Sugarcane weighing at sugarmill.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall,
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall,
 Sugarcane is a tropical, perennial grass that forms lateral shoots at the base to produce multiple stems, typically high and about in diameter. The stems grow into cane stalk, which when mature, constitutes around 75% of the entire plant. A mature stalk is typically composed of 11–16% fiber, 12–16% soluble sugars, 2–3% nonsugar carbohydrates, and 63–73% water. A sugarcane crop is sensitive to climate, soil type, irrigation, fertilizers, insects, disease control, varieties, and the harvest period. The average yield of cane stalk is per year, but this figure can vary between 30 and 180 tonnes per hectare depending on knowledge and crop management approach used in sugarcane cultivation. Sugarcane is a cash crop, but it is also used as livestock fodder. Sugarcane genome is one of the most complex plant genomes known, mostly due to interspecific hybridization and polyploidization.
Sugarcane is a tropical, perennial grass that forms lateral shoots at the base to produce multiple stems, typically high and about in diameter. The stems grow into cane stalk, which when mature, constitutes around 75% of the entire plant. A mature stalk is typically composed of 11–16% fiber, 12–16% soluble sugars, 2–3% nonsugar carbohydrates, and 63–73% water. A sugarcane crop is sensitive to climate, soil type, irrigation, fertilizers, insects, disease control, varieties, and the harvest period. The average yield of cane stalk is per year, but this figure can vary between 30 and 180 tonnes per hectare depending on knowledge and crop management approach used in sugarcane cultivation. Sugarcane is a cash crop, but it is also used as livestock fodder. Sugarcane genome is one of the most complex plant genomes known, mostly due to interspecific hybridization and polyploidization.
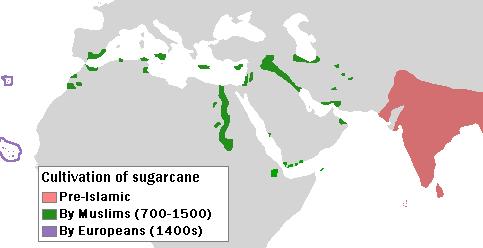 From Island Southeast Asia, ''S. officinarum'' was spread eastward into
From Island Southeast Asia, ''S. officinarum'' was spread eastward into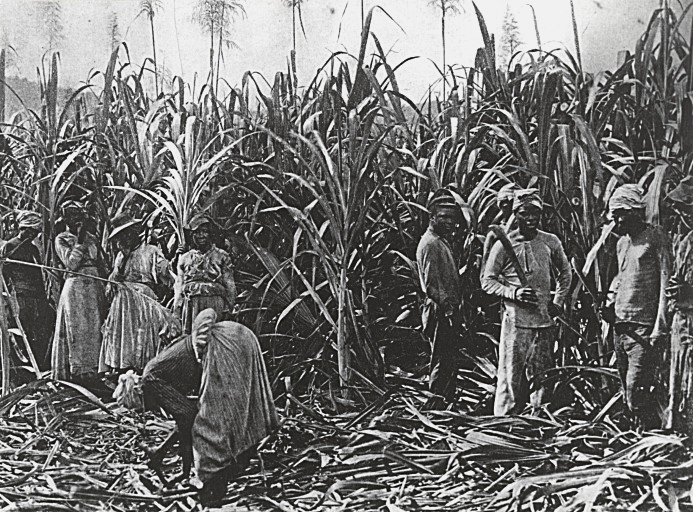  The passage of the 1833 Slavery Abolition Act led to the abolition of slavery through most of the
The passage of the 1833 Slavery Abolition Act led to the abolition of slavery through most of the  Between 1863 and 1900, merchants and plantation owners in
Between 1863 and 1900, merchants and plantation owners in 



 Sugarcane cultivation requires a tropical or subtropical climate, with a minimum of of annual moisture. It is one of the most Photosynthetic efficiency, efficient Photosynthesis, photosynthesizers in the plant kingdom. It is a C4 carbon fixation, C4 plant, able to convert up to 1% of incident solar energy into biomass. In primary growing regions across the tropics and subtropics, sugarcane crops can produce over 15 kg/m2 of cane. Once a major crop of the southeastern region of the United States, sugarcane cultivation declined there during the late 20th century, and is primarily confined to small plantations in Sugar Cane Growers Cooperative of Florida, Florida, Louisiana, and southeast Texas in the 21st century. Sugarcane cultivation ceased in Hawaii when the last operating sugar plantation in the state shut down in 2016.
Sugarcane is cultivated in the tropics and subtropics in areas with a plentiful supply of water for a continuous period of more than 6–7 months each year, either from natural rainfall or through irrigation. The crop does not tolerate severe frosts. Therefore, most of the world's sugarcane is grown between 22nd parallel north, 22°N and 22nd parallel south, 22°S, and some up to 33rd parallel north, 33°N and 33rd parallel south, 33°S. When sugarcane crops are found outside this range, such as the KwaZulu-Natal, Natal region of South Africa, it is normally due to anomalous climatic conditions in the region, such as warm ocean currents that sweep down the coast. In terms of altitude, sugarcane crops are found up to close to the equator in countries such as Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.
Sugarcane can be grown on many soils ranging from highly fertile, well-drained mollisols, through heavy cracking vertisols, infertile acid oxisols and ultisols, peaty histosols, to rocky andisols. Both plentiful sunshine and water supplies increase cane production. This has made desert countries with good irrigation facilities such as Egypt some of the highest-yielding sugarcane-cultivating regions. Sugarcane consumes 9% of the world's potash fertilizer production.
Although some sugarcanes produce seeds, modern stem cutting has become the most common reproduction method. Each cutting must contain at least one bud, and the cuttings are sometimes hand-planted. In more technologically advanced countries, such as the United States and Australia, billet planting is common. Billets (stalks or stalk sections) harvested by a mechanical harvester are planted by a machine that opens and recloses the ground. Once planted, a stand can be harvested several times; after each harvest, the cane sends up new stalks, called ratoons. Successive harvests give decreasing yields, eventually justifying replanting. Two to 10 harvests are usually made depending on the type of culture. In a country with a mechanical agriculture looking for a high production of large fields, as in North America, sugarcanes are replanted after two or three harvests to avoid a lowering yields. In countries with a more traditional type of agriculture with smaller fields and hand harvesting, as in the French island la Réunion, sugarcane is often harvested up to 10 years before replanting.
Sugarcane is harvested by hand and mechanically. Hand harvesting accounts for more than half of production, and is dominant in the developing world. In hand harvesting, the field is first set on fire. The fire burns up dry leaves, and chases away or kills venomous snakes, without harming the stalks and roots. Harvesters then cut the cane just above ground-level using cane knife, cane knives or machetes. A skilled harvester can cut of sugarcane per hour.
Mechanical harvesting uses a combine harvester, combine, or sugarcane harvester. The Austoft 7000 series, the original modern harvester design, has now been copied by other companies, including Cameco / Deere & Company, John Deere. The machine cuts the cane at the base of the stalk, strips the leaves, chops the cane into consistent lengths and deposits it into a transporter following alongside. The harvester then blows the trash back onto the field. Such machines can harvest each hour, but harvested cane must be rapidly processed. Once cut, sugarcane begins to lose its sugar content, and damage to the cane during mechanical harvesting accelerates this decline. This decline is offset because a modern chopper harvester can complete the harvest faster and more efficiently than hand cutting and loading. Austoft also developed a series of hydraulic high-lift infield transporters to work alongside its harvesters to allow even more rapid transfer of cane to, for example, the nearest railway siding. This mechanical harvesting does not require the field to be set on fire; the residue left in the field by the machine consists of cane tops and dead leaves, which serve as mulch for the next planting.
Sugarcane cultivation requires a tropical or subtropical climate, with a minimum of of annual moisture. It is one of the most Photosynthetic efficiency, efficient Photosynthesis, photosynthesizers in the plant kingdom. It is a C4 carbon fixation, C4 plant, able to convert up to 1% of incident solar energy into biomass. In primary growing regions across the tropics and subtropics, sugarcane crops can produce over 15 kg/m2 of cane. Once a major crop of the southeastern region of the United States, sugarcane cultivation declined there during the late 20th century, and is primarily confined to small plantations in Sugar Cane Growers Cooperative of Florida, Florida, Louisiana, and southeast Texas in the 21st century. Sugarcane cultivation ceased in Hawaii when the last operating sugar plantation in the state shut down in 2016.
Sugarcane is cultivated in the tropics and subtropics in areas with a plentiful supply of water for a continuous period of more than 6–7 months each year, either from natural rainfall or through irrigation. The crop does not tolerate severe frosts. Therefore, most of the world's sugarcane is grown between 22nd parallel north, 22°N and 22nd parallel south, 22°S, and some up to 33rd parallel north, 33°N and 33rd parallel south, 33°S. When sugarcane crops are found outside this range, such as the KwaZulu-Natal, Natal region of South Africa, it is normally due to anomalous climatic conditions in the region, such as warm ocean currents that sweep down the coast. In terms of altitude, sugarcane crops are found up to close to the equator in countries such as Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.
Sugarcane can be grown on many soils ranging from highly fertile, well-drained mollisols, through heavy cracking vertisols, infertile acid oxisols and ultisols, peaty histosols, to rocky andisols. Both plentiful sunshine and water supplies increase cane production. This has made desert countries with good irrigation facilities such as Egypt some of the highest-yielding sugarcane-cultivating regions. Sugarcane consumes 9% of the world's potash fertilizer production.
Although some sugarcanes produce seeds, modern stem cutting has become the most common reproduction method. Each cutting must contain at least one bud, and the cuttings are sometimes hand-planted. In more technologically advanced countries, such as the United States and Australia, billet planting is common. Billets (stalks or stalk sections) harvested by a mechanical harvester are planted by a machine that opens and recloses the ground. Once planted, a stand can be harvested several times; after each harvest, the cane sends up new stalks, called ratoons. Successive harvests give decreasing yields, eventually justifying replanting. Two to 10 harvests are usually made depending on the type of culture. In a country with a mechanical agriculture looking for a high production of large fields, as in North America, sugarcanes are replanted after two or three harvests to avoid a lowering yields. In countries with a more traditional type of agriculture with smaller fields and hand harvesting, as in the French island la Réunion, sugarcane is often harvested up to 10 years before replanting.
Sugarcane is harvested by hand and mechanically. Hand harvesting accounts for more than half of production, and is dominant in the developing world. In hand harvesting, the field is first set on fire. The fire burns up dry leaves, and chases away or kills venomous snakes, without harming the stalks and roots. Harvesters then cut the cane just above ground-level using cane knife, cane knives or machetes. A skilled harvester can cut of sugarcane per hour.
Mechanical harvesting uses a combine harvester, combine, or sugarcane harvester. The Austoft 7000 series, the original modern harvester design, has now been copied by other companies, including Cameco / Deere & Company, John Deere. The machine cuts the cane at the base of the stalk, strips the leaves, chops the cane into consistent lengths and deposits it into a transporter following alongside. The harvester then blows the trash back onto the field. Such machines can harvest each hour, but harvested cane must be rapidly processed. Once cut, sugarcane begins to lose its sugar content, and damage to the cane during mechanical harvesting accelerates this decline. This decline is offset because a modern chopper harvester can complete the harvest faster and more efficiently than hand cutting and loading. Austoft also developed a series of hydraulic high-lift infield transporters to work alongside its harvesters to allow even more rapid transfer of cane to, for example, the nearest railway siding. This mechanical harvesting does not require the field to be set on fire; the residue left in the field by the machine consists of cane tops and dead leaves, which serve as mulch for the next planting.

 Sugarcane processing produces cane sugar (sucrose) from sugarcane. Other products of the processing include bagasse, molasses, and filtercake.
Bagasse, the residual dry fiber of the cane after cane juice has been extracted, is used for several purposes:
*fuel for the boilers and kilns
*production of paper, paperboard products, and reconstituted panelboard
*agricultural mulch
*as a raw material for production of chemicals
Sugarcane processing produces cane sugar (sucrose) from sugarcane. Other products of the processing include bagasse, molasses, and filtercake.
Bagasse, the residual dry fiber of the cane after cane juice has been extracted, is used for several purposes:
*fuel for the boilers and kilns
*production of paper, paperboard products, and reconstituted panelboard
*agricultural mulch
*as a raw material for production of chemicals
 The primary use of bagasse and bagasse residue is as a fuel source for the boilers in the generation of process steam in sugar plants. Dried filtercake is used as an animal feed supplement, fertilizer, and source of sugarcane wax.
Molasses is produced in two forms: Molasses#Blackstrap Molasses, blackstrap, which has a characteristic strong flavor, and a purer molasses syrup. Blackstrap molasses is sold as a food and dietary supplement. It is also a common ingredient in animal feed, and is used to produce ethanol, rum, and citric acid. Purer molasses syrups are sold as molasses, and may also be blended with maple syrup, invert sugars, or corn syrup. Both forms of molasses are used in baking.
The primary use of bagasse and bagasse residue is as a fuel source for the boilers in the generation of process steam in sugar plants. Dried filtercake is used as an animal feed supplement, fertilizer, and source of sugarcane wax.
Molasses is produced in two forms: Molasses#Blackstrap Molasses, blackstrap, which has a characteristic strong flavor, and a purer molasses syrup. Blackstrap molasses is sold as a food and dietary supplement. It is also a common ingredient in animal feed, and is used to produce ethanol, rum, and citric acid. Purer molasses syrups are sold as molasses, and may also be blended with maple syrup, invert sugars, or corn syrup. Both forms of molasses are used in baking.

 Ethanol is generally available as a byproduct of sugar production. It can be used as a biofuel alternative to gasoline, and is widely used in cars in Brazil. It is an alternative to gasoline, and may become the primary product of sugarcane processing, rather than sugar.
Ethanol is generally available as a byproduct of sugar production. It can be used as a biofuel alternative to gasoline, and is widely used in cars in Brazil. It is an alternative to gasoline, and may become the primary product of sugarcane processing, rather than sugar.
 In Brazil, gasoline is required to contain at least 22% bioethanol. This bioethanol is sourced from Brazil's large sugarcane crop.
The production of ethanol from sugarcane is more energy efficient than from corn or sugar beets or palm/vegetable oils, particularly if cane bagasse is used to produce heat and power for the process. Furthermore, if biofuels are used for crop production and transport, the fossil energy input needed for each ethanol energy unit can be very low. EIA estimates that with an integrated sugar cane to ethanol technology, the well-to-wheels CO2 emissions can be 90% lower than conventional gasoline. A textbook on renewable energy describes the energy transformation:
In Brazil, gasoline is required to contain at least 22% bioethanol. This bioethanol is sourced from Brazil's large sugarcane crop.
The production of ethanol from sugarcane is more energy efficient than from corn or sugar beets or palm/vegetable oils, particularly if cane bagasse is used to produce heat and power for the process. Furthermore, if biofuels are used for crop production and transport, the fossil energy input needed for each ethanol energy unit can be very low. EIA estimates that with an integrated sugar cane to ethanol technology, the well-to-wheels CO2 emissions can be 90% lower than conventional gasoline. A textbook on renewable energy describes the energy transformation:
 Sugarcane is a major crop in many countries. It is one of the plants with the highest bioconversion efficiency. Sugarcane crop is able to efficiently fix solar energy, yielding some 55 tonnes of dry matter per hectare of land annually. After harvest, the crop produces sugar juice and bagasse, the fibrous dry matter. This dry matter is biomass with potential as fuel for energy production. Bagasse can also be used as an alternative source of pulp for paper production.
Sugarcane bagasse is a potentially abundant source of energy for large producers of sugarcane, such as Brazil, India, and China. According to one report, with use of latest technologies, bagasse produced annually in Brazil has the potential of meeting 20% of Brazil's energy consumption by 2020.
Sugarcane is a major crop in many countries. It is one of the plants with the highest bioconversion efficiency. Sugarcane crop is able to efficiently fix solar energy, yielding some 55 tonnes of dry matter per hectare of land annually. After harvest, the crop produces sugar juice and bagasse, the fibrous dry matter. This dry matter is biomass with potential as fuel for energy production. Bagasse can also be used as an alternative source of pulp for paper production.
Sugarcane bagasse is a potentially abundant source of energy for large producers of sugarcane, such as Brazil, India, and China. According to one report, with use of latest technologies, bagasse produced annually in Brazil has the potential of meeting 20% of Brazil's energy consumption by 2020.
File:Sugarcane bsri 34.jpg, Sugarcane fields in Bangladesh Sugarcane Research Institute (BSRI)
File:Sugarcane bD.jpg, Sugarcane fields in BSRI
File:Sugarcane Bd.jpg, Sugarcane fields in BSRI
File:Sugarcane re.jpg, Sugarcane fields in BSRI
File:Sugarcane vendor in Dhaka.jpg, Sugarcane vendor in Dhaka
File:Sugarcane stalks.jpg, Sugarcane stalks
File:Sugarcane flowering.JPG, Sugarcane flowering
File:Sugarcane plantation 01.jpg, Sugarcane plantation
File:Sugarcane field of Kachirapalayam.jpg, Leaves of sugarcane
File:Sugarcane in Hoshiarpur.jpg, Sugarcane plantation
File:Sugarcane of Chinna Salem.jpg, Sugarcane of China
File:Sugarcane of Salem.jpg, Sugarcane
File:Sugarcane Flowers in Java.jpg, Flowers of sugarcane
File:Woman collecting sugar canes in Vietnam.jpg, Sugarcane harvested by women, Hòa Bình Province, Vietnam
File:Cane syrup evaporator 1330.jpg, alt=Outdoor photo of series of rectangular metal trays divided by short internal metal sheets, Evaporator with baffled pan and foam dipper for making ribbon cane syrup
File:A video of Sugarcane juice extraction.ogv, A video of sugarcane juice extraction
File:CSIRO ScienceImage 10529 Sugarcane and bowl of sugar.jpg, Sugarcane and bowl of refined sugar
File:Cocktail Caipirinha raw.jpg, ''Caipirinha'', a cocktail made from sugarcane-derived ''cachaça''
File:Sugarcane Processing.jpg, Sugarcane processing
File:Mai saida rake.jpg, Hausa man selling sugarcane at Kaduna in Nigeria
from oecd
{{Authority control Saccharum, * Sugar Crops originating from Asia Energy crops Ethanol fuel Flora of tropical Asia Articles containing video clips Crops Tropical agriculture Plant common names
 Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall,
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also wid ...
grass (in the genus ''Saccharum
''Saccharum'' is a genus of tall perennial plants of the broomsedge tribe within the grass family.
The genus is widespread across tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions in Africa, Eurasia, Australia, the Americas, and assorted oceani ...
'', tribe Andropogoneae
The Andropogoneae, sometimes called the sorghum tribe, are a large tribe of grasses (family Poaceae) with roughly 1,200 species in 90 genera, mainly distributed in tropical and subtropical areas. They include such important crops as maize (corn), ...
) that is used for sugar production
Production may refer to:
Economics and business
* Production (economics)
* Production, the act of manufacturing goods
* Production, in the outline of industrial organization, the act of making products (goods and services)
* Production as a stati ...
. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sucrose, which accumulates in the stalk internodes. Sugarcanes belong to the grass family, Poaceae, an economically important flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
family that includes maize, wheat, rice, and sorghum, and many forage
Forage is a plant material (mainly plant leaves and stems) eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term ''forage'' has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also used ...
crops. It is native to the warm temperate and tropical regions of India, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
. The plant is also grown for biofuel production, especially in Brazil, as the canes can be used directly to produce ethyl alcohol (ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
).
Grown in tropical and subtropical regions, sugarcane is the world's largest crop by production quantity, totaling 1.9 billion tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s in 2020, with Brazil accounting for 40% of the world total. Sugarcane accounts for 79% of sugar produced globally (most of the rest is made from sugar beets). About 70% of the sugar produced comes from ''Saccharum officinarum
''Saccharum officinarum'' is a large, strong-growing species of grass in the genus '' Saccharum''. Its stout stalks are rich in sucrose, a simple sugar which accumulates in the stalk internodes. It originated in New Guinea, and is now cultivated ...
'' and its hybrids. All sugarcane species can interbreed
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in ...
, and the major commercial cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture ...
s are complex hybrids.
Sucrose (table sugar) is extracted from sugarcane in specialized mill factories. It is consumed directly in confectionery, used to sweeten beverages, as a preservative in jams and conserves, as a decorative finish for cakes and pâtisserie
A () is a type of Italian, French or Belgian bakery that specializes in pastries and sweets, as well as a term for such food items. In some countries, it is a legally controlled title that may only be used by bakeries that employ a licensed ...
, as a raw material in the food industry, or fermented to produce ethanol. Products derived from fermentation of sugar include falernum
Falernum (pronounced ) is either an 11% ABV syrup liqueur or a nonalcoholic syrup from the Caribbean. It is best known for its use in tropical drinks. It contains flavors of ginger, lime, and almond, and frequently cloves or allspice. It may be ...
, rum
Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is usually aged in oak barrels. Rum is produced in nearly every sugar-producing region of the world, such as the Ph ...
, and cachaça
''Cachaça'' () is a distilled spirit made from fermented sugarcane juice. Also known as ''pinga'', ''caninha'', and other names, it is the most popular spirit among distilled alcoholic beverages in Brazil.Cavalcante, Messias Soares. Todos os n ...
. In some regions, people use sugarcane reeds to make pens, mats, screens, and thatch. The young, unexpanded flower head
A pseudanthium (Greek for "false flower"; ) is an inflorescence that resembles a flower. The word is sometimes used for other structures that are neither a true flower nor a true inflorescence. Examples of pseudanthia include flower heads, compos ...
of ''Saccharum edule
''Saccharum edule'' is a species of sugarcane, that is a grass in the genus '' Saccharum'' with a fibrous stalk that is rich in sugar. It is cultivated in tropical climates in southeastern Asia. It has many common names which include duruka, tebu ...
'' (''duruka'') is eaten raw, steamed, or toasted, and prepared in various ways in Southeast Asia, such as certain island communities of Indonesia as well as in Oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
countries like Fiji.
Sugarcane was an ancient crop of the Austronesian and Papuan people. It was introduced to Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, and Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
in prehistoric times via Austronesian sailors. It was also introduced to southern China and India by Austronesian traders around 1200 to 1000 BC. The Persians and Greeks encountered the famous "reeds that produce honey without bees" in India between the sixth and fourth centuries BC. They adopted and then spread sugarcane agriculture. Merchants began to trade in sugar, which was considered a luxurious and expensive spice, from India. In the 18th century, sugarcane plantations began in the Caribbean, South American, Indian Ocean, and Pacific island nations. The need for sugar crop laborers became a major driver of large migrations, some people voluntarily accepting indentured servitude and others forcibly imported as slaves.
Etymology
The term "sugarcane" combines theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
word, शर्करा (''śárkarā'', later سُكَّر ''sukkar'' from Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, and ''sucre'' from Middle French
Middle French (french: moyen français) is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the 14th to the 16th century. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from ...
and Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
) with "cane", a crop grown on plantations in the Caribbean ''gana'', Hindi for ''cane''. This term was first used by Spanish settlers in the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
in the early 16th century.
Description
 Sugarcane is a tropical, perennial grass that forms lateral shoots at the base to produce multiple stems, typically high and about in diameter. The stems grow into cane stalk, which when mature, constitutes around 75% of the entire plant. A mature stalk is typically composed of 11–16% fiber, 12–16% soluble sugars, 2–3% nonsugar carbohydrates, and 63–73% water. A sugarcane crop is sensitive to climate, soil type, irrigation, fertilizers, insects, disease control, varieties, and the harvest period. The average yield of cane stalk is per year, but this figure can vary between 30 and 180 tonnes per hectare depending on knowledge and crop management approach used in sugarcane cultivation. Sugarcane is a cash crop, but it is also used as livestock fodder. Sugarcane genome is one of the most complex plant genomes known, mostly due to interspecific hybridization and polyploidization.
Sugarcane is a tropical, perennial grass that forms lateral shoots at the base to produce multiple stems, typically high and about in diameter. The stems grow into cane stalk, which when mature, constitutes around 75% of the entire plant. A mature stalk is typically composed of 11–16% fiber, 12–16% soluble sugars, 2–3% nonsugar carbohydrates, and 63–73% water. A sugarcane crop is sensitive to climate, soil type, irrigation, fertilizers, insects, disease control, varieties, and the harvest period. The average yield of cane stalk is per year, but this figure can vary between 30 and 180 tonnes per hectare depending on knowledge and crop management approach used in sugarcane cultivation. Sugarcane is a cash crop, but it is also used as livestock fodder. Sugarcane genome is one of the most complex plant genomes known, mostly due to interspecific hybridization and polyploidization.
History
The two centers of domestication for sugarcane are one for ''Saccharum officinarum
''Saccharum officinarum'' is a large, strong-growing species of grass in the genus '' Saccharum''. Its stout stalks are rich in sucrose, a simple sugar which accumulates in the stalk internodes. It originated in New Guinea, and is now cultivated ...
'' by Papuans
The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Arch ...
in New Guinea and another for ''Saccharum sinense
''Saccharum sinense'' or ''Saccharum'' × ''sinense'', synonym ''Saccharum'' × ''barberi'', sugarcane, is strong-growing species of grass (Poaceae) in the genus ''Saccharum''. It is originally cultivated in Guangzhou, China where it is still c ...
'' by Austronesians in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
and southern China. Papuans and Austronesians originally primarily used sugarcane as food for domesticated pigs. The spread of both ''S. officinarum'' and ''S. sinense'' is closely linked to the migrations of the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austro ...
. ''Saccharum barberi
''Saccharum sinense'' or ''Saccharum'' × ''sinense'', synonym ''Saccharum'' × ''barberi'', sugarcane, is strong-growing species of grass (Poaceae) in the genus '' Saccharum''. It is originally cultivated in Guangzhou, China where it is still ...
'' was only cultivated in India after the introduction of ''S. officinarum''.
''S. officinarum'' was first domesticated in New Guinea and the islands east of the Wallace Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a trans ...
by Papuans, where it is the modern center of diversity. Beginning around 6,000 BP, several strains were selectively bred
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
from the native ''Saccharum robustum
''Saccharum robustum'', the robust cane, is a species of plant found in New Guinea.
Ecology
''Eumetopina flavipes'', the island sugarcane planthopper, a species of planthopper present throughout South East Asia and is a vector for the Ramu stun ...
''. From New Guinea, it spread westwards to maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
after contact with Austronesians, where it hybridized with ''Saccharum spontaneum
''Saccharum spontaneum'' (wild sugarcane, Kans grass) is a grass native to the Indian Subcontinent. It is a perennial grass, growing up to three meters in height, with spreading rhizomatous roots.
In the Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands, a l ...
''.
The second domestication center is mainland southern China and Taiwan, where ''S. sinense'' was a primary cultigen
A cultigen () or cultivated plant is a plant that has been deliberately altered or selected by humans; it is the result of artificial selection. These plants, for the most part, have commercial value in horticulture, agriculture or forestry. Beca ...
of the Austronesian peoples. Words for sugarcane are reconstructed as '' *təbuS'' or ''*CebuS'' in Proto-Austronesian
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify ...
, which became ''*tebuh'' in Proto-Malayo-Polynesian
Proto-Malayo-Polynesian (PMP) is the reconstructed ancestor of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, which is by far the largest branch (by current speakers) of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Malayo-Polynesian is ancestral to all Austronesi ...
. It was one of the original major crops of the Austronesian peoples from at least 5,500 BP. Introduction of the sweeter ''S. officinarum'' may have gradually replaced it throughout its cultivated range in maritime Southeast Asia.
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
and Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
by Austronesian voyagers as a canoe plant
One of the major human migration events was the maritime settlement of the islands of the Indo-Pacific by the Austronesian peoples, believed to have started from at least 5,500 to 4,000 BP (3500 to 2000 BCE). These migrations were accompanied ...
by around 3,500 BP. It was also spread westward and northward by around 3,000 BP to China and India by Austronesian traders, where it further hybridized with ''S. sinense'' and ''S. barberi''. From there, it spread further into western Eurasia and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
.
The earliest known production of crystalline sugar began in northern India. The earliest evidence of sugar production comes from ancient Sanskrit and Pali texts. Around the eighth century, Muslim and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
traders introduced sugar from medieval India
Medieval India refers to a long period of Post-classical history of the Indian subcontinent between the "ancient period" and "modern period". It is usually regarded as running approximately from the breakup of the Gupta Empire in the 6th cen ...
to the other parts of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
in the Mediterranean, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, North Africa, and Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The t ...
. By the 10th century, sources state that every village in Mesopotamia grew sugarcane.Watson, Andrew (1983). ''Agricultural innovation in the early Islamic world''. Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pre ...
. pp. 26–27. It was among the early crops brought to the Americas by the Spanish, mainly Andalusians, from their fields in the Canary Islands, and the Portuguese from their fields in the Madeira Islands
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
. An article on sugarcane cultivation in Spain is included in Ibn al-'Awwam
Ibn al-'Awwam ( ar, ابن العوام), also called Abu Zakariya Ibn al-Awwam ( ar, أبو زكريا بن العوام), was a Muslim Arab agriculturist who flourished at Seville (modern-day southern Spain) in the later 12th century. He wrote a ...
's 12th-century ''Book on Agriculture''.
For thousands of years, cane was a heavy and unwieldy crop that had to be cut by hand and immediately ground to release the juice inside, lest it spoil within a day or two. Even before harvest time, rows had to be dug, stalks planted and plentiful wood chopped as fuel for boiling the liquid and reducing it to crystals and molasses. From the earliest traces of cane domestication on the Pacific island of New Guinea 10,000 years ago to its island-hopping advance to ancient India in 350 B.C., sugar was locally consumed and very labor-intensive. It remained little more than an exotic spice, medicinal glaze or sweetener for elite palates.
In colonial times, sugar formed one side of the triangle trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset t ...
of New World raw materials, along with European manufactured goods, and African slaves. Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
first brought sugarcane to the Caribbean during his second voyage to the Americas, initially to the island of Hispaniola (modern day Haiti and the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
). The first sugar harvest happened in Hispaniola in 1501; and many sugar mills had been constructed in Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
and Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
by the 1520s. The Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
took sugar to Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. By 1540, there were 800 cane sugar mill
A sugar cane mill is a factory that processes sugar cane to produce raw or white sugar.
The term is also used to refer to the equipment that crushes the sticks of sugar cane to extract the juice.
Processing
There are a number of steps in p ...
s in Santa Catarina Island
Santa Catarina Island ( pt, Ilha de Santa Catarina) is an island in the Brazilian state of Santa Catarina, located off the southern coast.
It is home to the state capital, Florianópolis.
Location
Santa Catarina Island is approximately 54 k ...
and there were another 2,000 on the north coast of Brazil, Demarara, and Suriname.
Sugar, often in the form of molasses, was shipped from the Caribbean to Europe or New England, where it was used to make rum
Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is usually aged in oak barrels. Rum is produced in nearly every sugar-producing region of the world, such as the Ph ...
. The profits from the sale of sugar were then used to purchase manufactured goods, which were then shipped to West Africa, where they were bartered for slaves. The slaves were then brought back to the Caribbean to be sold to sugar planters. The profits from the sale of the slaves were then used to buy more sugar, which was shipped to Europe. Toil in the sugar plantations became a main basis for a vast network of forced population movement, supplying people to work under brutal coercion.
France found its sugarcane islands so valuable that it effectively traded its portion of Canada, famously dismissed by Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his ''nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—es ...
as "a few acres of snow
"A few acres of snow" (in the original French, "", , with "") is one of several quotations from Voltaire, an 18th-century writer. They are representative of his sneering evaluation of Canada as lacking economic value and strategic importance to ...
", to Britain for their return of Guadeloupe, Martinique, and St. Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerin ...
at the end of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
. The Dutch similarly kept Suriname, a sugar colony in South America, instead of seeking the return of the New Netherlands
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva P ...
(New York).
Boiling house
A boilery or boiling house is a place of boiling, much as a bakery
A bakery is an establishment that produces and sells flour-based food baked in an oven such as bread, cookies, cakes, donuts, pastries, and pies. Some retail bakeries are a ...
s in the 17th through 19th centuries converted sugarcane juice
Sugarcane juice is the liquid extracted from pressed sugarcane. It is consumed as a beverage in many places, especially where sugarcane is commercially grown, such as Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, North Africa, and Latin America.
Sug ...
into raw sugar. These houses were attached to sugar plantations in the Western colonies. Slaves often ran the boiling process under very poor conditions. Rectangular boxes of brick or stone served as furnaces, with an opening at the bottom to stoke the fire and remove ashes. At the top of each furnace were up to seven copper kettles or boilers, each one smaller and hotter than the previous one. The cane juice began in the largest kettle. The juice was then heated and lime added to remove impurities. The juice was skimmed and then channeled to successively smaller kettles. The last kettle, the "teache", was where the cane juice became syrup. The next step was a cooling trough, where the sugar crystals hardened around a sticky core of molasses. This raw sugar was then shoveled from the cooling trough into hogsheads (wooden barrels), and from there into the curing house.
 The passage of the 1833 Slavery Abolition Act led to the abolition of slavery through most of the
The passage of the 1833 Slavery Abolition Act led to the abolition of slavery through most of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, and many of the emancipated slaves no longer worked on sugarcane plantations when they had a choice. West Indian planters, therefore, needed new workers, and they found cheap labour in China and India. The people were subject to indenture, a long-established form of contract, which bound them to unfree labour for a fixed term. The conditions where the indentured servants worked were frequently abysmal, owing to a lack of care among the planters. The first ships carrying indentured labourers from India left in 1836. The migrations to serve sugarcane plantations led to a significant number of ethnic Indians, Southeast Asians, and Chinese people settling in various parts of the world. In some islands and countries, the South Asian migrants now constitute between 10 and 50% of the population. Sugarcane plantations and Asian ethnic groups continue to thrive in countries such as Fiji, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
, Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Sri Lanka, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, British Guiana, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
, Martinique, French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
, Guadeloupe, Grenada, St. Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerin ...
, St. Vincent, St. Kitts, St. Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
, Suriname, Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and ...
, and Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
.
 Between 1863 and 1900, merchants and plantation owners in
Between 1863 and 1900, merchants and plantation owners in Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
and New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
(now part of the Commonwealth of Australia) brought between 55,000 and 62,500 people from the South Pacific Islands to work on sugarcane plantations. An estimated one-third of these workers were coerced or kidnapped into slavery (known as blackbirding
Blackbirding involves the coercion of people through deception or kidnapping to work as slaves or poorly paid labourers in countries distant from their native land. The term has been most commonly applied to the large-scale taking of people in ...
). Many others were paid very low wages. Between 1904 and 1908, most of the 10,000 remaining workers were deported in White Australia Policy, an effort to keep Australia racially homogeneous and protect white people, white workers from cheap foreign labour.
Cuban sugar derived from sugarcane was exported to the Soviet Union, USSR, where it received price supports and was ensured a guaranteed market. The Dissolution of the Soviet Union, 1991 dissolution of the Soviet state forced the closure of most of Cuba's sugar industry.
Sugarcane remains an important part of the economy of Guyana, Belize, Barbados, and Haiti, along with the
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, Guadeloupe, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, and other islands.
About 70% of the sugar produced globally comes from ''S. officinarum'' and hybrids using this species.

Cultivation



 Sugarcane cultivation requires a tropical or subtropical climate, with a minimum of of annual moisture. It is one of the most Photosynthetic efficiency, efficient Photosynthesis, photosynthesizers in the plant kingdom. It is a C4 carbon fixation, C4 plant, able to convert up to 1% of incident solar energy into biomass. In primary growing regions across the tropics and subtropics, sugarcane crops can produce over 15 kg/m2 of cane. Once a major crop of the southeastern region of the United States, sugarcane cultivation declined there during the late 20th century, and is primarily confined to small plantations in Sugar Cane Growers Cooperative of Florida, Florida, Louisiana, and southeast Texas in the 21st century. Sugarcane cultivation ceased in Hawaii when the last operating sugar plantation in the state shut down in 2016.
Sugarcane is cultivated in the tropics and subtropics in areas with a plentiful supply of water for a continuous period of more than 6–7 months each year, either from natural rainfall or through irrigation. The crop does not tolerate severe frosts. Therefore, most of the world's sugarcane is grown between 22nd parallel north, 22°N and 22nd parallel south, 22°S, and some up to 33rd parallel north, 33°N and 33rd parallel south, 33°S. When sugarcane crops are found outside this range, such as the KwaZulu-Natal, Natal region of South Africa, it is normally due to anomalous climatic conditions in the region, such as warm ocean currents that sweep down the coast. In terms of altitude, sugarcane crops are found up to close to the equator in countries such as Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.
Sugarcane can be grown on many soils ranging from highly fertile, well-drained mollisols, through heavy cracking vertisols, infertile acid oxisols and ultisols, peaty histosols, to rocky andisols. Both plentiful sunshine and water supplies increase cane production. This has made desert countries with good irrigation facilities such as Egypt some of the highest-yielding sugarcane-cultivating regions. Sugarcane consumes 9% of the world's potash fertilizer production.
Although some sugarcanes produce seeds, modern stem cutting has become the most common reproduction method. Each cutting must contain at least one bud, and the cuttings are sometimes hand-planted. In more technologically advanced countries, such as the United States and Australia, billet planting is common. Billets (stalks or stalk sections) harvested by a mechanical harvester are planted by a machine that opens and recloses the ground. Once planted, a stand can be harvested several times; after each harvest, the cane sends up new stalks, called ratoons. Successive harvests give decreasing yields, eventually justifying replanting. Two to 10 harvests are usually made depending on the type of culture. In a country with a mechanical agriculture looking for a high production of large fields, as in North America, sugarcanes are replanted after two or three harvests to avoid a lowering yields. In countries with a more traditional type of agriculture with smaller fields and hand harvesting, as in the French island la Réunion, sugarcane is often harvested up to 10 years before replanting.
Sugarcane is harvested by hand and mechanically. Hand harvesting accounts for more than half of production, and is dominant in the developing world. In hand harvesting, the field is first set on fire. The fire burns up dry leaves, and chases away or kills venomous snakes, without harming the stalks and roots. Harvesters then cut the cane just above ground-level using cane knife, cane knives or machetes. A skilled harvester can cut of sugarcane per hour.
Mechanical harvesting uses a combine harvester, combine, or sugarcane harvester. The Austoft 7000 series, the original modern harvester design, has now been copied by other companies, including Cameco / Deere & Company, John Deere. The machine cuts the cane at the base of the stalk, strips the leaves, chops the cane into consistent lengths and deposits it into a transporter following alongside. The harvester then blows the trash back onto the field. Such machines can harvest each hour, but harvested cane must be rapidly processed. Once cut, sugarcane begins to lose its sugar content, and damage to the cane during mechanical harvesting accelerates this decline. This decline is offset because a modern chopper harvester can complete the harvest faster and more efficiently than hand cutting and loading. Austoft also developed a series of hydraulic high-lift infield transporters to work alongside its harvesters to allow even more rapid transfer of cane to, for example, the nearest railway siding. This mechanical harvesting does not require the field to be set on fire; the residue left in the field by the machine consists of cane tops and dead leaves, which serve as mulch for the next planting.
Sugarcane cultivation requires a tropical or subtropical climate, with a minimum of of annual moisture. It is one of the most Photosynthetic efficiency, efficient Photosynthesis, photosynthesizers in the plant kingdom. It is a C4 carbon fixation, C4 plant, able to convert up to 1% of incident solar energy into biomass. In primary growing regions across the tropics and subtropics, sugarcane crops can produce over 15 kg/m2 of cane. Once a major crop of the southeastern region of the United States, sugarcane cultivation declined there during the late 20th century, and is primarily confined to small plantations in Sugar Cane Growers Cooperative of Florida, Florida, Louisiana, and southeast Texas in the 21st century. Sugarcane cultivation ceased in Hawaii when the last operating sugar plantation in the state shut down in 2016.
Sugarcane is cultivated in the tropics and subtropics in areas with a plentiful supply of water for a continuous period of more than 6–7 months each year, either from natural rainfall or through irrigation. The crop does not tolerate severe frosts. Therefore, most of the world's sugarcane is grown between 22nd parallel north, 22°N and 22nd parallel south, 22°S, and some up to 33rd parallel north, 33°N and 33rd parallel south, 33°S. When sugarcane crops are found outside this range, such as the KwaZulu-Natal, Natal region of South Africa, it is normally due to anomalous climatic conditions in the region, such as warm ocean currents that sweep down the coast. In terms of altitude, sugarcane crops are found up to close to the equator in countries such as Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.
Sugarcane can be grown on many soils ranging from highly fertile, well-drained mollisols, through heavy cracking vertisols, infertile acid oxisols and ultisols, peaty histosols, to rocky andisols. Both plentiful sunshine and water supplies increase cane production. This has made desert countries with good irrigation facilities such as Egypt some of the highest-yielding sugarcane-cultivating regions. Sugarcane consumes 9% of the world's potash fertilizer production.
Although some sugarcanes produce seeds, modern stem cutting has become the most common reproduction method. Each cutting must contain at least one bud, and the cuttings are sometimes hand-planted. In more technologically advanced countries, such as the United States and Australia, billet planting is common. Billets (stalks or stalk sections) harvested by a mechanical harvester are planted by a machine that opens and recloses the ground. Once planted, a stand can be harvested several times; after each harvest, the cane sends up new stalks, called ratoons. Successive harvests give decreasing yields, eventually justifying replanting. Two to 10 harvests are usually made depending on the type of culture. In a country with a mechanical agriculture looking for a high production of large fields, as in North America, sugarcanes are replanted after two or three harvests to avoid a lowering yields. In countries with a more traditional type of agriculture with smaller fields and hand harvesting, as in the French island la Réunion, sugarcane is often harvested up to 10 years before replanting.
Sugarcane is harvested by hand and mechanically. Hand harvesting accounts for more than half of production, and is dominant in the developing world. In hand harvesting, the field is first set on fire. The fire burns up dry leaves, and chases away or kills venomous snakes, without harming the stalks and roots. Harvesters then cut the cane just above ground-level using cane knife, cane knives or machetes. A skilled harvester can cut of sugarcane per hour.
Mechanical harvesting uses a combine harvester, combine, or sugarcane harvester. The Austoft 7000 series, the original modern harvester design, has now been copied by other companies, including Cameco / Deere & Company, John Deere. The machine cuts the cane at the base of the stalk, strips the leaves, chops the cane into consistent lengths and deposits it into a transporter following alongside. The harvester then blows the trash back onto the field. Such machines can harvest each hour, but harvested cane must be rapidly processed. Once cut, sugarcane begins to lose its sugar content, and damage to the cane during mechanical harvesting accelerates this decline. This decline is offset because a modern chopper harvester can complete the harvest faster and more efficiently than hand cutting and loading. Austoft also developed a series of hydraulic high-lift infield transporters to work alongside its harvesters to allow even more rapid transfer of cane to, for example, the nearest railway siding. This mechanical harvesting does not require the field to be set on fire; the residue left in the field by the machine consists of cane tops and dead leaves, which serve as mulch for the next planting.
Pests
The cane beetle (also known as cane grub) can substantially reduce crop yield by eating roots; it can be controlled with imidacloprid (Confidor) or chlorpyrifos (Lorsban). Other important pests are the larvae of some lepidoptera, butterfly/moth species, including the turnip moth, the sugarcane borer (''Diatraea saccharalis''), the Eldana, African sugarcane borer (''Eldana saccharina''), the Mexican rice borer (''Eoreuma loftini''), the African armyworm (''Spodoptera exempta''), leaf-cutting ants, termites, spittlebugs (especially ''Mahanarva fimbriolata'' and ''Deois flavopicta''), and the beetle ''Migdolus fryanus''. The planthopper insect ''Eumetopina flavipes'' acts as a virus vector, which causes the sugarcane disease ramu stunt.Pathogens
Numerous pathogens infect sugarcane, such as sugarcane grassy shoot disease caused by 'Candidatus Phytoplasma sacchari', whiptail disease or sugarcane smut, ''pokkah boeng'' caused by ''Fusarium moniliforme'', Xanthomonas axonopodis bacteria causes Gumming Disease, and red rot disease caused by ''Colletotrichum falcatum''. Virus, Viral diseases affecting sugarcane include sugarcane mosaic virus, maize streak virus, and sugarcane yellow leaf virus.Nitrogen fixation
Some sugarcane varieties are capable of Nitrogen fixation, fixing atmospheric nitrogen in association with the bacterium ''Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus''. Unlike legumes and other nitrogen-fixing plants that form root nodules in the soil in association with bacteria, ''G. diazotrophicus'' lives within the intercellular spaces of the sugarcane's stem. Coating seeds with the bacteria is a newly developed technology that can enable every crop species to fix nitrogen for its own use.Conditions for sugarcane workers
At least 20,000 people are estimated to have died of chronic kidney disease in Central America in the past two decades – most of them sugarcane workers along the Pacific coast. This may be due to working long hours in the heat without adequate fluid intake. Not only are they dying because of exhaustion but some of the workers are being exposed to several hazards such as, high temperatures, harmful pesticides, and poisonous or venomous animals. This all occurs during the process of cutting the sugarcane manually, also causing physical ailments by doing the same movements for hours every work day.Processing
Traditionally, sugarcane processing requires two stages. Mills extract raw sugar from freshly harvested cane and "mill-white" sugar is sometimes produced immediately after the first stage at sugar-extraction mills, intended for local consumption. Sugar crystals appear naturally white in color during the crystallization process. Sulfur dioxide is added to inhibit the formation of color-inducing molecules and to stabilize the sugar juices during evaporation. Refineries, often located nearer to consumers in North America, Europe, and Japan, then produce refined white sugar, which is 99% sucrose. These two stages are slowly merging. Increasing affluence in the sugarcane-producing tropics increases demand for refined sugar products, driving a trend toward combined milling and refining.Milling
 The primary use of bagasse and bagasse residue is as a fuel source for the boilers in the generation of process steam in sugar plants. Dried filtercake is used as an animal feed supplement, fertilizer, and source of sugarcane wax.
Molasses is produced in two forms: Molasses#Blackstrap Molasses, blackstrap, which has a characteristic strong flavor, and a purer molasses syrup. Blackstrap molasses is sold as a food and dietary supplement. It is also a common ingredient in animal feed, and is used to produce ethanol, rum, and citric acid. Purer molasses syrups are sold as molasses, and may also be blended with maple syrup, invert sugars, or corn syrup. Both forms of molasses are used in baking.
The primary use of bagasse and bagasse residue is as a fuel source for the boilers in the generation of process steam in sugar plants. Dried filtercake is used as an animal feed supplement, fertilizer, and source of sugarcane wax.
Molasses is produced in two forms: Molasses#Blackstrap Molasses, blackstrap, which has a characteristic strong flavor, and a purer molasses syrup. Blackstrap molasses is sold as a food and dietary supplement. It is also a common ingredient in animal feed, and is used to produce ethanol, rum, and citric acid. Purer molasses syrups are sold as molasses, and may also be blended with maple syrup, invert sugars, or corn syrup. Both forms of molasses are used in baking.
Refining
sugar refinery, Sugar refining further purifies the raw sugar. It is first mixed with heavy syrup and then centrifuged in a process called "affination". Its purpose is to wash away the sugar crystals' outer coating, which is less pure than the crystal interior. The remaining sugar is then dissolved to make a syrup, about 60% solids by weight. The sugar solution is clarified by the addition of phosphoric acid and calcium hydroxide, which combine to precipitate calcium phosphate. The calcium phosphate particles entrap some impurities and absorb others, and then float to the top of the tank, where they can be skimmed off. An alternative to this "phosphatation" technique is "carbonatation", which is similar, but uses carbon dioxide and calcium hydroxide to produce a calcium carbonate precipitate. After filtering any remaining solids, the clarified syrup is decolorized by filtration through activated carbon. Bone char or coal-based activated carbon is traditionally used in this role. Some remaining color-forming impurities are adsorbed by the carbon. The purified syrup is then concentrated to supersaturation and repeatedly crystallized in a vacuum, to produce white refined sugar. As in a sugar mill, the sugar crystals are separated from the molasses by centrifuging. Additional sugar is recovered by blending the remaining syrup with the washings from affination and again crystallizing to produce brown sugar. When no more sugar can be economically recovered, the final molasses still contains 20–30% sucrose and 15–25% glucose and fructose. To produce granulated sugar, in which individual grains do not clump, sugar must be dried, first by heating in a rotary dryer, and then by blowing cool air through it for several days.Ribbon cane syrup
Ribbon cane is a subtropical type that was once widely grown in the Southern United States, as far north as coastal North Carolina. The juice was extracted with horse- or mule-powered crushers; the juice was boiled, like maple syrup, in a flat pan, and then used in the syrup form as a food sweetener. It is not currently a commercial crop, but a few growers find ready sales for their product.Pollution from sugarcane processing
Particulate matter, combustion products, and volatile organic compounds are the primary pollutants emitted during the sugarcane processing. Combustion products include nitrogen oxides (NOX), carbon monoxide (CO), CO2, and sulfur oxides (SOX). Potential emission sources include the sugar granulators, sugar conveying and packaging equipment, bulk loadout operations, boilers, granular carbon and char regeneration kilns, regenerated adsorbent transport systems, kilns and handling equipment (at some facilities), carbonation tanks, multi-effect evaporator stations, and vacuum boiling pans.Production
In 2020, global production of sugarcane was 1.87 billion tonnes, with Brazil producing 40% of the world total, India with 20%, and China producing 6% (table). Worldwide, 26 million hectares were devoted to sugarcane cultivation in 2020. The average worldwide yield of sugarcane crops in 2020 was 71 tonnes per hectare, led by Peru with 123 tonnes per hectare. The theoretical possible yield for sugarcane is about 280 tonnes per hectare per year, and small experimental plots in Brazil have demonstrated yields of 236–280 tonnes of cane per hectare. From 2008 to 2016, production of standards-compliant sugarcane experienced a compound annual growth rate of about 52%, while conventional sugarcane increased at less than 1%.Ethanol
 Ethanol is generally available as a byproduct of sugar production. It can be used as a biofuel alternative to gasoline, and is widely used in cars in Brazil. It is an alternative to gasoline, and may become the primary product of sugarcane processing, rather than sugar.
Ethanol is generally available as a byproduct of sugar production. It can be used as a biofuel alternative to gasoline, and is widely used in cars in Brazil. It is an alternative to gasoline, and may become the primary product of sugarcane processing, rather than sugar.
 In Brazil, gasoline is required to contain at least 22% bioethanol. This bioethanol is sourced from Brazil's large sugarcane crop.
The production of ethanol from sugarcane is more energy efficient than from corn or sugar beets or palm/vegetable oils, particularly if cane bagasse is used to produce heat and power for the process. Furthermore, if biofuels are used for crop production and transport, the fossil energy input needed for each ethanol energy unit can be very low. EIA estimates that with an integrated sugar cane to ethanol technology, the well-to-wheels CO2 emissions can be 90% lower than conventional gasoline. A textbook on renewable energy describes the energy transformation:
In Brazil, gasoline is required to contain at least 22% bioethanol. This bioethanol is sourced from Brazil's large sugarcane crop.
The production of ethanol from sugarcane is more energy efficient than from corn or sugar beets or palm/vegetable oils, particularly if cane bagasse is used to produce heat and power for the process. Furthermore, if biofuels are used for crop production and transport, the fossil energy input needed for each ethanol energy unit can be very low. EIA estimates that with an integrated sugar cane to ethanol technology, the well-to-wheels CO2 emissions can be 90% lower than conventional gasoline. A textbook on renewable energy describes the energy transformation:
Presently, 75 tons of raw sugar cane are produced annually per hectare in Brazil. The cane delivered to the processing plant is called burned and cropped (b&c), and represents 77% of the mass of the raw cane. The reason for this reduction is that the stalks are separated from the leaves (which are burned and whose ashes are left in the field as fertilizer), and from the roots that remain in the ground to sprout for the next crop. Average cane production is, therefore, 58 tons of b&c per hectare per year.
Each ton of b&c yields 740 kg of juice (135 kg of sucrose and 605 kg of water) and 260 kg of moist bagasse (130 kg of dry bagasse). Since the lower heating value of sucrose is 16.5 Mjoule, J/kg, and that of the bagasse is 19.2 MJ/kg, the total heating value of a ton of b&c is 4.7 GJ of which 2.2 GJ come from the sucrose and 2.5 from the bagasse.
Per hectare per year, the biomass produced corresponds to 0.27 TJ. This is equivalent to 0.86 W per square meter. Assuming an average insolation of 225 W per square meter, the photosynthetic efficiency of sugar cane is 0.38%.
The 135 kg of sucrose found in 1 ton of b&c are transformed into 70 litres of ethanol with a combustion energy of 1.7 GJ. The practical sucrose-ethanol conversion efficiency is, therefore, 76% (compare with the theoretical 97%).
One hectare of sugar cane yields 4,000 litres of ethanol per year (without any additional energy input, because the bagasse produced exceeds the amount needed to distill the final product). This, however, does not include the energy used in tilling, transportation, and so on. Thus, the solar energy-to-ethanol conversion efficiency is 0.13%.
Bagasse applications
 Sugarcane is a major crop in many countries. It is one of the plants with the highest bioconversion efficiency. Sugarcane crop is able to efficiently fix solar energy, yielding some 55 tonnes of dry matter per hectare of land annually. After harvest, the crop produces sugar juice and bagasse, the fibrous dry matter. This dry matter is biomass with potential as fuel for energy production. Bagasse can also be used as an alternative source of pulp for paper production.
Sugarcane bagasse is a potentially abundant source of energy for large producers of sugarcane, such as Brazil, India, and China. According to one report, with use of latest technologies, bagasse produced annually in Brazil has the potential of meeting 20% of Brazil's energy consumption by 2020.
Sugarcane is a major crop in many countries. It is one of the plants with the highest bioconversion efficiency. Sugarcane crop is able to efficiently fix solar energy, yielding some 55 tonnes of dry matter per hectare of land annually. After harvest, the crop produces sugar juice and bagasse, the fibrous dry matter. This dry matter is biomass with potential as fuel for energy production. Bagasse can also be used as an alternative source of pulp for paper production.
Sugarcane bagasse is a potentially abundant source of energy for large producers of sugarcane, such as Brazil, India, and China. According to one report, with use of latest technologies, bagasse produced annually in Brazil has the potential of meeting 20% of Brazil's energy consumption by 2020.
Electricity production
A number of countries, in particular those lacking fossil fuels, have implemented energy conservation and efficiency measures to minimize the energy used in cane processing, and export any excess electricity to the grid. Bagasse is usually burned to produce steam, which in turn creates electricity. Current technologies, such as those in use inMauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
, produce over 100 kWh of electricity per tonne of bagasse. With a total world harvest of over one billion tonnes of sugar cane per year, the global energy potential from bagasse is over 100,000 GWh. Using Mauritius as a reference, an annual potential of 10,000 GWh of additional electricity could be produced throughout Africa. Electrical generation from bagasse could become quite important, particularly to the rural populations of sugarcane producing nations.
Recent cogeneration technology plants are being designed to produce from 200 to over 300 kWh of electricity per tonne of bagasse. As sugarcane is a seasonal crop, shortly after harvest the supply of bagasse would peak, requiring power generation plants to strategically manage the storage of bagasse.
Biogas production
A greener alternative to burning bagasse for the production of electricity is to convert bagasse into biogas. Technologies are being developed to use enzymes to transform bagasse into advanced biofuel and biogas.Sugarcane as food
In most countries where sugarcane is cultivated, several foods and popular dishes are derived directly from it, such as: * Raw sugarcane: chewed to extract the juice * ''Sayur nganten'': an Indonesian cuisine, Indonesian soup made with the stem of trubuk (''Saccharum edule''), a type of sugarcane * Sugarcane juice: a combination of fresh juice, extracted by hand or small mills, with a touch of lemon and ice to make a popular drink, known variously as ''air tebu'', ''usacha rass'', ''guarab'', ''guarapa,'' ''guarapo,'' ''papelón'', ''aseer asab'', ''ganna sharbat'', ''mosto'', ''caldo de cana'', or ''nước mía'' * Syrup: a traditional sweetener in soft drinks, now largely supplanted in the US by high fructose corn syrup, which is less expensive because of corn subsidies and sugar tariffs * Molasses: used as a Sugar substitute, sweetener and a syrup accompanying other foods, such as cheese or cookies * Jaggery: a solidified molasses, known as ''gur'', ''gud'', or ''gul'' in South Asia, is traditionally produced by evaporating juice to make a thick sludge, and then cooling and molding it in buckets. Modern production partially freeze dries the juice to reduce caramelization and lighten its color. It is used as sweetener in cooking traditional entrees, sweets, and desserts. * Falernum: a sweet, and slightly alcoholic drink made from sugarcane juice * ''Cachaça'': the most popular distilled alcoholic beverage in Brazil; it is a liquor made of the distillation of sugarcane juice. * Rum is a liquor made from sugarcane products, typically molasses, but sometimes also cane juice. It is most commonly produced in the Caribbean and environs. * Basi is a fermented alcoholic beverage made from sugarcane juice produced in thePhilippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Guyana.
* ''Panela'', solid pieces of sucrose and fructose obtained from the boiling and evaporation of sugarcane juice, is a food staple in Colombia and other countries in South and Central America.
* ''Rapadura'' is a sweet flour that is one of the simplest refinings of sugarcane juice, common in Latin American countries such as Brazil, Argentina, and Venezuela (where it is known as ''papelón'') and the Caribbean.
* Rock candy: crystallized cane juice
*'' Gâteau de Sirop''
*Viche (drink), Viche, a homebrewed Colombian alcoholic beverage
Sugarcane as feed
Many parts of the sugarcane are commonly used as animal feeds where the plants are cultivated. The leaves make a good forage for ruminants.Gallery
See also
* Sugar plantations in the Caribbean * Sugar plantations in Hawaii * Sugar industry of the Philippines * TrapicheReferences
External links
* * * Global sugar & sugar cane production statfrom oecd
{{Authority control Saccharum, * Sugar Crops originating from Asia Energy crops Ethanol fuel Flora of tropical Asia Articles containing video clips Crops Tropical agriculture Plant common names