Souks Tunis.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a
 In general a souk is synonymous with a bazaar or
In general a souk is synonymous with a bazaar or

 The Arabic word is a loan from
The Arabic word is a loan from
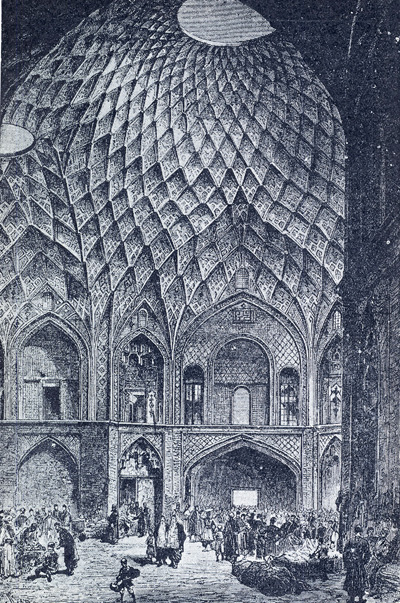
 During the Islamic period, bazaars in Iran developed along the same lines as those of the Sassanid period. Bazaars were typically situated in close proximity to ruling palaces, citadels or mosques, not only because the city afforded traders some protection, but also because palaces and cities generated substantial demand for goods and services.
From around the 10th century, as major cities increased in size, the souk or marketplace shifted to the center of urban cities where it spread out along the city streets, typically in a linear pattern.Moosavi, M. S. ''Bazaar and its Role in the Development of Iranian Traditional Cities'' orking Paper Tabriz Azad University, Iran, 2006 Around this time, permanent souks also became covered marketplaces.
City bazaars occupied a series of alleys along the length of the city, typically stretching from one city gate to a different gate on the other side of the city. The
During the Islamic period, bazaars in Iran developed along the same lines as those of the Sassanid period. Bazaars were typically situated in close proximity to ruling palaces, citadels or mosques, not only because the city afforded traders some protection, but also because palaces and cities generated substantial demand for goods and services.
From around the 10th century, as major cities increased in size, the souk or marketplace shifted to the center of urban cities where it spread out along the city streets, typically in a linear pattern.Moosavi, M. S. ''Bazaar and its Role in the Development of Iranian Traditional Cities'' orking Paper Tabriz Azad University, Iran, 2006 Around this time, permanent souks also became covered marketplaces.
City bazaars occupied a series of alleys along the length of the city, typically stretching from one city gate to a different gate on the other side of the city. The
 A temporary, seasonal souk is held at a set time that might be yearly, monthly or weekly. The oldest souks were set up annually, and were typically general festivals held outside cities. For example, Souk Ukadh was held yearly in pre-Islamic times in an area between
A temporary, seasonal souk is held at a set time that might be yearly, monthly or weekly. The oldest souks were set up annually, and were typically general festivals held outside cities. For example, Souk Ukadh was held yearly in pre-Islamic times in an area between
 Gharipour has pointed out that in spite of the centrality of souks and bazaars in Middle Eastern history, relatively little is known due to the lack of archaeological evidence. Souks are traditionally divided into specialized sections dealing in specific types of product, in the case of permanent souks each usually housed in a few narrow streets and named after the product it specializes in such as the
Gharipour has pointed out that in spite of the centrality of souks and bazaars in Middle Eastern history, relatively little is known due to the lack of archaeological evidence. Souks are traditionally divided into specialized sections dealing in specific types of product, in the case of permanent souks each usually housed in a few narrow streets and named after the product it specializes in such as the
File:The Moorish Bazaar.jpg, ''The Moorish Bazaar'', painting by Edwin Lord Weeks, 1873
File:Street Scene in India.JPG, ''Street Scene in India'', by Edwin Lord Weeks, circa 1885
File:Cashmere Travellers in a Street of Delhi.jpg, ''Cashmere Travellers in a Street of Delhi'' by Edwin Lord Weeks, 1880s
File:'Claudius Bombarnac' by Léon Benett 28.jpg, ''Bazaar in Samarkand'', illustration by
File:Sanandaj Bazaar.jpg, Bazaar in Sanandaj,
Iran Chamber Society on Architecture of the Bazaar at Isfahan
* {{Authority control Islamic culture Persian words and phrases Iranian folklore Shopping (activity)
 A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace
A marketplace or market place is a location where people regularly gather for the purchase and sale of provisions, livestock, and other goods. In different parts of the world, a marketplace may be described as a '' souk'' (from the Arabic), ' ...
consisting of multiple small stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, such as in the West, might also designate themselves as bazaars. The ones in the Middle East were traditionally located in vaulted or covered streets that had doors on each end and served as a city's central marketplace. Street market
A marketplace or market place is a location where people regularly gather for the purchase and sale of provisions, livestock, and other goods. In different parts of the world, a marketplace may be described as a ''souk'' (from the Arabic lang ...
s are the European and North American equivalents.
The term ''bazaar'' originates from Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, where it referred to a town's public market district. The term bazaar is sometimes also used to refer to the "network of merchants, bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
ers and craftsmen" who work in that area.
The term ''souk'' comes from Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
and refers to marketplaces in the Middle East and North Africa.
Evidence for the existence of bazaars or souks dates to around 3,000 BCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
. Although the lack of archaeological evidence has limited detailed studies of the evolution of bazaars, indications suggest that they initially developed outside city walls where they were often associated with servicing the needs of caravanserai. As towns and cities became more populous, these bazaars moved into the city center and developed in a linear pattern along streets stretching from one city gate to another gate on the opposite side of the city. Souks became covered walkways. Over time, these bazaars formed a network of trading centres which allowed for the exchange of produce and information. The rise of large bazaars and stock trading centres in the Muslim world allowed the creation of new capitals and eventually new empires. New and wealthy cities such as Isfahan, Vijaynagara
Vijayanagara () was the capital city of the historic Vijayanagara Empire. Located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, it spread over a large area and included the modern era Group of Monuments at Hampi site in Vijayanagara district, Bell ...
, Surat, Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
, Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra i ...
, and Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou;
Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrativ ...
were founded along trade routes and bazaars.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, Western interest in oriental culture led to the publication of many books about daily life in Middle Eastern countries. Souks, bazaars and the trappings of trade feature prominently in paintings and engravings, works of fiction and travel writing.
Shopping at a bazaar or market-place remains a central feature of daily life in many Middle-Eastern and South Asian cities and towns and the bazaar remains the "beating heart" of West Asian and South Asian life; in the Middle East, souks tend to be found in a city's medina (old quarter). Bazaars and souks are often important tourist attractions. A number of bazaar districts have been listed as World Heritage sites due to their historical and/or architectural significance.
Terminology by region
Bazaar
marketplace
A marketplace or market place is a location where people regularly gather for the purchase and sale of provisions, livestock, and other goods. In different parts of the world, a marketplace may be described as a '' souk'' (from the Arabic), ' ...
, and the term ''souk'' is used in Arabic-speaking countries.
The origin of the word ''bazaar'' comes from Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
''bāzār'', from Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
''wāzār'', from Old Persian ''vāčar'', from Proto-Indo-Iranian ''*wahā-čarana''. The term, bazaar, spread from Persia into Arabia and ultimately throughout the Middle East.
The term bazaar is a common word in the Indian subcontinent: hi, बाज़ार, bāzār; bn, বাজার, bājār; ne, बजार, bajār.
Differing meanings of "bazaar"
In North America, the United Kingdom and some other European countries, the termcharity bazaar
A charity bazaar, or "fancy faire", was an innovative and controversial fundraising sale in the Victorian era. Hospitals frequently used charity bazaars to raise funds because of their effectiveness. Commercial bazaars grew less popular in the 19t ...
can be used as a synonym for a " rummage sale", to describe charity
Charity may refer to:
Giving
* Charitable organization or charity, a non-profit organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being of persons
* Charity (practice), the practice of being benevolent, giving and sharing
* C ...
fundraising events held by churches or other community organisations in which either donated used goods (such as books, clothes and household items) or new and handcrafted (or home-baked) goods are sold for low prices, as at a church or other organisation's Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
bazaar, for example.
Although Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
offers many famous markets known as "bazaars" in English, the Turkish word "pazar" refers to an outdoor market held at regular intervals, not a permanent structure containing shops. English place names usually translate "çarşı" (shopping district in a downtown or downtown itself) as "bazaar" when they refer to an area with covered streets or passages. For example, the Turkish name for the Grand Bazaar in Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
is "Kapalıçarşı" (gated shopping area), while the Spice Bazaar
The Spice Bazaar ( tr, Mısır Çarşısı, meaning "Egyptian Bazaar") in Istanbul, Turkey is one of the largest bazaars in the city. Located in the Eminönü quarter of the Fatih district, it is the most famous covered shopping complex after th ...
is the "Mısır Çarşısı" (Egyptian shopping area).
In Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
, the word "bazar" means second-hand shop
__NOTOC__
A second-hand shop is a shop which sells used goods.
Temporary venues
People will sell used goods right in front of their home in what is called a "garage sale". The products would be set up in front of the garage.
In the UK, peo ...
. "Autobazar" is a shop which purchases and sells pre-owned cars.
Variations
In Indonesian, the word ''pasar'' means "market." The capital of Bali province, inIndonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, is Denpasar
Denpasar (; Balinese: ᬤᬾᬦ᭄ᬧᬲᬃ) is the capital of Bali and the main gateway to the island. The city is also a hub for other cities in the Lesser Sunda Islands.
With the rapid growth of the tourism industry in Bali, Denpasar has e ...
, which means "north market."
Souk
 The Arabic word is a loan from
The Arabic word is a loan from Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
"šūqā" ("street, market"), itself a loanword from the Akkadian "sūqu" ("street"). The spelling souk entered European languages likely through French during the French occupation of the Arab countries Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, and Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
in the 19th and 20th centuries. Thus, the word "souk" mostly refers to Arabic and North African traditional market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
Geography
*Märket, an ...
s. Other spellings of this word involving the letter "Q" (sooq, souq, and so'oq) were likely developed using English and thus refer to Western Asian or Arab traditional markets, as there were several British colonies
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Coun ...
there during the 19th and 20th centuries.
In Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also ref ...
the term ''al-sooq'' refers to markets in both the physical sense and the abstract economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
sense (e.g., an Arabic-speaker would speak of the ''sooq'' in the old city as well as the ''sooq'' for oil, and would call the concept of the free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
السوق الحرّ ''as-sūq al-ḥurr'').
Variations on "souk"
In northern Morocco, the Spanish corruption ''socco'' is often used as in theGrand Socco
The Grand Socco, officially the Place du 9 Avril 1947, is a historic quasi-circular roundabout square separating the old medina from newer developments in downtown Tangier, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is ...
and Petit Socco of Tangier
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capi ...
s.
In the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
the 'chowk' is often used to name a place with four-way crossroad, and comes from Sanskrit चतवार, meaning four. In Western Asia(Middle east), this term is used generally to designate the market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
Geography
*Märket, an ...
, but may also be used in Western cities, particularly those with a Muslim community.
In Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, the terms ''suq
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace consisting of multiple small stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East, the Balkans, North Africa and India. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, such as in the W ...
'' and sometimes '' monti'' are used for a marketplace.
In the United States, especially in Southern California and Nevada, an indoor swap meet is a type of bazaar, i.e. a permanent, indoor shopping center open during normal retail hours, with fixed "booths" or counters for the vendors.
History
Origins in Antiquity
Historical records document the concept of a bazaar existing in Iran as early as 3000 BC, where some large cities contained districts dedicated to trade and commerce. Archeological data also suggests the existence of market districts in ancientMesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
. Markets centers must have existed in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
to conduct international trade, but no archeological evidence for them has been found. In Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
Persia (550-330 BCE), documents indicate that crafts were sold in markets close to Persepolis. A network of bazaars had sprung up alongside ancient caravan trade routes. Bazaars located along these trade routes, formed networks, linking major cities with each other and in which goods, culture, people and information could be exchanged.Hanachi, P. and Yadollah, S., "Tabriz Historical Bazaar in the Context of Change," ICOMOS Conference Proceedings, Paris, 2011 Sources from around the same era also indicate that ancient Greeks regulated trade in areas at the center of their cities around '' stoa'' buildings. The ideas of Greek city planning were spread to the Middle East during the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
period, following the conquests of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
.Gharipour, M., "The Culture and Politics of Commerce," in ''The Bazaar in the Islamic City: Design, Culture, and History,'' Mohammad Gharipour (ed.), New York, The American University in Cairo Press, 2012, pp 3-15
The Greek historian, Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
, noted that in Egypt, roles were reversed compared with other cultures and Egyptian women frequented the market and carried on trade, while the men remain at home weaving cloth. He also described The Babylonian Marriage Market.
Sassanid rule in Iran was an important period for the development of urbanization and commerce. In Sassanid Iran the bazaar was usually the heart of a town or city, where it spread outwards and affected the development of other neighbourhoods. The bazaar usually contained, or was adjoined by, an open-air plaza that served as a forum of socio-economic activity.
Historically, souks were also held outside cities at locations where incoming caravans stopped and merchants displayed their goods for sale. Souks were established at caravanserai, places where a caravan or caravans arrived and remained for rest and refreshments. Since this might be infrequent, souks often extended beyond buying and selling goods to include major festivals involving various cultural and social activities. Any souk may serve a social function as being a place for people to meet in, in addition to its commercial function.
Islamic period

 During the Islamic period, bazaars in Iran developed along the same lines as those of the Sassanid period. Bazaars were typically situated in close proximity to ruling palaces, citadels or mosques, not only because the city afforded traders some protection, but also because palaces and cities generated substantial demand for goods and services.
From around the 10th century, as major cities increased in size, the souk or marketplace shifted to the center of urban cities where it spread out along the city streets, typically in a linear pattern.Moosavi, M. S. ''Bazaar and its Role in the Development of Iranian Traditional Cities'' orking Paper Tabriz Azad University, Iran, 2006 Around this time, permanent souks also became covered marketplaces.
City bazaars occupied a series of alleys along the length of the city, typically stretching from one city gate to a different gate on the other side of the city. The
During the Islamic period, bazaars in Iran developed along the same lines as those of the Sassanid period. Bazaars were typically situated in close proximity to ruling palaces, citadels or mosques, not only because the city afforded traders some protection, but also because palaces and cities generated substantial demand for goods and services.
From around the 10th century, as major cities increased in size, the souk or marketplace shifted to the center of urban cities where it spread out along the city streets, typically in a linear pattern.Moosavi, M. S. ''Bazaar and its Role in the Development of Iranian Traditional Cities'' orking Paper Tabriz Azad University, Iran, 2006 Around this time, permanent souks also became covered marketplaces.
City bazaars occupied a series of alleys along the length of the city, typically stretching from one city gate to a different gate on the other side of the city. The Bazaar of Tabriz
The Bazaar of Tabriz ( fa, بازار تبریز, also Romanized as ''Bāzār-e Tabriz'') is a historical market situated in the city center of Tabriz, Iran. It is one of the oldest bazaars in the Middle East and the largest covered bazaar in the ...
, for example, stretches along 1.5 kilometres of street and is the longest vaulted bazaar in the world. Moosavi argues that the Middle-Eastern bazaar evolved in a linear pattern, whereas the market places of the West were more centralised.
In pre-Islamic Arabia, two types of bazaar existed: permanent urban markets and temporary seasonal markets. The temporary seasonal markets were held at specific times of the year and became associated with particular types of produce. Suq Hijr in Bahrain was noted for its dates while Suq 'Adan was known for its spices and perfumes. In spite of the centrality of the Middle East in the history of bazaars, relatively little is known due to the lack of archaeological evidence. However, documentary sources point to permanent marketplaces in cities from as early as 550 BCE.
Nejad has made a detailed study of early bazaars in Iran and identifies two distinct types, based on their place within the economy, namely:Nejad, R. M., “Social bazaar and commercial bazaar: comparative study of spatial role of Iranian bazaar in the historical cities in different socio-economical context,” ''5th International Space Syntax Symposium Proceedings, ''Netherlands: Techne Press, D., 2005,
* ''Commercial bazaars'' (or retail bazaars): emerged as part of an urban economy not based on a merchant system
* ''Socio-commercial bazaars'': formed in economies based on a merchant system, socio-economic bazaars are situated on major trade routes and are well integrated into the city's structural and spatial systems
21st century
In the Middle East, the bazaar is considered to be "the beating heart of the city and a symbol of Islamic architecture and culture of high significance." Today, bazaars are popular sites for tourists and some of these ancient bazaars have been listed as world heritage sites or national monuments on the basis of their historical, cultural or architectural value. The Medina of Fez,Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, with its labyrinthine covered market streets was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
in 1981. Al-Madina Souq
Al-Madina Souq ( ar, سوق المدينة, Sūq al-Madīna) is the covered souq-market located at the heart of the Syrian city of Aleppo within the walled ancient part of the city. With its long and narrow alleys, al-Madina Souq is the largest ...
is part of the ancient city of Aleppo
The Ancient City of Aleppo ( ar, مدينة حلب القديمة, Madīnat Ḥalab al-Qadīma) is the historic city centre of Aleppo, Syria. Before the Syrian Civil War, many districts of the ancient city remained essentially unchanged since ...
in Syria, another UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
since 1986. The Bazaar complex at Tabriz
Tabriz ( fa, تبریز ; ) is a city in northwestern Iran, serving as the capital of East Azerbaijan Province. It is the List of largest cities of Iran, sixth-most-populous city in Iran. In the Quri Chay, Quru River valley in Iran's historic Aze ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
was listed in 2010 and Kemeraltı Bazaar of İzmir
İzmir ( , ; ), also spelled Izmir, is a metropolitan city in the western extremity of Anatolia, capital of the province of the same name. It is the third most populous city in Turkey, after Istanbul and Ankara and the second largest urban aggl ...
in 2020. The Bazaar of Qaisiyariye in Lar, Iran
Lar ( fa, لار, also Romanized as Lār; also known as Larestan) is a city and capital of Larestan County, Fars Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 51,961, in 12,891 families. Lar's inhabitants are Larestani people.
History ...
is on the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
.
Types
Seasonal
 A temporary, seasonal souk is held at a set time that might be yearly, monthly or weekly. The oldest souks were set up annually, and were typically general festivals held outside cities. For example, Souk Ukadh was held yearly in pre-Islamic times in an area between
A temporary, seasonal souk is held at a set time that might be yearly, monthly or weekly. The oldest souks were set up annually, and were typically general festivals held outside cities. For example, Souk Ukadh was held yearly in pre-Islamic times in an area between Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
and Ta’if
Taif ( ar, , translit=aṭ-Ṭāʾif, lit=The circulated or encircled, ) is a city and governorate in the Makkan Region of Saudi Arabia. Located at an elevation of in the slopes of the Hijaz Mountains, which themselves are part of the Sarat ...
during the sacred month of Dhu al-Qi'dah
Dhu al-Qa'dah ( ar, ذُو ٱلْقَعْدَة, ', ), also spelled Dhu al-Qi'dah or Zu al-Qa'dah, is the eleventh month in the Islamic calendar.
It could possibly mean "possessor or owner of the sitting and seating place" - the space occupied w ...
. While a busy market, it was more famous for its poetry competitions, judged by prominent poets such as Al-Khansa
Tumāḍir bint ʿAmr ibn al-Ḥārith ibn al-Sharīd al-Sulamīyah ( ar, تماضر بنت عمرو بن الحارث بن الشريد السُلمية), usually simply referred to as al-Khansāʾ ( ar, الخنساء, links=no, meaning "snub-n ...
and Al-Nabigha
Al-Nābighah (), al-Nābighah al-Dhubiyānī, or Nābighah al-Dhubyānī; real name Ziyad ibn Muawiyah (); was one of the last Arabian poets of pre-Islamic times. "Al-Nabigha" means "genius or intelligent" in Arabic.
His tribe, the Banu Dhubya ...
. An example of an Islamic annual souk is Al Mirbid
AL, Al, Ål or al may stand for:
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Al (''Aladdin'') or Aladdin, the main character in Disney's ''Aladdin'' media
* Al (''EastEnders''), a minor character in the British soap opera
* Al (''Fullmetal ...
just outside Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
, also famed for its poetry competitions in addition to its storytelling activities. Temporary souks tended to become known for specific types of produce. For example, Suq Hijr in Bahrain was noted for its dates while Suq 'Adan was known for its spices and perfumes. Political, economic and social changes have left only the small seasonal souks outside villages and small towns, primarily selling livestock and agricultural products.
Weekly markets have continued to function throughout the Arab world. Most of them are named from the day of the week on which they are held. They usually have open spaces specifically designated for their use inside cities. Examples of surviving markets are the Wednesday Market in Amman that specializes in the sale of used products, the Ghazl market held every Friday in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
specializing in pets; the Fina’ Market in Marrakech offers performance acts such as singing, music, acrobats and circus activities.
In tribal areas, where seasonal souks operated, neutrality from tribal conflicts was usually declared for the period of operation of a souk to permit the unhampered exchange of surplus goods. Some of the seasonal markets were held at specific times of the year and became associated with particular types of produce such as Suq Hijr in Bahrain, noted for its dates while Suq 'Adan was known for its spices and perfumes. In spite of the centrality of the Middle Eastern market place, relatively little is known due to the lack of archaeological evidence.Gharipour, M., "The Culture and Politics of Commerce," in ''The Bazaar in the Islamic City: Design, Culture, and History,'' Mohammad Gharipour (ed.), New York, The American University in Cairo Press, 2012, pp 4-5
Permanent
Permanent souks are more commonly occurring, but less renowned as they focus on commercial activity, and not entertainment. Until theUmayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
era, permanent souks were merely an open space where merchants would bring in their movable stalls during the day and remove them at night; no one had a right to specific pitch and it was usually first-come first-served. During the Umayyad era the governments started leasing, and then selling, sites to merchants. Merchants then built shops on their sites to store their goods at night. Finally, the area comprising a souk might be roofed over. With its long and narrow alleys, al-Madina Souk is the largest covered historic market in the world, with an approximate length of 13 kilometers. Al-Madina Souk is part of the Ancient City of Aleppo
The Ancient City of Aleppo ( ar, مدينة حلب القديمة, Madīnat Ḥalab al-Qadīma) is the historic city centre of Aleppo, Syria. Before the Syrian Civil War, many districts of the ancient city remained essentially unchanged since ...
, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
since 1986 in Syria.
Organization
 Gharipour has pointed out that in spite of the centrality of souks and bazaars in Middle Eastern history, relatively little is known due to the lack of archaeological evidence. Souks are traditionally divided into specialized sections dealing in specific types of product, in the case of permanent souks each usually housed in a few narrow streets and named after the product it specializes in such as the
Gharipour has pointed out that in spite of the centrality of souks and bazaars in Middle Eastern history, relatively little is known due to the lack of archaeological evidence. Souks are traditionally divided into specialized sections dealing in specific types of product, in the case of permanent souks each usually housed in a few narrow streets and named after the product it specializes in such as the gold souk
A Gold souk ( ar, سوق الذهب) is a gold market in Arab countries of Arabian Peninsula and particularly in GCC countries. The word ''souk'' is mostly used by Arabs for open markets. The term evolved through the expatriates settled in Gulf C ...
, the fabric souk, the spice souk, the leather souk, the copy souk (for books), etc. This promotes competition among sellers and helps buyers easily compare prices.
At the same time the whole assembly is collectively called a souk. Some of the prominent examples are Souk Al-Melh in Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
, Manama Souk in Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
, Bizouriyya Souk in Damascus, Saray Souk in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
, Khan Al-Zeit in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, and Zanqat Al-Niswaan in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
.
Though each neighbourhood within the city would have a local Souk selling food and other essentials, the main souk was one of the central structures of a large city, selling durable goods, luxuries and providing services such as money exchange. Workshops where goods for sale are produced (in the case of a merchant selling locally-made products) are typically located away from the souk itself. The souk was a level of municipal administration. The Muhtasib
A muḥtasib ( ar, محتسب, from the root ''ḥisbah'', or "accountability"Sami Zubaida (2005), Law and Power in the Islamic World, , pages 58-60) was "a holder of the office of al-hisbah in classical Islamic administrations", according to Ox ...
was responsible for supervising business practices and collecting taxes for a given souk while the Arif are the overseers for a specific trade.
Shopping at a souk or market place is part of daily life throughout much of the Middle East. Prices are commonly set by bargaining, also known as haggling, between buyers and sellers.
In art and literature – Orientalism
During the 18th and 19th centuries, Europeans conquered and excavated parts of North Africa and the Levant. These regions now make up what is called the Middle East, but in the past were known as the ''Orient.'' Europeans sharply divided peoples into two broad groups – the ''European West'' and the ''East or Orient''; ''us'' and the ''other.'' Europeans often saw Orientals as the opposite of Western civilization; the peoples could be threatening- they were "despotic, static and irrational whereas Europe was viewed as democratic, dynamic and rational." At the same time, the Orient was seen as exotic, mysterious, a place of fables and beauty. This fascination with the other gave rise to a genre of painting known as Orientalism. A proliferation of both Oriental fiction and travel writing occurred during the early modern period.Subject matter
Many of these works were lavishly illustrated with engravings of every day scenes of Oriental lifestyles, including scenes of market places and market trade. Artists focused on the exotic beauty of the land – the markets, caravans and snake charmers. Islamic architecture also became favorite subject matter. Some of these works were propaganda designed to justify European imperialism in the East, however many artists relied heavily on their everyday experiences for inspiration in their artworks. For example,Charles D'Oyly
Sir Charles D'Oyly, 7th Baronet (1781–1845), was a British public official and painter from Dacca (now Dhaka). He was a member of the Bengal Civil Service based in Calcutta, Dacca and Patna from 1797 to 1838. Although he held senior positions w ...
, who was born in India, published the ''Antiquities of Dacca'' featuring a series of 15 engraved plates of Dacca ow Dhaka, Bangladeshfeaturing scenes of markets, commerce, buildings and streetscapes. European society generally frowned on nude painting – but harems, concubines and slave markets, presented as quasi-documentary works, satisfied European desires for pornographic art. The Oriental female wearing a veil was a particularly tempting subject because she was hidden from view, adding to her mysterious allure.
Notable Orientalist artists
Notable artists in the Orientalist genre include: Jean-Léon Gérôme Delacroix (1824–1904),Alexandre-Gabriel Decamps
Alexandre-Gabriel Decamps (March 3, 1803August 22, 1860) was a French painter noted for his Orientalist works.
Life
Decamps was born in Paris. In his youth he travelled in the East, and reproduced Oriental life and scenery with a bold fidelity to ...
(1803–1860), Frederic Leighton
Frederic Leighton, 1st Baron Leighton, (3 December 1830 – 25 January 1896), known as Sir Frederic Leighton between 1878 and 1896, was a British painter, draughtsman, and sculptor. His works depicted historical, biblical, and classical subjec ...
(1830-1896), Eugène Alexis Girardet 1853-1907 and William Holman Hunt
William Holman Hunt (2 April 1827 – 7 September 1910) was an English painter and one of the founders of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. His paintings were notable for their great attention to detail, vivid colour, and elaborate symbolis ...
(1827–1910) who all found inspiration in Oriental street scenes, trading and commerce. French painter Jean-Étienne Liotard
Jean-Étienne Liotard (; 22 December 1702 – 12 June 1789) was a Swiss painter, art connoisseur and dealer. He is best known for his portraits in pastel, and for the works from his stay in Turkey. A Huguenot of French origin and citizen of the ...
visited Istanbul in the 17th century and painted pastels of Turkish domestic scenes. British painter John Frederick Lewis
John Frederick Lewis (1804–1876) was an English Orientalist painter. He specialized in Oriental and Mediterranean scenes in detailed watercolour or oils, very often repeating the same composition in a version in each medium. He lived for ...
who lived for several years in a traditional mansion in Cairo, painted highly detailed works showing realistic genre scenes of Middle Eastern life. Edwin Lord Weeks was a notable American example of a 19th-century artist and author in the Orientalism genre. His parents were wealthy tea and spice merchants who were able to fund his travels and interest in painting. In 1895 Weeks wrote and illustrated a book of travels titled ''From the Black Sea through Persia and India.'' Other notable painters in the Orientalist genre who included scenes of street life and market-based trade in their work are Jean-Léon Gérôme Delacroix (1824–1904), Alexandre-Gabriel Decamps
Alexandre-Gabriel Decamps (March 3, 1803August 22, 1860) was a French painter noted for his Orientalist works.
Life
Decamps was born in Paris. In his youth he travelled in the East, and reproduced Oriental life and scenery with a bold fidelity to ...
(1803–1860), Frederic Leighton
Frederic Leighton, 1st Baron Leighton, (3 December 1830 – 25 January 1896), known as Sir Frederic Leighton between 1878 and 1896, was a British painter, draughtsman, and sculptor. His works depicted historical, biblical, and classical subjec ...
(1830–1896), Eugène Alexis Girardet 1853–1907 and William Holman Hunt
William Holman Hunt (2 April 1827 – 7 September 1910) was an English painter and one of the founders of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. His paintings were notable for their great attention to detail, vivid colour, and elaborate symbolis ...
(1827–1910), who all found inspiration in Oriental street scenes, trading and commerce.
Orientalist literature
A proliferation of both Oriental fiction and travel writing occurred during the early modern period. Many English visitors to the Orient wrote narratives around their travels. British Romantic literature in the Orientalism tradition has its origins in the early eighteenth century, with the first translations of ''The Arabian Nights'' (translated into English from the French in 1705–08). The popularity of this work inspired authors to develop a new genre, the Oriental tale. Samuel Johnson's ''History of Rasselas, Prince of Abyssinia,'' (1759) is mid-century example of the genre. Byron's ''Oriental Tales,'' is another example of the Romantic Orientalism genre. Although these works were purportedly non-fiction, they were notoriously unreliable. Many of these accounts provided detailed descriptions of market places, trading and commerce. Examples of travel writing include: ''Les Mysteres de L'Egypte Devoiles'' byOlympe Audouard
Olympe Audouard (March 13, 1832 – January 12, 1890)N.N.: Adouard, Olympe'. In French. URL last accessed July 14, 2006. was a French feminist who demanded complete equality for women, including the rights to vote and to stand for election.
B ...
published in 1865 and Jacques Majorelle
Jacques Majorelle (7 March 1886 – 14 October 1962), son of the celebrated Art Nouveau furniture designer Louis Majorelle, was a French painter. He studied at the École des Beaux-Arts in Nancy in 1901 and later at the Académie Julian in Pa ...
's ''Road Trip Diary of a Painter in the Atlas and the Anti-Atlas'' published in 1922Marcilhac, F., ''La Vie et l'Oeuvre de Jacques Majorelle: 1886–1962,'' he Orientalists Volume 7 ARC Internationale edition, 1988.
Gallery of paintings and watercolours
Léon Benett
Léon Benett (born Hippolyte Léon Benet; 1839–1916) was a French painter and illustrator. He was born in Orange, Provence. He changed his name to "Léon Benett" to differentiate his career in the French administration from his work as a d ...
for a Jules Verne novel, 1893
File:Alexandre Defaux - The Bazaar, 1856.jpg, ''The Bazaar'', by Alexandre Defaux, 1856
File:Amadeo Preziosi - The Grand Bazaar - Google Art Project.jpg, ''The Grand Bazaar'', Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, by Amadeo Preziosi, late 19th century
File:Amadeo Preziosi - The Silk Bazaar - Google Art Project.jpg, ''The Silk Bazaar'' by Amedeo Preziosi, late 19th century
File:Anton Robert Leinweber - Souk des étoffes, Tunis.jpg, ''Souk des étoffes,'' Tunis by Anton Robert Leinweber, before 1921
File:Carpet Merchant in the Khan el Khaleel (1878) - TIMEA.jpg, ''Carpet Merchant in the Khan el Khaleel'', from Georg Ebers, ''Egypt: Descriptive, Historical, and Picturesque,'' Vol. 1, 1878
File:Charles Wilda - Inside the Souk, Cairo 1892.jpg, ''Inside the Souk'', Cairo by Charles Wilda
Charles Wilda, originally Karl (20 December 1854, Vienna – 11 June 1907, Vienna) was an Austrian Orientalist painter. He was the elder brother of the painter, .
Biography
He studied with Leopold Carl Müller at the Academy of Fine Arts Vie ...
, 1892
File:David Roberts bazaar coppersmiths.jpg, ''Bazaar of the Coppersmiths'' in Cairo by David Roberts, 1838
File:David Roberts Bazaar El Moo Ristan.jpg, ''Bazaar El Moo Ristan'' in Cairo, by David Roberts, 1838
Gallery of photographs
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
File:Ancient covered souq, Aleppo, Syria.jpg, Al-Madina Souq
Al-Madina Souq ( ar, سوق المدينة, Sūq al-Madīna) is the covered souq-market located at the heart of the Syrian city of Aleppo within the walled ancient part of the city. With its long and narrow alleys, al-Madina Souq is the largest ...
in Aleppo, Syria
File:Suq Aftimos.JPG, Muristan Souk entrance in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
File:Marrakesh spices.jpg, Spice Market, Marrakesh
File:Ouarzazate souk.jpg, Souk in Ouarzazate
Ouarzazate (; ar, ورزازات, Warzāzāt, ; ary, وارزازات, Wārzāzāt; shi, label=Berber, ⵡⴰⵔⵣⴰⵣⴰⵜ, Warzazat), nicknamed ''the door of the desert'', is a city and capital of Ouarzazate Province in the region of Dr� ...
, Morocco
File:Covered souks in Bur Dubai (5374108812).jpg, Covered souks in Bur Dubai
Bur Dubai (in Arabic: بر دبي) is a historic district in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, located on the western side of the Dubai Creek. The name literally translates to ''Mainland Dubai'', a reference to the traditional separation of the Bur ...
, United Arab Emirates
File:Medina Tripoli Libya.jpg, Souk in Tripoli, Libya
List of bazaars and souks
See also
*List of Orientalist artists
This is an incomplete list of artists who have produced works on Orientalist subjects, drawn from the Islamic world or other parts of Asia. Many artists listed on this page worked in many genres, and Orientalist subjects may not have formed a m ...
; Types of markets, bazaars and souks
* Bazaari
* Bedesten
A bedesten (variants: bezistan, bezisten, bedestan) is a type of covered market or market hall which was historically found in the cities of the Ottoman Empire. It was typically the central building of the commercial district of an Ottoman town or ...
(also known as bezistan, bezisten, bedesten) refers to a covered bazaar and an open bazaar in the Balkans.
* Haat bazaar
Haat or hat, even haat bazaar, is an open-air market that serves as a trading venue for local people in rural areas and towns of Indian subcontinent, especially in India, Nepal, Bangladesh and Bhutan. Haat bazaars are conducted on a regular ba ...
– (also known as a ''hat'') an open air bazaar or market in South Asia.
* Landa bazaar
Landa bazaar is a bazaar (marketplace) in Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of ...
– a terminal market or market for second hand goods (South Asia), such as Medina quarter
A medina (from ar, مدينة, translit=madīnah, lit=city) is a historical district in a number of North African cities, often corresponding to an old walled city. The term comes from the Arabic word simply meaning "city" or "town".
Histori ...
.
* Meena Bazaar
Meenā Bāzār or Mina Bazaar ( ur, , hi, मीना बाज़ार, bn, মীনা বাজার) is a special bazaar to sell items to raise money for charity and non-profit organizations. It also refers to a number of modern-day ...
– a bazaar that raises money for non-profit organisations.
* Pasar malam
''Pasar malam'' ( nl, Nacht Markt or Avondmarkt) is an Indonesian and Malay word that literally means "night market" (the word comes from ''bazaar'' in Persian). A ''pasar malam'' is a street market in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapor ...
– a night market in Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
that opens in the evening, typically held in the street in residential neighbourhoods.
* Pasar pagi – a morning market, typically a wet market that trades from dawn until midday, found in Malaysia, Indonesia and Singapore. A Wet market
A wet market (also called a public market or a traditional market) is a marketplace selling fresh foods such as meat, fish, produce and other consumption-oriented perishable goods in a non-supermarket setting, as distinguished from " dry mark ...
sells fresh meat, and produce. See also Dry goods
Dry goods is a historic term describing the type of product line a store carries, which differs by region. The term comes from the textile trade, and the shops appear to have spread with the mercantile trade across the British Empire (and forme ...
.
; Markets and retail in general
* Arcade
Arcade most often refers to:
* Arcade game, a coin-operated game machine
** Arcade cabinet, housing which holds an arcade game's hardware
** Arcade system board, a standardized printed circuit board
* Amusement arcade, a place with arcade games
* ...
– a covered passageway with stores along one or both sides.
* History of marketing
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
* Marketplace
A marketplace or market place is a location where people regularly gather for the purchase and sale of provisions, livestock, and other goods. In different parts of the world, a marketplace may be described as a '' souk'' (from the Arabic), ' ...
* Merchant
* Peddler
A peddler, in British English pedlar, also known as a chapman, packman, cheapjack, hawker, higler, huckster, (coster)monger, colporteur or solicitor, is a door-to-door and/or travelling vendor of goods.
In England, the term was mostly used f ...
* Retail
Retail is the sale of goods and services to consumers, in contrast to wholesaling, which is sale to business or institutional customers. A retailer purchases goods in large quantities from manufacturers, directly or through a wholesaler, and ...
* Shopping mall
A shopping mall (or simply mall) is a North American term for a large indoor shopping center, usually anchored by department stores. The term "mall" originally meant a pedestrian promenade with shops along it (that is, the term was used to refe ...
* Shōtengai
A shōtengai () is a style of Japanese commercial district, typically in the form of a local market street that is closed to car traffic. Local shōtengai cater to the needs of nearby residents with a diverse mix of small specialty shops and few ...
- a style of Japanese commercial district, typically in the form of a local market street that is closed to vehicular traffic.
References
Further reading
* ''The Persian Bazaar: Veiled Space of Desire'' (Mage Publications) by Mehdi Khansari * ''The Morphology of the Persian Bazaar'' (Agah Publications) by Azita Rajabi. *External links
Iran Chamber Society on Architecture of the Bazaar at Isfahan
* {{Authority control Islamic culture Persian words and phrases Iranian folklore Shopping (activity)