Tajiks in Bamiyan.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tajiks ( fa, تاجيک، تاجک, ''Tājīk, Tājek''; tg, Тоҷик) are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest
 The Tajiks are an Iranian people, speaking a variety of Persian, concentrated in the Oxus Basin, the Farḡāna valley (Tajikistan and parts of Uzbekistan) and on both banks of the upper Oxus, i.e., the
The Tajiks are an Iranian people, speaking a variety of Persian, concentrated in the Oxus Basin, the Farḡāna valley (Tajikistan and parts of Uzbekistan) and on both banks of the upper Oxus, i.e., the
 According to John Perry ('' Encyclopaedia Iranica''):
According to John Perry ('' Encyclopaedia Iranica''):
 The Tajiks are the principal ethnic group in most of Tajikistan, as well as in northern and western Afghanistan, though there are more Tajiks in Afghanistan than in Tajikistan. Tajiks are a substantial minority in Uzbekistan, as well as in overseas communities. Historically, the ancestors of the Tajiks lived in a larger territory in Central Asia than now.
The Tajiks are the principal ethnic group in most of Tajikistan, as well as in northern and western Afghanistan, though there are more Tajiks in Afghanistan than in Tajikistan. Tajiks are a substantial minority in Uzbekistan, as well as in overseas communities. Historically, the ancestors of the Tajiks lived in a larger territory in Central Asia than now.
 According to the World Factbook, Tajiks make up about 27% of the population in Afghanistan, but according to other sources, they form 37%–39% of the population. According to the Encyclopædia Britannica they constitute about one-fifth of the population. They are predominant in four of the largest cities in Afghanistan ( Kabul, Mazar-e Sharif, Herat, and Ghazni) and make up the largest ethnic group in the northern and western provinces of
According to the World Factbook, Tajiks make up about 27% of the population in Afghanistan, but according to other sources, they form 37%–39% of the population. According to the Encyclopædia Britannica they constitute about one-fifth of the population. They are predominant in four of the largest cities in Afghanistan ( Kabul, Mazar-e Sharif, Herat, and Ghazni) and make up the largest ethnic group in the northern and western provinces of
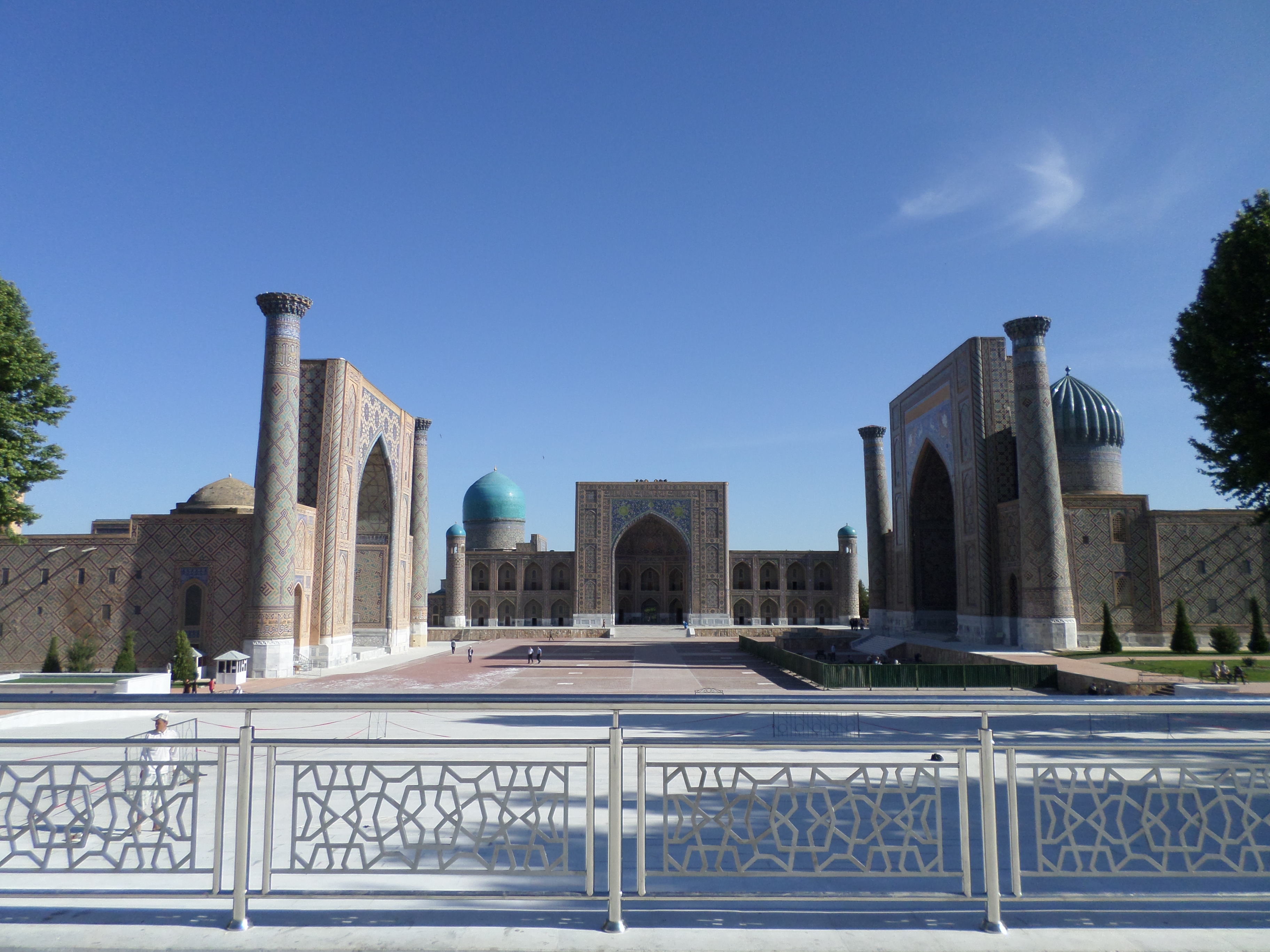 In Uzbekistan, the Tajiks are the largest part of the population of the ancient cities of
In Uzbekistan, the Tajiks are the largest part of the population of the ancient cities of
, ''European Security'', vol. 20, no. 2, Summer 2000.
 The language of the Tajiks is an eastern dialect of Persian, called Dari (derived from ''Darbārī'', " f/from theroyal courts", in the sense of "courtly language"), or also Parsi-e Darbari. In Tajikistan, where
The language of the Tajiks is an eastern dialect of Persian, called Dari (derived from ''Darbārī'', " f/from theroyal courts", in the sense of "courtly language"), or also Parsi-e Darbari. In Tajikistan, where
Turkic Loanwords in Persian
Encyclopædia Iranica. It has also adopted fewer Arabic loan words than Iranian Persian while retaining vocabulary that has fallen out of use in the latter language. In Tajikistan, in ordinary speech, also known as "zaboni kucha" (lit. "street language", as opposed to "zaboni adabi", lit. "literary language", which is used in schools, media etc.), many urban Tajiks prefer to use Russian loanwords instead of their literary Persian analogs. The dialects of modern Persian spoken throughout
 Various scholars have recorded the Zoroastrian,
Various scholars have recorded the Zoroastrian,
Tajiks
at '' Encyclopædia Britannica Online''
Tajik – The Ethnonym: Origins and Application
at '' Encyclopædia Iranica'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Tajik People Ethnic groups in Afghanistan Ethnic groups in Tajikistan Ethnic groups in Uzbekistan Iranian ethnic groups Ethnic groups divided by international borders
ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
in Tajikistan, and the second-largest in Afghanistan and Uzbekistan. They speak varieties of Persian, a Western Iranian language
The Western Iranic languages are a branch of the Iranic languages, attested from the time of Old Persian (6th century BC) and Median.
Languages
The traditional Northwestern branch is a convention for non-Southwestern languages, rather than a ...
. In Tajikistan, since the 1939 Soviet census, its small Pamiri and Yaghnobi ethnic groups are included as Tajiks. In China, the term is used to refer to its Pamiri ethnic groups, the Tajiks of Xinjiang, who speak the Eastern Iranian
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages emerging in Middle Iranian times (from c. the 4th century BC). The Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle Western Iranian diale ...
Pamiri languages. In Afghanistan, the Pamiris are counted as a separate ethnic group.
As a self-designation, the literary New Persian term ''Tajik'', which originally had some previous pejorative usage as a label for eastern Persians or Iranians, has become acceptable during the last several decades, particularly as a result of Soviet administration in Central Asia. Alternative names for the Tajiks are Eastern Persian Eastern Persian or Eastern Farsi may refer to:
* Dari language
Dari (, , ), also known as Dari Persian (, ), is the Variety (linguistics), variety of the Persian language spoken in Afghanistan. Dari is the term officially recognised and promot ...
, Fārsīwān (Persian-speaker), and Dīhgān (cf. tg, Деҳқон) which translates to "farmer or settled villager", in a wider sense "settled" in contrast to "nomadic" and was later used to describe a class of land-owning magnates as " Persian of noble blood" in contrast to Arabs, Turks and Romans during the Sassanid and early Islamic period.
History
 The Tajiks are an Iranian people, speaking a variety of Persian, concentrated in the Oxus Basin, the Farḡāna valley (Tajikistan and parts of Uzbekistan) and on both banks of the upper Oxus, i.e., the
The Tajiks are an Iranian people, speaking a variety of Persian, concentrated in the Oxus Basin, the Farḡāna valley (Tajikistan and parts of Uzbekistan) and on both banks of the upper Oxus, i.e., the Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world ...
(Mountain Badaḵšān, in Tajikistan) and northeastern Afghanistan (Badaḵšān). Historically, the ancient Tajiks were chiefly agriculturalists before the Arab Conquest of Iran
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
The ...
. While agriculture remained a stronghold, the Islamization of Iran also resulted in the rapid urbanization of historical Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
and Transoxiana that lasted until the devastating Mongolian invasion. Several surviving ancient urban centers of the Tajik people include Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, Khujand, and Termez.
Contemporary Tajiks are the descendants of ancient Eastern Iranian inhabitants of Central Asia, in particular, the Sogdia
Sogdia (Sogdian language, Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also ...
ns and the Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
ns, and possibly other groups, with an admixture of Western Iranian Persians and non-Iranian peoples. According to Richard Nelson Frye, a leading historian of Iranian and Central Asian history, the Persian migration to Central Asia may be considered the beginning of the modern Tajik nation, and ethnic Persians, along with some elements of East-Iranian Bactrians and Sogdians, as the main ancestors of modern Tajiks. In later works, Frye expands on the complexity of the historical origins of the Tajiks. In a 1996 publication, Frye explains that many "factors must be taken into account in explaining the evolution of the peoples whose remnants are the Tajiks in Central Asia" and that "the peoples of Central Asia, whether Iranian or Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
speaking, have one culture, one religion, one set of social values and traditions with only language separating them."
Regarding Tajiks, the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' states:
The geographical division between the eastern and western Iranians is often considered historically and currently to be the desert Dasht-e Kavir, situated in the center of the Iranian plateau.
Further according to Richard Foltz:
Modern History
During the Soviet-Afghan War, the Tajik-dominated Jamiat-e Islami founded by Burhanuddin Rabbani resisted the Red Army and the communistAfghan government
The government of Afghanistan, officially called the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is the central government of Afghanistan, a unitary state. Under the leadership of the Taliban, the government is a theocracy and an emirate with political powe ...
. Tajik commander, Ahmad Shah Massoud
)
, branch = Jamiat-e Islami / Shura-e Nazar Afghan Armed Forces United Islamic Front
, serviceyears = 1975–2001
, rank = General
, unit =
, commands = Mujahideen commander during the Soviet–Afghan Wa ...
, successfully repelled nine Soviet campaigns from taking Panjshir Valley and earned the nickname "Lion of Panjshir" ().
Name
The most plausible and generally accepted origin of the word is Middle Persian tāzīk 'Arab' (cf. New Persian tāzi), or an Iranian (Sogdian or Parthian) cognate word. The Muslim armies that invaded Transoxiana early in the eighth century, conquering the Sogdian principalities and clashing with theThe word also occurs in the Tonyukuk inscriptions as ''tözik'', used for a local Arab tribe in the Tashkent area. These Arabs were said to be from the Taz tribe, which is still found in Yemen. In the 7th-century, the Taz began to Islamize Transoxiana. According to the ''Qarluq Turks The Karluks (also Qarluqs, Qarluks, Karluqs, otk, 𐰴𐰺𐰞𐰸, Qarluq, Para-Mongol: Harluut, zh, s=葛逻禄, t=葛邏祿 ''Géluólù'' ; customary phonetic: ''Gelu, Khololo, Khorlo'', fa, خَلُّخ, ''Khallokh'', ar, قارلوق ...(see Bregel, Atlas, Maps 8–10) consisted not only of Arabs, but also of Persian converts from Fārs and the central Zagros region (Bartol'd arthold "Tadžiki," pp. 455–57). Hence the Turks of Central Asia adopted a variant of the Iranian word, täžik, to designate their Muslim adversaries in general. For example, the rulers of the south IndianChalukya dynasty The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynast ...and Rashtrakuta dynasty also referred to the Arabs as "Tajika" in the 8th and 9th century. By the eleventh century ( Yusof Ḵāṣṣ-ḥājeb, Qutadḡu bilig, lines 280, 282, 3265), theQarakhanid Turks The Kara-Khanid Khanate (; ), also known as the Karakhanids, Qarakhanids, Ilek Khanids or the Afrasiabids (), was a Turkic khanate that ruled Central Asia in the 9th through the early 13th century. The dynastic names of Karakhanids and Ilek ...applied this term more specifically to the Persian Muslims in the Oxus basin and Khorasan, who were variously the Turks' rivals, models, overlords (under the Samanid Dynasty), and subjects (from Ghaznavid times on). Persian writers of the Ghaznavid,Seljuq Seljuk or Saljuq (سلجوق) may refer to: * Seljuk Empire (1051–1153), a medieval empire in the Middle East and central Asia * Seljuk dynasty (c. 950–1307), the ruling dynasty of the Seljuk Empire and subsequent polities * Seljuk (warlord) (d ...and Atābak periods (ca. 1000–1260) adopted the term and extended its use to cover Persians in the rest ofGreater Iran Greater Iran ( fa, ایران بزرگ, translit=Irān-e Bozorg) refers to a region covering parts of Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Xinjiang, and the Caucasus, where both Culture of Iran, Iranian culture and Iranian langua ..., now under Turkish rule, as early as the poet ʿOnṣori, ca. 1025 (Dabirsiāqi, pp. 3377, 3408). Iranians soon accepted it as an ethnonym, as is shown by a Persian court official's referring to mā tāzikān "we Tajiks" (Bayhaqi, ed. Fayyāz, p. 594). The distinction between Turk and Tajik became stereotyped to express the symbiosis and rivalry of the (ideally) nomadic military executive and the urban civil bureaucracy (Niẓām al-Molk: tāzik, pp. 146, 178–79; Fragner, "Tādjīk. 2" in EI2 10, p. 63).
Encyclopaedia of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is an encyclopaedia of the academic discipline of Islamic studies published by Brill. It is considered to be the standard reference work in the field of Islamic studies. The first edition was published in ...
'', however, the oldest known usage of the word ''Tajik'' as a reference to Persians in Persian literature can be found in the writings of the Persian poet Jalal ad-Din Rumi. The 15th-century Turkic-speaking poet Mīr Alī Šer Navā'ī also used ''Tajik'' as a reference to Persians.
Location
 The Tajiks are the principal ethnic group in most of Tajikistan, as well as in northern and western Afghanistan, though there are more Tajiks in Afghanistan than in Tajikistan. Tajiks are a substantial minority in Uzbekistan, as well as in overseas communities. Historically, the ancestors of the Tajiks lived in a larger territory in Central Asia than now.
The Tajiks are the principal ethnic group in most of Tajikistan, as well as in northern and western Afghanistan, though there are more Tajiks in Afghanistan than in Tajikistan. Tajiks are a substantial minority in Uzbekistan, as well as in overseas communities. Historically, the ancestors of the Tajiks lived in a larger territory in Central Asia than now.
Tajikistan
Tajiks comprise around 84.3% of the population of Tajikistan. This number includes speakers of the Pamiri languages, including Wakhi and Shughni, and the Yaghnobi people who in the past were considered by the government of the Soviet Union nationalities separate from the Tajiks. In the 1926 and 1937 Soviet censuses, the Yaghnobis and Pamiri language speakers were counted as separate nationalities. After 1937, these groups were required to register as Tajiks.Afghanistan
 According to the World Factbook, Tajiks make up about 27% of the population in Afghanistan, but according to other sources, they form 37%–39% of the population. According to the Encyclopædia Britannica they constitute about one-fifth of the population. They are predominant in four of the largest cities in Afghanistan ( Kabul, Mazar-e Sharif, Herat, and Ghazni) and make up the largest ethnic group in the northern and western provinces of
According to the World Factbook, Tajiks make up about 27% of the population in Afghanistan, but according to other sources, they form 37%–39% of the population. According to the Encyclopædia Britannica they constitute about one-fifth of the population. They are predominant in four of the largest cities in Afghanistan ( Kabul, Mazar-e Sharif, Herat, and Ghazni) and make up the largest ethnic group in the northern and western provinces of Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
, Takhar, Badakhshan, Samangan, Parwan, Panjshir, Kapisa, Baghlan, Ghor, Badghis and Herat.
In Afghanistan, the Tajiks do not organize themselves by tribes and refer to themselves by the region, province, city, town, or village that they are from; such as ''Badakhshi'', ''Baghlani'', ''Mazari'', ''Panjsheri'', ''Kabuli'', ''Herati'', ''Kohistani'', etc. Although in the past, some non- Pashto speaking tribes were identified as Tajik, for example, the Furmuli.
Uzbekistan
Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
and Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, and are found in large numbers in the Surxondaryo Region in the south and along Uzbekistan's eastern border with Tajikistan. According to official statistics (2000), Surxondaryo Region accounts for 24.4% of all Tajiks in Uzbekistan, with another 34.3% in Samarqand and Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
regions.
Official statistics in Uzbekistan state that the Tajik community comprises 5% of the nation's total population. However, these numbers do not include ethnic Tajiks who, for a variety of reasons, choose to identify themselves as Uzbeks in population census forms. During the Soviet "Uzbekization
Uzbekisation or Uzbekization is the process of something or someone culturally non-Uzbek becoming, or being forced to become, Uzbek. The term is often used to describe the process by which the autonomous republic Tajik ASSR was incorporated with ...
" supervised by Sharof Rashidov, the head of the Uzbek Communist Party, Tajiks had to choose either stay in Uzbekistan and get registered as Uzbek in their passports or leave the republic for Tajikistan, which is mountainous and less agricultural. It is only in the last population census (1989) that the nationality could be reported not according to the passport, but freely declared based on the respondent's ethnic self-identification. This had the effect of increasing the Tajik population in Uzbekistan from 3.9% in 1979 to 4.7% in 1989. Some scholars estimate that Tajiks may make up 35% of Uzbekistan's population.Svante E. Cornell, "Uzbekistan: A Regional Player in Eurasian Geopolitics?", ''European Security'', vol. 20, no. 2, Summer 2000.
China
Chinese Tajiks or Mountain Tajiks in China ( Sarikoli: , ''Tujik''; ), including Sarikolis (majority) and Wakhis (minority) in China, are the Pamiri ethnic group that lives in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. They are one of the 56 nationalities officially recognized by the government of the People's Republic of China.Kazakhstan
According to the 1999 population census, there were 26,000 Tajiks in Kazakhstan (0.17% of the total population), about the same number as in the 1989 census.Kyrgyzstan
According toofficial statistics
Official statistics are statistics published by government agencies or other public bodies such as international organizations as a public good. They provide quantitative or qualitative information on all major areas of citizens' lives, such as e ...
, there were about 47,500 Tajiks in Kyrgyzstan in 2007 (0.9% of the total population), up from 42,600 in the 1999 census and 33,500 in the 1989 census.
Turkmenistan
According to the last Soviet census in 1989, there were 3,149 Tajiks in Turkmenistan, or less than 0.1% of the total population of 3.5 million at that time. The first population census of independent Turkmenistan conducted in 1995 showed 3,103 Tajiks in a population of 4.4 million (0.07%), most of them (1,922) concentrated in the eastern provinces ofLebap
Lebap Region ( tk, Lebap welaýaty/Лебап велаяты from the Persian ''Lab-e āb'') is one of the regions of Turkmenistan. It is in the northeast of the country, bordering Afghanistan, Uzbekistan along the Amu Darya. Its capital is T ...
and Mary adjoining the borders with Afghanistan and Uzbekistan.
Russia
The population of Tajiks in Russia was about 200,303 according to the 2010 census, up from 38,000 in the last Soviet census of 1989. Most Tajiks came to Russia after thedissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, often as guest workers in places like Moscow and Saint Petersburg or federal subjects near the Kazakhstan border. There are currently estimated to be over one million Tajik guest workers living in Russia, with their remittances accounting for as much as half of Tajikistan's economy.
Pakistan
There are an estimated 220,000Tajiks in Pakistan
Tajiks in Pakistan are residents of Pakistan who are of Tajik ancestry. The Tajiks are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
There are also Afghan Tajiks refu ...
as of 2012, mainly refugees from Afghanistan.The ethnic composition of the 1.7 million registered Afghan refugees living in Pakistan are believed to be 85% Pashtun and 15% Tajik, Uzbek and others. During the 1990s, as a result of the Tajikistan Civil War
The Tajikistani Civil War ( tg, Ҷанги шаҳрвандии Тоҷикистон, translit=Jangi shahrvandiyi Tojikiston / Çangi shahrvandiji Toçikiston; russian: Гражданская война в Таджикистане), also known ...
, between 700 and 1,200 Tajikistanis arrived in Pakistan, mainly as students, the children of Tajikistani refugees in Afghanistan. In 2002, around 300 requested to return home and were repatriated back to Tajikistan with the help of the IOM, UNHCR and the two countries' authorities.
Genetics
The dominant haplogroup among modern Tajiks is the Haplogroup R1a Y-DNA. ~45% of Tajik men share R1a (M17), ~18% J (M172), ~8% R2 (M124), and ~8% C (M130 & M48). Tajiks of Panjikent score 68% R1a, Tajiks of Khojant score 64% R1a. The high frequency of haplogroup R1a in the Tajiks probably reflects a strongfounder effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
. According to another genetic test, 63% of Tajik male samples from Tajikistan carry R1a.
An autosomal DNA study by Guarino-Vignon et al. 2022, analyzing 5019 individuals (3102 ancient and 1915 modern), revealed that Iranian peoples, specifically the Tajiks and Yaghnobis
The Yaghnobi people ( Yaghnobi: yaγnōbī́t or suγdī́t; tg, яғнобиҳо, yağnobiho/jaƣnoʙiho) are an Iranian ethnic minority in Tajikistan. They inhabit Tajikistan's Sughd province in the valleys of the Yaghnob, Qul and Varzob riv ...
, show strong genetic continuity with ancient Indo-Iranian samples from pre-Turkic Central Asia, including Iron Age samples from Turkmenistan. The authors found that Tajiks stayed largely unaffected by outside geneflow, and show continuity with ancient Indo-Iranian samples from Tajikistan and from modern Turkmenistan since the Iron Age, but have slightly higher affinity with "Baikal hunter-gatherers" and "South Asians" than Ancient Central Asian samples. In conclusion the authors summarized that Tajiks display "''a long-term continuity since the Iron Age with only limited recent impulses from other Eurasian groups''".
Culture
Language
 The language of the Tajiks is an eastern dialect of Persian, called Dari (derived from ''Darbārī'', " f/from theroyal courts", in the sense of "courtly language"), or also Parsi-e Darbari. In Tajikistan, where
The language of the Tajiks is an eastern dialect of Persian, called Dari (derived from ''Darbārī'', " f/from theroyal courts", in the sense of "courtly language"), or also Parsi-e Darbari. In Tajikistan, where Cyrillic
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = G ...
script is used, it is called the Tajiki language
Tajik (Tajik: , , ), also called Tajiki Persian (Tajik: , , ) or Tajiki, is the variety of Persian spoken in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan by Tajiks. It is closely related to neighbouring Dari with which it forms a continuum of mutually intelligible ...
. In Afghanistan, unlike in Tajikistan, Tajiks continue to use the Perso-Arabic script, as well as in Iran. However, when the Soviet Union introduced the Latin script in 1928, and later the Cyrillic script, the Persian dialect of Tajikistan came to be considered a separate (Persian) language. Since the 19th century, Tajiki has been strongly influenced by the Russian language and has incorporated many Russian language loan words
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because the ...
.Michael KnüppelTurkic Loanwords in Persian
Encyclopædia Iranica. It has also adopted fewer Arabic loan words than Iranian Persian while retaining vocabulary that has fallen out of use in the latter language. In Tajikistan, in ordinary speech, also known as "zaboni kucha" (lit. "street language", as opposed to "zaboni adabi", lit. "literary language", which is used in schools, media etc.), many urban Tajiks prefer to use Russian loanwords instead of their literary Persian analogs. The dialects of modern Persian spoken throughout
Greater Iran
Greater Iran ( fa, ایران بزرگ, translit=Irān-e Bozorg) refers to a region covering parts of Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Xinjiang, and the Caucasus, where both Culture of Iran, Iranian culture and Iranian langua ...
have a common origin. This is due to the fact that one of Greater Iran
Greater Iran ( fa, ایران بزرگ, translit=Irān-e Bozorg) refers to a region covering parts of Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Xinjiang, and the Caucasus, where both Culture of Iran, Iranian culture and Iranian langua ...
's historical cultural capitals, called Greater Khorasan, which included parts of modern Central Asia and much of Afghanistan and constitutes as the Tajik's ancestral homeland, played a key role in the development and propagation of Persian language and culture throughout much of Greater Iran
Greater Iran ( fa, ایران بزرگ, translit=Irān-e Bozorg) refers to a region covering parts of Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Xinjiang, and the Caucasus, where both Culture of Iran, Iranian culture and Iranian langua ...
after the Muslim conquest. Furthermore, early manuscripts of the historical Persian spoken in Mashhad
Mashhad ( fa, مشهد, Mašhad ), also spelled Mashad, is the List of Iranian cities by population, second-most-populous city in Iran, located in the relatively remote north-east of the country about from Tehran. It serves as the capital of R ...
during the development of Middle to New Persian show that their origins came from Sistan, in present-day Afghanistan.
Religion
 Various scholars have recorded the Zoroastrian,
Various scholars have recorded the Zoroastrian, Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, and Buddhist pre-Islamic heritage of the Tajik people. Early temples for fire worship have been found in Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
and Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
and excavations in present-day Tajikistan and Uzbekistan show remnants of Zoroastrian fire temples.
Today, however, the great majority of Tajiks follow Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
, although small Twelver and Ismaili
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-Sa ...
Shia minorities also exist in scattered pockets. Areas with large numbers of Shias include Herat, Badakhshan provinces in Afghanistan, the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Province in Tajikistan, and Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County
Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County (also known as Taxkorgan County, sometimes spelled Tashkurgan, Tashkorgan and Tash Kurghan Tadzhik Autonomous Hsien) is an autonomous county of Kashgar Prefecture in Western Xinjiang, China. The county seat is t ...
in China. Some of the famous Islamic scholars were from either modern or historical East-Iranian regions lying in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan and therefore can arguably be viewed as Tajiks. They include Abu Hanifa
Nuʿmān ibn Thābit ibn Zūṭā ibn Marzubān ( ar, نعمان بن ثابت بن زوطا بن مرزبان; –767), commonly known by his '' kunya'' Abū Ḥanīfa ( ar, أبو حنيفة), or reverently as Imam Abū Ḥanīfa by Sunni Mus ...
, Imam Bukhari, Tirmidhi, Abu Dawood, Nasir Khusraw and many others.
According to a 2009 U.S. State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other nati ...
release, the population of Tajikistan is 98% Muslim, (approximately 85% Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
and 5% Shia). In Afghanistan, the great number of Tajiks adhere to Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
. The smaller number of Tajiks who may follow Twelver Shia Islam are locally called Farsiwan
Fārsīwān (Pashto/ fa, فارسیوان or its regional forms: Pārsīwān or Pārsībān,The ''Encyc. Iranica'' makes clear in the article on Afghanistan — Ethnography that "The term Farsiwan also has the regional forms Parsiwan and Pars ...
. The community of Bukharian Jews in Central Asia speak a dialect of Persian. The Bukharian Jewish community in Uzbekistan is the largest remaining community of Central Asian Jews and resides primarily in Bukhara and Samarkand, while the Bukharaian Jews of Tajikistan live in Dushanbe and number only a few hundred. From the 1970s to the 1990s the majority of these Tajik-speaking Jews emigrated to the United States and to Israel in accordance with Aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel ...
. Recently, the Protestant community of Tajiks descent has experienced significant growth, a 2015 study estimates some 2,600 Muslim Tajik converted to Christianity.
Tajikistan marked 2009 as the year to commemorate the Tajik Sunni Muslim jurist Abu Hanifa
Nuʿmān ibn Thābit ibn Zūṭā ibn Marzubān ( ar, نعمان بن ثابت بن زوطا بن مرزبان; –767), commonly known by his '' kunya'' Abū Ḥanīfa ( ar, أبو حنيفة), or reverently as Imam Abū Ḥanīfa by Sunni Mus ...
, whose ancestry hailed from Parwan Province of Afghanistan, as the nation hosted an international symposium that drew scientific and religious leaders. The construction of one of the largest mosques in the world, funded by Qatar, was announced in October 2009. The mosque is planned to be built in Dushanbe and construction is said to be completed by 2014.
Recent developments
Cultural revival
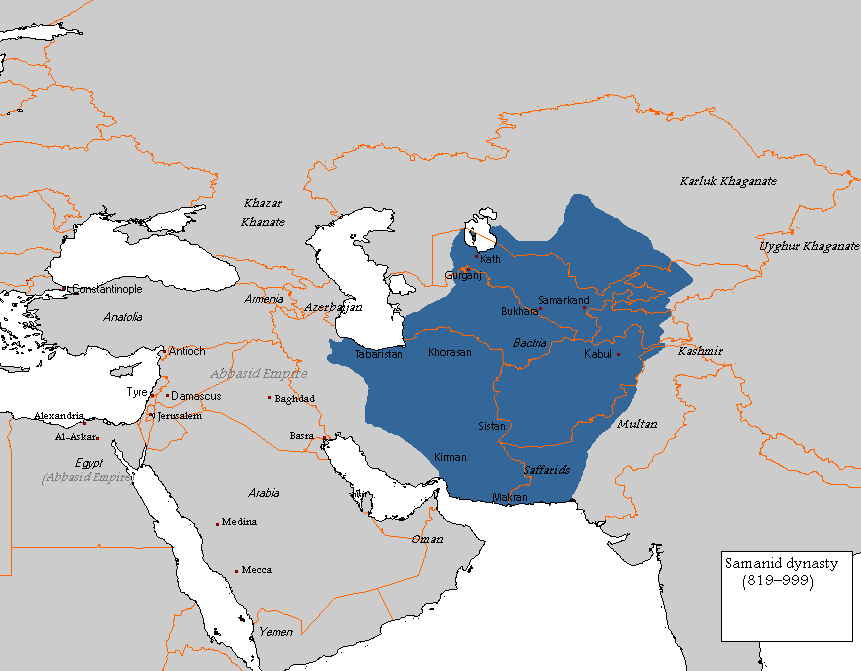
The collapse of the Soviet Union and the Civil War in Afghanistan both gave rise to a resurgence in Tajik nationalism across the region, including a trial to revert to the Perso-Arabic script in Tajikistan. Furthermore, Tajikistan in particular has been a focal point for this movement, and the government there has made a conscious effort to revive the legacy of theSamanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin. The empire was centred in Kho ...
empire, the first Tajik-dominated state in the region after the Arab advance. For instance, the President of Tajikistan, Emomalii Rahmon, dropped the Russian suffix "-ov" from his surname and directed others to adopt Tajik names when registering births. According to a government announcement in October 2009, approximately 4,000 Tajik nationals have dropped "ov" and "ev" from their surnames since the start of the year.
In September 2009, the Islamic Renaissance Party of Tajikistan proposed a draft law to have the nation's language referred to as "Tajiki-Farsi" rather than "Tajik." The proposal drew criticism from Russian media since the bill sought to remove the Russian language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European langua ...
as Tajikistan's inter-ethnic ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
''. In 1989, the original name of the language (Farsi) had been added to its official name in brackets, though Rahmon's government renamed the language to simply "Tajiki" in 1994. On 6 October 2009, Tajikistan adopted the law that removes Russian as the ''lingua franca'' and mandated Tajik as the language to be used in official documents and education, with an exception for members Tajikistan's ethnic minority groups, who would be permitted to receive an education in the language of their choosing.
See also
*Bukharan Jews
Bukharan Jews ( Bukharian: יהודיאני בוכארא/яҳудиёни Бухоро, ''Yahudiyoni Bukhoro''; he, יהודי בוכרה, ''Yehudey Bukhara''), in modern times also called Bukharian Jews ( Bukharian: יהודיאני בוכאר ...
* Farsiwan
Fārsīwān (Pashto/ fa, فارسیوان or its regional forms: Pārsīwān or Pārsībān,The ''Encyc. Iranica'' makes clear in the article on Afghanistan — Ethnography that "The term Farsiwan also has the regional forms Parsiwan and Pars ...
* Persian people
* Chagatai Tajiks
* Kharduri Tajiks
* Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County
Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County (also known as Taxkorgan County, sometimes spelled Tashkurgan, Tashkorgan and Tash Kurghan Tadzhik Autonomous Hsien) is an autonomous county of Kashgar Prefecture in Western Xinjiang, China. The county seat is t ...
* Tajiks of Xinjiang
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
*Tajiks
at '' Encyclopædia Britannica Online''
Tajik – The Ethnonym: Origins and Application
at '' Encyclopædia Iranica'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Tajik People Ethnic groups in Afghanistan Ethnic groups in Tajikistan Ethnic groups in Uzbekistan Iranian ethnic groups Ethnic groups divided by international borders