Management
Leadership
The agency's administration is located at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC, and provides overall guidance and direction. Except under exceptional circumstances, NASA civil service employees are required to be Citizenship in the United States, US citizens. NASA's administrator is nominated by the President of the United States subject to the approval of the United States Senate, US Senate, and serves at the President's pleasure as a senior space science advisor. The current administrator is Bill Nelson, appointed by President Joe Biden, since May 3, 2021.Strategic plan
NASA operates with four FY2022 strategic goals. * Expand human knowledge through new scientific discoveries * Extend human presence to the Moon and on towards Mars for sustainable long-term exploration, development, and utilization * Catalyze economic growth and drive innovation to address national challenges * Enhance capabilities and operations to catalyze current and future mission successBudget
NASA budget requests are developed by NASA and approved by the administration prior to submission to the United States Congress, U.S. Congress. Authorized budgets are those that have been included in enacted appropriations bills that are approved by both houses of Congress and enacted into law by the U.S. president. NASA fiscal year budget requests and authorized budgets are provided below.Organization
NASA funding and priorities are developed through its six Mission Directorates. Center-wide activities such as the Chief Engineer and Safety and Mission Assurance organizations are aligned to the headquarters function. The MSD budget estimate includes funds for these HQ functions. The administration operates 10 major field centers with several managing additional subordinate facilities across the country. Each is led by a Center Director (data below valid as of September 1, 2022).History
Establishment of NASA
Past administrators
NASA's first administrator was Dr. T. Keith Glennan who was appointed by President Dwight D. Eisenhower. During his term (1958–1961) he brought together the disparate projects in American space development research. James E. Webb, James Webb led the agency during the development of the Apollo program in the 1960s. James C. Fletcher has held the position twice; first during the Nixon administration in the 1970s and then at the request of Ronald Reagan following the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, ''Challenger'' disaster. Daniel Goldin held the post for nearly 10 years and is the longest serving administrator to date. He is best known for pioneering the "faster, better, cheaper" approach to space programs. Bill Nelson is currently serving as the 14th administrator of NASA.Insignia
The NASA seal was approved by Eisenhower in 1959, and slightly modified by President John F. Kennedy in 1961.s:Executive Order 10849, Executive Order 10849 (Wikisource) NASA's first logo was designed by the head of Lewis' Research Reports Division, James Modarelli, as a simplification of the 1959 seal. In 1975, the original logo was first dubbed "the meatball" to distinguish it from the newly designed "worm" logo which replaced it. The "meatball" returned to official use in 1992. The "worm" was brought out of retirement by administrator Jim Bridenstine in 2020.Facilities
NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC provides overall guidance and political leadership to the agency's ten field centers, through which all other facilities are administered. Ames Research Center (ARC) at Moffett Federal Airfield, Moffett Field is located in the Silicon Valley of central California and delivers wind-tunnel research on the aerodynamics of propeller-driven aircraft along with research and technology in aeronautics, spaceflight, and information technology. It provides leadership in astrobiology, small satellites, robotic lunar exploration, intelligent/adaptive systems and thermal protection. Armstrong Flight Research Center (AFRC) is located inside Edwards Air Force Base and is the home of the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), a modified Boeing 747 designed to carry a Space Shuttle orbiter back to Kennedy Space Center after a landing at Edwards AFB. The center focuses on flight testing of advanced aerospace systems. John H. Glenn Research Center, Glenn Research Center is based in Cleveland, Ohio and focuses on air-breathing and in-space propulsion and cryogenics, communications, power energy storage and conversion, microgravity sciences, and advanced materials. Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), located in Greenbelt, Maryland develops and operates uncrewed scientific spacecraft. GSFC also operates two spaceflight tracking and data acquisition networks (the Space Network and the Near Earth Network), develops and maintains advanced space and Earth science data information systems, and develops satellite systems for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center, Johnson Space Center (JSC) is the NASA center for human spaceflight training, research and flight control. It is home to the NASA Astronaut Corps, United States Astronaut Corps and is responsible for training astronauts from the US and its international partners, and includes the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center. JSC also operates the White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico to support rocket testing. Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), located in the San Gabriel Valley area of Los Angeles County, C and builds and operates robotic planetary spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating NASA's Deep Space Network, Deep Space Network (DSN). Langley Research Center (LaRC), located in Hampton, Virginia, Hampton, Virginia devotes two-thirds of its programs to aeronautics, and the rest to outer space, space. LaRC researchers use more than 40 wind tunnels to study improved aircraft and spacecraft safety, performance, and efficiency. The center was also home to early human spaceflight efforts including the team chronicled in the Hidden Figures story. John F. Kennedy Space Center, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), located west of Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, has been the launch site for every United States human space flight since 1968. KSC also manages and operates uncrewed rocket launch facilities for America's civil space program from three pads at Cape Canaveral. George C. Marshall Space Flight Center, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located on the Redstone Arsenal near Huntsville, Alabama, is one of NASA's largest centers and is leading the development of the Space Launch System in support of the Artemis program. Marshall is NASA's lead center for International Space Station (ISS) design and assembly; payloads and related crew training; and was the lead for Space Shuttle propulsion and its external tank. John C. Stennis Space Center, Stennis Space Center, originally the "Mississippi Test Facility", is located in Hancock County, Mississippi, on the banks of the Pearl River (Mississippi–Louisiana), Pearl River at the Mississippi–Louisiana border. Commissioned in October 1961, it is currently used for rocket testing by over 30 local, state, national, international, private, and public companies and agencies. It also contains the NASA Shared Services Center.Past human spaceflight programs
X-15 (1954–1968)
 NASA inherited NACA's X-15 experimental rocket-powered hypersonic speed, hypersonic research aircraft, developed in conjunction with the US Air Force and US Navy, Navy. Three planes were built starting in 1955. The X-15 was drop test, drop-launched from the wing of one of two NASA Boeing B-52 Stratofortresses, ''NB52A'' tail number 52-003, and ''NB52B'', tail number 52-008 (known as the ''Balls 8''). Release took place at an altitude of about and a speed of about .
Twelve pilots were selected for the program from the Air Force, Navy, and NACA. A total of 199 flights were made between June 1959 and December 1968, resulting in the Flight airspeed record, official world record for the highest speed ever reached by a crewed powered aircraft (current ), and a maximum speed of Mach 6.72, .Aircraft Museum X-15."
NASA inherited NACA's X-15 experimental rocket-powered hypersonic speed, hypersonic research aircraft, developed in conjunction with the US Air Force and US Navy, Navy. Three planes were built starting in 1955. The X-15 was drop test, drop-launched from the wing of one of two NASA Boeing B-52 Stratofortresses, ''NB52A'' tail number 52-003, and ''NB52B'', tail number 52-008 (known as the ''Balls 8''). Release took place at an altitude of about and a speed of about .
Twelve pilots were selected for the program from the Air Force, Navy, and NACA. A total of 199 flights were made between June 1959 and December 1968, resulting in the Flight airspeed record, official world record for the highest speed ever reached by a crewed powered aircraft (current ), and a maximum speed of Mach 6.72, .Aircraft Museum X-15."''Aerospaceweb.org'', November 24, 2008. The altitude record for X-15 was 354,200 feet (107.96 km). Eight of the pilots were awarded Air Force Astronaut Badge, astronaut wings for flying above , and two flights by Joseph A. Walker exceeded , qualifying as spaceflight according to the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, International Aeronautical Federation. The X-15 program employed mechanical techniques used in the later crewed spaceflight programs, including reaction control system jets for controlling the orientation of a spacecraft, space suits, and horizon definition for navigation.NASA, X-15 Hypersonic Research Program
, retrieved October 17, 2011 The atmospheric entry, reentry and landing data collected were valuable to NASA for designing the Space Shuttle.Aerospaceweb, North American X-15
. Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved on November 3, 2011.
Mercury (1958–1963)
 In 1958, NASA formed an engineering group, the Space Task Group, to manage their human spaceflight programs under the direction of Robert Gilruth. Their earliest programs were conducted under the pressure of the Cold War competition between the US and the Soviet Union. NASA inherited the US Air Force's Man in Space Soonest program, which considered many crewed spacecraft designs ranging from rocket planes like the X-15, to small ballistic space capsules.Encyclopedia Astronautica, Project 7969
In 1958, NASA formed an engineering group, the Space Task Group, to manage their human spaceflight programs under the direction of Robert Gilruth. Their earliest programs were conducted under the pressure of the Cold War competition between the US and the Soviet Union. NASA inherited the US Air Force's Man in Space Soonest program, which considered many crewed spacecraft designs ranging from rocket planes like the X-15, to small ballistic space capsules.Encyclopedia Astronautica, Project 7969, retrieved October 17, 2011 By 1958, the space plane concepts were eliminated in favor of the ballistic capsule, and NASA renamed it Project Mercury. The Mercury Seven, first seven astronauts were selected among candidates from the Navy, Air Force and Marine test pilot programs. On May 5, 1961, astronaut Alan Shepard became the first American in space aboard a capsule he named ''Mercury-Redstone 3, Freedom 7'', launched on a Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle, Redstone booster on a 15-minute ballistics, ballistic (suborbital) flight. John Glenn became the first American to be launched into orbit, on an Atlas LV-3B, Atlas launch vehicle on February 20, 1962, aboard Mercury-Atlas 6, ''Friendship 7''. Glenn completed three orbits, after which three more orbital flights were made, culminating in Gordon Cooper, L. Gordon Cooper's 22-orbit flight ''Mercury-Atlas 9, Faith 7'', May 15–16, 1963. Katherine Johnson, Mary Jackson (engineer), Mary Jackson, and Dorothy Vaughan were three of the human computers doing calculations on trajectories during the Space Race. Johnson was well known for doing trajectory calculations for John Glenn's mission in 1962, where she was running the same equations by hand that were being run on the computer. Mercury's competition from the Soviet Union (USSR) was the single-pilot Vostok programme, Vostok spacecraft. They sent the first man in space, cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, into a single Earth orbit aboard Vostok 1 in April 1961, one month before Shepard's flight. In August 1962, they achieved an almost four-day record flight with Andriyan Nikolayev aboard Vostok 3, and also conducted a concurrent Vostok 4 mission carrying Pavel Popovich.
Gemini (1961–1966)
 Based on studies to grow the Mercury spacecraft capabilities to long-duration flights, developing space rendezvous techniques, and precision Earth landing, Project Gemini was started as a two-man program in 1961 to overcome the Soviets' lead and to support the planned Apollo crewed lunar landing program, adding extravehicular activity (EVA) and space rendezvous, rendezvous and docking and berthing of spacecraft, docking to its objectives. The first crewed Gemini flight, Gemini 3, was flown by Gus Grissom and John Young (astronaut), John Young on March 23, 1965. Nine missions followed in 1965 and 1966, demonstrating an endurance mission of nearly fourteen days, rendezvous, docking, and practical EVA, and gathering medical data on the effects of weightlessness on humans.
Under the direction of Premier of the Soviet Union, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev, the USSR competed with Gemini by converting their Vostok spacecraft into a two- or three-man Voskhod (spacecraft), Voskhod. They succeeded in launching two crewed flights before Gemini's first flight, achieving a three-cosmonaut flight in 1964 and the first EVA in 1965. After this, the program was canceled, and Gemini caught up while spacecraft designer Sergei Korolev developed the Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spacecraft, their answer to Apollo.
Based on studies to grow the Mercury spacecraft capabilities to long-duration flights, developing space rendezvous techniques, and precision Earth landing, Project Gemini was started as a two-man program in 1961 to overcome the Soviets' lead and to support the planned Apollo crewed lunar landing program, adding extravehicular activity (EVA) and space rendezvous, rendezvous and docking and berthing of spacecraft, docking to its objectives. The first crewed Gemini flight, Gemini 3, was flown by Gus Grissom and John Young (astronaut), John Young on March 23, 1965. Nine missions followed in 1965 and 1966, demonstrating an endurance mission of nearly fourteen days, rendezvous, docking, and practical EVA, and gathering medical data on the effects of weightlessness on humans.
Under the direction of Premier of the Soviet Union, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev, the USSR competed with Gemini by converting their Vostok spacecraft into a two- or three-man Voskhod (spacecraft), Voskhod. They succeeded in launching two crewed flights before Gemini's first flight, achieving a three-cosmonaut flight in 1964 and the first EVA in 1965. After this, the program was canceled, and Gemini caught up while spacecraft designer Sergei Korolev developed the Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spacecraft, their answer to Apollo.
Apollo (1960–1972)
 The U.S. public's perception of the Soviet lead in the Space Race (by putting the first man into space) motivated President John F. Kennedy to ask the Congress on May 25, 1961, to commit the federal government to a program to land a man on the Moon by the end of the 1960s, which effectively launched the Apollo program.
Apollo was one of the most expensive American scientific programs ever. It cost more than $20 billion in 1960s dollars or an estimated $ in present-day US dollars. (In comparison, the Manhattan Project cost roughly $, accounting for inflation.) The Apollo program used the newly developed Saturn I and Saturn V rockets, which were far larger than the repurposed ICBMs of the previous Mercury and Gemini programs. They were used to launch the Apollo spacecraft, consisting of the Apollo command and service module, Command and Service Module (CSM) and the Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module (LM). The CSM ferried astronauts from Earth to Moon orbit and back, while the Lunar Module would land them on the Moon itself.
The planned first crew of 3 astronauts were killed due to a fire during a 1967 preflight test for the Apollo 204 mission (later renamed Apollo 1). The second crewed mission, Apollo 8, brought astronauts for the first time in a flight around the Moon in December 1968. Shortly before, the Soviets had sent an uncrewed spacecraft around the Moon. The next two missions (Apollo 9 and Apollo 10) practiced rendezvous and docking maneuvers required to conduct the Moon landing.
The Apollo 11 mission, launched in July 1969, landed the first humans on the Moon. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walked on the lunar surface, conducting Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package, experiments and Sample-return mission, sample collection, while Michael Collins (astronaut), Michael Collins orbited above in the CSM. Six subsequent Apollo missions (12 through 17) were launched; five of them were successful, while one (Apollo 13) was aborted after an in-flight emergency nearly killed the astronauts. Throughout these seven Apollo spaceflights, twelve men walked on the Moon. These missions returned a wealth of scientific data and of lunar samples. Topics covered by experiments performed included soil mechanics, meteoroids, seismology, Heat transfer, heat flow, Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment, lunar ranging, magnetic fields, and solar wind. The Moon landing marked the end of the space race; and as a gesture, Armstrong mentioned mankind when he stepped down on the Moon.
On July 3, 1969, the Soviets suffered a major setback on their Moon program when the rocket known as the N1 (rocket), N-1 had exploded in a fireball at its launch site at Baikonur Cosmodrome, Baikonur in Kazakhstan, destroying one of two launch pads. Each of the first four launches of N-1 resulted in failure before the end of the first stage flight effectively denying the Soviet Union the capacity to deliver the systems required for a crewed lunar landing.
Apollo set major List of space exploration milestones, 1957–1969, milestones in human spaceflight. It stands alone in sending crewed missions beyond low Earth orbit, and landing humans on another celestial body. Apollo 8 was the first crewed spacecraft to orbit another celestial body, while Apollo 17 marked the last moonwalk and the last crewed mission beyond low Earth orbit. The program spurred advances in many areas of technology peripheral to rocketry and crewed spaceflight, including avionics, telecommunications, and computers. Apollo sparked interest in many fields of engineering and left many physical facilities and machines developed for the program as landmarks. Many objects and artifacts from the program are on display at various locations throughout the world, notably at the National Air and Space Museum, Smithsonian's Air and Space Museums.
The U.S. public's perception of the Soviet lead in the Space Race (by putting the first man into space) motivated President John F. Kennedy to ask the Congress on May 25, 1961, to commit the federal government to a program to land a man on the Moon by the end of the 1960s, which effectively launched the Apollo program.
Apollo was one of the most expensive American scientific programs ever. It cost more than $20 billion in 1960s dollars or an estimated $ in present-day US dollars. (In comparison, the Manhattan Project cost roughly $, accounting for inflation.) The Apollo program used the newly developed Saturn I and Saturn V rockets, which were far larger than the repurposed ICBMs of the previous Mercury and Gemini programs. They were used to launch the Apollo spacecraft, consisting of the Apollo command and service module, Command and Service Module (CSM) and the Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module (LM). The CSM ferried astronauts from Earth to Moon orbit and back, while the Lunar Module would land them on the Moon itself.
The planned first crew of 3 astronauts were killed due to a fire during a 1967 preflight test for the Apollo 204 mission (later renamed Apollo 1). The second crewed mission, Apollo 8, brought astronauts for the first time in a flight around the Moon in December 1968. Shortly before, the Soviets had sent an uncrewed spacecraft around the Moon. The next two missions (Apollo 9 and Apollo 10) practiced rendezvous and docking maneuvers required to conduct the Moon landing.
The Apollo 11 mission, launched in July 1969, landed the first humans on the Moon. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walked on the lunar surface, conducting Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package, experiments and Sample-return mission, sample collection, while Michael Collins (astronaut), Michael Collins orbited above in the CSM. Six subsequent Apollo missions (12 through 17) were launched; five of them were successful, while one (Apollo 13) was aborted after an in-flight emergency nearly killed the astronauts. Throughout these seven Apollo spaceflights, twelve men walked on the Moon. These missions returned a wealth of scientific data and of lunar samples. Topics covered by experiments performed included soil mechanics, meteoroids, seismology, Heat transfer, heat flow, Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment, lunar ranging, magnetic fields, and solar wind. The Moon landing marked the end of the space race; and as a gesture, Armstrong mentioned mankind when he stepped down on the Moon.
On July 3, 1969, the Soviets suffered a major setback on their Moon program when the rocket known as the N1 (rocket), N-1 had exploded in a fireball at its launch site at Baikonur Cosmodrome, Baikonur in Kazakhstan, destroying one of two launch pads. Each of the first four launches of N-1 resulted in failure before the end of the first stage flight effectively denying the Soviet Union the capacity to deliver the systems required for a crewed lunar landing.
Apollo set major List of space exploration milestones, 1957–1969, milestones in human spaceflight. It stands alone in sending crewed missions beyond low Earth orbit, and landing humans on another celestial body. Apollo 8 was the first crewed spacecraft to orbit another celestial body, while Apollo 17 marked the last moonwalk and the last crewed mission beyond low Earth orbit. The program spurred advances in many areas of technology peripheral to rocketry and crewed spaceflight, including avionics, telecommunications, and computers. Apollo sparked interest in many fields of engineering and left many physical facilities and machines developed for the program as landmarks. Many objects and artifacts from the program are on display at various locations throughout the world, notably at the National Air and Space Museum, Smithsonian's Air and Space Museums.
Skylab (1965–1979)
 Skylab was the United States' first and only independently built space station. Conceived in 1965 as a workshop to be constructed in space from a spent Saturn IB upper stage, the station was constructed on Earth and launched on May 14, 1973, atop the first two stages of a Saturn V, into a orbit inclined at 50° to the equator. Damaged during launch by the loss of its thermal protection and one electricity-generating solar panel, it was repaired to functionality by its first crew. It was occupied for a total of 171 days by 3 successive crews in 1973 and 1974. It included a laboratory for studying the effects of microgravity environment, microgravity, and a Apollo Telescope Mount, solar observatory. NASA planned to have the in-development Space Shuttle dock with it, and elevate Skylab to a higher safe altitude, but the Shuttle was not ready for flight before Skylab's re-entry and demise on July 11, 1979.Benson, Charles Dunlap and William David Compton.
Skylab was the United States' first and only independently built space station. Conceived in 1965 as a workshop to be constructed in space from a spent Saturn IB upper stage, the station was constructed on Earth and launched on May 14, 1973, atop the first two stages of a Saturn V, into a orbit inclined at 50° to the equator. Damaged during launch by the loss of its thermal protection and one electricity-generating solar panel, it was repaired to functionality by its first crew. It was occupied for a total of 171 days by 3 successive crews in 1973 and 1974. It included a laboratory for studying the effects of microgravity environment, microgravity, and a Apollo Telescope Mount, solar observatory. NASA planned to have the in-development Space Shuttle dock with it, and elevate Skylab to a higher safe altitude, but the Shuttle was not ready for flight before Skylab's re-entry and demise on July 11, 1979.Benson, Charles Dunlap and William David Compton. Living and Working in Space: A History of Skylab
''. NASA publication SP-4208. To reduce cost, NASA modified one of the Saturn V rockets originally earmarked for a canceled Apollo mission to launch Skylab, which itself was a modified S-IVB, Saturn V fuel tank. Apollo spacecraft, launched on smaller Saturn IB rockets, were used for transporting astronauts to and from the station. Three crews, consisting of three men each, stayed aboard the station for periods of 28, 59, and 84 days. Skylab's habitable volume was , which was 30.7 times bigger than that of the Apollo Command Module.
Space Transportation System (1969–1972)
In February 1969, President Richard Nixon appointed a space task group headed by Vice President Spiro Agnew to recommend human spaceflight projects beyond Apollo. The group responded in September with the Integrated Program Plan (IPP), intended to support space stations in Earth and lunar orbit, a lunar surface base, and a human Mars landing. These would be supported by replacing NASA's existing expendable launch systems with a reusable infrastructure including Earth orbit shuttles, space tugs, and a nuclear thermal rocket, nuclear-powered trans-lunar and interplanetary shuttle. Despite the enthusiastic support of Agnew and NASA Administrator Thomas O. Paine, Nixon realized public enthusiasm, which translated into Congressional support, for the space program was waning as Apollo neared its climax, and vetoed most of these plans, except for the Space Shuttle program, Earth orbital shuttle, and a deferred Earth space station.Apollo–Soyuz (1972–1975)
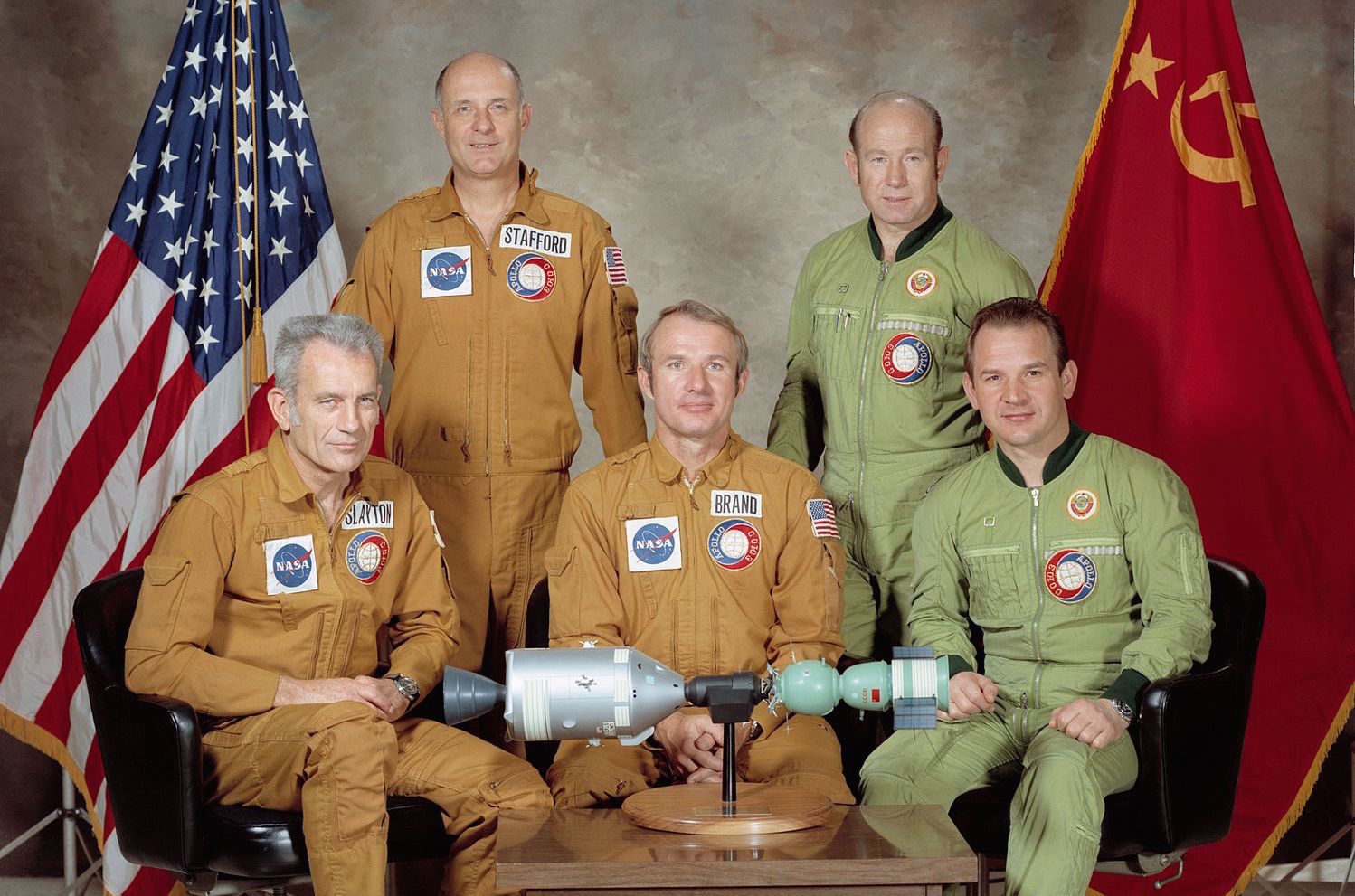 On May 24, 1972, US President Richard M. Nixon and Soviet Premier Alexei Kosygin signed an agreement calling for a joint crewed space mission, and declaring intent for all future international crewed spacecraft to be capable of docking with each other. This authorized the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project (ASTP), involving the rendezvous and docking in Earth orbit of a surplus Apollo command and service module with a Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spacecraft. The mission took place in July 1975. This was the last US human spaceflight until the first orbital flight of the Space Shuttle in April 1981.
The mission included both joint and separate scientific experiments and provided useful engineering experience for future joint US–Russian space flights, such as the Shuttle–''Mir'' programNASA, Shuttle-MIR history
On May 24, 1972, US President Richard M. Nixon and Soviet Premier Alexei Kosygin signed an agreement calling for a joint crewed space mission, and declaring intent for all future international crewed spacecraft to be capable of docking with each other. This authorized the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project (ASTP), involving the rendezvous and docking in Earth orbit of a surplus Apollo command and service module with a Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spacecraft. The mission took place in July 1975. This was the last US human spaceflight until the first orbital flight of the Space Shuttle in April 1981.
The mission included both joint and separate scientific experiments and provided useful engineering experience for future joint US–Russian space flights, such as the Shuttle–''Mir'' programNASA, Shuttle-MIR history, retrieved October 15, 2011 and the International Space Station.
Space Shuttle (1972–2011)
 The Space Shuttle was the only vehicle in the Space Transportation System to be developed, and became the major focus of NASA in the late 1970s and the 1980s. Originally planned as a frequently launchable, fully reusable vehicle, the design was changed to use an Space Shuttle external tank, expendable external propellant tank to reduce development cost, and four Space Shuttle orbiters were built by 1985. The first to launch, Space Shuttle Columbia, ''Columbia'', did so on April 12, 1981, the 20th anniversary of the Vostok 1, first human spaceflight.
The Shuttle flew 135 missions and carried 355 astronauts from 16 countries, many on multiple trips. Its major components were a spaceplane orbiter with an external fuel tank and two solid-fuel launch rockets at its side. The external tank, which was bigger than the spacecraft itself, was the only major component that was not reused. The shuttle could orbit in altitudes of 185–643 km (115–400 statute mile, miles)NASA, Shuttle Basics
The Space Shuttle was the only vehicle in the Space Transportation System to be developed, and became the major focus of NASA in the late 1970s and the 1980s. Originally planned as a frequently launchable, fully reusable vehicle, the design was changed to use an Space Shuttle external tank, expendable external propellant tank to reduce development cost, and four Space Shuttle orbiters were built by 1985. The first to launch, Space Shuttle Columbia, ''Columbia'', did so on April 12, 1981, the 20th anniversary of the Vostok 1, first human spaceflight.
The Shuttle flew 135 missions and carried 355 astronauts from 16 countries, many on multiple trips. Its major components were a spaceplane orbiter with an external fuel tank and two solid-fuel launch rockets at its side. The external tank, which was bigger than the spacecraft itself, was the only major component that was not reused. The shuttle could orbit in altitudes of 185–643 km (115–400 statute mile, miles)NASA, Shuttle Basics, retrieved October 18, 2011 and carry a maximum payload (to low orbit) of 24,400 kg (54,000 lb).
, retrieved October 18, 2011 Missions could last from 5 to 17 days and crews could be from 2 to 8 astronauts. On 20 missions (1983–1998) the Space Shuttle carried Spacelab, designed in cooperation with the European Space Agency (ESA). Spacelab was not designed for independent orbital flight, but remained in the Shuttle's cargo bay as the astronauts entered and left it through an airlock.Encyclopedia Astronautica, Spacelab
. Retrieved October 20, 2011 On June 18, 1983, Sally Ride became the first American woman in space, on board the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' STS-7 mission. Another famous series of missions were the STS-31, launch and later STS-61, successful repair of the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990 and 1993, respectively.Encyclopedia Astronautica, HST
. Retrieved October 20, 2011 In 1995, Russian-American interaction resumed with the Shuttle–Mir program, Shuttle–Mir missions (1995–1998). Once more an American vehicle docked with a Russian craft, this time a full-fledged space station. This cooperation has continued with Russia and the United States as two of the biggest partners in the largest space station built: the International Space Station (ISS). The strength of their cooperation on this project was even more evident when NASA began relying on Russian launch vehicles to service the ISS during the two-year grounding of the shuttle fleet following the 2003 Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster. The Shuttle fleet lost two orbiters and 14 astronauts in two disasters: ''Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, Challenger'' in 1986, and Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, ''Columbia'' in 2003. While the 1986 loss was mitigated by building the from replacement parts, NASA did not build another orbiter to replace the second loss. NASA's Space Shuttle program had 135 missions when the program ended with the successful landing of the Space Shuttle Atlantis, Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' at the Kennedy Space Center on July 21, 2011. The program spanned 30 years with 355 separate astronauts sent into space, many on multiple missions.
Constellation (2005–2010)
 While the Space Shuttle program was still suspended after the loss of ''Columbia'', President George W. Bush announced the Vision for Space Exploration including the retirement of the Space Shuttle after completing the International Space Station. The plan was enacted into law by the NASA Authorization Act of 2005 and directs NASA to develop and launch the Crew Exploration Vehicle (later called Orion (spacecraft), Orion) by 2010, return Americans to the Moon by 2020, land on Mars as feasible, repair the Hubble Space Telescope, and continue scientific investigation through robotic solar system exploration, human presence on the ISS, Earth observation, and astrophysics research. The crewed exploration goals prompted NASA's Constellation program.
On December 4, 2006, NASA announced it was planning a Lunar outpost (NASA), permanent Moon base. The goal was to start building the Moon base by 2020, and by 2024, have a fully functional base that would allow for crew rotations and in-situ resource utilization. However, in 2009, the Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee, Augustine Committee found the program to be on an "unsustainable trajectory." In February 2010, President Barack Obama's administration proposed eliminating public funds for it.
While the Space Shuttle program was still suspended after the loss of ''Columbia'', President George W. Bush announced the Vision for Space Exploration including the retirement of the Space Shuttle after completing the International Space Station. The plan was enacted into law by the NASA Authorization Act of 2005 and directs NASA to develop and launch the Crew Exploration Vehicle (later called Orion (spacecraft), Orion) by 2010, return Americans to the Moon by 2020, land on Mars as feasible, repair the Hubble Space Telescope, and continue scientific investigation through robotic solar system exploration, human presence on the ISS, Earth observation, and astrophysics research. The crewed exploration goals prompted NASA's Constellation program.
On December 4, 2006, NASA announced it was planning a Lunar outpost (NASA), permanent Moon base. The goal was to start building the Moon base by 2020, and by 2024, have a fully functional base that would allow for crew rotations and in-situ resource utilization. However, in 2009, the Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee, Augustine Committee found the program to be on an "unsustainable trajectory." In February 2010, President Barack Obama's administration proposed eliminating public funds for it.
Journey to Mars (2010–2017)
 President Obama's plan was to develop American private spaceflight capabilities to get astronauts to the International Space Station, replace Russian Soyuz capsules, and use Orion capsules for ISS emergency escape purposes. During a speech at the Kennedy Space Center on April 15, 2010, Obama proposed a new heavy-lift vehicle (HLV) to replace the formerly planned Ares V. In his speech, Obama called for a crewed mission to an asteroid as soon as 2025, and a crewed mission to Mars orbit by the mid-2030s. The NASA Authorization Act of 2010 was passed by Congress and signed into law on October 11, 2010. The act officially canceled the Constellation program.
The NASA Authorization Act of 2010 required a newly designed HLV be chosen within 90 days of its passing; the launch vehicle was given the name Space Launch System. The new law also required the construction of a beyond low earth orbit spacecraft. The Orion spacecraft, which was being developed as part of the Constellation program, was chosen to fulfill this role. The Space Launch System is planned to launch both Orion and other necessary hardware for missions beyond low Earth orbit. The SLS is to be upgraded over time with more powerful versions. The initial capability of SLS is required to be able to lift (later ) into Low Earth orbit, LEO. It is then planned to be upgraded to and then eventually to . The Orion capsule first flew on Exploration Flight Test 1 (EFT-1), an uncrewed test flight that was launched on December 5, 2014, atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket.
NASA undertook a feasibility study in 2012 and developed the Asteroid Redirect Mission as an uncrewed mission to move a boulder-sized near-Earth asteroid (or boulder-sized chunk of a larger asteroid) into lunar orbit. The mission would demonstrate ion thruster technology and develop techniques that could be used for planetary defense against an asteroid collision, as well as a cargo transport to Mars in support of a future human mission. The Moon-orbiting boulder might then later be visited by astronauts. The Asteroid Redirect Mission was cancelled in 2017 as part of the FY2018 NASA budget, the first one under President Donald Trump.
President Obama's plan was to develop American private spaceflight capabilities to get astronauts to the International Space Station, replace Russian Soyuz capsules, and use Orion capsules for ISS emergency escape purposes. During a speech at the Kennedy Space Center on April 15, 2010, Obama proposed a new heavy-lift vehicle (HLV) to replace the formerly planned Ares V. In his speech, Obama called for a crewed mission to an asteroid as soon as 2025, and a crewed mission to Mars orbit by the mid-2030s. The NASA Authorization Act of 2010 was passed by Congress and signed into law on October 11, 2010. The act officially canceled the Constellation program.
The NASA Authorization Act of 2010 required a newly designed HLV be chosen within 90 days of its passing; the launch vehicle was given the name Space Launch System. The new law also required the construction of a beyond low earth orbit spacecraft. The Orion spacecraft, which was being developed as part of the Constellation program, was chosen to fulfill this role. The Space Launch System is planned to launch both Orion and other necessary hardware for missions beyond low Earth orbit. The SLS is to be upgraded over time with more powerful versions. The initial capability of SLS is required to be able to lift (later ) into Low Earth orbit, LEO. It is then planned to be upgraded to and then eventually to . The Orion capsule first flew on Exploration Flight Test 1 (EFT-1), an uncrewed test flight that was launched on December 5, 2014, atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket.
NASA undertook a feasibility study in 2012 and developed the Asteroid Redirect Mission as an uncrewed mission to move a boulder-sized near-Earth asteroid (or boulder-sized chunk of a larger asteroid) into lunar orbit. The mission would demonstrate ion thruster technology and develop techniques that could be used for planetary defense against an asteroid collision, as well as a cargo transport to Mars in support of a future human mission. The Moon-orbiting boulder might then later be visited by astronauts. The Asteroid Redirect Mission was cancelled in 2017 as part of the FY2018 NASA budget, the first one under President Donald Trump.
Past robotic exploration programs
NASA has conducted many uncrewed and robotic spaceflight programs throughout its history. Uncrewed robotic programs launched the first American artificial satellites into Earth orbit for scientific and communications satellite, communications purposes and sent scientific probes to explore the planets of the Solar System, starting with Venus and Mars, and including "Voyager program, grand tours" of the outer planets. More than 1,000 uncrewed missions have been designed to explore the Earth and the Solar System.Early efforts
The first US uncrewed satellite was Explorer 1, which started as an ABMA/JPL project during the early part of the Space Race. It was launched in January 1958, two months after Sputnik 1, Sputnik. At the creation of NASA, the Explorer project was transferred to the agency and still continues. Its missions have been focusing on the Earth and the Sun, measuring magnetic fields and the solar wind, among other aspects. The Ranger missions developed technology to build and deliver robotic probes into orbit and to the vicinity of the Moon. Ranger 7 successfully returned images of the Moon in July 1964, followed by two more successful missions. NASA also played a role in the development and delivery of early communications satellite technology to orbit. Syncom 3 was the first geostationary satellite. It was an experimental geosynchronous communications satellite placed over the equator at 180 degrees longitude in the Pacific Ocean. The satellite provided live television coverage of the 1964 Olympic games in Tokyo, Japan and conducted various communications tests. Operations were turned over to the Department of Defense on January 1, 1965; Syncom 3 was to prove useful in the DoD's Vietnam communications. Programs like Syncom, Telstar, and Applications Technology Satellites (ATS) demonstrated the utility of communications satellites and delivered early telephonic and video satellite transmission.Planetary exploration
 Study of Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, or Mars has been the goal of more than ten uncrewed NASA programs. The first was Mariner program, Mariner in the 1960s and 1970s, which made multiple visits to Venus and Mars and one to Mercury (planet), Mercury. Probes launched under the Mariner program were also the first to make a planetary flyby (Mariner 2), to take the first pictures from another planet (Mariner 4), the first planetary orbiter (Mariner 9), and the first to make a gravity assist maneuver (''Mariner 10''). This is a technique where the satellite takes advantage of the gravity and velocity of planets to reach its destination.
''Magellan (spacecraft), Magellan'' orbited Venus for four years in the early 1990s capturing radar images of the planet's surface. ''MESSENGER'' orbited Mercury (planet), Mercury between 2011 and 2015 after a 6.5-year journey involving a complicated series of flybys of Venus and Mercury to reduce velocity sufficiently enough to enter Mercury orbit. ''MESSENGER'' became the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury and used its science payload to study Mercury's surface composition, geological history, internal magnetic field, and verified its polar deposits were dominantly water-ice.
From 1966 to 1968, the ''Lunar Orbiter program, Lunar Orbiter'' and ''Surveyor program, Surveyor'' missions provided higher quality photographs and other measurements to pave the way for the crewed Apollo missions to the Moon. ''Clementine (spacecraft), Clementine'' spent a couple of months mapping the Moon in 1994 before moving on to other mission objectives. ''Lunar Prospector'' spent 19 months from 1998 mapping the Moon's surface composition and looking for polar ice.
The first successful landing on Mars was made by ''Viking 1'' in 1976. ''Viking 2'' followed two months later. Twenty years later the ''Sojourner (rover), Sojourner'' rover was landed on Mars by ''Mars Pathfinder''.
After Mars, Jupiter was first visited by ''Pioneer 10'' in 1973. More than 20 years later ''Galileo (spacecraft), Galileo'' sent a probe into the planet's atmosphere and became the first spacecraft to orbit the planet. ''Pioneer 11'' became the first spacecraft to visit Saturn in 1979, with ''Voyager 2'' making the first (and so far, only) visits to Uranus and Neptune in 1986 and 1989, respectively. The first spacecraft to leave the Solar System was ''Pioneer 10'' in 1983. For a time, it was the most distant spacecraft, but it has since been surpassed by both ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''.
''Pioneers 10'' and ''11'' and both Voyager probes carry messages from the Earth to extraterrestrial life. Communication can be difficult with deep space travel. For instance, it took about three hours for a radio signal to reach the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft when it was more than halfway to Pluto. Contact with ''Pioneer 10'' was lost in 2003. Both Voyager probes continue to operate as they explore the outer boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space.
NASA continued to support ''in situ#Space-related, in situ'' exploration beyond the asteroid belt, including Pioneer and Voyager traverses into the unexplored trans-Pluto region, and gas giant orbiters ''Galileo (spacecraft), Galileo'' (1989–2003) and ''Cassini–Huygens, Cassini'' (1997–2017) exploring the Jovian and Saturnian systems respectively.
Study of Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, or Mars has been the goal of more than ten uncrewed NASA programs. The first was Mariner program, Mariner in the 1960s and 1970s, which made multiple visits to Venus and Mars and one to Mercury (planet), Mercury. Probes launched under the Mariner program were also the first to make a planetary flyby (Mariner 2), to take the first pictures from another planet (Mariner 4), the first planetary orbiter (Mariner 9), and the first to make a gravity assist maneuver (''Mariner 10''). This is a technique where the satellite takes advantage of the gravity and velocity of planets to reach its destination.
''Magellan (spacecraft), Magellan'' orbited Venus for four years in the early 1990s capturing radar images of the planet's surface. ''MESSENGER'' orbited Mercury (planet), Mercury between 2011 and 2015 after a 6.5-year journey involving a complicated series of flybys of Venus and Mercury to reduce velocity sufficiently enough to enter Mercury orbit. ''MESSENGER'' became the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury and used its science payload to study Mercury's surface composition, geological history, internal magnetic field, and verified its polar deposits were dominantly water-ice.
From 1966 to 1968, the ''Lunar Orbiter program, Lunar Orbiter'' and ''Surveyor program, Surveyor'' missions provided higher quality photographs and other measurements to pave the way for the crewed Apollo missions to the Moon. ''Clementine (spacecraft), Clementine'' spent a couple of months mapping the Moon in 1994 before moving on to other mission objectives. ''Lunar Prospector'' spent 19 months from 1998 mapping the Moon's surface composition and looking for polar ice.
The first successful landing on Mars was made by ''Viking 1'' in 1976. ''Viking 2'' followed two months later. Twenty years later the ''Sojourner (rover), Sojourner'' rover was landed on Mars by ''Mars Pathfinder''.
After Mars, Jupiter was first visited by ''Pioneer 10'' in 1973. More than 20 years later ''Galileo (spacecraft), Galileo'' sent a probe into the planet's atmosphere and became the first spacecraft to orbit the planet. ''Pioneer 11'' became the first spacecraft to visit Saturn in 1979, with ''Voyager 2'' making the first (and so far, only) visits to Uranus and Neptune in 1986 and 1989, respectively. The first spacecraft to leave the Solar System was ''Pioneer 10'' in 1983. For a time, it was the most distant spacecraft, but it has since been surpassed by both ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''.
''Pioneers 10'' and ''11'' and both Voyager probes carry messages from the Earth to extraterrestrial life. Communication can be difficult with deep space travel. For instance, it took about three hours for a radio signal to reach the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft when it was more than halfway to Pluto. Contact with ''Pioneer 10'' was lost in 2003. Both Voyager probes continue to operate as they explore the outer boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space.
NASA continued to support ''in situ#Space-related, in situ'' exploration beyond the asteroid belt, including Pioneer and Voyager traverses into the unexplored trans-Pluto region, and gas giant orbiters ''Galileo (spacecraft), Galileo'' (1989–2003) and ''Cassini–Huygens, Cassini'' (1997–2017) exploring the Jovian and Saturnian systems respectively.
Heliophysics
The missions below represent the robotic spacecraft that have been delivered and operated by NASA to study the heliosphere. The ''Helios (spacecraft), Helios A and Helios B'' missions were launched in the 1970s to study the Sun and were the first spacecraft to orbit inside of Mercury's orbit. The Fast Auroral SnapshoT Explorer, Fast Auroral Snapshot Explorer (FAST) mission was launched in August 1996 becoming the second SMEX mission placed in orbit. It studied the auroral zones near each pole during its transits in a highly elliptical orbit. The International Cometary Explorer, International Earth-Sun Explorer-3 (ISEE-3) mission was launched in 1978 and is the first spacecraft designed to operate at the Earth-Sun L1 libration point. It studied solar-terrestrial relationships at the outermost boundaries of the Earth's magnetosphere and the structure of the solar wind. The spacecraft was subsequently maneuvered out of the halo orbit and conducted a flyby of the Giacobini-Zinner comet in 1985 as the rechristened International Cometary Explorer (ICE). ''Ulysses (spacecraft), Ulysses'' was launched in 1990 and slingshotted around Jupiter to put it in an orbit to travel over the poles of the Sun. It was designed study the space environment above and below the poles and delivered scientific data for about 19 years. Additional spacecraft launched for studies of the heliosphere include: ''Cluster II (spacecraft), Cluster II'', ''IMAGE (spacecraft), IMAGE'', Polar (satellite), POLAR, ''Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager'', and the Van Allen Probes.Earth Science
The Earth Sciences Division of the NASA Science Mission Directorate leads efforts to study the planet Earth. Spacecraft have been used to study Earth since the mid-1960s. Efforts included the Television Infrared Observation Satellite (TIROS) and Nimbus program, Nimbus satellite systems of which there were many carrying weather research and forecasting from space from 1960 into the 2020s. The CRRES, Combined Release and Radiation Effects Satellite (CRRES) was launched in 1990 on a three-year mission to investigate fields, plasmas, and energetic particles inside the Earth's magnetosphere. The Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) was launched in 1991 by STS-48 to study the Earth's atmosphere especially the protective ozone layer. TOPEX/Poseidon was launched in 1992 and was the first significant oceanographic research satellite.
The ICESat, Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite (ICESat) was launched in 2003, operated for seven years, and measured ice sheet mass balance, cloud and aerosol heights, and well as topography and vegetation characteristics.
Over a dozen past robotic missions have focused on the study of the Earth and its environment. Some of these additional missions include Aquarius, Earth Observing-1 (EO-1), Jason-1, OSTM/Jason-2, Ocean Surface Topography Mission/Jason-2, and Radarsat-1 missions.
The CRRES, Combined Release and Radiation Effects Satellite (CRRES) was launched in 1990 on a three-year mission to investigate fields, plasmas, and energetic particles inside the Earth's magnetosphere. The Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) was launched in 1991 by STS-48 to study the Earth's atmosphere especially the protective ozone layer. TOPEX/Poseidon was launched in 1992 and was the first significant oceanographic research satellite.
The ICESat, Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite (ICESat) was launched in 2003, operated for seven years, and measured ice sheet mass balance, cloud and aerosol heights, and well as topography and vegetation characteristics.
Over a dozen past robotic missions have focused on the study of the Earth and its environment. Some of these additional missions include Aquarius, Earth Observing-1 (EO-1), Jason-1, OSTM/Jason-2, Ocean Surface Topography Mission/Jason-2, and Radarsat-1 missions.
Active programs
Human spaceflight
International Space Station (1993–present)
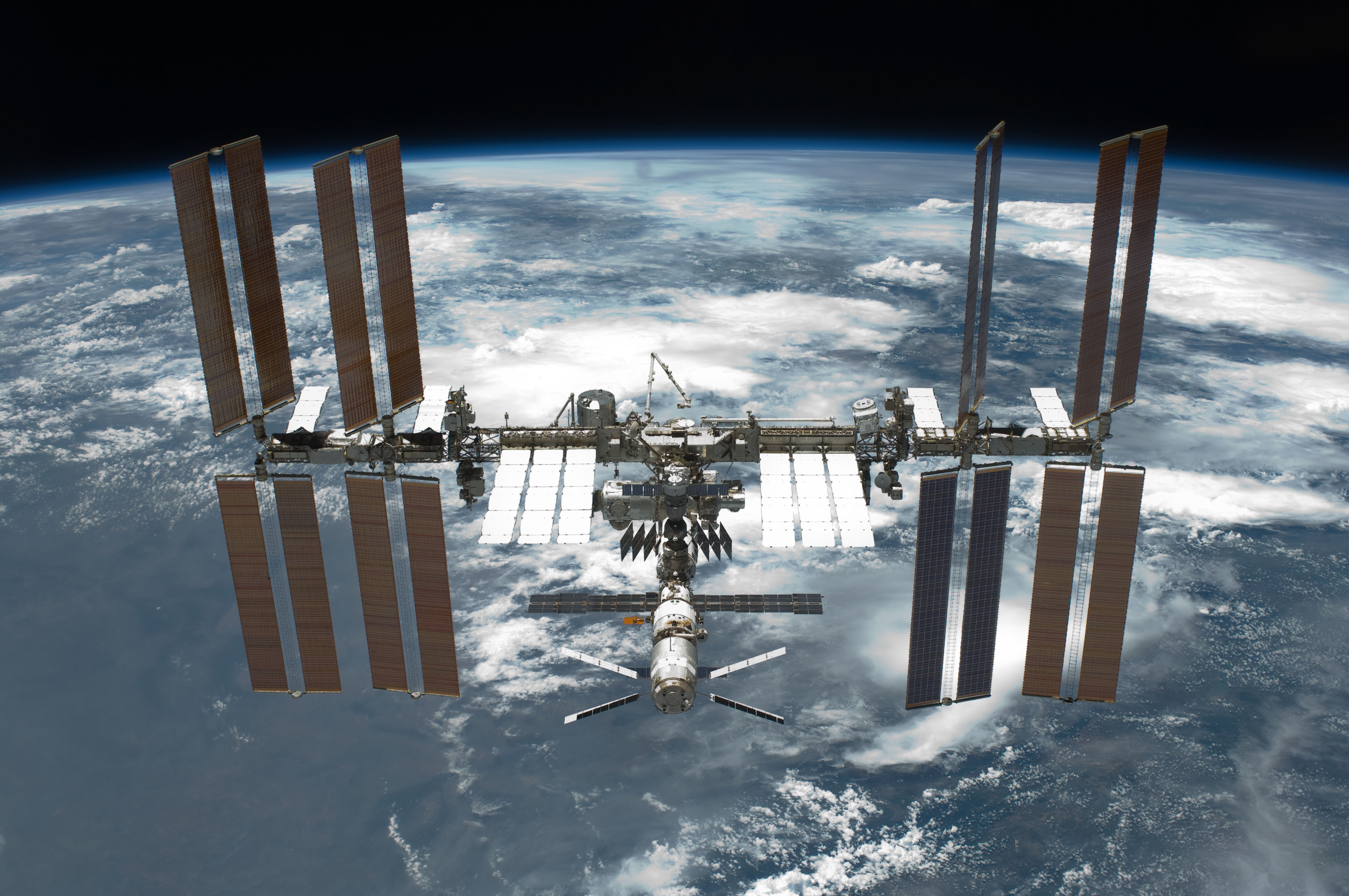 The International Space Station (ISS) combines NASA's Space Station Freedom, Space Station ''Freedom'' project with the Soviet/Russian ''Mir-2'' station, the European ''Columbus (ISS module), Columbus'' station, and the Japanese Japanese Experiment Module, Kibō laboratory module. NASA originally planned in the 1980s to develop ''Freedom'' alone, but US budget constraints led to the merger of these projects into a single multi-national program in 1993, managed by NASA, the Russian Federal Space Agency (RKA), the JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The station consists of pressurized modules, external Integrated Truss Structure, trusses, solar arrays and other components, which were Manufacturing of the International Space Station, manufactured in various factories around the world, and have been launched by Russian Proton (rocket), Proton and Soyuz (rocket family), Soyuz rockets, and the US Space Shuttles. The on-orbit assembly began in 1998, the completion of the US Orbital Segment occurred in 2009 and the completion of the Russian Orbital Segment occurred in 2010, though there are some debates of whether new modules should be added in the segment. The ownership and use of the space station is established in intergovernmental treaties and agreements which divide the station into two areas and allow Russian Federation, Russia to retain full ownership of the Russian Orbital Segment (with the exception of ''Zarya (ISS module), Zarya''), with the US Orbital Segment allocated between the other international partners.
Long-duration missions to the ISS are referred to as List of International Space Station expeditions, ISS Expeditions. Expedition crew members typically spend approximately six months on the ISS. The initial expedition crew size was three, temporarily decreased to two following the ''Columbia'' disaster. Since May 2009, expedition crew size has been six crew members. Crew size is expected to be increased to seven, the number the ISS was designed for, once the Commercial Crew Program becomes operational. The ISS has been continuously occupied for the past , having exceeded the previous record held by ''Mir''; and has been visited by astronauts and cosmonauts from List of International Space Station visitors, 15 different nations.
The station can be seen from the Earth with the naked eye and, as of , is the largest artificial satellite in Earth orbit with a mass and volume greater than that of any previous space station.International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) combines NASA's Space Station Freedom, Space Station ''Freedom'' project with the Soviet/Russian ''Mir-2'' station, the European ''Columbus (ISS module), Columbus'' station, and the Japanese Japanese Experiment Module, Kibō laboratory module. NASA originally planned in the 1980s to develop ''Freedom'' alone, but US budget constraints led to the merger of these projects into a single multi-national program in 1993, managed by NASA, the Russian Federal Space Agency (RKA), the JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The station consists of pressurized modules, external Integrated Truss Structure, trusses, solar arrays and other components, which were Manufacturing of the International Space Station, manufactured in various factories around the world, and have been launched by Russian Proton (rocket), Proton and Soyuz (rocket family), Soyuz rockets, and the US Space Shuttles. The on-orbit assembly began in 1998, the completion of the US Orbital Segment occurred in 2009 and the completion of the Russian Orbital Segment occurred in 2010, though there are some debates of whether new modules should be added in the segment. The ownership and use of the space station is established in intergovernmental treaties and agreements which divide the station into two areas and allow Russian Federation, Russia to retain full ownership of the Russian Orbital Segment (with the exception of ''Zarya (ISS module), Zarya''), with the US Orbital Segment allocated between the other international partners.
Long-duration missions to the ISS are referred to as List of International Space Station expeditions, ISS Expeditions. Expedition crew members typically spend approximately six months on the ISS. The initial expedition crew size was three, temporarily decreased to two following the ''Columbia'' disaster. Since May 2009, expedition crew size has been six crew members. Crew size is expected to be increased to seven, the number the ISS was designed for, once the Commercial Crew Program becomes operational. The ISS has been continuously occupied for the past , having exceeded the previous record held by ''Mir''; and has been visited by astronauts and cosmonauts from List of International Space Station visitors, 15 different nations.
The station can be seen from the Earth with the naked eye and, as of , is the largest artificial satellite in Earth orbit with a mass and volume greater than that of any previous space station.International Space Station, Retrieved October 20, 2011 The Russian Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz and American SpaceX Dragon 2, Dragon spacecraft are used to send astronauts to and from the ISS. Several uncrewed cargo spacecraft provide service to the ISS; they are the Russian Progress (spacecraft), Progress spacecraft which has done so since 2000, the European Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) since 2008, the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV) since 2009, the (uncrewed) SpaceX Dragon, Dragon since 2012, and the American Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus spacecraft since 2013. The Space Shuttle, before its retirement, was also used for cargo transfer and would often switch out expedition crew members, although it did not have the capability to remain docked for the duration of their stay. Between the retirement of the Shuttle in 2011 and the commencement of crewed Dragon flights in 2020, American astronauts exclusively used the Soyuz for crew transport to and from the ISS The highest number of people occupying the ISS has been thirteen; this occurred three times during the late Shuttle ISS assembly missions. The ISS program is expected to continue to 2030, after which the space station will be retired and destroyed in a controlled de-orbit.
Commercial Resupply Services (2008–present)
Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) are a contract solution to deliver cargo and supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) on a commmercial basis. NASA signed its first CRS contracts in 2008 and awarded $1.6 billion to SpaceX for twelve cargo Dragon (spacecraft), Dragon and $1.9 billion to Orbital Sciences for eight Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus flights, covering deliveries to 2016. Both companies evolved or created their launch vehicle products to support the solution (SpaceX with The Falcon 9 and Orbital with the Antares (rocket), Antares). SpaceX flew its first operational resupply mission (SpaceX CRS-1) in 2012. Orbital Sciences followed in 2014 (Cygnus CRS Orb-1). In 2015, NASA extended CRS-1 to twenty flights for SpaceX and twelve flights for Orbital ATK. A second phase of contracts (known as CRS-2) was solicited in 2014; contracts were awarded in January 2016 to Orbital ATK Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus, Sierra Nevada Corporation ''Dream Chaser'', and SpaceX ''SpaceX Dragon 2, Dragon 2'', for cargo transport flights beginning in 2019 and expected to last through 2024. In March 2022, NASA awarded an additional six CRS-2 missions each to both SpaceX and Northrop Grumman (formerly Orbital). Northrop Grumman successfully delivered Cygnus NG-17 to the ISS in February 2022. In July 2022, SpaceX launched its 25th CRS flight (SpaceX CRS-25) and successfully delivered its cargo to the ISS. In late 2022, Sierra Nevada continued to assemble their Dream Chaser CRS solution; current estimates put its first launch in early 2023.Commercial Crew Program (2011–present)
The Commercial Crew Program (CCP) provides Private spaceflight, commercially operated human spaceflight, crew transportation service to and from the International Space Station (ISS) under contract to NASA, conducting crew rotations between the List of International Space Station expeditions, expeditions of the International Space Station program. American space industry, space manufacturer SpaceX began providing service in 2020, using the SpaceX Dragon 2, Crew Dragon spacecraft, and NASA plans to add Boeing Defense, Space & Security, Boeing when its Boeing Starliner spacecraft becomes operational . NASA has contracted for six operational missions from Boeing and fourteen from SpaceX, ensuring sufficient support for ISS through 2030. The spacecraft are owned and operated by the vendor, and crew transportation is provided to NASA as a commercial service. Each mission sends up to four astronauts to the ISS, with an option for a fifth passenger available. Operational flights occur approximately once every six months for missions that last for approximately six months. A spacecraft remains docked to the ISS during its mission, and missions usually overlap by at least a few days. Between the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011 and the first operational CCP mission in 2020, NASA relied on the Soyuz program to transport its astronauts to the ISS. A Crew Dragon spacecraft is launched to space atop a Falcon 9 Block 5 launch vehicle and the capsule returns to Earth via splashdown in the ocean near Florida. The program's first operational mission, SpaceX Crew-1, launched on 16 November 2020. Boeing Starliner operational flights will now commence after its Boeing Crewed Flight Test, final test flight which was launched atop an Atlas V, Atlas V N22 launch vehicle. Instead of a splashdown, a Starliner capsule returns on land with airbags at one of four designated sites in the western United States.Artemis (2017–present)
 Since 2017, NASA's List of human spaceflight programs, crewed spaceflight program has been the Artemis program, which involves the help of US Private spaceflight, commercial spaceflight companies and international partners such as European Space Agency, ESA, JAXA, and Canadian Space Agency, CSA. The goal of this program is to land "the first woman and the next man" on the lunar south pole region by 2024. Artemis would be the first step towards the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable presence on the Moon, laying the foundation for companies to build a lunar economy, and eventually sending humans to Mars.
The Orion (spacecraft), Orion Crew Exploration Vehicle was held over from the canceled Constellation program for Artemis. Artemis 1 was the uncrewed initial launch of Space Launch System (SLS) that would also send an Orion spacecraft on a Distant Retrograde Orbit.
NASA's next major space initiative is to be the construction of the Lunar Gateway, a small space station in lunar orbit. This space station will be designed primarily for non-continuous human habitation. The first tentative steps of returning to crewed lunar missions will be Artemis 2, which is to include the Orion crew module, propelled by the SLS, and is to launch in 2024. This mission is to be a 10-day mission planned to briefly place a crew of four into a free-return trajectory, Lunar flyby. The construction of the Gateway would begin with the proposed Artemis 3, which is planned to deliver a crew of four to Lunar orbit along with the first modules of the Gateway. This mission would last for up to 30 days. NASA plans to build full scale deep space habitats such as the Lunar Gateway and the Nautilus-X as part of its Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP) program. In 2017, NASA was directed by the congressional NASA Transition Authorization Act of 2017 to get humans to Mars-orbit (or to the Martian surface) by the 2030s.
In support of the Artemis missions, NASA has been funding private companies to land robotic probes on the lunar surface in a program known as the Commercial Lunar Payload Services. As of March 2022, NASA has awarded contracts for robotic lunar probes to companies such as Intuitive Machines, Firefly Space Systems, and Astrobotic.
On April 16, 2021, NASA announced they had selected the SpaceX Starship, SpaceX Lunar Starship as its Human Landing System. The agency's Space Launch System rocket will launch four astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft for their multi-day journey to lunar orbit where they will transfer to SpaceX's Starship for the final leg of their journey to the surface of the Moon.
In November 2021, it was announced that the goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by 2024 had slipped to no earlier than 2025 due to numerous factors. Artemis 1 launched on November 16, 2022 and returned to Earth safely on December 11, 2022. As of June 2022, NASA plans to launch Artemis 2 in May 2024 and Artemis 3 sometime in 2025. Additional Artemis missions, Artemis 4 and Artemis 5, are planned to launch after 2025.
Since 2017, NASA's List of human spaceflight programs, crewed spaceflight program has been the Artemis program, which involves the help of US Private spaceflight, commercial spaceflight companies and international partners such as European Space Agency, ESA, JAXA, and Canadian Space Agency, CSA. The goal of this program is to land "the first woman and the next man" on the lunar south pole region by 2024. Artemis would be the first step towards the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable presence on the Moon, laying the foundation for companies to build a lunar economy, and eventually sending humans to Mars.
The Orion (spacecraft), Orion Crew Exploration Vehicle was held over from the canceled Constellation program for Artemis. Artemis 1 was the uncrewed initial launch of Space Launch System (SLS) that would also send an Orion spacecraft on a Distant Retrograde Orbit.
NASA's next major space initiative is to be the construction of the Lunar Gateway, a small space station in lunar orbit. This space station will be designed primarily for non-continuous human habitation. The first tentative steps of returning to crewed lunar missions will be Artemis 2, which is to include the Orion crew module, propelled by the SLS, and is to launch in 2024. This mission is to be a 10-day mission planned to briefly place a crew of four into a free-return trajectory, Lunar flyby. The construction of the Gateway would begin with the proposed Artemis 3, which is planned to deliver a crew of four to Lunar orbit along with the first modules of the Gateway. This mission would last for up to 30 days. NASA plans to build full scale deep space habitats such as the Lunar Gateway and the Nautilus-X as part of its Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP) program. In 2017, NASA was directed by the congressional NASA Transition Authorization Act of 2017 to get humans to Mars-orbit (or to the Martian surface) by the 2030s.
In support of the Artemis missions, NASA has been funding private companies to land robotic probes on the lunar surface in a program known as the Commercial Lunar Payload Services. As of March 2022, NASA has awarded contracts for robotic lunar probes to companies such as Intuitive Machines, Firefly Space Systems, and Astrobotic.
On April 16, 2021, NASA announced they had selected the SpaceX Starship, SpaceX Lunar Starship as its Human Landing System. The agency's Space Launch System rocket will launch four astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft for their multi-day journey to lunar orbit where they will transfer to SpaceX's Starship for the final leg of their journey to the surface of the Moon.
In November 2021, it was announced that the goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by 2024 had slipped to no earlier than 2025 due to numerous factors. Artemis 1 launched on November 16, 2022 and returned to Earth safely on December 11, 2022. As of June 2022, NASA plans to launch Artemis 2 in May 2024 and Artemis 3 sometime in 2025. Additional Artemis missions, Artemis 4 and Artemis 5, are planned to launch after 2025.
Commercial LEO Development (2021–present)
The Commercial Low Earth Orbit Destinations program is an initiative by NASA to support work on commercial space stations that the agency hopes to have in place by the end of the current decade to replace the "International Space Station". The three selected companies are: Blue Origin (et al.) with their Orbital Reef station concept, Nanoracks (et al.) with their Starlab Space Station concept, and Northrop Grumman with a station concept based on the HALO-module for the Gateway station.Robotic exploration
NASA has conducted many uncrewed and robotic spaceflight programs throughout its history. More than 1,000 uncrewed missions have been designed to explore the Earth and the Solar System.Mission selection process
NASA executes a mission development framework to plan, select, develop, and operate robotic missions. This framework defines cost, schedule and technical risk parameters to enable competitive selection of missions involving mission candidates that have been developed by principal investigators and their teams from across NASA, the broader U.S. Government research and development stakeholders, and industry. The mission development construct is defined by four umbrella programs.=Explorer program
= The Explorer program derives its origin from the earliest days of the U.S. Space program. In current form, the program consists of three classes of systems - Explorer program#Small Explorers (SMEX), Small Explorers (SMEX), Explorer program#Medium-Class Explorers (MIDEX), Medium Explorers (MIDEX), and Explorer program, University-Class Explorers (UNEX) missions. The NASA Explorer program office provides frequent flight opportunities for moderate cost innovative solutions from the heliophysics and astrophysics science areas. The Small Explorer missions are required to limit cost to NASA to below $150M (2022 dollars). Medium class explorer missions have typically involved NASA cost caps of $350M. The Explorer program office is based at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.=Discovery program
= The NASA Discovery program develops and delivers robotic spacecraft solutions in the planetary science domain. Discovery enables scientists and engineers to assemble a team to deliver a solution against a defined set of objectives and competitively bid that solution against other candidate programs. Cost caps vary but recent mission selection processes were accomplished using a $500M cost cap to NASA. The Planetary Mission Program Office is based at the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center and manages both the Discovery and New Frontiers missions. The office is part of the Science Mission Directorate. NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announced on June 2, 2021, that the ''DAVINCI, DAVINCI+'' and ''VERITAS (spacecraft), VERITAS'' missions were selected to launch to Venus in the late 2020s, having beat out competing proposals for missions to Jupiter's volcanic moon Io and Neptune's large moon Triton (moon), Triton that were also selected as Discovery program finalists in early 2020. Each mission has an estimated cost of $500 million, with launches expected between 2028 and 2030. Launch contracts will be awarded later in each mission's development.=New Frontiers program
= The New Frontiers program focuses on specific Solar System exploration goals identified as top priorities by the planetary science community. Primary objectives include Solar System exploration employing medium class spacecraft missions to conduct high-science-return investigations. New Frontiers builds on the development approach employed by the Discovery program but provides for higher cost caps and schedule durations than are available with Discovery. Cost caps vary by opportunity; recent missions have been awarded based on a defined cap of $1 Billion. The higher cost cap and projected longer mission durations result in a lower frequency of new opportunities for the program - typically one every several years. ''OSIRIS-REx'' and ''New Horizons'' are examples of New Frontiers missions. NASA has determined that the next opportunity to propose for the fifth round of New Frontiers missions will occur no later than the fall of 2024. Missions in NASA's New Frontiers Program tackle specific Solar System exploration goals identified as top priorities by the planetary science community. Exploring the Solar System with medium-class spacecraft missions that conduct high-science-return investigations is NASA's strategy to further understand the Solar System.= Large strategic missions
= Large strategic missions (formerly called Flagship missions) are strategic missions that are typically developed and managed by large teams that may span several NASA centers. The individual missions become the program as opposed to being part of a larger effort (see Discovery, New Frontiers, etc.). The James Webb Space Telescope is a strategic mission that was developed over a period of more than 20 years. Strategic missions are developed on an ad-hoc basis as program objectives and priorities are established. Missions like Voyager, had they been developed today, would have been strategic missions. Three of the Great Observatories were strategic missions (the Chandra X-ray Observatory, Chandra X-ray Observatory, Compton, and the Hubble Space Telescope). ''Europa Clipper'' is the next large strategic mission in development by NASA.Planetary science missions
NASA continues to play a material in exploration of the Solar System as it has for decades. Ongoing missions have current science objectives with respect to more than five extraterrestrial bodies within the Solar System – Moon (Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter), Mars (''Perseverance (rover), Perseverance'' rover), Jupiter (''Juno (spacecraft), Juno''), asteroid 101955 Bennu, Bennu (''OSIRIS-REx''), and Kuiper Belt Objects (''New Horizons''). The ''Juno'' extended mission will make multiple flybys of the Jovian moon Io in 2023 and 2024 after flybys of Ganymede (moon), Ganymede in 2021 and Europa (moon), Europa in 2022. ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2'' continue to provide science data back to Earth while continuing on their outward journeys into interstellar space. On November 26, 2011, NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission was successfully launched for Mars. The ''Curiosity (rover), Curiosity'' rover successfully landed on Mars on August 6, 2012, and subsequently began its search for evidence of past or present life on Mars. In September 2014, NASA's ''MAVEN'' spacecraft, which is part of the Mars Scout Program, successfully entered Mars orbit and, as of October 2022, continues its study of the atmosphere of Mars. NASA's ongoing Mars investigations include in-depth surveys of Mars by the ''Perseverance (rover), Perseverance'' rover and ''InSight''). NASA's ''Europa Clipper'', planned for launch in October 2024, will study the Galilean moon Europa through a series of flybys while in orbit around Jupiter. ''Dragonfly (spacecraft), Dragonfly'' will send a mobile robotic rotorcraft to Saturn's biggest moon, Titan (moon), Titan. As of May 2021, ''Dragonfly'' is scheduled for launch in June 2027.Astrophysics missions
 The NASA Science Mission Directorate Astrophysics division manages the agency's astrophysics science portfolio. NASA has invested significant resources in the development, delivery, and operations of various forms of space telescopes. These telescopes have provided the means to study the cosmos over a large range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Great Observatories that were launched in the 1980s and 1990s have provided a wealth of observations for study by physicists across the planent. The first of them, the Hubble Space Telescope, was delivered to orbit in 1990 and continues to function, in part due to prior servicing missions performed by the Space Shuttle. The other remaining active great observatory include the Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), launched by STS-93 in July 1999 and is now in a 64-hour elliptical orbit studying X-ray sources that are not readily viewable from terrestrial observatories.
The NASA Science Mission Directorate Astrophysics division manages the agency's astrophysics science portfolio. NASA has invested significant resources in the development, delivery, and operations of various forms of space telescopes. These telescopes have provided the means to study the cosmos over a large range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Great Observatories that were launched in the 1980s and 1990s have provided a wealth of observations for study by physicists across the planent. The first of them, the Hubble Space Telescope, was delivered to orbit in 1990 and continues to function, in part due to prior servicing missions performed by the Space Shuttle. The other remaining active great observatory include the Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), launched by STS-93 in July 1999 and is now in a 64-hour elliptical orbit studying X-ray sources that are not readily viewable from terrestrial observatories.
 The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) is a space observatory designed to improve the understanding of X-ray production in objects such as neutron stars and pulsar wind nebulae, as well as stellar and supermassive black holes. IXPE launched in December 2021 and is an international collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). It is part of the NASA Explorers Program, Small Explorers program (SMEX) which designs low-cost spacecraft to study heliophysics and astrophysics.
The Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory was launched in November 2004 and is Gamma-ray burst observatory that also monitors the afterglow in X-ray, and UV/Visible light at the location of a burst. The mission was developed in a joint partnership between Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) and an international consortium from the United States, United Kingdom, and Italy. Pennsylvania State University operates the mission as part of NASA's Explorer program, Medium Explorer program (MIDEX).
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope (FGST) is another gamma-ray focused space observatory that was launched to low Earth orbit in June 2008 and is being used to perform gamma-ray astronomy observations. In addition to NASA, the mission involves the United States Department of Energy, and government agencies in France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and Sweden.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched in December 2021 on an Ariane 5 rocket, operates in a halo orbit circling the Sun-Earth point. JWST's high sensitivity in the infrared spectrum and its imaging resolution will allow it to view more distant, faint, or older objects than its predecessors, including Hubble.
The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) is a space observatory designed to improve the understanding of X-ray production in objects such as neutron stars and pulsar wind nebulae, as well as stellar and supermassive black holes. IXPE launched in December 2021 and is an international collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). It is part of the NASA Explorers Program, Small Explorers program (SMEX) which designs low-cost spacecraft to study heliophysics and astrophysics.
The Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory was launched in November 2004 and is Gamma-ray burst observatory that also monitors the afterglow in X-ray, and UV/Visible light at the location of a burst. The mission was developed in a joint partnership between Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) and an international consortium from the United States, United Kingdom, and Italy. Pennsylvania State University operates the mission as part of NASA's Explorer program, Medium Explorer program (MIDEX).
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope (FGST) is another gamma-ray focused space observatory that was launched to low Earth orbit in June 2008 and is being used to perform gamma-ray astronomy observations. In addition to NASA, the mission involves the United States Department of Energy, and government agencies in France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and Sweden.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched in December 2021 on an Ariane 5 rocket, operates in a halo orbit circling the Sun-Earth point. JWST's high sensitivity in the infrared spectrum and its imaging resolution will allow it to view more distant, faint, or older objects than its predecessors, including Hubble.
Earth Sciences Program missions (1965–present)
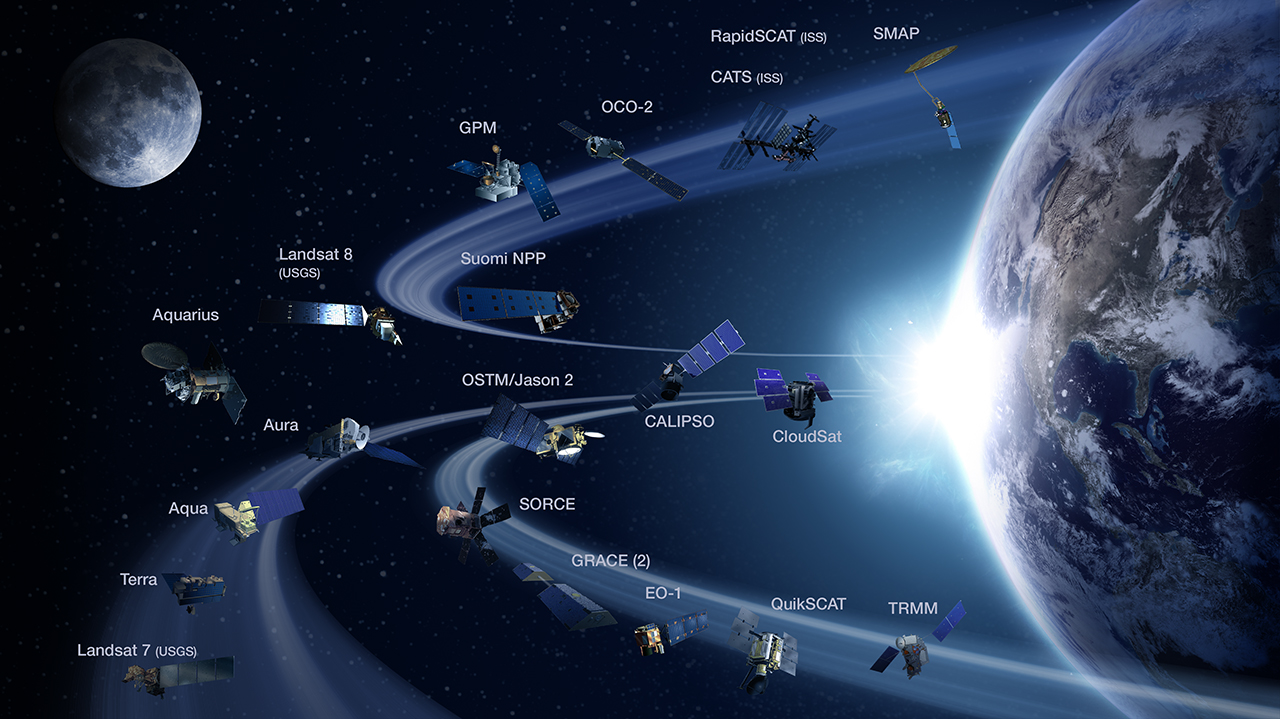 NASA Earth Science is a large, umbrella program comprising a range of terrestrial and space-based collection systems in order to better understand the Earth system and its response to natural and human-caused changes. Numerous systems have been developed and fielded over several decades to provide improved prediction for weather, climate, and other changes in the natural environment. Several of the current operating spacecraft programs include: Aqua (satellite), Aqua, Aura (satellite), Aura, Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2 (OCO-2), GRACE and GRACE-FO#GRACE Follow-On, Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-on (GRACE FO), and ICESat-2, Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite 2 (ICESat-2).
In addition to systems already in orbit, NASA is designing a new set of Earth Observing Systems to study, assess, and generate responses for climate change, natural hazards, forest fires, and real-time agricultural processes. The GOES-T satellite (designated GOES-18 after launch) joined the fleet of U.S. geostationary weather monitoring satellites in March 2022.
NASA also maintains the Earth Science Data Systems (ESDS) program to oversee the life cycle of NASA's Earth science data — from acquisition through processing and distribution. The primary goal of ESDS is to maximize the scientific return from NASA's missions and experiments for research and applied scientists, decision makers, and society at large.
The Earth Science program is managed by the Earth Science Division of the NASA Science Mission Directorate.
NASA Earth Science is a large, umbrella program comprising a range of terrestrial and space-based collection systems in order to better understand the Earth system and its response to natural and human-caused changes. Numerous systems have been developed and fielded over several decades to provide improved prediction for weather, climate, and other changes in the natural environment. Several of the current operating spacecraft programs include: Aqua (satellite), Aqua, Aura (satellite), Aura, Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2 (OCO-2), GRACE and GRACE-FO#GRACE Follow-On, Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-on (GRACE FO), and ICESat-2, Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite 2 (ICESat-2).
In addition to systems already in orbit, NASA is designing a new set of Earth Observing Systems to study, assess, and generate responses for climate change, natural hazards, forest fires, and real-time agricultural processes. The GOES-T satellite (designated GOES-18 after launch) joined the fleet of U.S. geostationary weather monitoring satellites in March 2022.
NASA also maintains the Earth Science Data Systems (ESDS) program to oversee the life cycle of NASA's Earth science data — from acquisition through processing and distribution. The primary goal of ESDS is to maximize the scientific return from NASA's missions and experiments for research and applied scientists, decision makers, and society at large.
The Earth Science program is managed by the Earth Science Division of the NASA Science Mission Directorate.
Space operations architecture
NASA invests in various ground and space-based infrastructures to support its science and exploration mandate. The agency maintains access to suborbital and orbital space launch capabilities and sustains ground station solutions to support its evolving fleet of spacecraft and remote systems.Deep Space Network (1963–present)
The ''NASA Deep Space Network'' (''DSN'') serves as the primary ground station solution for NASA's interplanetary spacecraft and select Earth-orbiting missions. The system employs ground station complexes near Barstow California in the United States, in Spain near Madrid, and in Australia near Canberra. The placement of these ground stations approximately 120 degrees apart around the planet provides the ability for communications to spacecraft throughout the Solar System even as the Earth rotates about its axis on a daily basis. The system is controlled at a 24x7 operations center at JPL in Pasadena California which manages recurring communications linkages with up to 40 spacecraft. The system is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).Near Space Network (1983–present)
 The Near Space Network (NSN) provides telemetry, commanding, ground-based tracking, data and communications services to a wide range of customers with satellites in low earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous orbit (GEO), highly elliptical orbits (HEO), and lunar orbits. The NSN accumulates ground station and antenna assets from the Near-Earth Network and the ''Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System'' (''TDRS'') which operates in geosynchronous orbit providing continuous real-time coverage for launch vehicles and low earth orbit NASA missions.
The NSN consists of 19 ground stations worldwide operated by the US Government and by contractors including Kongsberg Satellite Services (KSAT), Swedish Space Corporation (SSC), and South African National Space Agency (SANSA). The ground network averages between 120 and 150 spacecraft contacts a day with TDRS engaging with systems on a near-continuous basis as needed; the system is managed and operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center.
The Near Space Network (NSN) provides telemetry, commanding, ground-based tracking, data and communications services to a wide range of customers with satellites in low earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous orbit (GEO), highly elliptical orbits (HEO), and lunar orbits. The NSN accumulates ground station and antenna assets from the Near-Earth Network and the ''Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System'' (''TDRS'') which operates in geosynchronous orbit providing continuous real-time coverage for launch vehicles and low earth orbit NASA missions.
The NSN consists of 19 ground stations worldwide operated by the US Government and by contractors including Kongsberg Satellite Services (KSAT), Swedish Space Corporation (SSC), and South African National Space Agency (SANSA). The ground network averages between 120 and 150 spacecraft contacts a day with TDRS engaging with systems on a near-continuous basis as needed; the system is managed and operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center.
Sounding Rocket Program (1959–present)
 The ''NASA Sounding Rocket Program'' (''NSRP'') is located at the Wallops Flight Facility and provides launch capability, payload development and integration, and field operations support to execute suborbital missions. The program has been in operation since 1959 and is managed by the Goddard Space Flight Center using a combined US Government and contractor team. The NSRP team conducts approximately 20 missions per year from both Wallops and other launch locations worldwide to allow scientists to collect data "where it occurs". The program supports the strategic vision of the Science Mission Directorate collecting important scientific data for earth science, heliophysics, and astrophysics programs.
In June 2022, NASA conducted its first rocket launch from a commercial spaceport outside the US. It launched a Black Brant IX from the Arnhem Space Centre in Australia.
The ''NASA Sounding Rocket Program'' (''NSRP'') is located at the Wallops Flight Facility and provides launch capability, payload development and integration, and field operations support to execute suborbital missions. The program has been in operation since 1959 and is managed by the Goddard Space Flight Center using a combined US Government and contractor team. The NSRP team conducts approximately 20 missions per year from both Wallops and other launch locations worldwide to allow scientists to collect data "where it occurs". The program supports the strategic vision of the Science Mission Directorate collecting important scientific data for earth science, heliophysics, and astrophysics programs.
In June 2022, NASA conducted its first rocket launch from a commercial spaceport outside the US. It launched a Black Brant IX from the Arnhem Space Centre in Australia.
Launch Services Program (1990–present)
The NASA Launch Services Program (LSP) is responsible for procurement of launch services for NASA uncrewed missions and oversight of launch integration and launch preparation activity, providing added quality and mission assurance to meet program objectives. Since 1990, NASA has purchased expendable launch system, expendable launch vehicle launch services directly from commercial providers, whenever possible, for its scientific and applications missions. Expendable launch vehicles can accommodate all types of orbit inclinations and altitudes and are ideal vehicles for launching Earth-orbit and interplanetary missions. LSP operates from Kennedy Space Center and falls under the NASA Space Operations Mission Directorate (SOMD).Aeronautics Research
The ''Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate'' (''ARMD'') is one of five mission wikt:directorate, directorates within NASA, the other four being the Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, the Space Operations Mission Directorate, the Science Mission Directorate, and the Space Technology Mission Directorate. The ARMD is responsible for NASA's aeronautics, aeronautical research, which benefits the commercial aviation, commercial, military aviation, military, and general aviation sectors. ARMD performs its aeronautics research at four NASA facilities: Ames Research Center and Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Glenn Research Center in Ohio, and Langley Research Center in Virginia.NASA X-57 Maxwell aircraft (2016–present)
The ''NASA X-57 Maxwell'' is an experimental aircraft being developed by NASA to demonstrate the technologies required to deliver a highly efficient all-electric aircraft. The primary goal of the program is to develop and deliver all-electric technology solutions that can also achieve airworthiness certification with regulators. The program involves development of the system in several phases, or modifications, to incrementally grow the capability and operability of the system. The initial configuration of the aircraft has now completed ground testing as it approaches its first flights. In mid-2022, the X-57 was scheduled to fly before the end of the year. The development team includes staff from the NASA Armstrong, Glenn, and Langley centers along with number of industry partners from the United States and Italy.Next Generation Air Transportation System (2007–present)
NASA is collaborating with the Federal Aviation Administration and industry stakeholders to modernize the United States National Airspace System (NAS). Efforts began in 2007 with a goal to deliver major modernization components by 2025. The modernization effort intends to increase the safety, efficiency, capacity, access, flexibility, predictability, and resilience of the NAS while reducing the environmental impact of aviation. The Aviation Systems Division of NASA Ames operates the joint NASA/FAA North Texas Research Station. The station supports all phases of NextGen research, from concept development to prototype system field evaluation. This facility has already transitioned advanced NextGen concepts and technologies to use through technology transfers to the FAA. NASA contributions also include development of advanced automation concepts and tools that provide air traffic controllers, pilots, and other airspace users with more accurate real-time information about the nation's traffic flow, weather, and routing. Ames' advanced airspace modeling and simulation tools have been used extensively to model the flow of air traffic flow across the U.S., and to evaluate new concepts in airspace design, traffic flow management, and optimization.Technology research
Nuclear in-space power and propulsion (ongoing)
NASA has made use of technologies such as the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG), which is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator used to power spacecraft. Shortages of the required plutonium-238 have curtailed deep space missions since the turn of the millennium. An example of a spacecraft that was not developed because of a shortage of this material was ''New Horizons 2''. In July 2021, NASA announced contract awards for development of Nuclear thermal rocket, nuclear thermal propulsion reactors. Three contractors will develop individual designs over 12 months for later evaluation by NASA and the United States Department of Energy, U.S. Department of Energy. NASA's space nuclear technologies portfolio are led and funded by its Space Technology Mission Directorate.Other initiatives
''Free Space Optics''. NASA contracted a third party to study the probability of using Free Space Optics (FSO) to communicate with Optical (laser) Stations on the Ground (OGS) called laser-com Radio frequency, RF networks for satellite communications. ''Water Extraction from Lunar Soil''. On July 29, 2020, NASA requested American universities to propose new technologies for extracting water from the lunar soil and developing power systems. The idea will help the space agency conduct sustainable exploration of the Moon.Human Spaceflight Research (2005–present)
 NASA's Human Research Program (HRP) is designed to study the effects of space on human health and also to provide countermeasures and technologies for human space exploration. The medical effects of space exploration are reasonably limited in low Earth orbit or in travel to the Moon. Travel to Mars, however, is significantly longer and deeper into space and significant medical issues can result. This includes bone loss, radiation exposure, vision changes, circadian rhythm disturbances, heart remodeling, and immune alterations. In order to study and diagnose these ill-effects, HRP has been tasked with identifying or developing small portable instrumentation with low mass, volume, and power to monitor the health of astronauts. To achieve this aim, on May 13, 2022, NASA and SpaceX Crew-4 astronauts successfully tested its rHEALTH ONE universal biomedical analyzer for its ability to identify and analyzer biomarkers, cells, microorganisms, and proteins in a spaceflight environment.
NASA's Human Research Program (HRP) is designed to study the effects of space on human health and also to provide countermeasures and technologies for human space exploration. The medical effects of space exploration are reasonably limited in low Earth orbit or in travel to the Moon. Travel to Mars, however, is significantly longer and deeper into space and significant medical issues can result. This includes bone loss, radiation exposure, vision changes, circadian rhythm disturbances, heart remodeling, and immune alterations. In order to study and diagnose these ill-effects, HRP has been tasked with identifying or developing small portable instrumentation with low mass, volume, and power to monitor the health of astronauts. To achieve this aim, on May 13, 2022, NASA and SpaceX Crew-4 astronauts successfully tested its rHEALTH ONE universal biomedical analyzer for its ability to identify and analyzer biomarkers, cells, microorganisms, and proteins in a spaceflight environment.
Planetary Defense (2016–present)
NASA established the Planetary Defense Coordination Office (''PDCO'') in 2016 to catalog and track potentially hazardous near-Earth objects (NEO), such as asteroids and comets and develop potential responses and defenses against these threats. The PDCO is chartered to provide timely and accurate information to the government and the public on close approaches by Potentially hazardous objects (PHOs) and any potential for impact. The office functions within the Science Mission Directorate Planetary Science division. The PDCO augmented prior cooperative actions between the United States, the European Union, and other nations which had been scanning the sky for NEOs since 1998 in an effort called Spaceguard.Near Earth object detection (1998–present)
From the 1990s NASA has run many NEO detection programs from Earth bases observatories, greatly increasing the number of objects that have been detected. However, many asteroids are very dark and the ones that are near the Sun are much harder to detect from Earth-based telescopes which observe at night, and thus face away from the Sun. NEOs inside Earth orbit only reflect a part of light also rather than potentially a "full Moon" when they are behind the Earth and fully lit by the Sun. In 1998, the United States Congress gave NASA a mandate to detect 90% of near-Earth asteroids over diameter (that threaten global devastation) by 2008. This initial mandate was met by 2011. In 2005, the original USA Spaceguard mandate was extended by the George E. Brown, Jr. Near-Earth Object Survey Act, which calls for NASA to detect 90% of NEOs with diameters of or greater, by 2020 (compare to the 20-meter Chelyabinsk meteor that hit Russia in 2013). , it is estimated that less than half of these have been found, but objects of this size hit the Earth only about once in 2,000 years. In January 2020, NASA officials estimated it would take 30 years to find all objects meeting the size criteria, more than twice the timeframe that was built into the 2005 mandate. In June 2021, NASA authorized the development of the NEO Surveyor spacecraft to reduce that projected duration to achieve the mandate down to 10 years.Involvement in current robotic missions
NASA has incorporated planetary defense objectives into several ongoing missions. In 1999, NASA visited 433 Eros with the ''NEAR Shoemaker'' spacecraft which entered its orbit in 2000, closely imaging the asteroid with various instruments at that time. ''NEAR Shoemaker'' became the first spacecraft to successfully orbit and land on an asteroid, improving our understanding of these bodies and demonstrating our capacity to study them in greater detail. OSIRIS-REx used its suite of instruments to transmit radio tracking signals and capture optical images of 101955 Bennu, Bennu during its study of the asteroid that will help NASA scientists determine its precise position in the solar system and its exact orbital path. As Bennu has the potential for recurring approaches to the Earth-Moon system in the next 100–200 years, the precision gained from OSIRIS-REx will enable scientists to better predict the future gravitational interactions between Bennu and our planet and resultant changes in Bennu's onward flight path. The Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, WISE/NEOWISE mission was launched by NASA JPL in 2009 as an infrared-wavelength astronomical space telescope. In 2013, NASA repurposed it as the NEOWISE mission to find potentially hazardous near-Earth asteroids and comets; its mission has been extended into 2023. NASA and Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (JHAPL) jointly developed the first planetary defense purpose-built satellite, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) to test possible planetary defense concepts. DART was launched in November 2021 by a SpaceX Falcon 9 from California on a trajectory designed to impact the Dimorphos asteroid. Scientists were seeking to determine whether an impact could alter the subsequent path of the asteroid; a concept that could be applied to future planetary defense. On September 26, 2022, DART hit its target. In the weeks following impact, NASA declared DART a success, confirming it had shortened Dimorphos' orbital period around Didymos by about 32 minutes, surpassing the pre-defined success threshold of 73 seconds. NEO Surveyor, formerly called the Near-Earth Object Camera (NEOCam) mission, is a space-based infrared telescope under development to survey the Solar System for potentially hazardous object, potentially hazardous asteroids. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch in 2026.Study of Unidentified Aerial Phenomena (2022–present)
In June 2022, the head of the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, confirmed that NASA would join the hunt for Unidentified flying object, Unidentified Flying Objects (UFOs)/Unidentified Aerial Phenomena (UAPs). At a speech before the National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine, Zurbuchen said the space agency would bring a scientific perspective to efforts already underway by the Pentagon and intelligence agencies to make sense of dozens of such sightings. He said it was “high-risk, high-impact” research that the space agency should not shy away from, even if it is a controversial field of study.Collaboration
NASA Advisory Council
In response to the Apollo 1 accident, which killed three astronauts in 1967, Congress directed NASA to form an Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel (ASAP) to advise the NASA Administrator on safety issues and hazards in NASA's air and space programs. In the aftermath of the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster, Congress required that the ASAP submit an annual report to the NASA Administrator and to Congress. By 1971, NASA had also established the Space Program Advisory Council and the Research and Technology Advisory Council to provide the administrator with advisory committee support. In 1977, the latter two were combined to form the NASA Advisory Council (NAC). The NASA Authorization Act of 2014 reaffirmed the importance of ASAP.National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
NASA and NOAA have cooperated for decades on the development, delivery and operation of polar and geosynchronous weather satellites. The relationship typically involves NASA developing the space systems, launch solutions, and ground control technology for the satellites and NOAA operating the systems and delivering weather forecasting products to users. Multiple generations of NOAA Polar orbiting platforms have operated to provide detailed imaging of weather from low altitude. Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) provide near-real-time coverage of the western hemisphere to ensure accurate and timely understanding of developing weather phenomenon.United States Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the United States Armed Forces, while the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States government responsible for civil spaceflight. NASA and the Space Force's predecessors in the Air Force have a long-standing cooperative relationship, with the Space Force supporting NASA launches out of Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, and Vandenberg Space Force Base, to include range support and rescue operations from Task Force 45. NASA and the Space Force also partner on matters such as defending Earth from asteroids. Space Force members can be NASA astronauts, with Colonel Michael S. Hopkins, the commander of SpaceX Crew-1, commissioned into the Space Force from the International Space Station on December 18, 2020. In September 2020, the Space Force and NASA signed a memorandum of understanding formally acknowledging the joint role of both agencies. This new memorandum replaced a similar document signed in 2006 between NASA and Air Force Space Command.U.S. Geological Survey
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / United States Geological Survey, USGS program. On July 23, 1972, the ''Landsat 1, Earth Resources Technology Satellite'' was launched. This was eventually renamed to ''Landsat 1'' in 1975. The most recent satellite in the series, ''Landsat 9'', was launched on September 27, 2021. The instruments on the Landsat satellites have acquired millions of images. The images, archived in the United States and at Landsat receiving stations around the world, are a unique resource for global change research and applications in agriculture, cartography, geology, forestry, regional planning, surveillance and education, and can be viewed through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) "EarthExplorer" website. The collaboration between NASA and USGS involves NASA designing and delivering the space system (satellite) solution, launching the satellite into orbit with the USGS operating the system once in orbit. As of October 2022, nine satellites have been built with eight of them successfully operating in orbit.European Space Agency (ESA)
NASA collaborates with the European Space Agency on a wide range of scientific and exploration requirements. From participation with the Space Shuttle (the Spacelab missions) to major roles on the Artemis program (the Orion Service Module), ESA and NASA have supported the science and exploration missions of each agency. There are NASA payloads on ESA spacecraft and ESA payloads on NASA spacecraft. The agencies have developed joint missions in areas including heliophysics (e.g. Solar Orbiter) and astronomy (Hubble Space Telescope, James Webb Space Telescope). Under the Artemis Gateway partnership, ESA will contribute habitation and refueling modules, along with enhanced lunar communications, to the Gateway. NASA and ESA continue to advance cooperation in relation to Earth Science including climate change with agreements to cooperate on various missions including the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, Sentinel-6 series of spacecraftJapan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) cooperate on a range of space projects. JAXA is a direct participant in the Artemis program, including the Lunar Gateway effort. JAXA's planned contributions to Gateway include I-Hab's environmental control and life support system, batteries, thermal control, and imagery components, which will be integrated into the module by the European Space Agency (ESA) prior to launch. These capabilities are critical for sustained Gateway operations during crewed and uncrewed time periods. JAXA and NASA have collaborated on numerous satellite programs, especially in areas of Earth science. NASA has contributed to JAXA satellites and vice versa. Japanese instruments are flying on NASA's Terra (satellite), Terra and Aqua (satellite), Aqua satellites, and NASA sensors have flown on previous Japanese Earth-observation missions. The NASA-JAXA Global Precipitation Measurement mission was launched in 2014 and includes both NASA- and JAXA-supplied sensors on a NASA satellite launched on a JAXA rocket. The mission provides the frequent, accurate measurements of rainfall over the entire globe for use by scientists and weather forecasters.Roscosmos
NASA and Roscosmos have cooperated on the development and operation of the International Space Station since September 1993. The agencies have used launch systems from both countries to deliver station elements to orbit. Astronauts and Cosmonauts jointly maintain various elements of the station. Both countries provide access to the station via launch systems noting Russia's unique role as the sole provider of delivery of crew and cargo upon retirement of the space shuttle in 2011 and prior to commencement of NASA COTS and crew flights. In July 2022, NASA and Roscosmos signed a deal to share space station flights enabling crew from each country to ride on the systems provided by the other. Current geopolitical conditions in late 2022 make it unlikely that cooperation will be extended to other programs such as Artemis or lunar exploration.Indian Space Research Organisation
In September 2014, NASA and ISRO, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) signed a partnership to collaborate on and launch a joint radar mission, the ''NISAR (satellite), NASA-ISO Synthetic Aperature Radar'' (''NISAR'') mission. The mission is targeted to launch in 2024. NASA will provide the mission's L-band synthetic aperture radar, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder and payload data subsystem. ISRO provides the spacecraft bus, the S-band radar, the launch vehicle and associated launch services.Artemis Accords
The Artemis Accords have been established to define a framework for cooperating in the peaceful exploration and exploitation of the Moon, Mars, asteroids, and comets. The Accords were drafted by NASA and the U.S. State Department and are executed as a series of bilateral agreements between the United States and the participating countries. As of September 2022, 21 countries have signed the accords. They are Australia, Bahrain, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, France, Israel, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Luxembourg, Mexico, New Zealand, Poland, Romania, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States.China National Space Administration
The Wolf Amendment was passed by the U.S. Congress into law in 2011 and prevents NASA from engaging in direct, bilateral cooperation with the Chinese government and China-affiliated organizations such as the China National Space Administration without the explicit authorization from Congress and the Federal Bureau of Investigation. The law has been renewed annually since by inclusion in annual appropriations bills.Sustainability
Environmental impact
The exhaust gases produced by rocket propulsion systems, both in Earth's atmosphere and in space, can adversely affect the Earth's environment. Some hypergolic rocket propellants, such as hydrazine, are highly toxic prior to combustion, but decompose into less toxic compounds after burning. Rockets using hydrocarbon fuels, such as kerosene, release carbon dioxide and soot in their exhaust. However, carbon dioxide emissions are insignificant compared to those from other sources; on average, the United States consumed of liquid fuels per day in 2014, while a single Falcon 9 rocket first stage burns around of kerosene fuel per launch. Even if a Falcon 9 were launched every single day, it would only represent 0.006% of liquid fuel consumption (and carbon dioxide emissions) for that day. Additionally, the exhaust from LOx- and LH2- fueled engines, like the SSME, is almost entirely water vapor. NASA addressed environmental concerns with its canceled Constellation program in accordance with the National Environmental Policy Act in 2011. In contrast, ion engines use harmless noble gases like xenon for propulsion. An example of NASA's environmental efforts is the NASA Sustainability Base. Additionally, the Exploration Sciences Building was awarded the LEED Gold rating in 2010. On May 8, 2003, the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency recognized NASA as the first federal agency to directly use landfill gas to produce energy at one of its facilities—the Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland. In 2018, NASA along with other companies including Sensor Coating Systems, Pratt & Whitney, Monitor Coating and United Technologies Corp, UTRC launched the project CAUTION (CoAtings for Ultra High Temperature detectION). This project aims to enhance the temperature range of the Thermal history coating, Thermal History Coating up to and beyond. The final goal of this project is improving the safety of jet engines as well as increasing efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions.Climate change
NASA also researches and publishes on climate change. Its statements concur with the global scientific consensus that the global climate is warming. Robert Smith Walker, Bob Walker, who has advised US President Donald Trump on space issues, has advocated that NASA should focus on space exploration and that its climate study operations should be transferred to other agencies such as NOAA. Former NASA atmospheric scientist J. Marshall Shepherd countered that Earth science study was built into NASA's mission at creation of NASA, its creation in the 1958 National Aeronautics and Space Act. NASA won the 2020 Webby Award, 2020 Webby People's Voice Award for Green in the category Web.STEM Initiatives
''Educational Launch of Nanosatellites, Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa)''. Since 2011, the ELaNa program has provided opportunities for NASA to work with university teams to test emerging technologies and commercial-off-the-shelf solutions by providing launch opportunities for developed CubeSats using NASA procured launch opportunities. By example, two NASA-sponsored CubeSats launched in June 2022 on a Virgin Orbit LauncherOne vehicle as the ELaNa 39 mission. ''Cubes in Space''. NASA started an annual competition in 2014 named "Cubes in Space". It is jointly organized by NASA and the global education company ''I Doodle Learning'', with the objective of teaching school students aged 11–18 to design and build scientific experiments to be launched into space on a NASA rocket or balloon. On June 21, 2017, the world's smallest satellite, KalamSAT, was launched.Use of the metric system
US law requires the International System of Units to be used in all US Government programs, "except where impractical". In 1969, Apollo 11 landed on the Moon using a mix of United States customary units and Metric system, metric units. In the 1980s, NASA started the transition towards the metric system, but was still using both systems in the 1990s. On September 23, 1999, a mixup between NASA's use of SI units and Lockheed Martin Space's use of US units resulted in the loss of the Mars Climate Orbiter. In August 2007, NASA stated that all future missions and explorations of the Moon would be done entirely using the SI system. This was done to improve cooperation with space agencies of other countries that already use the metric system. As of 2007, NASA is predominantly working with SI units, but some projects still use US units, and some, including the International Space Station, use a mix of both.Media presence
NASA TV
Approaching 40 years of service, the NASA TV channel airs content ranging from live coverage of manned missions to video coverage of significant milestones for operating robotic spacecraft (e.g., rover landings on Mars for example) and domestic and international launches. The channel is delivered by NASA and is broadcast by satellite and over the Internet. The system initially started to capture archival footage of important space events for NASA managers and engineers and expanded as public interest grew. The Apollo 8 Christmas Eve broadcast while in orbit around the Moon was received by more than a billion people. NASA's video transmission of the Apollo 11 Moon landing was awarded a Primetime Emmy Awards, primetime Emmy in commemoration of the 40th anniversary of the landing. The channel is a product of the U.S. Government and is widely available across many television and Internet platforms.NASAcast
NASAcast is the official audio and video podcast of the NASA website. Created in late 2005, the podcast service contains the latest audio and video features from the NASA web site, including NASA TV, NASA TV's ''This Week at NASA'' and educational materials produced by NASA. Additional NASA podcasts, such as Science@NASA, are also featured and give subscribers an in-depth look at content by subject matter.NASA EDGE
 NASA EDGE is a video podcast which explores different missions, technologies and projects developed by NASA. The program was released by NASA on March 18, 2007, and, , there have been 200 vodcasts produced. It is a public outreach vodcast sponsored by NASA's Exploration Systems Mission Directorate and based out of the Exploration and Space Operations Directorate at Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, Hampton, Virginia. The NASA EDGE team takes an insiders look at current projects and technologies from NASA facilities around the United States, and it is depicted through personal interviews, on-scene broadcasts, computer animations, and personal interviews with top scientists and engineers at NASA.
The show explores the contributions NASA has made to society as well as the progress of current projects in materials and space exploration. NASA EDGE vodcasts can be downloaded from the NASA website and from iTunes.
In its first year of production, the show was downloaded over 450,000 times. the average download rate is more than 420,000 per month, with over one million downloads in December 2009 and January 2010.
NASA and the NASA EDGE have also developed interactive programs designed to complement the vodcast. The Lunar Electric Rover App allows users to drive a simulated Lunar Electric Rover between objectives, and it provides information about and images of the vehicle. The NASA EDGE Widget provides a graphical user interface for accessing NASA EDGE vodcasts, image galleries, and the program's Twitter feed, as well as a live NASA news feed.
NASA EDGE is a video podcast which explores different missions, technologies and projects developed by NASA. The program was released by NASA on March 18, 2007, and, , there have been 200 vodcasts produced. It is a public outreach vodcast sponsored by NASA's Exploration Systems Mission Directorate and based out of the Exploration and Space Operations Directorate at Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, Hampton, Virginia. The NASA EDGE team takes an insiders look at current projects and technologies from NASA facilities around the United States, and it is depicted through personal interviews, on-scene broadcasts, computer animations, and personal interviews with top scientists and engineers at NASA.
The show explores the contributions NASA has made to society as well as the progress of current projects in materials and space exploration. NASA EDGE vodcasts can be downloaded from the NASA website and from iTunes.
In its first year of production, the show was downloaded over 450,000 times. the average download rate is more than 420,000 per month, with over one million downloads in December 2009 and January 2010.
NASA and the NASA EDGE have also developed interactive programs designed to complement the vodcast. The Lunar Electric Rover App allows users to drive a simulated Lunar Electric Rover between objectives, and it provides information about and images of the vehicle. The NASA EDGE Widget provides a graphical user interface for accessing NASA EDGE vodcasts, image galleries, and the program's Twitter feed, as well as a live NASA news feed.
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Gallery
See also
* List of crewed spacecraft * List of NASA aircraft * List of space disasters * * : NASA people * * * *Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* Alexander, Joseph K. ''Science Advice to NASA: Conflict, Consensus, Partnership, Leadership'' (2019excerpt
* Bizony, Piers et al. ''The NASA Archives. 60 Years in Space'' (2019) * Brady, Kevin M. "NASA Launches Houston into Orbit How America's Space Program Contributed to Southeast Texas's Economic Growth, Scientific Development, and Modernization during the Late Twentieth Century." ''Journal of the West'' (2018) 57#4 pp 13–54. * Bromberg, Joan Lisa. ''NASA and the Space Industry'' (Johns Hopkins UP, 1999). * Clemons, Jack. ''Safely to Earth: The Men and Women Who Brought the Astronauts Home'' (2018
excerpt
* Dick, Steven J., and Roger D. Launius, eds. ''Critical Issues in the History of Spaceflight'' (NASA, 2006) * Launius, Roger D. "Eisenhower, Sputnik, and the Creation of NASA." ''Prologue-Quarterly of the National Archives'' 28.2 (1996): 127–143. * Pyle, Rod. ''Space 2.0: How Private Spaceflight, a Resurgent NASA, and International Partners are Creating a New Space Age'' (2019), overview of space exploratio
excerpt
* Spencer, Brett. "The Book and the Rocket: The Symbiotic Relationship between American Public Libraries and the Space Program, 1950–2015", ''Information & Culture'' 51, no. 4 (2016): 550–82. * Weinzierl, Matthew. "Space, the final economic frontier." ''Journal of Economic Perspectives'' 32.2 (2018): 173–92
online
, review of economics literature
External links
* **
NASA History Division
*
*
NODIS: NASA Online Directives Information System
*
NTRS: NASA Technical Reports Server
*
NASA History and the Challenge of Keeping the Contemporary Past
*
NASA podcasts
NASA Watch, an agency watchdog site
*
on howstuffworks.com {{Authority control NASA, 1958 establishments in Washington, D.C. Articles containing video clips Collier Trophy recipients Government agencies established in 1958 Independent agencies of the United States government Organizations based in Washington, D.C. Webby Award winners