TVA phosphate smelting furnace.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) is a federally owned
 The Tennessee Valley Authority is a government-owned
The Tennessee Valley Authority is a government-owned
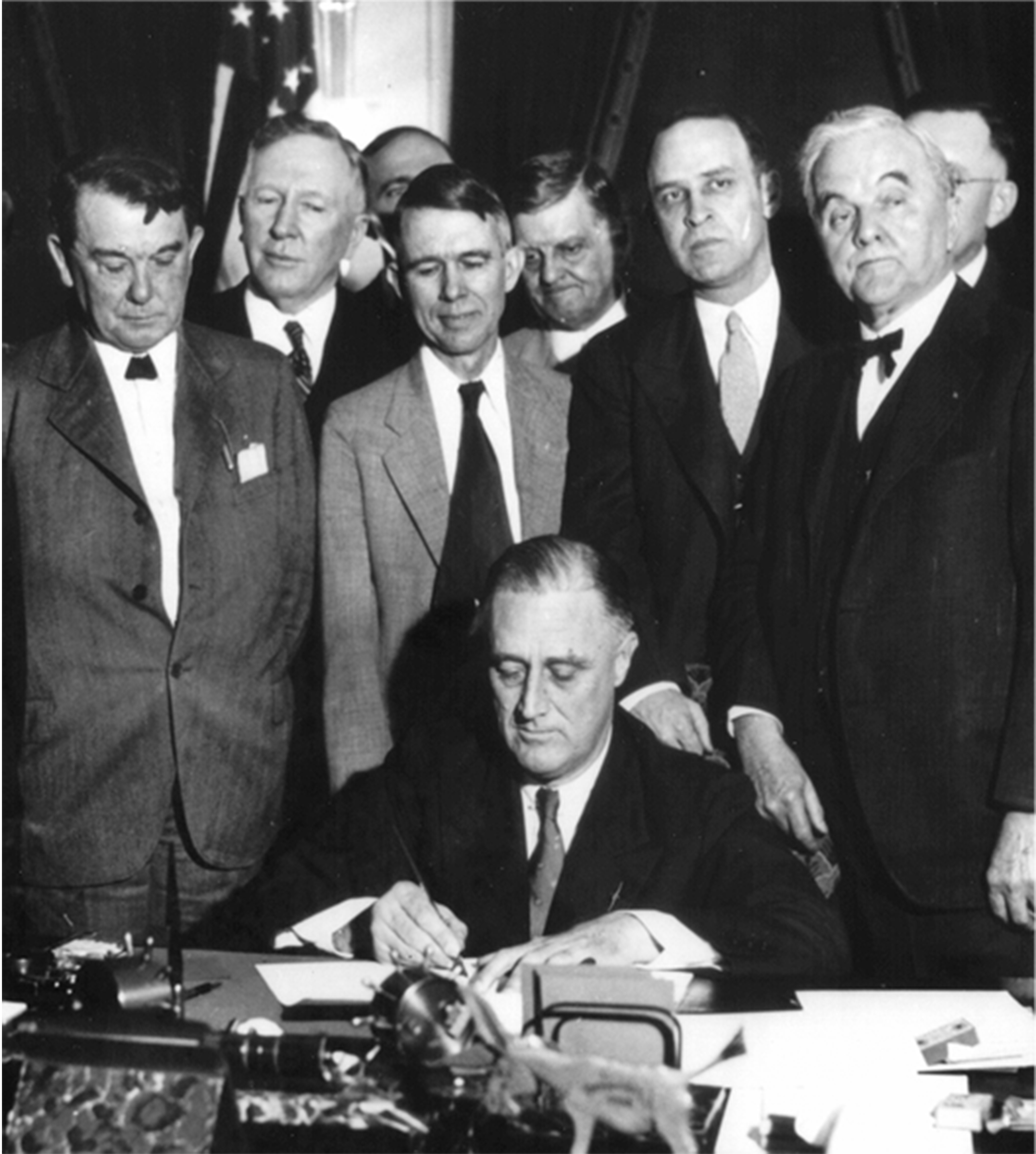 President Franklin Delano Roosevelt signed the Tennessee Valley Authority Act of Congress, Act (ch. 32, , codified as amended at , et seq.), creating the TVA. The agency was initially tasked with modernizing the region, using experts and electricity to combat human and economic problems. TVA developed fertilizers, and taught farmers ways to improve crop yields. In addition, it helped replant forests, control forest fires, and improve habitat for fish and wildlife.
The Authority hired many of the area's unemployed for a variety of jobs: they conducted habitat conservation, conservation, economic development, and social programs. For instance, a library service was instituted for this area. The professional staff at headquarters were generally composed of experts from outside the region. By 1934, TVA employed more than 9,000 people. The workers were classified by the usual racial and gender lines of the region, which limited opportunities for minorities and women. TVA hired a few African Americans, generally restricted for janitorial or other low-level positions. TVA recognized labor unions; its skilled and semi-skilled blue collar employees were unionized, a breakthrough in an area known for corporations hostile to miners' and textile workers' unions. Women were excluded from construction work.
President Franklin Delano Roosevelt signed the Tennessee Valley Authority Act of Congress, Act (ch. 32, , codified as amended at , et seq.), creating the TVA. The agency was initially tasked with modernizing the region, using experts and electricity to combat human and economic problems. TVA developed fertilizers, and taught farmers ways to improve crop yields. In addition, it helped replant forests, control forest fires, and improve habitat for fish and wildlife.
The Authority hired many of the area's unemployed for a variety of jobs: they conducted habitat conservation, conservation, economic development, and social programs. For instance, a library service was instituted for this area. The professional staff at headquarters were generally composed of experts from outside the region. By 1934, TVA employed more than 9,000 people. The workers were classified by the usual racial and gender lines of the region, which limited opportunities for minorities and women. TVA hired a few African Americans, generally restricted for janitorial or other low-level positions. TVA recognized labor unions; its skilled and semi-skilled blue collar employees were unionized, a breakthrough in an area known for corporations hostile to miners' and textile workers' unions. Women were excluded from construction work.
 Many local landowners were suspicious of government agencies, but TVA successfully introduced new agricultural methods into traditional farming communities by blending in and finding local champions. Tennessee farmers often rejected advice from TVA officials, so the officials had to find leaders in the communities and convince them that crop rotation and the judicious application of fertilizers could restore soil fertility. Once they had convinced the leaders, the rest followed.
TVA immediately embarked on the construction of several hydroelectric dams, with the first, Norris Dam in upper East Tennessee, breaking ground on October 1, 1933. These facilities, designed with the intent of also controlling floods, greatly improved the lives of farmers and rural residents, making their lives easier and farms in the Tennessee Valley more productive. They also provided new employment opportunities to the poverty-stricken regions in the Valley. At the same time, however, they required the Development-induced displacement, displacement of more than 125,000 valley residents or roughly 15,000 families, as well as some cemeteries and small towns, which caused some to oppose the projects, especially in rural areas. The projects also inundated several Native Americans in the United States, Native American archaeological sites, and graves were reinterred at new locations, along with new tombstones.
The available electricity attracted new industries to the region, including textile factory, mills, providing desperately needed jobs, many of which were filled by women. A few regions of the Tennessee Valley did not receive electricity until the late 1940s and early 1950s, however. TVA was one of the first federal hydropower agencies, and was quickly hailed as a success. While most of the nation's major hydropower systems are federally managed today, other attempts to create similar regional corporate agencies have failed. The most notable was the proposed Columbia Valley Authority for the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest, which was modeled off of TVA, but did not gain approval.
Many local landowners were suspicious of government agencies, but TVA successfully introduced new agricultural methods into traditional farming communities by blending in and finding local champions. Tennessee farmers often rejected advice from TVA officials, so the officials had to find leaders in the communities and convince them that crop rotation and the judicious application of fertilizers could restore soil fertility. Once they had convinced the leaders, the rest followed.
TVA immediately embarked on the construction of several hydroelectric dams, with the first, Norris Dam in upper East Tennessee, breaking ground on October 1, 1933. These facilities, designed with the intent of also controlling floods, greatly improved the lives of farmers and rural residents, making their lives easier and farms in the Tennessee Valley more productive. They also provided new employment opportunities to the poverty-stricken regions in the Valley. At the same time, however, they required the Development-induced displacement, displacement of more than 125,000 valley residents or roughly 15,000 families, as well as some cemeteries and small towns, which caused some to oppose the projects, especially in rural areas. The projects also inundated several Native Americans in the United States, Native American archaeological sites, and graves were reinterred at new locations, along with new tombstones.
The available electricity attracted new industries to the region, including textile factory, mills, providing desperately needed jobs, many of which were filled by women. A few regions of the Tennessee Valley did not receive electricity until the late 1940s and early 1950s, however. TVA was one of the first federal hydropower agencies, and was quickly hailed as a success. While most of the nation's major hydropower systems are federally managed today, other attempts to create similar regional corporate agencies have failed. The most notable was the proposed Columbia Valley Authority for the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest, which was modeled off of TVA, but did not gain approval.

 By the end of World War II, TVA had completed a navigation channel the length of the Tennessee River and had become the nation's largest electricity supplier. Even so, the demand for electricity was outstripping TVA's capacity to produce power from Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dams, and so TVA began to construct additional coal-fired plants. Political interference kept TVA from securing additional federal appropriations to do so, so it sought the authority to issue bonds. Several of TVA's coal-fired plants, including Johnsonville Fossil Plant, Johnsonville, Widows Creek Fossil Plant, Widows Creek, Shawnee Fossil Plant, Shawnee, Kingston Fossil Plant, Kingston, Gallatin Fossil Plant, Gallatin, and John Sevier Fossil Plant, John Sevier, began operations in the 1950s. In 1955 coal surpassed hydroelectricity as TVA's top generating source. On August 6, 1959, President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed into law an amendment to the TVA act, making the agency self-financing. During the 1950s, TVA's generating capacity nearly quadrupled.
The 1960s were years of further unprecedented economic growth in the Tennessee Valley. Capacity growth during this time slowed, but ultimately increased 56% between 1960 and 1970. To handle a projected future increase in electrical consumption, TVA began constructing 500 kilovolt (kV) transmission lines, the first of which was placed into service on May 15, 1965. Electric rates were among the nation's lowest during this time and stayed low as TVA brought larger, more efficient generating units into service. Plants completed during this time included Paradise Combined Cycle Plant#History, Paradise, Bull Run Fossil Plant, Bull Run, and Nickajack Dam. Expecting the Valley's electric power needs to continue to grow, TVA began building nuclear power in the United States, nuclear power plants in 1966 as a new source of power. During the 1960s and 1970s, TVA was engaged in what was up to that time its most controversial project – the Tellico Dam Project. The project was initially conceived in the 1940s but not completed until 1979.
By the end of World War II, TVA had completed a navigation channel the length of the Tennessee River and had become the nation's largest electricity supplier. Even so, the demand for electricity was outstripping TVA's capacity to produce power from Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dams, and so TVA began to construct additional coal-fired plants. Political interference kept TVA from securing additional federal appropriations to do so, so it sought the authority to issue bonds. Several of TVA's coal-fired plants, including Johnsonville Fossil Plant, Johnsonville, Widows Creek Fossil Plant, Widows Creek, Shawnee Fossil Plant, Shawnee, Kingston Fossil Plant, Kingston, Gallatin Fossil Plant, Gallatin, and John Sevier Fossil Plant, John Sevier, began operations in the 1950s. In 1955 coal surpassed hydroelectricity as TVA's top generating source. On August 6, 1959, President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed into law an amendment to the TVA act, making the agency self-financing. During the 1950s, TVA's generating capacity nearly quadrupled.
The 1960s were years of further unprecedented economic growth in the Tennessee Valley. Capacity growth during this time slowed, but ultimately increased 56% between 1960 and 1970. To handle a projected future increase in electrical consumption, TVA began constructing 500 kilovolt (kV) transmission lines, the first of which was placed into service on May 15, 1965. Electric rates were among the nation's lowest during this time and stayed low as TVA brought larger, more efficient generating units into service. Plants completed during this time included Paradise Combined Cycle Plant#History, Paradise, Bull Run Fossil Plant, Bull Run, and Nickajack Dam. Expecting the Valley's electric power needs to continue to grow, TVA began building nuclear power in the United States, nuclear power plants in 1966 as a new source of power. During the 1960s and 1970s, TVA was engaged in what was up to that time its most controversial project – the Tellico Dam Project. The project was initially conceived in the 1940s but not completed until 1979.
 Significant changes occurred in the economy of the Tennessee Valley and the nation, prompted by energy crises in 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 and accelerating fuel costs throughout the decade. The average cost of electricity in the Tennessee Valley increased fivefold from the early 1970s to the early 1980s. TVA's first nuclear reactor, Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Browns Ferry Unit 1, began commercial operation on August 1, 1974. In the early 1970s, TVA set out to construct a total of 17 nuclear reactors, due to a projection of further rapid increase in power demand. However, in the 1980s, ten of these reactors were cancelled. On August 6, 1981, the Tennessee Valley Authority Board voted to defer the Phipps Bend Nuclear Plant, Phipps Bend plant, as well as to slow down construction on all other projects. The Hartsville Nuclear Plant, Hartsville and Yellow Creek Nuclear Plant, Yellow Creek plants were cancelled in 1984 and Bellefonte Nuclear Plant, Bellefonte in 1988.
Significant changes occurred in the economy of the Tennessee Valley and the nation, prompted by energy crises in 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 and accelerating fuel costs throughout the decade. The average cost of electricity in the Tennessee Valley increased fivefold from the early 1970s to the early 1980s. TVA's first nuclear reactor, Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Browns Ferry Unit 1, began commercial operation on August 1, 1974. In the early 1970s, TVA set out to construct a total of 17 nuclear reactors, due to a projection of further rapid increase in power demand. However, in the 1980s, ten of these reactors were cancelled. On August 6, 1981, the Tennessee Valley Authority Board voted to defer the Phipps Bend Nuclear Plant, Phipps Bend plant, as well as to slow down construction on all other projects. The Hartsville Nuclear Plant, Hartsville and Yellow Creek Nuclear Plant, Yellow Creek plants were cancelled in 1984 and Bellefonte Nuclear Plant, Bellefonte in 1988.
 Construction of the Tellico Dam became controversial for political and environmental reasons, as laws had changed since early development in the valley. Scientists and other researchers had become more aware of the massive environmental effects of the dams and new lakes, and worried about preserving habitats and species. The Tellico Dam project was initially delayed because of concern over the snail darter, a threatened species. A lawsuit was filed under the Endangered Species Act and the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of protecting the snail darter in ''Tennessee Valley Authority v. Hill'' in 1978. The project also received controversy regarding the intent of the dam, as the project's main motive was to support recreational and tourism development, unlike earlier dams constructed by TVA. Land acquired by eminent domain for the Tellico Dam and its reservoir, specifically land that encountered minimal inundation, was sold to private developers for the construction of present-day Tellico Village, Tennessee, Tellico Village, a Planned community, planned retirement community.
The cancellation of several of the planned nuclear plants put the agency in deep financial trouble. Marvin T. Runyon became chairman of the TVA in January 1988. During his four-year tenure he claimed to reduce management layers, cut overhead costs by more than 30%, and achieved cumulative savings and efficiency improvements of $1.8 billion. He also claimed to have revitalized the nuclear program and instituted a rate freeze that continued for ten years.
Construction of the Tellico Dam became controversial for political and environmental reasons, as laws had changed since early development in the valley. Scientists and other researchers had become more aware of the massive environmental effects of the dams and new lakes, and worried about preserving habitats and species. The Tellico Dam project was initially delayed because of concern over the snail darter, a threatened species. A lawsuit was filed under the Endangered Species Act and the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of protecting the snail darter in ''Tennessee Valley Authority v. Hill'' in 1978. The project also received controversy regarding the intent of the dam, as the project's main motive was to support recreational and tourism development, unlike earlier dams constructed by TVA. Land acquired by eminent domain for the Tellico Dam and its reservoir, specifically land that encountered minimal inundation, was sold to private developers for the construction of present-day Tellico Village, Tennessee, Tellico Village, a Planned community, planned retirement community.
The cancellation of several of the planned nuclear plants put the agency in deep financial trouble. Marvin T. Runyon became chairman of the TVA in January 1988. During his four-year tenure he claimed to reduce management layers, cut overhead costs by more than 30%, and achieved cumulative savings and efficiency improvements of $1.8 billion. He also claimed to have revitalized the nuclear program and instituted a rate freeze that continued for ten years.
 As the electric-utility industry moved toward restructuring and deregulation, TVA began preparing for competition. It cut operating costs by nearly $800 million a year, reduced its workforce by more than half, increased the generating capacity of its plants, and developed a plan to meet the energy needs of the Tennessee Valley through the year 2020.
In 1996, Watts Bar Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Watts Bar Unit 1 began operation. This was the last commercial nuclear reactor in the United States to begin operation in the 20th century. In 2002, TVA began work to restart a previously mothballed nuclear reactor at Browns Ferry Nuclear Power Plant, Browns Ferry Unit 1, which was completed in May 2007. In 2004, TVA implemented recommendations from the Reservoir Operations Study (ROS) on how it operates the Tennessee River system (the nation's fifth largest). In 2005, the TVA announced its intention to construct an Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor at its Bellefonte Nuclear Generating Station, Bellefonte site in Alabama, filing the necessary applications in November 2007. In 2007 it announced plans to complete the unfinished Unit 2 at Watts Bar Nuclear Plant, Watts Bar, which began commercial operation in October 2016. Watts Bar Unit 2 is the first, and so far only, new nuclear reactor to enter service in the United States in the 21st century.
On December 22, 2008, an earthen dike at TVA's Kingston Fossil Plant broke, Kingston Fossil Plant coal fly ash slurry spill, spreading one billion gallons of wet coal ash across of land and into the tributaries of the Tennessee River. This produced damage from high levels of metal in the river. The TVA Office of the Inspector General's report, ''Inspection 2008-12283-02, Review of the Kingston Fossil Plant Ash Spill Cause Study and Observations About Ash Management,'' concluded that TVA culture had contributed to the spill.
In 2009, to gain more access to sustainable, green energy, TVA signed 20-year power purchase agreements with Maryland-based CVP Renewable Energy Co. and Chicago-based Invenergy Wind LLC for electricity generated by wind farms. In April 2011, TVA reached an agreement with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), four state governments, and three environmental groups to drastically reduce pollution and carbon emissions. Under the terms of the agreement, TVA was required to retire at least 18 of its 59 coal-fired units by the end of 2018, and install scrubbers in several others or convert them to make them cleaner, at a cost of $25 billion, by 2021. As a result, TVA closed several of its coal-fired power plants in the 2010s, converting some to natural gas. These include John Sevier in 2012, Shawnee Unit 10 in 2014, Widows Creek in 2015, Colbert in 2016, Johnsonville and Paradise Units 1 and 2 in 2017, Allen in 2018, and Paradise Unit 3 in 2020.
As the electric-utility industry moved toward restructuring and deregulation, TVA began preparing for competition. It cut operating costs by nearly $800 million a year, reduced its workforce by more than half, increased the generating capacity of its plants, and developed a plan to meet the energy needs of the Tennessee Valley through the year 2020.
In 1996, Watts Bar Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Watts Bar Unit 1 began operation. This was the last commercial nuclear reactor in the United States to begin operation in the 20th century. In 2002, TVA began work to restart a previously mothballed nuclear reactor at Browns Ferry Nuclear Power Plant, Browns Ferry Unit 1, which was completed in May 2007. In 2004, TVA implemented recommendations from the Reservoir Operations Study (ROS) on how it operates the Tennessee River system (the nation's fifth largest). In 2005, the TVA announced its intention to construct an Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor at its Bellefonte Nuclear Generating Station, Bellefonte site in Alabama, filing the necessary applications in November 2007. In 2007 it announced plans to complete the unfinished Unit 2 at Watts Bar Nuclear Plant, Watts Bar, which began commercial operation in October 2016. Watts Bar Unit 2 is the first, and so far only, new nuclear reactor to enter service in the United States in the 21st century.
On December 22, 2008, an earthen dike at TVA's Kingston Fossil Plant broke, Kingston Fossil Plant coal fly ash slurry spill, spreading one billion gallons of wet coal ash across of land and into the tributaries of the Tennessee River. This produced damage from high levels of metal in the river. The TVA Office of the Inspector General's report, ''Inspection 2008-12283-02, Review of the Kingston Fossil Plant Ash Spill Cause Study and Observations About Ash Management,'' concluded that TVA culture had contributed to the spill.
In 2009, to gain more access to sustainable, green energy, TVA signed 20-year power purchase agreements with Maryland-based CVP Renewable Energy Co. and Chicago-based Invenergy Wind LLC for electricity generated by wind farms. In April 2011, TVA reached an agreement with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), four state governments, and three environmental groups to drastically reduce pollution and carbon emissions. Under the terms of the agreement, TVA was required to retire at least 18 of its 59 coal-fired units by the end of 2018, and install scrubbers in several others or convert them to make them cleaner, at a cost of $25 billion, by 2021. As a result, TVA closed several of its coal-fired power plants in the 2010s, converting some to natural gas. These include John Sevier in 2012, Shawnee Unit 10 in 2014, Widows Creek in 2015, Colbert in 2016, Johnsonville and Paradise Units 1 and 2 in 2017, Allen in 2018, and Paradise Unit 3 in 2020.
 In 2018, TVA opened a new cybersecurity center in its downtown Chattanooga Office Complex. More than 20 Information Technology specialists monitor emails, Twitter feeds and network activity for cybersecurity threats and threats to grid security. Across TVA's digital platform, 2 billion activities occur each day. The center is staffed 24 hours a day to spot any threats to TVA's 16,000 miles of transmission lines.
Given continued economic pressure on the coal industry, the TVA board defied President Donald Trump and voted in February 2019 to close two aging coal plants, Paradise 3 and Bull Run. TVA chief executive William D. Johnson (CEO), Bill Johnson said the decision was not about coal, per se, but rather "about keeping rates as low as feasible." The TVA stated that decommissioning the two plants would reduce its carbon output by about 4.4% annually. TVA announced in April 2021 plans to completely phase out coal power by 2035. The following month, the TVA board voted to consider replacing almost all of their operating coal facilities with combined-cycle gas plants. Such plants considered for gas plant redevelopment include the Cumberland, Gallatin, Shawanee, and Kingston facilities.
In early February 2020, TVA awarded an outside company, Framatome, several multi-million-dollar contracts for work across the company's reactor fleet. This includes fuel for the Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, fuel handling equipment upgrades across the fleet and Steam generator (nuclear power), steam generator replacements at the Watts Bar Nuclear Plant. Framatome will provide its state-of-the-art ATRIUM 11 fuel for the three boiling water reactors at Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, Browns Ferry with the first use planned for 2023. This contract makes TVA the third U.S. utility to switch to the ATRIUM 11 fuel design. On August 3, 2020, president Donald Trump fired the TVA chairman and another board member, saying they were overpaid and had Outsourcing, outsourced 200 high-tech jobs. The move came after U.S. Tech Workers, a nonprofit that works to limit visas given to foreign technology workers, criticized the TVA for laying off its own workers and replacing them with contractors using foreign workers with H-1B visas.
Citing its plan to reach net-zero carbon emissions in 2050, the TVA Board voted to approve an advanced approach of nuclear energy technology with an estimated $200 million investment, known as the New Nuclear Program (NNP) in February 2022. The NNP would promote the construction of new nuclear power facilities, particularly small modular reactors, with the first facility being constructed in partnership with Oak Ridge National Laboratory at the Clinch River Breeder Reactor Project, Clinch River Nuclear Site in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, Oak Ridge.
On December 23, 2022 TVA had several hours of rolling blackouts due to the Late December 2022 North American winter storm. As many as 24,000 Nashville Electric Service customers were without power, with thousands more from smaller distributors affected as well.
In 2018, TVA opened a new cybersecurity center in its downtown Chattanooga Office Complex. More than 20 Information Technology specialists monitor emails, Twitter feeds and network activity for cybersecurity threats and threats to grid security. Across TVA's digital platform, 2 billion activities occur each day. The center is staffed 24 hours a day to spot any threats to TVA's 16,000 miles of transmission lines.
Given continued economic pressure on the coal industry, the TVA board defied President Donald Trump and voted in February 2019 to close two aging coal plants, Paradise 3 and Bull Run. TVA chief executive William D. Johnson (CEO), Bill Johnson said the decision was not about coal, per se, but rather "about keeping rates as low as feasible." The TVA stated that decommissioning the two plants would reduce its carbon output by about 4.4% annually. TVA announced in April 2021 plans to completely phase out coal power by 2035. The following month, the TVA board voted to consider replacing almost all of their operating coal facilities with combined-cycle gas plants. Such plants considered for gas plant redevelopment include the Cumberland, Gallatin, Shawanee, and Kingston facilities.
In early February 2020, TVA awarded an outside company, Framatome, several multi-million-dollar contracts for work across the company's reactor fleet. This includes fuel for the Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, fuel handling equipment upgrades across the fleet and Steam generator (nuclear power), steam generator replacements at the Watts Bar Nuclear Plant. Framatome will provide its state-of-the-art ATRIUM 11 fuel for the three boiling water reactors at Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, Browns Ferry with the first use planned for 2023. This contract makes TVA the third U.S. utility to switch to the ATRIUM 11 fuel design. On August 3, 2020, president Donald Trump fired the TVA chairman and another board member, saying they were overpaid and had Outsourcing, outsourced 200 high-tech jobs. The move came after U.S. Tech Workers, a nonprofit that works to limit visas given to foreign technology workers, criticized the TVA for laying off its own workers and replacing them with contractors using foreign workers with H-1B visas.
Citing its plan to reach net-zero carbon emissions in 2050, the TVA Board voted to approve an advanced approach of nuclear energy technology with an estimated $200 million investment, known as the New Nuclear Program (NNP) in February 2022. The NNP would promote the construction of new nuclear power facilities, particularly small modular reactors, with the first facility being constructed in partnership with Oak Ridge National Laboratory at the Clinch River Breeder Reactor Project, Clinch River Nuclear Site in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, Oak Ridge.
On December 23, 2022 TVA had several hours of rolling blackouts due to the Late December 2022 North American winter storm. As many as 24,000 Nashville Electric Service customers were without power, with thousands more from smaller distributors affected as well.

Tennessee Valley Authority
in the ''Federal Register'' *
WPA Photographs of TVA Archaeological Projects
*
* [https://www.tva.com/about-tva/our-history TVA history] * {{Authority control Tennessee Valley Authority, 1933 establishments in Tennessee 1933 establishments in the United States 73rd United States Congress American companies established in 1933 Appalachia Appalachian culture Appalachian Mountains Companies based in Knoxville, Tennessee Corporations chartered by the United States Congress Economic development organizations in the United States Electric power companies of the United States Energy companies established in 1933 Energy companies of the United States Energy infrastructure in Tennessee Government agencies established in 1933 Hydroelectric power companies of the United States Independent agencies of the United States government New Deal agencies New Deal in Tennessee Nuclear power companies of the United States Public utilities of the United States Tennessee River United States Department of Energy Water management authorities in the United States
electric utility
An electric utility is a company in the electric power industry (often a public utility) that engages in electricity generation and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. The electrical utility industry is a major pr ...
corporation
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and ...
in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. TVA's service area covers all of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, portions of Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
, and Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
, and small areas of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
, and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
. While owned by the federal government, TVA receives no taxpayer funding and operates similarly to a private for-profit company. It is headquartered in Knoxville, Tennessee
Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the state' ...
, and is the sixth largest power supplier and largest public utility in the country.
The TVA was created by Congress in 1933 as part of President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
's New Deal. Its initial purpose was to provide navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
, flood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
, electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its s ...
, fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
manufacturing, Urban planning, regional planning, and economic development to the Tennessee Valley, a region that had suffered from lack of infrastructure and poverty during the Great Depression, relative to the rest of the nation. TVA was envisioned both as a power supplier and a regional economic development agency that would work to help modernize the region's economy and society. Later it evolved primarily into an electric utility.. It was the first large regional planning agency of the U.S. federal government and remains the largest.
Under the leadership of David E. Lilienthal, the TVA also became the global model for the United States' later efforts to help modernize Agrarian society, agrarian societies in the developing world. Historically, the TVA has been documented as a success in its efforts to modernize the Tennessee Valley and helping to recruit new employment opportunities to the region. Despite its successes, historians have criticized its use of Eminent domain in the United States, eminent domain; it resulted in the Forced displacement, displacement of over 125,000 Tennessee Valley residents to build the agency's infrastructure projects.
Operation
corporation
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and ...
created by Title 16 of the United States Code, U.S. Code Title 16, Chapter 12A (Tennessee Valley Authority Act of 1933). It was initially founded as an agency to provide general economic development to the region through power generation, flood control, navigation assistance, fertilizer manufacturing, and agricultural development. Since the Depression years, it has developed primarily into a power utility. Despite its shares being owned by the federal government, TVA operates like a private corporation, and receives no taxpayer funding. The TVA Act authorizes the company to use Eminent domain in the United States, eminent domain.
TVA provides electricity to approximately ten million people through a diverse portfolio that includes nuclear power, nuclear, Coal-fired power station, coal-fired, natural gas-fired, hydroelectricity, hydroelectric, and renewable energy, renewable generation. TVA sells its power to 154 local power utilities, 5 direct industrial and institutional customers, and 12 area utilities. In addition to power generation, TVA provides flood control with its 29 hydroelectric dams. Resulting lakes and other areas also allow for recreational activities. The TVA also provides navigation and land management along rivers within its region of operation. TVA also assists governments and private companies on economic development projects.
TVA's headquarters are located in downtown Knoxville, with large administrative offices in Chattanooga, Tennessee, Chattanooga (training/development; supplier relations; power generation and transmission) and Nashville, Tennessee, Nashville (economic development) in Tennessee and Muscle Shoals, Alabama. TVA was originally headquartered in Muscle Shoals, but gradually moved its headquarters to Knoxville. At one point, TVA's headquarters were housed in the Old Customs House (Knoxville, Tennessee), Old Federal Customs House at the corner of Clinch Avenue and Market Street. The building is now operated as a museum and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
The Tennessee Valley Authority Police are the primary law enforcement in the United States, law enforcement agency for the company. Initially part of the TVA, in 1994 the TVA Police was authorized as a Federal law enforcement in the United States, federal law enforcement agency.
Board of directors
The Tennessee Valley Authority is governed by a nine-member part-time board of directors, nominated by the President of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate, Senate. A minimum of seven of the directors are required to be residents of TVA's service area. The members select the chair from their number, and serve five-year terms. They receive annual stipends of $45,000 ($50,000 for the chair). The board members choose the TVA's chief executive officer.History
Background
During the 1920s and the 1930s, Americans began to support the idea of public utility, public ownership of utilities, particularly hydroelectric power facilities. Many believed privately owned power companies were charging too much for power, did not employ fair operating practices, and were subject to abuse by their owners (utility holding companies), at the expense of consumers. The concept of government-owned electricity generation, generation facilities selling to publicly owned distribution utilities was controversial, however, and remains so today. During his 1932 presidential campaign,Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
expressed his belief that private utilities had "selfish purposes" and said, "Never shall the federal government part with its sovereignty or with its control of its power resources while I'm president of the United States." Senator George W. Norris of Nebraska also distrusted private utility companies, and in 1920 blocked a proposal from industrialist Henry Ford to build a private dam and create a utility to modernize the Tennessee Valley. The private sector practice of forming utility holding companies had resulted in them controlling 94 percent of generation by 1921, and they were essentially unregulated. In an effort to change this, Congress and Roosevelt enacted the Public Utility Holding Company Act of 1935 (PUHCA).
In 1930, Norris sponsored the Muscle Shoals Bill, which would have built a federal dam in the valley, but it was vetoed by President Herbert Hoover, who believed it to be socialism, socialistic. The idea behind the Muscle Shoals project became a core part of President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
's New Deal program that created the Tennessee Valley Authority, however.
Even by Depression standards, the Tennessee Valley was in dire economic straits in 1933. Thirty percent of the population was affected by malaria. The average income in the rural areas was $639 per year (equivalent to $ in ), with some families surviving on as little as $100 per year (equivalent to $ in ). Much of the land had been exhausted by poor farming practices, and the soil was erosion, eroded and depleted. Crop yields had fallen, reducing farm incomes. The best timber had been cut, and 10% of forests were lost to fires each year.
Early history
 President Franklin Delano Roosevelt signed the Tennessee Valley Authority Act of Congress, Act (ch. 32, , codified as amended at , et seq.), creating the TVA. The agency was initially tasked with modernizing the region, using experts and electricity to combat human and economic problems. TVA developed fertilizers, and taught farmers ways to improve crop yields. In addition, it helped replant forests, control forest fires, and improve habitat for fish and wildlife.
The Authority hired many of the area's unemployed for a variety of jobs: they conducted habitat conservation, conservation, economic development, and social programs. For instance, a library service was instituted for this area. The professional staff at headquarters were generally composed of experts from outside the region. By 1934, TVA employed more than 9,000 people. The workers were classified by the usual racial and gender lines of the region, which limited opportunities for minorities and women. TVA hired a few African Americans, generally restricted for janitorial or other low-level positions. TVA recognized labor unions; its skilled and semi-skilled blue collar employees were unionized, a breakthrough in an area known for corporations hostile to miners' and textile workers' unions. Women were excluded from construction work.
President Franklin Delano Roosevelt signed the Tennessee Valley Authority Act of Congress, Act (ch. 32, , codified as amended at , et seq.), creating the TVA. The agency was initially tasked with modernizing the region, using experts and electricity to combat human and economic problems. TVA developed fertilizers, and taught farmers ways to improve crop yields. In addition, it helped replant forests, control forest fires, and improve habitat for fish and wildlife.
The Authority hired many of the area's unemployed for a variety of jobs: they conducted habitat conservation, conservation, economic development, and social programs. For instance, a library service was instituted for this area. The professional staff at headquarters were generally composed of experts from outside the region. By 1934, TVA employed more than 9,000 people. The workers were classified by the usual racial and gender lines of the region, which limited opportunities for minorities and women. TVA hired a few African Americans, generally restricted for janitorial or other low-level positions. TVA recognized labor unions; its skilled and semi-skilled blue collar employees were unionized, a breakthrough in an area known for corporations hostile to miners' and textile workers' unions. Women were excluded from construction work.
 Many local landowners were suspicious of government agencies, but TVA successfully introduced new agricultural methods into traditional farming communities by blending in and finding local champions. Tennessee farmers often rejected advice from TVA officials, so the officials had to find leaders in the communities and convince them that crop rotation and the judicious application of fertilizers could restore soil fertility. Once they had convinced the leaders, the rest followed.
TVA immediately embarked on the construction of several hydroelectric dams, with the first, Norris Dam in upper East Tennessee, breaking ground on October 1, 1933. These facilities, designed with the intent of also controlling floods, greatly improved the lives of farmers and rural residents, making their lives easier and farms in the Tennessee Valley more productive. They also provided new employment opportunities to the poverty-stricken regions in the Valley. At the same time, however, they required the Development-induced displacement, displacement of more than 125,000 valley residents or roughly 15,000 families, as well as some cemeteries and small towns, which caused some to oppose the projects, especially in rural areas. The projects also inundated several Native Americans in the United States, Native American archaeological sites, and graves were reinterred at new locations, along with new tombstones.
The available electricity attracted new industries to the region, including textile factory, mills, providing desperately needed jobs, many of which were filled by women. A few regions of the Tennessee Valley did not receive electricity until the late 1940s and early 1950s, however. TVA was one of the first federal hydropower agencies, and was quickly hailed as a success. While most of the nation's major hydropower systems are federally managed today, other attempts to create similar regional corporate agencies have failed. The most notable was the proposed Columbia Valley Authority for the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest, which was modeled off of TVA, but did not gain approval.
Many local landowners were suspicious of government agencies, but TVA successfully introduced new agricultural methods into traditional farming communities by blending in and finding local champions. Tennessee farmers often rejected advice from TVA officials, so the officials had to find leaders in the communities and convince them that crop rotation and the judicious application of fertilizers could restore soil fertility. Once they had convinced the leaders, the rest followed.
TVA immediately embarked on the construction of several hydroelectric dams, with the first, Norris Dam in upper East Tennessee, breaking ground on October 1, 1933. These facilities, designed with the intent of also controlling floods, greatly improved the lives of farmers and rural residents, making their lives easier and farms in the Tennessee Valley more productive. They also provided new employment opportunities to the poverty-stricken regions in the Valley. At the same time, however, they required the Development-induced displacement, displacement of more than 125,000 valley residents or roughly 15,000 families, as well as some cemeteries and small towns, which caused some to oppose the projects, especially in rural areas. The projects also inundated several Native Americans in the United States, Native American archaeological sites, and graves were reinterred at new locations, along with new tombstones.
The available electricity attracted new industries to the region, including textile factory, mills, providing desperately needed jobs, many of which were filled by women. A few regions of the Tennessee Valley did not receive electricity until the late 1940s and early 1950s, however. TVA was one of the first federal hydropower agencies, and was quickly hailed as a success. While most of the nation's major hydropower systems are federally managed today, other attempts to create similar regional corporate agencies have failed. The most notable was the proposed Columbia Valley Authority for the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest, which was modeled off of TVA, but did not gain approval.

World War II
During World War II, the U.S. needed greater aluminum supplies to build airplanes. Aluminum plants required large amounts of electricity. To provide the power, TVA engaged in one of the largest hydropower construction programs ever undertaken in the U.S. By early 1942, when the effort reached its peak, 12 hydroelectric plants and one coal-fired steam plant were under construction at the same time, and design and construction employment reached a total of 28,000. In its first eleven years, TVA constructed a total of 16 hydroelectric dams. The largest project of this period was the Fontana Dam. After negotiations led by then-Vice-President Harry Truman, TVA purchased the land from Nantahala Power and Light, a wholly owned subsidiary of Alcoa, and built Fontana Dam. Also in 1942, TVA's first coal-fired plant, the 267-megawatt Watts Bar Steam Plant, began operation. The government originally intended the electricity generated from Fontana to be used by Alcoa factories. However, the abundance of TVA power was one of the major factors in the decision by the U.S. Army to locate uranium enrichment facilities in Oak Ridge, Tennessee for the world's first atomic bombs. This was part of an effort codenamed the Manhattan Project.Increasing power demand
 By the end of World War II, TVA had completed a navigation channel the length of the Tennessee River and had become the nation's largest electricity supplier. Even so, the demand for electricity was outstripping TVA's capacity to produce power from Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dams, and so TVA began to construct additional coal-fired plants. Political interference kept TVA from securing additional federal appropriations to do so, so it sought the authority to issue bonds. Several of TVA's coal-fired plants, including Johnsonville Fossil Plant, Johnsonville, Widows Creek Fossil Plant, Widows Creek, Shawnee Fossil Plant, Shawnee, Kingston Fossil Plant, Kingston, Gallatin Fossil Plant, Gallatin, and John Sevier Fossil Plant, John Sevier, began operations in the 1950s. In 1955 coal surpassed hydroelectricity as TVA's top generating source. On August 6, 1959, President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed into law an amendment to the TVA act, making the agency self-financing. During the 1950s, TVA's generating capacity nearly quadrupled.
The 1960s were years of further unprecedented economic growth in the Tennessee Valley. Capacity growth during this time slowed, but ultimately increased 56% between 1960 and 1970. To handle a projected future increase in electrical consumption, TVA began constructing 500 kilovolt (kV) transmission lines, the first of which was placed into service on May 15, 1965. Electric rates were among the nation's lowest during this time and stayed low as TVA brought larger, more efficient generating units into service. Plants completed during this time included Paradise Combined Cycle Plant#History, Paradise, Bull Run Fossil Plant, Bull Run, and Nickajack Dam. Expecting the Valley's electric power needs to continue to grow, TVA began building nuclear power in the United States, nuclear power plants in 1966 as a new source of power. During the 1960s and 1970s, TVA was engaged in what was up to that time its most controversial project – the Tellico Dam Project. The project was initially conceived in the 1940s but not completed until 1979.
By the end of World War II, TVA had completed a navigation channel the length of the Tennessee River and had become the nation's largest electricity supplier. Even so, the demand for electricity was outstripping TVA's capacity to produce power from Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dams, and so TVA began to construct additional coal-fired plants. Political interference kept TVA from securing additional federal appropriations to do so, so it sought the authority to issue bonds. Several of TVA's coal-fired plants, including Johnsonville Fossil Plant, Johnsonville, Widows Creek Fossil Plant, Widows Creek, Shawnee Fossil Plant, Shawnee, Kingston Fossil Plant, Kingston, Gallatin Fossil Plant, Gallatin, and John Sevier Fossil Plant, John Sevier, began operations in the 1950s. In 1955 coal surpassed hydroelectricity as TVA's top generating source. On August 6, 1959, President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed into law an amendment to the TVA act, making the agency self-financing. During the 1950s, TVA's generating capacity nearly quadrupled.
The 1960s were years of further unprecedented economic growth in the Tennessee Valley. Capacity growth during this time slowed, but ultimately increased 56% between 1960 and 1970. To handle a projected future increase in electrical consumption, TVA began constructing 500 kilovolt (kV) transmission lines, the first of which was placed into service on May 15, 1965. Electric rates were among the nation's lowest during this time and stayed low as TVA brought larger, more efficient generating units into service. Plants completed during this time included Paradise Combined Cycle Plant#History, Paradise, Bull Run Fossil Plant, Bull Run, and Nickajack Dam. Expecting the Valley's electric power needs to continue to grow, TVA began building nuclear power in the United States, nuclear power plants in 1966 as a new source of power. During the 1960s and 1970s, TVA was engaged in what was up to that time its most controversial project – the Tellico Dam Project. The project was initially conceived in the 1940s but not completed until 1979.
1970s and 1980s
 Significant changes occurred in the economy of the Tennessee Valley and the nation, prompted by energy crises in 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 and accelerating fuel costs throughout the decade. The average cost of electricity in the Tennessee Valley increased fivefold from the early 1970s to the early 1980s. TVA's first nuclear reactor, Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Browns Ferry Unit 1, began commercial operation on August 1, 1974. In the early 1970s, TVA set out to construct a total of 17 nuclear reactors, due to a projection of further rapid increase in power demand. However, in the 1980s, ten of these reactors were cancelled. On August 6, 1981, the Tennessee Valley Authority Board voted to defer the Phipps Bend Nuclear Plant, Phipps Bend plant, as well as to slow down construction on all other projects. The Hartsville Nuclear Plant, Hartsville and Yellow Creek Nuclear Plant, Yellow Creek plants were cancelled in 1984 and Bellefonte Nuclear Plant, Bellefonte in 1988.
Significant changes occurred in the economy of the Tennessee Valley and the nation, prompted by energy crises in 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 and accelerating fuel costs throughout the decade. The average cost of electricity in the Tennessee Valley increased fivefold from the early 1970s to the early 1980s. TVA's first nuclear reactor, Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Browns Ferry Unit 1, began commercial operation on August 1, 1974. In the early 1970s, TVA set out to construct a total of 17 nuclear reactors, due to a projection of further rapid increase in power demand. However, in the 1980s, ten of these reactors were cancelled. On August 6, 1981, the Tennessee Valley Authority Board voted to defer the Phipps Bend Nuclear Plant, Phipps Bend plant, as well as to slow down construction on all other projects. The Hartsville Nuclear Plant, Hartsville and Yellow Creek Nuclear Plant, Yellow Creek plants were cancelled in 1984 and Bellefonte Nuclear Plant, Bellefonte in 1988.
 Construction of the Tellico Dam became controversial for political and environmental reasons, as laws had changed since early development in the valley. Scientists and other researchers had become more aware of the massive environmental effects of the dams and new lakes, and worried about preserving habitats and species. The Tellico Dam project was initially delayed because of concern over the snail darter, a threatened species. A lawsuit was filed under the Endangered Species Act and the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of protecting the snail darter in ''Tennessee Valley Authority v. Hill'' in 1978. The project also received controversy regarding the intent of the dam, as the project's main motive was to support recreational and tourism development, unlike earlier dams constructed by TVA. Land acquired by eminent domain for the Tellico Dam and its reservoir, specifically land that encountered minimal inundation, was sold to private developers for the construction of present-day Tellico Village, Tennessee, Tellico Village, a Planned community, planned retirement community.
The cancellation of several of the planned nuclear plants put the agency in deep financial trouble. Marvin T. Runyon became chairman of the TVA in January 1988. During his four-year tenure he claimed to reduce management layers, cut overhead costs by more than 30%, and achieved cumulative savings and efficiency improvements of $1.8 billion. He also claimed to have revitalized the nuclear program and instituted a rate freeze that continued for ten years.
Construction of the Tellico Dam became controversial for political and environmental reasons, as laws had changed since early development in the valley. Scientists and other researchers had become more aware of the massive environmental effects of the dams and new lakes, and worried about preserving habitats and species. The Tellico Dam project was initially delayed because of concern over the snail darter, a threatened species. A lawsuit was filed under the Endangered Species Act and the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of protecting the snail darter in ''Tennessee Valley Authority v. Hill'' in 1978. The project also received controversy regarding the intent of the dam, as the project's main motive was to support recreational and tourism development, unlike earlier dams constructed by TVA. Land acquired by eminent domain for the Tellico Dam and its reservoir, specifically land that encountered minimal inundation, was sold to private developers for the construction of present-day Tellico Village, Tennessee, Tellico Village, a Planned community, planned retirement community.
The cancellation of several of the planned nuclear plants put the agency in deep financial trouble. Marvin T. Runyon became chairman of the TVA in January 1988. During his four-year tenure he claimed to reduce management layers, cut overhead costs by more than 30%, and achieved cumulative savings and efficiency improvements of $1.8 billion. He also claimed to have revitalized the nuclear program and instituted a rate freeze that continued for ten years.
1990s to late 2010s
 As the electric-utility industry moved toward restructuring and deregulation, TVA began preparing for competition. It cut operating costs by nearly $800 million a year, reduced its workforce by more than half, increased the generating capacity of its plants, and developed a plan to meet the energy needs of the Tennessee Valley through the year 2020.
In 1996, Watts Bar Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Watts Bar Unit 1 began operation. This was the last commercial nuclear reactor in the United States to begin operation in the 20th century. In 2002, TVA began work to restart a previously mothballed nuclear reactor at Browns Ferry Nuclear Power Plant, Browns Ferry Unit 1, which was completed in May 2007. In 2004, TVA implemented recommendations from the Reservoir Operations Study (ROS) on how it operates the Tennessee River system (the nation's fifth largest). In 2005, the TVA announced its intention to construct an Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor at its Bellefonte Nuclear Generating Station, Bellefonte site in Alabama, filing the necessary applications in November 2007. In 2007 it announced plans to complete the unfinished Unit 2 at Watts Bar Nuclear Plant, Watts Bar, which began commercial operation in October 2016. Watts Bar Unit 2 is the first, and so far only, new nuclear reactor to enter service in the United States in the 21st century.
On December 22, 2008, an earthen dike at TVA's Kingston Fossil Plant broke, Kingston Fossil Plant coal fly ash slurry spill, spreading one billion gallons of wet coal ash across of land and into the tributaries of the Tennessee River. This produced damage from high levels of metal in the river. The TVA Office of the Inspector General's report, ''Inspection 2008-12283-02, Review of the Kingston Fossil Plant Ash Spill Cause Study and Observations About Ash Management,'' concluded that TVA culture had contributed to the spill.
In 2009, to gain more access to sustainable, green energy, TVA signed 20-year power purchase agreements with Maryland-based CVP Renewable Energy Co. and Chicago-based Invenergy Wind LLC for electricity generated by wind farms. In April 2011, TVA reached an agreement with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), four state governments, and three environmental groups to drastically reduce pollution and carbon emissions. Under the terms of the agreement, TVA was required to retire at least 18 of its 59 coal-fired units by the end of 2018, and install scrubbers in several others or convert them to make them cleaner, at a cost of $25 billion, by 2021. As a result, TVA closed several of its coal-fired power plants in the 2010s, converting some to natural gas. These include John Sevier in 2012, Shawnee Unit 10 in 2014, Widows Creek in 2015, Colbert in 2016, Johnsonville and Paradise Units 1 and 2 in 2017, Allen in 2018, and Paradise Unit 3 in 2020.
As the electric-utility industry moved toward restructuring and deregulation, TVA began preparing for competition. It cut operating costs by nearly $800 million a year, reduced its workforce by more than half, increased the generating capacity of its plants, and developed a plan to meet the energy needs of the Tennessee Valley through the year 2020.
In 1996, Watts Bar Nuclear Plant#Unit 1, Watts Bar Unit 1 began operation. This was the last commercial nuclear reactor in the United States to begin operation in the 20th century. In 2002, TVA began work to restart a previously mothballed nuclear reactor at Browns Ferry Nuclear Power Plant, Browns Ferry Unit 1, which was completed in May 2007. In 2004, TVA implemented recommendations from the Reservoir Operations Study (ROS) on how it operates the Tennessee River system (the nation's fifth largest). In 2005, the TVA announced its intention to construct an Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor at its Bellefonte Nuclear Generating Station, Bellefonte site in Alabama, filing the necessary applications in November 2007. In 2007 it announced plans to complete the unfinished Unit 2 at Watts Bar Nuclear Plant, Watts Bar, which began commercial operation in October 2016. Watts Bar Unit 2 is the first, and so far only, new nuclear reactor to enter service in the United States in the 21st century.
On December 22, 2008, an earthen dike at TVA's Kingston Fossil Plant broke, Kingston Fossil Plant coal fly ash slurry spill, spreading one billion gallons of wet coal ash across of land and into the tributaries of the Tennessee River. This produced damage from high levels of metal in the river. The TVA Office of the Inspector General's report, ''Inspection 2008-12283-02, Review of the Kingston Fossil Plant Ash Spill Cause Study and Observations About Ash Management,'' concluded that TVA culture had contributed to the spill.
In 2009, to gain more access to sustainable, green energy, TVA signed 20-year power purchase agreements with Maryland-based CVP Renewable Energy Co. and Chicago-based Invenergy Wind LLC for electricity generated by wind farms. In April 2011, TVA reached an agreement with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), four state governments, and three environmental groups to drastically reduce pollution and carbon emissions. Under the terms of the agreement, TVA was required to retire at least 18 of its 59 coal-fired units by the end of 2018, and install scrubbers in several others or convert them to make them cleaner, at a cost of $25 billion, by 2021. As a result, TVA closed several of its coal-fired power plants in the 2010s, converting some to natural gas. These include John Sevier in 2012, Shawnee Unit 10 in 2014, Widows Creek in 2015, Colbert in 2016, Johnsonville and Paradise Units 1 and 2 in 2017, Allen in 2018, and Paradise Unit 3 in 2020.
Recent history
 In 2018, TVA opened a new cybersecurity center in its downtown Chattanooga Office Complex. More than 20 Information Technology specialists monitor emails, Twitter feeds and network activity for cybersecurity threats and threats to grid security. Across TVA's digital platform, 2 billion activities occur each day. The center is staffed 24 hours a day to spot any threats to TVA's 16,000 miles of transmission lines.
Given continued economic pressure on the coal industry, the TVA board defied President Donald Trump and voted in February 2019 to close two aging coal plants, Paradise 3 and Bull Run. TVA chief executive William D. Johnson (CEO), Bill Johnson said the decision was not about coal, per se, but rather "about keeping rates as low as feasible." The TVA stated that decommissioning the two plants would reduce its carbon output by about 4.4% annually. TVA announced in April 2021 plans to completely phase out coal power by 2035. The following month, the TVA board voted to consider replacing almost all of their operating coal facilities with combined-cycle gas plants. Such plants considered for gas plant redevelopment include the Cumberland, Gallatin, Shawanee, and Kingston facilities.
In early February 2020, TVA awarded an outside company, Framatome, several multi-million-dollar contracts for work across the company's reactor fleet. This includes fuel for the Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, fuel handling equipment upgrades across the fleet and Steam generator (nuclear power), steam generator replacements at the Watts Bar Nuclear Plant. Framatome will provide its state-of-the-art ATRIUM 11 fuel for the three boiling water reactors at Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, Browns Ferry with the first use planned for 2023. This contract makes TVA the third U.S. utility to switch to the ATRIUM 11 fuel design. On August 3, 2020, president Donald Trump fired the TVA chairman and another board member, saying they were overpaid and had Outsourcing, outsourced 200 high-tech jobs. The move came after U.S. Tech Workers, a nonprofit that works to limit visas given to foreign technology workers, criticized the TVA for laying off its own workers and replacing them with contractors using foreign workers with H-1B visas.
Citing its plan to reach net-zero carbon emissions in 2050, the TVA Board voted to approve an advanced approach of nuclear energy technology with an estimated $200 million investment, known as the New Nuclear Program (NNP) in February 2022. The NNP would promote the construction of new nuclear power facilities, particularly small modular reactors, with the first facility being constructed in partnership with Oak Ridge National Laboratory at the Clinch River Breeder Reactor Project, Clinch River Nuclear Site in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, Oak Ridge.
On December 23, 2022 TVA had several hours of rolling blackouts due to the Late December 2022 North American winter storm. As many as 24,000 Nashville Electric Service customers were without power, with thousands more from smaller distributors affected as well.
In 2018, TVA opened a new cybersecurity center in its downtown Chattanooga Office Complex. More than 20 Information Technology specialists monitor emails, Twitter feeds and network activity for cybersecurity threats and threats to grid security. Across TVA's digital platform, 2 billion activities occur each day. The center is staffed 24 hours a day to spot any threats to TVA's 16,000 miles of transmission lines.
Given continued economic pressure on the coal industry, the TVA board defied President Donald Trump and voted in February 2019 to close two aging coal plants, Paradise 3 and Bull Run. TVA chief executive William D. Johnson (CEO), Bill Johnson said the decision was not about coal, per se, but rather "about keeping rates as low as feasible." The TVA stated that decommissioning the two plants would reduce its carbon output by about 4.4% annually. TVA announced in April 2021 plans to completely phase out coal power by 2035. The following month, the TVA board voted to consider replacing almost all of their operating coal facilities with combined-cycle gas plants. Such plants considered for gas plant redevelopment include the Cumberland, Gallatin, Shawanee, and Kingston facilities.
In early February 2020, TVA awarded an outside company, Framatome, several multi-million-dollar contracts for work across the company's reactor fleet. This includes fuel for the Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, fuel handling equipment upgrades across the fleet and Steam generator (nuclear power), steam generator replacements at the Watts Bar Nuclear Plant. Framatome will provide its state-of-the-art ATRIUM 11 fuel for the three boiling water reactors at Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant, Browns Ferry with the first use planned for 2023. This contract makes TVA the third U.S. utility to switch to the ATRIUM 11 fuel design. On August 3, 2020, president Donald Trump fired the TVA chairman and another board member, saying they were overpaid and had Outsourcing, outsourced 200 high-tech jobs. The move came after U.S. Tech Workers, a nonprofit that works to limit visas given to foreign technology workers, criticized the TVA for laying off its own workers and replacing them with contractors using foreign workers with H-1B visas.
Citing its plan to reach net-zero carbon emissions in 2050, the TVA Board voted to approve an advanced approach of nuclear energy technology with an estimated $200 million investment, known as the New Nuclear Program (NNP) in February 2022. The NNP would promote the construction of new nuclear power facilities, particularly small modular reactors, with the first facility being constructed in partnership with Oak Ridge National Laboratory at the Clinch River Breeder Reactor Project, Clinch River Nuclear Site in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, Oak Ridge.
On December 23, 2022 TVA had several hours of rolling blackouts due to the Late December 2022 North American winter storm. As many as 24,000 Nashville Electric Service customers were without power, with thousands more from smaller distributors affected as well.
Facilities
Power stations
With a generating capacity of approximately 35 gigawatts (GW), TVA has the sixth highest generation capacity of any utility company in the United States. TVA's power mix as of 2022 is five coal-fired power plants, 29 hydroelectricity, hydroelectric dams, three nuclear power plant, nuclear plants (with seven operating reactors), nine simple-cycle natural gas combustion turbine plants, nine combined cycle gas plants, 1 pumped storage hydroelectric plant, 1 wind power, wind energy site, and 15 small solar energy sites. In fiscal year 2020, nuclear generation made up about 41% of TVA's total energy sales, natural gas 26%, coal 14%, hydroelectric 13%, and wind and solar 3%. TVA purchases about 15% of the power it sells from other power producers, which includes power from combined cycle natural gas plants, coal plants, and wind installations, and other renewables. The cost of Purchased Power is part of the "Fuel Cost Adjustment" (FCA) charge that is separate from the TVA Rate. Watts Bar Nuclear Plant produces tritium as a byproduct for the U.S. National Nuclear Security Administration, which requires tritium for nuclear weapons (for "boosted" fission primaries and for fusion secondaries).Electric transmission
TVA owns and operates its own electric grid, which consists of approximately of lines, one of the largest grids in the United States. This grid is part of the Eastern Interconnection of the North American power transmission grid, and is under the jurisdiction of the SERC Reliability Corporation. Like most North American utilities, TVA uses a maximum transmission voltage of 500 kilovolts (kV), with lines carrying this voltage using Overhead power line#Bundle conductors, bundled conductors with three conductors per phase. The vast majority of TVA's transmission lines carry 161 kV, with the company also operating a number of sub-transmission lines with a voltage of 69 kV.Recreation
TVA has conveyed approximately of property for recreation and preservation purposes including public parks, public access areas and roadside parks, wildlife refuges, national parks and forests, and other camps and recreation areas, comprising approximately 759 different sites.Megasites
To qualify for a TVA Megasite certificate the qualifications are at least 1,000 acres, with interstate access, the potential for rail service, environmental impact study, and utility service capable of serving a major manufacturing facility. Seven TVA Megasites have been developed so far with capital investments of over $5 billion. Locations: *Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville *Chattanooga, Tennessee, Chattanooga *Golden Triangle (Mississippi) (2 sites) *Hopkinsville, Kentucky *Blue Oval City, Memphis Regional Megasite *West Kentucky MegasiteCriticism and controversies
Allegations of federal government overreach
TVA was heralded by New Dealers and the New Deal Coalition not only as a successful economic development program for a depressed area but also as a democratic nation-building effort overseas because of its alleged grassroots inclusiveness as articulated by director David E. Lilienthal. However, the TVA was controversial early on, as some believed its creation was an overreach by the federal government. Supporters of TVA note that the agency's management of the Tennessee River system without appropriated federal funding saves federal taxpayers millions of dollars annually. Opponents, such as Dean Russell in ''The TVA Idea,'' in addition to condemning the project as being socialistic, argued that TVA created a "hidden loss" by preventing the creation of "factories and jobs that would have come into existence if the government had allowed the taxpayers to spend their money as they wished." Defenders note that TVA is overwhelmingly popular in Tennessee among conservatives and Liberalism, liberals alike, as Barry Goldwater discovered in 1964, when he proposed selling the agency. Historian Thomas McCraw concludes that Roosevelt "rescued the [power] industry from its own abuses" but "he might have done this much with a great deal less agitation and ill will". New Dealers hoped to build numerous other federal utility corporations around the country but were defeated by lobbyist Wendell_Willkie#TVA_battle, Wendell Willkie and the conservative coalition in Congress. The valley authority model did not replace the limited-purpose water programs of the Bureau of Reclamation and the United States Army Corps of Engineers, Army Corps of Engineers. However, it has been shown that in river policy, the strength of opposing interest groups also mattered. The TVA bill was passed in 1933 because reformers like Norris skillfully coordinated action at potential choke points and weakened the already disorganized opponents among the electric power industry Lobbying, lobbyists. In 1936, however, after regrouping, opposing river lobbyists and conservative coalition congressmen took advantage of the New Dealers' spending mood by expanding the Army Corps' flood control program. They also helped defeat further valley authorities, the most promising of the New Deal water policy reforms. When Democrats after 1945 proclaimed the Tennessee Valley Authority as a model for countries in the developing world to follow, conservative critics charged it was a top-heavy, centralized, technocratic venture that displaced locals and did so in insensitive ways. Thus, when the program was used as the basis for modernization programs in various parts of the third world during the Cold War, such as in the Mekong Delta in Vietnam, its failure brought a backlash of cynicism toward modernization programs that has persisted. Then-movie star Ronald Reagan had moved to television as the host and a frequent performer for ''General Electric Theater'' during 1954. Reagan was later fired by General Electric in 1962 in response to his publicly referring to the TVA (TVA being a major customer for GE turbines) as one of the problems of "big government". Some claim that Reagan was instead fired due to a criminal antitrust investigation involving him and the Screen Actors Guild. However, Reagan was only interviewed; nobody was actually charged with anything in the investigation. In 1963, U.S. Senator and Republican Party (United States), Republican presidential candidate Barry Goldwater was quoted in a ''Saturday Evening Post'' article by Stewart Alsop as saying, "You know, I think we ought to sell TVA." He had called for the sale to private companies of particular parts of the Authority, including its fertilizer production and steam-generation facilities, because "it would be better operated and would be of more benefit for more people if it were part of private industry." Goldwater's quotation was used against him in a TV ad by Doyle Dane Bernbach for President Lyndon Johnson's 1964 campaign, which depicted an auction taking place atop a dam. It was voiced over as follows: "In a ''Saturday Evening Post'' article dated August 31, 1963, Barry Goldwater said, 'You know, I think we ought to sell TVA.' This is a promise: President Johnson will not sell TVA. Vote for him on November 3. The stakes are too high for you to stay home."Legal challenges
TVA faced multiple constitutional challenges. The United States Supreme Court ruled TVA to be constitutional in ''Ashwander v. Tennessee Valley Authority'' (297 U.S. 288) in 1936. The Court noted that Commerce Clause, regulating commerce among the states includes regulation of streams and that controlling floods is required for keeping streams navigable; it also upheld the constitutionality of the TVA under the War Powers Clause, seeing its activities as a means of assuring the electric supply for the manufacture of munitions in the event of war. The argument before the court was that electricity generation was a by-product of navigation and flood control and therefore could be considered constitutional. The CEO of the Tennessee Electric Power Company (TEPCO), Jo Conn Guild, was vehemently opposed to the creation of TVA, and with the help of attorney Wendell Willkie, challenged the constitutionality of the TVA Act in federal court. The Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court again upheld the TVA Act, however, in its 1939 decision ''Tennessee Electric Power Company v. TVA''. On August 16, 1939, TEPCO was forced to sell its assets, including Hales Bar Dam, Ocoee Dams Ocoee Dam No. 1, 1 and Ocoee Dam No. 2, 2, Blue Ridge Dam and Great Falls Dam (Tennessee), Great Falls Dam to TVA for $78 million (equivalent to $ in ).Discrimination
In 1981 the TVA Board of Directors broke with previous tradition and took a hard line against white-collar unions during contract negotiations. As a result, a class action suit was filed in 1984 in U.S. court charging the agency with sex discrimination under Civil Rights Act of 1964#Title VII, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act based on the large number of women in one of the pay grades negatively impacted by the new contract. An out-of-court settlement of the lawsuit was reached in 1987, in which TVA agreed to contract modifications and paid the group $5 million but admitted no wrongdoing.Eminent domain and family removal controversies
TVA has received criticism its entire history for what some have perceived as excessive use of its authority of eminent domain in the United States, eminent domain and an unwillingness to compromise with landowners. All of TVA's hydroelectric projects were made possible through the use of eminent domain, and were controversial due to the more than 125,000 Tennessee Valley residents that were displaced by the agency. Residents who refused to sell their land were often forced to by court orders and lawsuits. Many of these projects also inundated historic Native American sites and early American Revolution-era settlements. Historians have criticized the TVA for forcing residents to sell their property at values less than the Just compensation, fair market value, and indirectly starting a unstable real estate market for farmland. In the most extreme circumstance, displaced residents committed suicide, unable to bear the events of their removal. On some occasions, land that TVA had acquired through eminent domain that was expected to be flooded by reservoirs was not flooded, and was given away to private developers.In popular culture
The 1960 film ''Wild River (film), Wild River'', directed by Elia Kazan, tells the story about a family forced to relocate from their land, which has been owned by their ancestors for generations, after TVA plans to construct a dam which will flood it. While fictional, the film depicts the real-life experiences of many people forced to give up their land to TVA to make way for hydroelectric projects, and was mostly inspired by the removal of families for the Norris Project. The 1970 James Dickey novel ''Deliverance (novel), Deliverance'', and its 1972 Deliverance, film adaptation focuses on four Atlanta businessmen taking a canoeing trip down a river that is being impounded by an electric utility, nodding to the TVA's early and controversial hydroelectric projects. The 1984 Mark Rydell film ''The River (1984 film), The River'', focuses on a East Tennessee family being confronted by the loss of their ancestral farm from the inundation of a nearby river by an electric utility. The film, shot on farmland near the Holston River in Hawkins County, Tennessee, Hawkins County, utilized flooding practical effects provided by the TVA. In the 2000 film ''O Brother, Where Art Thou?'', the family home of the protagonist, played by George Clooney, is flooded by a reservoir constructed by the TVA. This plays a central role in the pacing of the film and the broader depression-era Mississippi context of the narrative. "Song of the South (song), Song of the South" by country music, country and Southern rock band Alabama (band), Alabama features the lyrics "Papa got a job with the TVA" following the lyrics "Well momma got sick and daddy got down, The county got the farm and they moved to town" expressing the hardships and changes that southerners faced during the post recession era. The TVA and its impact on the region are featured in the Drive-By Truckers' songs "TVA" and "Uncle Frank". In "TVA," the singer reflects on time spent with family members and a girlfriend at Wilson Dam. In "Uncle Frank", the lyrics tell the story of an unnamed hydroelectric dam being built, and the effects on the community that would become flooded upon its completion. On November 19, 2012, Jason Isbell released a solo version of "TVA". The company still has a dominant presence in Northern Alabama, including Isbell's hometown of Muscle Shoals, as an employer and power distributor.See also
* Title 18 of the Code of Federal Regulations * Appalachian Regional Commission * Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority, modelled on the TVA * James Bay Energy Corporation, a Crown corporations of Canada, Crown corporation of the Quebec government for developing the James Bay Project for building various Robert-Bourassa generating station, dams on La Grande River, rivers * List of navigation authorities in the United States * Muscle Shoals Bill * Nashville Electric Service * New Deal * New Madrid Seismic Zone * 1811–12 New Madrid earthquakes * Norris, Tennessee * Tennessee Valley Authority Police * ''Tennessee Valley Authority v. Hill''Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Tennessee Valley Authority
in the ''Federal Register'' *
WPA Photographs of TVA Archaeological Projects
*
* [https://www.tva.com/about-tva/our-history TVA history] * {{Authority control Tennessee Valley Authority, 1933 establishments in Tennessee 1933 establishments in the United States 73rd United States Congress American companies established in 1933 Appalachia Appalachian culture Appalachian Mountains Companies based in Knoxville, Tennessee Corporations chartered by the United States Congress Economic development organizations in the United States Electric power companies of the United States Energy companies established in 1933 Energy companies of the United States Energy infrastructure in Tennessee Government agencies established in 1933 Hydroelectric power companies of the United States Independent agencies of the United States government New Deal agencies New Deal in Tennessee Nuclear power companies of the United States Public utilities of the United States Tennessee River United States Department of Energy Water management authorities in the United States