Muslims praying in a Masque in Bangladesh.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the
Sunni Islam: Oxford Bibliographies Online Research Guide
"Sunni Islam is the dominant division of the global Muslim community, and throughout history it has made up a substantial majority (85 to 90 percent) of that community." * * and

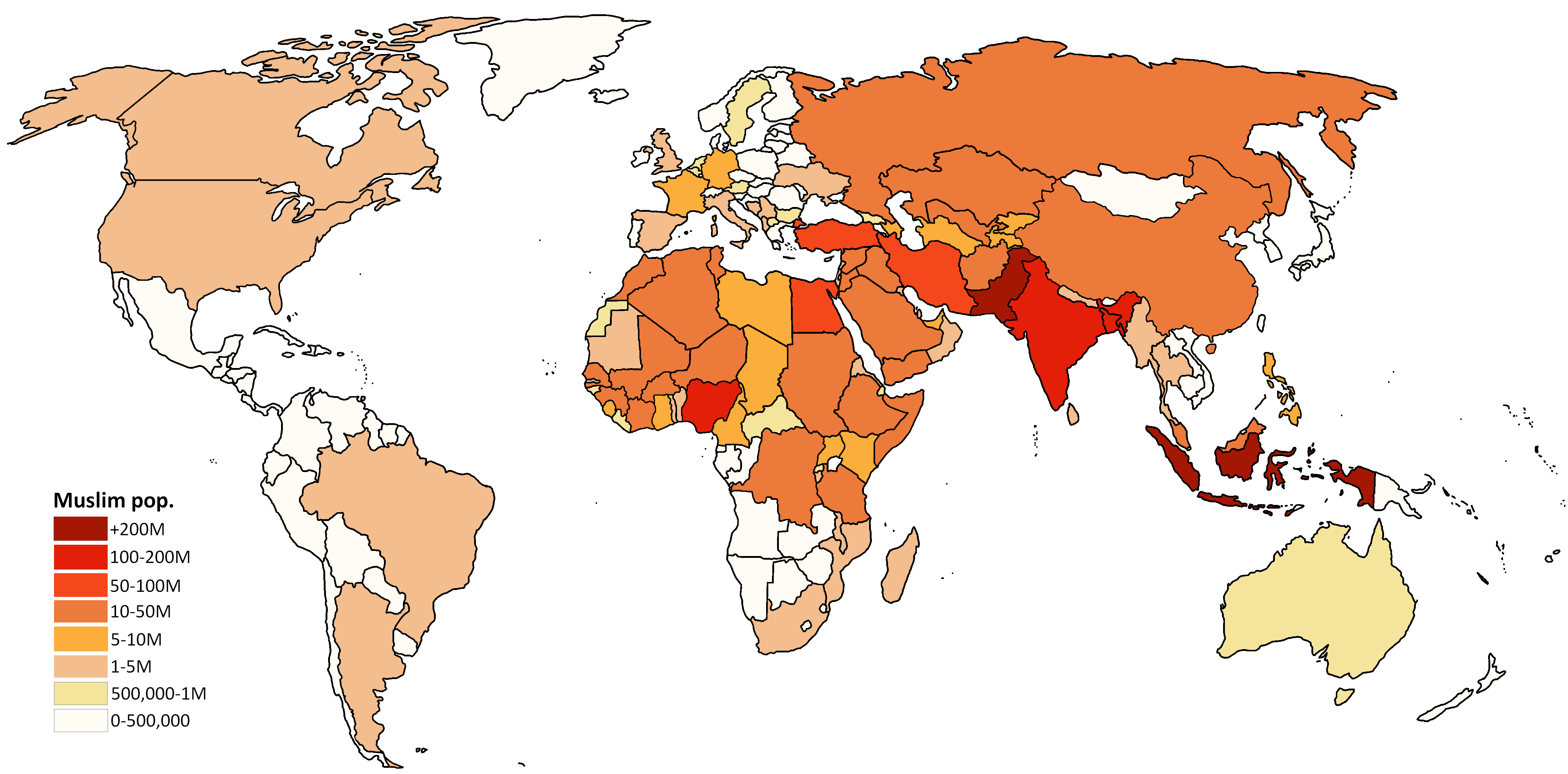 The most populous Muslim-majority country is Indonesia, home to 12.7% of the world's Muslims, followed by Pakistan (11.0%), Bangladesh (9.2%), Nigeria (5.3%) and Egypt (4.9%). About 20% of the world's Muslims live in the Middle East and North Africa.
Sizable minorities are also found in Islam in India, India, Islam in China, China, Islam in Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Islam in the Americas, the Americas, Islam in Australia, Australia and parts of
The most populous Muslim-majority country is Indonesia, home to 12.7% of the world's Muslims, followed by Pakistan (11.0%), Bangladesh (9.2%), Nigeria (5.3%) and Egypt (4.9%). About 20% of the world's Muslims live in the Middle East and North Africa.
Sizable minorities are also found in Islam in India, India, Islam in China, China, Islam in Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Islam in the Americas, the Americas, Islam in Australia, Australia and parts of
Ritual Prayer: Its Meaning and Manner
– The Islamic Supreme Council of America.
– University of Chicago
''Islamophobia Today'' Newspaper
– An Islamophobia news clearing house
Sammy Aziz Rahmatti, ''Understanding and Countering Islamophobia''
*Wiktionary:Wikisaurus:Muslim, WikiSaurus:Muslim * * {{Authority control Muslims, Islam, Quranic words and phrases Religious identity
Abrahamic
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
tradition. They consider the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham
''God of Abraham'' (Yiddish: גאָט פֿון אַבֿרהם, pronounced ''Got fun Avrohom'', ''Got fin Avruhom'') is a Jewish prayer in Yiddish, recited by women and girls in many Jewish communities at the conclusion of the Sabbath, marking it ...
(or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad ('' sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approva ...
'').
With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, 25% of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
(collectively), 6% of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, and 1% of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, 65% of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
, 42% of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, 32% of South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, and 42% of sub-Saharan Africa.
While there are several Islamic schools and branches
Islamic schools and branches have different understandings of Islam. There are many different sects or denominations, schools of Islamic jurisprudence, and schools of Islamic theology, or '' ʿaqīdah'' (creed). Within Islamic groups themselves ...
, the two largest denominations are Sunni Islam (75–90% of all Muslims)*
Sunni Islam: Oxford Bibliographies Online Research Guide
"Sunni Islam is the dominant division of the global Muslim community, and throughout history it has made up a substantial majority (85 to 90 percent) of that community." * * and
Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
(10–20% of all Muslims). By sheer numbers, South Asia accounts for the largest portion (31%) of the global Muslim population, primarily across three countries: Islam in Pakistan, Pakistan, Islam in India, India, and Islam in Bangladesh, Bangladesh. By country, Islam in Indonesia, Indonesia is the largest in the Muslim world, holding around 12% of all Muslims worldwide; outside of the Muslim-majority countries, India and Islam in China, China are home to the largest (11%) and second-largest (2%) Muslim populations, respectively. Due to high Muslim population growth, Islam is the Growth of religion, fastest-growing religion in the world.
Etymology
The word ''muslim'' ( ar, مسلم, ; , , or ''moslem'' , ) is the active participle of the same verb of which ''islām'' is a verbal noun, based on the triliteral ''S-L-M'' "to be whole, intact". A female adherent is a ''muslima'' ( ar, مسلمة) (also transliteration, transliterated as "Muslimah" ). The plural form in Arabic is ''muslimūn'' () or ''muslimīn'' (), and its feminine equivalent is ''muslimāt'' (). The ordinary word in English is "Muslim". In the 20th century the preferred spelling in English was "Moslem", but this has now fallen into disuse. The word ''Mosalman'' ( fa, مسلمان, alternatively ''Mussalman'') is a common equivalent for ''Muslim'' used in Central Asia, Central and South Asia. In English it was sometimes spelled Mussulman and has become Archaism, archaic in usage. Until at least the mid-1960s, many English-language writers used the term ''Mohammedans'' or ''Mahometans''. Although such terms were not necessarily intended to be pejorative, Muslims argue that the terms are offensive because they allegedly imply that Muslims worship Muhammad rather than God. Other obsolete terms include ''Muslimite'' and ''Muslimist''. In Medieval Europe, Muslims were commonly called Saracens. The Muslim philosopher Ibn Arabi said:Qualifier
To become a Muslim and to convert to Islam, it is essential to utter the ''Shahada'', one of the Five Pillars of Islam, a declaration of faith and trust that professes that there is tawhid, only one God in Islam, God ''( Allah)'' and thatMuhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
is God's messenger. It is a set statement normally recited in Arabic: ''ašhadu ʾal-lā ʾilāha ʾillā-llāhu wa ʾašhadu ʾanna muħammadan rasūlu-llāh'' () "I testify that there is no god [worthy of worship] except Allah, and Muhammad is the messenger of Allah."
In Sunni Islam, the shahada has two parts: ''la ilaha illa'llah'' (there is no god but Allah), and ''Muhammadun rasul Allah'' (Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
is the messenger of God),Lindsay, p. 140–141 which are sometimes referred to as the first ''shahada'' and the second ''shahada''.Cornell, p. 9 The first statement of the shahada is also known as the ''tahlil, tahlīl''.
In Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
, the shahada also has a third part, a phrase concerning Ali, the first Imamah (Shia doctrine), Shia Imam and the fourth Rashidun, Rashid caliph of Sunni Islam: (), which translates to "Ali is the ''wali'' of God".
In Quranism, Quranist Islam, the shahada is the testimony that there is no god but Allah (''la ilaha illa'llah'' ).
The religious practices of Muslims are enumerated in the Five Pillars of Islam: the declaration of faith (''shahadah''), daily prayers (''salat, salah''), almsgiving (''zakat''), fasting during the month of Ramadan (''sawm''), and the pilgrimage to Mecca (''hajj'') at least once in a lifetime.
In Islamic theology
The Qur'an describes many prophets and messengers within Judaism and Christianity, and their respective followers, as Muslim. Some of those that were mentioned are: Adam (Bible), Adam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Ishmael in Islam, Ishmael, Jacob, Islamic view of Moses, Moses, and Islamic view of Jesus, Jesus and his apostles are all considered to be Muslims in the Qur'an. The Qur'an states that these men were Muslims because they submitted to God, preached His message and upheld His values, which included praying, charity, fasting and pilgrimage. Thus, in Surah 3:52 of the Qur'an, Jesus' disciples tell him, "We believe in God; and you be our witness that we are Muslims (''wa-shahad be anna muslimūn'')." In Islamic belief, before the Qur'an, God had given the Tawrat (Torah) to Moses, the Zabur (Psalms) to David and the Injil (Gospel) to Jesus, who are all considered important Prophets of Islam, Muslim prophets.Demographics
 The most populous Muslim-majority country is Indonesia, home to 12.7% of the world's Muslims, followed by Pakistan (11.0%), Bangladesh (9.2%), Nigeria (5.3%) and Egypt (4.9%). About 20% of the world's Muslims live in the Middle East and North Africa.
Sizable minorities are also found in Islam in India, India, Islam in China, China, Islam in Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Islam in the Americas, the Americas, Islam in Australia, Australia and parts of
The most populous Muslim-majority country is Indonesia, home to 12.7% of the world's Muslims, followed by Pakistan (11.0%), Bangladesh (9.2%), Nigeria (5.3%) and Egypt (4.9%). About 20% of the world's Muslims live in the Middle East and North Africa.
Sizable minorities are also found in Islam in India, India, Islam in China, China, Islam in Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Islam in the Americas, the Americas, Islam in Australia, Australia and parts of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
. The country with the highest proportion of self-described Muslims as a proportion of its total population is Morocco.
Over 75–90% of Muslims are Sunni. The second and third largest sects, Shia and Ahmadiyya, make up 10–20%, and 1% respectively.
With about 1.9 billion followers (2019), almost a quarter of world population, earth's population, Islam is the major religious groups, second-largest and the Growth of religion, fastest-growing religion in the world, primarily due to the young age and high fertility rate of Muslims, with Muslims having a rate of (3.1) compared to the world average of (2.5). According to the same study, Religious conversion, religious switching has no impact on Muslim population, since the number of people who Convert to Islam, embrace Islam and those who Apostasy in Islam, leave Islam are roughly equal.
A Pew Center study in 2016 found that Muslims have the highest number of adherents under the age of 15 (34% of the total Muslim population) of any major religion, while only 7% are aged 60+ (the smallest percentage of any major religion). According to the same study, Muslims have the highest fertility rates (3.1) of any major religious group. The study also found that Muslims (tied with Hindus) have the lowest average levels of education with an average of 5.6 years of schooling, though both groups have made the largest gains in educational attainment in recent decades among major religions. About 36% of all Muslims have no formal schooling, and Muslims have the lowest average levels of higher education of any major religious group, with only 8% having Academic degree, graduate and post-graduate degrees.
Culture
Muslim culture or Islamic culture are terms used to describe the cultural practices common to Muslims and historically Islamic people. The early forms of Muslim culture, from the Rashidun Caliphate to early Umayyad period, were predominantly Arab, Byzantine, Persians, Persian and Levantine. With the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, Islamic empires, Muslim culture has influenced and assimilated much from the Persian culture, Persian, Egyptian culture, Egyptian, Caucasus, Caucasian, Turkic people, Turkic, Mongol, South Asian, Malay people, Malay, Somali people, Somali, Berber people, Berber, Indonesian, and Moro people, Moro cultures.See also
* Cultural Muslims *Islamic schools and branches
Islamic schools and branches have different understandings of Islam. There are many different sects or denominations, schools of Islamic jurisprudence, and schools of Islamic theology, or '' ʿaqīdah'' (creed). Within Islamic groups themselves ...
* Mohammedan
* Lists of Muslims
* List of converts to Islam
* Islamic holidays
* Muslim world
* Mumin
* Persecution of Muslims
References
External links
Ritual Prayer: Its Meaning and Manner
– The Islamic Supreme Council of America.
– University of Chicago
''Islamophobia Today'' Newspaper
– An Islamophobia news clearing house
Sammy Aziz Rahmatti, ''Understanding and Countering Islamophobia''
*Wiktionary:Wikisaurus:Muslim, WikiSaurus:Muslim * * {{Authority control Muslims, Islam, Quranic words and phrases Religious identity