Srtm ramp2.world.21600x10800.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort that obtained digital elevation models on a near-global scale from 56°S to
The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort that obtained digital elevation models on a near-global scale from 56°S to
 The elevation datasets are affected by mountain and desert no-data areas. These amount to no more than 0.2% of the total area surveyed, but can be a problem in areas of very high relief. They affect all summits over 8,000 meters, most summits over 7,000 meters, many Alpine and similar summits and ridges, and many gorges and canyons. There are some SRTM data sources which have filled these data voids, but some of these have used only
The elevation datasets are affected by mountain and desert no-data areas. These amount to no more than 0.2% of the total area surveyed, but can be a problem in areas of very high relief. They affect all summits over 8,000 meters, most summits over 7,000 meters, many Alpine and similar summits and ridges, and many gorges and canyons. There are some SRTM data sources which have filled these data voids, but some of these have used only
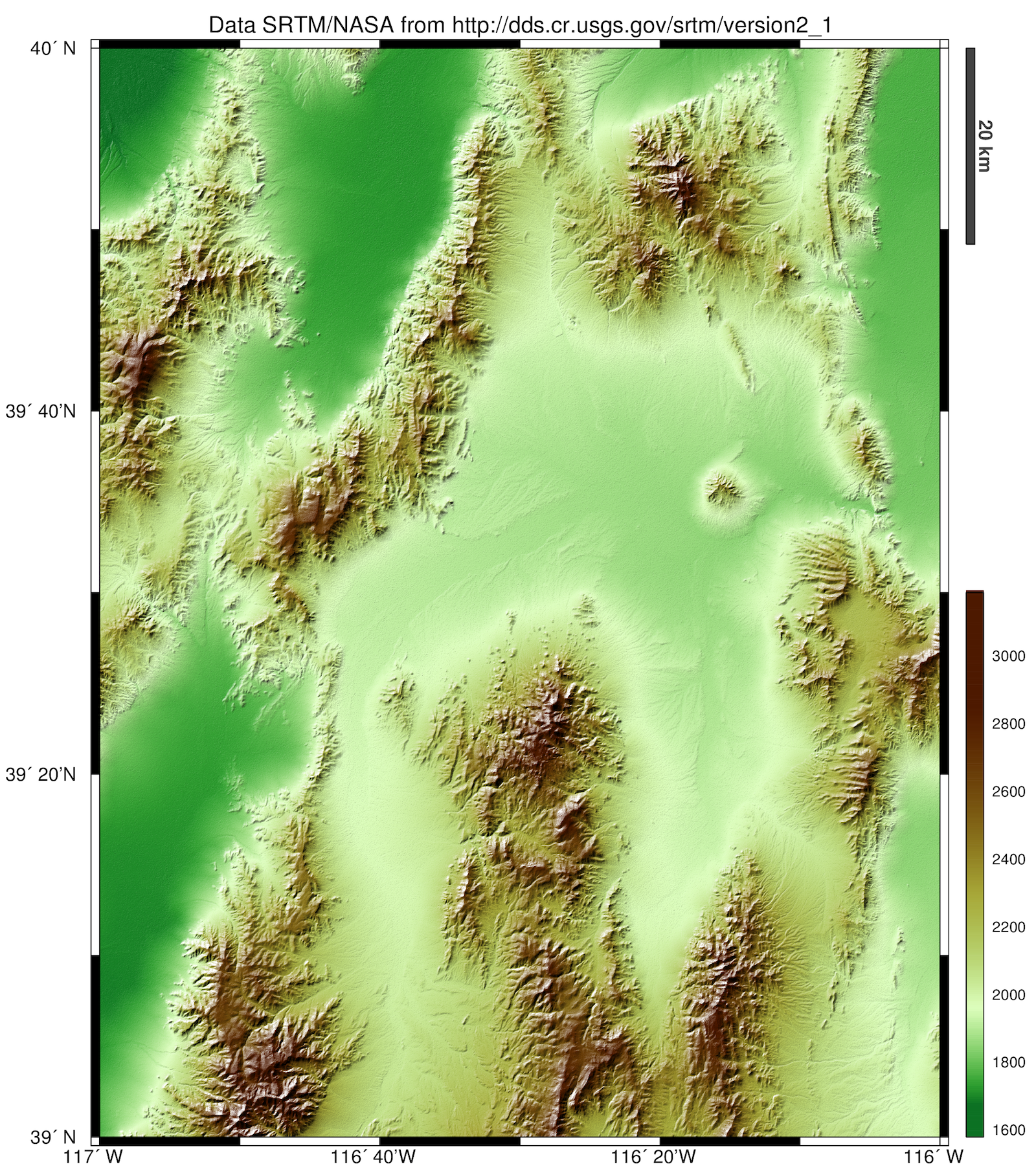 Groups of scientists have worked on algorithms to fill the voids of the original SRTM (v2.1) data. Three datasets offer global coverage void-filled SRTM data at full (3-arcsecond) resolution:
* The CGIAR-CSI version 4 provides the best global coverage using interpolation.
* The USGS HydroSHEDS dataset was generated for hydrological applications and is suitable for consistent drainage and water flow information. References are provided on the algorithms used and quality assessment.
* The void-filled SRTM data from Viewfinder Panoramas by Jonathan de Ferranti are high quality at full SRTM resolution. The data is filled using local survey maps and photographs. The OpenTopoMap website uses this fill. It has been partially updated for the 1-arcsecond release in the US.
In November 2013, LP DAAC released the NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Version 3.0 (SRTM Plus) Product collection with all voids eliminated. Voids were filled primarily from ASTER GDEM2, and secondarily from USGS GMTED2010 – or USGS National Elevation Dataset (NED) for the United States (except Alaska) and northernmost Mexico according to the announcement.
Groups of scientists have worked on algorithms to fill the voids of the original SRTM (v2.1) data. Three datasets offer global coverage void-filled SRTM data at full (3-arcsecond) resolution:
* The CGIAR-CSI version 4 provides the best global coverage using interpolation.
* The USGS HydroSHEDS dataset was generated for hydrological applications and is suitable for consistent drainage and water flow information. References are provided on the algorithms used and quality assessment.
* The void-filled SRTM data from Viewfinder Panoramas by Jonathan de Ferranti are high quality at full SRTM resolution. The data is filled using local survey maps and photographs. The OpenTopoMap website uses this fill. It has been partially updated for the 1-arcsecond release in the US.
In November 2013, LP DAAC released the NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Version 3.0 (SRTM Plus) Product collection with all voids eliminated. Voids were filled primarily from ASTER GDEM2, and secondarily from USGS GMTED2010 – or USGS National Elevation Dataset (NED) for the United States (except Alaska) and northernmost Mexico according to the announcement.
Official NASA SRTM site
(SRTM V1 and V2)
NASA MEaSUREs Products
(SRTM V3 and more)
NASA's server with SRTM data tiles
– Please read the accompanying documentation
– arcsecond-resolution derived data covering Australia * Void filled SRTM data a
CGIAR-CSI
USGS HydroSHEDS
– Full resolution SRTM-based DEM for hydrological applications * Software that can read and process SRTM data
3dem
GRASS GIS, SAGA GIS
MapWindow GISDG Terrain Viewer/Void KillerVirtual Terrain Project
– Unofficial SRTM data with voids corrected using topographic maps {{Jet Propulsion Laboratory Digital elevation models Space synthetic aperture radar 2000 in spaceflight Spacecraft instruments Topography techniques


 The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort that obtained digital elevation models on a near-global scale from 56°S to
The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort that obtained digital elevation models on a near-global scale from 56°S to 60°N
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Although it lies approximately twice as far away from the Equator as ...
, to generate the most complete high-resolution digital topographic database of Earth prior to the release of the ASTER GDEM
The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) is a Japanese remote sensing instrument onboard the Terra satellite launched by NASA in 1999. It has been collecting data since February 2000.
ASTER provides high-reso ...
in 2009. SRTM consisted of a specially modified radar system that flew on board the Space Shuttle Endeavour during the 11-day STS-99 mission in February 2000. The radar system was based on the older '' Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar'' (SIR-C/X-SAR), previously used on the Shuttle in 1994. To acquire topographic
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary scie ...
data, the SRTM payload was outfitted with two radar antennas. One antenna was located in the Shuttle's payload bay, the other – a critical change from the SIR-C/X-SAR, allowing single-pass interferometry – on the end of a 60-meter (200-foot) mast that extended from the payload bay once the Shuttle was in space. The technique employed is known as interferometric synthetic aperture radar. Intermap Technologies
Intermap Technologies () is a publicly traded company headquartered in Douglas County, Colorado, United States. Intermap provides geospatial solutions that allow GIS professionals in commercial and government organizations worldwide to build a bro ...
was the prime contractor for processing the interferometric synthetic aperture radar data.
The elevation models are arranged into tiles, each covering one degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathematics
...
of latitude and one degree of longitude, named according to their south western corners. For example, "n45e006" stretches from 45°N 6°E to 46°N 7°E and "s45w006" from 45°S 6°W to 44°S 5°W. The resolution of the raw data is one arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
(30 m along the equator) and coverage includes Africa, Europe, North America, South America, Asia, and Australia. A derived one arcsecond dataset with trees and other non-terrain features removed covering Australia was made available in November 2011; the raw data are restricted for government use. For the rest of the world, only three arcsecond (90 m along the equator) data are available. Each one arcsecond tile has 3,601 rows, each consisting of 3,601 16 bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
bigendian
In computing, endianness, also known as byte sex, is the order or sequence of bytes of a word of digital data in computer memory. Endianness is primarily expressed as big-endian (BE) or little-endian (LE). A big-endian system stores the most sig ...
cells. The dimensions of the three arcsecond tiles are 1201 x 1201. The original SRTM elevations were calculated relative to the WGS84 ellipsoid and then the EGM96
The Earth Gravitational Models (EGM) are a series of geopotential models of the Earth published by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). They are used as the geoid reference in the World Geodetic System.
The NGA provides the models ...
geoid separation values were added to convert to heights relative to the geoid for all the released products.
The elevation models derived from the SRTM data are used in geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
s. They can be downloaded freely over the Internet, and their file format (.hgt) is widely supported.
The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission is an international project spearheaded by the U.S. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency ( NGA), an agency of the U.S. Department of Defense, and the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration ( NASA). NASA transferred the SRTM payload to the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in 2003; the canister, mast, and antenna are now on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Virginia.
Versions
The USGS SRTM data is based on NASA's SIR-C instrument. It is available in at the following versions: * Version 1 (2003-2004) is almost the raw data. * Version 2.1 (~2005) is an edited version of v1. Artifacts are removed, but voids are not yet filled. There are 1-arcsecond data over the US. * Version 3 (2013), also known as SRTM Plus, is void-filled with ASTER GDEM and USGS GMTED2010. This release is available in global 1-arcsecond (30 meter) resolution since 2014. The SRTM also carries the X-SAR instrument operated by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Italian Space Agency (ASI). The resulting dataset is usually called SRTM/X-SAR, or SRTMX for short. The grid resolution is high at 25 meters, but it has many gaps. The data was made public in May 2011. The terminology regarding versions and resolutions can be confusing. "SRTM1" and "SRTM3" refers to the resolutions in 1 and 3 arc-seconds, not the versions of the format. On the other hand, "SRTM4.1" refers to a specific filled version by CGIAR-CSI. It is recommended to add a "v" in front of the version number to disambiguate.No-data areas
 The elevation datasets are affected by mountain and desert no-data areas. These amount to no more than 0.2% of the total area surveyed, but can be a problem in areas of very high relief. They affect all summits over 8,000 meters, most summits over 7,000 meters, many Alpine and similar summits and ridges, and many gorges and canyons. There are some SRTM data sources which have filled these data voids, but some of these have used only
The elevation datasets are affected by mountain and desert no-data areas. These amount to no more than 0.2% of the total area surveyed, but can be a problem in areas of very high relief. They affect all summits over 8,000 meters, most summits over 7,000 meters, many Alpine and similar summits and ridges, and many gorges and canyons. There are some SRTM data sources which have filled these data voids, but some of these have used only interpolation
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one often has a n ...
from surrounding data, and may therefore be very inaccurate. If the voids are large, or completely cover summit or ridge areas, no interpolation algorithms will give satisfactory results.
Void-filled SRTM datasets
 Groups of scientists have worked on algorithms to fill the voids of the original SRTM (v2.1) data. Three datasets offer global coverage void-filled SRTM data at full (3-arcsecond) resolution:
* The CGIAR-CSI version 4 provides the best global coverage using interpolation.
* The USGS HydroSHEDS dataset was generated for hydrological applications and is suitable for consistent drainage and water flow information. References are provided on the algorithms used and quality assessment.
* The void-filled SRTM data from Viewfinder Panoramas by Jonathan de Ferranti are high quality at full SRTM resolution. The data is filled using local survey maps and photographs. The OpenTopoMap website uses this fill. It has been partially updated for the 1-arcsecond release in the US.
In November 2013, LP DAAC released the NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Version 3.0 (SRTM Plus) Product collection with all voids eliminated. Voids were filled primarily from ASTER GDEM2, and secondarily from USGS GMTED2010 – or USGS National Elevation Dataset (NED) for the United States (except Alaska) and northernmost Mexico according to the announcement.
Groups of scientists have worked on algorithms to fill the voids of the original SRTM (v2.1) data. Three datasets offer global coverage void-filled SRTM data at full (3-arcsecond) resolution:
* The CGIAR-CSI version 4 provides the best global coverage using interpolation.
* The USGS HydroSHEDS dataset was generated for hydrological applications and is suitable for consistent drainage and water flow information. References are provided on the algorithms used and quality assessment.
* The void-filled SRTM data from Viewfinder Panoramas by Jonathan de Ferranti are high quality at full SRTM resolution. The data is filled using local survey maps and photographs. The OpenTopoMap website uses this fill. It has been partially updated for the 1-arcsecond release in the US.
In November 2013, LP DAAC released the NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Version 3.0 (SRTM Plus) Product collection with all voids eliminated. Voids were filled primarily from ASTER GDEM2, and secondarily from USGS GMTED2010 – or USGS National Elevation Dataset (NED) for the United States (except Alaska) and northernmost Mexico according to the announcement.
Highest Resolution Global Release
1-arc second global digital elevation model (30 meters) is available from the United States Geological Survey web site. The United States Government announced on September 23, 2014 over a United Nations Climate Summit that the highest possible resolution of global topographic data derived from the SRTM mission will be released to public. Before the end of the same year, a 1-arc second global digital elevation model (30 meters) was released. Most parts of the world have been covered by this dataset ranging from 54°S to 60°N latitude except for the Middle East and North Africa area. Missing coverage of the Middle East was completed in August 2015.Users
In early June 2011, there were 750,000 confirmed users of SRTM topography dataset. Users in 221 countries have accessed the site.See also
* Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar * Digital elevation model * National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency *Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer
The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) is a Japanese remote sensing instrument onboard the Terra satellite launched by NASA in 1999. It has been collecting data since February 2000.
ASTER provides high-reso ...
* SRTM Water Body Data
The SRTM Water Body Data (SWBD) is a geographical dataset (2003) encoding high-resolution worldwide coastline outlines in a vector format, published by NASA and designed for use in geographic information systems and mapping applications. It was cr ...
* WorldDEM private data with higher resolution, from newer satellite TerraSAR-X- TanDEM-X
Notes
References
* * * * Hennig, T., Kretsch, J, Salamonowicz, P, Pessagno, C, and Stein, W., The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Digital Earth Moving 2001, Springer Verlag, London, UK.Further reading
*External links
Official NASA SRTM site
(SRTM V1 and V2)
NASA MEaSUREs Products
(SRTM V3 and more)
NASA's server with SRTM data tiles
– Please read the accompanying documentation
– arcsecond-resolution derived data covering Australia * Void filled SRTM data a
CGIAR-CSI
USGS HydroSHEDS
– Full resolution SRTM-based DEM for hydrological applications * Software that can read and process SRTM data
3dem
GRASS GIS, SAGA GIS
MapWindow GIS
– Unofficial SRTM data with voids corrected using topographic maps {{Jet Propulsion Laboratory Digital elevation models Space synthetic aperture radar 2000 in spaceflight Spacecraft instruments Topography techniques