Saxon Coronation Stone( Edward).jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the
 The name of the Saxons may derive from a kind of knife associated with the ethnos; such a knife has the name ''
The name of the Saxons may derive from a kind of knife associated with the ethnos; such a knife has the name ''


 Saxons, along with
Saxons, along with
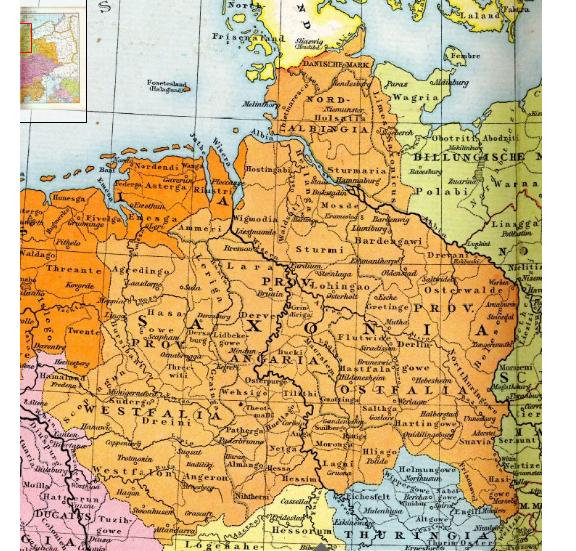 The continental Saxons living in what was known as '' Old Saxony'' (c. 531–804) appear to have become consolidated by the end of the eighth century. After subjugation by the Emperor
The continental Saxons living in what was known as '' Old Saxony'' (c. 531–804) appear to have become consolidated by the end of the eighth century. After subjugation by the Emperor
 The conversion of the Saxons in England from their original Germanic paganism, Germanic religion to
The conversion of the Saxons in England from their original Germanic paganism, Germanic religion to
"Popular Revolt, Dynastic Politics, and Aristocratic Factionalism in the Early Middle Ages: The Saxon Stellinga Reconsidered."
''Speculum (journal), Speculum'', Vol. 70, No. 3. (Jul., 1995), pp. 467–501. * Hummer, Hans J. ''Politics and Power in Early Medieval Europe: Alsace and the Frankish Realm 600–1000''. Cambridge University Press: 2005. * Timothy Reuter, Reuter, Timothy. ''Germany in the Early Middle Ages 800–1056''. New York: Longman, 1991. * Reuter, Timothy (trans.)
The Annals of Fulda
'. (Manchester Medieval series, Ninth-Century Histories, Volume II.) Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1992. * * Frank Stenton, Stenton, Sir Frank M. ''Anglo-Saxon England''. third ed. Oxford University Press, 1971. * John Michael Wallace-Hadrill, Wallace-Hadrill, J. M., translator.
The Fourth Book of the Chronicle of Fredegar with its Continuations
'. Connecticut: Greenwood Press, 1960. * James Westfall Thompson, Thompson, James Westfall. ''Feudal Germany''. 2 vol. New York: Frederick Ungar Publishing Co., 1928.
James Grout: ''Saxon Advent'', part of the Encyclopædia Romana
Saxons and Britons
* {{Authority control Saxons, History of North Rhine-Westphalia Early Germanic peoples German tribes Ingaevones
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
coast of northern Germania, in what is now Germany. In the late Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
, the name was used to refer to Germanic coastal raiders, and as a name similar to the later "Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
". Their origins are believed to be in or near the German North Sea coast where they appear later, in Carolingian times. In Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
times, continental Saxons had been associated with the activity and settlements on the coast of what later became Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
. Their precise origins are uncertain, and they are sometimes described as fighting inland, coming into conflict with the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
and Thuringians
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into confl ...
. There is possibly a single classical reference to a smaller homeland of an early Saxon tribe, but its interpretation is disputed. According to this proposal, the Saxons' earliest area of settlement is believed to have been Northern Albingia
Nordalbingia (german: Nordalbingien) (also Northern Albingia) was one of the four administrative regions of the medieval Duchy of Saxony, the others being Angria, Eastphalia, and Westphalia. The region's name is based on the Latin name ''Alba'' ...
. This general area is close to the probable homeland of the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
.
During the eighth and ninth centuries the Saxons of Old Saxony were in continual conflict with the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, whose kingdom at the time was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty. After thirty three years of conquest due to military campaigns led by the lord king and emperor Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
beginning in 772 and ending around 804, the Franks defeated the Saxons, forced them to convert to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
and seized the territory of Old Saxony, annexing it into the Carolingian domain, although the Franks had been enemies of the Saxons in the time of Clovis I, during the early Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
period of the fifth and sixth centuries.
Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesm ...
, Duke and prince of the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
and Mayor of the Palace of Austrasia, the grandfather of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
, had fought and led numerous campaigns against the Saxons.
In contrast, the English Saxons, today referred to in English as Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
, became a single nation bringing together migrant Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
( Frisians, Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
, Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
hence "English" and assimilated Celtic Britons populations. Their earliest weapons and clothing south of the Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
were based on late Roman military fashions, but later immigrants north of the Thames showed a stronger North German influence. The term "Anglo-Saxon", combining the names of the Angles and the Saxons, came into use by the eighth century (for example Paul the Deacon) to distinguish the Germanic inhabitants of Britain from continental Saxons (referred to in the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' as ''Ealdseaxe'', 'old Saxons'), but both the Saxons of Britain and those of Old Saxony (Northern Germany) continued to be referred to as 'Saxons' in an indiscriminate manner, especially in the languages of Britain and Ireland.
Although the English Saxons were no longer raiders, the political history of the continental Saxons is unclear until the time of the conflict between their semi-legendary hero Widukind
Widukind, also known as Wittekind, was a leader of the Saxons and the chief opponent of the Frankish king Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 777 to 785. Charlemagne ultimately prevailed, organized Saxony as a Frankish province, massacred th ...
and the Frankish emperor Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
. The continental Saxons are no longer a distinctive ethnic group or country but their name lives on in the names of several regions and states of Germany, including Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
(which includes central parts of the original Saxon homeland known as Old Saxony), Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
in Upper Saxony {{short description, Historic lands in Central Germany
Upper Saxony (german: Obersachsen) was the name given to the majority of the German lands held by the House of Wettin, in what is now called Central Germany (''Mitteldeutschland'').
Concept ...
, as well as Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
(which includes Old, Lower and Upper Saxon regions).
Etymology
 The name of the Saxons may derive from a kind of knife associated with the ethnos; such a knife has the name ''
The name of the Saxons may derive from a kind of knife associated with the ethnos; such a knife has the name ''seax
''Seax'' (; also sax, sæx, sex; invariant in plural, latinized ''sachsum'') is an Old English word for "knife". In modern archaeology, the term ''seax'' is used specifically for a type of small sword, knife or dagger typical of the Germanic p ...
'' in Old English, ''Sax'' in German, ''sachs'' in Old High German, and ''sax'' in Old Norse. The seax has had a lasting symbolic impact in the English counties of Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and Grea ...
and Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a historic county in southeast England. Its area is almost entirely within the wider urbanised area of London and mostly within the ceremonial county of Greater London, with small sections in neighbour ...
, both of which feature three seaxes in their ceremonial emblem. The names of these counties, along with the names " Sussex" and "Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
", contain a remnant of the root of the word "Saxon".
The Elizabethan-era play ''Edmund Ironside'' suggests that the name "Saxon" derives from the Latin ''saxa'' (stones; singular form: ''saxum''):
Saxon as a demonym
Celtic languages
In theCeltic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
, the words designating English nationality derive from the Latin word . The most prominent example, a loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
in English from Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well ...
(older spelling: ), is the word , used by Scots-, Scottish English- and Gaelic-speakers in the 21st century as a racially pejorative term for an English person. The ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a co ...
'' (OED) gives 1771 as the date of the earliest written use of the word in English. The Gaelic name for England is (older spelling: , genitive: ), and (formed with a common adjective suffix ) means "English" in reference to people and things, though not when naming the English language, which is .
, the Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
word for an Englishman (with meaning England), has the same derivation, as do the words used in Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
to describe the English people (, singular ) and the language and things English in general: and .
Cornish terms the English , from the same derivation. In the 16th century Cornish-speakers used the phrase to feign ignorance of the English language. The Cornish words for the English people and England are and ('Land aysof Saxons'). Similarly Breton, spoken in north-western France, has ('English'), ('the English language'), and for 'England'.
Romance languages
The label "Saxons" (in ro, Sași) also became attached to German settlers who settled during the 12th century in southeasternTransylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. From Transylvania, some of these Saxons migrated to neighbouring Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
, as the name of the town shows. Sascut
Sascut is a commune in Bacău County, Western Moldavia, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders B ...
lies in the part of Moldavia that forms part of present-day Romania.
During George Frideric Handel's visit to the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
(1706–09), much was made of his origins in Saxony; in particular, the Venetians greeted the 1709 performance of his opera ''Agrippina'' with the cry , "Cheers for the beloved Saxon!"
Non-Indo-European languages
TheFinns
Finns or Finnish people ( fi, suomalaiset, ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland.
Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these ...
and Estonians
Estonians or Estonian people ( et, eestlased) are a Finnic ethnic group native to Estonia who speak the Estonian language.
The Estonian language is spoken as the first language by the vast majority of Estonians; it is closely related to oth ...
have changed their usage of the root ''Saxon'' over the centuries to apply now to the whole country of Germany ( and respectively) and the Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
( and , respectively). The Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
word ( scissors) reflects the name of the old Saxon single-edged sword — seax
''Seax'' (; also sax, sæx, sex; invariant in plural, latinized ''sachsum'') is an Old English word for "knife". In modern archaeology, the term ''seax'' is used specifically for a type of small sword, knife or dagger typical of the Germanic p ...
— from which the name "Saxon" supposedly derives. In Estonian, means "a nobleman" or, colloquially, "a wealthy or powerful person". As a result of the 13th-century Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christian colonization and Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Christian military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the pagan Baltic, Finnic and West Slavic peoples around th ...
, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
's upper class comprised mostly persons of German origin until well into the 20th century.
Related personal names
The word survives as the surnames of / (in Low German or Low Saxon), and . TheDutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
female given name
A given name (also known as a forename or first name) is the part of a personal name quoted in that identifies a person, potentially with a middle name as well, and differentiates that person from the other members of a group (typically a ...
, , originally meant 'a Saxon woman' ( metathesis of ''Saxia'').
Saxony as a toponym
Following the downfall ofHenry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
(11291195, Duke of Saxony 11421180), and the subsequent splitting of the Saxon tribal duchy into several territories, the name of the Saxon duchy was transferred to the lands of the Ascanian
The House of Ascania (german: Askanier) was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.
The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ''Schloss ...
family. This led to the differentiation between Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
(lands settled by the Saxon tribe) and Upper Saxony {{short description, Historic lands in Central Germany
Upper Saxony (german: Obersachsen) was the name given to the majority of the German lands held by the House of Wettin, in what is now called Central Germany (''Mitteldeutschland'').
Concept ...
(the lands belonging to the House of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its ori ...
). Gradually, the latter region became known as "Saxony", ultimately usurping the name's original geographical meaning. The area formerly known as Upper Saxony now lies in Central Germany - in the eastern part of the present-day Federal Republic of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between ...
: note the names of the federal states of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
and Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
.
History
Early history


Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
's ''Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
'', written in the second century, is sometimes considered to contain the first mentioning of the Saxons. Some copies of this text mention a tribe called ''Saxones'' in the area to the north of the lower Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
. However, other versions refer to the same tribe as ''Axones''. This may be a misspelling of the tribe that Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
in his '' Germania'' called ''Aviones The Aviones or Auiones (*''Awioniz'' meaning "island people") were one of the Nerthus-worshipping Germanic tribes of the 1st century mentioned by Tacitus in '' Germania'', and they lived either in the southern Jutland Peninsula, or on Öland. They ...
''. According to this theory, "Saxones" was the result of later scribes trying to correct a name that meant nothing to them. On the other hand, Schütte, in his analysis of such problems in ''Ptolemy's Maps of Northern Europe'', believed that "Saxones" is correct. He notes that the loss of first letters occurs in numerous places in various copies of Ptolemy's work, and also that the manuscripts without "Saxones" are generally inferior overall.
Schütte remarks that there was a medieval tradition of calling this area "Old Saxony" (covering Westphalia, Angria and Eastphalia). This view is in line with Bede who mentions Old Saxony was near the Rhine, somewhere to the north of the river Lippe
The Lippe () is a river in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is a right tributary of the Rhine and in length with an elevation difference of 125 metres and a catchment area of 4.890 km².
The source is located at the edge of the Teutoburg ...
(Westphalia, northeastern part of modern German state Nordrhein-Westfalen).
The first undisputed mention of the Saxon name in its modern form is from AD 356, when Julian, later the Roman emperor, mentioned them in a speech as allies of Magnentius
Magnus Magnentius ( 303 – 11 August 353) was a Roman general and usurper against Constantius II from 350 to 353. Of Germanic descent, Magnentius served with distinction in Gaul under the Western emperor Constans. On 18 January 350 Magnentius ...
, a rival emperor in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
. Zosimus Zosimus, Zosimos, Zosima or Zosimas may refer to:
People
*
* Rufus and Zosimus (died 107), Christian saints
* Zosimus (martyr) (died 110), Christian martyr who was executed in Umbria, Italy
* Zosimos of Panopolis, also known as ''Zosimus Alchem ...
mentions a specific tribe of Saxons, called the ''Kouadoi'', which have been interpreted as a misunderstanding for the Chauci
The Chauci (german: Chauken, and identical or similar in other regional modern languages) were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rivers Ems and Elbe, on both sides of the Weser and ranging as far inland as the ...
, or Chamavi
The Chamavi, Chamãves or Chamaboe () were a Germanic tribe of Roman imperial times whose name survived into the Early Middle Ages. They first appear under that name in the 1st century AD '' Germania'' of Tacitus as a Germanic tribe that lived t ...
. They entered the Rhineland and displaced the recently settled Salian Franks
The Salian Franks, also called the Salians (Latin: ''Salii''; Greek: Σάλιοι, ''Salioi''), were a northwestern subgroup of the early Franks who appear in the historical record in the fourth and fifth centuries. They lived west of the Low ...
from Batavi, whereupon some of the Salians began to move into the Belgian
Belgian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to, Belgium
* Belgians, people from Belgium or of Belgian descent
* Languages of Belgium, languages spoken in Belgium, such as Dutch, French, and German
*Ancient Belgian language, an extinct languag ...
territory of Toxandria
Texandria (also Toxiandria; later Toxandria, Taxandria), is a region mentioned in the 4th century AD and during the Middle Ages. It was situated in the southern part of the modern Netherlands and in the northern part of present-day Belgium, current ...
, supported by Julian.
Both in this case and in others the Saxons were associated with using boats for their raids. In order to defend against Saxon raiders, the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
created a military district called the '' Litus Saxonicum'' ("Saxon Shore") on both sides of the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
.
In 441–442 AD, Saxons are mentioned for the first time as inhabitants of Britain, when an unknown Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switze ...
historian wrote: "The British provinces (...) have been reduced to Saxon rule".
Saxons as inhabitants of present-day Northern Germany are first mentioned in 555, when the Frankish king Theudebald
Theudebald or Theodebald (in modern English, ''Theobald''; in French, ''Thibaut'' or ''Théodebald''; in German, ''Theudowald'') (c. 535–555), son of Theudebert I and Deuteria, was the king of Metz, Rheims, or Austrasia—as it is vari ...
died, and the Saxons used the opportunity for an uprising. The uprising was suppressed by Chlothar I, Theudebald's successor. Some of their Frankish successors fought against the Saxons, others were allied with them. The Thuringians
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into confl ...
frequently appeared as allies of the Saxons.
Netherlands
In the Netherlands, Saxons occupied the territory south of the Frisians and north of the Franks. In the west it reached as far as theGooi
The Gooi () is an area around Hilversum, in the centre of the Netherlands. It is a slightly hilly area characterised by its green landscape, its historical charm, the wealth of its inhabitants, and its villas. The Gooi is known in the Netherlan ...
region, in the south as far as the Lower Rhine. After the conquest of Charlemagne, this area formed the main part of the Bishopric of Utrecht. The Saxon duchy of Hamaland
Hamaland (also Hameland) was a medieval Carolingian vassal county in the east of the modern-day Netherlands. Its name originated from the former Chamavi inhabitants that merged into the newly formed confederation of Franks. It is located east of ...
played an important role in the formation of the duchy of Guelders.
The local language, although strongly influenced by standard Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, is still officially recognised as Dutch Low Saxon
Dutch Low Saxon ( or ''Nederlaands Nedersaksies''; nl, Nederlands Nedersaksisch) are the Low Saxon dialects of the Low German language that are spoken in the northeastern Netherlands and are written there with local, unstandardised orthographie ...
.
Italy and Provence
In 569, some Saxons accompanied theLombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
into Italy under the leadership of Alboin
Alboin (530s – 28 June 572) was king of the Lombards from about 560 until 572. During his reign the Lombards ended their migrations by settling in Italy, the northern part of which Alboin conquered between 569 and 572. He had a lasting effe ...
and settled there. In 572, they raided southeastern Gaul as far as ''Stablo'', now Estoublon
Estoublon (; oc, Estoblon) is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur in southeastern France.
Geography
The river Asse flows southwest through the western part of the commune.
Population
See also ...
. Divided, they were easily defeated by the Gallo-Roman
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context ...
general Mummolus
Mummolus (also spelled Mommolus or Mummulus), was a Gallo-Roman patrician and prefect who served Guntram, King of Burgundy, as a general in the 6th century.
He was born Eunius to Peonius, Count of Auxerre. Peonius sent his son to Guntram with gi ...
. When the Saxons regrouped, a peace treaty was negotiated whereby the Italian Saxons were allowed to settle with their families in Austrasia. Gathering their families and belongings in Italy, they returned to Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
in two groups in 573. One group proceeded by way of Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard dialect, Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes departments of France, department in France. The Nice urban unit, agg ...
and another via Embrun, Hautes-Alpes, Embrun, joining up at Avignon. They plundered the territory and were as a consequence stopped from crossing the Rhône by Mummolus. They were forced to pay compensation for what they had robbed before they could enter Austrasia. These people are known only by documents, and their settlement cannot be compared to the archeological artifacts and remains that attest to Saxon settlements in northern and western Gaul.
Gaul
A Saxon king named Wulf and Eadwacer, Eadwacer conquered Angers in 463, to be dislodged by Childeric I and theSalian Franks
The Salian Franks, also called the Salians (Latin: ''Salii''; Greek: Σάλιοι, ''Salioi''), were a northwestern subgroup of the early Franks who appear in the historical record in the fourth and fifth centuries. They lived west of the Low ...
, allies of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. It is possible that Saxon settlement of Great Britain began in response to expanding Frankish control of the English Channel, Channel coast.
Some Saxons already lived along the Saxon shore of Gaul as Roman foederati. They can be traced in documents, but also in archeology and in toponymy. The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' mentions the ''Tribunus cohortis primae novae Armoricanae, Grannona in litore Saxonico''. The location of ''Grannona'' is uncertain and was identified by the historians and toponymists at different places: mainly with the town known today as Granville, Manche, Granville (in Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
) or nearby. The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' does not explain where these "Roman" soldiers came from. Some toponymists have proposed Graignes, Manche, Graignes (''Grania'' 1109–1113) as the location for ''Grannona''/''Grannonum''. Although some scholars believe it could be the same element ''*gran'', that is recognised in Guernsey (''Greneroi'' 11th century), it most likely derives from the Gaulish language, Gaulish god Grannus, Grannos. This location is closer to Bayeux, where Gregory of Tours evokes otherwise the ''Saxones Bajocassini'' (Bessin Saxons), which were ineffective against the Breton Waroch II in 579.
A Saxon unit of ''laeti'' settled at Bayeuxthe ''Saxones Baiocassenses''. These Saxons became subjects of Clovis I late in the fifth century. The Saxons of Bayeux comprised a standing army and were often called upon to serve alongside the local National service, levy of their region in Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
military campaigns. In 589, the Saxons wore their hair in the Bretons, Breton fashion at the orders of Fredegund and fought with them as allies against Guntram. Beginning in 626, the Saxons of the Bessin were used by Dagobert I for his campaigns against the Basques. One of their own, Aeghyna, was created a ''Duke of Gascony, dux'' over the region of Duchy of Vasconia, Vasconia.
In 843 and 846 under king Charles the Bald, other official documents mention a ''pagus'' called ''Otlinga Saxonia'' in the Bessin region, but the meaning of ''Otlinga'' is unclear. Different Bessin toponyms were identified as typically Saxon, ex : Cottun (''Coltun'' 1035–1037 ; ''Cola''s "town"). It is the only place name in Normandy that can be interpreted as a ''-tun'' one (English ''-ton''; cf. Colton (disambiguation), Colton). In contrast to this one example in Normandy are numerous ''-thun'' villages in the north of France, in Boulonnais (land area), Boulonnais, for example Alincthun, Verlincthun, and Pelingthun, showing, with other toponyms, an important Saxon or Anglo-Saxon settlement. Comparing the concentration of ''-ham''/''-hem'' (Anglo-Saxon ''hām'' > home) toponyms in the Bessin and in the Boulonnais gives more examples of Saxon settlement. In the area known today as Normandy, the ''-ham'' cases of Bessin are uniquethey do not exist elsewhere. Other cases were considered, but there is no determining example. For example, Canehan (''Kenehan'' 1030/''Canaan'' 1030–1035) could be the biblical name ''Canaan'' or Airan (''Heidram'' 9th century), the Germanic masculine name ''Hairammus''.
The Bessin examples are clear; for example, Ouistreham (''Oistreham'' 1086), Étréham (''Oesterham'' 1350 ?), Huppain (''*Hubbehain'' ; ''Hubba''s "home"), and Surrain (''Surrehain'' 11thcentury). Another significant example can be found in the Norman onomastics: the widespread surname Lecesne, with variant spellings: LeCesne, Lesène, Lecène, and Cesne. It comes from Gallo-Romance *SAXINU "the Saxon", which is ''saisne'' in Old French. These examples are not derived from more recent Anglo-Scandinavian toponyms, because in that case they would have been numerous in the Norman regions (pays deCaux, Basse-Seine, North-Cotentin) settled by Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
. That is not the case, nor does Bessin belong to the ''pagii'', which were affected by an important wave of Anglo-Scandinavian immigration.
In addition, archaeological finds add evidence to the documents and the results of toponymic research. Around the city of Caen and in the Bessin (Vierville-sur-Mer, Bénouville, Calvados, Bénouville, Giverville, Hérouvillette), excavations have yielded numerous examples of Anglo-Saxon jewellery, design elements, settings, and weapons. All of these things were discovered in cemeteries in a context of the fifth, sixth and seventh centuries AD.
The oldest Saxon site found in France to date is Vron, in Picardy. Archaeologists excavated a large cemetery with tombs dating from the Roman Empire until the sixth century. Furniture and other grave goods, as well as the human remains, revealed a group of people buried in the fourth and fifth centuries AD. Physically different from the usual local inhabitants found before this period, they instead resembled the Germanic populations of the north. Starting around 375 AD the burials are located in the region known in Roman times as the Saxon Shores. 92% of these burials were inhumations, and sometimes included weapons of typical Germanic type. Starting from around 440 AD the burial ground displaced eastward. The burials were now arranged in rows and displayed a strong Anglo-Saxon influence until around 520 AD, when this influence subsided. Archaeological material, neighbouring toponymy, and historical accounts support the conclusion of settlement of Saxon foederati with their families on the shores of the English Channel. Further anthropological research by Joël Blondiaux shows these people were from Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
.
Saxons in Britain
 Saxons, along with
Saxons, along with Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Frisians and Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
, invaded or migrated to the island of Great Britain (Britannia) around the time of the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. Saxon raiders had been harassing the eastern and southern shores of Britannia for centuries before, prompting the construction of a string of coastal forts called the ''Litora Saxonica'' or Saxon Shore forts, Saxon Shore. Before the End of Roman rule in Britain, end of Roman rule in Britannia, many Saxons and other folk had been permitted to settle in these areas as farmers.
According to tradition, the Saxons (and other tribes) first entered Britain en masse as part of an agreement to protect the Britons (historical), Britons from the incursions of the Picts, Gaels and others. The story, as reported in such sources as the ''Historia Brittonum'' and Gildas, indicates that the British king Vortigern allowed the Germanic warlords, later named as Hengist and Horsa by Bede, to settle their people on the Isle of Thanet in exchange for their service as mercenaries. According to Bede, Hengist manipulated Vortigern into granting more land and allowing for more settlers to come in, paving the way for the Germanic settlement of Britain.
Historians are divided about what followed: some argue that the takeover of southern Great Britain by the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
was peaceful. The known account from a native Briton who lived in the mid-5th century AD, Gildas, described events as a forced takeover by armed attack:
Gildas described how the Saxons were later slaughtered at the battle of Mons Badonicus 44 years before he wrote his history, and their conquest of Britain halted. The eighth-century English historian Bede tells how their advance resumed thereafter. He said this resulted in a swift overrunning of the entirety of South-Eastern Britain, and the foundation of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
Four separate Saxon realms emerged:
# East Saxons: created the Kingdom of Essex.
# Middle Saxons: created the province of Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a historic county in southeast England. Its area is almost entirely within the wider urbanised area of London and mostly within the ceremonial county of Greater London, with small sections in neighbour ...
# South Saxons: led by Aelle of Sussex, Aelle, created the Kingdom of Sussex
# West Saxons: created the Kingdom of Wessex
During the period of the reigns from Egbert of Wessex, Egbert to Alfred the Great, the kings of Wessex emerged as Bretwalda, unifying the country. They eventually organised it as the kingdom of England in the face of Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
invasions.
Later Saxons in Germany
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
, a political entity called the Duchy of Saxony (804-1296) appeared, covering Westphalia, Eastphalia, Angria and Nordalbingia (Holstein, southern part of modern-day Schleswig-Holstein state).
The Saxons long resisted becoming Christianity, Christians and being incorporated into the orbit of the Frankish kingdom. In 776 the Saxons promised to convert to Christianity and vow loyalty to the king, but, during Charlemagne's campaign in Hispania (778), the Saxons advanced to Cologne-Deutz, Deutz on the Rhine and plundered along the river. This was an oft-repeated pattern when Charlemagne was distracted by other matters.
They were conquered by Charlemagne in a long series of annual campaigns, the Saxon Wars (772804). With defeat came enforced baptism and Religious conversion, conversion as well as the union of the Saxons with the rest of the Germanic, Frankish empire. Their sacred tree or pillar, a symbol of Irminsul, was destroyed. Charlemagne deported 10,000 Nordalbingian Saxons to Neustria and gave their largely vacant lands in Wagria (approximately modern Plön and Ostholstein districts) to the loyal king of the Abotrites. Einhard, Charlemagne's biographer, says on the closing of this grand conflict:
The war that had lasted so many years was at length ended by their acceding to the terms offered by the king; which were renunciation of their national religious customs and the worship of devils, acceptance of the sacraments of the Christian faith and religion, and union with the Franks to form one people.Under Carolingian dynasty, Carolingian rule, the Saxons were reduced to tributary status. There is evidence that the Saxons, as well as Slavic tributaries such as the Abodrites and the Wends, often provided troops to their Carolingian overlords. The dukes of Saxony became kings (Henry the Fowler, Henry I, the Fowler, 919) and later the first emperors (Henry's son, Otto I, the Great) of Germany during the tenth century, but they lost this position in 1024. The duchy was divided in 1180 when Duke
Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
refused to follow his cousin, Emperor Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick Barbarossa, into war in Lombardy.
During the High Middle Ages, under the Salian dynasty, Salian emperors and, later, under the Teutonic Knights, German settlers moved east of the Saale into the area of a western Slavic tribe, the Sorbs. The Sorbs were gradually Germanisation, Germanised. This region subsequently acquired the name Saxony through political circumstances, though it was initially called the March of Meissen. The rulers of Meissen acquired control of the Duchy of Saxony (only a remnant of the previous Duchy) in 1423; they eventually applied the name ''Saxony'' to the whole of their kingdom. Since then, this part of eastern Germany has been referred to as Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
(german: Sachsen), a source of some misunderstanding about the original homeland of the Saxons, with a central part in the present-day German state of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
(german: Niedersachsen, links=no).
Culture
Social structure
Bede, a Northumbrian writing around the year 730, remarks that "the old (that is, the continental) Saxons have no king, but they are governed by several ealdormen (or ''satrapa'') who, during war, cast lots for leadership but who, in time of peace, are equal in power." The ''regnum Saxonum'' was divided into three provinces – Westphalia, Eastphalia and Angria – which comprised about one hundred ''pagi'' or ''Gau (country subdivision), Gaue''. Each ''Gau'' had its own satrap with enough military power to level whole villages that opposed him.Goldberg, 473. In the mid-9th century, Nithard first described the social structure of the Saxons beneath their leaders. The caste structure was rigid; in the Old Saxon, Saxon language the three castes, excluding slaves, were called the ''edhilingui'' (related to the term aetheling), ''frilingi'' and ''lazzi''. These terms were subsequently Latinisation of names, Latinised as ''nobiles'' or ''nobiliores''; ''ingenui'', ''ingenuiles'' or ''liberi''; and ''liberti'', ''liti'' or ''serviles''.Goldberg, 471. According to very early traditions that are presumed to contain a good deal of historical truth, the ''edhilingui'' were the descendants of the Saxons who led the tribe out of Holstein and during the migrations of the sixth century. They were a conquering warrior elite. The ''frilingi'' represented the descendants of the ''amicii'', ''auxiliarii'' and ''manumissi'' of that caste. The ''lazzi'' represented the descendants of the original inhabitants of the conquered territories, who were forced to make oaths of submission and pay tribute to the ''edhilingui''. The ''Lex Saxonum'' regulated the Saxons' unusual society. Intermarriage between the castes was forbidden by the ''Lex,'' and wergilds were set based upon caste membership. The ''edhilingui'' were worth 1,440 solidi, or about 700 head of cattle, the highest wergild on the continent; the price of a bride was also very high. This was six times as much as that of the ''frilingi'' and eight times as much as the ''lazzi''. The gulf between noble and ignoble was very large, but the difference between a freeman and an indentured labourer was small. According to the ''Vita Lebuini antiqua'', an important source for early Saxon history, the Saxons held an annual council at Marklo (Westphalia) where they "confirmed their laws, gave judgment on outstanding cases, and determined by common counsel whether they would go to war or be in peace that year." All three castes participated in the general council; twelve representatives from each caste were sent from each ''Gau''. In 782, Charlemagne abolished the system of ''Gaue'' and replaced it with the ''Grafschaftsverfassung'', the system of County, counties typical of Francia. By prohibiting the Marklo councils, Charlemagne pushed the ''frilingi'' and ''lazzi'' out of political power. The old Saxon system of ''Abgabengrundherrschaft'', lordship based on dues and taxes, was replaced by a form of feudalism based on service and labour, personal relationships and oaths.Religion
Germanic Religion
Saxon religious practices were closely related to their political practices. The annual councils of the entire tribe began with invocations of the gods. The procedure by which dukes were elected in wartime, by drawing lots, is presumed to have had religious significance, i.e. in giving trust to divine providenceit seemsto guide the random decision making.Goldberg, 474. There were also sacred rituals and objects, such as the pillars called Irminsul; these were believed to connect heaven and earth, as with other examples of trees or ladders to heaven in numerous religions.Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
had one such pillar chopped down in 772 close to the Eresburg stronghold.
Early Saxon religious practices in Britain can be gleaned from place names and the Germanic calendar in use at that time. The Germanic gods Woden, Frigg, Týr, Tiw and Thunor, who are attested to in every Germanic tradition, were worshipped in Wessex, Sussex and Essex. They are the only ones directly attested to, though the names of the third and fourth months (March and April) of the Month#Old English calendar, Old English calendar bear the names ''Hrethmonath'' and ''Eosturmonath'', meaning "month of Hretha" and "month of Ēostre." It is presumed that these are the names of two goddesses who were worshipped around that season.Stenton, 97–98. The Saxons offered cakes to their gods in February (''Solmonath''). There was a religious festival associated with the harvest, ''Halegmonath'' ("holy month" or "month of offerings", September). The Saxon calendar began on 25 December, and the months of December and January were called Yule (or ''Giuli''). They contained a ''Modra niht'' or "night of the mothers", another religious festival of unknown content.
The Saxon freemen and servile class remained faithful to their original beliefs long after their nominal conversion to Christianity. Nursing a hatred of the upper class, which, with Frankish assistance, had marginalised them from political power, the lower classes (the ''plebeium vulgus'' or ''cives'') were a problem for Christian authorities as late as 836. The ''Translatio S.Liborii'' remarks on their obstinacy in pagan ''ritus et superstitio'' (usage and superstition).
Christianity
 The conversion of the Saxons in England from their original Germanic paganism, Germanic religion to
The conversion of the Saxons in England from their original Germanic paganism, Germanic religion to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
occurred in the early to late seventh century under the influence of the already converted Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
of Kingdom of Kent, Kent. In the 630s, Birinus became the "apostle to the West Saxons" and converted Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
, whose first Christian king was Cynegils. The West Saxons begin to emerge from obscurity only with their conversion to Christianity and keeping written records. The Gewisse, a West Saxon people, were especially resistant to Christianity; Birinus exercised more efforts against them and ultimately succeeded in conversion. In Wessex, Bishop of Winchester, a bishopric was founded at Dorchester, Oxfordshire, Dorchester. The South Saxons were first evangelised extensively under England, Anglian influence; Aethelwalh of Sussex was converted by Wulfhere of Mercia, Wulfhere, King of Mercia and allowed Wilfrid, Archbishop of York, Bishop of York, to evangelise his people beginning in 681. The chief South Saxon bishopric was Bishop of Selsey, that of Selsey. The Kingdom of Essex, East Saxons were more pagan than the southern or western Saxons; their territory had a superabundance of pagan sites. Their king, Saebert of Essex, Saeberht, was converted early and a diocese was established at Diocese of London, London. Its first bishop, Mellitus, was expelled by Saeberht's heirs. The conversion of the East Saxons was completed under Cedd in the 650s and 660s.
The continental Saxons were evangelised largely by English missionaries in the late seventh and early eighth centuries. Around 695, two early English missionaries, Hewald the White and Hewald the Black, were martyred by the ''vicani'', that is, villagers. Throughout the century that followed, villagers and other peasants proved to be the greatest opponents of Christianisation, while missionaries often received the support of the ''edhilingui'' and other noblemen. Saint Lebuin, an Englishman who between 745 and 770 preached to the Saxons, mainly in the eastern Netherlands, built a church and made many friends among the nobility. Some of them rallied to save him from an angry mob at the annual council at Marklo (near river Weser, Bremen). Social tensions arose between the Christianity-sympathetic noblemen and the pagan lower castes, who were staunchly faithful to their traditional religion.
Under Charlemagne, the Saxon Wars had as their chief object the conversion and integration of the Saxons into the Frankish empire. Though much of the highest caste converted readily, forced baptisms and forced tithing made enemies of the lower orders. Even some contemporaries found the methods employed to win over the Saxons wanting, as this excerpt from a letter of Alcuin of York to his friend Meginfrid, written in 796, shows:
If the light yoke and sweet burden of Christ were to be preached to the most obstinate people of the Saxons with as much determination as the payment of tithes has been exacted, or as the force of the legal decree has been applied for fault of the most trifling sort imaginable, perhaps they would not be averse to their baptismal vows.Charlemagne's successor, Louis the Pious, reportedly treated the Saxons more as Alcuin would have wished, and as a consequence they were faithful subjects. The lower classes, however, revolted against Frankish overlordship in favour of their old paganism as late as the 840s, when the ''Stellinga'' rose up against the Saxon leadership, who were allied with the Frankish emperor Lothair I. After the suppression of the ''Stellinga'', in 851 Louis the German brought relics from Rome to Saxony to foster a devotion to the Roman Catholic Church. The Poeta Saxo, in his verse ''Annales'' of Charlemagne's reign (written between 888 and 891), laid an emphasis on his conquest of Saxony. He celebrated the Frankish monarch as on par with the Roman emperors and as the bringer of Christian salvation to people. References are made to periodic outbreaks of pagan worship, especially of Freya, among the Saxon peasantry as late as the 12th century.
=Christian literature
= In the ninth century, the Saxon nobility became vigorous supporters of monasticism and formed a bulwark of Christianity against the existing Slavic paganism to the east and the Nordic paganism of the Vikings to the north. Much Christian literature was produced in the vernacular Old Saxon, the notable ones being a result of the literary output and wide influence of Saxon monasteries such as Abbey of Fulda, Fulda, Abbey of Corvey, Corvey and Verden an der Aller, Verden; and the theological controversy between the Augustine of Hippo, Augustinian, Gottschalk (theologian), Gottschalk and Rabanus Maurus. From an early date, Charlemagne and Louis the Pious supported Christian vernacular literature, vernacular works in order to evangelise the Saxons more efficiently. The ''Heliand'', a verse epic of the life of Christ in a Germanic setting, and ''Genesis'', another epic retelling of the events of Book of Genesis, the first book of the Bible, were commissioned in the early ninth century by Louis to disseminate scriptural knowledge to the masses. A council of Tours in 813 and then a synod of Mainz in 848 both declared that Homily, homilies ought to be preached in the vernacular. The earliest preserved text in the Saxon language is a baptismal vow from the late eighth or early ninth century; the vernacular was used extensively in an effort to Christianise the lowest castes of Saxon society.Hummer, 138–139.See also
* List of Germanic tribesNotes
References
* Bernard Bachrach, Bachrach, Bernard S. ''Merovingian Military Organisation, 481–751''. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1971. * Goldberg, Eric J"Popular Revolt, Dynastic Politics, and Aristocratic Factionalism in the Early Middle Ages: The Saxon Stellinga Reconsidered."
''Speculum (journal), Speculum'', Vol. 70, No. 3. (Jul., 1995), pp. 467–501. * Hummer, Hans J. ''Politics and Power in Early Medieval Europe: Alsace and the Frankish Realm 600–1000''. Cambridge University Press: 2005. * Timothy Reuter, Reuter, Timothy. ''Germany in the Early Middle Ages 800–1056''. New York: Longman, 1991. * Reuter, Timothy (trans.)
The Annals of Fulda
'. (Manchester Medieval series, Ninth-Century Histories, Volume II.) Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1992. * * Frank Stenton, Stenton, Sir Frank M. ''Anglo-Saxon England''. third ed. Oxford University Press, 1971. * John Michael Wallace-Hadrill, Wallace-Hadrill, J. M., translator.
The Fourth Book of the Chronicle of Fredegar with its Continuations
'. Connecticut: Greenwood Press, 1960. * James Westfall Thompson, Thompson, James Westfall. ''Feudal Germany''. 2 vol. New York: Frederick Ungar Publishing Co., 1928.
External links
James Grout: ''Saxon Advent'', part of the Encyclopædia Romana
Saxons and Britons
* {{Authority control Saxons, History of North Rhine-Westphalia Early Germanic peoples German tribes Ingaevones