Necklace (3922815556).jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A necklace is an article of
A necklace is an article of

 In
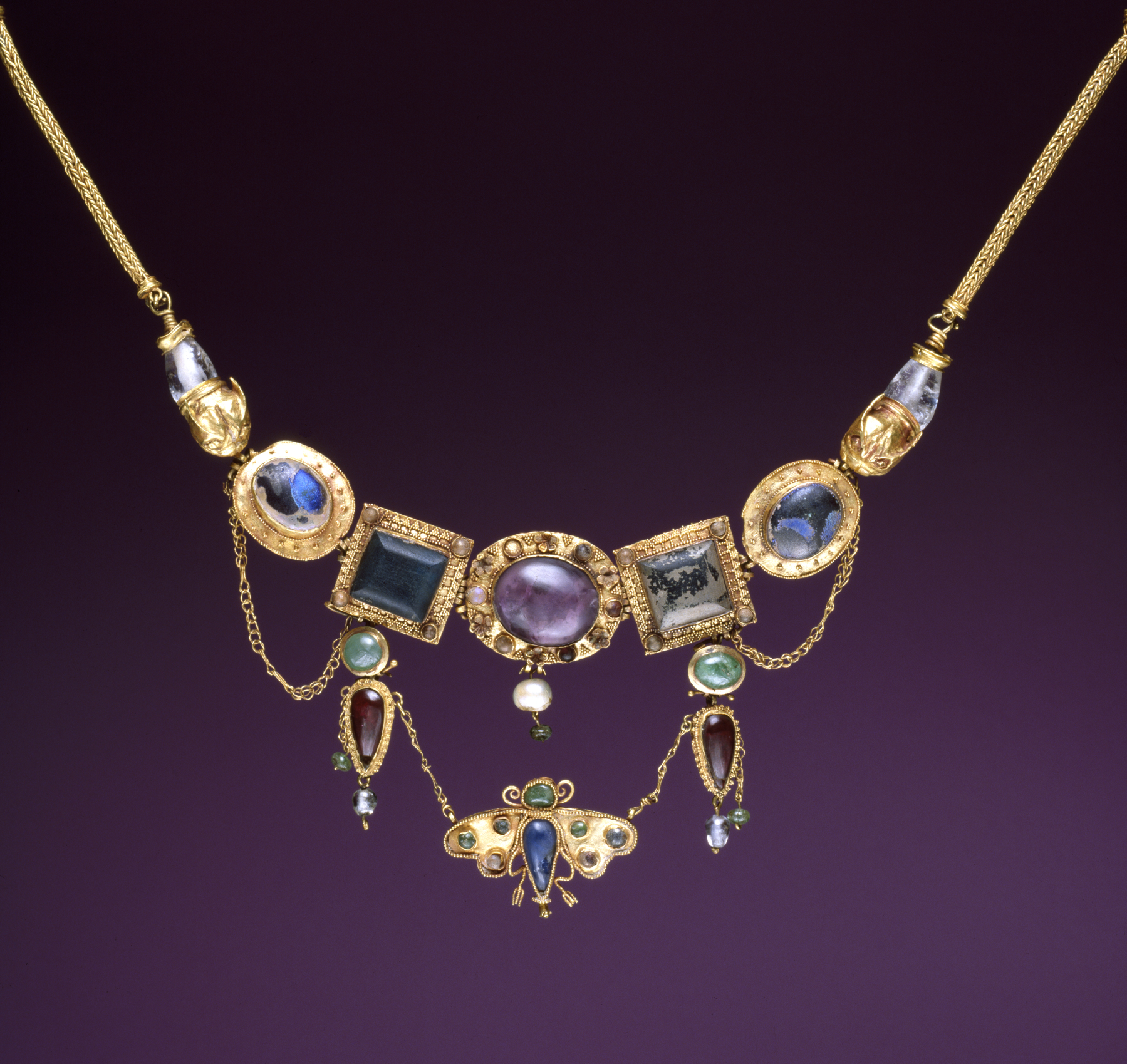
In  Later in the empire, following barbarian invasions, colorful and gaudy jewellery became popular. In the
Later in the empire, following barbarian invasions, colorful and gaudy jewellery became popular. In the
 AD 400 - 1300: Early European barbarian groups favored wide, intricate gold collars not unlike the torc.
AD 400 - 1300: Early European barbarian groups favored wide, intricate gold collars not unlike the torc.
brooches
and a bracelet. Highly embellished Gothic style necklaces from England reflected the crenelations, vertical lines and high relief of the cathedrals. Eugénie de Montijo, Empress Eugénie popularised bare décolletage with multiple necklaces on the throat, shoulders, and bosom. There was also an interest in antiquity; mosaic jewellery and Roman and Greek necklaces were reproduced. Machine-made jewellery and electroplating allowed for an influx of inexpensive imitation necklaces. 1870–1910: The Edwardian era saw a resurgence of pearl necklaces, in addition to a dog-collar style of necklace made of gold or platinum with inset diamonds, emeralds, or rubies. The Art Nouveau movement inspired symbolic, abstract designs with natural and animal motifs. The materials used - glass, porcelain, bronze, ivory, mother of pearl, horn, and enamel - were not used for their value, but for their appearance. 1910–1970: Chanel popularised costume jewelry, costume jewellery, and ropes of glass beads were common. The Art Deco movement created chunky, geometric jewellery that combined multiple types of gems and steel. By the 1960s costume jewellery was widely worn, which resulted in seasonal, ever-changing styles of necklaces and other jewellery. Real jewellery that was common in this period included wholly geometric or organically shaped silver necklaces, and precious gems set in platinum or gold necklaces inspired by the time of the French colonial empire, French Empire. Love beads (a single strand of stone or glass beads) and pendant necklaces (most often made of leather cords or metal chains with metal pendants) became popular and were worn mostly by men.
 In China, there is a custom of wearing a necklace with a Lock charm, longevity lock pendant. These lock charms were sometimes personally tied around the necks of children by Buddhist or Taoist priests. The longevity lock is known as () and is an important form of amulet for children for thousand of years in Chinese culture. According to Chinese beliefs, the protect children from evil spirits and bad luck by locking its wearer's soul and life inside of the lock. The is often made with precious materials, such as gold, silver, and jade, and having auspicious words carved on it. This form of necklace continues to be worn in present-days China.
In China, there is a custom of wearing a necklace with a Lock charm, longevity lock pendant. These lock charms were sometimes personally tied around the necks of children by Buddhist or Taoist priests. The longevity lock is known as () and is an important form of amulet for children for thousand of years in Chinese culture. According to Chinese beliefs, the protect children from evil spirits and bad luck by locking its wearer's soul and life inside of the lock. The is often made with precious materials, such as gold, silver, and jade, and having auspicious words carved on it. This form of necklace continues to be worn in present-days China.
 ;Collar
:A collar is about 30 centimetres (12 inch) to 33 centimetres (13inch) long and sits high on the neck.
; Choker
: A choker is a close-fitting, short necklace, 35 centimetres (14 in) to 41 centimetres (16 in) long.
; Princess necklace
: A princess necklace is 45 centimetres (18 in) to 50 centimetres (20 in) long.
; Matinee necklace
: A matinee length necklace is 56 centimetres (22 in) to 58 centimetres (23 in) long.
; Opera necklace
: An opera necklace is 75 centimetres (30 in) to 90 centimetres (35 in) long and sits at the breastbone.
; Rope necklace
: A rope necklace is any necklace longer than opera length.
; Lariat necklace
: A lariat is a very long variation on the rope, without a clasp, often worn draped multiple times around the neck.
;Collar
:A collar is about 30 centimetres (12 inch) to 33 centimetres (13inch) long and sits high on the neck.
; Choker
: A choker is a close-fitting, short necklace, 35 centimetres (14 in) to 41 centimetres (16 in) long.
; Princess necklace
: A princess necklace is 45 centimetres (18 in) to 50 centimetres (20 in) long.
; Matinee necklace
: A matinee length necklace is 56 centimetres (22 in) to 58 centimetres (23 in) long.
; Opera necklace
: An opera necklace is 75 centimetres (30 in) to 90 centimetres (35 in) long and sits at the breastbone.
; Rope necklace
: A rope necklace is any necklace longer than opera length.
; Lariat necklace
: A lariat is a very long variation on the rope, without a clasp, often worn draped multiple times around the neck.
File:Late Western Zhou Jade Necklace.jpg, Necklace, Late Zhou dynasty (c.1046 to 256 BC), China
File:Tiffany Opal Necklace.jpg, Tiffany Opal Necklace
File:Minoan gold necklace archmus Heraklion.jpg, Minoan Gold Necklace (Archmus Heraklion)
File:Napoleon-diamond-necklace.jpg, Napoleonic-era Diamond Necklace
File:Post Emerald Necklace 01.jpg, Emerald Necklace
File:Egyptian carnelian necklace.JPG, Carnelian, Limestone, and Quartz Egyptian necklace
File:Ancient Byzantine gold necklace (Met).jpg, Gold Ancient Byzantine Necklace with Pendants
File:KHM Wien VIIb 133 - Golden Vandal necklace, c. 300 AD.jpg, Gold and Glass Vandal necklace, c. AD 300
File:Getty Villa - Necklace with relief pendant - 83.AM.225(1).jpg, Necklace with Relief Pendant
File:KHM Wien VIIa 2 - Silver necklace, 600-650 AD.jpg, Silver necklace, c. AD 600-650
File:Beads from a Necklace MET dp30573.jpg, Frankish Glass Bead Necklace
File:Necklace MET ES1799.jpg, Gold and Platinum Necklace
File:Necklace with Pendant Cross MET 40502.jpg, Byzantine Christian cross necklace
File:Necklace with Pendant Crosses MET dp30693.jpg, Byzantine Christian cross necklace
File:Necklace MET 2014.294 d.jpg, German Metal Necklace
File:Sea necklace.jpg, Necklace made from crochet lace, pearls, and sterling silver.
File:Necklace MET DT5736.jpg, Gold and Platinum French Necklace
File:Glass necklace BM WA 133334.jpg, Glass Necklace
File:Rosaline Pearl Necklace.jpg, Rosaline Pearl Necklace
File:Dirce Repossi White Gold and Diamonds Necklace.jpg, Dirce Repossi White Gold and Diamonds Necklace
File:Roman - Necklace with Pendant Coins - Walters 571600.jpg, Gold Roman Necklace with Pendant Coins and Braided Chain- Walters 571600
File:Uranium-glass-necklace.jpg, Uranium glass necklace, circa 1940/1950. Uranium glass glows bright green under ultraviolet light.
 Non-jewellery items are also used similar to a necklace to be worn on a neck, for example lanyards holding badges and cards.
Non-jewellery items are also used similar to a necklace to be worn on a neck, for example lanyards holding badges and cards.
 A necklace is an article of
A necklace is an article of jewellery
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry (U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a wester ...
that is worn around the neck. Necklaces may have been one of the earliest types of adornment worn by humans. They often serve ceremonial
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan origin, via the Latin '' caerimonia''.
Church and civil (secular ...
, religious
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
, magical, or funerary
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect ...
purposes and are also used as symbols of wealth and status, given that they are commonly made of precious metals and stones.
The main component of a necklace is the band, chain, or cord that wraps around the neck. These are most often rendered in precious metals such as gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
, and platinum. Necklaces often have additional attachments suspended or inset into the necklace itself. These attachments typically include pendants, lockets, amulets, crosses, and precious and semi-precious materials such as diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, ...
, pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
s, rubies
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sap ...
, emeralds, garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
s, and sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sa ...
s. They are made with many different type of materials and are used for many things and sometimes classed as clothing.
Historical Necklaces

Prehistoric neckware
Prehistoric peoples often used natural materials such as feathers, bone, shells, and plant materials to create necklaces. Evidence of earlyUpper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
necklace making in southern Africa and east Africa dates back to 50,000 BP. By the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
metallic jewellery had replaced pre-metallic adornments. Necklaces were first depicted in statuary and art of the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, ...
, and early necklaces made of precious metals with inset stones were created in Europe.
Ancient civilizations
InAncient Mesopotamia
The history of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing i ...
, cylinder seals
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in length, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
were often strung and worn as jewellery. In Ancient Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, necklaces were made of carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used ...
, lapis lazuli, agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Anci ...
, and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, which was also made into gold chains. Ancient Sumerians created necklaces and beads from gold, silver, lapis lazuli and carnelian. In Ancient Egypt, a number of difference necklace types were worn. Upper-class Ancient Egyptians wore collars of organic or semi-precious and precious materials for religious, celebratory, and funerary purposes. These collars were often ornamented with semi-precious, glass, pottery, and hollow beads. Beads
A bead is a small, decorative object that is formed in a variety of shapes and sizes of a material such as stone, bone, shell, glass, plastic, wood, or pearl and with a small hole for threading or stringing. Beads range in size from under ...
made from a variety of precious and semi-precious materials were also commonly strung together to create necklaces. Gold that was fashioned into stylised plant, animal, and insect shapes were common as well. Amulets were also turned into necklaces. In Ancient Crete
The history of Crete goes back to the 7th millennium BC, preceding the ancient Minoan civilization by more than four millennia. The palace-based Minoan civilization was the first civilization in Europe.
After the Minoan civilization was devasta ...
necklaces were worn by all classes; peasants wore stones on flax thread while the wealthy wore beads of agate, pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
, carnelian, amethyst, and rock crystal
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
. Pendants shaped into birds, animals, and humans were also worn, in addition to paste beads. In
In Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
, delicately made gold necklaces created with repoussé and plaited gold wires were worn. Most often these necklaces were ornamented with blue or green enameled rosettes, animal shapes, or vase-shaped pendant
A pendant is a loose-hanging piece of jewellery, generally attached by a small loop to a necklace, which may be known as a "pendant necklace". A pendant earring is an earring with a piece hanging down. Its name stems from the Latin word ' ...
s that were often detailed with fringes. It was also common to wear long gold chains with suspended cameos and small containers of perfume. New elements were introduced in the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
; colored stones allowed for poly-chromatic pieces, and animal-head finials and spear-like or bud shaped pendants were hung from chains. Ancient Etruscans used granulation
Granulation is the process of forming grains or granules from a powdery or solid substance, producing a granular material. It is applied in several technological processes in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Typically, granulation invo ...
to create granulated gold beads which were strung with glass and faience beads to create colorful necklaces. In Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
necklaces were among the many types of jewellery
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry (U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a wester ...
worn by the Roman elite. Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
necklaces were often ornamented with foreign and semi-precious objects such as amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In ...
, pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
, amethyst, sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sa ...
, and diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, ...
. In addition, ropes of pearls, gold plates inset with enamel, and lustrous stones set in gold filigree were often worn. Many large necklaces and the materials that adorned the necklaces were imported from the Near East .  Later in the empire, following barbarian invasions, colorful and gaudy jewellery became popular. In the
Later in the empire, following barbarian invasions, colorful and gaudy jewellery became popular. In the Byzantine era
The Byzantine calendar, also called the Roman calendar, the Creation Era of Constantinople or the Era of the World ( grc, Ἔτη Γενέσεως Κόσμου κατὰ Ῥωμαίους, also or , abbreviated as ε.Κ.; literal translation of ...
, ropes of pearls and embossed gold chains were most often worn, but new techniques such as the use of niello
Niello is a black mixture, usually of sulphur, copper, silver, and lead, used as an inlay on engraved or etched metal, especially silver. It is added as a powder or paste, then fired until it melts or at least softens, and flows or is pushed ...
allowed for necklaces with brighter, more predominant gemstones. The Early Byzantine Era also saw a shift to distinctly Christian jewellery which displayed the new Christian iconography.
Timeline of non-classical European necklaces
2000 BC – AD 400: Bronze amulets embossed with coral were common. In Celtic and Gallic Europe, the most popular necklace was the heavy metaltorc
A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some had hook and ring closures and a few had ...
, made most often out of bronze, but sometimes out of silver, gold, or glass or amber beads.  AD 400 - 1300: Early European barbarian groups favored wide, intricate gold collars not unlike the torc.
AD 400 - 1300: Early European barbarian groups favored wide, intricate gold collars not unlike the torc. Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
often wore gold and silver pieces with complex detailing and inlaid with colored glass and semi-precious stones, especially garnet. Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian groups worked mainly in silver, due to a deficit of gold, and wrought patterns and animal forms into neck-rings. In the Gothic period
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern Europe, North ...
necklaces were uncommon, though there are a few records of diamond, ruby, and pearl necklaces. It was not until the adoption of lower necklines later in the Middle Ages that necklaces became common.
1400 – 1500: During the Renaissance it was fashionable for men to wear a number of chains, plaques, and pendants around their necks, and by the end of the 15th century the wealthiest men would wear great, shoulder covering collars inlaid with gems. Women typically wore simpler pieces, such as gold chains, or strung beads or pearls. By the end of the period, larger, more heavily adorned pieces were common among the wealthy, particularly in Italy.
1500–1600: Long pearl ropes and chains with precious stones were commonly worn. In the latter half of the century, natural adornments, such as coral and pearl, were joined with enamel and metals to create intricate pendants. Heavily jeweled, delicately framed cameo pendants were popular as well. Chokers, last worn commonly in Ancient history, antiquity, also made a resurgence at this time.
1600–1700: Few men in the Baroque period wore jewellery, and for women necklaces were unsophisticated, often a simple strand of pearls or delicately linked and embellished strands of metal with small stones. Later in the century, after the invention of new diamond cutting techniques, priority was for the first time given to the jewels themselves, not their settings; it was common for jewels to be pinned to black velvet ribbons. Miniatures also grew in popularity, and were often made into portrait pendants or lockets.
1700–1800: Portrait pendants were still worn, and in extravagantly jeweled settings. The newly wealthy bourgeoisie delighted in jewellery, and the new imitation stones and imitation gold allowed them more access to the necklaces of the time. In the early part of the century, the dominant styles were a velvet ribbon with suspended pendants and the Rivière (jewellery), rivière necklace, a single row of large precious stones. By mid-century colorful, whimsical necklaces made of real and imitation gems were popular, and the end of the century saw a neo-Classical resurgence. In the Age of Enlightenment gowns often featured a neck ruffle which women accented with neck ribbons rather than traditional necklaces, but some women did wear chokers inlaid with rubies and diamonds. Seed pearls were introduced to the United States during the Federalist Era, leading to an increase in lacy pearl necklaces.
1800–1870: The low necklines of the Court dress, court gowns fashionable at this time led to the use of large necklaces set with precious jewels. In Napoleon, Napoleon's court that ancient Greek style was fashionable, and women wore strands of pearls or gold chains with cameos and jewels. In the Romantic period necklaces were extravagant: it was fashionable to wear a tight, gem-encrusted collar with matching jewel pendants attached and rosettes of gems with pearl borders. It was also common to wear jeweled brooches attached to neck ribbons. Some necklaces were opulent in that they were made to be dismantled and reconfigured into a shorter necklacebrooches
and a bracelet. Highly embellished Gothic style necklaces from England reflected the crenelations, vertical lines and high relief of the cathedrals. Eugénie de Montijo, Empress Eugénie popularised bare décolletage with multiple necklaces on the throat, shoulders, and bosom. There was also an interest in antiquity; mosaic jewellery and Roman and Greek necklaces were reproduced. Machine-made jewellery and electroplating allowed for an influx of inexpensive imitation necklaces. 1870–1910: The Edwardian era saw a resurgence of pearl necklaces, in addition to a dog-collar style of necklace made of gold or platinum with inset diamonds, emeralds, or rubies. The Art Nouveau movement inspired symbolic, abstract designs with natural and animal motifs. The materials used - glass, porcelain, bronze, ivory, mother of pearl, horn, and enamel - were not used for their value, but for their appearance. 1910–1970: Chanel popularised costume jewelry, costume jewellery, and ropes of glass beads were common. The Art Deco movement created chunky, geometric jewellery that combined multiple types of gems and steel. By the 1960s costume jewellery was widely worn, which resulted in seasonal, ever-changing styles of necklaces and other jewellery. Real jewellery that was common in this period included wholly geometric or organically shaped silver necklaces, and precious gems set in platinum or gold necklaces inspired by the time of the French colonial empire, French Empire. Love beads (a single strand of stone or glass beads) and pendant necklaces (most often made of leather cords or metal chains with metal pendants) became popular and were worn mostly by men.
East Asia
China
In Qing dynasty China, a court necklace called ()'','' was worn by the Qing dynasty emperors and other members of the imperial family. The court necklace originated from a Buddhist rosary sent in 1643 by the Dalai Lama to the first emperor of the Qing dynasty. The necklace is composed of 108 small beads, with 4 large beads of contrasting stones to symbolize the 4 seasons, and was placed between groups of 27 beads. The necklace was also practical as it could be used for mathematical calculations in the absence of an abacus.
Necklace with longevity lock pendant
 In China, there is a custom of wearing a necklace with a Lock charm, longevity lock pendant. These lock charms were sometimes personally tied around the necks of children by Buddhist or Taoist priests. The longevity lock is known as () and is an important form of amulet for children for thousand of years in Chinese culture. According to Chinese beliefs, the protect children from evil spirits and bad luck by locking its wearer's soul and life inside of the lock. The is often made with precious materials, such as gold, silver, and jade, and having auspicious words carved on it. This form of necklace continues to be worn in present-days China.
In China, there is a custom of wearing a necklace with a Lock charm, longevity lock pendant. These lock charms were sometimes personally tied around the necks of children by Buddhist or Taoist priests. The longevity lock is known as () and is an important form of amulet for children for thousand of years in Chinese culture. According to Chinese beliefs, the protect children from evil spirits and bad luck by locking its wearer's soul and life inside of the lock. The is often made with precious materials, such as gold, silver, and jade, and having auspicious words carved on it. This form of necklace continues to be worn in present-days China.
() was a ring-like neck ornament or fashionable necklace which was originally a Buddhist ornament depicted in Buddhist arts (e.g. sculptures and paintings) in China; the have roots in ancient India where its earlier prototype is the Indian ornament ''keyūra.'' The depictions of the ''keyūra'' was introduced in China along with Buddhism''.'' The depictions of in China, such as those found in Dunhuang, evolved in shape and styles showing the cultural integration of foreign (non-Chinese) culture and the native Chinese culture due to the special characteristics of its geography.'''' The eventually evolved from an ornament in Buddhist arts and eventually became an actual necklace by the Tang dynasty.'''' The then became a classical form of necklace in Chinese society throughout centuries.'''' It continues to be worn in present-day, especially as a common Hanfu accessories, hanfu accessory being used by Hanfu enthusiasts since the Hanfu Movement, Hanfu movement. It comes in variety of styles, shapes, and materials.
Oceania
Tasmania
Shell necklaces
Aboriginal Tasmanian women have been making shell necklaces from maireener (''Phasianotrochus irisodontes'') shells for at least 2,600 years, with some major collections in museums. The continuation of the practice is being threatened by reducing supply, and sixth-generation Aboriginal Tasmanian, Palawa woman Lola Greeno is concerned that the practice will die out.Necklace lengths
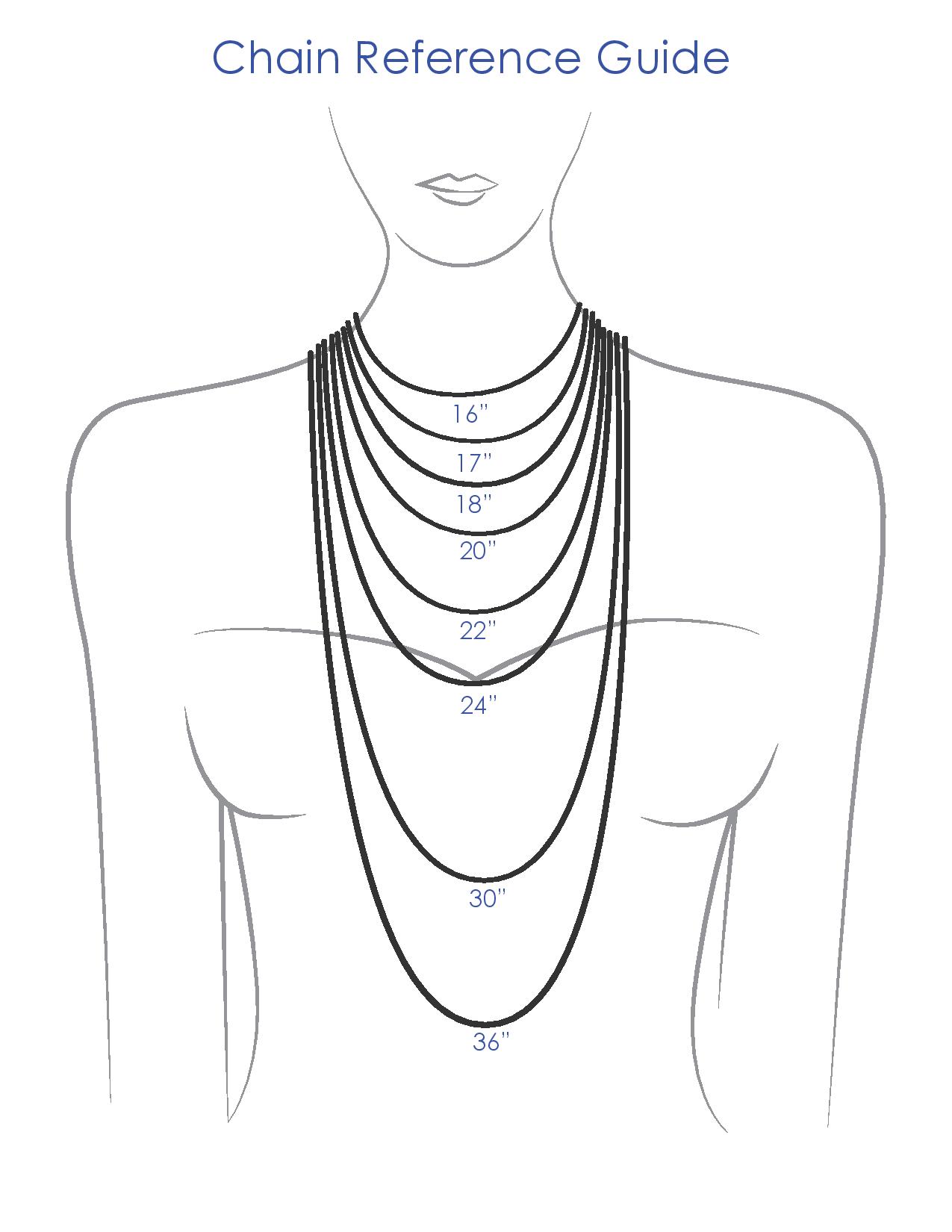
Necklaces are typically classified by length: ;Collar
:A collar is about 30 centimetres (12 inch) to 33 centimetres (13inch) long and sits high on the neck.
; Choker
: A choker is a close-fitting, short necklace, 35 centimetres (14 in) to 41 centimetres (16 in) long.
; Princess necklace
: A princess necklace is 45 centimetres (18 in) to 50 centimetres (20 in) long.
; Matinee necklace
: A matinee length necklace is 56 centimetres (22 in) to 58 centimetres (23 in) long.
; Opera necklace
: An opera necklace is 75 centimetres (30 in) to 90 centimetres (35 in) long and sits at the breastbone.
; Rope necklace
: A rope necklace is any necklace longer than opera length.
; Lariat necklace
: A lariat is a very long variation on the rope, without a clasp, often worn draped multiple times around the neck.
;Collar
:A collar is about 30 centimetres (12 inch) to 33 centimetres (13inch) long and sits high on the neck.
; Choker
: A choker is a close-fitting, short necklace, 35 centimetres (14 in) to 41 centimetres (16 in) long.
; Princess necklace
: A princess necklace is 45 centimetres (18 in) to 50 centimetres (20 in) long.
; Matinee necklace
: A matinee length necklace is 56 centimetres (22 in) to 58 centimetres (23 in) long.
; Opera necklace
: An opera necklace is 75 centimetres (30 in) to 90 centimetres (35 in) long and sits at the breastbone.
; Rope necklace
: A rope necklace is any necklace longer than opera length.
; Lariat necklace
: A lariat is a very long variation on the rope, without a clasp, often worn draped multiple times around the neck.
Gallery
Other neck uses
 Non-jewellery items are also used similar to a necklace to be worn on a neck, for example lanyards holding badges and cards.
Non-jewellery items are also used similar to a necklace to be worn on a neck, for example lanyards holding badges and cards.
See also
* Carcanet * Cross necklace * Choker * Collar (jewelry), Collar * Figaro chain * Jewellery chain * Livery collar * Locket * Love beads * Pendant * Torc * Usekh collarFurther reading
*''Jewelry 7,000 Years'' ed. Hugh Tait. . *''Jewelry Through the Ages'' by Guido Gregorietti. . *''20,000 Years of Fashion: The History of Costume and Personal Adornment'' by Francois Boucher. .References
{{Authority control Necklaces,