PCS pool cover.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose
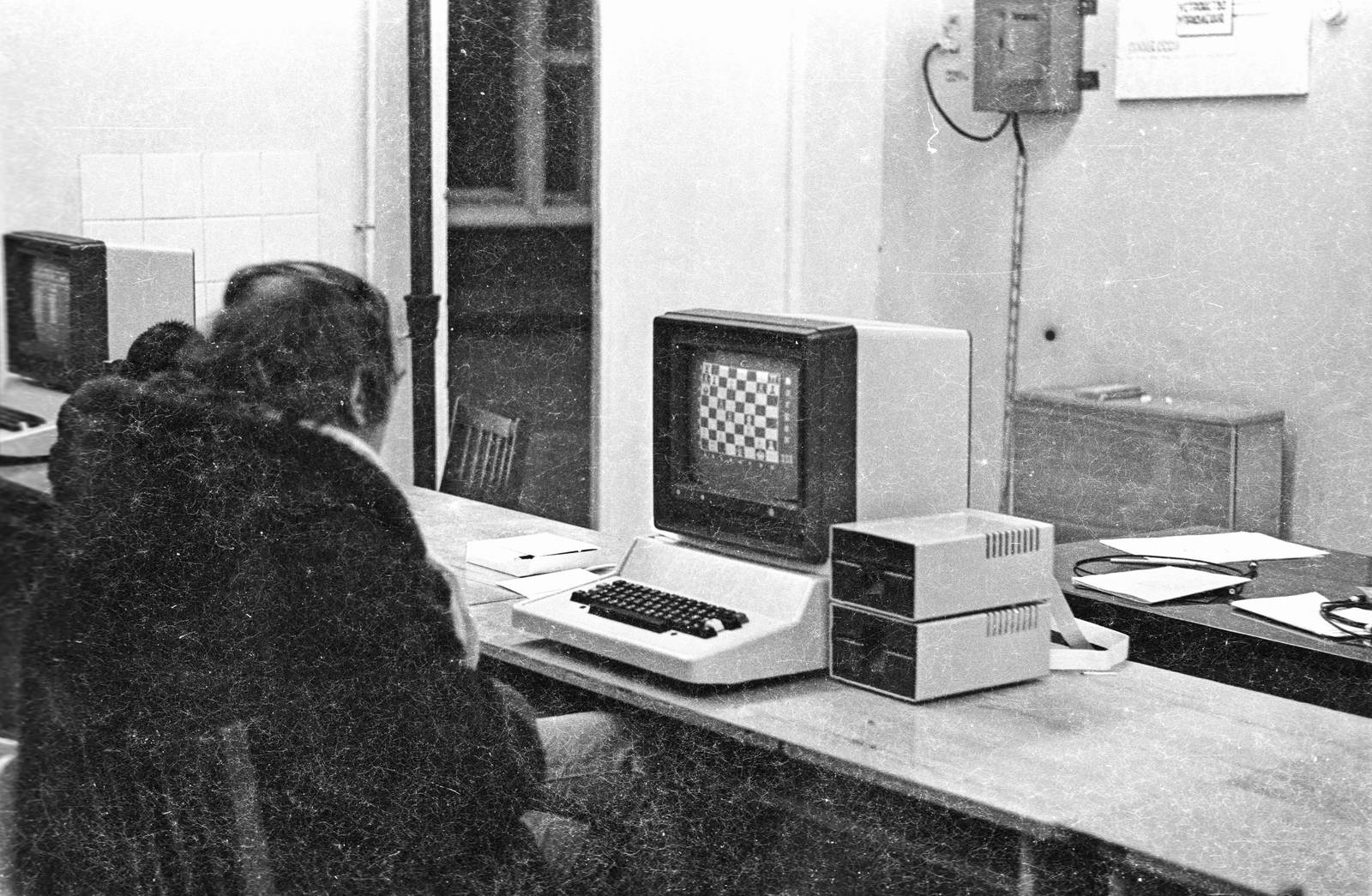
 In the history of computing, early experimental machines could be operated by a single attendant. For example, ENIAC which became operational in 1946 could be run by a single, albeit highly trained, person. This mode pre-dated the batch programming, or time-sharing modes with multiple users connected through terminals to mainframe computers. Computers intended for laboratory, instrumentation, or engineering purposes were built, and could be operated by one person in an interactive fashion. Examples include such systems as the Bendix G15 and LGP-30 of 1956, and the Soviet MIR series of computers developed from 1965 to 1969. By the early 1970s, people in academic or research institutions had the opportunity for single-person use of a computer system in interactive mode for extended durations, although these systems would still have been too expensive to be owned by a single person.
The personal computer was made possible by major advances in semiconductor technology. In 1959, the silicon
In the history of computing, early experimental machines could be operated by a single attendant. For example, ENIAC which became operational in 1946 could be run by a single, albeit highly trained, person. This mode pre-dated the batch programming, or time-sharing modes with multiple users connected through terminals to mainframe computers. Computers intended for laboratory, instrumentation, or engineering purposes were built, and could be operated by one person in an interactive fashion. Examples include such systems as the Bendix G15 and LGP-30 of 1956, and the Soviet MIR series of computers developed from 1965 to 1969. By the early 1970s, people in academic or research institutions had the opportunity for single-person use of a computer system in interactive mode for extended durations, although these systems would still have been too expensive to be owned by a single person.
The personal computer was made possible by major advances in semiconductor technology. In 1959, the silicon  1974 saw the introduction of what is considered by many to be the first true "personal computer", the
1974 saw the introduction of what is considered by many to be the first true "personal computer", the  The first successfully mass-marketed personal computer to be announced was the Commodore PET after being revealed in January 1977. However, it was back-ordered and not available until later that year. Commodore press release. "The PET computer made its debut recently as the first 100 units were shipped to waiting customers in mid-October 1977." Three months later (April), the
The first successfully mass-marketed personal computer to be announced was the Commodore PET after being revealed in January 1977. However, it was back-ordered and not available until later that year. Commodore press release. "The PET computer made its debut recently as the first 100 units were shipped to waiting customers in mid-October 1977." Three months later (April), the 
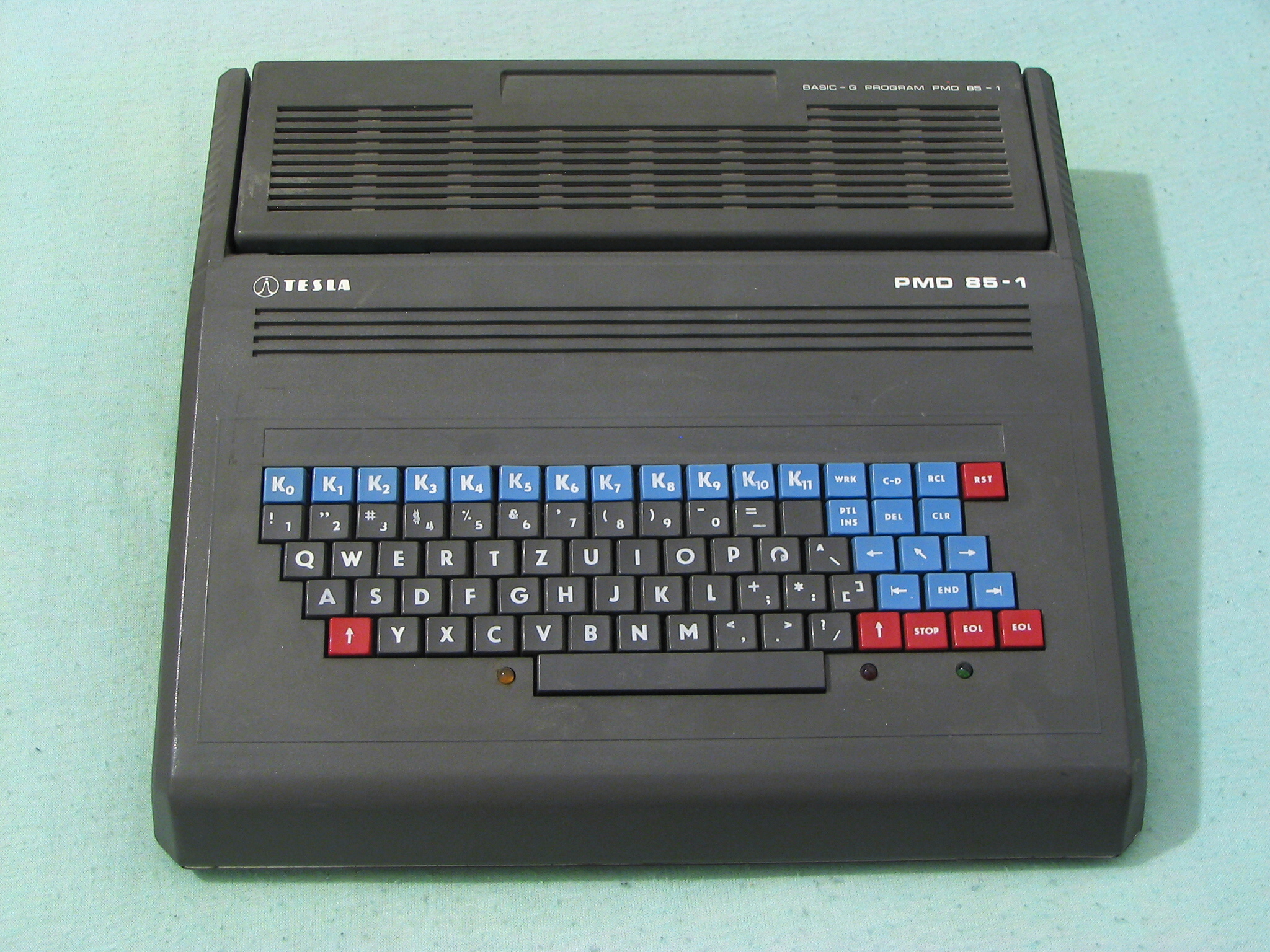 During the early 1980s, home computers were further developed for household use, with software for personal productivity, programming and games. They typically could be used with a television already in the home as the computer display, with low-detail blocky graphics and a limited color range, and text about 40 characters wide by 25 characters tall. Sinclair Research, a UK company, produced the ZX Seriesthe ZX80 (1980), ZX81 (1981), and the ZX Spectrum; the latter was introduced in 1982, and totaled 8 million unit sold. Following came the
During the early 1980s, home computers were further developed for household use, with software for personal productivity, programming and games. They typically could be used with a television already in the home as the computer display, with low-detail blocky graphics and a limited color range, and text about 40 characters wide by 25 characters tall. Sinclair Research, a UK company, produced the ZX Seriesthe ZX80 (1980), ZX81 (1981), and the ZX Spectrum; the latter was introduced in 1982, and totaled 8 million unit sold. Following came the
 A workstation is a high-end personal computer designed for technical, mathematical, or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. Workstations are used for tasks such as
A workstation is a high-end personal computer designed for technical, mathematical, or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. Workstations are used for tasks such as
 Before the widespread use of PCs, a computer that could fit on a desk was remarkably small, leading to the "desktop" nomenclature. More recently, the phrase usually indicates a particular style of computer case. Desktop computers come in a variety of styles ranging from large vertical
Before the widespread use of PCs, a computer that could fit on a desk was remarkably small, leading to the "desktop" nomenclature. More recently, the phrase usually indicates a particular style of computer case. Desktop computers come in a variety of styles ranging from large vertical
 The potential utility of portable computers was apparent early on. Alan Kay described the Dynabook in 1972, but no hardware was developed. The
The potential utility of portable computers was apparent early on. Alan Kay described the Dynabook in 1972, but no hardware was developed. The
 A
A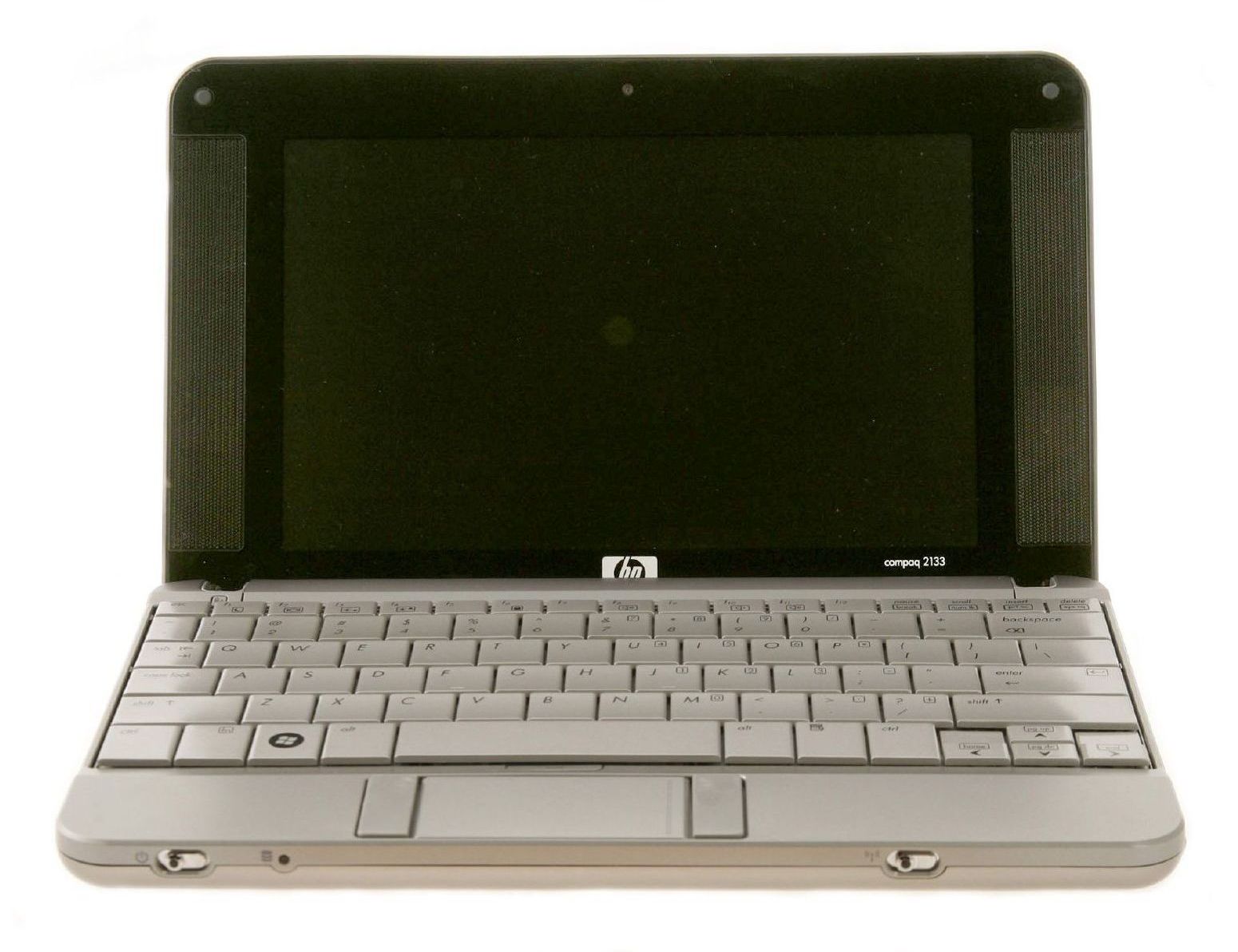 
 A
A
 Smartphones are often similar to tablet computers, the difference being that smartphones always have
Smartphones are often similar to tablet computers, the difference being that smartphones always have

 Computer software is any kind of computer program,
Computer software is any kind of computer program,  Software applications are common for word processing, Internet browsing, Internet faxing, e-mail and other digital messaging, multimedia playback, playing of
Software applications are common for word processing, Internet browsing, Internet faxing, e-mail and other digital messaging, multimedia playback, playing of
ImageSize=width:375 height:350
PlotArea=left:60 bottom:51 top:10 right:16
AlignBars=justify
Period=from:0 till:400
TimeAxis=orientation:horizontal
Colors=
id:gray value:gray(0.5)
id:line1 value:gray(0.9)
id:line2 value:gray(0.7)
ScaleMajor=unit:year increment:50 start:0 gridcolor:line2
ScaleMinor=unit:year increment:50 start:0 gridcolor:line1
BarData=
bar:1996 text:1996
bar:1997 text:1997
bar:1998 text:1998
bar:1999 text:1999
bar:2000 text:2000
bar:2001 text:2001
bar:2002 text:2002
bar:2003 text:2003
bar:2004 text:2004
bar:2005 text:2005
bar:2006 text:2006
bar:2007 text:2007
bar:2008 text:2008
bar:2009 text:2009
bar:2010 text:2010
bar:2011 text:2011
bar:2012 text:2012
bar:2013 text:2013
bar:2014 text:2014
bar:2015 text:2015
bar:2016 text:2016
bar:2017 text:2017
PlotData=
color:tan1 width:10
bar:1996 from:start till:70.90000 text:70.9 million
bar:1997 from:start till:80.60000 text:80.6 million
bar:1998 from:start till:92.90000 text:92.9 million
bar:1999 from:start till:113.500000 text:113.5 million
bar:2000 from:start till:134.700000 text:134.7 million
bar:2001 from:start till:128.10000 text:128.1 million
bar:2002 from:start till:132.40000 text:132.4 million
bar:2003 from:start till:168.90000 text:168.9 million
bar:2004 from:start till:189.0000 text:189 million
bar:2005 from:start till:218.50000 text:218.5 million
bar:2006 from:start till:239.4 text:239.4 million
bar:2007 from:start till:271.20000 text:271.2 million
bar:2008 from:start till:290.80000 text:290.8 million
bar:2009 from:start till:308.30000 text:308.3 million
bar:2010 from:start till:350.90000 text:350.9 million
bar:2011 from:start till:365.400000 text:365.4 million
bar:2012 from:start till:351.100000 text:351.1 million
bar:2013 from:start till:316.50000 text:316.5 million
bar:2014 from:start till:313.70000 text:313.7 million
bar:2015 from:start till:287.70000 text:287.7 million
bar:2016 from:start till:269.70000 text:269.7 million
bar:2017 from:start till:259.40000 text:259.4 million
TextData=
pos:(70,20) textcolor:gray fontsize:S text:Worldwide PC sales
TextData=
pos:(70,5) textcolor:gray fontsize:S text:(1996–2017)
 In 2001, 125 million personal computers were shipped in comparison to 48,000 in 1977. More than 500 million personal computers were in use in 2002 and one billion personal computers had been sold worldwide from the mid-1970s up to this time. Of the latter figure, 75% were professional or work related, while the rest were sold for personal or home use. About 81.5% of personal computers shipped had been
In 2001, 125 million personal computers were shipped in comparison to 48,000 in 1977. More than 500 million personal computers were in use in 2002 and one billion personal computers had been sold worldwide from the mid-1970s up to this time. Of the latter figure, 75% were professional or work related, while the rest were sold for personal or home use. About 81.5% of personal computers shipped had been
Jan 13, 2011, retrieved at September 12, 2011 308.3 million units in 2009
May 27, 2010, Andy Patrizio, earthweb.com, retrieved at September 12, 2011 and 302.2 million units in 2008.Worldwide PC Shipments in 2008
March 16, 2009, ZDNet, retrieved at September 12, 2011
January 14, 2009, Andy Patrizio, internetnews.com, retrieved at September 12, 2011 The shipments were 264 million units in the year 2007, according to iSuppli, up 11.2% from 239 million in 2006. In 2004, the global shipments were 183 million units, an 11.6% increase over 2003. In 2003, 152.6 million computers were shipped, at an estimated value of $175 billion. In 2002, 136.7 million PCs were shipped, at an estimated value of $175 billion. In 2000, 140.2 million personal computers were shipped, at an estimated value of $226 billion. Worldwide shipments of personal computers surpassed the 100-million mark in 1999, growing to 113.5 million units from 93.3 million units in 1998. In 1999, Asia had 14.1 million units shipped. As of June 2008, the number of personal computers in use worldwide hit one billion, while another billion is expected to be reached by 2014. Mature markets like the United States, Western Europe and Japan accounted for 58% of the worldwide installed PCs. The emerging markets were expected to double their installed PCs by 2012 and to take 70% of the second billion PCs. About 180 million computers (16% of the existing installed base) were expected to be replaced and 35 million to be dumped into landfill in 2008. The whole installed base grew 12% annually. Based on International Data Corporation (IDC) data for Q2 2011, for the first time China surpassed US in PC shipments by 18.5 million and 17.7 million respectively. This trend reflects the rising of emerging markets as well as the relative stagnation of mature regions. In the developed world, there has been a vendor tradition to keep adding functions to maintain high prices of personal computers. However, since the introduction of the One Laptop per Child foundation and its low-cost XO-1 laptop, the computing industry started to pursue the price too. Although introduced only one year earlier, there were 14 million
Dissecting a PC
*
*
** How to Build a Computer *
Global archive with product data-sheets of PCs and Workstations
{{Authority control American inventions Classes of computers Home appliances Office equipment Time Person of the Year
 A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PC ...
whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user
In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrat ...
, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a class of smaller general purpose computers that developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, ...
s and mainframe
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise ...
s, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. Primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s, the term home computer was also used.
Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with the machines. While personal computer users may develop their own applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software (" freeware"), which is most often proprietary, or free and open-source software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source ...
, which is provided in "ready-to-run", or binary, form. Software for personal computers is typically developed and distributed independently from the hardware or operating system manufacturers. Many personal computer users no longer need to write their own programs to make any use of a personal computer, although end-user programming is still feasible. This contrasts with mobile systems, where software is often available only through a manufacturer-supported channel, and end-user program development may be discouraged by lack of support by the manufacturer.
Since the early 1990s, Microsoft operating systems and Intel hardware dominated much of the personal computer market, first with MS-DOS and then with Windows. Alternatives to Microsoft's Windows operating systems occupy a minority share of the industry. These include Apple's macOS and free and open-source
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source ...
Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux.
The advent of personal computers and the concurrent Digital Revolution have significantly affected the lives of people in all countries.
Terminology
The term "PC" is aninitialism
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in ''NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, as ...
for "personal computer". While the IBM Personal Computer incorporated the designation in its model name, the term originally described personal computers of any brand.
In some contexts, "PC" is used to contrast with "Mac", an Apple Macintosh computer. Since none of these Apple products were mainframes or time-sharing systems, they were all "personal computers" and not "PC" (brand) computers.
In 1995, a CBS segment on the growing popularity of PC reported "For many newcomers PC stands for Pain and Confusion".
History

 In the history of computing, early experimental machines could be operated by a single attendant. For example, ENIAC which became operational in 1946 could be run by a single, albeit highly trained, person. This mode pre-dated the batch programming, or time-sharing modes with multiple users connected through terminals to mainframe computers. Computers intended for laboratory, instrumentation, or engineering purposes were built, and could be operated by one person in an interactive fashion. Examples include such systems as the Bendix G15 and LGP-30 of 1956, and the Soviet MIR series of computers developed from 1965 to 1969. By the early 1970s, people in academic or research institutions had the opportunity for single-person use of a computer system in interactive mode for extended durations, although these systems would still have been too expensive to be owned by a single person.
The personal computer was made possible by major advances in semiconductor technology. In 1959, the silicon
In the history of computing, early experimental machines could be operated by a single attendant. For example, ENIAC which became operational in 1946 could be run by a single, albeit highly trained, person. This mode pre-dated the batch programming, or time-sharing modes with multiple users connected through terminals to mainframe computers. Computers intended for laboratory, instrumentation, or engineering purposes were built, and could be operated by one person in an interactive fashion. Examples include such systems as the Bendix G15 and LGP-30 of 1956, and the Soviet MIR series of computers developed from 1965 to 1969. By the early 1970s, people in academic or research institutions had the opportunity for single-person use of a computer system in interactive mode for extended durations, although these systems would still have been too expensive to be owned by a single person.
The personal computer was made possible by major advances in semiconductor technology. In 1959, the silicon integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
(IC) chip was developed by Robert Noyce
Robert Norton Noyce (December 12, 1927 – June 3, 1990), nicknamed "the Mayor of Silicon Valley", was an American physicist and entrepreneur who co-founded Fairchild Semiconductor in 1957 and Intel Corporation in 1968. He is also credited wit ...
at Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of int ...
, and the metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistor was developed by Mohamed Atalla
Mohamed M. Atalla ( ar, محمد عطاالله; August 4, 1924 – December 30, 2009) was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions to ...
and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs. The MOS integrated circuit was commercialized by RCA in 1964, and then the silicon-gate MOS integrated circuit was developed by Federico Faggin at Fairchild in 1968. Faggin later used silicon-gate MOS technology to develop the first single-chip microprocessor, the Intel 4004, in 1971. The first microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PC ...
s, based on microprocessors, were developed during the early 1970s. Widespread commercial availability of microprocessors, from the mid-1970s onwards, made computers cheap enough for small businesses and individuals to own.
In what was later to be called the Mother of All Demos
"The Mother of All Demos" is a name retroactively applied to a landmark computer demonstration, given at the Association for Computing Machinery / Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (ACM/IEEE)—Computer Society's Fall Joint Compu ...
, SRI researcher Douglas Engelbart
Douglas Carl Engelbart (January 30, 1925 – July 2, 2013) was an American engineer and inventor, and an early computer and Internet pioneer. He is best known for his work on founding the field of human–computer interaction, particularly ...
in 1968 gave a preview of features that would later become staples of personal computers: e-mail, hypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typi ...
, word processing, video conferencing, and the mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
. The demonstration required technical support staff and a mainframe time-sharing computer that were far too costly for individual business use at the time.
Early personal computersgenerally called microcomputerswere often sold in a kit
Kit may refer to:
Places
*Kitt, Indiana, US, formerly Kit
* Kit, Iran, a village in Mazandaran Province
* Kit Hill, Cornwall, England
People
* Kit (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Kit (surname)
Animals
* Young animals:
...
form and in limited volumes, and were of interest mostly to hobbyists and technicians. Minimal programming was done with toggle switches to enter instructions, and output was provided by front panel lamps. Practical use required adding peripherals such as keyboards, computer displays, disk drives, and printers.
Micral N
Micral is a series of microcomputers produced by the French company Réalisation d'Études Électroniques (:fr:R2E, R2E), beginning with the Micral N in early 1973. The Micral N was the first commercially available microprocessor-based computer.
...
was the earliest commercial, non-kit microcomputer based on a microprocessor, the Intel 8008. It was built starting in 1972, and a few hundred units were sold. This had been preceded by the Datapoint 2200 in 1970, for which the Intel 8008 had been commissioned, though not accepted for use. The CPU design implemented in the Datapoint 2200 became the basis for x86 architecture used in the original IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
and its descendants.
In 1973, the IBM Los Gatos Scientific Center developed a portable computer prototype called SCAMP (Special Computer APL Machine Portable) based on the IBM PALM processor with a Philips compact cassette drive, small CRT
CRT or Crt may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Medicine and biology
* Calreticulin, a protein
*Capillary refill time, for blood to refill capillaries
*Cardiac resynchronization therapy and CRT defibrillator (CRT-D)
* Catheter-re ...
, and full function keyboard. SCAMP emulated an IBM 1130 minicomputer in order to run APL/1130. In 1973, APL was generally available only on mainframe computers, and most desktop sized microcomputers such as the Wang 2200 or HP 9800 offered only BASIC
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ...
. Because SCAMP was the first to emulate APL/1130 performance on a portable, single user computer, ''PC Magazine
''PC Magazine'' (shortened as ''PCMag'') is an American computer magazine published by Ziff Davis. A print edition was published from 1982 to January 2009. Publication of online editions started in late 1994 and have continued to the present d ...
'' in 1983 designated SCAMP a "revolutionary concept" and "the world's first personal computer". This seminal, single user portable computer now resides in the Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.. Successful demonstrations of the 1973 SCAMP prototype led to the IBM 5100 portable microcomputer launched in 1975 with the ability to be programmed in both APL and BASIC for engineers, analysts, statisticians, and other business problem-solvers. In the late 1960s such a machine would have been nearly as large as two desks and would have weighed about half a ton.
Another desktop portable APL machine, the MCM/70
The MCM/70 was a pioneering microcomputer first built in 1973 in Toronto, Ontario, Canada and released the next year. This makes it one of the first microcomputers in the world, the second to be shipped in completed form, and the first portable co ...
, was demonstrated in 1973 and shipped in 1974. It used the Intel 8008 processor.
A seminal step in personal computing was the 1973 Xerox Alto, developed at Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center (PARC). It had a graphical user interface (GUI
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, inste ...
) which later served as inspiration for Apple's Macintosh, and Microsoft's Windows operating system. The Alto was a demonstration project, not commercialized, as the parts were too expensive to be affordable.Roy A. Allan, A Bibliography of the Personal Computer lectronic resource the Books and Periodical Articles, Allan Publishing – 2006, p. 73
Also in 1973 Hewlett Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components ...
introduced fully BASIC
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ...
programmable microcomputers that fit entirely on top of a desk, including a keyboard, a small one-line display, and printer. The Wang 2200 microcomputer of 1973 had a full-size cathode ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), pictu ...
(CRT) and cassette tape storage. These were generally expensive specialized computers sold for business or scientific uses.
 1974 saw the introduction of what is considered by many to be the first true "personal computer", the
1974 saw the introduction of what is considered by many to be the first true "personal computer", the Altair 8800
The Altair 8800 is a microcomputer designed in 1974 by MITS and based on the Intel 8080 CPU. Interest grew quickly after it was featured on the cover of the January 1975 issue of Popular Electronics and was sold by mail order through advertiseme ...
created by Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems (MITS). Based on the 8-bit Intel 8080 Microprocessor, Wayne Green visited MITS in August 1975 and interviewed Ed Roberts. Article has several paragraphs on the design of the Altair 8800. the Altair is widely recognized as the spark that ignited the microcomputer revolution as the first commercially successful personal computer. The computer bus
In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin '' omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This ex ...
designed for the Altair was to become a ''de facto'' standard in the form of the S-100 bus, and the first programming language for the machine was Microsoft's founding product, Altair BASIC. "This announcement ltair 8800ranks with IBM's announcement of the System/360 a decade earlier as one of the most significant in the history of computing."
In 1976, Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
and Steve Wozniak
Stephen Gary Wozniak (; born August 11, 1950), also known by his nickname "Woz", is an American electronics engineer, computer programmer, philanthropist, inventor, and technology entrepreneur. In 1976, with business partner Steve Jobs, he c ...
sold the Apple I computer circuit board, which was fully prepared and contained about 30 chips. The Apple I computer differed from the other kit-style hobby computers of era. At the request of Paul Terrell, owner of the Byte Shop
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
, Jobs and Wozniak were given their first purchase order, for 50 Apple I computers, only if the computers were assembled and tested and not a kit computer. Terrell wanted to have computers to sell to a wide range of users, not just experienced electronics hobbyists who had the soldering skills to assemble a computer kit. The Apple I as delivered was still technically a kit computer, as it did not have a power supply, case, or keyboard when it was delivered to the Byte Shop.
 The first successfully mass-marketed personal computer to be announced was the Commodore PET after being revealed in January 1977. However, it was back-ordered and not available until later that year. Commodore press release. "The PET computer made its debut recently as the first 100 units were shipped to waiting customers in mid-October 1977." Three months later (April), the
The first successfully mass-marketed personal computer to be announced was the Commodore PET after being revealed in January 1977. However, it was back-ordered and not available until later that year. Commodore press release. "The PET computer made its debut recently as the first 100 units were shipped to waiting customers in mid-October 1977." Three months later (April), the Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-m ...
(usually referred to as the "Apple") was announced with the first units being shipped 10 June 1977, and the TRS-80 from Tandy Corporation / Tandy Radio Shack
RadioShack, formerly RadioShack Corporation, is an American retailer founded in 1921.
At its peak in 1999, RadioShack operated over 8,000 worldwide stores named RadioShack or Tandy Electronics in the United States, Mexico, United Kingdom, Austra ...
following in August 1977, which sold over 100,000 units during its lifetime. Together, these 3 machines were referred to as the "1977 trinity". Mass-market, ready-assembled computers had arrived, and allowed a wider range of people to use computers, focusing more on software applications and less on development of the processor hardware.
In 1977 the Heath company introduced personal computer kits known as Heathkits, starting with the Heathkit H8, followed by the Heathkit H89 in late 1979. With the purchase of the Heathkit H8 you would obtain the chassis and CPU card to assemble yourself, additional hardware such as the H8-1 memory board that contained 4k of RAM could also be purchased in order to run software. The Heathkit H11 model was released in 1978 and was one of the first 16-bit personal computers; however, due to its high retail cost of $1,295 was discontinued in 1982.

 During the early 1980s, home computers were further developed for household use, with software for personal productivity, programming and games. They typically could be used with a television already in the home as the computer display, with low-detail blocky graphics and a limited color range, and text about 40 characters wide by 25 characters tall. Sinclair Research, a UK company, produced the ZX Seriesthe ZX80 (1980), ZX81 (1981), and the ZX Spectrum; the latter was introduced in 1982, and totaled 8 million unit sold. Following came the
During the early 1980s, home computers were further developed for household use, with software for personal productivity, programming and games. They typically could be used with a television already in the home as the computer display, with low-detail blocky graphics and a limited color range, and text about 40 characters wide by 25 characters tall. Sinclair Research, a UK company, produced the ZX Seriesthe ZX80 (1980), ZX81 (1981), and the ZX Spectrum; the latter was introduced in 1982, and totaled 8 million unit sold. Following came the Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in the Guinness ...
, totaled 17 million units sold and the Amstrad CPC series (464–6128).
In the same year, the NEC PC-98 was introduced, which was a very popular personal computer that sold in more than 18 million units. Another famous personal computer, the revolutionary Amiga 1000, was unveiled by Commodore on 23 July 1985. The Amiga 1000 featured a multitasking, windowing operating system, color graphics with a 4096-color palette, stereo sound, Motorola 68000 CPU, 256 KB RAM, and 880 KB 3.5-inch disk drive, for US$1,295.
IBM's first PC was introduced on 12 August 1981 setting what became a mass market standard for PC architecture.
In 1982 "The Computer" was named Machine of the Year by '' Time'' magazine.
Somewhat larger and more expensive systems were aimed at office and small business use. These often featured 80-column text displays but might not have had graphics or sound capabilities. These microprocessor-based systems were still less costly than time-shared mainframes or minicomputers.
Workstations were characterized by high-performance processors and graphics displays, with large-capacity local disk storage, networking capability, and running under a multitasking operating system. Eventually, due to the influence of the IBM PC on the personal computer market, personal computers and home computers lost any technical distinction. Business computers acquired color graphics capability and sound, and home computers and game systems users used the same processors and operating systems as office workers. Mass-market computers had graphics capabilities and memory comparable to dedicated workstations of a few years before. Even local area networking, originally a way to allow business computers to share expensive mass storage and peripherals, became a standard feature of personal computers used at home.
An increasingly important set of uses for personal computers relied on the ability of the computer to communicate with other computer systems, allowing interchange of information. Experimental public access to a shared mainframe computer system was demonstrated as early as 1973 in the Community Memory project, but bulletin board system
A bulletin board system (BBS), also called computer bulletin board service (CBBS), is a computer server running software that allows users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user can perform functions such as ...
s and online service providers became more commonly available after 1978. Commercial Internet service providers emerged in the late 1980s, giving public access to the rapidly growing network.
In 1991, the World Wide Web was made available for public use. The combination of powerful personal computers with high-resolution graphics and sound, with the infrastructure provided by the Internet, and the standardization of access methods of the Web browsers, established the foundation for a significant fraction of modern life, from bus time tables through unlimited distribution of free videos through to online user-edited encyclopedias.
Types
Stationary
Workstation
 A workstation is a high-end personal computer designed for technical, mathematical, or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. Workstations are used for tasks such as
A workstation is a high-end personal computer designed for technical, mathematical, or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. Workstations are used for tasks such as computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
, drafting and modeling, computation-intensive scientific and engineering calculations, image processing, architectural
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings o ...
modeling, and computer graphics for animation and motion picture visual effects.
Desktop computer
 Before the widespread use of PCs, a computer that could fit on a desk was remarkably small, leading to the "desktop" nomenclature. More recently, the phrase usually indicates a particular style of computer case. Desktop computers come in a variety of styles ranging from large vertical
Before the widespread use of PCs, a computer that could fit on a desk was remarkably small, leading to the "desktop" nomenclature. More recently, the phrase usually indicates a particular style of computer case. Desktop computers come in a variety of styles ranging from large vertical tower case
In personal computing, a tower is a form of desktop computer whose case height is much greater than its width, thus having the appearance of an upstanding tower block, as opposed to a traditional desktop or "pizza box" computer whose width is g ...
s to small models which can be tucked behind or rest directly beneath (and support) LCD monitor
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in cont ...
s.
While the term "desktop" often refers to a computer with a vertically aligned computer tower case
In personal computing, a tower is a form of desktop computer whose case height is much greater than its width, thus having the appearance of an upstanding tower block, as opposed to a traditional desktop or "pizza box" computer whose width is g ...
, these varieties often rest on the ground or underneath desks. Despite this seeming contradiction, the term "desktop" does typically refer to these vertical tower cases as well as the horizontally aligned models which are designed to literally rest on top of desks and are therefore more appropriate to the "desktop" term, although both types qualify for this "desktop" label in most practical situations aside from certain physical arrangement differences. Both styles of these computer cases hold the systems hardware components
Circuit Component may refer to:
•Are devices that perform functions when they are connected in a circuit.
In engineering, science, and technology Generic systems
* System components, an entity with discrete structure, such as an assem ...
such as the motherboard, processor chip and other internal operating parts. Desktop computers have an external monitor with a display screen and an external keyboard, which are plugged into ports on the back of the computer case. Desktop computers are popular for home and business computing applications as they leave space on the desk for multiple monitors.
A gaming computer is a desktop computer that generally comprises a high-performance video card, processor and RAM, to improve the speed and responsiveness of demanding video games.
An all-in-one computer
An all-in-one computer or all-in-one PC (AIO) is a personal computer that integrates the system's internal components into the same case as the display, thus occupying a smaller footprint (with fewer cables) than desktops that incorporate a tower ...
(also known as single-unit PCs) is a desktop computer that combines the monitor and processor within a single unit. A separate keyboard and mouse are standard input devices, with some monitors including touchscreen capability. The processor and other working components are typically reduced in size relative to standard desktops, located behind the monitor, and configured similarly to laptops.
A nettop computer was introduced by Intel in February 2008, characterized by low cost and lean functionality. These were intended to be used with an Internet connection to run Web
Web most often refers to:
* Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal
* World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system
Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to:
Computing
* WEB, a literate programming system created by ...
browsers and Internet applications.
A Home theater PC (HTPC) combines the functions of a personal computer and a digital video recorder
A digital video recorder (DVR) is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes with direct to d ...
. It is connected to a TV set or an appropriately sized computer display, and is often used as a digital photo viewer, music and video player, TV receiver, and digital video recorder. HTPCs are also referred to as media center systems or media servers. The goal is to combine many or all components of a home theater
Home cinema, also called home theaters or theater rooms, are home entertainment audio-visual systems that seek to reproduce a movie theater experience and mood using consumer electronics-grade video and home audio, audio equipment that is set ...
setup into one box. HTPCs can also connect to services providing on-demand movies and TV shows. HTPCs can be purchased pre-configured with the required hardware and software needed to add television programming to the PC, or can be assembled from components.
Keyboard computers are computers inside of keyboards, generally still designed to be connected to an external computer monitor
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The di ...
or television. Examples include the Atari ST
The Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the Atari 8-bit family. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985 and was widely available in July. It was the first pers ...
, Amstrad CPC, BBC Micro, Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in the Guinness ...
, MSX
MSX is a standardized home computer architecture, announced by Microsoft and ASCII Corporation on June 16, 1983. It was initially conceived by Microsoft as a product for the Eastern sector, and jointly marketed by Kazuhiko Nishi, then vice-p ...
, Raspberry Pi 400, and the ZX Spectrum.
Portable
 The potential utility of portable computers was apparent early on. Alan Kay described the Dynabook in 1972, but no hardware was developed. The
The potential utility of portable computers was apparent early on. Alan Kay described the Dynabook in 1972, but no hardware was developed. The Xerox NoteTaker
The Xerox NoteTaker is a portable computer developed at Xerox PARC in Palo Alto, California, in 1978. Although it did not enter production, and only around ten prototypes were built, it strongly influenced the design of the later Osborne 1 and Com ...
was produced in a very small experimental batch around 1978. In 1975, the IBM 5100 could be fit into a transport case, making it a portable computer, but it weighed about 50 pounds.
Before the introduction of the IBM PC, portable computers consisting of a processor, display, disk drives and keyboard, in a suit-case style portable housing, allowed users to bring a computer home from the office or to take notes at a classroom. Examples include the Osborne 1 and Kaypro; and the Commodore SX-64. These machines were AC-powered and included a small CRT display screen. The form factor was intended to allow these systems to be taken on board an airplane as carry-on baggage, though their high power demand meant that they could not be used in flight. The integrated CRT display made for a relatively heavy package, but these machines were more portable than their contemporary desktop equals. Some models had standard or optional connections to drive an external video monitor, allowing a larger screen or use with video projectors.
IBM PC-compatible suitcase format computers became available soon after the introduction of the PC, with the Compaq Portable
The Compaq Portable was an early portable computer which was one of the first IBM PC compatible systems. It was Compaq Computer Corporation's first product, to be followed by others in the Compaq Portable series and later Compaq Deskpro series. ...
being a leading example of the type. Later models included a hard drive to give roughly equivalent performance to contemporary desktop computers.
The development of thin plasma display and LCD screens permitted a somewhat smaller form factor, called the "lunchbox" computer. The screen formed one side of the enclosure, with a detachable keyboard and one or two half-height floppy disk drives, mounted facing the ends of the computer. Some variations included a battery, allowing operation away from AC outlets.Scott Mueller, ''Upgrading and Repairing Laptops'', Que Publishing, 2004, , pp. 18–21
Notebook computers such as the TRS-80 Model 100 and Epson HX-20
The Epson HX-20 (also known as the HC-20) was the first "true" laptop computer.Michael R. Peres''The Focal Encyclopedia of Photography'', page 306 Taylor & Francis It was invented in July 1980 by Yukio Yokozawa, who worked for Suwa Seikosha, a bra ...
had roughly the plan dimensions of a sheet of typing paper ( ANSI A or ISO A4). These machines had a keyboard with slightly reduced dimensions compared to a desktop system, and a fixed LCD display screen coplanar with the keyboard. These displays were usually small, with 8 to 16 lines of text, sometimes only 40 columns line length. However, these machines could operate for extended times on disposable or rechargeable batteries. Although they did not usually include internal disk drives, this form factor often included a modem for telephone communication and often had provisions for external cassette or disk storage. Later, clam-shell format laptop computers with similar small plan dimensions were also called "notebooks".
Laptop
 A
A laptop
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper li ...
computer is designed for portability with " clamshell" design, where the keyboard and computer components are on one panel, with a hinged second panel containing a flat display screen. Closing the laptop protects the screen and keyboard during transportation. Laptops generally have a rechargeable battery
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
, enhancing their portability. To save power, weight and space, laptop graphics chips are in many cases integrated into the CPU or chipset and use system RAM, resulting in reduced graphics performance when compared to desktop machines, that more typically have a graphics card installed. For this reason, desktop computers are usually preferred over laptops for gaming purposes.
Unlike desktop computers, only minor internal upgrades (such as memory and hard disk drive) are feasible owing to the limited space and power available. Laptops have the same input and output ports as desktops, for connecting to external displays, mice, cameras, storage devices and keyboards. Laptops are also a little more expensive compared to desktops, as the miniaturized components for laptops themselves are expensive.
A desktop replacement computer is a portable computer that provides the full capabilities of a desktop computer
A desktop computer (often abbreviated desktop) is a personal computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a case that houses the power supply ...
. Such computers are currently large laptops. This class of computers usually includes more powerful components and a larger display than generally found in smaller portable computers, and may have limited battery capacity or no battery.

Netbook
Netbook was a commonly used term that identified a product class of small and inexpensive laptops which were sold from 2007 to around 2013. These machines were designed primarily as cost-effective tools for consumers to access the Inte ...
s, also called mini notebooks or subnotebooks, were a subgroup of laptops suited for general computing tasks and accessing web-based applications. Initially, the primary defining characteristic of netbooks was the lack of an optical disc drive, smaller size, and lower performance than full-size laptops. By mid-2009 netbooks had been offered to users "free of charge", with an extended service contract purchase of a cellular data plan. Ultrabooks and Chromebooks have since filled the gap left by Netbooks. Unlike the generic Netbook name, Ultrabook and Chromebook are technically both specifications by Intel and Google respectively.
Tablet
 A
A tablet
Tablet may refer to:
Medicine
* Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill"
Computing
* Tablet computer, a mobile computer that is primarily operated by touching the s ...
uses a touchscreen display, which can be controlled using either a stylus
A stylus (plural styli or styluses) is a writing utensil or a small tool for some other form of marking or shaping, for example, in pottery. It can also be a computer accessory that is used to assist in navigating or providing more precision w ...
pen or finger. Some tablets may use a "hybrid" or "convertible" design, offering a keyboard that can either be removed as an attachment, or a screen that can be rotated and folded directly over top the keyboard. Some tablets may use desktop-PC operating system such as Windows or Linux, or may run an operating system designed primarily for tablets. Many tablet computers have USB ports, to which a keyboard or mouse can be connected.
Smartphone
 Smartphones are often similar to tablet computers, the difference being that smartphones always have
Smartphones are often similar to tablet computers, the difference being that smartphones always have cellular
Cellular may refer to:
*Cellular automaton, a model in discrete mathematics
* Cell biology, the evaluation of cells work and more
* ''Cellular'' (film), a 2004 movie
*Cellular frequencies, assigned to networks operating in cellular RF bands
*Cell ...
integration. They are generally smaller than tablets, and may not have a slate form factor.
Ultra-mobile PC
The ultra-mobile PC (UMP) is a small tablet computer. It was developed by Microsoft, Intel and Samsung, among others. Current UMPCs typically feature the Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, or Linux operating system, and low-voltage Intel Atom orVIA C7-M
The VIA C7 is an x86 central processing unit designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies.
Product history
The C7 delivers a number of improvements to the older VIA C3 cores but is nearly identical to the latest VIA C3 Nehemiah ...
processors.
Pocket PC
A pocket PC is a hardware specification for a handheld-sized computer ( personal digital assistant, PDA) that runs the Microsoft Windows Mobile operating system. It may have the capability to run an alternative operating system likeNetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was forked. It continues to be actively developed and is a ...
or Linux. Pocket PCs have many of the capabilities of desktop PCs
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or techn ...
. Numerous applications are available for handhelds adhering to the Microsoft Pocket PC specification, many of which are freeware. Microsoft-compliant Pocket PCs can also be used with many other add-ons like GPS receivers, barcode readers, RFID
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electromag ...
readers and cameras.
In 2007, with the release of Windows Mobile 6, Microsoft dropped the name Pocket PC in favor of a new naming scheme: devices without an integrated phone are called Windows Mobile Classic instead of Pocket PC, while devices with an integrated phone and a touch screen are called Windows Mobile Professional.
Palmtop and handheld computers
Palmtop PCs were miniature pocket-sized computers running DOS that first came about in the late 1980s, typically in a clamshell form factor with a keyboard. Non-x86 based devices were often called palmtop computers, examples being Psion Series 3. In later years a hardware specification called Handheld PC was later released by Microsoft that run the Windows CE operating system.Hardware
Computer hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the computer case, case, central processing unit (CPU), Random-access memory, random access memory (RAM), Computer monitor, monitor, Computer mouse, mouse, Computer keyboard, ...
is a comprehensive term for all physical and tangible parts of a computer, as distinguished from the data it contains or operates on, and the software that provides instructions for the hardware to accomplish tasks. Some sub-systems of a personal computer may contain processors that run a fixed program, or firmware
In computing, firmware is a specific class of computer software that provides the low-level control for a device's specific hardware. Firmware, such as the BIOS of a personal computer, may contain basic functions of a device, and may provide h ...
, such as a keyboard controller. Firmware usually is not changed by the end user of the personal computer.
Most 2010s-era computers require users only to plug in the power supply, monitor, and other cables. A typical desktop computer
A desktop computer (often abbreviated desktop) is a personal computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a case that houses the power supply ...
consists of a computer case (or "tower"), a metal chassis that holds the power supply, motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
, a storage device such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, and often an optical disc drive
In computing, an optical disc drive is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only r ...
. Most towers have empty space where users can add additional components. External devices such as a computer monitor
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The di ...
or visual display unit, keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Musi ...
, and a pointing device (mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
) are usually found in a personal computer.
The motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
connects all processor, memory and peripheral devices together. The RAM, graphics card and processor are in most cases mounted directly onto the motherboard. The central processing unit (microprocessor chip) plugs into a CPU socket, while the ram modules plug into corresponding ram sockets. Some motherboards have the video display adapter, sound and other peripherals integrated onto the motherboard, while others use expansion slots for graphics cards, network cards, or other I/O devices. The graphics card or sound card may employ a break out box A breakout box is a piece of electrical test equipment used to support integration testing, expedite maintenance, and streamline the troubleshooting process at the system, subsystem, and component-level by simplifying the access to test signals. B ...
to keep the analog parts away from the electromagnetic radiation inside the computer case. Disk drives, which provide mass storage, are connected to the motherboard with one cable, and to the power supply through another cable. Usually, disk drives are mounted in the same case as the motherboard; expansion chassis are also made for additional disk storage.
For large amounts of data, a tape drive can be used or extra hard disks can be put together in an external case. The keyboard and the mouse are external devices plugged into the computer through connectors on an I/O panel on the back of the computer case. The monitor is also connected to the input/output (I/O) panel, either through an onboard port on the motherboard, or a port on the graphics card. Capabilities of the personal computer's hardware can sometimes be extended by the addition of expansion cards connected via an expansion bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
. Standard peripheral buses often used for adding expansion cards in personal computers include PCI
PCI may refer to:
Business and economics
* Payment card industry, businesses associated with debit, credit, and other payment cards
** Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, a set of security requirements for credit card processors
* Pro ...
, PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common ...
(PCIe), and AGP
AGP may refer to:
Science and technology
* Accelerated Graphics Port, a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a graphics card to a computer's motherboard
* Advance Game Port, a third-party GameCube accessory
* Aerosol-generating proce ...
(a high-speed PCI bus dedicated to graphics adapters, found in older computers). Most modern personal computers have multiple physical PCI Express expansion slots, with some having PCI slots as well.
A peripheral
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by the ...
is "a device connected to a computer to provide communication (such as input and output) or auxiliary functions (such as additional storage)". Peripherals generally connect to the computer through the use of USB ports or inputs located on the I/O panel. USB flash drives provide portable storage using flash memory which allows users to access the files stored on the drive on any computer. Memory cards also provide portable storage for users, commonly used on other electronics such as mobile phones and digital cameras, the information stored on these cards can be accessed using a memory card reader to transfer data between devices. Webcams, which are either built into computer hardware or connected via USB are video cameras that records video in real time to either be saved to the computer or streamed somewhere else over the internet. Game controllers can be plugged in via USB and can be used as an input device for video games as an alternative to using keyboard and mouse. Headphones
Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an au ...
and speakers can be connected via USB or through an auxiliary port (found on I/O panel) and allow users to listen to audio accessed on their computer; however, speakers may also require an additional power source to operate. Microphones can be connected through an audio input port on the I/O panel and allow the computer to convert sound into an electrical signal to be used or transmitted by the computer.
Software
 Computer software is any kind of computer program,
Computer software is any kind of computer program, procedure
Procedure may refer to:
* Medical procedure
* Instructions or recipes, a set of commands that show how to achieve some result, such as to prepare or make something
* Procedure (business), specifying parts of a business process
* Standard operat ...
, or documentation that performs some task on a computer system. The term includes application software such as word processors that perform productive tasks for users, system software such as operating systems that interface with computer hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the computer case, case, central processing unit (CPU), Random-access memory, random access memory (RAM), Computer monitor, monitor, Computer mouse, mouse, Computer keyboard, ...
to provide the necessary services for application software, and middleware that controls and co-ordinates distributed systems.
 Software applications are common for word processing, Internet browsing, Internet faxing, e-mail and other digital messaging, multimedia playback, playing of
Software applications are common for word processing, Internet browsing, Internet faxing, e-mail and other digital messaging, multimedia playback, playing of computer game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device to gener ...
, and computer programming. The user may have significant knowledge of the operating environment and application programs, but is not necessarily interested in programming nor even able to write programs for the computer. Therefore, most software written primarily for personal computers tends to be designed with simplicity of use, or " user-friendliness" in mind. However, the software industry continuously provide a wide range of new products for use in personal computers, targeted at both the expert and the non-expert user.
Operating system
An operating system (OS) manages computer resources and provides programmers with an interface used to access those resources. An operating system processes system data and user input, and responds by allocating and managing tasks and internal system resources as a service to users and programs of the system. An operating system performs basic tasks such as controlling and allocating memory, prioritizing system requests, controlling input and output devices, facilitating computer networking, and managing files. Common contemporary desktop operating systems areMicrosoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
, macOS, Linux, Solaris
Solaris may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Literature, television and film
* ''Solaris'' (novel), a 1961 science fiction novel by Stanisław Lem
** ''Solaris'' (1968 film), directed by Boris Nirenburg
** ''Solaris'' (1972 film), directed by ...
and FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular ...
. Windows, macOS, and Linux all have server and personal variants. With the exception of Microsoft Windows, the designs of each of them were inspired by or directly inherited from the Unix operating system.
Early personal computers used operating systems that supported command line interaction, using an alphanumeric display and keyboard. The user had to remember a large range of commands to, for example, open a file for editing or to move text from one place to another. Starting in the early 1960s, the advantages of a graphical user interface began to be explored, but widespread adoption required lower-cost graphical display equipment. By 1984, mass-market computer systems using graphical user interfaces were available; by the turn of the 21st century, text-mode operating systems were no longer a significant fraction of the personal computer market.
Applications
Generally, a computer user uses application software to carry out a specific task. System software supports applications and provides common services such as memory management, network connectivity and device drivers, all of which may be used by applications but are not directly of interest to the end user. A simplifiedanalogy
Analogy (from Greek ''analogia'', "proportion", from ''ana-'' "upon, according to" lso "against", "anew"+ ''logos'' "ratio" lso "word, speech, reckoning" is a cognitive process of transferring information or meaning from a particular subject ( ...
in the world of hardware would be the relationship of an electric light bulb (an application) to an electric power generation plant (a system): the power plant merely generates electricity, not itself of any real use until harnessed to an application like the electric light that performs a service that benefits the user.
Typical examples of software applications are word processors, spreadsheets, and media players
A media player could refer to:
*Digital media player, home appliances that play digital media
*Media player software, software that plays digital media
*Portable media player, portable hardware that plays digital media
*Windows Media Player
Wi ...
. Multiple applications bundled together as a package are sometimes referred to as an ''application suite''. Microsoft Office and LibreOffice, which bundle together a word processor, a spreadsheet, and several other discrete applications, are typical examples. The separate applications in a suite usually have a user interface that has some commonality making it easier for the user to learn and use each application. Often, they may have some capability to interact with each other in ways beneficial to the user; for example, a spreadsheet might be able to be embedded in a word processor document even though it had been created in the separate spreadsheet application.
End-user development
End-user development (EUD) or end-user programming (EUP) refers to activities and tools that allow end-users – people who are not professional software developers – to program computers. People who are not professional developers can use EUD ...
tailors systems to meet the user's specific needs. User-written software include spreadsheet templates, word processor macros, scientific simulations, graphics and animation scripts; even email filters are a kind of user software. Users create this software themselves and often overlook how important it is.
Gaming
PC gaming
A personal computer game, also known as a PC game or computer game, is a type of video game played on a personal computer (PC) rather than a video game console or arcade cabinet, arcade machine. Its defining characteristics include: more divers ...
is popular among the high-end PC market. According to an April 2018 market analysis done by ''Newzoo'', PC gaming has fallen behind both console and mobile gaming in terms of market share sitting at a 24% share of the entire market. The market for PC gaming still continues to grow and is expected to generate $32.3 billion in revenue in the year 2021. PC gaming is at the forefront of competitive gaming, known as esports
Esports, short for electronic sports, is a form of competition using video games. Esports often takes the form of organized, multiplayer video game competitions, particularly between professional players, individually or as teams. Although orga ...
, with games such as '' Overwatch'' and '' Counter-Strike: Global Offensive'' leading the industry that is suspected to surpass a trillion dollars in revenue in 2019.
Sales
Market share
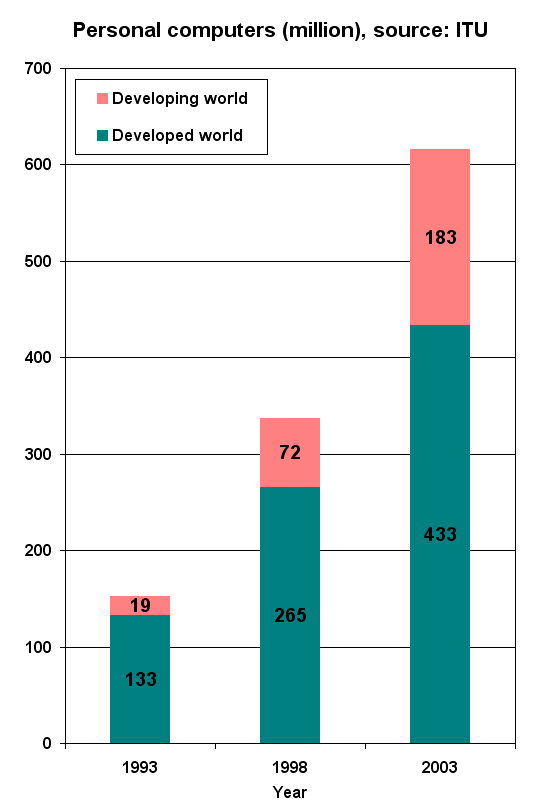
 In 2001, 125 million personal computers were shipped in comparison to 48,000 in 1977. More than 500 million personal computers were in use in 2002 and one billion personal computers had been sold worldwide from the mid-1970s up to this time. Of the latter figure, 75% were professional or work related, while the rest were sold for personal or home use. About 81.5% of personal computers shipped had been
In 2001, 125 million personal computers were shipped in comparison to 48,000 in 1977. More than 500 million personal computers were in use in 2002 and one billion personal computers had been sold worldwide from the mid-1970s up to this time. Of the latter figure, 75% were professional or work related, while the rest were sold for personal or home use. About 81.5% of personal computers shipped had been desktop computer
A desktop computer (often abbreviated desktop) is a personal computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a case that houses the power supply ...
s, 16.4% laptop
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper li ...
s and 2.1% servers. The United States had received 38.8% (394 million) of the computers shipped, Europe 25% and 11.7% had gone to the Asia-Pacific region, the fastest-growing market as of 2002. The second billion was expected to be sold by 2008. Almost half of all households in Western Europe had a personal computer and a computer could be found in 40% of homes in United Kingdom, compared with only 13% in 1985.
The global personal computer shipments were 350.9 million units in 2010,Global PC shipments grew 13.8 percent in 2010 – Gartner studyJan 13, 2011, retrieved at September 12, 2011 308.3 million units in 2009
May 27, 2010, Andy Patrizio, earthweb.com, retrieved at September 12, 2011 and 302.2 million units in 2008.Worldwide PC Shipments in 2008
March 16, 2009, ZDNet, retrieved at September 12, 2011
January 14, 2009, Andy Patrizio, internetnews.com, retrieved at September 12, 2011 The shipments were 264 million units in the year 2007, according to iSuppli, up 11.2% from 239 million in 2006. In 2004, the global shipments were 183 million units, an 11.6% increase over 2003. In 2003, 152.6 million computers were shipped, at an estimated value of $175 billion. In 2002, 136.7 million PCs were shipped, at an estimated value of $175 billion. In 2000, 140.2 million personal computers were shipped, at an estimated value of $226 billion. Worldwide shipments of personal computers surpassed the 100-million mark in 1999, growing to 113.5 million units from 93.3 million units in 1998. In 1999, Asia had 14.1 million units shipped. As of June 2008, the number of personal computers in use worldwide hit one billion, while another billion is expected to be reached by 2014. Mature markets like the United States, Western Europe and Japan accounted for 58% of the worldwide installed PCs. The emerging markets were expected to double their installed PCs by 2012 and to take 70% of the second billion PCs. About 180 million computers (16% of the existing installed base) were expected to be replaced and 35 million to be dumped into landfill in 2008. The whole installed base grew 12% annually. Based on International Data Corporation (IDC) data for Q2 2011, for the first time China surpassed US in PC shipments by 18.5 million and 17.7 million respectively. This trend reflects the rising of emerging markets as well as the relative stagnation of mature regions. In the developed world, there has been a vendor tradition to keep adding functions to maintain high prices of personal computers. However, since the introduction of the One Laptop per Child foundation and its low-cost XO-1 laptop, the computing industry started to pursue the price too. Although introduced only one year earlier, there were 14 million
netbook
Netbook was a commonly used term that identified a product class of small and inexpensive laptops which were sold from 2007 to around 2013. These machines were designed primarily as cost-effective tools for consumers to access the Inte ...
s sold in 2008. Besides the regular computer manufacturers, companies making especially rugged versions of computers have sprung up, offering alternatives for people operating their machines in extreme weather or environments.
In 2011, Deloitte consulting firm predicted that, smartphones and tablet computers as computing devices would surpass the PCs sales (as has happened since 2012). As of 2013, worldwide sales of PCs had begun to fall as many consumers moved to tablets and smartphones. Sales of 90.3 million units in the fourth quarter of 2012 represented a 4.9% decline from sales in the fourth quarter of 2011. Global PC sales fell sharply in the first quarter of 2013, according to IDC data. The 14% year-over-year decline was the largest on record since the firm began tracking in 1994, and double what analysts had been expecting. The decline of Q2 2013 PC shipments marked the fifth straight quarter of falling sales. "This is horrific news for PCs," remarked an analyst. "It's all about mobile computing now. We have definitely reached the tipping point." Data from Gartner showed a similar decline for the same time period. China's Lenovo Group bucked the general trend as strong sales to first-time buyers in the developing world allowed the company's sales to stay flat overall. Windows 8, which was designed to look similar to tablet/smartphone software, was cited as a contributing factor in the decline of new PC sales. "Unfortunately, it seems clear that the Windows 8 launch not only didn't provide a positive boost to the PC market, but appears to have slowed the market," said IDC Vice President Bob O’Donnell.
In August 2013, Credit Suisse published research findings that attributed around 75% of the operating profit share of the PC industry to Microsoft (operating system) and Intel (semiconductors). According to IDC, in 2013 PC shipments dropped by 9.8% as the greatest drop-ever in line with consumers trends to use mobile devices.
In the second quarter of 2018, PC sales grew for the first time since the first quarter of 2012. According to research firm Gartner, the growth mainly came from the business market while the consumer market experienced decline.
In 2020, as the result of the COVID-19 Pandemic with more people working at home and learning remotely, PC sales grew by 26.1% compared to previous years according to IDC. According to Canalys, 2020 was the highest growth rate for the PC market since 2011.
Average selling price
Selling prices of personal computers steadily declined due to lower costs of production and manufacture, while the capabilities of computers increased. In 1975, an Altair kit sold for around only , but required customers to solder components into circuit boards; peripherals required to interact with the system in alphanumeric form instead of blinking lights would add another , and the resultant system was of use only to hobbyists.Marvin B. Sussman ''Personal Computers and the Family'' Routledge, 1985 , p. 90. At their introduction in 1981, the price of the Osborne 1 and its competitor Kaypro was considered an attractive price point; these systems had text-only displays and only floppy disks for storage. By 1982, Michael Dell observed that a personal computer system selling at retail for about was made of components that cost the dealer about ; typical gross margin on a computer unit was around . The total value of personal computer purchases in the US in 1983 was about , comparable to total sales of pet food. By late 1998, the average selling price of personal computer systems in the United States had dropped below . ForMicrosoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
systems, the average selling price
The average selling price (ASP) of goods or commodities is the average price at which a particular product or commodity is sold across channels or markets. The term is especially used in the retail sector and technology distribution. In lodging
...
(ASP) showed a decline in 2008/2009, possibly due to low-cost netbook
Netbook was a commonly used term that identified a product class of small and inexpensive laptops which were sold from 2007 to around 2013. These machines were designed primarily as cost-effective tools for consumers to access the Inte ...
s, drawing for desktop computer
A desktop computer (often abbreviated desktop) is a personal computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a case that houses the power supply ...
s and $689 for laptop
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper li ...
s at U.S. retail in August 2008. In 2009, ASP had further fallen to for desktops and to for notebooks by January and to in February. According to research firm NPD, the average selling price of all Windows portable PCs has fallen from in October 2008 to in October 2009.
Environmental impact
External costs of environmental impact are not fully included in the selling price of personal computers. Personal computers have become a large contributor to the 50 million tons of discarded electronic waste generated annually, according to the United Nations Environment Programme. To address the electronic waste issue affecting developing countries and the environment, extended producer responsibility (EPR) acts have been implemented in various countries and states. In the absence of comprehensive national legislation or regulation on the export and import of electronic waste, theSilicon Valley Toxics Coalition
The Silicon Valley Toxics Coalition (SVTC) was formed in San Jose, California- as a research and advocacy group that promoted safe environmental practices in the high tech industry. The organization was founded in 1982 after leaks at manufacturi ...
and BAN (Basel Action Network) teamed up with electronic recyclers in the US and Canada to create an e-steward program for the orderly disposal of electronic waste. Some organizations oppose EPR regulation, and claim that manufacturers naturally move toward reduced material and energy use.
See also
* List of computer system manufacturers *List of home computers
The home computers between 1977 and about 1995 were different from today's uniform and predictable machines. During this time it made economic sense for manufacturers to make microcomputers aimed at the home user. By simplifying the machines, and ...
* Public computer
* Portable computer
* Desktop replacement computer
* Quiet PC
* Pocket PC
A Pocket PC (P/PC, PPC) is a class of personal digital assistant (PDA) that runs the Windows Mobile or Windows Embedded Compact operating system that has some of the abilities of modern desktop PCs. The name was introduced by Microsoft in 2000 ...
* Market share of personal computer vendors
* Personal Computer Museum
The Personal Computer Museum was located in Brantford, Ontario, Canada, in a building formerly owned by the municipal government.
The building was built with bricks reclaimed from the Brantford Opera House.
Over fifty interactive personal compute ...
* Enthusiast computer
References
Further reading
* ''Accidental Empires: How the boys of Silicon Valley make their millions, battle foreign competition, and still can't get a date'', Robert X. Cringely, Addison-Wesley Publishing, (1992), * ''PC Magazine'', Vol. 2, No. 6, November 1983, ‘'SCAMP: The Missing Link in the PC's Past?‘’External links
* How Stuff Works pages: *Dissecting a PC
*
*
** How to Build a Computer *
Global archive with product data-sheets of PCs and Workstations
{{Authority control American inventions Classes of computers Home appliances Office equipment Time Person of the Year