Molecule2.gif on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

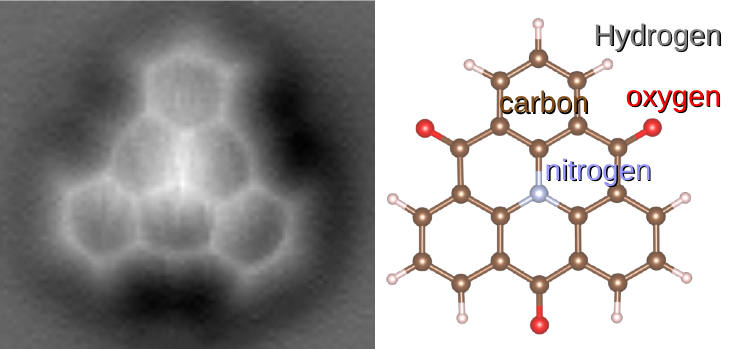 A molecule is a group of two or more
A molecule is a group of two or more
 ), Earth (classical element), earth (
), Earth (classical element), earth ( ), Air (classical element), air (
), Air (classical element), air ( ), and Water (classical element), water (
), and Water (classical element), water ( )) and "forces" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact.
A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence Aether (classical element), aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe.
In a more concrete manner, however, the concept of aggregates or units of bonded atoms, i.e. "molecules", traces its origins to
)) and "forces" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact.
A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence Aether (classical element), aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe.
In a more concrete manner, however, the concept of aggregates or units of bonded atoms, i.e. "molecules", traces its origins to 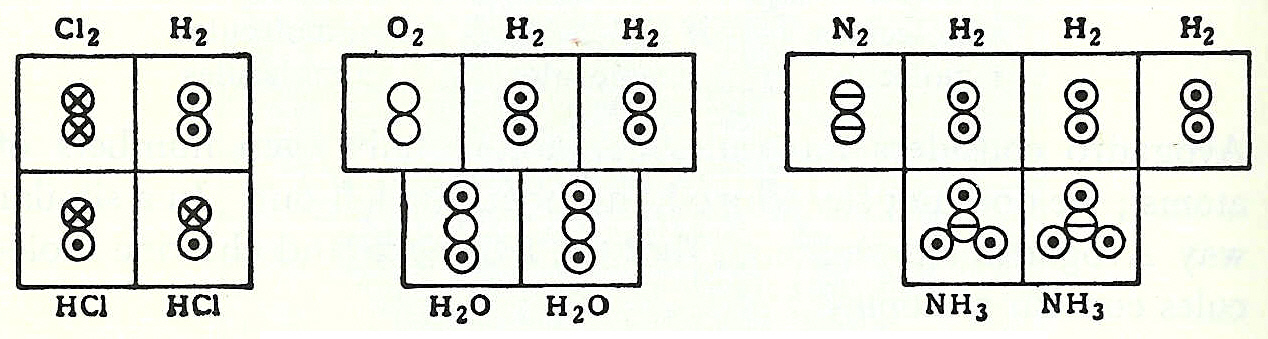 In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named Linus Pauling was learning the Dalton model, Dalton hook-and-eye bonding method, which was the mainstream description of bonds between atoms at the time. Pauling, however, wasn't satisfied with this method and looked to the newly emerging field of quantum physics for a new method. In 1926, French physicist Jean Perrin received the Nobel Prize in physics for proving, conclusively, the existence of molecules. He did this by calculating Avogadro's number using three different methods, all involving liquid phase systems. First, he used a gamboge soap-like emulsion, second by doing experimental work on Brownian motion, and third by confirming Einstein's theory of particle rotation in the liquid phase.
In 1927, the physicists Fritz London and Walter Heitler applied the new quantum mechanics to the deal with the saturable, nondynamic forces of attraction and repulsion, i.e., exchange forces, of the hydrogen molecule. Their valence bond treatment of this problem, in their joint paper, was a landmark in that it brought chemistry under quantum mechanics. Their work was an influence on Pauling, who had just received his doctorate and visited Heitler and London in Zürich on a Guggenheim Fellowship.
Subsequently, in 1931, building on the work of Heitler and London and on theories found in Lewis' famous article, Pauling published his ground-breaking article "The Nature of the Chemical Bond" in which he used quantum mechanics to calculate properties and structures of molecules, such as angles between bonds and rotation about bonds. On these concepts, Pauling developed hybridization theory to account for bonds in molecules such as CH4, in which four sp³ hybridised orbitals are overlapped by hydrogen's ''1s'' orbital, yielding four Sigma bond, sigma (σ) bonds. The four bonds are of the same length and strength, which yields a molecular structure as shown below:
In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named Linus Pauling was learning the Dalton model, Dalton hook-and-eye bonding method, which was the mainstream description of bonds between atoms at the time. Pauling, however, wasn't satisfied with this method and looked to the newly emerging field of quantum physics for a new method. In 1926, French physicist Jean Perrin received the Nobel Prize in physics for proving, conclusively, the existence of molecules. He did this by calculating Avogadro's number using three different methods, all involving liquid phase systems. First, he used a gamboge soap-like emulsion, second by doing experimental work on Brownian motion, and third by confirming Einstein's theory of particle rotation in the liquid phase.
In 1927, the physicists Fritz London and Walter Heitler applied the new quantum mechanics to the deal with the saturable, nondynamic forces of attraction and repulsion, i.e., exchange forces, of the hydrogen molecule. Their valence bond treatment of this problem, in their joint paper, was a landmark in that it brought chemistry under quantum mechanics. Their work was an influence on Pauling, who had just received his doctorate and visited Heitler and London in Zürich on a Guggenheim Fellowship.
Subsequently, in 1931, building on the work of Heitler and London and on theories found in Lewis' famous article, Pauling published his ground-breaking article "The Nature of the Chemical Bond" in which he used quantum mechanics to calculate properties and structures of molecules, such as angles between bonds and rotation about bonds. On these concepts, Pauling developed hybridization theory to account for bonds in molecules such as CH4, in which four sp³ hybridised orbitals are overlapped by hydrogen's ''1s'' orbital, yielding four Sigma bond, sigma (σ) bonds. The four bonds are of the same length and strength, which yields a molecular structure as shown below:

 A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are termed ''shared pairs'' or ''bonding pairs'', and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is termed ''covalent bonding''.
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are termed ''shared pairs'' or ''bonding pairs'', and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is termed ''covalent bonding''.
 Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. The ions are atoms that have lost one or more electrons (termed cations) and atoms that have gained one or more electrons (termed anions). This transfer of electrons is termed ''electrovalence'' in contrast to covalent bond, covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complicated nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4+ or SO42−. At normal temperatures and pressures, ionic bonding mostly creates solids (or occasionally liquids) without separate identifiable molecules, but the vaporization/sublimation of such materials does produce separate molecules where electrons are still transferred fully enough for the bonds to be considered ionic rather than covalent.
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. The ions are atoms that have lost one or more electrons (termed cations) and atoms that have gained one or more electrons (termed anions). This transfer of electrons is termed ''electrovalence'' in contrast to covalent bond, covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complicated nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4+ or SO42−. At normal temperatures and pressures, ionic bonding mostly creates solids (or occasionally liquids) without separate identifiable molecules, but the vaporization/sublimation of such materials does produce separate molecules where electrons are still transferred fully enough for the bonds to be considered ionic rather than covalent.
 For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such chemical nomenclature requires many words and terms which are not part of chemical formulas.
For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such chemical nomenclature requires many words and terms which are not part of chemical formulas.
 Molecules have fixed mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity (chemistry), reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different biochemistry, biochemical activities.
Molecules have fixed mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity (chemistry), reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different biochemistry, biochemical activities.
 Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (frequency spectrum, spectrum) of molecules interacting with probing signals of known energy (or frequency, according to Planck's constant, Planck's formula). Molecules have quantized energy levels that can be analyzed by detecting the molecule's energy exchange through absorbance or Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission.
Spectroscopy does not generally refer to diffraction studies where particles such as neutrons, electrons, or high energy X-rays interact with a regular arrangement of molecules (as in a crystal).
Microwave spectroscopy commonly measures changes in the rotation of molecules, and can be used to identify molecules in outer space. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules, including stretching, bending or twisting motions. It is commonly used to identify the kinds of bonds or functional groups in molecules. Changes in the arrangements of electrons yield absorption or emission lines in ultraviolet, visible or near infrared light, and result in colour. Nuclear resonance spectroscopy measures the environment of particular nuclei in the molecule, and can be used to characterise the numbers of atoms in different positions in a molecule.
Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (frequency spectrum, spectrum) of molecules interacting with probing signals of known energy (or frequency, according to Planck's constant, Planck's formula). Molecules have quantized energy levels that can be analyzed by detecting the molecule's energy exchange through absorbance or Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission.
Spectroscopy does not generally refer to diffraction studies where particles such as neutrons, electrons, or high energy X-rays interact with a regular arrangement of molecules (as in a crystal).
Microwave spectroscopy commonly measures changes in the rotation of molecules, and can be used to identify molecules in outer space. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules, including stretching, bending or twisting motions. It is commonly used to identify the kinds of bonds or functional groups in molecules. Changes in the arrangements of electrons yield absorption or emission lines in ultraviolet, visible or near infrared light, and result in colour. Nuclear resonance spectroscopy measures the environment of particular nuclei in the molecule, and can be used to characterise the numbers of atoms in different positions in a molecule.
Molecule of the MonthSchool of Chemistry, University of Bristol
{{Authority control Molecular physics, Molecules, Chemistry Matter

 A molecule is a group of two or more
A molecule is a group of two or more atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, ...
s held together by attractive forces known as chemical bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of ...
s; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, ...
, and biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zero. The term molecule may or may no ...
s.
A molecule may be homonuclear
Homonuclear molecules, or homonuclear species, are molecules composed of only one element. Homonuclear molecules may consist of various numbers of atoms. The size of the molecule an element can form depends on the element's properties, and some el ...
, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear
A heteronuclear molecule is a molecule composed of atoms of more than one chemical element. For example, a molecule of water (H2O) is heteronuclear because it has atoms of two different elements, hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O).
Similarly, a heteronu ...
, a chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
composed of more than one element, e.g. water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
(two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from ...
regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions
In chemistry, a non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule. The ...
, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds ...
s, are typically not considered single molecules.
Concepts similar to molecules have been discussed since ancient times, but modern investigation into the nature of molecules and their bonds began in the 17th century. Refined over time by scientists such as Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of ...
, Amedeo Avogadro
Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto (, also , ; 9 August 17769 July 1856) was an Italian scientist, most noted for his contribution to molecular theory now known as Avogadro's law, which states that equal volume ...
, Jean Perrin, and Linus Pauling, the study of molecules is today known as molecular physics
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, m ...
or molecular chemistry.
Etymology
According to Merriam-Webster and the Online Etymology Dictionary, the word "molecule" derives from theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
"moles Moles can refer to:
* Moles de Xert, a mountain range in the Baix Maestrat comarca, Valencian Community, Spain
* The Moles (Australian band)
*The Moles, alter ego of Scottish band Simon Dupree and the Big Sound
People
*Abraham Moles, French engin ...
" or small unit of mass. The word is derived from French ' (1678), from New Latin
New Latin (also called Neo-Latin or Modern Latin) is the revival of Literary Latin used in original, scholarly, and scientific works since about 1500. Modern scholarly and technical nomenclature, such as in zoological and botanical taxonomy ...
', diminutive of Latin ' "mass, barrier". The word, which until the late 18th century was used only in Latin form, became popular after being used in works of philosophy by Descartes.History
The definition of the molecule has evolved as knowledge of the structure of molecules has increased. Earlier definitions were less precise, defining molecules as the smallestparticles
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
of pure chemical substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., w ...
s that still retain their composition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
*Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
*Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include v ...
and chemical properties. This definition often breaks down since many substances in ordinary experience, such as rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
, salt (chemistry), salts, and metals, are composed of large crystalline networks of chemical bond, chemically bonded atoms or ions, but are not made of discrete molecules.
The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific and Greek philosophers such as Leucippus and Democritus who argued that all the universe is composed of Atomic theory, atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined Classical element, fundamental elements (Fire (classical element), fire (Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of ...
's 1661 hypothesis, in his famous treatise ''The Sceptical Chymist'', that matter is composed of ''clusters of particles'' and that chemical change results from the rearrangement of the clusters. Boyle argued that matter's basic elements consisted of various sorts and sizes of particles, called "corpuscles", which were capable of arranging themselves into groups. In 1789, William Higgins (chemist), William Higgins published views on what he called combinations of "ultimate" particles, which foreshadowed the concept of valency bonds. If, for example, according to Higgins, the force between the ultimate particle of oxygen and the ultimate particle of nitrogen were 6, then the strength of the force would be divided accordingly, and similarly for the other combinations of ultimate particles.
Amedeo Avogadro
Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto (, also , ; 9 August 17769 July 1856) was an Italian scientist, most noted for his contribution to molecular theory now known as Avogadro's law, which states that equal volume ...
created the word "molecule". His 1811 paper "Essay on Determining the Relative Masses of the Elementary Molecules of Bodies", he essentially states, i.e. according to J. R. Partington, Partington's ''A Short History of Chemistry'', that:In coordination with these concepts, in 1833 the French chemist Marc Antoine Auguste Gaudin presented a clear account of Avogadro's hypothesis, regarding atomic weights, by making use of "volume diagrams", which clearly show both semi-correct molecular geometries, such as a linear water molecule, and correct molecular formulas, such as H2O:
 In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named Linus Pauling was learning the Dalton model, Dalton hook-and-eye bonding method, which was the mainstream description of bonds between atoms at the time. Pauling, however, wasn't satisfied with this method and looked to the newly emerging field of quantum physics for a new method. In 1926, French physicist Jean Perrin received the Nobel Prize in physics for proving, conclusively, the existence of molecules. He did this by calculating Avogadro's number using three different methods, all involving liquid phase systems. First, he used a gamboge soap-like emulsion, second by doing experimental work on Brownian motion, and third by confirming Einstein's theory of particle rotation in the liquid phase.
In 1927, the physicists Fritz London and Walter Heitler applied the new quantum mechanics to the deal with the saturable, nondynamic forces of attraction and repulsion, i.e., exchange forces, of the hydrogen molecule. Their valence bond treatment of this problem, in their joint paper, was a landmark in that it brought chemistry under quantum mechanics. Their work was an influence on Pauling, who had just received his doctorate and visited Heitler and London in Zürich on a Guggenheim Fellowship.
Subsequently, in 1931, building on the work of Heitler and London and on theories found in Lewis' famous article, Pauling published his ground-breaking article "The Nature of the Chemical Bond" in which he used quantum mechanics to calculate properties and structures of molecules, such as angles between bonds and rotation about bonds. On these concepts, Pauling developed hybridization theory to account for bonds in molecules such as CH4, in which four sp³ hybridised orbitals are overlapped by hydrogen's ''1s'' orbital, yielding four Sigma bond, sigma (σ) bonds. The four bonds are of the same length and strength, which yields a molecular structure as shown below:
In 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named Linus Pauling was learning the Dalton model, Dalton hook-and-eye bonding method, which was the mainstream description of bonds between atoms at the time. Pauling, however, wasn't satisfied with this method and looked to the newly emerging field of quantum physics for a new method. In 1926, French physicist Jean Perrin received the Nobel Prize in physics for proving, conclusively, the existence of molecules. He did this by calculating Avogadro's number using three different methods, all involving liquid phase systems. First, he used a gamboge soap-like emulsion, second by doing experimental work on Brownian motion, and third by confirming Einstein's theory of particle rotation in the liquid phase.
In 1927, the physicists Fritz London and Walter Heitler applied the new quantum mechanics to the deal with the saturable, nondynamic forces of attraction and repulsion, i.e., exchange forces, of the hydrogen molecule. Their valence bond treatment of this problem, in their joint paper, was a landmark in that it brought chemistry under quantum mechanics. Their work was an influence on Pauling, who had just received his doctorate and visited Heitler and London in Zürich on a Guggenheim Fellowship.
Subsequently, in 1931, building on the work of Heitler and London and on theories found in Lewis' famous article, Pauling published his ground-breaking article "The Nature of the Chemical Bond" in which he used quantum mechanics to calculate properties and structures of molecules, such as angles between bonds and rotation about bonds. On these concepts, Pauling developed hybridization theory to account for bonds in molecules such as CH4, in which four sp³ hybridised orbitals are overlapped by hydrogen's ''1s'' orbital, yielding four Sigma bond, sigma (σ) bonds. The four bonds are of the same length and strength, which yields a molecular structure as shown below:
Molecular science
The science of molecules is called ''molecular chemistry'' or ''molecular physics
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, m ...
'', depending on whether the focus is on chemistry or physics. Molecular chemistry deals with the laws governing the interaction between molecules that results in the formation and breakage of chemical bonds, while molecular physics deals with the laws governing their structure and properties. In practice, however, this distinction is vague. In molecular sciences, a molecule consists of a stable system (bound state) composed of two or more atoms. Polyatomic ions may sometimes be usefully thought of as electrically charged molecules. The term ''unstable molecule'' is used for very reactivity (chemistry), reactive species, i.e., short-lived assemblies (Resonance (chemistry), resonances) of electrons and atomic nucleus, nuclei, such as radical (chemistry), radicals, molecular ions, Rydberg molecules, transition states, van der Waals bonding, van der Waals complexes, or systems of colliding atoms as in Bose–Einstein condensate.
Prevalence
Molecules as components of matter are common. They also make up most of the oceans and atmosphere. Most organic substances are molecules. The substances of life are molecules, e.g. proteins, the amino acids of which they are composed, the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), sugars, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins. The nutrient minerals are generally ionic compounds, thus they are not molecules, e.g. iron sulfate. However, the majority of familiar solid substances on Earth are made partly or completely of crystals or ionic compounds, which are not made of molecules. These include all of the minerals that make up the substance of the Earth, sand, clay, pebbles, rocks, boulders, Crust (geology), bedrock, the Mantle (geology), molten interior, and the Earth core, core of the Earth. All of these contain many chemical bonds, but are ''not'' made of identifiable molecules. No typical molecule can be defined for salts nor for network solid, covalent crystals, although these are often composed of repeating unit cells that extend either in a Plane (mathematics), plane, e.g. graphene; or three-dimensionally e.g. diamond, quartz, sodium chloride. The theme of repeated unit-cellular-structure also holds for most metals which are condensed phases with metallic bonding. Thus solid metals are not made of molecules. In glasses, which are solids that exist in a vitreous disordered state, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds with no presence of any definable molecule, nor any of the regularity of repeating unit-cellular-structure that characterizes salts, covalent crystals, and metals.Bonding
Molecules are generally held together by covalent bonding. Several non-metallic elements exist only as molecules in the environment either in compounds or as homonuclear molecules, not as free atoms: for example, hydrogen. While some people say a metallic crystal can be considered a single giant molecule held together by metallic bonding, others point out that metals behave very differently than molecules.Covalent
Ionic
 Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. The ions are atoms that have lost one or more electrons (termed cations) and atoms that have gained one or more electrons (termed anions). This transfer of electrons is termed ''electrovalence'' in contrast to covalent bond, covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complicated nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4+ or SO42−. At normal temperatures and pressures, ionic bonding mostly creates solids (or occasionally liquids) without separate identifiable molecules, but the vaporization/sublimation of such materials does produce separate molecules where electrons are still transferred fully enough for the bonds to be considered ionic rather than covalent.
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. The ions are atoms that have lost one or more electrons (termed cations) and atoms that have gained one or more electrons (termed anions). This transfer of electrons is termed ''electrovalence'' in contrast to covalent bond, covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complicated nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4+ or SO42−. At normal temperatures and pressures, ionic bonding mostly creates solids (or occasionally liquids) without separate identifiable molecules, but the vaporization/sublimation of such materials does produce separate molecules where electrons are still transferred fully enough for the bonds to be considered ionic rather than covalent.
Molecular size
Most molecules are far too small to be seen with the naked eye, although molecules of many polymers can reach macroscopic sizes, including biopolymers such as DNA. Molecules commonly used as building blocks for organic synthesis have a dimension of a few angstroms (Å) to several dozen Å, or around one billionth of a meter. Single molecules cannot usually be observed by light (as noted above), but small molecules and even the outlines of individual atoms may be traced in some circumstances by use of an atomic force microscope. Some of the largest molecules are macromolecules or supermolecules. The smallest molecule is the diatomic hydrogen (H2), with a bond length of 0.74 Å. Effective molecular radius is the size a molecule displays in solution. The table of permselectivity for different substances contains examples.Molecular formulas
Chemical formula types
The chemical formula for a molecule uses one line of chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to one typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A compound's empirical formula is a very simple type of chemical formula. It is the simplest integer ratio of the chemical elements that constitute it. For example, water is always composed of a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) is always composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 2:6:1 ratio. However, this does not determine the kind of molecule uniquely – dimethyl ether has the same ratios as ethanol, for instance. Molecules with the sameatom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, ...
s in different arrangements are called isomers. Also carbohydrates, for example, have the same ratio (carbon:hydrogen:oxygen= 1:2:1) (and thus the same empirical formula) but different total numbers of atoms in the molecule.
The molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. However different isomers can have the same atomic composition while being different molecules.
The empirical formula is often the same as the molecular formula but not always. For example, the molecule acetylene has molecular formula C2H2, but the simplest integer ratio of elements is CH.
The molecular mass can be calculated from the chemical formula and is expressed in conventional atomic mass units equal to 1/12 of the mass of a neutral carbon-12 (12carbon, C isotope) atom. For network solids, the term formula unit is used in stoichiometric calculations.
Structural formula
 For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such chemical nomenclature requires many words and terms which are not part of chemical formulas.
For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such chemical nomenclature requires many words and terms which are not part of chemical formulas.
Molecular geometry
 Molecules have fixed mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity (chemistry), reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different biochemistry, biochemical activities.
Molecules have fixed mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity (chemistry), reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different biochemistry, biochemical activities.
Molecular spectroscopy
 Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (frequency spectrum, spectrum) of molecules interacting with probing signals of known energy (or frequency, according to Planck's constant, Planck's formula). Molecules have quantized energy levels that can be analyzed by detecting the molecule's energy exchange through absorbance or Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission.
Spectroscopy does not generally refer to diffraction studies where particles such as neutrons, electrons, or high energy X-rays interact with a regular arrangement of molecules (as in a crystal).
Microwave spectroscopy commonly measures changes in the rotation of molecules, and can be used to identify molecules in outer space. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules, including stretching, bending or twisting motions. It is commonly used to identify the kinds of bonds or functional groups in molecules. Changes in the arrangements of electrons yield absorption or emission lines in ultraviolet, visible or near infrared light, and result in colour. Nuclear resonance spectroscopy measures the environment of particular nuclei in the molecule, and can be used to characterise the numbers of atoms in different positions in a molecule.
Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (frequency spectrum, spectrum) of molecules interacting with probing signals of known energy (or frequency, according to Planck's constant, Planck's formula). Molecules have quantized energy levels that can be analyzed by detecting the molecule's energy exchange through absorbance or Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission.
Spectroscopy does not generally refer to diffraction studies where particles such as neutrons, electrons, or high energy X-rays interact with a regular arrangement of molecules (as in a crystal).
Microwave spectroscopy commonly measures changes in the rotation of molecules, and can be used to identify molecules in outer space. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules, including stretching, bending or twisting motions. It is commonly used to identify the kinds of bonds or functional groups in molecules. Changes in the arrangements of electrons yield absorption or emission lines in ultraviolet, visible or near infrared light, and result in colour. Nuclear resonance spectroscopy measures the environment of particular nuclei in the molecule, and can be used to characterise the numbers of atoms in different positions in a molecule.
Theoretical aspects
The study of molecules by molecular physics and theoretical chemistry is largely based on quantum mechanics and is essential for the understanding of the chemical bond. The simplest of molecules is the hydrogen molecule-ion, H2+, and the simplest of all the chemical bonds is the one-electron bond. H2+ is composed of two positively charged protons and one negatively charged electron, which means that the Schrödinger equation for the system can be solved more easily due to the lack of electron–electron repulsion. With the development of fast digital computers, approximate solutions for more complicated molecules became possible and are one of the main aspects of computational chemistry. When trying to define rigorously whether an arrangement of atoms is ''sufficiently stable'' to be considered a molecule, IUPAC suggests that it "must correspond to a depression on the potential energy surface that is deep enough to confine at least one vibrational state". This definition does not depend on the nature of the interaction between the atoms, but only on the strength of the interaction. In fact, it includes weakly bound species that would not traditionally be considered molecules, such as the helium Dimer (chemistry), dimer, helium dimer, He2, which has one vibrational bound state and is so loosely bound that it is only likely to be observed at very low temperatures. Whether or not an arrangement of atoms is ''sufficiently stable'' to be considered a molecule is inherently an operational definition. Philosophically, therefore, a molecule is not a fundamental entity (in contrast, for instance, to an elementary particle); rather, the concept of a molecule is the chemist's way of making a useful statement about the strengths of atomic-scale interactions in the world that we observe.See also
* Atom * Chemical polarity * Chemical structure * Covalent bond * Diatomic molecule * List of compounds * List of interstellar and circumstellar molecules * Molecular biology * Molecular design software * Molecular engineering * Molecular geometry * Molecular Hamiltonian * Molecular ion * Molecular modelling * Molecular promiscuity * Molecular orbital * Non-covalent bonding * Periodic systems of small molecules * Small molecule * Comparison of software for molecular mechanics modeling * Van der Waals molecule * World Wide Molecular MatrixReferences
External links
Molecule of the MonthSchool of Chemistry, University of Bristol
{{Authority control Molecular physics, Molecules, Chemistry Matter