Squirrel fish.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Squirrels are members of the

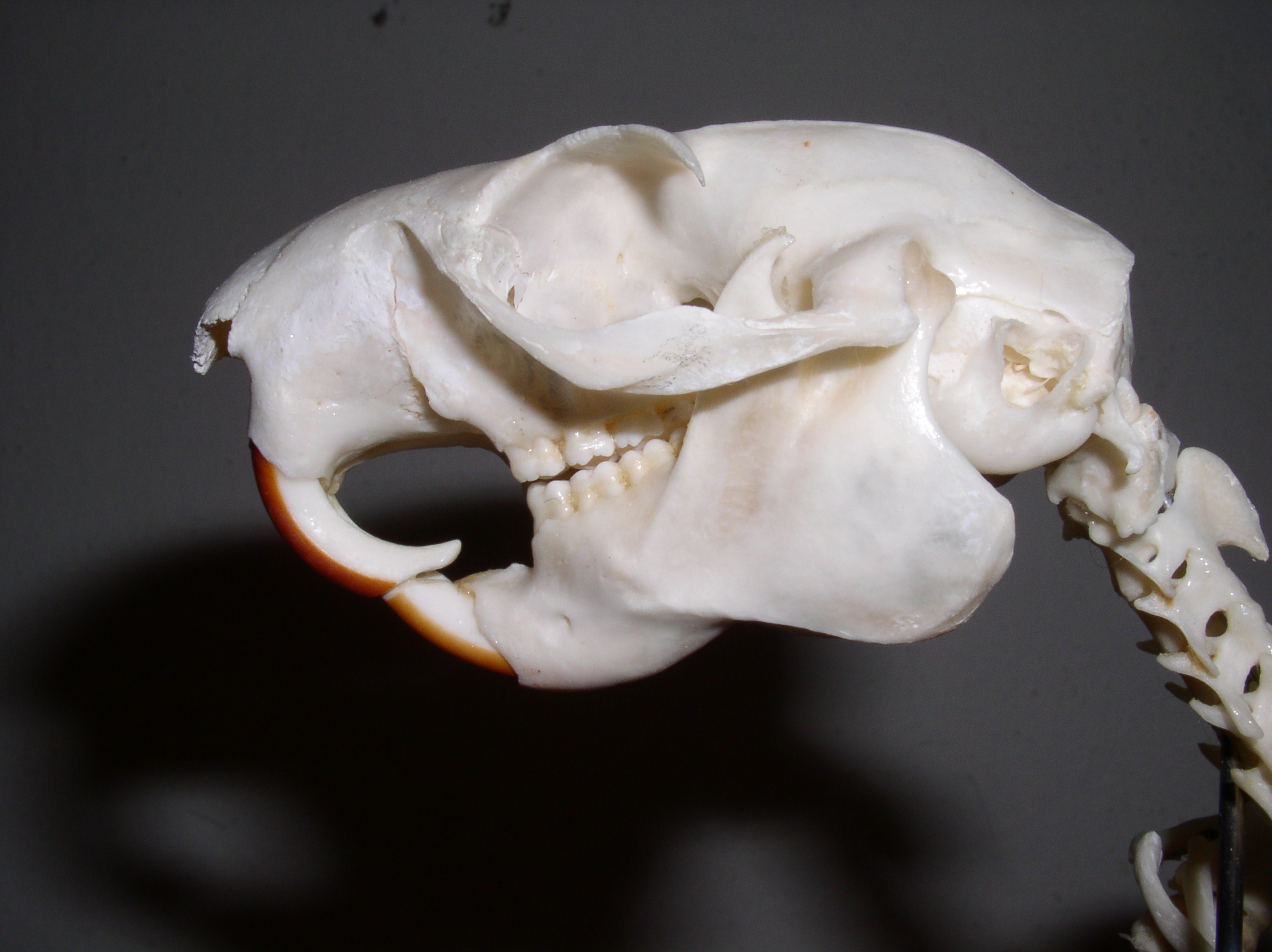 Squirrels are generally small animals, ranging in size from the African pygmy squirrel and least pygmy squirrel at in total length and just in weight, to the Bhutan giant flying squirrel at up to in total length, and several
Squirrels are generally small animals, ranging in size from the African pygmy squirrel and least pygmy squirrel at in total length and just in weight, to the Bhutan giant flying squirrel at up to in total length, and several
. squirrels.org. Retrieved 14 December 2010. As their large eyes indicate, squirrels have an excellent sense of
File:Squirrel enjoying in the sun.jpg, Squirrel in sunlight
File:Squirrel in Chandigarh.jpg, Squirrel in
 Squirrels mate either once or twice a year and, following a gestation period of three to six weeks, give birth to a number of offspring that varies by species. The young are
Squirrels mate either once or twice a year and, following a gestation period of three to six weeks, give birth to a number of offspring that varies by species. The young are
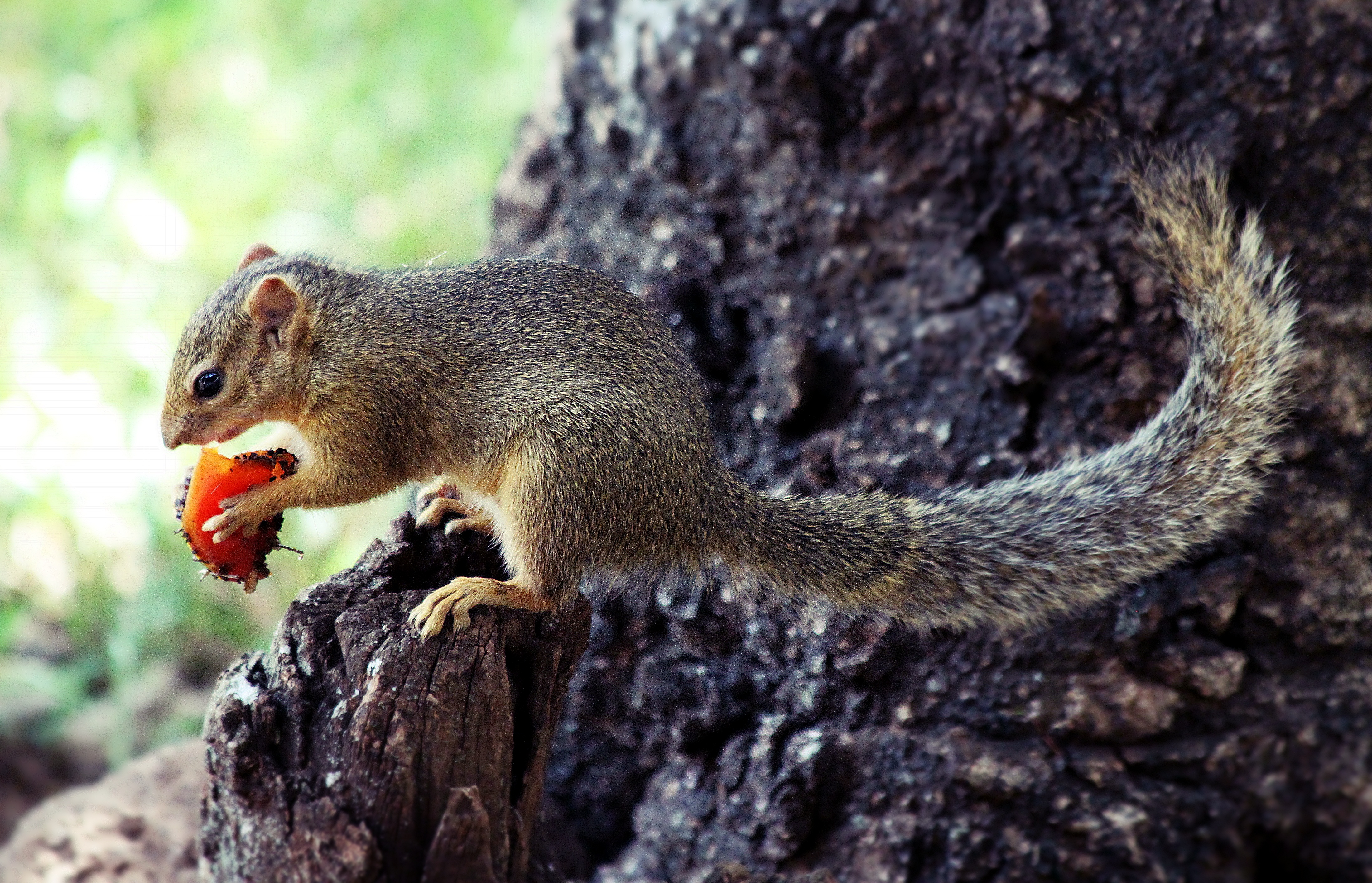

 Because squirrels cannot digest
Because squirrels cannot digest
 The living squirrels are divided into five subfamilies, with about 58 genera and some 285 species. The oldest squirrel fossil, ''Hesperopetes'', dates back to the Chadronian (late
The living squirrels are divided into five subfamilies, with about 58 genera and some 285 species. The oldest squirrel fossil, ''Hesperopetes'', dates back to the Chadronian (late
"Sciuridae (Squirrels)"
Version of 13 May 2006. Retrieved 10 December 2007. * * Thorington, R.W. and Hoffmann, R.S. (2005): "Family Sciuridae". In: ''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference'': 754ŌĆō818. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. * Whitaker, John O. Jr. and Elman, Robert (1980): ''The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Mammals'' (2nd ed.). Alfred A. Knopf, Jr., Alfred Knopf, New York.
Tree of Life: Sciuridae
How to identify squirrel tracks in the wild
{{Authority control Squirrels, Articles containing video clips Extant Eocene first appearances Rodents by common name Taxa named by Gotthelf Fischer von Waldheim
family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
s. The squirrel family includes tree squirrel
Tree squirrels are the members of the squirrel family (Sciuridae) commonly just referred to as "squirrels." They include more than 100 arboreal species native to all continents except Antarctica and Oceania.
They do not form a single natural, o ...
s, ground squirrel
Ground squirrels are members of the squirrel family of rodents ( Sciuridae), which generally live on or in the ground, rather than trees. The term is most often used for the medium-sized ground squirrels, as the larger ones are more commonly known ...
s (including chipmunk
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as ...
s and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squirrels are indigenous to the Americas, Eurasia, and Africa, and were introduced by humans to Australia. The earliest known fossilized squirrels date from the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''─ōß╣ōs'', " ...
epoch, and among other living rodent families, the squirrels are most closely related to the mountain beaver
The mountain beaver (''Aplodontia rufa'')Other names include mountain boomer, ground bear, giant mole, gehalis, lesser sasquatch, sewellel, suwellel, showhurll, showtl, and showte, as well as a number of Chinookan and other Native American terms ...
and to the dormice
A dormouse is a rodent of the family Gliridae (this family is also variously called Myoxidae or Muscardinidae by different taxonomists). Dormice are nocturnal animals found in Africa, Asia, and Europe. They are named for their long, dormant hibe ...
.
Etymology
The word ''squirrel'', first attested in 1327, comes from theAnglo-Norman Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
* Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
* Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 10 ...
which is from the Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intellig ...
, the reflex of a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word , which was taken from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
word (; from ) 'shadow-tailed', referring to the long bushy tail which many of its members have.
The native Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
word for the squirrel, , survived only into Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
(as ) before being replaced. The Old English word is of Common Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic br ...
origin, cognates of which are still used in other Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, E ...
, including the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(diminutive of , which is not as frequently used), the Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
/, the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, the Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
and the Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
.
A group of squirrels is called a "dray" or a "scurry".
Characteristics

marmot
Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, ...
species, which can weigh or more. Squirrels typically have slender bodies with very long very bushy tails and large eyes. In general, their fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket t ...
is soft and silky, though much thicker in some species than others. The coat color of squirrels is highly variable betweenŌĆöand often even withinŌĆöspecies.
In most squirrel species, the hind limbs are longer than the fore limbs, while all species have either four or five toes on each foot. The feet, which include an often poorly developed thumb, have soft pads on the undersidesMilton (1984) and versatile, sturdy claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
s for grasping and climbing
Climbing is the activity of using one's hands, feet, or any other part of the body to ascend a steep topographical object that can range from the world's tallest mountains (e.g. the eight thousanders), to small boulders. Climbing is done ...
. Tree squirrels
Tree squirrels are the members of the squirrel family (Sciuridae) commonly just referred to as "squirrels." They include more than 100 arboreal species native to all continents except Antarctica and Oceania.
They do not form a single natural, or ...
, unlike most mammals, can descend a tree head-first. They do so by rotating their ankles 180 degrees, enabling the hind feet to point backward and thus grip the tree bark from the opposite direction.
Squirrels live in almost every habitat, from tropical rainforest to semiarid desert, avoiding only the high polar regions and the driest of deserts
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
. They are predominantly herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpar ...
, subsisting on seeds and nuts, but many will eat insects
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of j ...
and even small vertebrates.Squirrel Place. squirrels.org. Retrieved 14 December 2010. As their large eyes indicate, squirrels have an excellent sense of
vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, which is especially important for the tree-dwelling species. Many also have a good sense of touch
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It ...
, with vibrissa
Vibrissae (; singular: vibrissa; ), more generally called Whiskers, are a type of stiff, functional hair used by mammals to sense their environment. These hairs are finely specialised for this purpose, whereas other types of hair are coarser ...
e on their limbs as well as their heads.
The teeth of sciurids follow the typical rodent pattern, with large incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
s (for gnawing) that grow throughout life, and cheek teeth (for grinding) that are set back behind a wide gap, or diastema
A diastema (plural diastemata, from Greek ╬┤╬╣╬¼ŽāŽä╬Ę╬╝╬▒, space) is a space or gap between two teeth. Many species of mammals have diastemata as a normal feature, most commonly between the incisors and molars. More colloquially, the condition ...
. The typical dental formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolog ...
for sciurids is .
Many juvenile squirrels die in the first year of life. Adult squirrels can have a lifespan of 5 to 10 years in the wild. Some can survive 10 to 20 years in captivity. Premature death may occur when a nest falls from the tree, in which case the mother may abandon her young if their body temperature is not correct. Many such baby squirrels have been rescued and fostered by a professional wildlife rehabilitator until they could be safely returned to the wild, although the density of squirrel populations in many places and the constant care required by premature squirrels means that few rehabilitators are willing to spend their time doing this and such animals are routinely euthanized
Animal euthanasia ( euthanasia from el, ╬ĄßĮÉ╬Ė╬▒╬Į╬▒Žā╬»╬▒; "good death") is the act of killing an animal or allowing it to die by withholding extreme medical measures. Reasons for euthanasia include incurable (and especially painful) conditi ...
instead.
Stated purposes of squirrels' tails, to benefit the squirrel, include:
* To keep rain, wind, or cold off itself.
* To cool off when hot, by pumping more blood through its tail.
* As a counterbalance when jumping about in trees.
* As a parachute when jumping.
* To signal with.
The hairs from squirrel tails are prized in fly fishing when tying fishing flies. A special quality of squirrel tail hair is that it is all guard hair
Guard hair or overhair is the outer layer of hair of most mammals, which overlay the fur. Guard hairs are long and coarse and protect the rest of the pelage (fur) from abrasion and frequently from moisture. They are visible on the surface of the fu ...
s, not undercoat.
When the squirrel sits upright, its tail folded up its back may stop predators looking from behind from seeing the characteristic shape of a small mammal.
Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which a ...
File:Squirrel near Chandigarh.jpg, Squirrel near Chandigarh
File:Squirrel on mango tree.jpg, Squirrel on mango tree
''Mangifera indica'', commonly known as mango, is a species of flowering plant in the family Anacardiaceae. It is a large fruit tree, capable of growing to a height of . There are two distinct genetic populations in modern mangoesthe "Indian t ...
Behavior
 Squirrels mate either once or twice a year and, following a gestation period of three to six weeks, give birth to a number of offspring that varies by species. The young are
Squirrels mate either once or twice a year and, following a gestation period of three to six weeks, give birth to a number of offspring that varies by species. The young are altricial
In biology, altricial species are those in which the young are underdeveloped at the time of birth, but with the aid of their parents mature after birth. Precocial species are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the mome ...
, being born naked, toothless, and blind. In most species of squirrel, the female alone looks after the young, which are weaned
Weaning is the process of gradually introducing an infant human or another mammal to what will be its adult diet while withdrawing the supply of its mother's milk.
The process takes place only in mammals, as only mammals produce milk. The infan ...
at six to ten weeks and become sexually mature by the end of their first year. In general, the ground-dwelling squirrel species are social, often living in well-developed colonies, while the tree-dwelling species are more solitary.
Ground squirrels and tree squirrels are usually either diurnal or crepuscular, while the flying squirrels tend to be nocturnalŌĆöexcept for lactating flying squirrels and their young, which have a period of diurnality during the summer.
Feeding

cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of ╬▓(1ŌåÆ4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
, they must rely on foods rich in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
, carbohydrates, and fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
s. In temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5┬░ to 66.5┬░ N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
regions, early spring is the hardest time of year for squirrels because the nuts they buried are beginning to sprout (and thus are no longer available to eat), while many of the usual food sources are not yet available. During these times, squirrels rely heavily on tree buds. Squirrels, being primarily herbivores
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
, eat a wide variety of plants, as well as nut
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Co ...
s, seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
s, conifer cone
A conifer cone (in formal botanical usage: strobilus, plural strobili) is a seed-bearing organ on gymnosperm plants. It is usually woody, ovoid to globular, including scales and bracts arranged around a central axis, especially in conife ...
s, fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
s, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, and green vegetation. Some squirrels, however, also consume meat, especially when faced with hunger. Squirrels have been known to eat small birds, young snakes, and smaller rodents, as well as bird eggs and insects. Some tropical squirrel species have shifted almost entirely to a diet of insects.
Squirrels, like pigeons and other fauna, are synanthropes, in that they benefit and thrive from their interaction in human environments. This gradual process of successful interaction is called synurbanization, wherein squirrels lose their inherent fear of humans in an urban area, urban environment. When squirrels were almost completely eradicated during the Industrial Revolution in New York City, New York, they were later re-introduced to "entertain and remind" humans of nature. The squirrel blended into the urban environment so efficiently that when synanthropic behavior stops (i.e. people do not leave trash outside during particularly cold winters), they can become aggressive in their search for food.
Aggression and predatory behavior has been observed in various species of ground squirrels, in particular the thirteen-lined ground squirrel. For example, Bernard Bailey, a scientist in the 1920s, observed a thirteen-lined ground squirrel preying upon a young chicken. Wistrand reported seeing this same species eating a freshly killed snake. There has also been at least one report of squirrels preying on atypical animals, such as an incident in 2005 where a pack of black squirrels killed and ate a large stray dog in Lazo, Russia. Squirrel attacks on humans are exceedingly rare, but do occur.
Whitaker examined the stomachs of 139 thirteen-lined ground squirrels and found bird flesh in four of the specimens and the remains of a short-tailed shrew in one; Bradley, examining the stomachs of white-tailed antelope squirrels, found at least 10% of his 609 specimens' stomachs contained some type of vertebrate, mostly lizards and rodents. Morgart observed a white-tailed antelope squirrel capturing and eating a Perognathus flavus, silky pocket mouse.
Taxonomy
 The living squirrels are divided into five subfamilies, with about 58 genera and some 285 species. The oldest squirrel fossil, ''Hesperopetes'', dates back to the Chadronian (late
The living squirrels are divided into five subfamilies, with about 58 genera and some 285 species. The oldest squirrel fossil, ''Hesperopetes'', dates back to the Chadronian (late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''─ōß╣ōs'', " ...
, about 40ŌĆō35 million years ago) and is similar to modern flying squirrels.
A variety of fossil squirrels, from the latest Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''─ōß╣ōs'', " ...
to the Miocene, have not been assigned with certainty to any living lineage. At least some of these probably were variants of the oldest basal (evolution), basal "protosquirrels" (in the sense that they lacked the full range of living squirrels' autapomorphy, autapomorphies). The distribution and diversity of such ancient and ancestral forms suggest the squirrels as a group may have originated in North America.Steppan & Hamm (2006)
Apart from these sometimes little-known fossil forms, the phylogeny of the living squirrels is fairly straightforward. The three main lineages are the Ratufinae (Oriental giant squirrels), Sciurillinae and all other subfamilies. The Ratufinae contain a mere handful of living species in tropical Asia. The Neotropical Pygmy Squirrel, neotropical pygmy squirrel of tropical South America is the sole living member of the Sciurillinae. The third lineage, by far the largest, has a near-cosmopolitan distribution. This further supports the hypothesis that the common ancestor of all squirrels, living and fossil, lived in North America, as these three most ancient lineages seem to have evolutionary radiation, radiated from there; if squirrels had originated in Eurasia, for example, one would expect quite ancient lineages in Africa, but African squirrels seem to be of more recent origin.
The main group of squirrels can be split into five subfamilies. The Callosciurinae, 60 species mostly found in South East Asia; the Ratufinae 4 cat-sized species found in South Asia, south and southeast Asia; the Sciurinae contains the flying squirrels (Pteromyini) and the Sciurini, tree squirrels, 83 species found world wide; Sciurillinae a single South American species; and Xerinae includes three Tribe (biology), tribes of mostly terrestrial squirrels, including the Marmotini (marmot
Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, ...
s, chipmunk
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as ...
s, prairie dogs, and other Holarctic ground squirrels), Xerini (African and some Eurasian ground squirrels), and Protoxerini (African tree squirrels).
Taxonomy list
* Basal (evolution), Basal and ''incertae sedis'' Sciuridae (all fossil) ** ''Hesperopetes'' ** ''Kherem (genus), Kherem'' ** ''Lagrivea'' ** ''Oligosciurus'' ** ''Plesiosciurus'' ** ''Prospermophilus'' ** ''Sciurion'' ** ''Similisciurus'' ** ''Sinotamias'' ** ''Vulcanisciurus'' * Subfamily Cedromurinae (fossil) * Subfamily Ratufinae ŌĆō Oriental giant squirrels (1 genus, 4 species) * Subfamily Sciurillinae ŌĆō neotropical pygmy squirrel (monotypic) * Subfamily Sciurinae ** Tribe Sciurini ŌĆō tree squirrels (5 genera, about 38 species) ** Tribe Pteromyini ŌĆō true flying squirrels (15 genera, about 45 species) * Subfamily Callosciurinae ŌĆō Asian ornate squirrels ** Tribe Callosciurini (13 genera, nearly 60 species) ** Tribe Funambulini palm squirrels (1 genus, 5 species) * Subfamily Xerinae ŌĆō terrestrial squirrels ** Tribe Xerini ŌĆō spiny squirrels (3 genera, 6 species) ** Tribe Protoxerini (6 genera, about 50 species) ** Tribe Marmotini ŌĆō ground squirrels, marmots, chipmunks, prairie dogs, etc. (6 genera, about 90 species)Society
Squirrels are a cause for concern because they often Electrical disruptions caused by squirrels, cause electrical disruptions. It has been hypothesis, hypothesized that the threat to the internet, infrastructure and services posed by squirrels may exceed that posed by Cyberattack, cyber-attacks.See also
* American red squirrel * Animal track * Black squirrel * Eastern gray squirrel * Fox squirrel * List of animal names#squirrel * Red squirrel * Tree squirrel#Relationship with humans, Squirrel relationship with humans * Variant CreutzfeldtŌĆōJakob disease (Kuru (disease), Kuru) from eating squirrel brains. * Western gray squirrelReferences
Further reading
* Milton, Katherine (1984): "Family Sciuridae". In: Macdonald, D. (ed.): ''The Encyclopedia of Mammals'': 612ŌĆō623. Facts on File, New York. . * Steppan, Scott J. and Hamm, Shawn M. (2006): Tree of Life Web Project ŌĆ"Sciuridae (Squirrels)"
Version of 13 May 2006. Retrieved 10 December 2007. * * Thorington, R.W. and Hoffmann, R.S. (2005): "Family Sciuridae". In: ''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference'': 754ŌĆō818. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. * Whitaker, John O. Jr. and Elman, Robert (1980): ''The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Mammals'' (2nd ed.). Alfred A. Knopf, Jr., Alfred Knopf, New York.
External links
Tree of Life: Sciuridae
How to identify squirrel tracks in the wild
{{Authority control Squirrels, Articles containing video clips Extant Eocene first appearances Rodents by common name Taxa named by Gotthelf Fischer von Waldheim