Somalia, ,
Osmanya script
The Osmanya script ( so, Farta Cismaanya 𐒍𐒖𐒇𐒂𐒖 𐒋𐒘𐒈𐒑𐒛𐒒𐒕𐒖), also known as Far Soomaali (𐒍𐒖𐒇 𐒘𐒝𐒈𐒑𐒛𐒘, "Somali writing") and, in Arabic, as ''al-kitābah al-ʿuthmānīyah'' (الكتا ...
: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of Somalia
[The ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of th]
Provisional Constitution
, (; ), is a
country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while ...
in the
Horn of Africa. The country is bordered by
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
to the west,
Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
to the northwest, the
Gulf of Aden to the north, the
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
to the east, and
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
to the southwest. Somalia has the longest coastline on
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
's mainland.
Its terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains, and highlands.
Hot conditions prevail year-round, with periodic monsoon winds and irregular rainfall.
Somalia has an estimated population of around million, of which over 2 million live in the
capital and largest city
Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Oc ...
, and has been described as Africa's most culturally homogeneous country. Around 85% of its residents are ethnic
Somalis
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared ...
,
who have historically inhabited the country's north. Ethnic minorities are largely concentrated in the south.
[.] The official languages of Somalia are
Somali and
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
.
Most people in the country are
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, the majority of them
Sunni.
[.]
In antiquity, Somalia was an important commercial center. It is among the most probable locations of the ancient
Land of Punt
The Land of Punt ( Egyptian: '' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported gold, aromatic resins, blackwood, ebony, ivory an ...
. During the Middle Ages, several powerful Somali empires dominated the regional trade, including the
Ajuran Sultanate
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in th ...
, the
Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din II ...
, and the
Sultanate of the Geledi
The Sultanate of the Geledi ( so, Saldanadda Geledi, ar, سلطنة غلدي) also known as the Gobroon Dynasty Somali Sultanate: The Geledi City-state Over 150 Years - Virginia Luling (2002) Page 229 was a Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the ...
.
In the late 19th century,
Somali Sultanates like the
Isaaq Sultanate
The Isaaq Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Isaaq, Wadaad writing, Wadaad: , ar, السلطنة الإسحاقية) was a Somali people, Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries. It spanned the territorie ...
and the
Majeerteen Sultanate
The Majeerteen Sultanate ( so, Suldanadda Majeerteen 𐒈𐒚𐒐𐒆𐒖𐒒𐒖𐒆𐒆𐒖 𐒑𐒖𐒃𐒜𐒇𐒂𐒜𐒒, lit=Boqortooyada Majerteen, ar, سلطنة مجرتين), also known as Majeerteen Kingdom or Majeerteenia and Migiu ...
were colonized by both the
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
and
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
Empire. European colonists merged the tribal territories into two
colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
, which were
Italian Somaliland
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th centu ...
and the
British Somaliland Protectorate
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate ( so, Dhulka Maxmiyada Soomaalida ee Biritishka), was a British protectorate in present-day Somaliland. During its existence, the territory was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Som ...
.
Meanwhile, in the interior, the Dervishes led by
Mohammed Abdullah Hassan
Sayid Mohamed Abdullahi Hassan ( so, Sayid Maxamed Cabdulle Xasan; 1856–1920) was a Somali religious and military leader of the Dervish movement, which led a two-decade long confrontation with various colonial empires including the British, ...
engaged in a two-decade confrontation against Abyssinia, Italian Somaliland, and British Somaliland and were finally defeated in the
1920 Somaliland Campaign.
[Diiwaanka gabayadii, 1856–1921, Maxamad Cabdulle Xasan · 1999, PAGE 219] Italy acquired full control of the northeastern, central, and southern parts of the area after successfully waging the
Campaign of the Sultanates against the ruling
Majeerteen Sultanate
The Majeerteen Sultanate ( so, Suldanadda Majeerteen 𐒈𐒚𐒐𐒆𐒖𐒒𐒖𐒆𐒆𐒖 𐒑𐒖𐒃𐒜𐒇𐒂𐒜𐒒, lit=Boqortooyada Majerteen, ar, سلطنة مجرتين), also known as Majeerteen Kingdom or Majeerteenia and Migiu ...
and
Sultanate of Hobyo
The Sultanate of Hobyo ( so, Saldanadda Hobyo, ar, سلطنة هوبيو), also known as the Sultanate of Obbia,''New International Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, (Dodd, Mead: 1916), p.283. was a 19th-century Somali kingdom in present-day northeaste ...
.
In 1960, the two territories united to form the independent
Somali Republic
The Somali Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Soomaaliyeed; it, Repubblica Somala; ar, الجمهورية الصومالية, Jumhūriyyat aṣ-Ṣūmālīyyah) was a sovereign state composed of Somalia and Somaliland, following the unification o ...
under a civilian government.
[''The Illustrated Library of The World and Its Peoples: Africa, North and East'', Greystone Press: 1967, p. 338.]
Siad Barre of the
Supreme Revolutionary Council seized power in 1969 and established the
Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the socialist military government gave to Som ...
, brutally attempting to squash the
Somaliland War of Independence
The Somaliland War of Independence ( so, Dagaalkii Xoraynta Soomaaliland, lit=Somaliland Liberation War) was a rebellion waged by the Somali National Movement against the ruling military junta in Somalia led by General Siad Barre lasting from i ...
in the north of the country. The SRC subsequently collapsed 22 years later, in 1991, with the onset of the
Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War ( so, Dagaalkii Sokeeye ee Soomaaliya; ar, الحرب الأهلية الصومالية ) is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Bar ...
and
Somaliland soon declared independence.
Somaliland still controls the northwestern portion of Somalia representing just over 27% of its territory. Since this period most regions returned to
customary
Custom, customary, or consuetudinary may refer to:
Traditions, laws, and religion
* Convention (norm), a set of agreed, stipulated or generally accepted rules, norms, standards or criteria, often taking the form of a custom
* Norm (social), a r ...
and
religious law
Religious law includes ethical
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, ...
. In the early 2000s, a number of interim federal administrations were created. The
Transitional National Government
The Transitional National Government (TNG) was the internationally recognized central government of Somalia from 2000 to 2004.
Overview
The TNG was established in April–May 2000 at the Somalia National Peace Conference held in Arta, Djibouti. ...
(TNG) was established in 2000, followed by the formation of the
Transitional Federal Government
The Transitional Federal Government (TFG) ( so, Dowladda Federaalka Kumeelgaarka, ar, الحكومة الاتحادية الانتقالية) was internationally recognized as a provisional government of the Republic of Somalia from 14 October ...
(TFG) in 2004, which reestablished the
Somali Armed Forces
The Somali Armed Forces are the military forces of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Headed by the president as commander-in-chief, they are constitutionally mandated to ensure the nation's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity. Ch ...
.
In 2006, with a
US-backed Ethiopian intervention, the TFG assumed control of most of the nation's southern conflict zones from the newly formed
Islamic Courts Union
The Islamic Courts Union ( so, Midowga Maxkamadaha Islaamiga) was a legal and political organization formed to address the lawlessness that had been gripping Somalia since the fall of the Siad Barre regime in 1991 during the Somali Civil War.
Th ...
(ICU). The ICU subsequently splintered into more radical groups, including
jihadist
Jihadism is a neologism which is used in reference to "militant Islamic movements that are perceived as existentially threatening to the West" and "rooted in political Islam."Compare: Appearing earlier in the Pakistani and Indian media, Wes ...
s
al-Shabaab, which battled the TFG and its
AMISOM allies for control of the region.
By mid-2012, the insurgents had lost most of the territory they had seized, and a search for more permanent democratic institutions began.
Despite this, insurgents still control much of central and southern Somalia,
and wield influence in government-controlled areas,
with the town of
Jilib
Jilib (other names: Gilib, Gelib, Jillib, Jillio; ) is a city in Somalia, It is north of Kismaayo.
History
During the Middle Ages, Jilib and its surrounding area was part of the Ajuran Empire that governed much of southern Somalia and eastern Eth ...
acting as the insurgents' de facto capital.
A new provisional
constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
was passed in August 2012, reforming Somalia as a
federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
. The same month, the
Federal Government of Somalia was formed
and a period of reconstruction began in
Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Oc ...
, despite al-Shabaab frequently carrying out
attacks there.
Somalia's
GDP per capita is one of the world's lowest, and it belongs to the
least developed country group. In 2019, Somalia had the lowest
HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
in the world, and in the same year, 69% of Somalia's population was living below the poverty line. As of 2020, Somalia is placed the second highest in the Fragile States Index. It has maintained an
informal economy mainly based on livestock, remittances from
Somalis working abroad, and telecommunications.
It is a member of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, the
Arab League,
African Union,
Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
, and the
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
.
History
Prehistory

Somalia was likely one of the first lands to be settled by early humans due to its location.
Hunter-gatherers who would later migrate out of Africa likely settled here before their migrations.
During the Stone Age, the Doian and Hargeisan cultures flourished here.
The oldest evidence of burial customs in the Horn of Africa comes from cemeteries in Somalia dating back to the 4th millennium BCE. The stone implements from the Jalelo site in the north were also characterized in 1909 as important artifacts demonstrating the archaeological universality during the Paleolithic between the East and the West.
According to linguists, the first
Afroasiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic su ...
-speaking populations arrived in the region during the ensuing
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
period from the family's proposed
urheimat
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ''Urheimat'' (, from German '' ur-'' "original" and ''Heimat'', home) of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is the r ...
("original homeland") in the
Nile Valley, or the
Near East.
The
Laas Geel
Laas Geel ( so, Laas Geel), also spelled Laas Gaal, are cave formations on the rural outskirts of Hargeisa, Somaliland, situated in the Maroodi Jeex region of the country. They contain some of the earliest known cave paintings of domesticated Afr ...
complex on the outskirts of
Hargeisa
Hargeisa (; so, Hargeysa, ar, هرجيسا) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland. It is located in the Maroodi Jeex region of the Horn of Africa. It succeeded Burco as the capital of the British Somaliland Protector ...
in northwestern Somalia dates back approximately 5,000 years, and has
rock art depicting both wild animals and decorated cows. Other
cave paintings are found in the northern
Dhambalin
Dhambalin ("half, vertically cut mountain") is an archaeological site in the central Sahil province of Somaliland. The sandstone rock shelter contains rock art depicting various animals such as horned cattle and goats, as well as giraffes, an ani ...
region, which feature one of the earliest known depictions of a hunter on horseback. The rock art is dated to 1,000 to 3,000 BCE. Additionally, between the towns of
Las Khorey
Las Khorey ( so, Laasqoray, ar, لاسقُرَى ) is a historic coastal town in the Sanaag region of Somaliland.
History
The Las Khorey settlement is several centuries old. Between the town and El Ayo lies Karinhegane, a site containing numer ...
and
El Ayo
El Ayo ( so, Ceelaayo, ar, عيلايو), also known as El Ayum, is a coastal town in the eastern Sanaag region of Somaliland, near the border with Somalia. There is a base of the Puntland Maritime Police Force, which is effectively controlled ...
in northern Somalia lies
Karinhegane, the site of numerous cave paintings of both real and mythical animals. Each painting has an inscription below it, which collectively have been estimated to be around 2,500 years old.
Antiquity and classical era
Ancient
pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilat ...
ical structures,
mausoleums, ruined cities and stone walls, such as the
Wargaade Wall
Wargaade Wall is an ancient stone construction in Wargaade, Somalia. It enclosed a large historic settlement in the region.
Overview
Graves and unglazed sherds of pottery dating from antiquity have been found during excavations in the area. The ...
, are evidence of an old civilization that once thrived in the Somali peninsula.
This civilization enjoyed a trading relationship with
ancient Egypt and
Mycenaean Greece since the second millennium BCE, supporting the hypothesis that Somalia or adjacent regions were the location of the ancient
Land of Punt
The Land of Punt ( Egyptian: '' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported gold, aromatic resins, blackwood, ebony, ivory an ...
.
The Puntites native to the region, traded
myrrh, spices, gold, ebony, short-horned cattle, ivory and
frankincense with the Egyptians, Phoenicians, Babylonians, Indians, Chinese and Romans through their commercial ports. An Egyptian expedition sent to Punt by the
18th dynasty Queen
Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut (; also Hatchepsut; Egyptian: '' ḥꜣt- špswt'' "Foremost of Noble Ladies"; or Hatasu c. 1507–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the second historically confirmed female pharaoh, af ...
is recorded on the temple reliefs at
Deir el-Bahari
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri ( ar, الدير البحري, al-Dayr al-Baḥrī, the Monastery of the North) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part o ...
, during the reign of the Puntite King Parahu and Queen Ati.
In 2015, isotopic analysis of ancient baboon mummies from Punt that had been brought to Egypt as gifts indicated that the specimens likely originated from an area encompassing eastern Somalia and the Eritrea-Ethiopia corridor.
In the
classical era
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, the
Macrobians
The Macrobians (Μακροβίοι) were an ancient Proto-Somali tribal kingdom positioned in the Horn of Africa mentioned by Herodotus.Herodotus, the Histories book 3.114 They are one of the legendary peoples postulated at the extremity of the ...
, who may have been ancestral to Somalis, established a powerful tribal kingdom that ruled large parts of modern Somalia. They were reputed for their longevity and wealth, and were said to be the "tallest and handsomest of all men".
[The Geography of Herodotus: Illustrated from Modern Researches and Discoveries](_blank)
by James Talboys Wheeler, pg 1xvi, 315, 526 The Macrobians were warrior herders and seafarers. According to Herodotus' account, the
Persian Emperor
This is a list of monarchs of Persia (or monarchs of the Iranian peoples, Iranic peoples, in present-day Iran), which are known by the royal title Shah or King of Kings#Iran, Shahanshah. This list starts from the establishment of the Medes aroun ...
Cambyses II, upon his
conquest of Egypt in 525 BC, sent ambassadors to Macrobia, bringing luxury gifts for the Macrobian king to entice his submission. The Macrobian ruler, who was elected based on his stature and beauty, replied instead with a challenge for his Persian counterpart in the form of an unstrung bow: if the Persians could manage to draw it, they would have the right to invade his country; but until then, they should thank the gods that the Macrobians never decided to invade their empire.
[John Kitto, James Taylor, ''The popular cyclopædia of Biblical literature: condensed from the larger work'', (Gould and Lincoln: 1856), p.302.] The Macrobians were a regional power reputed for their advanced architecture and
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
wealth, which was so plentiful that they shackled their prisoners in golden chains.
The
camel is believed to have been domesticated in the Horn region sometime between the 2nd and 3rd millennium BCE. From there, it spread to
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
.
During the classical period, the
Barbara city-states also known as
sesea
The Monumentum Adulitanum was an ancient bilingual inscription in Ge'ez and Greek depicting the military campaigns of an Adulite king. The original text was inscribed on a throne in Adulis ( Ge'ez: መንበር ''manbar'') written in Ge'ez in bo ...
of
Mosylon
Mosylon ( grc, Μοσυλλόν and Μόσυλον), also known as Mosullon, was an ancient proto-Somali trading center on or near the site that later became the city of Bosaso.
History
Mosylon was the most prominent emporium on the Red Sea coas ...
,
Opone
Opone ( grc, Οπώνη) was an ancient proto-Somali city situated in the Horn of Africa. It is primarily known for its trade with the Ancient Egyptians, Romans, Greeks, Persians, and the states of ancient India. Through archaeological remains, t ...
,
Mundus,
Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kin ...
,
Malao
Malao ( grc, Μαλαὼ) was an ancient proto-Somali port in present-day Somaliland. The town was situated on the site of what later became the city of Berbera. It was a key trading member involved in the Red Sea-Indian Ocean commerce in the ea ...
,
Avalites
Avalites ( grc, Αὐαλίτης or ) was a small port in what is today Somalia that dominated trade in the Red Sea and Mediterranean.
Location
There has been a series of disputes as to the location of Avalites According to the ''Periplus of th ...
,
Essina
Essina ( grc, Εσσίνα) was an ancient Proto-Somali emporium located on the southeastern coast of Somalia in the Horn of Africa.Ptolemy's Topography of Eastern Equatorial Africa, by Henry Schlichter Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Socie ...
,
Nikon
(, ; ), also known just as Nikon, is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, specializing in optics and imaging products. The companies held by Nikon form the Nikon Group.
Nikon's products include cameras, camera ...
and
Sarapion
Sarapion ( grc, Σαράπιον, also spelled Serapion) was an ancient proto-Somali port city in present-day Somalia. It was situated on a site that later became Mogadishu. Sarapion was briefly mentioned in Ptolemy's '' Geographia'' as one of the ...
developed a lucrative trade network, connecting with merchants from
Ptolemaic Egypt,
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
,
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
,
Parthian Persia,
Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), ...
, the
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom ( Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity.
The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, ...
, and the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. They used the ancient Somali maritime vessel known as the ''
beden
The Beden, badan, or alternate type names Beden-seyed and Beden-safar, is a fast, ancient Somali single or double-masted maritime vessel and ship, typified by its towering stern-post and powerful rudder. It is also the longest surviving sewn boa ...
'' to transport their cargo.

After the
Roman conquest of the Nabataean Empire and the Roman naval presence at
Aden to curb piracy, Arab and Somali merchants agreed with the Romans to bar Indian ships from trading in the free port cities of the
Arabian peninsula to protect the interests of Somali and Arab merchants in the lucrative commerce between the Red and Mediterranean Seas.
[.] However, Indian merchants continued to trade in the port cities of the Somali peninsula, which was free from Roman interference. For centuries, Indian merchants brought large quantities of cinnamon to Somalia and Arabia from
Ceylon and the
Spice Islands
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
. The source of the cinnamon and other spices is said to have been the best-kept secret of Arab and Somali merchants in their trade with the Roman and Greek world; the Romans and Greeks believed the source to have been the Somali peninsula. The collusive agreement among Somali and Arab traders inflated the price of Indian and Chinese cinnamon in North Africa, the Near East, and Europe, and made the cinnamon trade a very profitable revenue generator, especially for the Somali merchants through whose hands large quantities were shipped across sea and land routes.
Birth of Islam and the Middle Ages
 Islam
Islam was introduced to the area early on by the first Muslims of Mecca fleeing prosecution during the first
Hejira with
Masjid al-Qiblatayn
The Masjid al-Qiblatayn ( ar, مسجد القبلتين, lit=Mosque of the Two Qiblas), also spelt Masjid al-Qiblatain, is a mosque in Medina believed by Muslims to be the place where the final Islamic prophet, Muhammad, received the command to ...
in
Zeila
Zeila ( so, Saylac, ar, زيلع, Zayla), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila (or Hawilah) with the Bibl ...
being built before the
Qibla
The qibla ( ar, قِبْلَة, links=no, lit=direction, translit=qiblah) is the direction towards the Kaaba in the Sacred Mosque in Mecca, which is used by Muslims in various religious contexts, particularly the direction of prayer for the ...
h towards
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
. It is one of the oldest
mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
s in Africa. In the late 9th century,
Al-Yaqubi
ʾAbū l-ʿAbbās ʾAḥmad bin ʾAbī Yaʿqūb bin Ǧaʿfar bin Wahb bin Waḍīḥ al-Yaʿqūbī (died 897/8), commonly referred to simply by his nisba al-Yaʿqūbī, was an Arab Muslim geographer and perhaps the first historian of world cult ...
wrote that Muslims were living along the northern Somali seaboard.
He also mentioned that the
Adal Kingdom had its capital in the city.
According to
Leo Africanus
Joannes Leo Africanus (born al-Hasan Muhammad al-Wazzan, ar, الحسن محمد الوزان ; c. 1494 – c. 1554) was an Andalusian diplomat and author who is best known for his 1526 book '' Cosmographia et geographia de Affrica'', later ...
, the
Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din II ...
was governed by local
Somali dynasties and its realm encompassed the geographical area between the Bab el Mandeb and Cape Guardafui. It was thus flanked to the south by the
Ajuran Empire
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in th ...
and to the west by the
Abyssinian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historica ...
.
Throughout the Middle Ages, Arab immigrants arrived in Somaliland, a historical experience which would later lead to the legendary stories about Muslim
sheikhs such as
Daarood
The Darod ( so, Daarood, ar, دارود) is a Somali clan. The forefather of this clan was Sheikh Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, more commonly known as ''Darood''. The clan primarily settles the apex of the Horn of Africa and its peripheri ...
and
Ishaaq bin Ahmed
Sheikh Ishaaq bin Ahmed bin Muhammad bin al-Hussein al-Hashimi, more commonly known as Sheikh Ishaaq or Sheikh Isaaq (, ) was the semi-legendary Arab forefather of the Somali Isaaq clan-family in the Horn of Africa, whose traditional territory ...
(the purported ancestors of the
Darod
The Darod ( so, Daarood, ar, دارود) is a Somali clan. The forefather of this clan was Sheikh Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, more commonly known as ''Darood''. The clan primarily settles the apex of the Horn of Africa and its peripheries ...
and
Isaaq
The Isaaq (also Isaq, Ishaak, Isaac) ( so, Reer Sheekh Isxaaq, ar, بني إسحاق, Banī Isḥāq) is a Somali clan. It is one of the major Somali clans in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory. Pe ...
clans, respectively) travelling from
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
to Somalia and marrying into the local
Dir clan.
In 1332, the Zeila-based King of Adal was slain in a military campaign aimed at halting Abyssinian emperor
Amda Seyon I
Amda Seyon I ( gez, ዐምደ ፡ ጽዮን , am, አምደ ፅዮን , "Pillar of Zion"), throne name Gebre Mesqel (ገብረ መስቀል ) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1314 to 1344 and a member of the Solomonic dynasty.
He is best known ...
's march toward the city. When the last Sultan of Ifat,
Sa'ad ad-Din II
Sa'ad ad-Din II ( ar, سعد الدين زنكي), reigned – c. 1403 or c. 1414, was a Sultan of the Ifat Sultanate. He was the brother of Haqq ad-Din II, and the father of Mansur ad-Din, Sabr ad-Din II and Badlay ibn Sa'ad ad-Din. The hist ...
, was also killed by Emperor
Dawit I
Dawit I ( gez, ዳዊት) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1382 to 6 October 1413, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. He was the younger son of Newaya Krestos.
Reign
Taddesse Tamrat discusses a tradition that early in his reign, Dawit campaign ...
in Zeila in 1410, his children escaped to Yemen, before returning in 1415. In the early 15th century, Adal's capital was moved further inland to the town of
Dakkar
Dakkar or Doggor, also known as Aw-Barkhadle () was a historical town located near Hargeisa in modern-day Somaliland. It was part of the Muslim empires in the Horn of Africa during the middle ages and served as the capital of the Adal Sultanate ...
, where
Sabr ad-Din II
Sabr ad-Din III ( ar, الصبر الدين الثاني) (died 1422 or 1423) was a Sultan of Adal and the oldest son of Sa'ad ad-Din II. Sabr ad-Din returned to the Horn of Africa from Yemen to reclaim his father's realm. He defeated the Ethiop ...
, the eldest son of Sa'ad ad-Din II, established a new base after his return from Yemen.

Adal's headquarters were again relocated the following century, this time southward to
Harar
Harar ( amh, ሐረር; Harari: ሀረር; om, Adare Biyyo; so, Herer; ar, هرر) known historically by the indigenous as Gey (Harari: ጌይ ''Gēy'', ) is a walled city in eastern Ethiopia. It is also known in Arabic as the City of Saint ...
. From this new capital, Adal organised an effective army led by Imam
Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi
Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi ( so, Axmed Ibraahim al-Qaasi or Axmed Gurey, Harari: አሕመድ ኢብራሂም አል-ጋዚ, ar, أحمد بن إبراهيم الغازي ; 1506 – 21 February 1543) was an imam and general of the Adal Sultan ...
(Ahmad "Gurey" or "Gran"; both meaning "the left-handed") that invaded the Abyssinian empire.
This 16th-century campaign is historically known as the
Conquest of Abyssinia (''Futuh al-Habash''). During the war, Imam Ahmad pioneered the use of cannons supplied by the Ottoman Empire, which he imported through Zeila and deployed against Abyssinian forces and their Portuguese allies led by
Cristóvão da Gama
Cristóvão da Gama ( 1516 – 29 August 1542), anglicised as Christopher da Gama, was a Portuguese military commander who led a Portuguese army of 400 musketeers on a crusade in Ethiopia (1541–1543) against the Adal Muslim army of Imam A ...
. Some scholars argue that this conflict proved, through their use on both sides, the value of firearms such as the
matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of rope that is touched to the gunpowder by a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or trigger with his finger. Befor ...
musket, cannon, and the
arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
over traditional weapons.
During the
Ajuran Sultanate
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in th ...
period, the city-states and republics of
Merca
Merca ( so, Marka, Maay: ''Marky'', ar, مركة) is a historic port city in the southern Lower Shebelle province of Somalia. It is located approximately to the southwest of the nation's capital Mogadishu. Merca is the traditional home territory ...
,
Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Oc ...
,
Barawa
Barawa ( so, Baraawe, Maay: ''Barawy'', ar, ﺑﺮﺍﻭة ''Barāwa''), also known as Barawe and Brava, is the capital of the South West State of Somalia.Pelizzari, Elisa. "Guerre civile et question de genre en Somalie. Les événements et le ...
,
Hobyo
Hobyo (; so, Hobyo), is an ancient port city in Galmudug state in the north-central Mudug region of Somalia.
Hobyo was founded as a coastal outpost by the Ajuran Empire during the 13th century.Lee V. Cassanelli, ''The shaping of Somali society: ...
and their respective ports flourished and had a lucrative foreign commerce with ships sailing to and from Arabia, India,
Venetia, Persia, Egypt, Portugal, and as far away as China.
Vasco da Gama, who passed by Mogadishu in the 15th century, noted that it was a large city with houses several storeys high and large palaces in its centre, in addition to many mosques with cylindrical minarets. The
Harla
The Harla, also known as Harala, or Arla, are an extinct ethnic group that once inhabited Djibouti, Ethiopia and northern Somalia. They spoke the now-extinct Harla language, which belonged to either the Cushitic or Semitic branches of the Afroas ...
, an early
Hamitic
Hamites is the name formerly used for some Northern and Horn of Africa peoples in the context of a now-outdated model of dividing humanity into different races which was developed originally by Europeans in support of colonialism and slavery. T ...
group of tall stature who inhabited parts of Somalia, Tchertcher and other areas in the Horn, also erected various
tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
. These masons are believed to have been ancestral to ethnic Somalis.
In the 16th century,
Duarte Barbosa
Duarte Barbosa (c. 14801 May 1521) was a Portuguese writer and officer from Portuguese India (between 1500 and 1516). He was a Christian pastor and scrivener in a '' feitoria'' in Kochi, and an interpreter of the local language, Malayalam. Barbo ...
noted that many ships from the
Kingdom of Cambaya in modern-day India sailed to Mogadishu with cloth and spices, for which they in return received gold, wax and ivory. Barbosa also highlighted the abundance of meat, wheat, barley, horses, and fruit on the coastal markets, which generated enormous wealth for the merchants. Mogadishu, the center of a thriving textile industry known as ''toob benadir'' (specialized for the markets in Egypt, among other places), together with Merca and Barawa, also served as a transit stop for
Swahili merchants from
Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town is ...
and
Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban cent ...
and for the gold trade from
Kilwa
Kilwa Kisiwani (English: ''Kilwa Island'') is an island, national historic site, and hamlet community located in the township of Kilwa Masoko, the district seat of Kilwa District in the Tanzanian region of Lindi Region in southern Tanzania. K ...
.
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
merchants from the
Hormuz brought their Indian textile and fruit to the Somali coast in exchange for
grain and wood.
Trading relations were established with
Malacca in the 15th century, with cloth, ambergris and porcelain being the main commodities of the trade. Giraffes, zebras and incense were exported to the
Ming Empire
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
of China, which established Somali merchants as leaders in the commerce between East Asia and the Horn. Hindu merchants from
Surat and Southeast African merchants from
Pate, seeking to bypass both the
Portuguese India blockade ( and later the Omani interference), used the Somali ports of Merca and Barawa (which were out of the two powers' direct jurisdiction) to conduct their trade in safety and without interference.
Early modern era and the scramble for Africa
In the
early modern period, successor states to the Adal Sultanate and Ajuran Sultanate began to flourish in Somalia. These included the
Hiraab Imamate
The Hiraab Imamate ( so, Saldanadda Hiraab) also known as the Yacquubi Dynasty was a Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa during the late 17th century and 19th century until it was incorporated into Italian Somaliland. The Imamate ...
, the
Sultanate of the Geledi
The Sultanate of the Geledi ( so, Saldanadda Geledi, ar, سلطنة غلدي) also known as the Gobroon Dynasty Somali Sultanate: The Geledi City-state Over 150 Years - Virginia Luling (2002) Page 229 was a Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the ...
(Gobroon dynasty), the
Majeerteen Sultanate
The Majeerteen Sultanate ( so, Suldanadda Majeerteen 𐒈𐒚𐒐𐒆𐒖𐒒𐒖𐒆𐒆𐒖 𐒑𐒖𐒃𐒜𐒇𐒂𐒜𐒒, lit=Boqortooyada Majerteen, ar, سلطنة مجرتين), also known as Majeerteen Kingdom or Majeerteenia and Migiu ...
(Migiurtinia), and the
Sultanate of Hobyo
The Sultanate of Hobyo ( so, Saldanadda Hobyo, ar, سلطنة هوبيو), also known as the Sultanate of Obbia,''New International Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, (Dodd, Mead: 1916), p.283. was a 19th-century Somali kingdom in present-day northeaste ...
(Obbia). They continued the tradition of castle-building and seaborne trade established by previous Somali empires.
Sultan
Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim
Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim ( so, Yuusuf Maxamuud Ibrahiim, ar, يوسف محمود ابراهيم) was a Somali people, Somali ruler. He was the third and most powerful Sultan of the Geledi sultanate, reigning from 1798 to 1848. Under the reign of Sul ...
, the third Sultan of the House of Gobroon, started the golden age of the Gobroon Dynasty. His army came out victorious during the Bardheere Jihad, which restored stability in the region and revitalized the East African
ivory trade. He also had cordial relations and received gifts from the rulers of neighbouring and distant kingdoms such as the Omani,
Witu and Yemeni Sultans.
Sultan Ibrahim's son
Ahmed Yusuf succeeded him as one of the most important figures in 19th-century East Africa, receiving tribute from Omani governors and creating alliances with important Muslim families on the East African coast. In Somalland, the
Isaaq Sultanate
The Isaaq Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Isaaq, Wadaad writing, Wadaad: , ar, السلطنة الإسحاقية) was a Somali people, Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries. It spanned the territorie ...
was established in 1750. The Isaaq Sultanate was a
Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the
Horn of Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries. It spanned the territories of the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (also Isaq, Ishaak, Isaac) ( so, Reer Sheekh Isxaaq, ar, بني إسحاق, Banī Isḥāq) is a Somali clan. It is one of the major Somali clans in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory. Pe ...
clan, descendants of the
Banu Hashim clan,
[I. M. Lewis, ''A pastoral democracy: a study of pastoralism and politics among the Northern Somali of the Horn of Africa'', (LIT Verlag Münster: 1999), p. 157.] in modern-day
Somaliland and
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
. The sultanate was governed by the Rer Guled branch established by the first sultan, Sultan
Guled Abdi, of the
Eidagale
The Eidagale (Ciidagale), ar, عيدَغَلي, (which translates to "army joiner"), Full Name: Da'ud ibn Al-Qādhī Ismā'īl ibn ash-Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad, is a major Somali clan and is a sub-division of the Garhajis clan of the Isa ...
clan. The sultanate is the pre-colonial predecessor to the modern
Republic of Somaliland.
According to oral tradition, prior to the Guled dynasty the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (also Isaq, Ishaak, Isaac) ( so, Reer Sheekh Isxaaq, ar, بني إسحاق, Banī Isḥāq) is a Somali clan. It is one of the major Somali clans in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory. Pe ...
clan-family were ruled by a dynasty of the Tolje'lo branch starting from, descendants of Ahmed nicknamed Tol Je'lo, the eldest son of
Sheikh Ishaaq's
Harari wife. There were eight Tolje'lo rulers in total, starting with Boqor Harun () who ruled the Isaaq Sultanate for centuries starting from the 13th century. The last Tolje'lo ruler
Garad
Garad ( Harari: ገራድ, , , Oromo: ''Garaada'') is a term used to refer to a clan leader or regional administrator. It was used primarily by Muslims in the Horn of Africa that were associated with Islamic states, most notably the Adal Sultanat ...
Dhuh Barar ( so, Dhuux Baraar) was overthrown by a coalition of Isaaq clans. The once strong Tolje'lo clan were scattered and took refuge amongst the
Habr Awal
The Habr Awal, also contemporarily known as the Subeer Awal, and alternately romanized as the Zubeyr Awal ( so, Habar Awal, ar, هبر أول, Full Name: '' Zubeyr ibn Abd al-Raḥmān ibn ash- Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad)'' is a major clan of ...
with whom they still mostly live.


In the late 19th century, after the
Berlin Conference
The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, also known as the Congo Conference (, ) or West Africa Conference (, ), regulated European colonisation and trade in Africa during the New Imperialism period and coincided with Germany's sudden emergenc ...
of 1884, European powers began the
Scramble for Africa. In that year, a British protectorate was declared over part of Somalia, on the African coast opposite South Yemen.
[Langers Encyclopedia of World History, 594.] Initially, this region was under the control of the Indian Office, and so administered as part of the Indian Empire; in 1898 it was transferred to control by London.
In 1889, the protectorate and later colony of
Italian Somalia
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th centur ...
was officially established by
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
through various treaties signed with a number of chiefs and sultans; Sultan
Yusuf Ali Kenadid
Yusuf Ali Kenadid ( so, Yuusuf Cali Keenadiid; 1837 - 14 August 1911) was a Somali Sultan. He was the founder of the Sultanate of Hobyo in April 1878. He was succeeded atop the throne by his son Ali Yusuf Kenadid.
Family
Yusuf Ali Kenadid was bo ...
first sent a request to Italy in late December 1888 to make his
Sultanate of Hobyo
The Sultanate of Hobyo ( so, Saldanadda Hobyo, ar, سلطنة هوبيو), also known as the Sultanate of Obbia,''New International Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, (Dodd, Mead: 1916), p.283. was a 19th-century Somali kingdom in present-day northeaste ...
an Italian protectorate before later signing a treaty in 1889.
The Dervish movement successfully repulsed the British Empire four times and forced it to retreat to the coastal region. The
Darawiish defeated the Italian, British, Abyssinian colonial powers on numerous occasions, most notably, the 1903 victory at Cagaarweyne commanded by
Suleiman Aden Galaydh,
forcing the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
to retreat to the coastal region in the late 1900s. The Dervishes were finally defeated in 1920 by British airpower.
The dawn of
fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy an ...
in the early 1920s heralded a change of strategy for Italy, as the north-eastern sultanates were soon to be forced within the boundaries of ''La Grande Somalia'' ("''
Greater Somalia''") according to the plan of Fascist Italy. With the arrival of Governor
Cesare Maria De Vecchi
Cesare Maria De Vecchi, 1st Conte di Val Cismon (14 November 1884 – 23 June 1959) was an Italian soldier, colonial administrator and Fascist politician.
Biography
De Vecchi was born in Casale Monferrato on 14 November 1884. After graduating ...
on 15 December 1923, things began to change for that part of Somaliland known as
Italian Somaliland
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th centu ...
. The last piece of land acquired by Italy in Somalia was
Oltre Giuba
Oltre Giuba or Trans-Juba ( ar, شرق جوبا الإيطالية) was an Italian colony in the territory of Jubaland in present-day southern Somalia. It lasted for one year, from 1924 until 1925, when it was absorbed into Italian Somaliland. ' ...
, present-day
Jubaland region, in 1925.
The Italians began local infrastructure projects, including the construction of hospitals, farms and schools.
, under
Benito Mussolini, attacked Abyssinia (Ethiopia) in 1935, with an aim to colonize it. The invasion was condemned by the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
, but little was done to stop it or to liberate occupied Ethiopia. In 1936, Italian Somalia was integrated into
Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa ( it, Africa Orientale Italiana, AOI) was an Italian colony in the Horn of Africa. It was formed in 1936 through the merger of Italian Somalia, Italian Eritrea, and the newly occupied Ethiopian Empire, conquered in the S ...
, alongside Eritrea and Ethiopia, as the
Somalia Governorate. On 3 August 1940, Italian troops, including Somali colonial units, crossed from Ethiopia to
invade British Somaliland, and by 14 August, succeeded in taking
Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
from the British.
A British force, including troops from several African countries, launched the
campaign in January 1941 from Kenya to liberate British Somaliland and Italian-occupied Ethiopia and conquer Italian Somaliland. By February most of Italian Somaliland was captured and, in March, British Somaliland was retaken from the sea. The forces of the British Empire operating in Somaliland comprised the three divisions of South African, West African, and East African troops. They were assisted by Somali forces led by Abdulahi Hassan with Somalis of the
Isaaq
The Isaaq (also Isaq, Ishaak, Isaac) ( so, Reer Sheekh Isxaaq, ar, بني إسحاق, Banī Isḥāq) is a Somali clan. It is one of the major Somali clans in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory. Pe ...
,
Dhulbahante
The Dhulbahante ( so, Dhulbahante, ar, دلبةنتئ) is a Somali clan family, part of the Harti clan which itself belongs to the largest Somali clan-family — the Darod. They are the traditional inhabitants of the physiographic Nugaal in its ...
, and
Warsangali
The Warsangali ( so, Warsangeli, ar, قبيلة ورسنجلي) is a major Somali sub clan, part of the Harti clan which itself belongs to one of the largest Somali clan-families - the Darod. In the Somali language, the name Warsangali means ...
clans prominently participating. The number of
Italian Somalis
Italian Somalis ( it, Italo-Somali) are Somali descendants from Italian colonists, as well as long-term Italian residents in Somalia.
History
In 1892, the Italian explorer Luigi Robecchi Bricchetti for the first time labeled as ''Somalia'' the ...
began to decline after World War II, with fewer than 10,000 remaining in 1960.
Independence (1960–1969)

Following World War II, Britain retained control of both
British Somaliland and Italian Somaliland as protectorates. In 1945, during the
Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
, the United Nations granted Italy trusteeship of Italian Somaliland as the
Trust Territory of Somaliland
The Trust Territory of Somaliland, officially the "Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian administration" ( it, Amministrazione fiduciaria italiana della Somalia), was a United Nations Trust Territory situated in present-day Somalia. Its c ...
, on the condition first proposed by the Somali Youth League (SYL) and other nascent Somali political organizations, such as Hizbia Digil Mirifle Somali (HDMS) and the Somali National League (SNL)—that Somalia achieve independence within ten years.
British Somaliland remained a protectorate of Britain until 1960.
To the extent that Italy held the territory by UN mandate, the trusteeship provisions gave the Somalis the opportunity to gain experience in Western political education and self-government. These were advantages that British Somaliland, which was to be incorporated into the new Somali state, did not have. Although in the 1950s British colonial officials attempted, through various administrative development efforts, to make up for past neglect, the protectorate stagnated in political administrative development. The disparity between the two territories in economic development and political experience would later cause serious difficulties integrating the two parts.
Meanwhile, in 1948, under pressure from their World War II allies and to the dismay of the Somalis, the British returned the
Haud
The Haud (also Hawd) (, ), formerly known as the Hawd Reserve Area is a plateau situated in the Horn of Africa consisting of thorn-bush and grasslands. The region includes the southern part of Somaliland as well as the northern and eastern part ...
(an important Somali grazing area that was presumably protected by British treaties with the Somalis in 1884 and 1886) and the
Somali Region
The Somali Region ( so, Deegaanka Soomaalida, am, ሱማሌ ክልል, Sumalē Kilil, ar, المنطقة الصومالية), also known as Soomaali Galbeed (''Western Somalia'') and officially the Somali Regional State, is a regional stat ...
to Ethiopia, based on a treaty they signed in 1897 in which the British ceded Somali territory to the Ethiopian Emperor
Menelik in exchange for his help against possible advances by the French.
Britain included the conditional provision that the Somali residents would retain their autonomy, but Ethiopia immediately claimed sovereignty over the area. This prompted an unsuccessful bid by Britain in 1956 to buy back the Somali lands it had turned over.
Britain also granted administration of the almost exclusively Somali-inhabited
Northern Frontier District
The North Eastern Province ( so, Gobolka Woqooyi Bari, 𐒌𐒙𐒁𐒙𐒐𐒏𐒖 𐒓𐒙𐒎𐒝𐒕𐒘 𐒁𐒖𐒇𐒘) is one of the former provinces in Kenya. It has a land area of 127,358.5 km2, with its capital at Garissa. Previ ...
(NFD) to Kenyan nationalists. This was despite a
plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
in which, according to a British colonial commission, almost all of the territory's ethnic Somalis favored joining the newly formed Somali Republic.
A
referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
was held in neighbouring
Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
(then known as
French Somaliland) in 1958, on the eve of Somalia's independence in 1960, to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, largely due to a combined yes vote by the sizable
Afar ethnic group and resident Europeans.
There was also widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls.
The majority of those who voted 'no' were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia, as had been proposed by
Mahmoud Harbi
Mahamoud Harbi Farah ( ar, محمود الحربي, so, Maxamuud Xarbi Faarax) (1921 – 29 September 1960) was a Djiboutian politician of Somali ethnicity. A pan-Somalist, he was the Vice President of the Government Council of French Somal ...
, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later.
Djibouti finally gained independence from
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
in 1977, and
Hassan Gouled Aptidon
Hassan Gouled Aptidon ( so, Xasan Guuleed Abtidoon; ar, حسن جوليد أبتيدون) (October 15, 1916 – November 21, 2006) was the first President of Djibouti from 1977 to 1999.
Biography
He was born in the small village of Gerisa in t ...
, a Somali who had campaigned for a 'yes' vote in the referendum of 1976, eventually became Djibouti's first president (1977–1999).
On 1 July 1960, five days after the former British Somaliland protectorate obtained independence as the State of Somaliland, the territory united with the Trust Territory of Somaliland to form the
Somali Republic
The Somali Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Soomaaliyeed; it, Repubblica Somala; ar, الجمهورية الصومالية, Jumhūriyyat aṣ-Ṣūmālīyyah) was a sovereign state composed of Somalia and Somaliland, following the unification o ...
,
[Encyclopædia Britannica, ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica'', (Encyclopædia Britannica: 2002), p.835] albeit within boundaries drawn up by Italy and Britain. A government was formed by
Abdullahi Issa and
Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal
Mohamed Haji Ibrahim Egal ( so, Maxamed Xaaji Ibraahim Cigaal, ar, محمد الحاج ابراهيم عقال; August 15, 1928 – May 3, 2002) was a Somali politician who served as the President of Somaliland from 1993 to his death in 2002. H ...
with other members of the trusteeship and protectorate governments, with
Abdulcadir Muhammed Aden as President of the
Somali National Assembly,
Aden Abdullah Osman Daar
Aden Abdulle Osman Daar ( so, Aadan Cabdulle Cismaan Dacar, ar, آدم عبد الله عثمان دعر) (December 9, 1908 – June 8, 2007), popularly known as Aden Adde, was a Somali politician who served as the first president of the So ...
as
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
of the Somali Republic, and
Abdirashid Ali Shermarke
Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke ( so, Cabdirashiid Cali Sharmaarke, ar, عبد الرشيد علي شارماركي) (8 June 1919 – 15 October 1969), also known as Abdirashid Shermarke, was Prime Minister of Somali Republic from 12 July 1960, to 14 J ...
as
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
(later to become president from 1967 to 1969). On 20 July 1961 and through a
popular referendum
A popular referendum (also known, depending on jurisdiction, as citizens' veto, people's veto, veto referendum, citizen referendum, abrogative referendum, rejective referendum, suspensive referendum or statute referendum)Maija SetäläReferendum ...
, was ratified popularly by the people of Somalia under Italian trusteeship, Most of the people from the former Somaliland Protectorate didn't participate in the referendum, although only a small number of Somalilanders who participated the referendum voted against the
new constitution, which was first drafted in 1960.
In 1967, Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal became Prime Minister, a position to which he was appointed by Shermarke. Egal would later become the President of the autonomous
Somaliland region in northwestern Somalia.
On 15 October 1969, while paying a visit to the northern town of
Las Anod
Las Anod ( so, Laascaanood; ar, لاسعانود) is the administrative capital of the Sool, Somaliland, Sool region of Somaliland.
Territorial dispute
The city is disputed by Puntland and Somaliland. The former bases its claim due to the ki ...
, Somalia's then President Abdirashid Ali Shermarke was shot dead by one of his own bodyguards. His assassination was quickly followed by a military
coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
on 21 October 1969 (the day after his funeral), in which the
Somali Army
The Somali National Army ( Somali: ''Xooga Dalka Soomaaliyeed,'' lit. ''"Somali Ground Forces"'') is the ground forces component of the Somali Armed Forces, and is the largest out of the three service branches that make up the majority of the A ...
seized power without encountering armed opposition — essentially a bloodless takeover. The putsch was spearheaded by Major General
Mohamed Siad Barre
Mohamed Siad Barre ( so, Maxamed Siyaad Barre, Osmanya script: ; ar, محمد سياد بري; c. 1910 – 2 January 1995) was a Somali head of state and general who served as the 3rd president of the Somali Democratic Republic from 1969 to 199 ...
, who at the time commanded the army.
Somali Democratic Republic (1969–1991)

Alongside Barre, the
Supreme Revolutionary Council (SRC) that assumed power after President Sharmarke's assassination was led by Lieutenant Colonel
Salaad Gabeyre Kediye
Salaad Gabeyre Kediye ( so, Salaad Gabeyre Kediye, 1933 – 3 July 1972), also known as Salah Gaveire Kedie, was a Somali senior military official and a revolutionary who was executed by the Siad Barre regime.
Biography
Kediye was born in Harard ...
and Chief of Police
Jama Korshel
Jama Ali Korshel ( so, Jaamac Cali Qoorsheel, ar, جامع علي قورشيل) was a Somali army Major General and former Head of the Somali Police Force. He was the Vice President of the Supreme Revolutionary Council.
Biography
Korshel was b ...
. Kediye officially held the title "Father of the Revolution", and Barre shortly afterwards became the head of the SRC. The SRC subsequently renamed the country the Somali Democratic Republic,
[''The Encyclopedia Americana: complete in thirty volumes. Skin to Sumac'', Vol. 25, Grolier: 1995, p. 214, .] dissolved the parliament and the Supreme Court, and suspended the constitution.
[de la Fosse Wiles, Peter John (1982]
''The New Communist Third World: an essay in political economy''
Taylor & Francis, p. 279 .
The revolutionary army established large-scale public works programs and successfully implemented an urban and rural
literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
campaign, which helped dramatically increase the literacy rate. In addition to a nationalization program of industry and land, the new regime's foreign policy placed an emphasis on Somalia's traditional and religious links with the
Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
, eventually joining the
Arab League in February, 1974. That same year, Barre also served as chairman of the
Organisation of African Unity
The Organisation of African Unity (OAU; french: Organisation de l'unité africaine, OUA) was an intergovernmental organization established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, with 32 signatory governments. One of the main heads for OAU's ...
(OAU), the predecessor of the
African Union (AU).
In July 1976, Barre's SRC disbanded itself and established in its place the
Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party
The Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party (SRSP), , it, Partito Socialista Rivoluzionario Somalo was the ruling party of the Somali Democratic Republic from 1976 to 1991.
History
SRSP was created by the military regime of Siad Barre under S ...
(SRSP), a one-party government based on
scientific socialism
Scientific socialism is a term coined in 1840 by Pierre-Joseph Proudhon in his book '' What is Property?'' to mean a society ruled by a scientific government, i.e., one whose sovereignty rests upon reason, rather than sheer will: Thus, in a given ...
and Islamic tenets. The SRSP was an attempt to reconcile the official state ideology with the official state religion by
adapting Marxist precepts to local circumstances. Emphasis was placed on the Muslim principles of social progress, equality and justice, which the government argued formed the core of scientific socialism and its own accent on self-sufficiency, public participation and popular control, as well as direct ownership of the means of production. While the SRSP encouraged private investment on a limited scale, the administration's overall direction was essentially
communist.
In July 1977, the
Ogaden War broke out after Barre's government used a plea for national unity to justify an
aggressive
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
incorporation of the predominantly Somali-inhabited
Ogaden region of Ethiopia into a Pan-Somali
Greater Somalia, along with the rich agricultural lands of south-eastern Ethiopia, infrastructure, and strategically important areas as far north as Djibouti. In the first week of the conflict, Somali armed forces took southern and central Ogaden and for most of the war, the Somali army scored continuous victories on the Ethiopian army and followed them as far as
Sidamo. By September 1977, Somalia controlled 90% of the Ogaden and captured strategic cities such as
Jijiga
Jijiga (, am, ጅጅጋ, ''Jijiga'') is the capital city of Somali Region, Ethiopia. It became the capital of the Somali Region in 1995 after it was moved from Gode. Located in the Fafan Zone with 70 km (37 mi) west of the bord ...
and put heavy pressure on
Dire Dawa, threatening the train route from the latter city to Djibouti. After the siege of Harar, a massive unprecedented Soviet intervention consisting of 20,000
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
n forces and several thousand Soviet experts came to the aid of Ethiopia's communist
Derg regime. By 1978, the Somali troops were ultimately pushed out of the Ogaden. This shift in support by the Soviet Union motivated the Barre government to seek allies elsewhere. It eventually settled on the Soviets'
Cold War arch-rival, the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, which had been courting the Somali government for some time. All in all, Somalia's initial friendship with the Soviet Union and later partnership with the United States enabled it to build the largest army in Africa.
A new constitution was promulgated in 1979 under which elections for a People's Assembly were held. However, Barre's Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party
politburo continued to rule.
In October 1980, the SRSP was disbanded, and the Supreme Revolutionary Council was re-established in its place.
By that time, Barre's government had become increasingly unpopular. Many Somalis had become disillusioned with life under military dictatorship.
The regime was weakened further in the 1980s as the Cold War drew to a close and Somalia's strategic importance was diminished. The government became increasingly
authoritarian, and
resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objective ...
s, encouraged by Ethiopia, sprang up across the country, eventually leading to the
Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War ( so, Dagaalkii Sokeeye ee Soomaaliya; ar, الحرب الأهلية الصومالية ) is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Bar ...
. Among the militia groups were the
Somali Salvation Democratic Front
Somali Salvation Democratic Front (SSDF) ( so, Jabhadda Diimuqraadiga Badbaadinta Soomaaliyeed), initially known as the Democratic Front for Salvation of Somalia, was a political and paramilitary umbrella organization in Somalia. Founded in 1978 ...
(SSDF),
United Somali Congress
The United Somali Congress (USC) was one of the major rebel organizations in Somalia. Formed in 1987, it played a leading role in the ouster of the government of Siad Barre in 1991, and became a target of the Unified Task Force campaign in 199 ...
(USC),
Somali National Movement
The Somali National Movement ( so, Dhaqdhaqaaqa Wadaniga Soomaaliyeed, ar, الحركة الوطنية الصومالية) was one of the first and most important organized guerilla groups opposed to the Siad Barre regime in the 1980s to the 19 ...
(SNM) and the
Somali Patriotic Movement
The Somali Patriotic Movement (SPM, so, Dhaqdhaqaaqa Wadaniga Soomaaliyeed, ar, الحركة الوطنية الصومالية) is a political party and paramilitary organization in Somalia, and a key faction in the Somali Civil War. (SPM), together with the non-violent political oppositions of the
Somali Democratic Movement
Over the course of the Somali Civil War, there have been many revolutionary movements and militia groups run by competing rebel leaders which have held ''de facto'' control over vast areas within Somalia.
Prior to the fall of Siad Barre (through ...
(SDM), the
Somali Democratic Alliance (SDA) and the Somali Manifesto Group (SMG).
Somalia Civil War
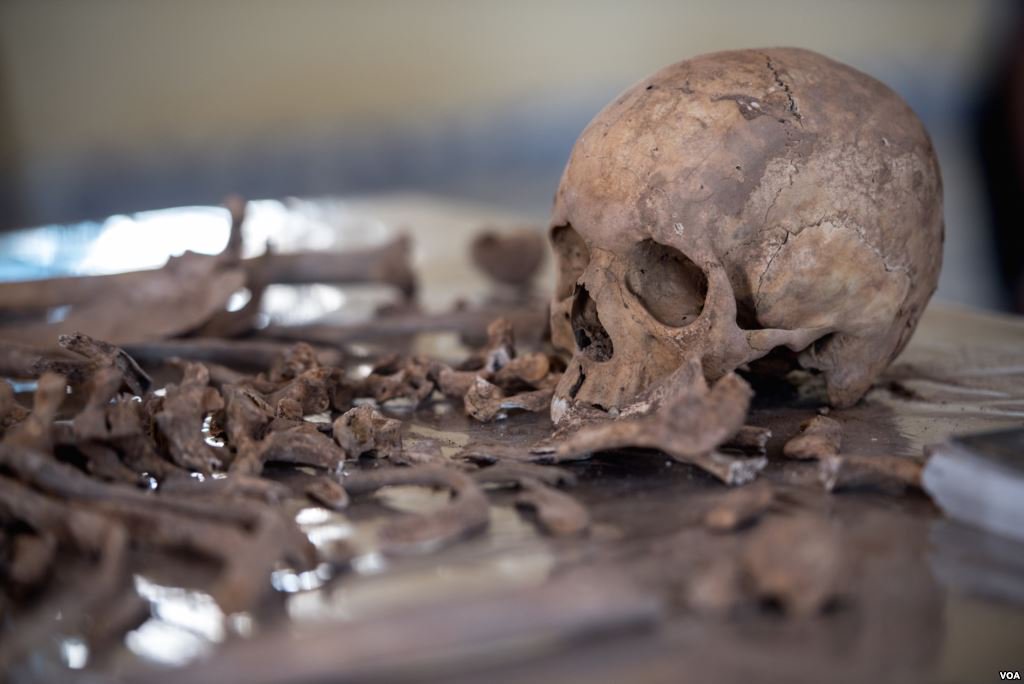


As the
moral authority Moral authority is authority premised on principles, or fundamental truths, which are independent of written, or positive, laws. As such, moral authority necessitates the existence of and adherence to truth. Because truth does not change, the princi ...
of Barre's government was gradually eroded, many Somalis became disillusioned with life under military rule. By the mid-1980s, resistance movements supported by Ethiopia's communist
Derg administration had sprung up across the country. Barre responded by ordering punitive measures against those he perceived as locally supporting the guerrillas, especially in the northern regions. The clampdown included bombing of cities, with the northwestern administrative centre of
Hargeisa
Hargeisa (; so, Hargeysa, ar, هرجيسا) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland. It is located in the Maroodi Jeex region of the Horn of Africa. It succeeded Burco as the capital of the British Somaliland Protector ...
, a
Somali National Movement
The Somali National Movement ( so, Dhaqdhaqaaqa Wadaniga Soomaaliyeed, ar, الحركة الوطنية الصومالية) was one of the first and most important organized guerilla groups opposed to the Siad Barre regime in the 1980s to the 19 ...
(SNM) stronghold, among the targeted areas in 1988.
The bombardment was led by General
Mohammed Said Hersi Morgan
Major General Mohammed Said Hersi Morgan ( so, Maxamed Siciid Xirsi Moorgan, ar, محمد سعيد حيرسي مورغان), also known as General Morgan or Colonel Morgan, is a Somali military and faction leader. He was the son-in-law of Siad B ...
, Barre's son-in-law.
During 1990, in the capital city of Mogadishu, the residents were prohibited from gathering publicly in groups greater than three or four. Fuel shortages caused long lines of cars at petrol stations. Inflation had driven the price of pasta (ordinary dry Italian noodles, a staple at that time) to five U.S. dollars per kilogram. The price of
khat
Khat or qat ( ''ch’at''; Oromo: ''Jimaa'', so, qaad, khaad, khat or chat, ar, القات ''al-qāt'') is a flowering plant native to eastern and southern Africa. Khat contains the alkaloid cathinone, a stimulant, which is said to cause e ...
, imported daily from Kenya, was also five U.S. dollars per standard bunch. Paper currency notes were of such low value that several bundles were needed to pay for simple restaurant meals.
A thriving black market existed in the centre of the city as banks experienced shortages of local currency for exchange. At night, the city of Mogadishu lay in darkness. Close monitoring of all visiting foreigners was in effect. Harsh
exchange control
Foreign exchange controls are various forms of controls imposed by a government on the purchase/sale of foreign currencies by residents, on the purchase/sale of local currency by nonresidents, or the transfers of any currency across national bor ...
regulations were introduced to prevent export of foreign currency. Although no travel restrictions were placed on foreigners, photographing many locations was banned. During daytime in Mogadishu, the appearance of any government military force was extremely rare. Alleged late-night operations by government authorities, however, included "disappearances" of individuals from their homes.
In 1991, the Barre administration was ousted by a coalition of clan-based opposition groups, backed by Ethiopia's then-ruling
Derg regime and
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
. Following a meeting of the
Somali National Movement
The Somali National Movement ( so, Dhaqdhaqaaqa Wadaniga Soomaaliyeed, ar, الحركة الوطنية الصومالية) was one of the first and most important organized guerilla groups opposed to the Siad Barre regime in the 1980s to the 19 ...
and northern clans' elders, the northern former British portion of the country
declared its independence as the
Republic of Somaliland in May 1991. Although independent and relatively stable compared to the tumultuous south, it has not been recognized by any foreign government.

Many of the opposition groups subsequently began competing for influence in the power vacuum that followed the ouster of Barre's regime. In the south, armed factions led by USC commanders General
Mohamed Farah Aidid
Mohamed Farrah Hassan Aidid ( so, Maxamed Faarax Xasan Caydiid; ar, محمد فرح حسن عيديد; 15 December 1934 – 1 August 1996) was a Somali general and diplomat.
Educated in both Rome and Moscow, he served as a chief in the Italian ...
and
Ali Mahdi Mohamed
Ali Mahdi Muhammad ( so, Cali Mahdi Maxamed, ar, علي مهدي محمد) (1 January 1939 – 10 March 2021) was a Somali entrepreneur and politician. He served as President of Somalia from 26 January 1991 to 3 January 1997. The Cairo Agreem ...
, in particular, clashed as each sought to exert authority over the capital. In 1991, a multi-phased international conference on Somalia was held in neighbouring Djibouti. Aidid boycotted the first meeting in protest.
Owing to the legitimacy bestowed on Muhammad by the Djibouti conference, he was subsequently recognized by the international community as the new President of Somalia. Djibouti,
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
,
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
and
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
were among the countries that officially extended recognition to Muhammad's administration.
He was not able to exert his authority beyond parts of the capital. Power was instead vied with other faction leaders in the southern half of Somalia and with autonomous sub-national entities in the north. The Djibouti conference was followed by two abortive agreements for national reconciliation and disarmament, which were signed by 15 political stakeholders: an agreement to hold an Informal Preparatory Meeting on National Reconciliation, and the 1993 Addis Ababa Agreement made at the Conference on National Reconciliation.
In the early 1990s, due to the protracted lack of a permanent central authority, Somalia began to be characterized as a "
failed state
A failed state is a political body that has disintegrated to a point where basic conditions and responsibilities of a sovereign government no longer function properly (see also fragile state and state collapse). A state can also fail if the ...
". Political scientist
Ken Menkhaus argues that evidence suggested that the nation had already attained failed state status by the mid-1980s, while
Robert I. Rotberg similarly posits that the state failure had preceded the ouster of the Barre administration. Hoehne (2009), Branwen (2009) and Verhoeven (2009) also used Somalia during this period as a case study to critique various aspects of the "state failure" discourse.
Transitional institutions
The Transitional National Government (TNG) was established in April–May 2000 at the Somalia National Peace Conference (SNPC) held in Arta, Djibouti.
Abdiqasim Salad Hassan was selected as the President of the nation's new Transitional National Government (TNG), an interim administration formed to guide Somalia to its third permanent republican government.
The TNG's internal problems led to the replacement of the Prime Minister four times in three years, and the administrative body's reported bankruptcy in December 2003. Its mandate ended at the same time.
On 10 October 2004, legislators elected
Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed as the first President of the
Transitional Federal Government
The Transitional Federal Government (TFG) ( so, Dowladda Federaalka Kumeelgaarka, ar, الحكومة الاتحادية الانتقالية) was internationally recognized as a provisional government of the Republic of Somalia from 14 October ...
(TFG), the Transitional National Government's successor.
the TFG was the second interim administration aiming to restore national institutions to Somalia after the 1991 collapse of the Siad Barre regime and the ensuing civil war.
The Transitional Federal Government (TFG) was the internationally recognised government of Somalia until 20 August 2012, when its tenure officially ended.
It was established as one of the
Transitional Federal Institutions (TFIs) of government as defined in the
Transitional Federal Charter (TFC) adopted in November 2004 by the
Transitional Federal Parliament
The Transitional Federal Parliament of the Somali Republic (TFP) ( so, Golaha Shacabka Federaalka Kumeelgaarka ee Jamhuuriyada Soomaaliya; often ''Baarlamaanka Federaalka Soomaaliya'') was the national parliament of Somalia from 2004 until 2012.
...
(TFP). The Transitional Federal Government officially comprised the
executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dir ...
branch of government, with the TFP serving as the
legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known ...
branch. The government was headed by the
President of Somalia, to whom the
cabinet reported through the
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
. However, it was also used as a general term to refer to all three branches collectively.
Islamic Courts Union

In 2006, the
Islamic Courts Union
The Islamic Courts Union ( so, Midowga Maxkamadaha Islaamiga) was a legal and political organization formed to address the lawlessness that had been gripping Somalia since the fall of the Siad Barre regime in 1991 during the Somali Civil War.
Th ...
(ICU), assumed control of much of the southern part of the country for 6 months and imposed
Shari'a
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the ...
law. Top UN officials have referred to this brief period as a 'Golden era' in the history of Somali politics.
Transitional Federal Government
The Transitional Federal Government sought to re-establish its authority, and, with the assistance of
Ethiopian troops,
African Union peacekeepers and air support by the United States, drove out the ICU and solidified its rule. On 8 January 2007, TFG President
Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed, entered Mogadishu with the Ethiopian military support for the first time since being elected to office. The government then relocated to
Villa Somalia
Villa Somalia ( so, Madaxtooyada Soomaaliya, ar, فيلا الصومال) is a building in Mogadishu, the capital of Somalia. It serves as the palace and principal workplace of the President of Somalia.
History
The edifice was built in the Ar ...
in the capital from its interim location in
Baidoa. This marked the first time since the fall of the Siad Barre regime in 1991 that the federal government controlled most of the country.
Al Shabaab insurgency
Al-Shabaab opposed the Ethiopian military's presence in Somalia and continued an insurgency against the TFG. Throughout 2007 and 2008, Al-Shabaab scored military victories, seizing control of key towns and ports in both central and southern Somalia. By January 2009, Al-Shabaab and other militias had forced the Ethiopian troops to retreat, leaving behind an under-equipped African Union peacekeeping force to assist the Transitional Federal Government's troops.
Owing to a lack of funding and human resources, an
arms embargo that made it difficult to re-establish a national security force, and general indifference on the part of the international community, Yusuf found himself obliged to deploy thousands of troops from Puntland to Mogadishu to sustain the battle against insurgent elements in the southern part of the country. Financial support for this effort was provided by the autonomous region's government. This left little revenue for Puntland's own security forces and civil service employees, leaving the territory vulnerable to piracy and terrorist attacks.
On 29 December 2008, Yusuf announced before a united parliament in Baidoa his resignation as President of Somalia. In his speech, which was broadcast on national radio, Yusuf expressed regret at failing to end the country's seventeen-year conflict as his government had been mandated to do. He also blamed the international community for their failure to support the government, and said that the speaker of parliament would succeed him in office per the
Charter of the Transitional Federal Government.
End of transitional period

Between 31 May and 9 June 2008, representatives of Somalia's federal government and the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia (ARS) participated in peace talks in Djibouti brokered by the former United Nations Special Envoy to Somalia,
Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah. The conference ended with a signed agreement calling for the withdrawal of Ethiopian troops in exchange for the cessation of armed confrontation. Parliament was subsequently expanded to 550 seats to accommodate ARS members, which then elected
Sheikh Sharif Sheikh Ahmed, as president.

With the help of a small team of African Union troops, the TFG began a
counteroffensive
In the study of military tactics, a counter-offensive is a large-scale strategic offensive military operation, usually by forces that had successfully halted the enemy's offensive, while occupying defensive positions.
The counter-offensive i ...
in February 2009 to assume full control of the southern half of the country. To solidify its rule, the TFG formed an alliance with the Islamic Courts Union, other members of the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia, and
Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a
Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a (ASWJ) ( so, Ahlu Suna Waljamaaca) is a Somalia-based paramilitary group consisting of moderate Sufis opposed to radical Salafism. The group opposes hardline capital punishment or limb amputations advocated by extremist i ...
, a moderate
Sufi militia. Furthermore, Al-Shabaab and Hizbul Islam, the two main Islamist groups in opposition, began to fight amongst themselves in mid-2009. As a truce, in March 2009, the TFG announced that it would re-implement Shari'a as the nation's official judicial system. However, conflict continued in the southern and central parts of the country. Within months, the TFG had gone from holding about 70% of south-central Somalia's conflict zones, to losing control of over 80% of the disputed territory to the Islamist insurgents.
In October 2011, a coordinated operation,
Operation Linda Nchi
Operation Linda Nchi ( sw, Linda Nchi; "Protect the Country") had the Kenya Defence Forces enter southern Somalia beginning in 2011. The Kenyan government declared the operation completed in March 2012, but its forces then joined AMISOM in So ...
between the Somali and Kenyan militaries and multinational forces began against the Al-Shabaab in southern Somalia. By September 2012, Somali, Kenyan, and
Raskamboni forces had managed to capture Al-Shabaab's last major stronghold, the southern port of Kismayo. In July 2012, three European Union operations were launched to engage with Somalia:
EUTM Somalia, EU Naval Force Somalia
Operation Atalanta
Operation Atalanta, formally European Union Naval Force (EU NAVFOR) Somalia, is a current counter-piracy military operation at sea off the Horn of Africa and in the Western Indian Ocean, that is the first naval operation conducted by the Eu ...
off the Horn of Africa, and EUCAP Nestor.

As part of the official "Roadmap for the End of Transition", a political process that provided clear benchmarks leading toward the formation of permanent democratic institutions in Somalia, the Transitional Federal Government's interim mandate ended on 20 August 2012.
The
Federal Parliament of Somalia was concurrently inaugurated.
Federal government
The
Federal Government of Somalia, the first permanent central government in the country since the start of the civil war, was established in August 2012. In August 2014, the Somali government-led
Operation Indian Ocean
Operation Indian Ocean was a joint military operation between the Somali military, AMISOM and the United States military against the Al-Shabaab militant group aimed at eliminating the remaining insurgent-held areas in southern Somalia. It offic ...
was launched against insurgent-held pockets in the countryside.
Geography
Somalia is bordered by
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
to the west, the
Gulf of Aden to the north, the Somali Sea and
Guardafui Channel
The Guardafui Channel ( so, Marinka Gardafuul) is an oceanic strait off the tip of the Horn of Africa that lies between the Puntland region of Somalia and Socotra to the west of the Arabian Sea. It connects the Gulf of Aden to the north with the ...
to the east, and
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
to the southwest. With a land area of 637,657 square kilometers, Somalia's terrain consists mainly of
plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
s,
plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s and
highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
s.
is more than 3,333 kilometers in length, the longest of mainland Africa.
It has been described as being roughly shaped "like a tilted number seven".
In the far north, the rugged east–west ranges of the
Ogo Mountains
The Ogo Mountains, also known as the Galgodon Highlands, (, ) are a mountain range in Somaliland. They cross the Sanaag and Togdheer regions. With a mean peak height of , the ecology of this landform is semi-desert.
Ecology
Due to the Ogo ...
lie at varying distances from the Gulf of Aden coast. Hot conditions prevail year-round, along with periodic
monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
winds and irregular rainfall.
Geology suggests the presence of valuable mineral deposits. Somalia is separated from
Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, ...
by the Somali Sea and is separated from
Socotra
Socotra or Soqotra (; ar, سُقُطْرَىٰ ; so, Suqadara) is an island of the Republic of Yemen in the Indian Ocean, under the ''de facto'' control of the UAE-backed Southern Transitional Council, a secessionist participant in Yemen’ ...
by the
Guardafui Channel
The Guardafui Channel ( so, Marinka Gardafuul) is an oceanic strait off the tip of the Horn of Africa that lies between the Puntland region of Somalia and Socotra to the west of the Arabian Sea. It connects the Gulf of Aden to the north with the ...
.
Administrative divisions
Somalia is officially divided into thirteen
regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
and five claimed regions (''gobollada'', singular ''gobol''),
which in turn are subdivided into districts. The regions are:
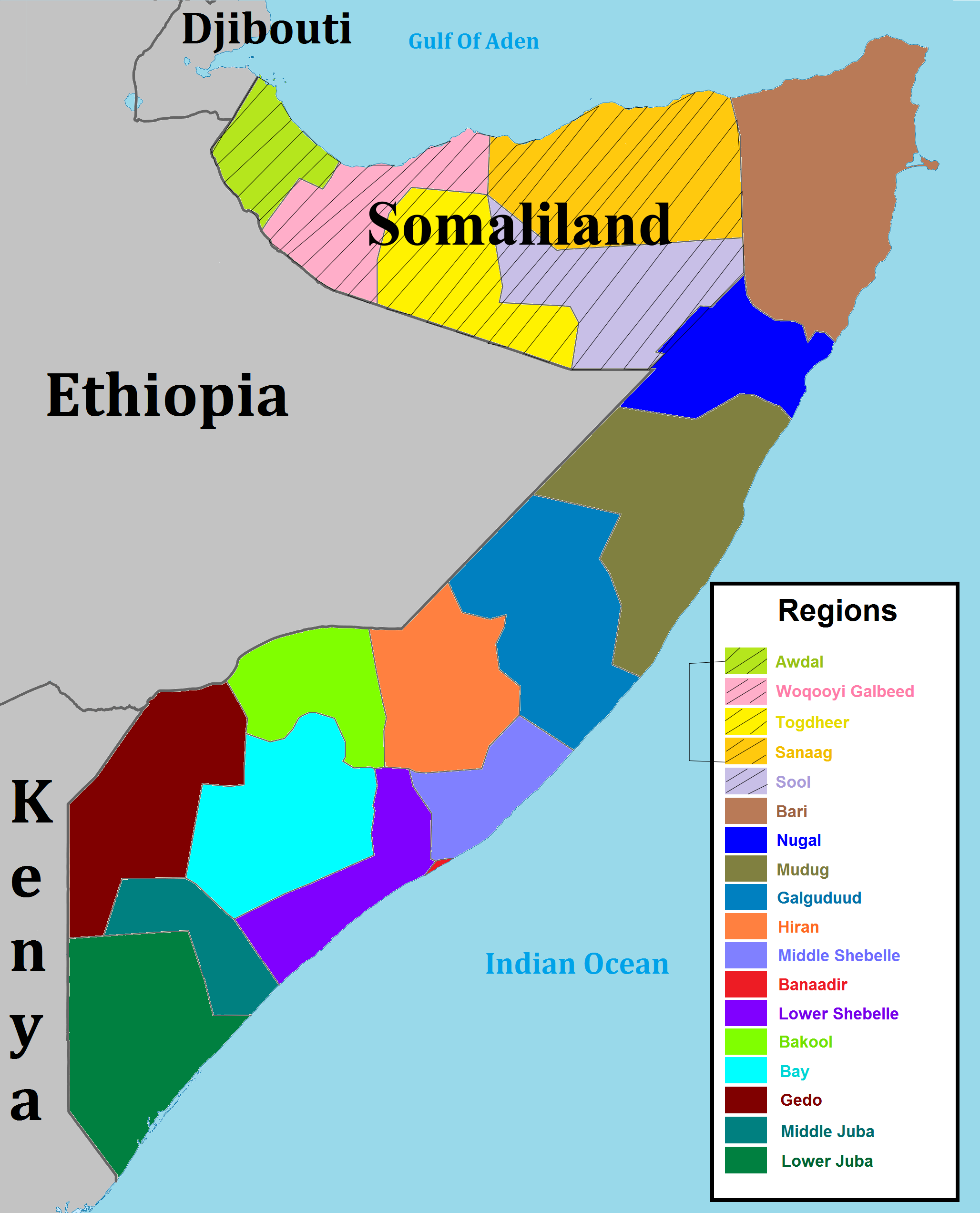
Northern Somalia is now ''de facto'' divided up among the
autonomous regions
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy— ...
of
Puntland
Puntland ( so, Puntland, ar, أرض البنط, it, Terra di Punt or ''Paese di Punt''), officially the Puntland State of Somalia ( so, Dowlad Goboleedka Puntland ee Soomaaliya, ar, ولاية أرض البنط الصومالية), is a F ...
(which considers itself an
autonomous state
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy— ...
) and
Somaliland (a self-declared but
unrecognized sovereign state). In central Somalia,
Galmudug
Galmudug ( ar, جلمدج; it, Galmudugh), officially Galmudug State of Somalia ( so, Dowlad Goboleedka Galmudug ee Soomaaliya), is a Federal Member State in central Somalia, with its capital at Dhusamareb. It is bordered to the north by the Pu ...
is another regional entity that emerged just south of Puntland.
Jubaland in the far south is a fourth autonomous region within the federation.
In 2014, a new
Southwestern Somalia
The South-West State of Somalia ( so, Goboleedka Koonfur Galbeed ee Soomaaliya, Maay Maay: ''Koofur Orsi''), is a Federal Member State in southwestern Somalia. It was founded by Hasan Muhammad Nur Shatigadud, leader of the Somalia RRA on 1 A ...
was likewise established. In April 2015, a formation conference was also launched for a new
Central Regions State.
The Federal Parliament is tasked with selecting the ultimate number and boundaries of the autonomous regional states (officially ''Federal Member States'') within the Federal Republic of Somalia.
Location

Somalia is bordered by Kenya to the southwest, the
Gulf of Aden to the north, the
Guardafui Channel
The Guardafui Channel ( so, Marinka Gardafuul) is an oceanic strait off the tip of the Horn of Africa that lies between the Puntland region of Somalia and Socotra to the west of the Arabian Sea. It connects the Gulf of Aden to the north with the ...
and Indian Ocean to the east, and Ethiopia to the west. The country claims a border with
Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
through the disputed territory of
Somaliland to the northwest. It lies between latitudes
2°S and
12°N, and longitudes
41° and
52°E. Strategically located at the mouth of the
Bab el Mandeb gateway to the
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
and the
Suez Canal, the country occupies the tip of a region that, due to its resemblance on the map to a
rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species ...
' horn, is commonly referred to as the Horn of Africa.
[Hadden, Robert Lee. 2007]
"The Geology of Somalia: A Selected Bibliography of Somalian Geology, Geography and Earth Science"
Engineer Research and Development Laboratories, Topographic Engineering Center
Waters
Somalia has the longest coastline on the mainland of Africa, with a seaboard that stretches . Its terrain consists mainly of
plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
s,
plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s and
highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
s. The nation has a total area of of which constitutes land, with of water. Somalia's land boundaries extend to about ; of that is shared with Djibouti, with Kenya, and with Ethiopia. Its maritime claims include
territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potent ...
of .
Somalia has several islands and archipelagos on its coast, including the
Bajuni Islands
The Bajuni Islands ( it, Isole Giuba, also known as the Bajun Islands or Baajun Islands) are an archipelago in southern Somalia. They are situated in the Somali sea in the southern coast of Jubaland, from Kismayo to Ras Kiyamboni (not to be confuse ...
and the
Saad ad-Din Archipelago: see
islands of Somalia The islands of Somalia are located adjacent to the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Guardafui Channel at the apex of its territory, and the Somali Sea to the east.
Gulf of Aden
Somalia's only islands in the Gulf of Aden are located in the Zeila Archi ...
.

Habitat
Somalia contains seven terrestrial ecoregions:
Ethiopian montane forests
The Ethiopian montane forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in eastern Africa. It covers the middle elevations of the Ethiopian Highlands in Ethiopia and extends into neighboring Eritrea, Sudan, Djibouti, and Somaliland. The ecore ...
,
Northern Zanzibar–Inhambane coastal forest mosaic
Northern Zanzibar–Inhambane coastal forest mosaic, also known as the Northern Swahili coastal forests and woodlands, is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of coastal East Africa. The ecoregion includes a variety of habitats, including f ...
,
Somali Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets,
Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands
The Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands ecoregion is a semi-desert strip on or near the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden coasts in Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somaliland. This ecoregion lies mainly between sea level and 800 meters (m) eleva ...
,
Hobyo grasslands and shrublands,
Somali montane xeric woodlands
The Somali montane xeric shrublands is a desert and xeric scrubland ecoregion in Somalia. The ecoregion lies in the rugged Karkaar Mountains, which run parallel and close to Somalia's northern coast on the Gulf of Aden, and follows coast from C ...
, and
East African mangroves
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
.
In the north, a scrub-covered, semi-desert plain referred as the ''
Guban
The Guban ( so, Guban, 'burnt' or 'burned') is the indigenous name for northwestern Somaliland.
References
*Hadden, Robert Lee. 2007"The Geology of Somalia: A Selected Bibliography of Somalian Geology, Geography and Earth Science."Engineer Resea ...
'' lies parallel to the Gulf of Aden
littoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal a ...
. With a width of twelve kilometres in the west to as little as two kilometres in the east, the plain is bisected by watercourses that are essentially beds of dry sand except during the rainy seasons. When the rains arrive, the Guban's low bushes and grass clumps transform into lush vegetation.
This coastal strip is part of the
Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands
The Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands ecoregion is a semi-desert strip on or near the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden coasts in Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somaliland. This ecoregion lies mainly between sea level and 800 meters (m) eleva ...
ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
.
Cal Madow
Cal Madow (also Calmadow, Al Madow, Al Medu, or Al Mado; so, Buuraha Calmadow; ar, عَلَمْدُو, ʿAlamdū) is a mountain range in Somaliland. It stretches across an area between the east of Erigavo, Somaliland, to the Bari region of So ...
is a
mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
in the northeastern part of the country. Extending from several kilometres west of the city of
Bosaso
Bosaso ( so, Boosaaso, ar, بوصاصو), historically known as Bender Cassim is a city in the northeastern Bari province ('' gobol'') of Somalia. It is the seat of the Bosaso District. Located on the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden, the mu ...
to the northwest of
Erigavo
Erigavo ( so, Ceerigaabo, ), also spelled as Erigabo, is the capital and largest city of the Sanaag region of Somaliland.
History
The Erigavo settlement is several centuries old. The surrounding area was supposedly built by the Madigan Dir. ...
, it features Somalia's highest
peak Peak or The Peak may refer to:
Basic meanings Geology
* Mountain peak
** Pyramidal peak, a mountaintop that has been sculpted by erosion to form a point Mathematics
* Peak hour or rush hour, in traffic congestion
* Peak (geometry), an (''n''-3)-di ...
,
Shimbiris
Mount Shimbiris is the highest peak in Somaliland. It has an elevation of above sea level. It is located in the Al Madow mountain range in the Sanaag region. SRTM data shows that its often-quoted elevation of is slightly low.
There is no vehi ...
, which sits at an elevation of about .
The rugged east–west ranges of the Karkaar Mountains also lie to the interior of the Gulf of Aden littoral.
In the central regions, the country's northern mountain ranges give way to shallow plateaus and typically dry watercourses that are referred to locally as the ''Ogo''. The Ogo's western plateau, in turn, gradually merges into the
Haud
The Haud (also Hawd) (, ), formerly known as the Hawd Reserve Area is a plateau situated in the Horn of Africa consisting of thorn-bush and grasslands. The region includes the southern part of Somaliland as well as the northern and eastern part ...
, an important grazing area for livestock.
Somalia has only two permanent rivers, the
Jubba
Thawb ( ar, ثَوْب "garment"), also spelled thobe or tobe and known by various other names in different regions, is an ankle-length robe, usually with long sleeves. It is commonly worn in the Arabian Peninsula, the Middle East, North Afr ...
and
Shabele, both of which begin in the
Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...
. These rivers mainly flow southwards, with the Jubba River entering the Indian Ocean at
Kismayo
Kismayo ( so, Kismaayo, Maay: ''Kismanyy'', ar, كيسمايو, ; it, Chisimaio) is a port city in the southern Lower Juba (Jubbada Hoose) province of Somalia. It is the commercial capital of the autonomous Jubaland region.
The city is situa ...
. The Shabele River at one time apparently used to enter the sea near
Merca
Merca ( so, Marka, Maay: ''Marky'', ar, مركة) is a historic port city in the southern Lower Shebelle province of Somalia. It is located approximately to the southwest of the nation's capital Mogadishu. Merca is the traditional home territory ...
, but now reaches a point just southwest of Mogadishu. After that, it consists of swamps and dry reaches before finally disappearing in the desert terrain east of
Jilib
Jilib (other names: Gilib, Gelib, Jillib, Jillio; ) is a city in Somalia, It is north of Kismaayo.
History
During the Middle Ages, Jilib and its surrounding area was part of the Ajuran Empire that governed much of southern Somalia and eastern Eth ...
, near the Jubba River.
Environment
Somalia is a
semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
country with about 1.64%
arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for th ...
.
The first local environmental organizations were Ecoterra Somalia and the Somali Ecological Society, both of which helped promote awareness about ecological concerns and mobilized environmental programs in all governmental sectors as well as in civil society. From 1971 onward, a massive tree-planting campaign on a nationwide scale was introduced by the Siad Barre government to halt the advance of thousands of acres of wind-driven
sand dunes that threatened to engulf towns, roads and farm land. By 1988, 265 hectares of a projected 336 hectares had been treated, with 39 range reserve sites and 36 forestry plantation sites established.
In 1986, the Wildlife Rescue, Research and Monitoring Centre was established by Ecoterra International, with the goal of sensitizing the public to ecological issues. This educational effort led in 1989 to the so-called "Somalia proposal" and a decision by the Somali government to adhere to the
(CITES), which established for the first time a worldwide ban on the trade of elephant ivory.

Later, Fatima Jibrell, a prominent Somali environmental activist, mounted a successful campaign to conserve old-growth forests of acacia trees in the northeastern part of Somalia.
These trees, which can live for 500 years, were being cut down to make charcoal which was highly in demand in the Arabian Peninsula, where the region's Bedouin tribes believe the acacia to be sacred.
[Geoffrey Gilbert (2004) ''World poverty'', ABC-CLIO, p. 111, .] However, while being a relatively inexpensive fuel that meets a user's needs, the production of charcoal often leads to deforestation and desertification.
As a way of addressing this problem, Jibrell and the Horn of Africa Relief and Development Organization (Horn Relief; now Adeso), an organization of which she was the founder and executive director, trained a group of teens to educate the public on the permanent damage that producing charcoal can create. In 1999, Horn Relief coordinated a peace march in the northeastern Puntland region of Somalia to put an end to the so-called "charcoal wars". As a result of Jibrell's lobbying and education efforts, the Puntland government in 2000 prohibited the exportation of charcoal. The government has also since enforced the ban, which has reportedly led to an 80% drop in exports of the product.
Jibrell was awarded the Goldman Environmental Prize in 2002 for her efforts against environmental degradation and desertification.
In 2008, she also won the National Geographic Society/Buffett Foundation Award for Leadership in Conservation.
Following the massive 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, tsunami of December 2004, there have also emerged allegations that after the outbreak of the
Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War ( so, Dagaalkii Sokeeye ee Soomaaliya; ar, الحرب الأهلية الصومالية ) is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Bar ...
in the late 1980s, Somalia's long, remote shoreline was used as a dump site for the disposal of toxic waste. The huge waves that battered northern Somalia after the tsunami are believed to have stirred up tons of nuclear and toxic waste that might have been dumped illegally in the country by foreign firms.
The European Green Party followed up these revelations by presenting before the press and the European Parliament in Strasbourg copies of contracts signed by two European companies — the Italian Swiss firm, Achair Partners, and an Italian waste broker, Progresso — and representatives of the then President of Somalia, the faction leader Ali Mahdi Mohamed, to accept 10 million tonnes of toxic waste in exchange for $80 million (then about £60 million).
According to reports by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the waste has resulted in far higher than normal cases of respiratory infections, mouth ulcers and bleeding, abdominal haemorrhages and unusual skin infections among many inhabitants of the areas around the northeastern towns of
Hobyo
Hobyo (; so, Hobyo), is an ancient port city in Galmudug state in the north-central Mudug region of Somalia.
Hobyo was founded as a coastal outpost by the Ajuran Empire during the 13th century.Lee V. Cassanelli, ''The shaping of Somali society: ...
and Benadir on the Indian Ocean coast — diseases consistent with radiation sickness. UNEP adds that the situation along the Somali coastline poses a very serious environmental hazard not only in Somalia, but also in the eastern Africa sub-region.
Climate

Owing to Somalia's proximity to the equator, there is not much seasonal variation in its climate. Hot conditions prevail year-round along with periodic
monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
winds and irregular rainfall. Mean daily maximum temperatures range from , except at higher elevations along the eastern seaboard, where the effects of a cold offshore current can be felt. In Mogadishu, for instance, average afternoon highs range from in April. Some of the highest mean annual temperatures in the world have been recorded in the country;
Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
on the northwestern coast has an afternoon high that averages more than from June through September. Nationally, mean daily minimums usually vary from about .
The greatest range in climate occurs in northern Somalia, where temperatures sometimes surpass in July on the littoral plains and drop below the freezing point during December in the highlands.
In this region, relative humidity ranges from about 40% in the mid-afternoon to 85% at night, changing somewhat according to the season.
Unlike the climates of most other countries at this latitude, conditions in Somalia range from arid in the northeastern and central regions to Semi-arid climate, semiarid in the northwest and south. In the northeast, annual rainfall is less than ; in the central plateaus, it is about . The northwestern and southwestern parts of the nation, however, receive considerably more rain, with an average of falling per year. Although the coastal regions are hot and humid throughout the year, the hinterland is typically dry and hot.
There are four main seasons around which pastoral and agricultural life revolve, and these are dictated by shifts in the wind patterns. From December to March is the ''Jilal'', the harshest dry season of the year. The main rainy season, referred to as the ''Gu'', lasts from April to June. This period is characterized by the southwest monsoons, which rejuvenate the pasture land, especially the central plateau, and briefly transform the desert into lush vegetation. From July to September is the second dry season, the ''Xagaa'' (pronounced "Hagaa"). The ''Dayr'', which is the shortest rainy season, lasts from October to December.
The ''tangambili'' periods that intervene between the two monsoons (October–November and March–May) are hot and humid.
Wildlife

Somalia contains a variety of mammals due to its geographical and climatic diversity. Wildlife still occurring includes cheetah, lion, reticulated giraffe, baboon, serval, African bush elephant, elephant, bushpig, gazelle, ibex, kudu, dik-dik, oribi, Somali wild ass, reedbuck and Grévy's zebra, elephant shrew, rock hyrax, golden mole and antelope. It also has a large population of the dromedary camel.
Somalia is home to around 727 species of birds. Of these, eight are endemic, one has been introduced by humans, and one is rare or accidental. Fourteen species are globally threatened. Birds species found exclusively in the country include the ''Columba oliviae, Somali Pigeon'', ''Alaemon hamertoni'' (Alaudidae), Lesser Hoopoe-Lark, ''Heteromirafra archeri'' (Alaudidae), Archer's Lark, ''Mirafra ashi'', Ash's Bushlark, ''Mirafra somalica'' (Alaudidae), Somali Bushlark, ''Spizocorys obbiensis'' (Alaudidae), Obbia Lark, ''Carduelis johannis'' (Fringillidae), and Warsangli Linnet.
Somalia's territorial waters are prime fishing grounds for highly migratory marine species, such as tuna. A narrow but productive continental shelf contains several demersal fish and crustacean species. Fish species found exclusively in the nation include ''Cirrhitichthys randalli'' (Cirrhitidae), ''Symphurus fuscus'' (Cynoglossidae), ''Parapercis simulata'' OC (Pinguipedidae), ''Cociella somaliensis'' OC (Platycephalidae), and ''Pseudochromis melanotus'' (Pseudochromidae).
There are roughly 235 species of reptiles. Of these, almost half live in the northern areas. Reptiles endemic to Somalia include the Hughes' saw-scaled viper, the Southern Somali garter snake, a racer (''Platyceps messanai''), a diadem snake (''Spalerosophis josephscorteccii''), the Somali sand boa, the angled worm lizard, a spiny-tailed lizard (''Uromastyx macfadyeni''), Lanza's agama, a gecko (''Hemidactylus granchii''), the Somali semaphore gecko, and a sand lizard (Mesalina or Eremias). A colubrid snake (''Aprosdoketophis andreonei'') and Haacke-Greer's skink (''Haackgreerius miopus'') are endemic species.
Politics and government

Somalia is a parliamentary representative democracy, representative democratic republic. The
President of Somalia is the head of state and commander-in-chief of the
Somali Armed Forces
The Somali Armed Forces are the military forces of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Headed by the president as commander-in-chief, they are constitutionally mandated to ensure the nation's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity. Ch ...
and selects a
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
to act as head of government.
The
Federal Parliament of Somalia is the national parliament of Somalia. The bicameral National Legislature consists of the House of the People (lower house) and the Somalian Senate, Senate (upper house), whose members are elected to serve four-year terms. The parliament elects the President, Speaker of Parliament and Deputy Speakers. It also has the authority to pass and veto laws.
The Judiciary of Somalia is defined by the Constitution of Somalia, Provisional Constitution of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Adopted on 1 August 2012 by a National Constitutional Assembly in Mogadishu, the document was formulated by a committee of specialists chaired by attorney and Speaker of the Federal Parliament, Mohamed Osman Jawari. It provides the legal foundation for the existence of the Federal Republic and source of legal authority.
The national court structure is organized into three tiers: the Constitutional Court, Federal Government level courts and States and regions of Somalia, State level courts. A nine-member Judicial Service Commission appoints any Federal tier member of the judiciary. It also selects and presents potential Constitutional Court judges to the House of the People of the Federal Parliament for approval. If endorsed, the President appoints the candidate as a judge of the Constitutional Court. The five-member Constitutional Court adjudicates issues pertaining to the constitution, in addition to various Federal and sub-national matters.
Somali law draws from a mixture of three different systems: Civil law (legal system), civil law, Sharia, Islamic law and Xeer, customary law.
After the collapse of Somalia in 1991, there were no relations or any contact between the government of Somaliland, Somaliland government, which declared itself a country and the government of Somalia.
Foreign relations

Somalia's Foreign relations of Somalia, foreign relations are handled by the President as the head of state, the Prime Minister as the head of government, and the federal Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Somalia), Ministry of Foreign Affairs.

According to Article 54 of the national constitution, the allocation of powers and resources between the Federal Government and the Federal Republic of Somalia's constituent Federal Member States shall be negotiated and agreed upon by the Federal Government and the Federal Member States, except in matters pertaining to foreign affairs, national defence, citizenship and immigration, and monetary policy. Article 53 also stipulates that the Federal Government shall consult the Federal Member States on major issues related to international agreements, including negotiations vis-a-vis foreign trade, finance and treaties.
The Federal Government maintains Bilateralism, bilateral relations with a number of other central governments in the international community. Among these are Djibouti–Somalia relations, Djibouti, Ethiopia–Somalia relations, Ethiopia, Egypt–Somalia relations, Egypt, the Somalia–United Arab Emirates relations, United Arab Emirates, Somalia–Yemen relations, Yemen, Somalia–Turkey relations, Turkey, Italy–Somalia relations, Italy, the Somalia–United Kingdom relations, United Kingdom, Denmark–Somalia relations, Denmark, France–Somalia relations, France, the Somalia–United States relations, United States, the China–Somalia relations, People's Republic of China, Japan–Somalia relations, Japan, Russia–Somalia relations, Russian Federation and Somalia–South Korea relations, South Korea.
Additionally, Somalia has several List of diplomatic missions of Somalia, diplomatic missions abroad. There are likewise various List of diplomatic missions in Somalia, foreign embassies and consulates based in the capital Mogadishu and elsewhere in the country.
Somalia is also a member of many international organizations, such as the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, African Union and
Arab League. It was a founding member of the
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
in 1969. Other memberships include the African Development Bank, Group of 77, Intergovernmental Authority on Development, International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, International Civil Aviation Organization, International Development Association, International Finance Corporation,
Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
, World Federation of Trade Unions and World Meteorological Organization.
Military

The
Somali Armed Forces
The Somali Armed Forces are the military forces of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Headed by the president as commander-in-chief, they are constitutionally mandated to ensure the nation's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity. Ch ...
(SAF) are the military forces of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Headed by the President as Commander in Chief, they are constitutionally mandated to ensure the nation's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity.
The SAF was initially made up of the Somali National Army, Army, Somali Navy, Navy, Somali Air Force, Air Force, Somali Police Force, Police Force and the National Security Service (Somalia), National Security Service. In the post-independence period, it grew to become among the larger militaries on the continent.
The subsequent outbreak of the Somali Civil War, civil war in 1991 led to the disbandment of the Somali National Army.
In 2004, the gradual process of reconstituting the military was put in motion with the establishment of the Transitional Federal Government (TFG). The Somali Armed Forces are now overseen by the Ministry of Defence (Somalia), Ministry of Defence of the Federal Government of Somalia, formed in mid-2012. In January 2013, the Somali federal government also re-opened the national intelligence service in Mogadishu, renaming the agency the National Intelligence and Security Agency (NISA). The Somaliland Armed Forces, Somaliland and Puntland Security Force, Puntland regional governments maintain their own security and police forces.
Human rights
Both male and female LGBT rights in Somalia, same-sex sexual activity are Capital punishment for homosexuality, punishable by death within Somalia.
On October 3, 2020, a UN human rights investigator raised concerns over Somali government's backtracking of human rights commitments. According to information collected by the investigator, Somali authorities were regressing on commitments to protect peoples' economic, social and cultural rights.
Economy


According to the Central Intelligence Agency, CIA and the Central Bank of Somalia, despite experiencing civil unrest, Somalia has maintained a healthy informal economy, based mainly on livestock, remittance/Wire transfer, money transfer companies and Communications in Somalia, telecommunications.
Owing to a dearth of formal government statistics and the recent Somali Civil War, civil war, it is difficult to gauge the size or growth of the economy. For 1994, the CIA estimated the Gross domestic product, GDP at $3.3 billion. In 2001, it was estimated to be $4.1 billion. By 2009, the CIA estimated that the GDP had grown to $5.731 billion, with a projected real growth rate of 2.6%.
According to a 2007 British Chambers of Commerce report, the private sector also grew, particularly in the service sector. Unlike the pre-civil war period when most services and the industrial sector were Government-owned corporation, government-run, there has been substantial, albeit unmeasured, private investment in commercial activities; this has been largely financed by the Somali diaspora, and includes trade and marketing, money transfer services, transportation, communications, fishery equipment, airlines, telecommunications, education, health, construction and hotels.
Libertarianism, Libertarian economist Peter Leeson attributes this increased economic activity to the Somali customary law (referred to as ''Xeer''), which he suggests provides a stable environment to conduct business in.
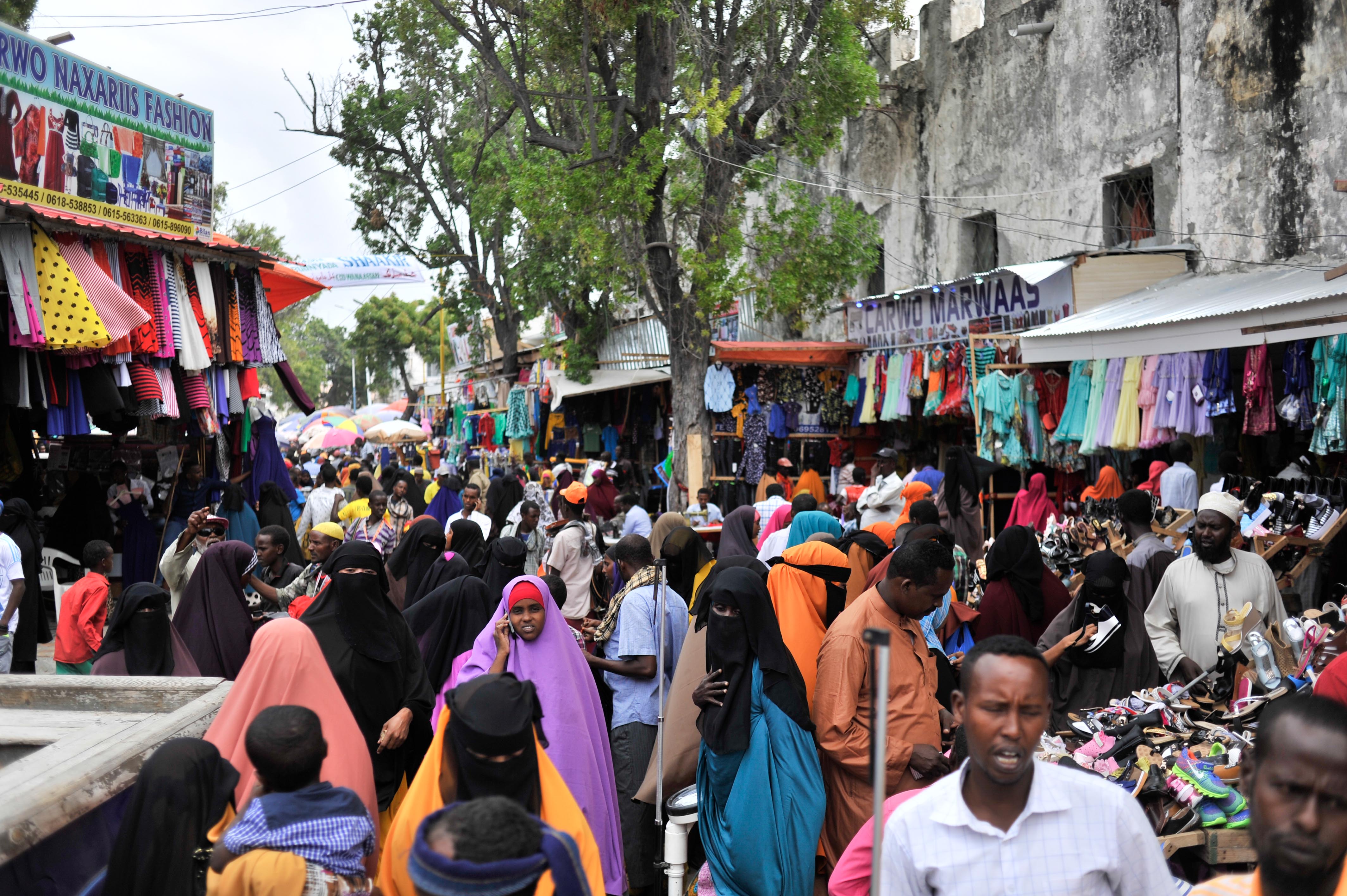

According to the Central Bank of Somalia, the country's GDP per capita is $226, a slight reduction in real terms from 1990. About 43% of the population lives on less than 1 US dollar a day, with around 24% of those found in urban areas and 54% living in rural areas.
Somalia's economy consists of both traditional and modern production, with a gradual shift toward modern industrial techniques. Somalia has the largest population of camels in the world. According to the Central Bank of Somalia, about 80% of the population are nomadic or semi-nomadic pastoralists, who keep goats, sheep, camels and cattle. The nomads also gather resins and gums to supplement their income.
Agriculture
Agriculture is the most important economic sector of Somalia. It accounts for about 65% of the GDP and employs 65% of the workforce.
Livestock contributes about 40% to GDP and more than 50% of export earnings.
Other principal exports include fish, charcoal and bananas; sugar, sorghum and Maize, corn are products for the domestic market.
According to the Central Bank of Somalia, imports of goods total about $460 million per year, surpassing aggregate imports prior to the start of the civil war in 1991. Exports, which total about $270 million annually, have also surpassed pre-war aggregate export levels. Somalia has a trade deficit of about $190 million per year, but this is exceeded by remittances sent by Somalis in the diaspora, estimated to be about $1 billion.
With the advantage of being located near the Arabian Peninsula, Somali traders have increasingly begun to challenge Australia's traditional dominance over the Gulf Arab livestock and meat market, offering quality animals at very low prices. In response, Gulf Arab states have started to make strategic investments in the country, with
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
building livestock export infrastructure and the United Arab Emirates purchasing large farmlands. Somalia is also a major world supplier of
frankincense and
myrrh.

The modest Secondary sector of the economy, industrial sector, based on the processing of agricultural products, accounts for 10% of Somalia's GDP.
According to the Somali Chamber of Commerce and Industry, over six private airline firms also offer commercial flights to both domestic and international locations, including Daallo Airlines, Jubba Airways, African Express Airways, East Africa 540, Central Air and Hajara.
In 2008, the Puntland government signed a multimillion-dollar deal with Dubai's Lootah Group, a regional industrial group operating in the Middle East and Africa. According to the agreement, the first phase of the investment is worth United Arab Emirates dirham, Dhs 170 m and will see a set of new companies established to operate, manage and build
Bosaso
Bosaso ( so, Boosaaso, ar, بوصاصو), historically known as Bender Cassim is a city in the northeastern Bari province ('' gobol'') of Somalia. It is the seat of the Bosaso District. Located on the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden, the mu ...
's free trade zone and sea and airport facilities. The Bosaso Airport Company is slated to develop the airport complex to meet international standards, including a new runway, main and auxiliary buildings, taxi and apron areas, and security perimeters.
Prior to the outbreak of the civil war in 1991, the roughly 53 state-owned small, medium and large manufacturing firms were foundering, with the ensuing conflict destroying many of the remaining industries. However, primarily as a result of substantial local investment by the Somali diaspora, many of these small-scale plants have re-opened and newer ones have been created. The latter include fish-canning and meat-processing plants in the northern regions, as well as about 25 factories in the Mogadishu area, which manufacture pasta, mineral water, Confectionery, confections, plastic bags, Textile, fabric, hides and skins, detergent and soap, aluminium, foam mattresses and pillows, fishing boats, carry out packaging, and Stonemasonry, stone processing.
In 2004, an $8.3 million Coca-Cola bottling plant also opened in the city, with investors hailing from various constituencies in Somalia. Foreign direct investment, Foreign investment also included multinationals including General Motors and Dole Food Company, Dole Fruit.
Monetary and payment system

The Central Bank of Somalia is the official Central bank, monetary authority of Somalia.
In terms of financial management, it is in the process of assuming the task of both formulating and implementing monetary policy.
Owing to a lack of confidence in the local currency, the United States dollar, US dollar is widely accepted as a medium of exchange alongside the Somali shilling. Dollarization notwithstanding, the large issuance of the Somali shilling has increasingly fuelled price hikes, especially for low value transactions. According to the Central Bank, this inflationary environment is expected to come to an end as soon as the bank assumes full control of monetary policy and replaces the presently circulating currency introduced by the private sector.
Although Somalia has had no central monetary authority for more than 15 years between the outbreak of the civil war in 1991 and the subsequent re-establishment of the Central Bank of Somalia in 2009, the nation's payment system is fairly advanced primarily due to the widespread existence of private Economy of Somalia#Finance, money transfer operators (MTO) that have acted as informal banking networks.
These remittance firms (''hawalas'') have become a large industry in Somalia, with an estimated US$1.6 billion annually remitted to the region by Somali people, Somalis in the diaspora via money transfer companies.
Most are members of the Somali Money Transfer Association (SOMTA), an umbrella organization that regulates the community's money transfer sector, or its predecessor, the Somali Financial Services Association (SFSA).
The largest of the Somali MTOs is Dahabshiil, a Somali-owned firm employing more than 2,000 people across 144 countries with branches in London and Dubai.

As the reconstituted Central Bank of Somalia fully assumes its monetary policy responsibilities, some of the existing money transfer companies are expected in the near future to seek licenses so as to develop into full-fledged commercial banks. This will serve to expand the national payments system to include formal cheques, which in turn is expected to reinforce the efficacy of the use of monetary policy in domestic Macroeconomics, macroeconomic management.
With a significant improvement in local security, Somali expatriates began returning to the country for investment opportunities. Coupled with modest foreign investment, the inflow of funds have helped the Somali shilling increase considerably in value. By March 2014, the currency had appreciated by almost 60% against the U.S. dollar over the previous 12 months. The Somali shilling was the strongest among the 175 global currencies traded by Bloomberg L.P., Bloomberg, rising close to 50 percentage points higher than the next most robust global currency over the same period.
The Somalia Stock Exchange (SSE) is the national Stock exchange, bourse of Somalia. It was founded in 2012 by the Somali diplomat Idd Mohamed, Ambassador extraordinary and deputy permanent representative to the United Nations. The SSE was established to attract investment from both Somali-owned firms and global companies in order to accelerate the ongoing post-conflict reconstruction process in Somalia.
Energy and natural resources
The World Bank reports that electricity is now in large part supplied by local businesses.
Among these domestic firms is the Somali Energy Company, which performs generation, transmission and distribution of electric power. In 2010, the nation produced 310 million kWh and consumed 288.3 million kWh of electricity, ranked 170th and 177th, respectively, according to the CIA.
Somalia has reserves of several natural resources, including uranium, iron ore, tin, gypsum, bauxite, copper, salt and natural gas. The CIA reports that there are 5.663 billion cubic metres of proven natural gas reserves.
The presence or extent of proven oil reserves in Somalia is uncertain. The CIA asserts that there are no proven reserves of oil in the country,
while UNCTAD suggests that most proven oil reserves in Somalia lie off its northwestern coast, in the Somaliland region. An oil group listed in Sydney, Range Resources, estimates that the Puntland region in the northeast has the potential to produce to of oil, compared to the 6.7 billion barrels of proven oil reserves in Sudan. As a result of these developments, the Somalia Petroleum Corporation was established by the federal government.
In the late 1960s, UN geologists also discovered major uranium deposits and other rare mineral reserves in Somalia. The find was the largest of its kind, with industry experts estimating that the amount of the deposits could amount to over 25% of the world's then known uranium reserves of 800,000 tons. In 1984, the IUREP Orientation Phase Mission to Somalia reported that the country had 5,000 tons of uranium reasonably assured resources (RAR), 11,000 tons of uranium estimated additional resources (EAR) in calcrete deposits, as well as 0–150,000 tons of uranium speculative resources (SR) in sandstone and calcrete deposits. Somalia evolved into a major world supplier of uranium, with American, UAE, Italian and Brazilian mineral companies vying for extraction rights. Link Natural Resources has a stake in the central region, and Kilimanjaro Capital has a stake in the Amsas-Coriole-Afgoi (ACA) Block, which includes uranium exploration.
The Trans-National Industrial Electricity and Gas Company is an energy conglomerate (company), conglomerate based in Mogadishu. It unites five major Somali companies from the Commerce, trade, finance, security and telecommunications sectors, following a 2010 joint agreement signed in Istanbul to provide electricity and gas infrastructure in Somalia. With an initial investment budget of $1 billion, the company launched the Somalia Peace Dividend Project, a labour-intensive energy program aimed at facilitating local industrialization initiatives.
According to the Central Bank of Somalia, as the nation embarks on the path of reconstruction, the economy is expected to not only match its pre-civil war levels, but also to accelerate in growth and development due to Somalia's untapped natural resources.
Telecommunications and media

After the start of the civil war, various new telecommunications companies began to spring up and compete to provide missing infrastructure. Funded by Somali entrepreneurs and backed by expertise from China, South Korea and Europe, these nascent telecommunications firms offer affordable mobile phone and Internet services that are not available in many other parts of the continent. Customers can conduct Electronic funds transfer, money transfers (such as through the popular Dahabshiil) and other banking activities via mobile phones, as well as easily gain wireless Internet access.
After forming partnerships with multinational corporations such as Sprint Nextel, Sprint, ITT Corporation, ITT and Telenor, these firms now offer the cheapest and clearest phone calls in Africa. These Somali telecommunication companies also provide services to every city and town in Somalia. There are presently around 25 mainlines per 1,000 persons, and the local availability of telephone lines (''tele-density'') is higher than in neighbouring countries; three times greater than in adjacent Ethiopia.
Prominent Somali telecommunications companies include Golis Telecom Somalia, Golis Telecom Group, Hormuud Telecom, Somafone, NationLink Telecom, Nationlink, Netco (Somalia), Netco, Telcom (Somalia), Telcom and Somali Telecom Group. Hormuud Telecom alone grosses about $40 million a year. Despite their rivalry, several of these companies signed an inter-connectivity deal in 2005 that allows them to set prices, maintain and expand their networks, and ensure that competition does not get out of control.
Investment in the telecom industry is held to be one of the clearest signs that Somalia's economy has continued to develop despite civil strife in parts of the country.
The state-run Somali National Television is the principal national public service TV channel. After a twenty-year hiatus, the station was officially re-launched on 4 April 2011. Its radio counterpart Radio Mogadishu also broadcasts from the capital. Somaliland National TV and Puntland TV and Radio air from the northern regions.
Additionally, Somalia has several private television and radio networks. Among these are Horn Cable Television and Universal Television (Somalia), Universal TV.
The political Xog Doon and Xog Ogaal and Horyaal Sports broadsheets publish out of the capital. There are also a number of online media outlets covering local news, including Garowe Online, Wardheernews, and Puntland Post.
The internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Somalia is .so. It was officially relaunched on 1 November 2010 by .SO Registry, which is regulated by the nation's Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications.
On 22 March 2012, the Somali Cabinet also unanimously approved the National Communications Act. The bill paves the way for the establishment of a National Communications regulator in the broadcasting and telecommunications sectors.
In November 2013, following a Memorandum of Understanding signed with Emirates Post in April of the year, the federal Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications officially reconstituted the Somali Postal Service (Somali Post). In October 2014, the ministry also relaunched postal delivery from abroad. The postal system is slated to be implemented in each of the country's 18 administrative provinces via a new postal coding and numbering system.
Tourism

Somalia has a number of local attractions, consisting of historical sites, beaches, waterfalls, mountain ranges and national parks. The tourist industry is regulated by the national Ministry of Tourism. The autonomous Puntland and Somaliland regions maintain their own tourism offices.
The Somali Tourism Association (SOMTA) also provides consulting services from within the country on the national tourist industry.
As of March 2015, the Ministry of Tourism and Wildlife of the Southwestern Somalia, South West State announced that it is slated to establish additional game reserves and wildlife ranges.
The United States Government recommends travelers to not travel to Somalia.
Notable sights include the
Laas Geel
Laas Geel ( so, Laas Geel), also spelled Laas Gaal, are cave formations on the rural outskirts of Hargeisa, Somaliland, situated in the Maroodi Jeex region of the country. They contain some of the earliest known cave paintings of domesticated Afr ...
caves containing Neolithic
rock art; the
Cal Madow
Cal Madow (also Calmadow, Al Madow, Al Medu, or Al Mado; so, Buuraha Calmadow; ar, عَلَمْدُو, ʿAlamdū) is a mountain range in Somaliland. It stretches across an area between the east of Erigavo, Somaliland, to the Bari region of So ...
, Golis Mountains and
Ogo Mountains
The Ogo Mountains, also known as the Galgodon Highlands, (, ) are a mountain range in Somaliland. They cross the Sanaag and Togdheer regions. With a mean peak height of , the ecology of this landform is semi-desert.
Ecology
Due to the Ogo ...
; the Iskushuban and Lamadaya waterfalls; and the Hargeisa National Park, Jilib National Park, Kismayo National Park and Lag Badana National Park.
Transport

Somalia's network of roads is long. , streets are Road surface, paved and are unpaved.
A highway connects major cities in the northern part of the country, such as
Bosaso
Bosaso ( so, Boosaaso, ar, بوصاصو), historically known as Bender Cassim is a city in the northeastern Bari province ('' gobol'') of Somalia. It is the seat of the Bosaso District. Located on the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden, the mu ...
, Galkayo and Garowe, with towns in the south.
The Somali Civil Aviation Authority (SOMCAA) is Somalia's national civil aviation authority body. After a long period of management by the Civil Aviation Caretaker Authority for Somalia (CACAS), SOMCAA is slated to re-assume control of Somalia's airspace by 31 December 2013.
Sixty-two airports across Somalia accommodate aerial transportation; seven of these have paved runways. Among the latter, four airports have runways of over ; two are between and one is long.
There are fifty-five airports with unpaved landing areas. One has a runway of over 3,047 m; four are between 2,438 m and 3,047 m in length; twenty are 1,524 m to 2,437 m; twenty-four are 914 m to 1,523 m; and six are under .
Major airports in the nation include the Aden Adde International Airport in Mogadishu, the Hargeisa International Airport in Hargeisa, the Kismayo Airport in
Kismayo
Kismayo ( so, Kismaayo, Maay: ''Kismanyy'', ar, كيسمايو, ; it, Chisimaio) is a port city in the southern Lower Juba (Jubbada Hoose) province of Somalia. It is the commercial capital of the autonomous Jubaland region.
The city is situa ...
, the Baidoa Airport in Baidoa, and the Bender Qassim International Airport in Bosaso.
Established in 1964, Somali Airlines was the flag carrier of Somalia. It suspended operations during the civil war. However, a reconstituted Somali government later began preparations in 2012 for an expected relaunch of the airline, with the first new Somali Airlines aircraft scheduled for delivery by the end of December 2013. According to the Somali Chamber of Commerce and Industry, the void created by the closure of Somali Airlines has since been filled by various Somali-owned private carriers. Over six of these private airline firms offer commercial flights to both domestic and international locations, including Daallo Airlines, Jubba Airways, African Express Airways, East Africa 540, Central Air and Hajara.
Possessing the longest coastline on the continent,
Somalia has several major seaports. Maritime transport facilities are found in the port cities of Mogadishu, Bosaso,
Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
,
Kismayo
Kismayo ( so, Kismaayo, Maay: ''Kismanyy'', ar, كيسمايو, ; it, Chisimaio) is a port city in the southern Lower Juba (Jubbada Hoose) province of Somalia. It is the commercial capital of the autonomous Jubaland region.
The city is situa ...
and
Merca
Merca ( so, Marka, Maay: ''Marky'', ar, مركة) is a historic port city in the southern Lower Shebelle province of Somalia. It is located approximately to the southwest of the nation's capital Mogadishu. Merca is the traditional home territory ...
. There is also one merchant marine. Established in 2008, it is cargo-based.
Demographics
Somalia lacks reliable population data. The country had an estimated population of around million inhabitants in ; the total population according to the 1975 census was 3.3 million. A United Nations Population Fund survey conducted in 2013 and 2014 estimated the total population to be 12,316,895.
About 85% of local residents are Somali people, ethnic Somalis,
who have historically inhabited the northern part of the country.
They have traditionally been organized into nomadic pastoral clans, loose empires, sultanates and city-states.
[.] Somali Civil War, Civil strife in the early 1990s greatly increased the size of the Somali diaspora, as many of the best educated Somalis left the country.
Non-Somali ethnic minority groups make up the remainder of Somalia's population, and are largely concentrated in the southern regions.
They include Bravanese people, Bravanese, Somali Bantu, Bantus, Bajuni people, Bajuni, People of Ethiopia, Ethiopians (especially Oromo people, Oromos), Demographics of Yemen, Yemenis, Indians, Persian people, Persians, Italian Somalis, Italians and British people, Britons. The Bantus, the largest ethnic minority group in Somalia, are the descendants of Slavery in Somalia, slaves who were brought in from southeastern Africa by Arab and Somali traders. In 1940, there were about 50,000 Italian Somalis, Italians living in Italian Somaliland. Most Europeans left after independence, while a small number of Westerners are still present in Somalia mainly working for international organizations operating in Somalia.
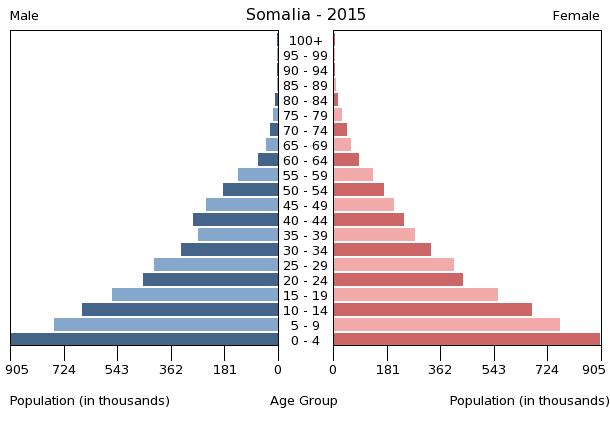
A sizable Somali diaspora exists in various Western world, Western countries, such as the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
(in particular in the state of Minnesota) and in the United Kingdom (particularly in London), Sweden, Canada, Norway, the Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, Finland, Australia, Switzerland, Austria, and
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, as well on the Arabian peninsula, and several African nations, such as Uganda and South Africa. The Somali diaspora is deeply involved in the politics and development of Somalia. The president of Somalia, Farmaajo, Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed, was a former diaspora Somali and held Citizenship of the United States, US citizenship which he voluntarily renounced in 2019.
Somalia's population is expanding at a growth rate of 1.75% per annum and a birth rate of 40.87 births per 1,000 people.
The total fertility rate of Somalia is 6.08 children born per woman (2014 estimates), the fourth highest in the world, according to the CIA World Factbook.
Most local residents are young, with a median age of 17.7 years; about 44% of the population is between the ages of 0–14 years, 52.4% is between the ages of 15–64 years, and only 2.3% is 65 years of age or older.
The Sex ratio, gender ratio is roughly balanced, with proportionally about as many men as women.
There is little reliable statistical information on urbanization in Somalia. Rough estimates have been made indicating a rate of urbanization of 4.79% per annum (2005–2010 est.), with many towns quickly growing into cities.
Many ethnic minorities have also moved from rural areas to urban centres since the onset of the civil war, particularly to
Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Oc ...
and
Kismayo
Kismayo ( so, Kismaayo, Maay: ''Kismanyy'', ar, كيسمايو, ; it, Chisimaio) is a port city in the southern Lower Juba (Jubbada Hoose) province of Somalia. It is the commercial capital of the autonomous Jubaland region.
The city is situa ...
. , 37.7% of the nation's population live in towns and cities, with the percentage rapidly increasing.
Languages
Somali and Arabic language, Arabic are the official languages of Somalia.
The Somali language is the mother tongue of the Somali people, the nation's most populous ethnic group.
It is a member of the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic language family, and its nearest relatives are the Oromo language, Oromo, Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho languages. Somali is the best documented of the Cushitic languages, with academic studies of it dating from before 1900.

Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern Somali, Northern, Benadiri Somali, Benadir and Maay language, Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast, from Adale to south of
Merca
Merca ( so, Marka, Maay: ''Marky'', ar, مركة) is a historic port city in the southern Lower Shebelle province of Somalia. It is located approximately to the southwest of the nation's capital Mogadishu. Merca is the traditional home territory ...
including Mogadishu, as well as in the immediate hinterland. The coastal dialects have additional phonemes that do not exist in Standard Somali. Maay is principally spoken by the Digil and Mirifle (Rahanweyn) clans in the southern areas of Somalia. Benadiri is the main dialect spoken in the country, in contrast to Northern Somali which is the main dialect spoken in Somaliland.
A number of writing systems have been used over the years for transcribing the Somali language. Of these, the Somali alphabet is the most widely used, and has been the official writing script in Somalia since the Supreme Revolutionary Council formally introduced it in October 1972. The script was developed by the Somali Linguistics, linguist Shire Jama Ahmed specifically for the Somali language, and uses all letters of the English Latin alphabet except ''p'', ''v'' and ''z''. Besides Ahmed's Latin script, other orthographies that have been used for centuries for writing Somali include the long-established Arabic alphabet, Arabic script and Wadaad's writing. Indigenous writing systems developed in the 20th century include the Osmanya alphabet, Osmanya, Borama alphabet, Borama and Kaddare alphabet, Kaddare scripts, which were invented by Osman Yusuf Kenadid, Sheikh Abdurahman Sheikh Nuur and Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare, respectively.
In addition to Somali, Arabic language, Arabic is an official national language in Somalia.
Around 2 million Somalis speak it
due to centuries-old ties with the
Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
, the far-reaching influence of the Arabic media, and religious education.
[Helena Dubnov (2003) ''A grammatical sketch of Somali'', Kِppe, pp. 70–71.]
English language, English is widely spoken and taught. It used to be an administrative language in the British Somaliland protectorate and due to globalization is now also prominent across Somalia. English is the medium of instruction at many universities across Somalia, and is one of the primary working languages of major Non-governmental organization, NGOs operating in Somalia. Italian language, Italian was an official language in Italian Somaliland and during the trusteeship period, but its use significantly diminished following independence. It is now most frequently heard among older generations, government officials, and in educated circles.
Other minority languages include Bravanese dialect, Bravanese, a variant of the Bantu languages, Bantu Swahili language that is spoken along the coast by the Bravanese people, as well as Bajuni dialect, Kibajuni, a Swahili dialect that is the mother tongue of the Bajuni people, Bajuni minority ethnic group.
Urban areas
Religion

According to the Pew Research Center, 99.8% of Somalia's population is Muslim.
The majority belong to the
Sunni branch of
Islam and the Shafi'i school of Islamic jurisprudence.
Sufism, the mysticism, mystical sect of Islam, is also well established, with many local ''jama'a'' (''Zaouia, zawiya'') or congregations of the various ''Tariqah, tariiqa'' or Sufi orders. The constitution of Somalia likewise defines Islam as the state religion of the Federal Republic of Somalia, and Islamic sharia law as the basic source for national legislation. It also stipulates that no law that is inconsistent with the basic tenets of Shari'a can be enacted.
Islam entered the region very early on, as a group of persecuted Muslims had sought refuge across the
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
in the Horn of Africa at the urging of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Islam may thus have been introduced into Somalia well before the faith even took root in its place of origin.
In addition, the Somali community has produced numerous notable Islamic sheikhs and clerics over the centuries, many of whom have significantly shaped the course of Muslim learning and practice in the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and well beyond. Among these Islamic scholars is the 14th-century Somali theologian and jurist Uthman bin Ali Zayla'i of
Zeila
Zeila ( so, Saylac, ar, زيلع, Zayla), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila (or Hawilah) with the Bibl ...
, who wrote the single most authoritative text on the Hanafi school of Islam, consisting of four volumes known as the ''Tabayin al-Haqa'iq li Sharh Kanz al-Daqa'iq''.
Christianity is a minority religion in Somalia, with adherents representing less than 0.1% of the population in 2010 according to the Pew Research Center.
The number of Christians in Somalia is estimated at about 1,000 people.
There is one Catholicism, Catholic diocese for the whole country, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Mogadiscio, Diocese of Mogadishu, which estimates that there were only about one hundred Catholic practitioners in 2004.
In 1913, during the early part of the colonial era, there were virtually no Christians in the Somali territories, with only about 100–200 followers coming from the schools and orphanages of the few Catholic missions in the
British Somaliland protectorate. There were also no known Catholic missions in Italian Somaliland during the same period. In the 1970s, during the reign of Somalia's then Marxism, Marxist government, church-run schools were closed and Missionary, missionaries sent home. There has been no archbishop in the country since 1989, and the Mogadishu Cathedral, cathedral in Mogadishu was severely damaged during the civil war. In December 2013, the Ministry of Justice and Religious Affairs also released a directive prohibiting the celebration of Christian festivities in the country.
According to the Pew Research Center, less than 0.1% of Somalia's population in 2010 were adherents of folk religions.
These mainly consisted of some non-Somali ethnic minority groups in the southern parts of the country, who practice animism. In the case of the Somali Bantu, Bantu, these religious traditions were inherited from their ancestors in Southeast Africa.
Additionally, according to the Pew Research Center, less than 0.1% of Somalia's population in 2010 were adherents of Judaism, Hinduism, Buddhism, or Irreligion by country, unaffiliated with any religion.
Health

Until the collapse of the federal government in 1991, the organizational and administrative structure of Somalia's healthcare sector was overseen by the Ministry of Health. Regional medical officials enjoyed some authority, but healthcare was largely centralized. The Socialism, socialist government of former President of Somalia
Siad Barre had put an end to private medical practice in 1972. Much of the national budget was devoted to military expenditure, leaving few resources for healthcare, among other services.
Somalia's public healthcare system was largely destroyed during the ensuing civil war. As with other previously nationalized sectors, informal providers have filled the vacuum and replaced the former government monopoly over healthcare, with access to facilities witnessing a significant increase.
Many new healthcare centres, clinics, hospitals and pharmacies have in the process been established through home-grown Somali initiatives.
The cost of medical consultations and treatment in these facilities is low, at $5.72 per visit in health centres (with a population coverage of 95%), and $1.89–3.97 per outpatient visit and $7.83–13.95 per bed day in primary through tertiary hospitals.
Comparing the 2005–2010 period with the half-decade just prior to the outbreak of the conflict (1985–1990), life expectancy actually increased from an average of 47 years for men and women to 48.2 years for men and 51 years for women.
[UNDP (2001). Human Development Report 2001-Somalia. New York: UNDP.] Similarly, the number of one-year-olds fully immunized against measles rose from 30% in 1985–1990 to 40% in 2000–2005,
[World Bank and UNDP (2003). Socio-Economic Survey-Somalia-2004. Washington, D.C./New York: UNDP and World Bank.] and for tuberculosis, it grew nearly 20% from 31% to 50% over the same period.
The number of infants with low birth weight fell from 16 per 1,000 to 0.3, a 15% drop in total over the same time frame.
Between 2005 and 2010 as compared to the 1985–1990 period, infant mortality per 1,000 births also fell from 152 to 109.6.
Significantly, maternal mortality per 100,000 births fell from 1,600 in the pre-war 1985–1990 half-decade to 1,100 in the 2000–2005 period.
The number of physicians per 100,000 people also rose from 3.4 to 4 over the same time frame,
as did the percentage of the population with access to sanitation services, which increased from 18% to 26%.
According to United Nations Population Fund data on the midwifery workforce, there is a total of 429 midwives (including nurse-midwives) in Somalia, with a density of one midwife per 1,000 live births. Eight midwifery institutions presently exist in the country, two of which are private. Midwifery education programs on average last from 12 to 18 months, and operate on a sequential basis. The number of student admissions per total available student places is a maximum 100%, with 180 students enrolled . Midwifery is regulated by the government, and a license is required to practice professionally. A live registry is also in place to keep track of licensed midwives. In addition, midwives in the country are officially represented by a local midwives association, with 350 registered members.

According to a 2005 World Health Organization estimate, about 97.9% of Somalia's women and girls underwent Female genital mutilation, a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to the horn of Africa and parts of the Near East. Encouraged by women in the community, it is primarily intended to protect chastity, deter promiscuity, and offer protection from assault. By 2013, UNICEF in conjunction with the Somali authorities reported that the prevalence rate among 1- to 14-year-old girls in the autonomous northern Puntland and Somaliland regions had dropped to 25% following a social and religious awareness campaign. About 93% of Somalia's male population is also reportedly circumcised.
Somalia has one of the lowest HIV infection rates on the continent. This is attributed to the Muslim nature of Somali society and adherence of Somalis to Islamic morals.
While the estimated HIV prevalence rate in Somalia in 1987 (the first case report year) was 1% of adults,
a 2012 report from UNAIDS says that since 2004, estimates from 0.7% to 1% have been assumed.
Although healthcare is now largely concentrated in the private sector, the country's public healthcare system is in the process of being rebuilt, and is overseen by the Ministry of Health. The Minister of Health is Qamar Adan Ali. The autonomous Puntland region maintains its own Ministry of Health, as does the Somaliland region in northwestern Somalia.
Some of the prominent healthcare facilities in the country are East Bardera Mothers and Children's Hospital, Abudwak Maternity and Children's Hospital, Edna Adan Maternity Hospital and West Bardera Maternity Unit.
Education
Following the outbreak of the civil war in 1991, the task of running schools in Somalia was initially taken up by community education committees established in 94% of the local schools. Numerous problems had arisen with regard to access to education in rural areas and along gender lines, quality of educational provisions, responsiveness of school curricula, educational standards and controls, management and planning capacity, and financing. To address these concerns, educational policies are being developed that are aimed at guiding the scholastic process. In the autonomous Puntland region, the latter includes a gender sensitive national education policy compliant with world standards, such as those outlined in the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) and the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW). Examples of this and other educational measures at work are the regional government's enactment of legislation aimed at securing the educational interests of girls, promoting the growth of an Early childhood education, Early Childhood Development (ECD) program designed to reach parents and care-givers in their homes as well as in the ECD centers for 0 to 5-year-old children, and introducing incentive packages to encourage teachers to work in remote rural areas.
The Ministry of Education (Somalia), Ministry of Education is officially responsible for education in Somalia, and oversees the nation's Primary education, primary, Secondary education, secondary, Vocational education, technical and vocational schools, as well as primary and technical Teacher education, teacher training and Nonformal learning, non-formal education. About 15% of the government's budget is allocated toward scholastic instruction. The autonomous Puntland and Somaliland macro-regions maintain their own Ministries of Education.
In 2006, Puntland was the second territory in Somalia after Somaliland to introduce free primary schools, with teachers now receiving their salaries from the Puntland administration. From 2005/2006 to 2006/2007, there was a significant increase in the number of schools in Puntland, up 137 institutions from just one year prior. During the same period, the number of classes in the region increased by 504, with 762 more teachers also offering their services.
Total student enrollment increased by 27% over the previous year, with girls lagging only slightly behind boys in attendance in most regions. The highest class enrollment was observed in the northernmost Bari, Somalia, Bari region, and the lowest was observed in the under-populated Ayn region. The distribution of classrooms was almost evenly split between urban and rural areas, with marginally more pupils attending and instructors teaching classes in urban areas.

Higher education in Somalia is now largely private. Several universities in the country, including Mogadishu University, have been scored among the 100 best universities in Africa in spite of the harsh environment, which has been hailed as a triumph for grass-roots initiatives.
Other universities also offering higher education in the south include Benadir University, the Somalia National University, Kismayo University and the University of Gedo. In Puntland, higher education is provided by the Puntland State University and East Africa University. In Somaliland, it is provided by Amoud University, the University of Hargeisa, Somaliland University of Technology and Burao University.
Madrasah, Qu'ranic schools (also known as ''dugsi quran'' or ''mal'aamad quran'') remain the basic system of traditional religious instruction in Somalia. They provide Islamic education for children, thereby filling a clear religious and social role in the country. Known as the most stable local, non-formal system of education providing basic religious and moral instruction, their strength rests on community support and their use of locally made and widely available teaching materials. The Qu'ranic system, which teaches the greatest number of students relative to other educational sub-sectors, is often the only system accessible to Somalis in nomadic as compared to urban areas. A study from 1993 found, among other things, that about 40% of pupils in Qur'anic schools were female. To address shortcomings in religious instruction, the Somali government on its own part also subsequently established the Ministry of Endowment and Islamic Affairs, under which Qur'anic education is now regulated.
Culture
Cuisine

The cuisine of Somalia, which varies from region to region, is a mixture of diverse culinary influences. It is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are, therefore no pork dishes, alcoholic beverages, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated. ''Qaddo'' or lunch is often elaborate.
Varieties of 'bariis' (rice), the most popular probably being basmati, usually act as the main dish. Spices including cumin, cardamom, cloves, cinnamon and Salvia officinalis, garden sage are used to add aromas to these different rice dishes. Somalis serve dinner as late as 9 pm. During Ramadan (calendar month), Ramadan, the evening meal is often presented after Tarawih prayers; sometimes up to 11 pm.
'Xalwo' (halva) is a popular Confectionery, confection reserved for special festive occasions, such as Eid ul-Fitr, Eid celebrations or wedding receptions. It is made from corn starch, sugar, cardamom powder, nutmeg powder and ghee. Peanuts are also sometimes added to enhance texture and flavour. After meals, homes are traditionally perfumed using
frankincense () or incense (), which is prepared inside an incense burner referred to as a ''dabqaad''.
Music
Somalia has a rich musical heritage centred on traditional Somali folklore. Most Somali songs are Pentatonic scale, pentatonic. That is, they only use five Pitch (music), pitches per octave in contrast to a Heptatonic scale, heptatonic (seven note) scale like the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Ethiopia, Sudan or the Arabian Peninsula, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (), songwriters () and Singing, singers ( or "voice").
Literature
Somali scholars have for centuries produced many notable examples of Islamic literature ranging from poetry to Hadith. With the adoption of the Somali alphabet, Latin alphabet in 1972 as the nation's standard orthography, numerous contemporary Somali authors have also released novels, some of which have received worldwide acclaim. Of these modern writers, Nuruddin Farah is the most celebrated. Books such as ''From a Crooked Rib'' and ''Links'' are considered important literary achievements, works that have earned Farah, among other accolades, the 1998 Neustadt International Prize for Literature. Farah Mohamed Jama Awl, Faarax M.J. Cawl is another prominent Somali writer who is best known for his Dervish movement (Nugaal), Dervish era novel, ''Ignorance is the enemy of love''.
Sports

Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Somalia. Important domestic competitions are the Somalia League and Somalia Cup, with the Somalia national football team playing internationally.
Basketball is also played in the country. The FIBA Africa Championship 1981 was hosted in Mogadishu from 15 to 23 December December 1981, during which the Somalia national basketball team, national basketball team received the bronze medal. The squad also takes part in the Basketball at the Pan Arab Games, basketball event at the Pan Arab Games.
In 2013, a Somalia national bandy team was formed in Borlänge. It later participated in the Bandy World Championship 2014 in Irkutsk and Shelekhov in Russia.
In the martial arts, Faisal Jeylani Aweys and Mohamed Deq Abdulle of the Somalia national taekwondo team, national taekwondo team took home a silver medal and fourth place, respectively, at the 2013 Open World Taekwondo Challenge Cup in Tongeren. The Somali Olympic Committee has devised a special support program to ensure continued success in future tournaments. Additionally, Mohamed Jama has won both world and European titles in K-1 and Muay Thai, Thai Boxing.
Architecture

Somali architecture is a rich and diverse tradition of engineering and design involving multiple types of constructions and edifices, such as Stonemasonry, stone cities, castles, citadels, Fortification, fortresses,
mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
s,
mausoleums, temples, towers, monuments, cairns, megaliths, menhirs, dolmens, tombs, Tumulus, tumuli, steles, cisterns, Aqueduct (water supply), aqueducts and lighthouses. Spanning the country's ancient, medieval and early modern periods, it also embraces the fusion of Somalo-Islamic architecture with contemporary Western designs.
In ancient Somalia,
pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilat ...
ical structures known in Somali as ''taalo'' were a popular burial style, with hundreds of these dry stone monuments scattered around the country today. Houses were built of Ashlar, dressed stone similar to the ones in
ancient Egypt. There are also examples of courtyards and large stone walls enclosing settlements, such as the Wargaade Wall.
The adoption of Islam in Somalia's early medieval history brought Islamic architecture, Islamic architectural influences from
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
and Persia. This stimulated a shift in construction from dry stone and other related materials to Coral rag, coral stone, Mudbrick, sun dried bricks, and the widespread use of limestone in Somali architecture. Many of the new architectural designs, such as mosques, were built on the ruins of older structures, a practice that would continue over and over again throughout the following centuries.
[.]
See also
* Outline of Somalia
* Index of Somalia-related articles
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
* Mauri, Arnaldo, ''Somalia'', in G, Dell'Amore (ed.), "Banking Systems of Africa", Cariplo-Finafrica, Milan, 1971, pp. 209–21
Banking Development in Somalia*
*
* Shay, Shaul. ''Somalia in Transition Since 2006.'' Piscataway, NJ: Transaction Publishers, 2014.
*
*
*
External links
*
Federal Government of Somalia
Somalia ''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
*
*
Somalia profilefrom BBC News
{{Authority control
Somalia,
1960 establishments in Somalia
Arabic-speaking countries and territories
Countries in Africa
East African countries
Federal republics
Horn African countries
Least developed countries
Member states of the African Union
Member states of the Arab League
Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Member states of the United Nations
States and territories established in 1960
Countries and territories where Somali is an official language
 Somalia was likely one of the first lands to be settled by early humans due to its location. Hunter-gatherers who would later migrate out of Africa likely settled here before their migrations. During the Stone Age, the Doian and Hargeisan cultures flourished here. The oldest evidence of burial customs in the Horn of Africa comes from cemeteries in Somalia dating back to the 4th millennium BCE. The stone implements from the Jalelo site in the north were also characterized in 1909 as important artifacts demonstrating the archaeological universality during the Paleolithic between the East and the West.
According to linguists, the first
Somalia was likely one of the first lands to be settled by early humans due to its location. Hunter-gatherers who would later migrate out of Africa likely settled here before their migrations. During the Stone Age, the Doian and Hargeisan cultures flourished here. The oldest evidence of burial customs in the Horn of Africa comes from cemeteries in Somalia dating back to the 4th millennium BCE. The stone implements from the Jalelo site in the north were also characterized in 1909 as important artifacts demonstrating the archaeological universality during the Paleolithic between the East and the West.
According to linguists, the first  After the Roman conquest of the Nabataean Empire and the Roman naval presence at Aden to curb piracy, Arab and Somali merchants agreed with the Romans to bar Indian ships from trading in the free port cities of the Arabian peninsula to protect the interests of Somali and Arab merchants in the lucrative commerce between the Red and Mediterranean Seas.. However, Indian merchants continued to trade in the port cities of the Somali peninsula, which was free from Roman interference. For centuries, Indian merchants brought large quantities of cinnamon to Somalia and Arabia from Ceylon and the
After the Roman conquest of the Nabataean Empire and the Roman naval presence at Aden to curb piracy, Arab and Somali merchants agreed with the Romans to bar Indian ships from trading in the free port cities of the Arabian peninsula to protect the interests of Somali and Arab merchants in the lucrative commerce between the Red and Mediterranean Seas.. However, Indian merchants continued to trade in the port cities of the Somali peninsula, which was free from Roman interference. For centuries, Indian merchants brought large quantities of cinnamon to Somalia and Arabia from Ceylon and the  Islam was introduced to the area early on by the first Muslims of Mecca fleeing prosecution during the first Hejira with
Islam was introduced to the area early on by the first Muslims of Mecca fleeing prosecution during the first Hejira with  Adal's headquarters were again relocated the following century, this time southward to
Adal's headquarters were again relocated the following century, this time southward to 
 In the late 19th century, after the
In the late 19th century, after the  Following World War II, Britain retained control of both British Somaliland and Italian Somaliland as protectorates. In 1945, during the
Following World War II, Britain retained control of both British Somaliland and Italian Somaliland as protectorates. In 1945, during the  Alongside Barre, the Supreme Revolutionary Council (SRC) that assumed power after President Sharmarke's assassination was led by Lieutenant Colonel
Alongside Barre, the Supreme Revolutionary Council (SRC) that assumed power after President Sharmarke's assassination was led by Lieutenant Colonel 
 As the
As the  Many of the opposition groups subsequently began competing for influence in the power vacuum that followed the ouster of Barre's regime. In the south, armed factions led by USC commanders General
Many of the opposition groups subsequently began competing for influence in the power vacuum that followed the ouster of Barre's regime. In the south, armed factions led by USC commanders General  In 2006, the
In 2006, the  Between 31 May and 9 June 2008, representatives of Somalia's federal government and the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia (ARS) participated in peace talks in Djibouti brokered by the former United Nations Special Envoy to Somalia, Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah. The conference ended with a signed agreement calling for the withdrawal of Ethiopian troops in exchange for the cessation of armed confrontation. Parliament was subsequently expanded to 550 seats to accommodate ARS members, which then elected Sheikh Sharif Sheikh Ahmed, as president.
Between 31 May and 9 June 2008, representatives of Somalia's federal government and the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia (ARS) participated in peace talks in Djibouti brokered by the former United Nations Special Envoy to Somalia, Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah. The conference ended with a signed agreement calling for the withdrawal of Ethiopian troops in exchange for the cessation of armed confrontation. Parliament was subsequently expanded to 550 seats to accommodate ARS members, which then elected Sheikh Sharif Sheikh Ahmed, as president.
 Northern Somalia is now ''de facto'' divided up among the
Northern Somalia is now ''de facto'' divided up among the 
 Somalia is a
Somalia is a  Later, Fatima Jibrell, a prominent Somali environmental activist, mounted a successful campaign to conserve old-growth forests of acacia trees in the northeastern part of Somalia. These trees, which can live for 500 years, were being cut down to make charcoal which was highly in demand in the Arabian Peninsula, where the region's Bedouin tribes believe the acacia to be sacred.Geoffrey Gilbert (2004) ''World poverty'', ABC-CLIO, p. 111, . However, while being a relatively inexpensive fuel that meets a user's needs, the production of charcoal often leads to deforestation and desertification. As a way of addressing this problem, Jibrell and the Horn of Africa Relief and Development Organization (Horn Relief; now Adeso), an organization of which she was the founder and executive director, trained a group of teens to educate the public on the permanent damage that producing charcoal can create. In 1999, Horn Relief coordinated a peace march in the northeastern Puntland region of Somalia to put an end to the so-called "charcoal wars". As a result of Jibrell's lobbying and education efforts, the Puntland government in 2000 prohibited the exportation of charcoal. The government has also since enforced the ban, which has reportedly led to an 80% drop in exports of the product. Jibrell was awarded the Goldman Environmental Prize in 2002 for her efforts against environmental degradation and desertification. In 2008, she also won the National Geographic Society/Buffett Foundation Award for Leadership in Conservation.
Following the massive 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, tsunami of December 2004, there have also emerged allegations that after the outbreak of the
Later, Fatima Jibrell, a prominent Somali environmental activist, mounted a successful campaign to conserve old-growth forests of acacia trees in the northeastern part of Somalia. These trees, which can live for 500 years, were being cut down to make charcoal which was highly in demand in the Arabian Peninsula, where the region's Bedouin tribes believe the acacia to be sacred.Geoffrey Gilbert (2004) ''World poverty'', ABC-CLIO, p. 111, . However, while being a relatively inexpensive fuel that meets a user's needs, the production of charcoal often leads to deforestation and desertification. As a way of addressing this problem, Jibrell and the Horn of Africa Relief and Development Organization (Horn Relief; now Adeso), an organization of which she was the founder and executive director, trained a group of teens to educate the public on the permanent damage that producing charcoal can create. In 1999, Horn Relief coordinated a peace march in the northeastern Puntland region of Somalia to put an end to the so-called "charcoal wars". As a result of Jibrell's lobbying and education efforts, the Puntland government in 2000 prohibited the exportation of charcoal. The government has also since enforced the ban, which has reportedly led to an 80% drop in exports of the product. Jibrell was awarded the Goldman Environmental Prize in 2002 for her efforts against environmental degradation and desertification. In 2008, she also won the National Geographic Society/Buffett Foundation Award for Leadership in Conservation.
Following the massive 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, tsunami of December 2004, there have also emerged allegations that after the outbreak of the  Somalia contains a variety of mammals due to its geographical and climatic diversity. Wildlife still occurring includes cheetah, lion, reticulated giraffe, baboon, serval, African bush elephant, elephant, bushpig, gazelle, ibex, kudu, dik-dik, oribi, Somali wild ass, reedbuck and Grévy's zebra, elephant shrew, rock hyrax, golden mole and antelope. It also has a large population of the dromedary camel.
Somalia is home to around 727 species of birds. Of these, eight are endemic, one has been introduced by humans, and one is rare or accidental. Fourteen species are globally threatened. Birds species found exclusively in the country include the ''Columba oliviae, Somali Pigeon'', ''Alaemon hamertoni'' (Alaudidae), Lesser Hoopoe-Lark, ''Heteromirafra archeri'' (Alaudidae), Archer's Lark, ''Mirafra ashi'', Ash's Bushlark, ''Mirafra somalica'' (Alaudidae), Somali Bushlark, ''Spizocorys obbiensis'' (Alaudidae), Obbia Lark, ''Carduelis johannis'' (Fringillidae), and Warsangli Linnet.
Somalia's territorial waters are prime fishing grounds for highly migratory marine species, such as tuna. A narrow but productive continental shelf contains several demersal fish and crustacean species. Fish species found exclusively in the nation include ''Cirrhitichthys randalli'' (Cirrhitidae), ''Symphurus fuscus'' (Cynoglossidae), ''Parapercis simulata'' OC (Pinguipedidae), ''Cociella somaliensis'' OC (Platycephalidae), and ''Pseudochromis melanotus'' (Pseudochromidae).
There are roughly 235 species of reptiles. Of these, almost half live in the northern areas. Reptiles endemic to Somalia include the Hughes' saw-scaled viper, the Southern Somali garter snake, a racer (''Platyceps messanai''), a diadem snake (''Spalerosophis josephscorteccii''), the Somali sand boa, the angled worm lizard, a spiny-tailed lizard (''Uromastyx macfadyeni''), Lanza's agama, a gecko (''Hemidactylus granchii''), the Somali semaphore gecko, and a sand lizard (Mesalina or Eremias). A colubrid snake (''Aprosdoketophis andreonei'') and Haacke-Greer's skink (''Haackgreerius miopus'') are endemic species.
Somalia contains a variety of mammals due to its geographical and climatic diversity. Wildlife still occurring includes cheetah, lion, reticulated giraffe, baboon, serval, African bush elephant, elephant, bushpig, gazelle, ibex, kudu, dik-dik, oribi, Somali wild ass, reedbuck and Grévy's zebra, elephant shrew, rock hyrax, golden mole and antelope. It also has a large population of the dromedary camel.
Somalia is home to around 727 species of birds. Of these, eight are endemic, one has been introduced by humans, and one is rare or accidental. Fourteen species are globally threatened. Birds species found exclusively in the country include the ''Columba oliviae, Somali Pigeon'', ''Alaemon hamertoni'' (Alaudidae), Lesser Hoopoe-Lark, ''Heteromirafra archeri'' (Alaudidae), Archer's Lark, ''Mirafra ashi'', Ash's Bushlark, ''Mirafra somalica'' (Alaudidae), Somali Bushlark, ''Spizocorys obbiensis'' (Alaudidae), Obbia Lark, ''Carduelis johannis'' (Fringillidae), and Warsangli Linnet.
Somalia's territorial waters are prime fishing grounds for highly migratory marine species, such as tuna. A narrow but productive continental shelf contains several demersal fish and crustacean species. Fish species found exclusively in the nation include ''Cirrhitichthys randalli'' (Cirrhitidae), ''Symphurus fuscus'' (Cynoglossidae), ''Parapercis simulata'' OC (Pinguipedidae), ''Cociella somaliensis'' OC (Platycephalidae), and ''Pseudochromis melanotus'' (Pseudochromidae).
There are roughly 235 species of reptiles. Of these, almost half live in the northern areas. Reptiles endemic to Somalia include the Hughes' saw-scaled viper, the Southern Somali garter snake, a racer (''Platyceps messanai''), a diadem snake (''Spalerosophis josephscorteccii''), the Somali sand boa, the angled worm lizard, a spiny-tailed lizard (''Uromastyx macfadyeni''), Lanza's agama, a gecko (''Hemidactylus granchii''), the Somali semaphore gecko, and a sand lizard (Mesalina or Eremias). A colubrid snake (''Aprosdoketophis andreonei'') and Haacke-Greer's skink (''Haackgreerius miopus'') are endemic species.
 Somalia is a parliamentary representative democracy, representative democratic republic. The President of Somalia is the head of state and commander-in-chief of the
Somalia is a parliamentary representative democracy, representative democratic republic. The President of Somalia is the head of state and commander-in-chief of the  Somalia's Foreign relations of Somalia, foreign relations are handled by the President as the head of state, the Prime Minister as the head of government, and the federal Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Somalia), Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Somalia's Foreign relations of Somalia, foreign relations are handled by the President as the head of state, the Prime Minister as the head of government, and the federal Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Somalia), Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
 According to Article 54 of the national constitution, the allocation of powers and resources between the Federal Government and the Federal Republic of Somalia's constituent Federal Member States shall be negotiated and agreed upon by the Federal Government and the Federal Member States, except in matters pertaining to foreign affairs, national defence, citizenship and immigration, and monetary policy. Article 53 also stipulates that the Federal Government shall consult the Federal Member States on major issues related to international agreements, including negotiations vis-a-vis foreign trade, finance and treaties.
The Federal Government maintains Bilateralism, bilateral relations with a number of other central governments in the international community. Among these are Djibouti–Somalia relations, Djibouti, Ethiopia–Somalia relations, Ethiopia, Egypt–Somalia relations, Egypt, the Somalia–United Arab Emirates relations, United Arab Emirates, Somalia–Yemen relations, Yemen, Somalia–Turkey relations, Turkey, Italy–Somalia relations, Italy, the Somalia–United Kingdom relations, United Kingdom, Denmark–Somalia relations, Denmark, France–Somalia relations, France, the Somalia–United States relations, United States, the China–Somalia relations, People's Republic of China, Japan–Somalia relations, Japan, Russia–Somalia relations, Russian Federation and Somalia–South Korea relations, South Korea.
Additionally, Somalia has several List of diplomatic missions of Somalia, diplomatic missions abroad. There are likewise various List of diplomatic missions in Somalia, foreign embassies and consulates based in the capital Mogadishu and elsewhere in the country.
Somalia is also a member of many international organizations, such as the
According to Article 54 of the national constitution, the allocation of powers and resources between the Federal Government and the Federal Republic of Somalia's constituent Federal Member States shall be negotiated and agreed upon by the Federal Government and the Federal Member States, except in matters pertaining to foreign affairs, national defence, citizenship and immigration, and monetary policy. Article 53 also stipulates that the Federal Government shall consult the Federal Member States on major issues related to international agreements, including negotiations vis-a-vis foreign trade, finance and treaties.
The Federal Government maintains Bilateralism, bilateral relations with a number of other central governments in the international community. Among these are Djibouti–Somalia relations, Djibouti, Ethiopia–Somalia relations, Ethiopia, Egypt–Somalia relations, Egypt, the Somalia–United Arab Emirates relations, United Arab Emirates, Somalia–Yemen relations, Yemen, Somalia–Turkey relations, Turkey, Italy–Somalia relations, Italy, the Somalia–United Kingdom relations, United Kingdom, Denmark–Somalia relations, Denmark, France–Somalia relations, France, the Somalia–United States relations, United States, the China–Somalia relations, People's Republic of China, Japan–Somalia relations, Japan, Russia–Somalia relations, Russian Federation and Somalia–South Korea relations, South Korea.
Additionally, Somalia has several List of diplomatic missions of Somalia, diplomatic missions abroad. There are likewise various List of diplomatic missions in Somalia, foreign embassies and consulates based in the capital Mogadishu and elsewhere in the country.
Somalia is also a member of many international organizations, such as the  The
The 
 According to the Central Bank of Somalia, the country's GDP per capita is $226, a slight reduction in real terms from 1990. About 43% of the population lives on less than 1 US dollar a day, with around 24% of those found in urban areas and 54% living in rural areas.
Somalia's economy consists of both traditional and modern production, with a gradual shift toward modern industrial techniques. Somalia has the largest population of camels in the world. According to the Central Bank of Somalia, about 80% of the population are nomadic or semi-nomadic pastoralists, who keep goats, sheep, camels and cattle. The nomads also gather resins and gums to supplement their income.
According to the Central Bank of Somalia, the country's GDP per capita is $226, a slight reduction in real terms from 1990. About 43% of the population lives on less than 1 US dollar a day, with around 24% of those found in urban areas and 54% living in rural areas.
Somalia's economy consists of both traditional and modern production, with a gradual shift toward modern industrial techniques. Somalia has the largest population of camels in the world. According to the Central Bank of Somalia, about 80% of the population are nomadic or semi-nomadic pastoralists, who keep goats, sheep, camels and cattle. The nomads also gather resins and gums to supplement their income.
 The modest Secondary sector of the economy, industrial sector, based on the processing of agricultural products, accounts for 10% of Somalia's GDP. According to the Somali Chamber of Commerce and Industry, over six private airline firms also offer commercial flights to both domestic and international locations, including Daallo Airlines, Jubba Airways, African Express Airways, East Africa 540, Central Air and Hajara. In 2008, the Puntland government signed a multimillion-dollar deal with Dubai's Lootah Group, a regional industrial group operating in the Middle East and Africa. According to the agreement, the first phase of the investment is worth United Arab Emirates dirham, Dhs 170 m and will see a set of new companies established to operate, manage and build
The modest Secondary sector of the economy, industrial sector, based on the processing of agricultural products, accounts for 10% of Somalia's GDP. According to the Somali Chamber of Commerce and Industry, over six private airline firms also offer commercial flights to both domestic and international locations, including Daallo Airlines, Jubba Airways, African Express Airways, East Africa 540, Central Air and Hajara. In 2008, the Puntland government signed a multimillion-dollar deal with Dubai's Lootah Group, a regional industrial group operating in the Middle East and Africa. According to the agreement, the first phase of the investment is worth United Arab Emirates dirham, Dhs 170 m and will see a set of new companies established to operate, manage and build  The Central Bank of Somalia is the official Central bank, monetary authority of Somalia. In terms of financial management, it is in the process of assuming the task of both formulating and implementing monetary policy.
Owing to a lack of confidence in the local currency, the United States dollar, US dollar is widely accepted as a medium of exchange alongside the Somali shilling. Dollarization notwithstanding, the large issuance of the Somali shilling has increasingly fuelled price hikes, especially for low value transactions. According to the Central Bank, this inflationary environment is expected to come to an end as soon as the bank assumes full control of monetary policy and replaces the presently circulating currency introduced by the private sector.
Although Somalia has had no central monetary authority for more than 15 years between the outbreak of the civil war in 1991 and the subsequent re-establishment of the Central Bank of Somalia in 2009, the nation's payment system is fairly advanced primarily due to the widespread existence of private Economy of Somalia#Finance, money transfer operators (MTO) that have acted as informal banking networks.
These remittance firms (''hawalas'') have become a large industry in Somalia, with an estimated US$1.6 billion annually remitted to the region by Somali people, Somalis in the diaspora via money transfer companies. Most are members of the Somali Money Transfer Association (SOMTA), an umbrella organization that regulates the community's money transfer sector, or its predecessor, the Somali Financial Services Association (SFSA). The largest of the Somali MTOs is Dahabshiil, a Somali-owned firm employing more than 2,000 people across 144 countries with branches in London and Dubai.
The Central Bank of Somalia is the official Central bank, monetary authority of Somalia. In terms of financial management, it is in the process of assuming the task of both formulating and implementing monetary policy.
Owing to a lack of confidence in the local currency, the United States dollar, US dollar is widely accepted as a medium of exchange alongside the Somali shilling. Dollarization notwithstanding, the large issuance of the Somali shilling has increasingly fuelled price hikes, especially for low value transactions. According to the Central Bank, this inflationary environment is expected to come to an end as soon as the bank assumes full control of monetary policy and replaces the presently circulating currency introduced by the private sector.
Although Somalia has had no central monetary authority for more than 15 years between the outbreak of the civil war in 1991 and the subsequent re-establishment of the Central Bank of Somalia in 2009, the nation's payment system is fairly advanced primarily due to the widespread existence of private Economy of Somalia#Finance, money transfer operators (MTO) that have acted as informal banking networks.
These remittance firms (''hawalas'') have become a large industry in Somalia, with an estimated US$1.6 billion annually remitted to the region by Somali people, Somalis in the diaspora via money transfer companies. Most are members of the Somali Money Transfer Association (SOMTA), an umbrella organization that regulates the community's money transfer sector, or its predecessor, the Somali Financial Services Association (SFSA). The largest of the Somali MTOs is Dahabshiil, a Somali-owned firm employing more than 2,000 people across 144 countries with branches in London and Dubai.
 As the reconstituted Central Bank of Somalia fully assumes its monetary policy responsibilities, some of the existing money transfer companies are expected in the near future to seek licenses so as to develop into full-fledged commercial banks. This will serve to expand the national payments system to include formal cheques, which in turn is expected to reinforce the efficacy of the use of monetary policy in domestic Macroeconomics, macroeconomic management.
With a significant improvement in local security, Somali expatriates began returning to the country for investment opportunities. Coupled with modest foreign investment, the inflow of funds have helped the Somali shilling increase considerably in value. By March 2014, the currency had appreciated by almost 60% against the U.S. dollar over the previous 12 months. The Somali shilling was the strongest among the 175 global currencies traded by Bloomberg L.P., Bloomberg, rising close to 50 percentage points higher than the next most robust global currency over the same period.
The Somalia Stock Exchange (SSE) is the national Stock exchange, bourse of Somalia. It was founded in 2012 by the Somali diplomat Idd Mohamed, Ambassador extraordinary and deputy permanent representative to the United Nations. The SSE was established to attract investment from both Somali-owned firms and global companies in order to accelerate the ongoing post-conflict reconstruction process in Somalia.
As the reconstituted Central Bank of Somalia fully assumes its monetary policy responsibilities, some of the existing money transfer companies are expected in the near future to seek licenses so as to develop into full-fledged commercial banks. This will serve to expand the national payments system to include formal cheques, which in turn is expected to reinforce the efficacy of the use of monetary policy in domestic Macroeconomics, macroeconomic management.
With a significant improvement in local security, Somali expatriates began returning to the country for investment opportunities. Coupled with modest foreign investment, the inflow of funds have helped the Somali shilling increase considerably in value. By March 2014, the currency had appreciated by almost 60% against the U.S. dollar over the previous 12 months. The Somali shilling was the strongest among the 175 global currencies traded by Bloomberg L.P., Bloomberg, rising close to 50 percentage points higher than the next most robust global currency over the same period.
The Somalia Stock Exchange (SSE) is the national Stock exchange, bourse of Somalia. It was founded in 2012 by the Somali diplomat Idd Mohamed, Ambassador extraordinary and deputy permanent representative to the United Nations. The SSE was established to attract investment from both Somali-owned firms and global companies in order to accelerate the ongoing post-conflict reconstruction process in Somalia.
 Somalia has reserves of several natural resources, including uranium, iron ore, tin, gypsum, bauxite, copper, salt and natural gas. The CIA reports that there are 5.663 billion cubic metres of proven natural gas reserves.
The presence or extent of proven oil reserves in Somalia is uncertain. The CIA asserts that there are no proven reserves of oil in the country, while UNCTAD suggests that most proven oil reserves in Somalia lie off its northwestern coast, in the Somaliland region. An oil group listed in Sydney, Range Resources, estimates that the Puntland region in the northeast has the potential to produce to of oil, compared to the 6.7 billion barrels of proven oil reserves in Sudan. As a result of these developments, the Somalia Petroleum Corporation was established by the federal government.
In the late 1960s, UN geologists also discovered major uranium deposits and other rare mineral reserves in Somalia. The find was the largest of its kind, with industry experts estimating that the amount of the deposits could amount to over 25% of the world's then known uranium reserves of 800,000 tons. In 1984, the IUREP Orientation Phase Mission to Somalia reported that the country had 5,000 tons of uranium reasonably assured resources (RAR), 11,000 tons of uranium estimated additional resources (EAR) in calcrete deposits, as well as 0–150,000 tons of uranium speculative resources (SR) in sandstone and calcrete deposits. Somalia evolved into a major world supplier of uranium, with American, UAE, Italian and Brazilian mineral companies vying for extraction rights. Link Natural Resources has a stake in the central region, and Kilimanjaro Capital has a stake in the Amsas-Coriole-Afgoi (ACA) Block, which includes uranium exploration.
The Trans-National Industrial Electricity and Gas Company is an energy conglomerate (company), conglomerate based in Mogadishu. It unites five major Somali companies from the Commerce, trade, finance, security and telecommunications sectors, following a 2010 joint agreement signed in Istanbul to provide electricity and gas infrastructure in Somalia. With an initial investment budget of $1 billion, the company launched the Somalia Peace Dividend Project, a labour-intensive energy program aimed at facilitating local industrialization initiatives.
According to the Central Bank of Somalia, as the nation embarks on the path of reconstruction, the economy is expected to not only match its pre-civil war levels, but also to accelerate in growth and development due to Somalia's untapped natural resources.
Somalia has reserves of several natural resources, including uranium, iron ore, tin, gypsum, bauxite, copper, salt and natural gas. The CIA reports that there are 5.663 billion cubic metres of proven natural gas reserves.
The presence or extent of proven oil reserves in Somalia is uncertain. The CIA asserts that there are no proven reserves of oil in the country, while UNCTAD suggests that most proven oil reserves in Somalia lie off its northwestern coast, in the Somaliland region. An oil group listed in Sydney, Range Resources, estimates that the Puntland region in the northeast has the potential to produce to of oil, compared to the 6.7 billion barrels of proven oil reserves in Sudan. As a result of these developments, the Somalia Petroleum Corporation was established by the federal government.
In the late 1960s, UN geologists also discovered major uranium deposits and other rare mineral reserves in Somalia. The find was the largest of its kind, with industry experts estimating that the amount of the deposits could amount to over 25% of the world's then known uranium reserves of 800,000 tons. In 1984, the IUREP Orientation Phase Mission to Somalia reported that the country had 5,000 tons of uranium reasonably assured resources (RAR), 11,000 tons of uranium estimated additional resources (EAR) in calcrete deposits, as well as 0–150,000 tons of uranium speculative resources (SR) in sandstone and calcrete deposits. Somalia evolved into a major world supplier of uranium, with American, UAE, Italian and Brazilian mineral companies vying for extraction rights. Link Natural Resources has a stake in the central region, and Kilimanjaro Capital has a stake in the Amsas-Coriole-Afgoi (ACA) Block, which includes uranium exploration.
The Trans-National Industrial Electricity and Gas Company is an energy conglomerate (company), conglomerate based in Mogadishu. It unites five major Somali companies from the Commerce, trade, finance, security and telecommunications sectors, following a 2010 joint agreement signed in Istanbul to provide electricity and gas infrastructure in Somalia. With an initial investment budget of $1 billion, the company launched the Somalia Peace Dividend Project, a labour-intensive energy program aimed at facilitating local industrialization initiatives.
According to the Central Bank of Somalia, as the nation embarks on the path of reconstruction, the economy is expected to not only match its pre-civil war levels, but also to accelerate in growth and development due to Somalia's untapped natural resources.
 After the start of the civil war, various new telecommunications companies began to spring up and compete to provide missing infrastructure. Funded by Somali entrepreneurs and backed by expertise from China, South Korea and Europe, these nascent telecommunications firms offer affordable mobile phone and Internet services that are not available in many other parts of the continent. Customers can conduct Electronic funds transfer, money transfers (such as through the popular Dahabshiil) and other banking activities via mobile phones, as well as easily gain wireless Internet access.
After forming partnerships with multinational corporations such as Sprint Nextel, Sprint, ITT Corporation, ITT and Telenor, these firms now offer the cheapest and clearest phone calls in Africa. These Somali telecommunication companies also provide services to every city and town in Somalia. There are presently around 25 mainlines per 1,000 persons, and the local availability of telephone lines (''tele-density'') is higher than in neighbouring countries; three times greater than in adjacent Ethiopia. Prominent Somali telecommunications companies include Golis Telecom Somalia, Golis Telecom Group, Hormuud Telecom, Somafone, NationLink Telecom, Nationlink, Netco (Somalia), Netco, Telcom (Somalia), Telcom and Somali Telecom Group. Hormuud Telecom alone grosses about $40 million a year. Despite their rivalry, several of these companies signed an inter-connectivity deal in 2005 that allows them to set prices, maintain and expand their networks, and ensure that competition does not get out of control.
Investment in the telecom industry is held to be one of the clearest signs that Somalia's economy has continued to develop despite civil strife in parts of the country.
The state-run Somali National Television is the principal national public service TV channel. After a twenty-year hiatus, the station was officially re-launched on 4 April 2011. Its radio counterpart Radio Mogadishu also broadcasts from the capital. Somaliland National TV and Puntland TV and Radio air from the northern regions.
Additionally, Somalia has several private television and radio networks. Among these are Horn Cable Television and Universal Television (Somalia), Universal TV. The political Xog Doon and Xog Ogaal and Horyaal Sports broadsheets publish out of the capital. There are also a number of online media outlets covering local news, including Garowe Online, Wardheernews, and Puntland Post.
The internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Somalia is .so. It was officially relaunched on 1 November 2010 by .SO Registry, which is regulated by the nation's Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications.
On 22 March 2012, the Somali Cabinet also unanimously approved the National Communications Act. The bill paves the way for the establishment of a National Communications regulator in the broadcasting and telecommunications sectors.
In November 2013, following a Memorandum of Understanding signed with Emirates Post in April of the year, the federal Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications officially reconstituted the Somali Postal Service (Somali Post). In October 2014, the ministry also relaunched postal delivery from abroad. The postal system is slated to be implemented in each of the country's 18 administrative provinces via a new postal coding and numbering system.
After the start of the civil war, various new telecommunications companies began to spring up and compete to provide missing infrastructure. Funded by Somali entrepreneurs and backed by expertise from China, South Korea and Europe, these nascent telecommunications firms offer affordable mobile phone and Internet services that are not available in many other parts of the continent. Customers can conduct Electronic funds transfer, money transfers (such as through the popular Dahabshiil) and other banking activities via mobile phones, as well as easily gain wireless Internet access.
After forming partnerships with multinational corporations such as Sprint Nextel, Sprint, ITT Corporation, ITT and Telenor, these firms now offer the cheapest and clearest phone calls in Africa. These Somali telecommunication companies also provide services to every city and town in Somalia. There are presently around 25 mainlines per 1,000 persons, and the local availability of telephone lines (''tele-density'') is higher than in neighbouring countries; three times greater than in adjacent Ethiopia. Prominent Somali telecommunications companies include Golis Telecom Somalia, Golis Telecom Group, Hormuud Telecom, Somafone, NationLink Telecom, Nationlink, Netco (Somalia), Netco, Telcom (Somalia), Telcom and Somali Telecom Group. Hormuud Telecom alone grosses about $40 million a year. Despite their rivalry, several of these companies signed an inter-connectivity deal in 2005 that allows them to set prices, maintain and expand their networks, and ensure that competition does not get out of control.
Investment in the telecom industry is held to be one of the clearest signs that Somalia's economy has continued to develop despite civil strife in parts of the country.
The state-run Somali National Television is the principal national public service TV channel. After a twenty-year hiatus, the station was officially re-launched on 4 April 2011. Its radio counterpart Radio Mogadishu also broadcasts from the capital. Somaliland National TV and Puntland TV and Radio air from the northern regions.
Additionally, Somalia has several private television and radio networks. Among these are Horn Cable Television and Universal Television (Somalia), Universal TV. The political Xog Doon and Xog Ogaal and Horyaal Sports broadsheets publish out of the capital. There are also a number of online media outlets covering local news, including Garowe Online, Wardheernews, and Puntland Post.
The internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Somalia is .so. It was officially relaunched on 1 November 2010 by .SO Registry, which is regulated by the nation's Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications.
On 22 March 2012, the Somali Cabinet also unanimously approved the National Communications Act. The bill paves the way for the establishment of a National Communications regulator in the broadcasting and telecommunications sectors.
In November 2013, following a Memorandum of Understanding signed with Emirates Post in April of the year, the federal Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications officially reconstituted the Somali Postal Service (Somali Post). In October 2014, the ministry also relaunched postal delivery from abroad. The postal system is slated to be implemented in each of the country's 18 administrative provinces via a new postal coding and numbering system.
 Somalia has a number of local attractions, consisting of historical sites, beaches, waterfalls, mountain ranges and national parks. The tourist industry is regulated by the national Ministry of Tourism. The autonomous Puntland and Somaliland regions maintain their own tourism offices. The Somali Tourism Association (SOMTA) also provides consulting services from within the country on the national tourist industry. As of March 2015, the Ministry of Tourism and Wildlife of the Southwestern Somalia, South West State announced that it is slated to establish additional game reserves and wildlife ranges. The United States Government recommends travelers to not travel to Somalia.
Notable sights include the
Somalia has a number of local attractions, consisting of historical sites, beaches, waterfalls, mountain ranges and national parks. The tourist industry is regulated by the national Ministry of Tourism. The autonomous Puntland and Somaliland regions maintain their own tourism offices. The Somali Tourism Association (SOMTA) also provides consulting services from within the country on the national tourist industry. As of March 2015, the Ministry of Tourism and Wildlife of the Southwestern Somalia, South West State announced that it is slated to establish additional game reserves and wildlife ranges. The United States Government recommends travelers to not travel to Somalia.
Notable sights include the  Somalia's network of roads is long. , streets are Road surface, paved and are unpaved. A highway connects major cities in the northern part of the country, such as
Somalia's network of roads is long. , streets are Road surface, paved and are unpaved. A highway connects major cities in the northern part of the country, such as  A sizable Somali diaspora exists in various Western world, Western countries, such as the
A sizable Somali diaspora exists in various Western world, Western countries, such as the  Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern Somali, Northern, Benadiri Somali, Benadir and Maay language, Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast, from Adale to south of
Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern Somali, Northern, Benadiri Somali, Benadir and Maay language, Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast, from Adale to south of  According to the Pew Research Center, 99.8% of Somalia's population is Muslim. The majority belong to the Sunni branch of Islam and the Shafi'i school of Islamic jurisprudence. Sufism, the mysticism, mystical sect of Islam, is also well established, with many local ''jama'a'' (''Zaouia, zawiya'') or congregations of the various ''Tariqah, tariiqa'' or Sufi orders. The constitution of Somalia likewise defines Islam as the state religion of the Federal Republic of Somalia, and Islamic sharia law as the basic source for national legislation. It also stipulates that no law that is inconsistent with the basic tenets of Shari'a can be enacted.
Islam entered the region very early on, as a group of persecuted Muslims had sought refuge across the
According to the Pew Research Center, 99.8% of Somalia's population is Muslim. The majority belong to the Sunni branch of Islam and the Shafi'i school of Islamic jurisprudence. Sufism, the mysticism, mystical sect of Islam, is also well established, with many local ''jama'a'' (''Zaouia, zawiya'') or congregations of the various ''Tariqah, tariiqa'' or Sufi orders. The constitution of Somalia likewise defines Islam as the state religion of the Federal Republic of Somalia, and Islamic sharia law as the basic source for national legislation. It also stipulates that no law that is inconsistent with the basic tenets of Shari'a can be enacted.
Islam entered the region very early on, as a group of persecuted Muslims had sought refuge across the  According to a 2005 World Health Organization estimate, about 97.9% of Somalia's women and girls underwent Female genital mutilation, a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to the horn of Africa and parts of the Near East. Encouraged by women in the community, it is primarily intended to protect chastity, deter promiscuity, and offer protection from assault. By 2013, UNICEF in conjunction with the Somali authorities reported that the prevalence rate among 1- to 14-year-old girls in the autonomous northern Puntland and Somaliland regions had dropped to 25% following a social and religious awareness campaign. About 93% of Somalia's male population is also reportedly circumcised.
Somalia has one of the lowest HIV infection rates on the continent. This is attributed to the Muslim nature of Somali society and adherence of Somalis to Islamic morals. While the estimated HIV prevalence rate in Somalia in 1987 (the first case report year) was 1% of adults, a 2012 report from UNAIDS says that since 2004, estimates from 0.7% to 1% have been assumed.
Although healthcare is now largely concentrated in the private sector, the country's public healthcare system is in the process of being rebuilt, and is overseen by the Ministry of Health. The Minister of Health is Qamar Adan Ali. The autonomous Puntland region maintains its own Ministry of Health, as does the Somaliland region in northwestern Somalia.
Some of the prominent healthcare facilities in the country are East Bardera Mothers and Children's Hospital, Abudwak Maternity and Children's Hospital, Edna Adan Maternity Hospital and West Bardera Maternity Unit.
According to a 2005 World Health Organization estimate, about 97.9% of Somalia's women and girls underwent Female genital mutilation, a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to the horn of Africa and parts of the Near East. Encouraged by women in the community, it is primarily intended to protect chastity, deter promiscuity, and offer protection from assault. By 2013, UNICEF in conjunction with the Somali authorities reported that the prevalence rate among 1- to 14-year-old girls in the autonomous northern Puntland and Somaliland regions had dropped to 25% following a social and religious awareness campaign. About 93% of Somalia's male population is also reportedly circumcised.
Somalia has one of the lowest HIV infection rates on the continent. This is attributed to the Muslim nature of Somali society and adherence of Somalis to Islamic morals. While the estimated HIV prevalence rate in Somalia in 1987 (the first case report year) was 1% of adults, a 2012 report from UNAIDS says that since 2004, estimates from 0.7% to 1% have been assumed.
Although healthcare is now largely concentrated in the private sector, the country's public healthcare system is in the process of being rebuilt, and is overseen by the Ministry of Health. The Minister of Health is Qamar Adan Ali. The autonomous Puntland region maintains its own Ministry of Health, as does the Somaliland region in northwestern Somalia.
Some of the prominent healthcare facilities in the country are East Bardera Mothers and Children's Hospital, Abudwak Maternity and Children's Hospital, Edna Adan Maternity Hospital and West Bardera Maternity Unit.
 Higher education in Somalia is now largely private. Several universities in the country, including Mogadishu University, have been scored among the 100 best universities in Africa in spite of the harsh environment, which has been hailed as a triumph for grass-roots initiatives. Other universities also offering higher education in the south include Benadir University, the Somalia National University, Kismayo University and the University of Gedo. In Puntland, higher education is provided by the Puntland State University and East Africa University. In Somaliland, it is provided by Amoud University, the University of Hargeisa, Somaliland University of Technology and Burao University.
Madrasah, Qu'ranic schools (also known as ''dugsi quran'' or ''mal'aamad quran'') remain the basic system of traditional religious instruction in Somalia. They provide Islamic education for children, thereby filling a clear religious and social role in the country. Known as the most stable local, non-formal system of education providing basic religious and moral instruction, their strength rests on community support and their use of locally made and widely available teaching materials. The Qu'ranic system, which teaches the greatest number of students relative to other educational sub-sectors, is often the only system accessible to Somalis in nomadic as compared to urban areas. A study from 1993 found, among other things, that about 40% of pupils in Qur'anic schools were female. To address shortcomings in religious instruction, the Somali government on its own part also subsequently established the Ministry of Endowment and Islamic Affairs, under which Qur'anic education is now regulated.
Higher education in Somalia is now largely private. Several universities in the country, including Mogadishu University, have been scored among the 100 best universities in Africa in spite of the harsh environment, which has been hailed as a triumph for grass-roots initiatives. Other universities also offering higher education in the south include Benadir University, the Somalia National University, Kismayo University and the University of Gedo. In Puntland, higher education is provided by the Puntland State University and East Africa University. In Somaliland, it is provided by Amoud University, the University of Hargeisa, Somaliland University of Technology and Burao University.
Madrasah, Qu'ranic schools (also known as ''dugsi quran'' or ''mal'aamad quran'') remain the basic system of traditional religious instruction in Somalia. They provide Islamic education for children, thereby filling a clear religious and social role in the country. Known as the most stable local, non-formal system of education providing basic religious and moral instruction, their strength rests on community support and their use of locally made and widely available teaching materials. The Qu'ranic system, which teaches the greatest number of students relative to other educational sub-sectors, is often the only system accessible to Somalis in nomadic as compared to urban areas. A study from 1993 found, among other things, that about 40% of pupils in Qur'anic schools were female. To address shortcomings in religious instruction, the Somali government on its own part also subsequently established the Ministry of Endowment and Islamic Affairs, under which Qur'anic education is now regulated.
 The cuisine of Somalia, which varies from region to region, is a mixture of diverse culinary influences. It is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are, therefore no pork dishes, alcoholic beverages, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated. ''Qaddo'' or lunch is often elaborate.
Varieties of 'bariis' (rice), the most popular probably being basmati, usually act as the main dish. Spices including cumin, cardamom, cloves, cinnamon and Salvia officinalis, garden sage are used to add aromas to these different rice dishes. Somalis serve dinner as late as 9 pm. During Ramadan (calendar month), Ramadan, the evening meal is often presented after Tarawih prayers; sometimes up to 11 pm.
'Xalwo' (halva) is a popular Confectionery, confection reserved for special festive occasions, such as Eid ul-Fitr, Eid celebrations or wedding receptions. It is made from corn starch, sugar, cardamom powder, nutmeg powder and ghee. Peanuts are also sometimes added to enhance texture and flavour. After meals, homes are traditionally perfumed using frankincense () or incense (), which is prepared inside an incense burner referred to as a ''dabqaad''.
The cuisine of Somalia, which varies from region to region, is a mixture of diverse culinary influences. It is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are, therefore no pork dishes, alcoholic beverages, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated. ''Qaddo'' or lunch is often elaborate.
Varieties of 'bariis' (rice), the most popular probably being basmati, usually act as the main dish. Spices including cumin, cardamom, cloves, cinnamon and Salvia officinalis, garden sage are used to add aromas to these different rice dishes. Somalis serve dinner as late as 9 pm. During Ramadan (calendar month), Ramadan, the evening meal is often presented after Tarawih prayers; sometimes up to 11 pm.
'Xalwo' (halva) is a popular Confectionery, confection reserved for special festive occasions, such as Eid ul-Fitr, Eid celebrations or wedding receptions. It is made from corn starch, sugar, cardamom powder, nutmeg powder and ghee. Peanuts are also sometimes added to enhance texture and flavour. After meals, homes are traditionally perfumed using frankincense () or incense (), which is prepared inside an incense burner referred to as a ''dabqaad''.
 Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Somalia. Important domestic competitions are the Somalia League and Somalia Cup, with the Somalia national football team playing internationally.
Basketball is also played in the country. The FIBA Africa Championship 1981 was hosted in Mogadishu from 15 to 23 December December 1981, during which the Somalia national basketball team, national basketball team received the bronze medal. The squad also takes part in the Basketball at the Pan Arab Games, basketball event at the Pan Arab Games.
In 2013, a Somalia national bandy team was formed in Borlänge. It later participated in the Bandy World Championship 2014 in Irkutsk and Shelekhov in Russia.
In the martial arts, Faisal Jeylani Aweys and Mohamed Deq Abdulle of the Somalia national taekwondo team, national taekwondo team took home a silver medal and fourth place, respectively, at the 2013 Open World Taekwondo Challenge Cup in Tongeren. The Somali Olympic Committee has devised a special support program to ensure continued success in future tournaments. Additionally, Mohamed Jama has won both world and European titles in K-1 and Muay Thai, Thai Boxing.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Somalia. Important domestic competitions are the Somalia League and Somalia Cup, with the Somalia national football team playing internationally.
Basketball is also played in the country. The FIBA Africa Championship 1981 was hosted in Mogadishu from 15 to 23 December December 1981, during which the Somalia national basketball team, national basketball team received the bronze medal. The squad also takes part in the Basketball at the Pan Arab Games, basketball event at the Pan Arab Games.
In 2013, a Somalia national bandy team was formed in Borlänge. It later participated in the Bandy World Championship 2014 in Irkutsk and Shelekhov in Russia.
In the martial arts, Faisal Jeylani Aweys and Mohamed Deq Abdulle of the Somalia national taekwondo team, national taekwondo team took home a silver medal and fourth place, respectively, at the 2013 Open World Taekwondo Challenge Cup in Tongeren. The Somali Olympic Committee has devised a special support program to ensure continued success in future tournaments. Additionally, Mohamed Jama has won both world and European titles in K-1 and Muay Thai, Thai Boxing.
 Somali architecture is a rich and diverse tradition of engineering and design involving multiple types of constructions and edifices, such as Stonemasonry, stone cities, castles, citadels, Fortification, fortresses,
Somali architecture is a rich and diverse tradition of engineering and design involving multiple types of constructions and edifices, such as Stonemasonry, stone cities, castles, citadels, Fortification, fortresses,