical centre or (less commonly) gravitational centre. I ...
of the Federal Republic is in Thuringia, within the municipality of Vogtei next to Mühlhausen. The centre of Thuringia is eight kilometres south of the capital's Cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
, in the municipality of Rockhausen.
Climate
Thuringia's climate istemperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
with humid westerly winds predominating. Increasingly as one moves from the north-west to the south-east, the climate shows continental features: winters can be cold for long periods, and summers can become warm. Dry periods are often recorded, especially within the Thuringian Basin, leeward to mountains in all directions. It is Germany's driest area, with annual precipitation of only 400 to 500 mm.
Artern, in the north-east, is warm and dry, with a mean annual temperature of 8.5 °C and mean precipitation of 450 mm; contrast this with wet, cool Oberhof, in the Thuringian Forest, where temperature averages only 4.4 °C and mean annual precipitation reaches 1300 mm.
Nature and environment

 Due to many centuries of intensive settlement, most of the area is shaped by human influence. The original natural vegetation of Thuringia is forest with beech as its predominant species, as can still be found in the
Due to many centuries of intensive settlement, most of the area is shaped by human influence. The original natural vegetation of Thuringia is forest with beech as its predominant species, as can still be found in the Hainich
Hainich is a forested hill chain in the state of Thuringia in Germany, between the towns of Eisenach, Mühlhausen and Bad Langensalza. Hainich covers an area of around 160 km² (61,8 sq mi), of which, since 31 December 1997, half has be ...
mountains today. In the uplands, a mixture of beech and spruce would be natural. However, most of the plains have been cleared and are in intensive agricultural use while most of the forests are planted with spruce and pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
. Since 1990, Thuringia's forests have been managed aiming for a more natural and tough vegetation more resilient to climate change as well as diseases and vermin. In comparison to the forest, agriculture is still quite conventional and dominated by large structures and monocultures. Problems here are caused especially by increasingly prolonged dry periods during the summer months.
Environmental damage in Thuringia has been reduced to a large extent after 1990. The condition of forests, rivers and air was improved by modernizing factories, houses (decline of coal heating) and cars, and contaminated areas such as the former Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
surface mines around Ronneburg have been remediated. Today's environmental problems are the salination of the Werra
The Werra (), a river in central Germany, is the right-bank headwater of the Weser. "Weser" is a synonym in an old dialect of German. The Werra has its source near Eisfeld in southern Thuringia. After the Werra joins the river Fulda in the ...
river, caused by discharges of K+S KS and variants may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* , a German postwar commando frogman force
* , a Norwegian type of company
* Norwegian Association of Local and Regional Authorities
* PenAir, Peninsula Airways, Anchorage, Alaska, US (IA ...
salt mines around Unterbreizbach
Unterbreizbach is a municipality in the Wartburgkreis district of Thuringia, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russi ...
and overfertilisation in agriculture, damaging the soil and small rivers.
Environment and nature protection has been of growing importance and attention since 1990. Large areas, especially within the forested mountains, are protected as natural reserves, including Thuringia's first national park within the Hainich
Hainich is a forested hill chain in the state of Thuringia in Germany, between the towns of Eisenach, Mühlhausen and Bad Langensalza. Hainich covers an area of around 160 km² (61,8 sq mi), of which, since 31 December 1997, half has be ...
mountains, founded in 1997, the Rhön Biosphere Reserve
The Rhön Biosphere Reserve includes the entire central area of the Rhön Mountains, a low mountain range in the German states of Hesse, Bavaria and Thuringia.
Aim
In 1991 the Rhön was recognised at international level by UNESCO as a biosph ...
, the Thuringian Forest Nature Park
Thuringian Forest Nature Park (german: Naturpark Thüringer Wald) is one of two nature parks in the state of Thuringia, Germany.
Founded in 1990, and expanded in 2018, the nature park now covers and area of more than . It extends around the Rennst ...
and the South Harz Nature Park.
Demographics
Demographic history
During the Middle Ages, Thuringia was at the border between Germanic and Slavic territories, marked by theSaale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale (german: Sächsische Saale) and Thuringian Saale (german: Thüringische Saale), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale ...
river. The main Slavic tribe in what is now Thuringia were the Sorbs proper, who unified all tribes in what is now southern half of Eastern Germany. The Ostsiedlung movement led to the assimilation of Slavic people between the 11th and the 13th century under German rule. The population growth increased during the 18th century and stayed high until World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, before it slowed within the 20th century and changed to a decline since 1990. Since the beginning of Urbanisation around 1840, the Thuringian cities have higher growth rates resp. smaller rates of decline than rural areas (many villages lost half of their population since 1950, whereas the biggest cities (Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
and Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
) kept growing).
Current population
The current population is 2,120,237 (December 31, 2020) with an annual rate of decrease of about 0.5%, which varies widely between the local regions. In 2012, 905,000 Thuringians lived in a municipality with more than 20,000 inhabitants, this is anurbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
rate of 42% which continues to rise.
In July 2013, there were 41,000 non-Germans by citizenship living in Thuringia (1.9% of the population − among the smallest proportions of any state in Germany). Nevertheless, the number rose from 33,000 in July 2011, an increase of 24% in only two years. About 4% of the population are migrants (including persons that already received the German citizenship). The biggest groups of foreigners by citizenship are (as of 2012): Russians in Germany, Russians (3,100), Poles in Germany, Poles (3,000), Turks in Germany, Turks (2,100) and Ukrainians in Germany, Ukrainians (2,000). The number of foreigners varies between regions: the college towns Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
, Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
, Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
and Ilmenau have the highest rates, whereas there are almost no migrants living in the most rural smaller municipalities.
The Thuringian population has a significant human sex ratio, sex ratio gap, caused by the emigration of young women, especially in rural areas. Overall, there are 115 to 120 men per 100 women in the 25–40 age group ("family founders") which has negative consequences for the birth ratio. Furthermore, the population is getting older and older with some rural municipalities recording more than 30% of over-65s (pensioners). This is a problem for the regional labour market, as there are twice as many people leaving as entering the job market annually.
Natural and spatial tendencies
The birth rate was about 1.8 children per women in the 1970s and 1980s, shrinking to 0.8 in 1994 during the economic crisis after the reunification and rose again to more than 1.4 children in 2010, which is a higher level than in West Germany. Nevertheless, there are only 17,000 births compared to 27,000 deaths per year, so that the annual natural change of the Thuringian population is about −0.45%. In 2015 there were 17.934 births, the highest number since 1990. Migration plays an important role in Thuringia. The internal migration shows a strong tendency from rural areas towards the big cities. From 2008 to 2012, there was a net migration from Thuringia toErfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
of +6,700 persons (33 per 1000 inhabitants), +1,800 to Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
(19 per 1000), +1,400 to Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
(14 per 1000), +1,400 to Eisenach (33 per 1000) and +1,300 to Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
(21 per 1000). Between Thuringia and the other German states, the balance is negative: In 2012, Thuringia lost 6,500 persons to other federal states, the most to Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
and Berlin. Only with Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
and Brandenburg the balance is positive. The international migration is fluctuating heavily. In 2009, the balance was +700, in 2010 +1,800, in 2011 +2,700 and in 2012 +4,800. The most important countries of origin of the Thuringia migrants from 2008 to 2012 were Poland (+1,700), Romania (+1,200), Afghanistan (+1,100) and Serbia/Montenegro/Kosovo (+1,000), whereas the balance was negative with Switzerland (−2,800) and Austria (−900).
Vital statistics
*Births January–November 2016 = *Births January–November 2017 = *Deaths January–November 2016 = *Deaths January–November 2017 = *Natural growth January–November 2016 = *Natural growth January–November 2017 =Cities, towns and villages
Of the approximately 850 municipalities of Thuringia, 126 are classed as towns (within a district) or cities (forming their own urban district). Most of the towns are small with a population of less than 10,000; only the ten biggest ones have a population greater than 30,000. The first towns emerged during the 12th century, whereas the latest ones received town status only in the 20th century. Today, all municipalities within districts are equal in law, whether they are towns or villages. Independent cities (i.e. urban districts) have greater powers (the same as any district) than towns within a district.Religion
Since theProtestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
, the most prominent Christian denomination in Thuringia has been Lutheranism. During the GDR period, church membership was discouraged and has continued shrinking since the reunification in 1990. Today over two thirds of the population is non-religious. The Protestant Evangelical Church in Germany has had the largest number of members in the state, adhered to by 20.8% of the population in 2018. Members of the Catholic Church formed 7.6% of the population, while 71.6% of Thuringians were non-religious or adhere to other faiths. The highest Protestant concentrations are in the small villages of southern and western Thuringia, whereas the bigger cities are even more non-religious (up to 88% in Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
). Catholic regions are Eichsfeld in the northwest and parts of the Rhön Mountains around Geisa in the southwest. Protestant church membership is shrinking rapidly, whereas the Catholic Church is somewhat more stable because of Catholic migration from Poland, Southern Europe and West Germany. Other religions play no significant role in Thuringia. There are only a few thousand Muslims (largely migrants) and about 750 Jews (mostly migrants from Russia) living in Thuringia. Furthermore, there are some Orthodox communities of Eastern European migrants and some traditional Protestant Free churches in Thuringia without any societal influence.
The Protestant parishes of Thuringia belong to the Evangelical Church in Central Germany or to the Evangelical Church of Hesse Electorate-Waldeck (Schmalkalden region). Catholic dioceses are Roman Catholic Diocese of Erfurt, Erfurt (most of Thuringia), Roman Catholic Diocese of Dresden-Meissen, Dresden-Meissen (eastern parts) and Roman Catholic Diocese of Fulda, Fulda (Rhön around Geisa in the very west).
Politics
National
Thuringia is a stronghold for the Alternative for Germany (AfD), the party emerged as the largest in Thuringia in the 2021 German federal election, 2021 national elections. In 2017 the party got 22.7%, while in 2021 they got 24.0%.List of Ministers-Presidents of Thuringia
October 2019 state election
, - bgcolor=#E9E9E9 , - , colspan=9 align=center,Thüringer Landesamt für Statistik
Local government
Thuringia is divided into 17 districts (''Landkreise''): #Altenburger Land
Altenburger Land is a district in Thuringia, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the district of Greiz, the Burgenlandkreis (Saxony-Anhalt), and the districts Leipzig, Mittelsachsen and Zwickau in Saxony. The district is a mem ...
# Eichsfeld (district), Eichsfeld
# Gotha (district), Gotha
# Greiz (district), Greiz
# Hildburghausen (district), Hildburghausen
# Ilm-Kreis
# Kyffhäuserkreis
# Nordhausen (district), Nordhausen
# Saale-Holzland-Kreis
# Saale-Orla-Kreis
# Saalfeld-Rudolstadt
# Schmalkalden-Meiningen
# Sömmerda (district), Sömmerda
# Sonneberg (district), Sonneberg
# Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis
# Wartburgkreis
# Weimarer Land
Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
(EF)
* Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
(G)
* Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
(J)
* Suhl
Suhl () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located SW of Erfurt, NE of Würzburg and N of Nuremberg. With its 37,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest of the six urban districts within Thuringia. Together with its northern neighbour-town Zella- ...
(SHL)
* Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
(WE)
Economy
 Thuringia's economy is marked by the economic transition that happened after the German reunification and led to the closure of most of the factories within the Land. The unemployment rate reached a peak in 2005. Since that year, the economy has seen an upturn and the general economic situation has improved.
Thuringia's economy is marked by the economic transition that happened after the German reunification and led to the closure of most of the factories within the Land. The unemployment rate reached a peak in 2005. Since that year, the economy has seen an upturn and the general economic situation has improved.
Agriculture and forestry
Agriculture and forestry have declined in importance over the decades. Nevertheless, they are more important than in most other areas of Germany, especially within rural regions. 54% of Thuringia's territory is in agricultural use. The fertile basins such as the largeThuringian Basin
The Thuringian Basin (german: Thüringer Becken) is a depression in the central and northwest part of Thuringia in Germany which is crossed by several rivers, the longest of which is the Unstrut. It stretches about from north to south and around ...
or the smaller Goldene Aue The Goldene Aue (German: "golden lowland", also " ... bottom" or " ... meadow" / " ... pasture", with "Au referring to a low-lying area, often a wetland) is a valley in eastern Germany, in the states Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt. It is situated betw ...
, Orlasenke and Osterland are in intensive use for growing cereals, vegetables, fruits and energy crops. Important products are apples, strawberries, cherries and plums in the fruit sector, cabbage, potatoes, cauliflower, tomatoes (grown in greenhouses), onions, cucumbers and asparagus in the vegetable sector, as well as maize, rapeseed, wheat, barley and sugar beets in the crop sector.
Meat production and processing is also an important activity, with swine, cattle, chickens and turkeys in focus. Furthermore, there are many milk and cheese producers, as well as laying hens. Trout and carp are traditionally bred in aquaculture in many villages.
Most agricultural enterprises are large cooperatives, founded as Landwirtschaftliche Produktionsgenossenschaft during the GDR period, and meat producers are part of multinational companies. Traditional private peasant agriculture is an exception, as is organic farming.
Thuringia's only wine-growing district is around Bad Sulza north of Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
and Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
along the Ilm Ilm or ILM may refer to:
Acronyms
* Identity Lifecycle Manager, a Microsoft Server Product
* '' I Love Money,'' a TV show on VH1
* Independent Loading Mechanism, a mounting system for CPU sockets
* Industrial Light & Magic, an American motion ...
and Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale (german: Sächsische Saale) and Thuringian Saale (german: Thüringische Saale), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale ...
valley. Its production is marketed as Saale-Unstrut wines.
Forestry plays an important role in Thuringia because 32% of the Thuringian territory is forested. The most common trees are spruce, pine and beech. There are many wood and pulp-paper factories near the forested areas.
Industry and mining
Like most other regions of central and southern Germany, Thuringia has a significant industrial sector reaching back to the mid-19th-century industrialisation. The economic transition after the German reunification in 1990 led to the closure of most large-scale factories and companies, leaving small and medium-sized ones to dominate the manufacturing sector. Well-known industrial centres areJena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
(a world centre for optical instruments with companies like Carl Zeiss AG, Carl Zeiss, Schott AG, Schott and Jenoptik) and Eisenach, where BMW started its car production in the 1920s and an Opel factory is based today. The most important industrial branches today are engineering and metalworking, vehicle production and food industries. Especially the small and mid-sized towns in central and southwestern Thuringia (e.g. Arnstadt, Schmalkalden and Ohrdruf, Thuringia, Ohrdruf) are highly industrialised, whereas there are fewer industrial companies in the northern and eastern parts of the Land. Traditional industries like production of glass, porcelain and toys collapsed during the economic crises between 1930 and 1990.
Mining was important in Thuringia since the later Middle Ages, especially within the mining towns of the Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side i ...
such as Schmalkalden, Suhl
Suhl () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located SW of Erfurt, NE of Würzburg and N of Nuremberg. With its 37,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest of the six urban districts within Thuringia. Together with its northern neighbour-town Zella- ...
and Ilmenau. Following the industrial revolution, the old iron, copper and silver mines declined because the competition from imported metal was too strong. On the other hand, the late 19th century brought new types of mines to Thuringia: the lignite surface mining around Meuselwitz near Altenburg in the east of the Land started in the 1870s, and two potash mining districts were established around 1900. These are the ''Südharzrevier'' in the north of the state, between Bischofferode in the west and Roßleben in the east with Sondershausen at its centre, and the ''Werrarevier'' on the Hessian border around Vacha, Germany, Vacha and Bad Salzungen in the west. Together, they accounted for a significant part of the world's potash production in the mid-20th century. After the reunification, the ''Südharzrevier'' was abandoned, whereas K+S KS and variants may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* , a German postwar commando frogman force
* , a Norwegian type of company
* Norwegian Association of Local and Regional Authorities
* PenAir, Peninsula Airways, Anchorage, Alaska, US (IA ...
took over the mines in the ''Werrarevier''. Between 1950 and 1990, uranium mining was also important to cover the Soviet Union's need for this metal. The centre was Ronneburg near Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
in eastern Thuringia and the operating company Wismut (mining company), Wismut was under direct Soviet control.
General economic parameters
The GDP of Thuringia is below the national average, in line with the other former East German Lands. Until 2004, Thuringia was one of the weakest regions within the European Union. The accession of several new countries, the crisis in southern Europe and the sustained economic growth in Germany since 2005 has brought the Thuringian GDP close to the EU average since then. The high economic subsidies granted by the federal government and the EU after 1990 are being reduced gradually and will end around 2020. The unemployment rate reached its peak of 17.1% in 2005. Since then, it has decreased to 5.3% in 2019, which is only slightly above the national average. The decrease is caused on the one hand by the emergence of new jobs and on the other by a marked decrease in the working-age population, caused by emigration and low birth rates for decades. The wages in Thuringia are low compared to rich bordering Lands likeHesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
and Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
. Therefore, many Thuringians are working in other German Lands and even in Austria and Switzerland as weekly commuters. Nevertheless, the demographic transition in Thuringia leads to a lack of workers in some sectors. External immigration into Thuringia has been encouraged by the government since about 2010 to counter this problem.
The economic progress is quite different between the regions of Thuringia. The big cities along the Bundesautobahn 4, A4 motorway such as Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
, Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
and Eisenach and their surroundings are booming, whereas nearly all the rural regions, especially in the north and east, have little economic impetus and employment, which is a big issue in regional planning. Young people in these areas often have to commute long distances, and many emigrate soon after finishing school.
The unemployment rate stood at 5.3% in 2019 and was higher than the German average.
Tourism
Tourism is an important branch of the economy. Thuringia has a number of well known destinations: Wartburg, Wartburg castle (UNESCO World Heritage Site), Weimar, Classical Weimar (UNESCO World Heritage Site), Bauhaus and its Sites in Weimar, Dessau and Bernau, Bauhaus Weimar (UNESCO World Heritage Site),Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side i ...
, Oberhof or Rennsteig (ridge walk). City tourism with the centers of Erfurt, Weimar, Jena, Eisenach and Mühlhausen is experiencing dynamic growth. A total of around 9.2 million overnight stays were booked in 2016, compared to 8.3 million ten years earlier. Around 6% of the bookings were made by foreign guests.
Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
File:Falkenstein Thüringen.jpg, Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side i ...
File:Schanzenanlage im Kanzlersgrund bei Oberhof.jpg, Oberhof
File:Erfurter Dom von Oben 08.jpg, Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
skyline
File:Kraemerbruecke und Aegidienkirche Erfurt 2017.jpg, Krämerbrücke in Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
File:Muehlhausen Marienkirche.jpg, Oldtown of Mühlhausen
File:Schloss Friedenstein Gotha 2.JPG, Friedenstein Palace, Gotha
Infrastructure
Transport

 As Germany's most central state, Thuringia is an important hub of transit traffic. The transportation infrastructure was in very poor condition after the GDR period. Since 1990, many billions of Euros have been invested to improve the condition of roads and railways within Thuringia.
During the 1930s, the first two Autobahn, motorways were built across the Land, the Bundesautobahn 4, A4 motorway as an important east–west connection in central Germany and the main link between Berlin and south-west Germany, and the Bundesautobahn 9, A9 motorway as the main north–south route in eastern Germany, connecting Berlin with Munich. The A4 runs from Frankfurt in
As Germany's most central state, Thuringia is an important hub of transit traffic. The transportation infrastructure was in very poor condition after the GDR period. Since 1990, many billions of Euros have been invested to improve the condition of roads and railways within Thuringia.
During the 1930s, the first two Autobahn, motorways were built across the Land, the Bundesautobahn 4, A4 motorway as an important east–west connection in central Germany and the main link between Berlin and south-west Germany, and the Bundesautobahn 9, A9 motorway as the main north–south route in eastern Germany, connecting Berlin with Munich. The A4 runs from Frankfurt in Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
via Eisenach, Gotha, Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
, Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
, Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
and Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cit ...
to Dresden in Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, connecting Thuringia's most important cities. At Hermsdorf, Thuringia, Hermsdorf junction it is connected with the A9. Both highways were widened from four to six lanes (three each way) after 1990, including some extensive re-routing in the Eisenach and Jena areas. Furthermore, three new motorways were built during the 1990s and 2000s. The Bundesautobahn 71, A71 crosses the Land in southwest–northeast direction, connecting Würzburg in Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
via Meiningen, Suhl
Suhl () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located SW of Erfurt, NE of Würzburg and N of Nuremberg. With its 37,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest of the six urban districts within Thuringia. Together with its northern neighbour-town Zella- ...
, Ilmenau, Arnstadt, Erfurt and Sömmerda with Sangerhausen and Halle (Saale), Halle in Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
. The crossing of the Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side i ...
by the A71 has been one of Germany's most expensive motorway segments with various tunnels (including Germany's longest road tunnel, the Rennsteig Tunnel) and large bridges. The Bundesautobahn 73, A73 starts at the A71 south of Erfurt in Suhl and runs south towards Nuremberg in Bavaria. The Bundesautobahn 38, A38 is another west–east connection in the north of Thuringia running from Göttingen in Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
via Heilbad Heiligenstadt, Heiligenstadt and Nordhausen to Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
in Saxony. Furthermore, there is a dense network of Bundesstraße, federal highways complementing the motorway network. The upgrading of federal highways is prioritised in the federal trunk road programme 2015 (''Bundesverkehrswegeplan'' 2015). Envisaged projects include upgrades of the Bundesstraße 247, B247 from Gotha to Leinefelde to improve Mühlhausen's connection to the national road network, the Bundesstraße 19, B19 from Eisenach to Meiningen to improve access to Bad Salzungen and Schmalkalden, and the Bundesstraße 88, B88 and Bundesstraße 281, B281 for strengthening the Saalfeld/Rudolstadt region.
The first railways in Thuringia had been built in the 1840s and the network of main lines was finished around 1880. By 1920, many branch lines had been built, giving Thuringia one of the densest rail networks in the world before World War II with about 2,500 km of track. Between 1950 and 2000 most of the branch lines were abandoned, reducing Thuringia's network by half compared to 1940. On the other hand, most of the main lines were refurbished after 1990, resulting in improved speed of travel. The most important railway lines at present are the Thuringian Railway, connecting Halle (Saale), Halle and Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
via Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
, Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
, Gotha and Eisenach with Frankfurt and Kassel and the Saal Railway from Halle/Leipzig via Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
and Saalfeld to Nuremberg. The former has an hourly Intercity-Express, ICE/Intercity (Deutsche Bahn), IC service from Dresden to Frankfurt while the latter is served hourly by ICE trains from Berlin to Munich. In 2017, a new high speed line will be opened, diverting long-distance services from these mid-19th century lines. Both ICE routes will then use the Erfurt–Leipzig/Halle high-speed railway, and the Berlin-Munich route will continue via the Nuremberg–Erfurt high-speed railway. Only the segment west of Erfurt of the Frankfurt-Dresden line will continue to be used by ICE trains after 2017, with an increased line speed of 200 km/h (currently 160 km/h). Erfurt Hauptbahnhof, Erfurt's central station, which was completely rebuilt for this purpose in the 2000s (decade), will be the new connection between both ICE lines. The most important regional railway lines in Thuringia are the Neudietendorf–Ritschenhausen railway from Erfurt to Würzburg and Meiningen, the Weimar–Gera railway from Erfurt to Chemnitz, the Sangerhausen–Erfurt railway from Erfurt to Magdeburg, the Gotha–Leinefelde railway from Erfurt to Göttingen, the Halle–Kassel railway from Halle via Nordhausen to Kassel and the Leipzig–Hof railway from Leipzig via Altenburg to Zwickau and Hof, Bavaria, Hof. Most regional and local lines have hourly service, but some run only every other hour.
A few small airports are in Thuringia. In public transport is Erfurt–Weimar Airport, used for charter flights to the Mediterranean and other holiday destinations. In private flights, Leipzig–Altenburg Airport is a further key airport.
International hub airports are Frankfurt Airport, Berlin Brandenburg Airport and Munich Airport in adjacent states.
Thuringia is the only state without barge or ship waterways; its rivers are too small to be navigable to them.
Energy and water supply
The traditional energy supply of Thuringia is lignite, mined in the bordering Leipzig region. Since 2000, the importance of environmentally unfriendly lignite combustion has declined in favour of renewable energies, which reached an amount of 40% (in 2013), and more clean gas combustion, often carried out as Cogeneration in the municipal power stations. The most important forms of renewable energies are Wind power and Biomass, followed by Solar energy and Hydroelectricity. Furthermore, Thuringia hosts two big Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, pumped storage stations: theGoldisthal Pumped Storage Station
The Goldisthal Pumped Storage Station is a pumped-storage power station in the Thüringer Mountains at the upper run of the river Schwarza in Goldisthal, Germany. It was constructed between 1997 and 2004. It has an installed capacity of , the la ...
and the Hohenwarte Dam.
The water supply is granted by the big dams, like the Leibis-Lichte Dam
The Leibis-Lichte Dam (german: Talsperre Leibis –Lichte) is a dam in the German state of Thuringia in the Thuringian Highland. The dam was completed in 2005 to impound the River Lichte, between the Lichte municipality section Geiersthal and ...
, within the Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side i ...
and the Thuringian Highland
The Thuringian Highland, Thuringian Highlands or Thuringian-Vogtlandian Slate MountainsKohl, Horst; Marcinek, Joachim and Nitz, Bernhard (1986). ''Geography of the German Democratic Republic'', VEB Hermann Haack, Gotha, p. 7 ff. . (german: Thüring ...
, making a drinking water exporter of Thuringia.
Health
Health care provision in Thuringia improved after 1990, as did the level of general health. Life expectancy rose, nevertheless it is still a bit lower than the German average. This is caused by a relatively unhealthy lifestyle of the Thuringians, especially in high consumption of grains, industrial seed oils, refined carbohydrates and alcohol, which led to significant higher rates of obesity compared to the German average. Health care in Thuringia is currently undergoing a concentration process. Many smaller hospitals in the rural towns are closing, whereas the bigger ones in centres likeJena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
and Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
get enlarged. Overall, there is an oversupply of hospital beds, caused by rationalisation processes in the German health care system, so that many smaller hospitals generate losses. On the other hand, there is a lack of family doctors, especially in rural regions with increased need of health care provision because of overageing.
Education
In Germany, the educational system is part of the sovereignty of the Länder; therefore each Land has its own school and college system.School system
The Thuringian school system was developed after the reunification in 1990, combining some elements of the former GDR school system with theBavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
n school system. Most German school rankings attest that Thuringia has one of the most successful education systems in Germany, resulting in high-quality outcomes.
Early-years education is quite common in Thuringia. Since the 1950s, nearly all children have been using the service, whereas early-years education is less developed in western Germany. Its inventor Friedrich Fröbel lived in Thuringia and founded the world's first Kindergartens there in the 19th century. The Thuringian primary school takes four years and most primary schools are all-day schools offering optional extracurricular activities in the afternoon. At the age of ten, pupils are separated according to aptitude and proceed to either the Gymnasium (Germany), Gymnasium or the Regelschule. The former leads to the Abitur exam after a further eight years and prepares for higher education, while the latter has a more vocational focus and finishes with exams after five or six years, comparable to the Hauptschule and Realschule found elsewhere in Germany.
Universities
 The German higher education system comprises two forms of academic institutions: university, universities and polytechnics (Fachhochschule). The
The German higher education system comprises two forms of academic institutions: university, universities and polytechnics (Fachhochschule). The University of Jena
The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (german: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany.
The un ...
is the biggest amongst Thuringia's four universities and offers nearly every discipline. It was founded in 1558, and today has 21,000 students. The second-largest is the Technische Universität Ilmenau with 7,000 students, founded in 1894, which offers many technical disciplines such as engineering and mathematics. The University of Erfurt
The University of Erfurt (german: Universität Erfurt) is a public university located in Erfurt, the capital city of the German state of Thuringia. It was founded in 1379, and closed in 1816. It was re-established in 1994, three years after Germ ...
, founded in 1392, has 5,000 students today and an emphasis on humanities and teacher training. The Bauhaus University, Weimar, Bauhaus University Weimar with 4,000 students is Thuringia's smallest university, specialising in creative subjects such as architecture and arts. It was founded in 1860 and came to prominence as Germany's leading art school during the inter-war period, the Bauhaus.
The polytechnics of Thuringia are based in Fachhochschule Erfurt, Erfurt (4,500 students), Ernst-Abbe-Fachhochschule Jena, Jena (5,000 students), Nordhausen University of Applied Sciences, Nordhausen (2,500 students) and Fachhochschule Schmalkalden, Schmalkalden (3,000 students). In addition, there is a civil service college in Thüringer Fachhochschule für öffentliche Verwaltung, Gotha with 500 students, the Hochschule für Musik Franz Liszt, Weimar, College of Music "Franz Liszt" in Weimar (800 students) as well as two private colleges, the Adam-Ries-Fachhochschule in Erfurt (500 students) and the SRH College for nursing and allied medical subjects (''SRH Fachhochschule für Gesundheit Gera'') in Gera (500 students). The most recent institution of higher education in Thuringia is the Duale Hochschule Gera-Eisenach (1400 students), a cooperative state college founded in 2016 through a merger of the colleges (''Berufsakademie'') in Gera and Eisenach.
Research
Thuringia's leading research centre isJena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
, followed by Ilmenau. Both focus on technology, in particular life sciences and optics at Jena and information technology at Ilmenau. Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
is a centre of Germany's horticultural research, whereas Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
and Gotha with their various archives and libraries are centres of historic and cultural research. Most of the research in Thuringia is publicly funded basic research due to the lack of large companies able to invest significant amounts in applied research, with the notable exception of the optics sector at Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
.
Personalities
References
External links
Official government site
Official Directory
* *Thuringian flags at *# *# * {{Authority control Thuringia, States of the Weimar Republic NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1920 1952 disestablishments in East Germany States and territories established in 1990 States of Germany Former republics