RWE -Tower Dortmund.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
RWE AG is a German multinational
 In 2011, RWE unbundled its transmission system by selling its majority stake in the transmission system operator Amprion (RWE Transportnetz Strom GmbH), but keeping 25.1% in the company.
On 14 August 2012, RWE AG announced that the company would cut 2,400 more jobs to reduce costs. Previously the company had announced to eliminate 5,000 jobs and 3,000 jobs through divestments as anticipated of closing all nuclear reactors by 2022.
In August 2013, RWE completed the disposal of NET4GAS, the Czech gas transmission network operator, for €1.6billion to a consortium consisting of Allianz and
In 2011, RWE unbundled its transmission system by selling its majority stake in the transmission system operator Amprion (RWE Transportnetz Strom GmbH), but keeping 25.1% in the company.
On 14 August 2012, RWE AG announced that the company would cut 2,400 more jobs to reduce costs. Previously the company had announced to eliminate 5,000 jobs and 3,000 jobs through divestments as anticipated of closing all nuclear reactors by 2022.
In August 2013, RWE completed the disposal of NET4GAS, the Czech gas transmission network operator, for €1.6billion to a consortium consisting of Allianz and
RWE aims to be carbon neutral by 2040
''
 RWE operates in Asia-Pacific, Europe and the United States. The group is organized around four core areas:
* Offshore Wind
* Onshore Wind/Solar
* Hydro/Biomass/Gas
* Supply & Trading
In addition to these core areas, there is a Coal/Nuclear segment.
In the UK, RWE fully owns RWE Generation UK plc., which operates a number of natural gas and renewable energy power stations across the UK. RWE's last coal-fired power station in the UK,
RWE operates in Asia-Pacific, Europe and the United States. The group is organized around four core areas:
* Offshore Wind
* Onshore Wind/Solar
* Hydro/Biomass/Gas
* Supply & Trading
In addition to these core areas, there is a Coal/Nuclear segment.
In the UK, RWE fully owns RWE Generation UK plc., which operates a number of natural gas and renewable energy power stations across the UK. RWE's last coal-fired power station in the UK,
 RWE has long been among the top targets of climate activists, in part as a result of a long-running, high-profile battle to preserve a forest in western Germany that is threatened by the planned expansion of one of the group's
RWE has long been among the top targets of climate activists, in part as a result of a long-running, high-profile battle to preserve a forest in western Germany that is threatened by the planned expansion of one of the group's
PDF
of the EU to the
energy company
The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy ind ...
headquartered in Essen. It generates and trades electricity in Asia-Pacific, Europe and the United States. The company is Europe's most climate threatening Company, the world's number two in offshore wind power
Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. There are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of c ...
and Europe's third largest in renewable energy. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, RWE Group was ranked as the 297th -largest public company in the world.
RWE confirmed in December 2015, that it would separate its renewable energy generation, power grid and retail operations into a separate company, Innogy SE, during 2016, and sell a 10% holding in the business through an initial public offering
An initial public offering (IPO) or stock launch is a public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also to retail (individual) investors. An IPO is typically underwritten by one or more investme ...
. The restructuring was caused by an effort to reduce the group's exposure to nuclear decommissioning costs, required due to a German government policy of closing all nuclear power stations by 2022.
In July 2019, RWE's handling of the conflict with activists in the Hambach Forest
Hambach Forest (german: Hambacher Wald, Hambacher Forst (), Bürgewald, Die Bürge) is an ancient forest located near in North Rhine-Westphalia, western Germany, between Cologne and Aachen. It was planned to be cleared as part of the Hambach ...
were strongly criticized in the media. The company finally agreed to refrain from clearing the forest until autumn 2020.
In July 2020, RWE completed a far-reaching asset swap deal with E.ON first announced in 2018, whereby the international renewable generation portfolio of E.ON and Innogy were transferred to RWE.
History
Pre-World War I
The company was founded in Essen in 1898, as Rheinisch-Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk Aktiengesellschaft (Rhenish-Westphalian Power Plant) by Elektrizitäts-Actien-Gesellschaft vorm. W. Lahmeyer & Company (EAG) and others. The full name was used until 1990 when it was renamed to RWE AG. Its first power station started operating in Essen in 1900. In 1902, EAG sold its shares to a consortium formed by Ruhr industrialistsHugo Stinnes
Hugo Dieter Stinnes (12 February 1870 – 10 April 1924) was a German industrialist and politician. During the late era of the German Empire and early Weimar Republic, he was considered to be one of the most influential entrepreneurs in Europe.
...
and August Thyssen.
In 1906, it expanded its operations beyond Essen by acquiring Elektrizitätswerk Berggeist AG in Brühl, and Bergische Elektrizitätswerke GmbH, Solingen
Solingen (; li, Solich) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located some 25 km east of Düsseldorf along the northern edge of the region called Bergisches Land, south of the Ruhr area, and, with a 2009 population of 161,366 ...
. During the same year, it also acquired shareholdings in the tramway companies Bochum-Gelsenkirchener Straßenbahn AG and Rheinische Bahngesellschaft AG.
In 1908, RWE signed demarcation contracts with Städtische Elektrizitätswerk Dortmund and Elektrizitätswerk Westfalen AG. Together they created Westfälische Verbands-Elektrizitätswerk AG. RWE contributed to the newly established company by its power station in Dortmund–Kruckel and the supply grid in Witten/Dortmund. Later all these companies formed Vereinigte Elektrizitätswerke Westfalen AG (VEW).
In 1909, RWE opened the Reisholz Power Plant and acquired a stake in the tram company Süddeutsche Eisenbahngesellschaft AG. RWE also started to build its own gas supply network in 1909. Deliveries of coal gas to the Bergisches Land region started in 1912. In 1914, RWE opened Vorgebirgszentrale power plant in Hürth
Hürth is a town in the Rhein-Erft-Kreis, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Hürth shares borders with the city of Cologne and is about 6 km to the southwest of Cologne city centre, at the northeastern slope of the natural preserve Kott ...
. By 1920, the plant had installed capacity of 190 megawatts, which made it the largest in Europe.
Before World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, municipalities of Essen, Mülheim an der Ruhr, and Gelsenkirchen, became shareholders in RWE. By the 1920s, Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ru ...
, Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
, Krefeld
Krefeld ( , ; li, Krieëvel ), also spelled Crefeld until 1925 (though the spelling was still being used in British papers throughout the Second World War), is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located northwest of Düsseldorf, i ...
, Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in No ...
, and Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf ( , , ; often in English sources; Low Franconian and Ripuarian language, Ripuarian: ''Düsseldörp'' ; archaic nl, Dusseldorp ) is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second- ...
also became shareholders and municipalities owned the majority of RWE's shares. In 1925, the Prussian state
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
became a shareholder in RWE. In 1929, municipalities and the Rhine Province combined their shareholdings into a holding company Kommunale Aufnahmegruppe für Aktien GmbH.
Interwar years and World War II
In 1920, RWE acquired Niedersächsische Kraftwerke AG, located inOsnabrück
Osnabrück (; wep, Ossenbrügge; archaic ''Osnaburg'') is a city in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population ...
. In 1922, it expanded its coal business by acquiring three anthracite mines in Essen and a majority stake in the lignite company Braunkohlen- und Briketwerke Roddergrube AG. In 1923, it acquired its founder company EAG. Three years later, the company acquired a stake in Rheinische Elektrizitäts-Aktiengesellschaft (Rheinelektra) and became a shareholder in the newly established Ruhrgas
Ruhrgas AG (original name: Aktiengesellschaft für Kohleverwertung; later: E.ON Ruhrgas) was the largest natural gas transportation and trading company based in Essen, Germany. The company was founded in 1926 and it finally ceased to exist on 2 Ma ...
gas company in exchange of its gas grid. In 1927, RWE and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
swapped their holdings in the Brunswick and Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
coalfields and RWE became an owner of Braunkohlen-Industrie AG Zukunft.
In 1932, RWE acquired a majority stake in the coal company Rheinische Aktiengesellschaft für Braunkohlenbergbau (Rheinbraun). In 1936, it acquired Niederrheinische Braunkohlenwerke AG, an operator of the Frimmersdorf Power Plant
Frimmersdorf Power Station, located in Grevenbroich, is a decommissioned lignite-fired power station in Germany. The power station was one of the largest lignite-fired power stations in Germany. It had fourteen units with a total output capacit ...
.
On 1 May 1933, the executive board including Ernst Henke joined the NSDAP
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
as a unified body.
Since autumn 1943, the Essen state police had been investigating Wilhelm Ricken, RWE's technical director and designated general director, for "subversion of the military". The then First Mayor of Essen, Just Dillgardt, who was also second chairman of RWE's supervisory board, had reported Ricken to the state police. Previously, he had received a tip from the then commercial director and fellow board member of Ricken, Friedrich Praedel. This "board member" of RWE is said to have pushed Dillgardt to press charges. Wilhelm Ricken was then arrested on 20 October 1943, and sentenced to death on 8 March 1944, by the Volksgerichtshof (People's Court), partly because of his statement that "the war would end like 1918". On 2 May 1944, Wilhelm Ricken was executed in Berlin-Plötzensee.
In 2015, a " stumbling block" was placed at this final address in Essen to commemorate Ricken's fate.
Developments since World War II
During World War II, the infrastructure owned by RWE was severely damaged but mostly repaired by 1948. In 1952, the company was excluded from the Allies' control. In 1957, RWE acquired the coal company Neurath AG. RWE and the Bavarian state-owned 'Bayernwerk' joined forces to build Germany's first industrialnuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat fr ...
. The Kahl experimental nuclear power plant (15 megawatts), constructed right next to RWE's Dettingen hard coal fired power plant, supplied its first electricity in 1962. Until its closure in 1985, this plant would serve as a source of important findings which supported the design and operation of commercial nuclear reactors.
RWE's nuclear operations started in 1961, when RWE and Bayernwerk (now part of E.ON) started to build the first German industrial nuclear reactor—the Kahl Nuclear Power Plant
The Kahl plant was the first nuclear power plant ever to be built in Germany. It was located in Karlstein am Main and was an (at the time) experimental boiling water reactor. It was built by General Electric and supplied by Siemens. At the end o ...
. In 1962, they started to build the Gundremmingen Nuclear Power Plant. In 1965, at the request of the surrounding municipalities, the Karnap power plant in Essen started to burn domestic waste.
In 1969, RWE acquired a stake in ''Gelsenkirchener Bergwerks-Aktiengesellschaft'' which allowed its expansion into the oil industry. However, in 1974, it was sold to VEBA AG.
In 1971, founded ''Gesellschaft für elektrischen Straßenverkehr'', a company to develop an electric car for commercial scale production. The prototype presented in 1983 was produced in cooperation with Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
and named City-Stromer.
In 1988, RWE again expanded into the oil industry by acquiring Deutsche Texaco, formerly known as Deutsche Erdoel AG, which was renamed RWE-DEA AG für Mineralöl und Chemie (RWE-DEA). RWE was reorganized to hold energy, mining and raw materials; petroleum and chemicals; waste management; mechanical and plant engineering; and construction divisions.
In the 1990s, RWE acquired a number of assets in the former East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
, including stakes in the mining company Lausitzer Braunkohle AG (LAUBAG) and the power company VEAG. In 2000, RWE and VEW merged to create a "new" RWE, and stakes in LAUBAG and VEAG (now both merged into Vattenfall Europe
Vattenfall is a Swedish multinational power company owned by the Swedish State. Beyond Sweden, the company generates power in Denmark, Finland, Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom.
The company's name is Swedish for "waterfall", and ...
) were sold to avoid competition violation.
In 2001, RWE took over the British company Thames Water
Thames Water Utilities Ltd, known as Thames Water, is a large private utility company responsible for the public water supply and waste water treatment in most of Greater London, Luton, the Thames Valley, Surrey, Gloucestershire, north Wiltsh ...
. In 2002, it acquired American Water Works Company, based in New Jersey, which became a subsidiary of Thames Water. In 2006, RWE sold Thames Water to Kemble Water Limited, a consortium led by Macquarie Group. RWE previously owned American Water, the United States' largest investor-owned water utility, but this was divested in 2008.
In 2002, RWE acquired the British electricity and gas utility company Innogy for £3 billion (US$4.3 billion). Innogy was subsequently renamed RWE npower plc.
As a result of the assets swap with RAG AG
RAG AG, formerly Ruhrkohle AG, is the largest German coal mining corporation. The company headquarters are in Essen in the Ruhr area. The company was founded on 27 November 1968, consolidating several coalmining corporations into the Ruhrko ...
, RWE gave away its stake in the power company STEAG. It received almost full control of the renewable energy company Harpen AG. The full control of Harpen was achieved in 2005. In 2003, RWE also achieved full control over Thyssengas. In the same year, it decided to divest its American coal company Consol Energy
Consol Energy Inc. is an American energy company with interests in coal headquartered in the suburb of Cecil Township, in the Southpointe complex, just outside Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In 2017, Consol formed two separate entities: CNX Resour ...
.
 In 2011, RWE unbundled its transmission system by selling its majority stake in the transmission system operator Amprion (RWE Transportnetz Strom GmbH), but keeping 25.1% in the company.
On 14 August 2012, RWE AG announced that the company would cut 2,400 more jobs to reduce costs. Previously the company had announced to eliminate 5,000 jobs and 3,000 jobs through divestments as anticipated of closing all nuclear reactors by 2022.
In August 2013, RWE completed the disposal of NET4GAS, the Czech gas transmission network operator, for €1.6billion to a consortium consisting of Allianz and
In 2011, RWE unbundled its transmission system by selling its majority stake in the transmission system operator Amprion (RWE Transportnetz Strom GmbH), but keeping 25.1% in the company.
On 14 August 2012, RWE AG announced that the company would cut 2,400 more jobs to reduce costs. Previously the company had announced to eliminate 5,000 jobs and 3,000 jobs through divestments as anticipated of closing all nuclear reactors by 2022.
In August 2013, RWE completed the disposal of NET4GAS, the Czech gas transmission network operator, for €1.6billion to a consortium consisting of Allianz and Borealis
Borealis (Latin for ''northern'' or ''of the north'') may refer to:
Astronomy
* Borealis Basin or North Polar Basin, a basin on the planet Mars
* Borealis quadrangle, an area on the planet Mercury
** Borealis Planitia, a basin within the quadran ...
. The company (named Transgas A.S. then) was privatized to RWE in 2002. In the 2000s, RWE also acquired energy companies in Poland (STOEN S.A.) and Slovenia (VSE a.s).
It also owned RWE Dea (now DEA AG
DEA Deutsche Erdoel AG was an international oil and gas company headquartered in Hamburg, Germany. It was a subsidiary of L1 Energy. In 2018, DEA owned stakes in oil and gas licenses in various countries and operated natural gas underground storage ...
), which produced some of the oil and gas RWE sold (annual production is around 2 million m3 of crude oil (about 365,000 BOE) ) and 3 billion m3 of natural gas (about 18 million BOE, 49,300 BOE) a day. In March 2015, RWE closed the sale of RWE Dea to a group led by Russian billionaire Mikhail Fridman
Mikhail Maratovich Fridman (also transliterated Mikhail Friedman; russian: Михаил Маратович Фридман; he, מיכאיל פרידמן; born 21 April 1964) is a Ukrainian-born, Russian–Israeli businessman, billionaire, and ...
despite opposition from UK regulators. The $5.6 billion deal, announced in 2014, required approval from 14 countries where RWE Dea operates in Europe, the Middle East and Africa.
On 1 April 2016, RWE transferred its renewable, network and retail businesses into a separate company named Innogy
Innogy SE was an energy company based in Essen, Germany. It is now merged and integrated into German energy company E.ON.
History
The company was created on 1 April 2016, by splitting the renewable, network and retail businesses of RWE into ...
, which is listed at the Frankfurt Stock Exchange
The Frankfurt Stock Exchange (german: link=no, Börse Frankfurt, former German name – FWB) is the world's 12th largest stock exchange by market capitalization. It has operations from 8:00 am to 10:00 pm ( German time).
Organisation
Loca ...
.
The new entity combined RWE subsidiaries RWE Innogy, RWE Deutschland, RWE Effizienz, RWE Vertrieb and RWE Energiedienstleistungen.
In March 2018, it was announced that E.ON will acquire Innogy in a complex €43 billion deal of assets swap with RWE. As a result, RWE will take a 16.7% stake in E.ON.
Following the purchase of E.ON's renewables business and nuclear electricity generation assets, RWE is expected to become Europe's third-largest renewable energy provider behind Spain's Iberdrola
Iberdrola () is a Spanish multinational electric utility company based in Bilbao, Spain. Iberdrola has a workforce of around 34,000 employees serving around 31.67 million customers. Subsidiaries include Scottish Power (United Kingdom) ...
and Italy's Enel
Enel S.p.A. is an Italian multinational manufacturer and distributor of electricity and gas. Enel, which originally stood for Ente nazionale per l'energia elettrica (National Electricity Board), was first established as a public body at the ...
, and the second-largest in the market for offshore wind power.Tobias Buck (September 30, 2019)RWE aims to be carbon neutral by 2040
''
Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and published digitally that focuses on business and economic current affairs. Based in London, England, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Ni ...
''.
Financial data
Operations
Aberthaw Power Station
Aberthaw Power Station refers to two decommissioned coal-fired and co-fired biomass power stations on the coast of South Wales, near Barry in the Vale of Glamorgan. They were located at Limpert Bay, near the villages of Gileston and West Aberth ...
in South Wales, was closed in March 2020. The company owns the gas-fired power stations Staythorpe
Staythorpe is a hamlet and civil parish in the Newark and Sherwood district of Nottinghamshire, England. During the 2021 census, the population was recorded as 93 residents.
Geography
The settlement is situated 3 miles west of Newark-on-Trent ...
in Nottinghamshire, Pembroke in West Wales, Little Barford
Little Barford is a hamlet and civil parish in the Borough of Bedford in Bedfordshire, England about northeast of the county town of Bedford.
The 2011 census combines other data for Little Barford with Wyboston, Chawston and Colesden civil par ...
in Bedfordshire, Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, and Didcot 'B' Station in Oxfordshire. It has previously closed its Didcot 'A' Power Station in Oxfordshire, Littlebrook Power Station
The Littlebrook Power Station were a series of four oil and coal-fired power stations situated on the south bank of the River Thames, next to the Queen Elizabeth 2 Bridge and the Dartford Tunnel in Dartford, Kent. The final power station, Li ...
in Kent, Fawley Power Station
Fawley Power Station was an oil-fired power station located on the western side of Southampton Water, between the villages of Fawley and Calshot in Hampshire, England. Its chimney was a prominent (and navigationally useful) landmark, but it ...
in Hampshire, and Tilbury Power Station in Essex.
RWE jointly owns one third of the Urenco Group
The Urenco Group is a British-German-Dutch nuclear fuel consortium operating several uranium enrichment plants in Germany, the Netherlands, United States, and United Kingdom. It supplies nuclear power stations in about 15 countries, and sta ...
with E.ON. The remaining stakes are held by the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
governments, with one-third each.
Fuel mix disclosure
In 2019, RWE produced a total of 153.2 TWh of electricity from the following sources: 33.2%natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, 32% lignite, 13.8% nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
, 10.7% renewables
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
, 9.3% hard coal and 1.2% pumped storage
Pumping may refer to:
* The operation of a pump, for moving a liquid from one location to another
**The use of a breast pump for extraction of milk
* Pumping (audio), a creative misuse of dynamic range compression
* Pumping (computer systems), th ...
. In 2019, the company generated 88.1 Mt of CO2. Electricity production at the German branch of RWE had the following environmental implications in 2006: 700 μg/kWh radioactive waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons r ...
and 752 g/kWh emissions. In 2007, the company ranked between the 28th and the 29th place of emitters by country.
Criticism and controversies

 RWE has long been among the top targets of climate activists, in part as a result of a long-running, high-profile battle to preserve a forest in western Germany that is threatened by the planned expansion of one of the group's
RWE has long been among the top targets of climate activists, in part as a result of a long-running, high-profile battle to preserve a forest in western Germany that is threatened by the planned expansion of one of the group's coal mine
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
s. RWE also operates some of the largest coal-fired power stations in Europe.
In 2018, RWE was the largest producer of carbon dioxide emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and la ...
in Europe.
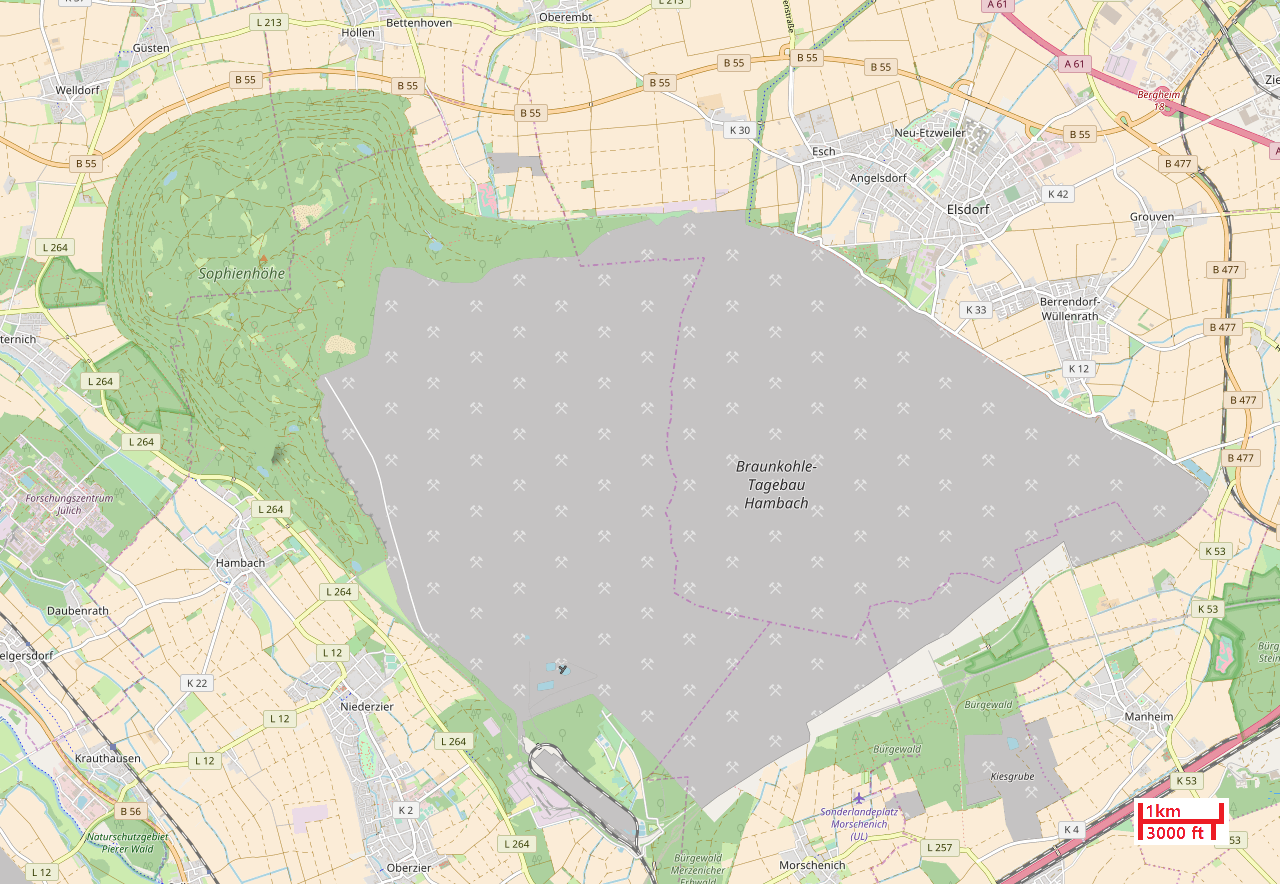
Since 2012, environmentalists have protested against RWE because of the Hambach surface mine
The Tagebau Hambach is a large open-pit coal mine (german: Tagebau) in Niederzier and Elsdorf, North Rhine–Westphalia, Germany. It is operated by RWE and used for mining lignite.
The mine is on the site of the ancient Hambach Forest, w ...
situated in the area of Hambach Forest
Hambach Forest (german: Hambacher Wald, Hambacher Forst (), Bürgewald, Die Bürge) is an ancient forest located near in North Rhine-Westphalia, western Germany, between Cologne and Aachen. It was planned to be cleared as part of the Hambach ...
. In November 2017, in the lawsuit filed by ''Bund für Umwelt und Naturschutz Deutschland
Bund für Umwelt und Naturschutz Deutschland (; BUND, ) is a German non-governmental organisation (NGO) dedicated to preserving nature and protecting the environment. The name means "German Federation for the Environment and Nature Conservation". ...
'' (BUND), the German arm of Friends of the Earth, the Higher Administrative Court in Münster
Münster (; nds, Mönster) is an independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a state di ...
ruled to end the tree cutting. According to BUND, Hambach Forest is a habitat type 9160 of annex I of the European Habitats Directive
The Habitats Directive (more formally known as Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the Conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora) is a directive adopted by the European Community in 1992 as a response to the Berne Convention. The E ...
(Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992).
Opponents also argue that an environmental impact assessment study for the mine was never conducted. The Administrative Court in Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
denied the necessity of such a study in November 2017, because the permission for the mining operations was given in the 1970s, long before environmental impact assessment studies became mandatory. In October 2018, an estimated 50,000 protesters turned out against the company's planned continued forest clear-cutting for its open-pit coal mine expansion while a court order delayed the process until at least late 2020, to explore if it violated EU environmental regulations.
In September 2021, it was revealed that RWE are among a number of fossil fuel companies suing governments for enacting green policies against climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. RWE are suing the Dutch government for $1.6bn following their move to phase out and shut down coal power plants.
Sponsorship
Between 2001 and 2007, RWE was the main kit sponsor of GermanBundesliga
The Bundesliga (; ), sometimes referred to as the Fußball-Bundesliga () or 1. Bundesliga (), is a professional association football league in Germany. At the top of the German football league system, the Bundesliga is Germany's primary footba ...
club Bayer 04 Leverkusen.
See also
* Gesellschaft für Nuklear-Service * Rheinisches BraunkohlerevierReferences
Further reading
* Energy in South East Europe: Corporate Profiles on major investment firms in South East Europe (April 2004)of the EU to the
2004 enlargement of the European Union
The largest expansion of the European Union (EU), in terms of territory, number of states, and population took place on 1 May 2004.
The simultaneous accessions concerned the following countries (sometimes referred to as the "A10" countries): ...
.
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Rwe Companies based in Essen Companies listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange Electric power companies of Germany Nuclear power companies of Germany Public utilities established in 1898 German brands 1898 establishments in Germany Multinational companies headquartered in Germany Coal companies of Germany