Masonic Temple Alexandria.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Freemasonry or Masonry refers to Fraternity, fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of Stonemasonry, stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups:
* Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned.
* Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions.
The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Masonic Lodge, Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lodge is independent, and they do not necessarily recognise each other as being legitimate.
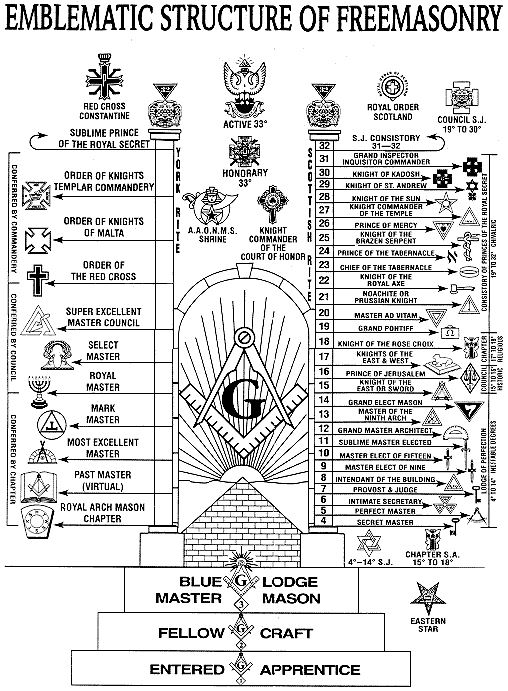
The degrees of Freemasonry retain the three grades of medieval craft guilds, those of Apprenticeship, Entered Apprentice, Journeyman or fellow (now called Fellowcraft), and Master craftsman, Master Mason. The candidate of these three degrees is progressively taught the meanings of the symbols of Freemasonry and entrusted with grips, signs, and words to signify to other members that he has been so initiated. The degrees are part allegorical morality play and part lecture. These three degrees form Craft (or Blue Lodge) Freemasonry, and members of any of these degrees are known as Freemasons or Masons. There are additional degrees, which vary with locality and jurisdiction, and are usually administered by their own bodies (separate from those who administer the Craft degrees).
Due to misconceptions about Freemasonry’s tradition of not discussing its rituals with non-members, the fraternity has become associated with many Masonic conspiracy theories, conspiracy theories.
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to Fraternity, fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of Stonemasonry, stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups:
* Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned.
* Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions.
The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Masonic Lodge, Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lodge is independent, and they do not necessarily recognise each other as being legitimate.
The degrees of Freemasonry retain the three grades of medieval craft guilds, those of Apprenticeship, Entered Apprentice, Journeyman or fellow (now called Fellowcraft), and Master craftsman, Master Mason. The candidate of these three degrees is progressively taught the meanings of the symbols of Freemasonry and entrusted with grips, signs, and words to signify to other members that he has been so initiated. The degrees are part allegorical morality play and part lecture. These three degrees form Craft (or Blue Lodge) Freemasonry, and members of any of these degrees are known as Freemasons or Masons. There are additional degrees, which vary with locality and jurisdiction, and are usually administered by their own bodies (separate from those who administer the Craft degrees).
Due to misconceptions about Freemasonry’s tradition of not discussing its rituals with non-members, the fraternity has become associated with many Masonic conspiracy theories, conspiracy theories.
 The Masonic lodge is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry. The Lodge meets regularly and conducts the usual formal business of any small organisation (approve minutes, elect new members, appoint officers and take their reports, consider correspondence, bills and annual accounts, organise social and charitable events, etc.). In addition to such business, the meeting may perform a ceremony to confer a Masonic ritual and symbolism, Masonic degree"Frequently Asked Questions"
The Masonic lodge is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry. The Lodge meets regularly and conducts the usual formal business of any small organisation (approve minutes, elect new members, appoint officers and take their reports, consider correspondence, bills and annual accounts, organise social and charitable events, etc.). In addition to such business, the meeting may perform a ceremony to confer a Masonic ritual and symbolism, Masonic degree"Frequently Asked Questions"
''United Grand Lodge of England'' retrieved 30 October 2013 or receive a lecture, which is usually on some aspect of Masonic history or ritual. At the conclusion of the meeting, the Lodge may hold a formal dinner, or ''festive board'', sometimes involving toasting and song. The bulk of Masonic ritual consists of degree ceremonies. Candidates for Freemasonry are progressively ''initiated'' into Freemasonry, first in the degree of Entered Apprentice. At some later time, in separate ceremonies, they will be ''passed'' to the degree of Fellowcraft; and then ''raised'' to the degree of Master Mason. In each of these ceremonies, the candidate must first take the new obligations of the degree, and is then entrusted with secret knowledge including passwords, signs and grips (secret handshakes) confined to his new rank."Words, Grips and Signs"
H. L. Haywood, ''Symbolical Masonry'', 1923, Chapter XVIII, ''Sacred Texts'' website, retrieved 9 January 2014 Another ceremony is the annual installation of the Master of the Lodge and his appointed or elected officers. In some jurisdictions an ''Installed Master'' elected, obligated and invested to preside over a Lodge, is valued as a separate rank with its own secrets and distinctive title and attributes; after each full year in the Chair the Master invests his elected successor and becomes a Past Master with privileges in the Lodge and Grand Lodge. In other jurisdictions, the grade is not recognised, and no inner ceremony conveys new secrets during the installation of a new Master of the Lodge. Most Lodges have some sort of social functions, allowing members, their partners and non-Masonic guests to meet openly. Often coupled with these events is the discharge of every Mason's and Lodge's collective obligation to contribute to charity. This occurs at many levels, including in annual dues, subscriptions, fundraising events, Lodges and Grand Lodges. Masons and their charities contribute for the relief of need in many fields, such as education, health and old age. Private Lodges form the backbone of Freemasonry, with the sole right to elect their own candidates for initiation as Masons or admission as joining Masons, and sometimes with exclusive rights over residents local to their premises. There are non-local Lodges where Masons meet for wider or narrower purposes, such or in association with some hobby, sport, Masonic research, business, profession, regiment or college. The rank of Master Mason also entitles a Freemason to explore Masonry further through other degrees, administered separately from the basic Craft or "Blue Lodge" degrees described here, but generally having a similar structure and meetings.Michael Johnstone, ''The Freemasons'', Arcturus, 2005, pp. 101–120 There is much diversity and little consistency in Freemasonry, because each Masonic jurisdiction is independent and sets its own rules and procedures while Grand Lodges have limited jurisdiction over their constituent member Lodges, which are ultimately private clubs. The wording of the ritual, the number of officers present, the layout of the meeting room, etc. varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
''Maconnieke Encyclopedie'', retrieved 31 October 2013 Almost all Masonic Lodge Officers, officers of a Lodge are elected or appointed annually. Every Masonic Lodge has a Master, two Wardens, a treasurer and a secretary. There is also always a Tyler (Masonic), Tyler, or outer guard, outside the door of a working Lodge, who may be paid to secure its privacy. Other offices vary between jurisdictions. Each Masonic Lodge exists and operates according to ancient principles known as the ''Landmarks of Freemasonry'', which elude any universally accepted definition.
 Candidates for Freemasonry will usually have met the most active members of the Lodge they are joining before being elected for initiation. The process varies among Grand Lodges, but in modern times interested people often look up a local Lodge through the Internet and will typically be introduced to a Lodge social function or open evening. The onus is upon candidates to ask to join; while they may be encouraged to ask, they may not be invited. Once the initial inquiry is made, a formal application may be proposed and seconded or announced in open Lodge and a more or less formal interview usually follows. If the candidate wishes to proceed, references are taken up during a period of notice so that members may enquire into the candidate's suitability and discuss it. Finally the Lodge takes an officially secret ballot on each application before a candidate is either initiated or rejected."How to become a Freemason"
Candidates for Freemasonry will usually have met the most active members of the Lodge they are joining before being elected for initiation. The process varies among Grand Lodges, but in modern times interested people often look up a local Lodge through the Internet and will typically be introduced to a Lodge social function or open evening. The onus is upon candidates to ask to join; while they may be encouraged to ask, they may not be invited. Once the initial inquiry is made, a formal application may be proposed and seconded or announced in open Lodge and a more or less formal interview usually follows. If the candidate wishes to proceed, references are taken up during a period of notice so that members may enquire into the candidate's suitability and discuss it. Finally the Lodge takes an officially secret ballot on each application before a candidate is either initiated or rejected."How to become a Freemason"
''Masonic Lodge of Education'', retrieved 20 November 2013 The exact number of adverse ballots (“blackballs”) required to reject a candidate varies between Masonic jurisdictions. As an example, the United Grand Lodge of England only requires a single “blackball", while the Grand Lodge of New York requires three. A minimum requirement of every body of Freemasons is that each candidate must be "free and of good reputation". The question of freedom, a standard feudal requirement of mediaeval guilds, is nowadays one of independence: the object is that every Mason should be a proper and responsible person. Thus, each Grand Lodge has a standard minimum age, varying greatly and often subject to dispensation in particular cases. (For example, in England the standard minimum age to join is 21, but university lodges are given dispensations to initiate undergraduates below that age.) Additionally, most Grand Lodges require a candidate to declare a belief in a Supreme Being (although every candidate must interpret this condition in his own way, as all religious discussion is commonly prohibited). In a few cases, the candidate may be required to be of a specific religion. The form of Freemasonry most common in Scandinavia (known as the Swedish Rite), for example, accepts only Christians. At the other end of the spectrum, "Liberal" or Continental Freemasonry, exemplified by the Grand Orient de France, does not require a declaration of belief in any deity and accepts atheists (the cause of the distinction from the rest of Freemasonry)."Faut-il croire en Dieu?"
Foire aux Questions, ''Grand Orient de France'', Retrieved 23 November 2013
''Pietre-Stones'', retrieved 23 November 2013 During the ceremony of initiation, the candidate is required to undertake an obligation, swearing on the religious volume sacred to his personal faith to do good as a Mason. In the course of three degrees, Masons will promise to keep the secrets of their degree from lower degrees and outsiders, as far as practicality and the law permit, and to support a fellow Mason in distress. There is formal instruction as to the duties of a Freemason, but on the whole, Freemasons are left to explore the craft in the manner they find most satisfying. Some will simply enjoy the dramatics, or the management and administration of the lodge, others will explore the history, ritual and symbolism of the craft, others will focus their involvement on their Lodge's sociopolitical side, perhaps in association with other lodges, while still others will concentrate on the lodge's charitable functions.
 Grand Lodges and Grand Orients are independent and sovereign bodies that govern Masonry in a given country, state or geographical area (termed a ''jurisdiction''). There is no single overarching governing body that presides over worldwide Freemasonry; connections between different jurisdictions depend solely on mutual recognition.
Freemasonry, as it exists in various forms all over the world, has a membership estimated at around 6 million worldwide. The fraternity is administratively organised into independent Grand Lodges (or sometimes Grand Orients), each of which governs its own Masonic jurisdiction, which consists of subordinate (or ''constituent'') Lodges. The largest single jurisdiction, in terms of membership, is the United Grand Lodge of England (with local organisation into Provincial Grand Lodges possessing a combined membership estimated at around a quarter million). The Grand Lodge of Scotland and Grand Lodge of Ireland (taken together) have approximately 150,000 members. In the United States, there are 51 Grand Lodges (one in each state and the District of Columbia) which together have a total membership just under 2 million.
Grand Lodges and Grand Orients are independent and sovereign bodies that govern Masonry in a given country, state or geographical area (termed a ''jurisdiction''). There is no single overarching governing body that presides over worldwide Freemasonry; connections between different jurisdictions depend solely on mutual recognition.
Freemasonry, as it exists in various forms all over the world, has a membership estimated at around 6 million worldwide. The fraternity is administratively organised into independent Grand Lodges (or sometimes Grand Orients), each of which governs its own Masonic jurisdiction, which consists of subordinate (or ''constituent'') Lodges. The largest single jurisdiction, in terms of membership, is the United Grand Lodge of England (with local organisation into Provincial Grand Lodges possessing a combined membership estimated at around a quarter million). The Grand Lodge of Scotland and Grand Lodge of Ireland (taken together) have approximately 150,000 members. In the United States, there are 51 Grand Lodges (one in each state and the District of Columbia) which together have a total membership just under 2 million.
 Regularity is a concept based on adherence to Masonic Landmarks, the basic membership requirements, tenets and rituals of the craft. Each Grand Lodge sets its own definition of what these landmarks are, and thus what is Regular and what is Irregular (and the definitions do not necessarily agree between Grand Lodges). Essentially, every Grand Lodge will hold that ''its'' landmarks (its requirements, tenets and rituals) are Regular, and judge other Grand Lodges based on those. If the differences are significant, one Grand Lodge may declare the other "Irregular" and withdraw or withhold recognition.
The most commonly shared rules for Recognition (based on Regularity) are those given by the United Grand Lodge of England in 1929:
* The Grand Lodge should be established by an existing regular Grand Lodge, or by at least three regular Lodges.
* A belief in a supreme being and scripture is a condition of membership.
* Initiates should take their vows on that scripture.
* Only men can be admitted, and no relationship exists with mixed Lodges.
* The Grand Lodge has complete control over the first three degrees, and is not subject to another body.
* All Lodges shall display a volume of scripture with the square and compasses while in session.
* There is no discussion of politics or religion.
* "Ancient landmarks, customs and usages" observed.''UGLE Book of Constitutions'', "Basic Principles for Grand Lodge Recognition", any year since 1930, page numbers may vary.
Regularity is a concept based on adherence to Masonic Landmarks, the basic membership requirements, tenets and rituals of the craft. Each Grand Lodge sets its own definition of what these landmarks are, and thus what is Regular and what is Irregular (and the definitions do not necessarily agree between Grand Lodges). Essentially, every Grand Lodge will hold that ''its'' landmarks (its requirements, tenets and rituals) are Regular, and judge other Grand Lodges based on those. If the differences are significant, one Grand Lodge may declare the other "Irregular" and withdraw or withhold recognition.
The most commonly shared rules for Recognition (based on Regularity) are those given by the United Grand Lodge of England in 1929:
* The Grand Lodge should be established by an existing regular Grand Lodge, or by at least three regular Lodges.
* A belief in a supreme being and scripture is a condition of membership.
* Initiates should take their vows on that scripture.
* Only men can be admitted, and no relationship exists with mixed Lodges.
* The Grand Lodge has complete control over the first three degrees, and is not subject to another body.
* All Lodges shall display a volume of scripture with the square and compasses while in session.
* There is no discussion of politics or religion.
* "Ancient landmarks, customs and usages" observed.''UGLE Book of Constitutions'', "Basic Principles for Grand Lodge Recognition", any year since 1930, page numbers may vary.


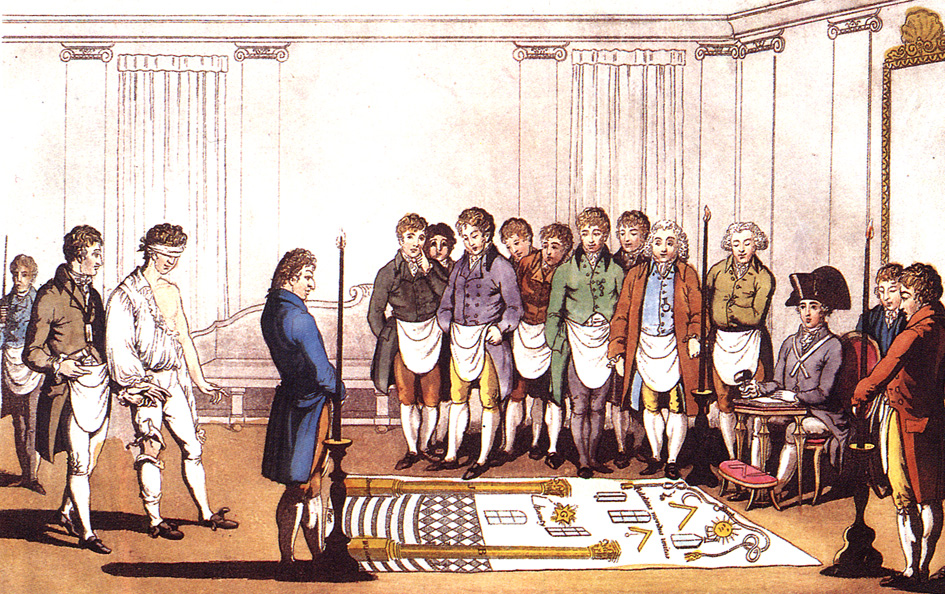
 Freemasonry describes itself as a "beautiful system of morality, veiled in allegory and illustrated by symbols". The symbolism is mainly, but not exclusively, drawn from the tools of stonemasons – the square and compasses, the level and plumb rule, the trowel, the rough and smooth ashlars, among others. Moral lessons are attributed to each of these tools, although the assignment is by no means consistent. The meaning of the symbolism is taught and explored through ritual, and in lectures and articles by individual Masons who offer their personal insights and opinions.
According to the Academic study of Western esotericism, scholar of Western esotericism Jan A. M. Snoek: "the best way to characterize Freemasonry is in terms of what it is not, rather than what it is". All Freemasons begin their journey in the "craft" by being progressively "initiated", "passed" and "raised" into the three degrees of Craft, or Blue Lodge Masonry. During these three rituals, the candidate is progressively taught the Masonic symbols, and entrusted with grips or tokens, signs, and words to signify to other Masons which degrees he has taken. The dramatic allegorical ceremonies include explanatory lectures, and revolve around the construction of the Temple of Solomon, and the artistry and death of the chief architect, Hiram Abiff. The degrees are those of "Entered apprentice", "Fellowcraft" and "Master Mason". While many different versions of these rituals exist, with various lodge layouts and versions of the Hiramic legend, each version is recognizable to any Freemason from any jurisdiction.
In some jurisdictions, the main themes of each degree are illustrated by tracing boards. These painted depictions of Masonic themes are exhibited in the lodge according to which degree is being worked, and are explained to the candidate to illustrate the legend and symbolism of each degree.
The idea of Masonic brotherhood probably descends from a 16th-century legal definition of a "brother" as one who has taken an oath of mutual support to another. Accordingly, Masons swear at each degree to keep the contents of that degree secret, and to support and protect their brethren unless they have broken the law. In most Lodges, the oath or obligation is taken on a ''Volume of Sacred Law'', whichever book of divine revelation is appropriate to the religious beliefs of the individual brother (usually the Bible in the Anglo-American tradition). In ''Progressive'' continental Freemasonry, books other than scripture are permissible, a cause of rupture between Grand Lodges.
Freemasonry describes itself as a "beautiful system of morality, veiled in allegory and illustrated by symbols". The symbolism is mainly, but not exclusively, drawn from the tools of stonemasons – the square and compasses, the level and plumb rule, the trowel, the rough and smooth ashlars, among others. Moral lessons are attributed to each of these tools, although the assignment is by no means consistent. The meaning of the symbolism is taught and explored through ritual, and in lectures and articles by individual Masons who offer their personal insights and opinions.
According to the Academic study of Western esotericism, scholar of Western esotericism Jan A. M. Snoek: "the best way to characterize Freemasonry is in terms of what it is not, rather than what it is". All Freemasons begin their journey in the "craft" by being progressively "initiated", "passed" and "raised" into the three degrees of Craft, or Blue Lodge Masonry. During these three rituals, the candidate is progressively taught the Masonic symbols, and entrusted with grips or tokens, signs, and words to signify to other Masons which degrees he has taken. The dramatic allegorical ceremonies include explanatory lectures, and revolve around the construction of the Temple of Solomon, and the artistry and death of the chief architect, Hiram Abiff. The degrees are those of "Entered apprentice", "Fellowcraft" and "Master Mason". While many different versions of these rituals exist, with various lodge layouts and versions of the Hiramic legend, each version is recognizable to any Freemason from any jurisdiction.
In some jurisdictions, the main themes of each degree are illustrated by tracing boards. These painted depictions of Masonic themes are exhibited in the lodge according to which degree is being worked, and are explained to the candidate to illustrate the legend and symbolism of each degree.
The idea of Masonic brotherhood probably descends from a 16th-century legal definition of a "brother" as one who has taken an oath of mutual support to another. Accordingly, Masons swear at each degree to keep the contents of that degree secret, and to support and protect their brethren unless they have broken the law. In most Lodges, the oath or obligation is taken on a ''Volume of Sacred Law'', whichever book of divine revelation is appropriate to the religious beliefs of the individual brother (usually the Bible in the Anglo-American tradition). In ''Progressive'' continental Freemasonry, books other than scripture are permissible, a cause of rupture between Grand Lodges.
 Since the middle of the 19th century, Masonic historians have sought the origins of the movement in a series of similar documents known as the Old Charges, dating from the Regius Poem in about 1425 to the beginning of the 18th century. Alluding to the membership of a lodge of operative masons, they relate it to a mythologised history of the craft, the duties of its grades, and the manner in which oaths of fidelity are to be taken on joining. The 15th century also sees the first evidence of ceremonial regalia.
There is no clear mechanism by which these local trade organisations became today's Masonic Lodges. The earliest rituals and passwords known, from operative lodges around the turn of the 17th–18th centuries, show continuity with the rituals developed in the later 18th century by accepted or speculative Masons, as those members who did not practice the physical craft gradually came to be known. The minutes of the Lodge of Edinburgh (Mary's Chapel) No. 1 in Scotland show a continuity from an operative lodge in 1598 to a modern speculative Lodge. It is reputed to be the oldest Masonic Lodge in the world.
Since the middle of the 19th century, Masonic historians have sought the origins of the movement in a series of similar documents known as the Old Charges, dating from the Regius Poem in about 1425 to the beginning of the 18th century. Alluding to the membership of a lodge of operative masons, they relate it to a mythologised history of the craft, the duties of its grades, and the manner in which oaths of fidelity are to be taken on joining. The 15th century also sees the first evidence of ceremonial regalia.
There is no clear mechanism by which these local trade organisations became today's Masonic Lodges. The earliest rituals and passwords known, from operative lodges around the turn of the 17th–18th centuries, show continuity with the rituals developed in the later 18th century by accepted or speculative Masons, as those members who did not practice the physical craft gradually came to be known. The minutes of the Lodge of Edinburgh (Mary's Chapel) No. 1 in Scotland show a continuity from an operative lodge in 1598 to a modern speculative Lodge. It is reputed to be the oldest Masonic Lodge in the world.
 Alternatively, Thomas De Quincey in his work titled ''Rosicrucians and Freemasonry'' put forward the theory that suggested that Freemasonry may have been an outgrowth of Rosicrucianism. The theory had also been postulated in 1803 by German professor; J. G. Buhle.
The first Grand Lodge, the Grand Lodge of London and Westminster, later called the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Grand Lodge of England, was founded on St John's Day, 24 June 1717, when four existing London Lodges met for a joint dinner. Over the next decade, most of the existing Lodges in England joined the new regulatory body, which itself entered a period of self-publicity and expansion. New lodges were created and the fraternity began to grow.
During the course of the 18th century, as aristocrats and artists crowded out the craftsmen originally associated with the organization, Freemasonry became fashionable throughout Europe and the European colonization of the Americas, American colonies.
Between 1730 and 1750, the Grand Lodge endorsed several significant changes that some Lodges could not endorse. A rival Grand Lodge was formed on 17 July 1751, which called itself the "Antient Grand Lodge of England” to signify that these lodges were maintaining older traditions, and rejected changes that “modern” Lodges had adopted (historians still use these terms - “Ancients” and “Moderns” - to differentiate the two bodies). These two Grand Lodges vied for supremacy until the Moderns promised to return to the ancient ritual. They united on 27 December 1813 to form the United Grand Lodge of England.I. R. Clarke, "The Formation of the Grand Lodge of the Antients"
Alternatively, Thomas De Quincey in his work titled ''Rosicrucians and Freemasonry'' put forward the theory that suggested that Freemasonry may have been an outgrowth of Rosicrucianism. The theory had also been postulated in 1803 by German professor; J. G. Buhle.
The first Grand Lodge, the Grand Lodge of London and Westminster, later called the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Grand Lodge of England, was founded on St John's Day, 24 June 1717, when four existing London Lodges met for a joint dinner. Over the next decade, most of the existing Lodges in England joined the new regulatory body, which itself entered a period of self-publicity and expansion. New lodges were created and the fraternity began to grow.
During the course of the 18th century, as aristocrats and artists crowded out the craftsmen originally associated with the organization, Freemasonry became fashionable throughout Europe and the European colonization of the Americas, American colonies.
Between 1730 and 1750, the Grand Lodge endorsed several significant changes that some Lodges could not endorse. A rival Grand Lodge was formed on 17 July 1751, which called itself the "Antient Grand Lodge of England” to signify that these lodges were maintaining older traditions, and rejected changes that “modern” Lodges had adopted (historians still use these terms - “Ancients” and “Moderns” - to differentiate the two bodies). These two Grand Lodges vied for supremacy until the Moderns promised to return to the ancient ritual. They united on 27 December 1813 to form the United Grand Lodge of England.I. R. Clarke, "The Formation of the Grand Lodge of the Antients"
Ars Quatuor Coronatorum, vol 79 (1966), p. 270-73, ''Grand Lodge of British Columbia and Yukon'', retrieved 28 June 2012 The Grand Lodge of Ireland and the Grand Lodge of Scotland were formed in 1725 and 1736, respectively, although neither persuaded all of the existing lodges in their countries to join for many years.
 English Freemasonry spread to France in the 1720s, first as lodges of expatriates and exiled Jacobitism, Jacobites, and then as distinctively French lodges that still follow the ritual of the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Moderns. From France and England, Freemasonry spread to most of Continental Europe during the course of the 18th century. The Grande Loge de France formed under the Grand Mastership of the Duke of Clermont, who exercised only nominal authority. His successor, the Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, Duke of Orléans, reconstituted the central body as the Grand Orient de France in 1773. Briefly eclipsed during the French Revolution, French Freemasonry continued to grow in the next century, at first under the leadership of Alexandre Francois Auguste de Grasse, Comte de Grassy-Tilly. A career Army officer, he lived with his family in Charleston, South Carolina from 1793 to the early 1800s, after leaving Saint-Domingue, now Haiti, during the years of the Haitian Revolution.
English Freemasonry spread to France in the 1720s, first as lodges of expatriates and exiled Jacobitism, Jacobites, and then as distinctively French lodges that still follow the ritual of the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Moderns. From France and England, Freemasonry spread to most of Continental Europe during the course of the 18th century. The Grande Loge de France formed under the Grand Mastership of the Duke of Clermont, who exercised only nominal authority. His successor, the Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, Duke of Orléans, reconstituted the central body as the Grand Orient de France in 1773. Briefly eclipsed during the French Revolution, French Freemasonry continued to grow in the next century, at first under the leadership of Alexandre Francois Auguste de Grasse, Comte de Grassy-Tilly. A career Army officer, he lived with his family in Charleston, South Carolina from 1793 to the early 1800s, after leaving Saint-Domingue, now Haiti, during the years of the Haitian Revolution.
''Phoenix Masonry'', retrieved 5 March 2013 Later organisations with a similar aim emerged in the United States, but distinguished the names of the degrees from those of male masonry. Maria Deraismes was initiated into Freemasonry in 1882, then resigned to allow her lodge to rejoin their Grand Lodge. Having failed to achieve acceptance from any masonic governing body, she and Georges Martin (freemason), Georges Martin started a mixed masonic lodge that worked masonic ritual. Annie Besant spread the phenomenon to the English-speaking world. Disagreements over ritual led to the formation of exclusively female bodies of Freemasons in England, which spread to other countries. Meanwhile, the French had re-invented Adoption as an all-female lodge in 1901, only to cast it aside again in 1935. The lodges, however, continued to meet, which gave rise, in 1959, to a body of women practising continental Freemasonry. In general, Continental Freemasonry is sympathetic to Freemasonry amongst women, dating from the 1890s when French lodges assisted the emergent co-masonic movement by promoting enough of their members to the 33rd degree of the Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite to allow them, in 1899, to form their own grand council, recognised by the other Continental Grand Councils of that Rite."Histoire du Droit Humain"
''Droit Humain'', retrieved 12 August 2013 The United Grand Lodge of England issued a statement in 1999 recognising the two women's grand lodges there, The Order of Women Freemasons and The Honourable Fraternity of Ancient Freemasons, to be regular in all but the participants. While they were not, therefore, recognised as regular, they were part of Freemasonry "in general". The attitude of most regular Anglo-American grand lodges remains that women Freemasons are not legitimate Masons. In 2018, guidance was released by the United Grand Lodge of England stating that, in regard to transgender women, "A Freemason who after initiation ceases to be a man does not cease to be a Freemason". The guidance also states that transgender men are allowed to apply to become Freemasons.
 During the Age of the Enlightenment in the 18th century, Freemasons comprised an international network of like-minded men, often meeting in secret in ritualistic programs at their lodges. They promoted the ideals of the Enlightenment, and helped diffuse these values across Britain and France and other places. British Freemasonry offered a systematic creed with its own myths, values and set of rituals. It fostered new codes of conduct – including a communal understanding of liberty and equality inherited from guild sociability – "liberty, fraternity, and equality" Scottish soldiers and Jacobite Scots brought to the Continent ideals of fraternity which reflected not the local system of Scottish customs but the institutions and ideals originating in the English Revolution against royal absolutism. Freemasonry was particularly prevalent in France – by 1789, there were between 50,000 and 100,000 French Masons, making Freemasonry the most popular of all Enlightenment associations.
Jacob argues that Masonic lodges probably had an effect on society as a whole, for they “reconstituted the polity and established a constitutional form of self-government, complete with constitutions and laws, elections and representatives”. In other words, the micro-society set up within the lodges constituted a normative model for society as a whole. This was especially true on the Continent: when the first lodges began to appear in the 1730s, their embodiment of British values was often seen as threatening by state authorities. For example, the Parisian lodge that met in the mid 1720s was composed of English Jacobitism, Jacobite exiles. Furthermore, freemasons all across Europe made reference to the Enlightenment in general in the 18th century. In French lodges, for example, the line “As the means to be enlightened I search for the enlightened” was a part of their initiation rites. British lodges assigned themselves the duty to “initiate the unenlightened”. Many lodges praised the Grand Architect, the masonic terminology for the divine being who created a scientifically ordered universe.
On the other hand, historian Robert Roswell Palmer noted that lodges operated separately and Masons politically did not act together as a group. American historians, while noting that Benjamin Franklin and George Washington were leading Masons, have downplayed the group's importance in the era of the American Revolution. Daniel Roche contests freemasonry’s claims for egalitarianism, writing that “the real equality of the lodges was elitist”, only attracting men of similar social backgrounds.
In long-term historical perspective, Norman Davies has argued that Freemasonry was a powerful force in Europe, from about 1700 to the twentieth century. It expanded rapidly during the Age of Enlightenment, reaching practically every country in Europe, as well as the European colonies in the New World and Asia. Davies states, "In the nineteenth century and beyond it would be strongly associated with the cause of Liberalism." In Catholic lands it was anti-clerical and came under heavy attack from the Catholic Church. In the 20th century it was suppressed by Fascist and Communist regimes. It was especially attractive to royalty, aristocrats and politicians and businessmen, as well as intellectuals, artists and political activists. Davies notes that prominent members included Montesquieu, Voltaire, Robert Walpole, Sir Robert Walpole, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Benjamin Franklin, and George Washington. Steven Bullock notes that in the late 18th century, English lodges were headed by the Prince of Wales, Prussian lodges by king Frederick the Great, and French lodges by royal princes. Emperor Napoleon selected as Grand Master of France his own brother.
During the Age of the Enlightenment in the 18th century, Freemasons comprised an international network of like-minded men, often meeting in secret in ritualistic programs at their lodges. They promoted the ideals of the Enlightenment, and helped diffuse these values across Britain and France and other places. British Freemasonry offered a systematic creed with its own myths, values and set of rituals. It fostered new codes of conduct – including a communal understanding of liberty and equality inherited from guild sociability – "liberty, fraternity, and equality" Scottish soldiers and Jacobite Scots brought to the Continent ideals of fraternity which reflected not the local system of Scottish customs but the institutions and ideals originating in the English Revolution against royal absolutism. Freemasonry was particularly prevalent in France – by 1789, there were between 50,000 and 100,000 French Masons, making Freemasonry the most popular of all Enlightenment associations.
Jacob argues that Masonic lodges probably had an effect on society as a whole, for they “reconstituted the polity and established a constitutional form of self-government, complete with constitutions and laws, elections and representatives”. In other words, the micro-society set up within the lodges constituted a normative model for society as a whole. This was especially true on the Continent: when the first lodges began to appear in the 1730s, their embodiment of British values was often seen as threatening by state authorities. For example, the Parisian lodge that met in the mid 1720s was composed of English Jacobitism, Jacobite exiles. Furthermore, freemasons all across Europe made reference to the Enlightenment in general in the 18th century. In French lodges, for example, the line “As the means to be enlightened I search for the enlightened” was a part of their initiation rites. British lodges assigned themselves the duty to “initiate the unenlightened”. Many lodges praised the Grand Architect, the masonic terminology for the divine being who created a scientifically ordered universe.
On the other hand, historian Robert Roswell Palmer noted that lodges operated separately and Masons politically did not act together as a group. American historians, while noting that Benjamin Franklin and George Washington were leading Masons, have downplayed the group's importance in the era of the American Revolution. Daniel Roche contests freemasonry’s claims for egalitarianism, writing that “the real equality of the lodges was elitist”, only attracting men of similar social backgrounds.
In long-term historical perspective, Norman Davies has argued that Freemasonry was a powerful force in Europe, from about 1700 to the twentieth century. It expanded rapidly during the Age of Enlightenment, reaching practically every country in Europe, as well as the European colonies in the New World and Asia. Davies states, "In the nineteenth century and beyond it would be strongly associated with the cause of Liberalism." In Catholic lands it was anti-clerical and came under heavy attack from the Catholic Church. In the 20th century it was suppressed by Fascist and Communist regimes. It was especially attractive to royalty, aristocrats and politicians and businessmen, as well as intellectuals, artists and political activists. Davies notes that prominent members included Montesquieu, Voltaire, Robert Walpole, Sir Robert Walpole, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Benjamin Franklin, and George Washington. Steven Bullock notes that in the late 18th century, English lodges were headed by the Prince of Wales, Prussian lodges by king Frederick the Great, and French lodges by royal princes. Emperor Napoleon selected as Grand Master of France his own brother.
First published in M. D. J. Scanlan, ed., ''The Social Impact of Freemasonry on the Modern Western World'', The Canonbury Papers I (London: Canonbury Masonic Research Centre, 2002), pp. 116–34, ''Pietre-Stones'' website, retrieved 9 January 2014 The Grand Masters of both the Moderns and the Antients Grand Lodges called on Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger, William Pitt (who was not a Freemason) and explained to him that Freemasonry was a supporter of the law and lawfully constituted authority and was much involved in charitable work. As a result, Freemasonry was specifically exempted from the terms of the Act, provided that each private lodge's Secretary placed with the local "Clerk of the Peace" a list of the members of his lodge once a year. This continued until 1967, when the obligation of the provision was rescinded by Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament. Freemasonry in the United States faced political pressure following the 1826 kidnapping of William Morgan (anti-Mason), William Morgan by Freemasons and his subsequent disappearance. Reports of the "Morgan Affair", together with opposition to Jacksonian democracy (Andrew Jackson was a prominent Mason), helped fuel an Anti-Masonic movement. The short-lived Anti-Masonic Party was formed, which fielded candidates for the presidential elections of 1828 and 1832.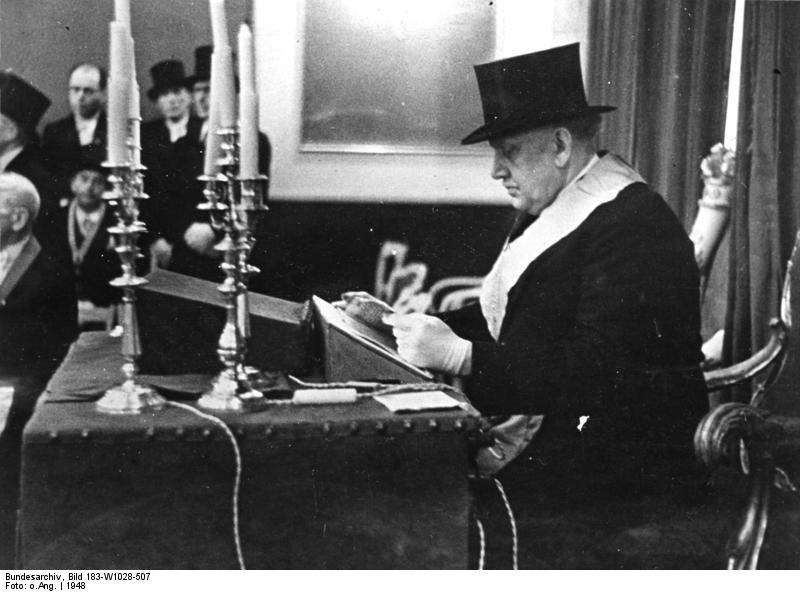 In Italy, Freemasonry has become linked to a scandal concerning the Propaganda Due lodge (a.k.a. P2). This lodge was chartered by the Grande Oriente d'Italia in 1877, as a lodge for visiting Masons unable to attend their own lodges. Under Licio Gelli's leadership, in the late 1970s, P2 became involved in the financial scandals that nearly bankrupted the Vatican Bank. However, by this time the lodge was operating independently and irregularly, as the Grand Orient had revoked its charter and expelled Gelli in 1976.
Conspiracy theorists have long associated Freemasonry with the New World Order (conspiracy theory), New World Order and the Illuminati, and state that Freemasonry as an organisation is either bent on world domination or already secretly in control of world politics. Historically Freemasonry has attracted criticism, and suppression from both the politically far right (e.g., Nazi Germany) and the far left (e.g. the former Communist states in Eastern Europe).
Freemasonry is viewed with distrust even in some modern democracies.Hodapp, Christopher. ''Freemasons for Dummies''. Indianapolis: Wiley, 2005. p. 86. In the UK, Masons working in the justice system, such as judges and police officers, were from 1999 to 2009 required to disclose their membership.Bright, Martin (12 June 2005).
In Italy, Freemasonry has become linked to a scandal concerning the Propaganda Due lodge (a.k.a. P2). This lodge was chartered by the Grande Oriente d'Italia in 1877, as a lodge for visiting Masons unable to attend their own lodges. Under Licio Gelli's leadership, in the late 1970s, P2 became involved in the financial scandals that nearly bankrupted the Vatican Bank. However, by this time the lodge was operating independently and irregularly, as the Grand Orient had revoked its charter and expelled Gelli in 1976.
Conspiracy theorists have long associated Freemasonry with the New World Order (conspiracy theory), New World Order and the Illuminati, and state that Freemasonry as an organisation is either bent on world domination or already secretly in control of world politics. Historically Freemasonry has attracted criticism, and suppression from both the politically far right (e.g., Nazi Germany) and the far left (e.g. the former Communist states in Eastern Europe).
Freemasonry is viewed with distrust even in some modern democracies.Hodapp, Christopher. ''Freemasons for Dummies''. Indianapolis: Wiley, 2005. p. 86. In the UK, Masons working in the justice system, such as judges and police officers, were from 1999 to 2009 required to disclose their membership.Bright, Martin (12 June 2005).
MPs told to declare links to Masons
, ''The Guardian'' While a parliamentary inquiry found that there had been no evidence of wrongdoing, the government believed that Masons' potential loyalties to support fellow Masons should be transparent to the public. The policy of requiring a declaration of masonic membership by applicants for judicial office (judges and magistrates) was ended in 2009 by Secretary of State for Justice, Justice Secretary Jack Straw (who had initiated the requirement in the 1990s). Straw stated that the rule was considered disproportionate, since no impropriety or malpractice had been shown as a result of judges being Freemasons. Freemasonry is both successful and controversial in France. As of the early 21st century, membership is rising, but reporting of it in popular media is often negative. In some countries anti-Masonry is often related to antisemitism and anti-Zionism. For example, in 1980, the Iraqi Law of Iraq, legal and Iraqi Penal Code, penal code was changed by Saddam Hussein's ruling Ba'ath Party (Iraq), Ba'ath Party, making it a felony to "promote or acclaim Zionist principles, including Freemasonry, or who associate [themselves] with Zionist organisations". Professor Andrew Prescott of the University of Sheffield writes: "Since at least the time of the The Protocols of the Elders of Zion, Protocols of the Elders of Zion, antisemitism has gone hand in hand with anti-masonry, so it is not surprising that allegations that 11 September 2001 attacks, 11 September was a Zionist plot have been accompanied by suggestions that the attacks were inspired by a masonic world order".
 The preserved records of the ''Reich Security Main Office, Reichssicherheitshauptamt'' (the Reich Security Main Office) show the persecution of Freemasons during the Holocaust. RSHA Amt VII (Written Records), overseen by Professor Franz Six, was responsible for "ideological" tasks, by which was meant the creation of antisemitic and anti-Masonic propaganda. While the number of victims is not accurately known, historians estimate that between 80,000 and 200,000 Freemasons were killed under the Nacht und Nebel, Nazi regime.''Freemasons for Dummies'', by Christopher Hodapp, Wiley Publishing Inc., Indianapolis, 2005, p. 85, sec. "Hitler and the Nazi" Masonic concentration camp inmates were classified as political prisoners and wore an inverted Nazi concentration camp badge, red triangle. Hitler believed Freemasons had succumbed to Jews conspiring against Germany.
The small blue Myosotis, forget-me-not flower was first used by the Grand Lodge ''Zur Sonne'' in 1926, as a Masonic emblem at the annual convention in Bremen, Germany. In 1938, a forget-me-not badge, made by the same factory as the Masonic badge, was chosen for the Nazi Party's ''Winterhilfswerk'', the annual charity drive of the National Socialist People's Welfare (the welfare branch of the Nazi party). This coincidence enabled Freemasons to wear the forget-me-not badge as a secret sign of membership.Also in:
After World War II, the forget-me-not flower was used again as a Masonic emblem in 1948 at the first Annual Convention of the United Grand Lodges of Germany in 1948. The badge is now sometimes worn in the coat lapel by Freemasons around the world to remember all who suffered in the name of Freemasonry, especially those during the Nazi era.
The preserved records of the ''Reich Security Main Office, Reichssicherheitshauptamt'' (the Reich Security Main Office) show the persecution of Freemasons during the Holocaust. RSHA Amt VII (Written Records), overseen by Professor Franz Six, was responsible for "ideological" tasks, by which was meant the creation of antisemitic and anti-Masonic propaganda. While the number of victims is not accurately known, historians estimate that between 80,000 and 200,000 Freemasons were killed under the Nacht und Nebel, Nazi regime.''Freemasons for Dummies'', by Christopher Hodapp, Wiley Publishing Inc., Indianapolis, 2005, p. 85, sec. "Hitler and the Nazi" Masonic concentration camp inmates were classified as political prisoners and wore an inverted Nazi concentration camp badge, red triangle. Hitler believed Freemasons had succumbed to Jews conspiring against Germany.
The small blue Myosotis, forget-me-not flower was first used by the Grand Lodge ''Zur Sonne'' in 1926, as a Masonic emblem at the annual convention in Bremen, Germany. In 1938, a forget-me-not badge, made by the same factory as the Masonic badge, was chosen for the Nazi Party's ''Winterhilfswerk'', the annual charity drive of the National Socialist People's Welfare (the welfare branch of the Nazi party). This coincidence enabled Freemasons to wear the forget-me-not badge as a secret sign of membership.Also in:
After World War II, the forget-me-not flower was used again as a Masonic emblem in 1948 at the first Annual Convention of the United Grand Lodges of Germany in 1948. The badge is now sometimes worn in the coat lapel by Freemasons around the world to remember all who suffered in the name of Freemasonry, especially those during the Nazi era.
online
* Dickie, John. ''The Craft: How the Freemasons Made the Modern World'' (PublicAffairs, 2020)
excerpt
* Fozdar, Vahid. " 'That Grand Primeval and Fundamental Religion': The Transformation of Freemasonry into a British Imperial Cult." ''Journal of World History'' 22#3 (2011), pp. 493–525
online
* Hamill, John. ''The Craft: A History of English Freemasonry'' (1986) * Harland-Jacobs, Jessica L. ''Builders of Empire: Freemasons and British Imperialism, 1717-1927'' (2007) * Hoffmann, Stefan-Ludwig. ''Freemasonry and German Civil Society, 1840-1918'' (U of Michigan Press, 2007)
excerpt
see als
online review
* Jacob, Margaret C. ''Living the Enlightenment: Freemasonry and Politics in Eighteenth-Century Europe'' (1991
excerpt
* Jacob, Margaret C. ''The Origins of Freemasonry: Facts and Fictions'' (U of Pennsylvania Press, 2007). * Jacob, Margaret, and Matthew Crow. "Freemasonry and the Enlightenment." in ''Handbook of Freemasonry'' (Brill, 2014) pp. 100–116
online
* Loiselle, Kenneth. "Freemasonry and the Catholic Enlightenment in Eighteenth-Century France." ''Journal of Modern History'' 94.3 (2022): 499-536
online
* Önnerfors, Andreas. ''Freemasonry: a very short introduction'' (Oxford University Press, 2017
excerpt
* Racine, Karen. "Freemasonry" in Michael S. Werner, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Mexico: History, Society, and Culture'' (Fitzroy Dearborn, 1997) 1:538–540. * Snoek Jan A.M. and Henrik Bogdan. "The History of Freemasonry: An Overview" in Bogdan and Snoek, eds. ''Handbook of Freemasonry'' (Brill, 2014) ch. 2 pp 13–32
online
* Stevenson, David. "Four Hundred Years of Freemasonry in Scotland.” ''Scottish Historical Review,'' 90#230 (2011), pp. 280–95
online
* Stevenson, David. ''The First Freemasons. Scotland's Early Lodges and Their Members'' (1988) * Weisberger, R. William et al. '' Freemasonry on Both Sides of the Atlantic: Essays concerning the Craft in the British Isles, Europe, the United States, and Mexico'' (2002), 969pp * Weisberger, R. William. ''Speculative Freemasonry and the Enlightenment: A Study of the Craft in London, Paris, Prague and Vienna'' (Columbia University Press, 1993) 243 pp.
online
* Hackett, David G. ''That Religion in Which All Men Agree : Freemasonry in American Culture'' (U of California Press, 2015
excerpt
* Hinks, Peter P. et al. ''All Men Free and Brethren: Essays on the History of African American Freemasonry '' (Cornell UP, 2013). * Kantrowitz, Stephen. " 'Intended for the Better Government of Man': The Political History of African American Freemasonry in the Era of Emancipation." ''Journal of American History'' 96#4, (2010), pp. 1001–26
online
* Weisberger, R. William et al. '' Freemasonry on Both Sides of the Atlantic: Essays concerning the Craft in the British Isles, Europe, the United States, and Mexico'' (2002), 969pp * York, Neil L. “Freemasons and the American Revolution.” ''Historian'' 55#2 (1993), pp. 315–30
online
online
Web of Hiram
at the University of Bradford. A database of donated Masonic material.
of the ''Pietre-Stones Review of Freemasonry''
''The Constitutions of the Free-Masons''
(1734), James Anderson, Benjamin Franklin, Paul Royster. Hosted by the Libraries at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln
by William Morgan, from Project Gutenberg * ,
The United Grand Lodge of England's Library and Museum of Freemasonry
, London
Articles on Judaism and Freemasonry
Anti-Masonry: Points of View
– Edward L. King's Masonic website
The International Order of Co-Freemasonry ''Le Droit Humain''
* {{Authority control Freemasonry,
Masonic lodge
''United Grand Lodge of England'' retrieved 30 October 2013 or receive a lecture, which is usually on some aspect of Masonic history or ritual. At the conclusion of the meeting, the Lodge may hold a formal dinner, or ''festive board'', sometimes involving toasting and song. The bulk of Masonic ritual consists of degree ceremonies. Candidates for Freemasonry are progressively ''initiated'' into Freemasonry, first in the degree of Entered Apprentice. At some later time, in separate ceremonies, they will be ''passed'' to the degree of Fellowcraft; and then ''raised'' to the degree of Master Mason. In each of these ceremonies, the candidate must first take the new obligations of the degree, and is then entrusted with secret knowledge including passwords, signs and grips (secret handshakes) confined to his new rank."Words, Grips and Signs"
H. L. Haywood, ''Symbolical Masonry'', 1923, Chapter XVIII, ''Sacred Texts'' website, retrieved 9 January 2014 Another ceremony is the annual installation of the Master of the Lodge and his appointed or elected officers. In some jurisdictions an ''Installed Master'' elected, obligated and invested to preside over a Lodge, is valued as a separate rank with its own secrets and distinctive title and attributes; after each full year in the Chair the Master invests his elected successor and becomes a Past Master with privileges in the Lodge and Grand Lodge. In other jurisdictions, the grade is not recognised, and no inner ceremony conveys new secrets during the installation of a new Master of the Lodge. Most Lodges have some sort of social functions, allowing members, their partners and non-Masonic guests to meet openly. Often coupled with these events is the discharge of every Mason's and Lodge's collective obligation to contribute to charity. This occurs at many levels, including in annual dues, subscriptions, fundraising events, Lodges and Grand Lodges. Masons and their charities contribute for the relief of need in many fields, such as education, health and old age. Private Lodges form the backbone of Freemasonry, with the sole right to elect their own candidates for initiation as Masons or admission as joining Masons, and sometimes with exclusive rights over residents local to their premises. There are non-local Lodges where Masons meet for wider or narrower purposes, such or in association with some hobby, sport, Masonic research, business, profession, regiment or college. The rank of Master Mason also entitles a Freemason to explore Masonry further through other degrees, administered separately from the basic Craft or "Blue Lodge" degrees described here, but generally having a similar structure and meetings.Michael Johnstone, ''The Freemasons'', Arcturus, 2005, pp. 101–120 There is much diversity and little consistency in Freemasonry, because each Masonic jurisdiction is independent and sets its own rules and procedures while Grand Lodges have limited jurisdiction over their constituent member Lodges, which are ultimately private clubs. The wording of the ritual, the number of officers present, the layout of the meeting room, etc. varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
''Maconnieke Encyclopedie'', retrieved 31 October 2013 Almost all Masonic Lodge Officers, officers of a Lodge are elected or appointed annually. Every Masonic Lodge has a Master, two Wardens, a treasurer and a secretary. There is also always a Tyler (Masonic), Tyler, or outer guard, outside the door of a working Lodge, who may be paid to secure its privacy. Other offices vary between jurisdictions. Each Masonic Lodge exists and operates according to ancient principles known as the ''Landmarks of Freemasonry'', which elude any universally accepted definition.
Joining a lodge
 Candidates for Freemasonry will usually have met the most active members of the Lodge they are joining before being elected for initiation. The process varies among Grand Lodges, but in modern times interested people often look up a local Lodge through the Internet and will typically be introduced to a Lodge social function or open evening. The onus is upon candidates to ask to join; while they may be encouraged to ask, they may not be invited. Once the initial inquiry is made, a formal application may be proposed and seconded or announced in open Lodge and a more or less formal interview usually follows. If the candidate wishes to proceed, references are taken up during a period of notice so that members may enquire into the candidate's suitability and discuss it. Finally the Lodge takes an officially secret ballot on each application before a candidate is either initiated or rejected."How to become a Freemason"
Candidates for Freemasonry will usually have met the most active members of the Lodge they are joining before being elected for initiation. The process varies among Grand Lodges, but in modern times interested people often look up a local Lodge through the Internet and will typically be introduced to a Lodge social function or open evening. The onus is upon candidates to ask to join; while they may be encouraged to ask, they may not be invited. Once the initial inquiry is made, a formal application may be proposed and seconded or announced in open Lodge and a more or less formal interview usually follows. If the candidate wishes to proceed, references are taken up during a period of notice so that members may enquire into the candidate's suitability and discuss it. Finally the Lodge takes an officially secret ballot on each application before a candidate is either initiated or rejected."How to become a Freemason"''Masonic Lodge of Education'', retrieved 20 November 2013 The exact number of adverse ballots (“blackballs”) required to reject a candidate varies between Masonic jurisdictions. As an example, the United Grand Lodge of England only requires a single “blackball", while the Grand Lodge of New York requires three. A minimum requirement of every body of Freemasons is that each candidate must be "free and of good reputation". The question of freedom, a standard feudal requirement of mediaeval guilds, is nowadays one of independence: the object is that every Mason should be a proper and responsible person. Thus, each Grand Lodge has a standard minimum age, varying greatly and often subject to dispensation in particular cases. (For example, in England the standard minimum age to join is 21, but university lodges are given dispensations to initiate undergraduates below that age.) Additionally, most Grand Lodges require a candidate to declare a belief in a Supreme Being (although every candidate must interpret this condition in his own way, as all religious discussion is commonly prohibited). In a few cases, the candidate may be required to be of a specific religion. The form of Freemasonry most common in Scandinavia (known as the Swedish Rite), for example, accepts only Christians. At the other end of the spectrum, "Liberal" or Continental Freemasonry, exemplified by the Grand Orient de France, does not require a declaration of belief in any deity and accepts atheists (the cause of the distinction from the rest of Freemasonry)."Faut-il croire en Dieu?"
Foire aux Questions, ''Grand Orient de France'', Retrieved 23 November 2013
''Pietre-Stones'', retrieved 23 November 2013 During the ceremony of initiation, the candidate is required to undertake an obligation, swearing on the religious volume sacred to his personal faith to do good as a Mason. In the course of three degrees, Masons will promise to keep the secrets of their degree from lower degrees and outsiders, as far as practicality and the law permit, and to support a fellow Mason in distress. There is formal instruction as to the duties of a Freemason, but on the whole, Freemasons are left to explore the craft in the manner they find most satisfying. Some will simply enjoy the dramatics, or the management and administration of the lodge, others will explore the history, ritual and symbolism of the craft, others will focus their involvement on their Lodge's sociopolitical side, perhaps in association with other lodges, while still others will concentrate on the lodge's charitable functions.
Organisation
Grand Lodges
Recognition, amity and regularity
Relations between Grand Lodges are determined by the concept of ''Recognition''. Each Grand Lodge maintains a list of other Grand Lodges that it recognises. When two Grand Lodges recognise and are in Masonic communication with each other, they are said to be ''wikt:amity, in amity'', and the brethren of each may visit each other's Lodges and interact Masonically. When two Grand Lodges are not in amity, inter-visitation is not allowed. There are many reasons one Grand Lodge will withhold or withdraw recognition from another, but the two most common are ''Exclusive Jurisdiction'' and ''Regularity''.Exclusive Jurisdiction
Exclusive Jurisdiction is a concept whereby normally only one Grand Lodge will be recognised in any geographical area. If two Grand Lodges claim jurisdiction over the same area, the other Grand Lodges will have to choose between them, and they may not all decide to recognise the same one. (In 1849, for example, the Grand Lodge of New York split into two rival factions, each claiming to be the legitimate Grand Lodge. Other Grand Lodges had to choose between them until the schism was healed). Exclusive Jurisdiction can be waived when the two overlapping Grand Lodges are themselves in Amity and agree to share jurisdiction. For example, since the Grand Lodge of Connecticut is in Amity with the Prince Hall Grand Lodge of Connecticut, the principle of Exclusive Jurisdiction does not apply, and other Grand Lodges may recognise both, likewise the five distinct kinds of lodges in Germany have nominally united under one Grand Lodge, in order to obtain international recognition.Regularity
 Regularity is a concept based on adherence to Masonic Landmarks, the basic membership requirements, tenets and rituals of the craft. Each Grand Lodge sets its own definition of what these landmarks are, and thus what is Regular and what is Irregular (and the definitions do not necessarily agree between Grand Lodges). Essentially, every Grand Lodge will hold that ''its'' landmarks (its requirements, tenets and rituals) are Regular, and judge other Grand Lodges based on those. If the differences are significant, one Grand Lodge may declare the other "Irregular" and withdraw or withhold recognition.
The most commonly shared rules for Recognition (based on Regularity) are those given by the United Grand Lodge of England in 1929:
* The Grand Lodge should be established by an existing regular Grand Lodge, or by at least three regular Lodges.
* A belief in a supreme being and scripture is a condition of membership.
* Initiates should take their vows on that scripture.
* Only men can be admitted, and no relationship exists with mixed Lodges.
* The Grand Lodge has complete control over the first three degrees, and is not subject to another body.
* All Lodges shall display a volume of scripture with the square and compasses while in session.
* There is no discussion of politics or religion.
* "Ancient landmarks, customs and usages" observed.''UGLE Book of Constitutions'', "Basic Principles for Grand Lodge Recognition", any year since 1930, page numbers may vary.
Regularity is a concept based on adherence to Masonic Landmarks, the basic membership requirements, tenets and rituals of the craft. Each Grand Lodge sets its own definition of what these landmarks are, and thus what is Regular and what is Irregular (and the definitions do not necessarily agree between Grand Lodges). Essentially, every Grand Lodge will hold that ''its'' landmarks (its requirements, tenets and rituals) are Regular, and judge other Grand Lodges based on those. If the differences are significant, one Grand Lodge may declare the other "Irregular" and withdraw or withhold recognition.
The most commonly shared rules for Recognition (based on Regularity) are those given by the United Grand Lodge of England in 1929:
* The Grand Lodge should be established by an existing regular Grand Lodge, or by at least three regular Lodges.
* A belief in a supreme being and scripture is a condition of membership.
* Initiates should take their vows on that scripture.
* Only men can be admitted, and no relationship exists with mixed Lodges.
* The Grand Lodge has complete control over the first three degrees, and is not subject to another body.
* All Lodges shall display a volume of scripture with the square and compasses while in session.
* There is no discussion of politics or religion.
* "Ancient landmarks, customs and usages" observed.''UGLE Book of Constitutions'', "Basic Principles for Grand Lodge Recognition", any year since 1930, page numbers may vary.
Other degrees, orders, and bodies
Blue Lodges, known as Craft Lodges in the United Kingdom, offer only the three traditional degrees. In most jurisdictions, the rank of past or installed master is also conferred in Blue/Craft Lodges. Master Masons are able to extend their Masonic experience by taking further degrees, in appendant or other bodies whether or not approved by their own Grand Lodge. The Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite is a system of 33 degrees, including the three Blue Lodge degrees administered by a local or national Supreme Council. This system is popular in North America, South America and in Continental Europe. In America, the York Rite, with a similar range, administers three orders of Masonry, namely the Royal Arch Masonry, Royal Arch, Cryptic Masonry, and Knights Templar (Freemasonry), Knights Templar. In Britain, separate bodies administer each order. Freemasons are encouraged to join the Holy Royal Arch, which is linked to Order of Mark Master Masons, Mark Masonry in Scotland and Ireland, but completely separate in England. In England, the Royal Arch is closely associated with the Craft, automatically having many Grand Officers in common, including H.R.H the Duke of Kent as both Grand Master of the Craft and First Grand Principal of the Royal Arch. The English Knights Templar and Cryptic Masonry share the Mark Grand Lodge offices and staff at Mark Masons Hall. The Ancient and Accepted Rite (similar to the Scottish Rite), requires a member to proclaim the Trinitarian Christian faith, and is administered from Duke Street in London. In the Nordic countries, the Swedish Rite is dominant; a variation of it is also used in parts of Germany.Ritual and symbolism


 Freemasonry describes itself as a "beautiful system of morality, veiled in allegory and illustrated by symbols". The symbolism is mainly, but not exclusively, drawn from the tools of stonemasons – the square and compasses, the level and plumb rule, the trowel, the rough and smooth ashlars, among others. Moral lessons are attributed to each of these tools, although the assignment is by no means consistent. The meaning of the symbolism is taught and explored through ritual, and in lectures and articles by individual Masons who offer their personal insights and opinions.
According to the Academic study of Western esotericism, scholar of Western esotericism Jan A. M. Snoek: "the best way to characterize Freemasonry is in terms of what it is not, rather than what it is". All Freemasons begin their journey in the "craft" by being progressively "initiated", "passed" and "raised" into the three degrees of Craft, or Blue Lodge Masonry. During these three rituals, the candidate is progressively taught the Masonic symbols, and entrusted with grips or tokens, signs, and words to signify to other Masons which degrees he has taken. The dramatic allegorical ceremonies include explanatory lectures, and revolve around the construction of the Temple of Solomon, and the artistry and death of the chief architect, Hiram Abiff. The degrees are those of "Entered apprentice", "Fellowcraft" and "Master Mason". While many different versions of these rituals exist, with various lodge layouts and versions of the Hiramic legend, each version is recognizable to any Freemason from any jurisdiction.
In some jurisdictions, the main themes of each degree are illustrated by tracing boards. These painted depictions of Masonic themes are exhibited in the lodge according to which degree is being worked, and are explained to the candidate to illustrate the legend and symbolism of each degree.
The idea of Masonic brotherhood probably descends from a 16th-century legal definition of a "brother" as one who has taken an oath of mutual support to another. Accordingly, Masons swear at each degree to keep the contents of that degree secret, and to support and protect their brethren unless they have broken the law. In most Lodges, the oath or obligation is taken on a ''Volume of Sacred Law'', whichever book of divine revelation is appropriate to the religious beliefs of the individual brother (usually the Bible in the Anglo-American tradition). In ''Progressive'' continental Freemasonry, books other than scripture are permissible, a cause of rupture between Grand Lodges.
Freemasonry describes itself as a "beautiful system of morality, veiled in allegory and illustrated by symbols". The symbolism is mainly, but not exclusively, drawn from the tools of stonemasons – the square and compasses, the level and plumb rule, the trowel, the rough and smooth ashlars, among others. Moral lessons are attributed to each of these tools, although the assignment is by no means consistent. The meaning of the symbolism is taught and explored through ritual, and in lectures and articles by individual Masons who offer their personal insights and opinions.
According to the Academic study of Western esotericism, scholar of Western esotericism Jan A. M. Snoek: "the best way to characterize Freemasonry is in terms of what it is not, rather than what it is". All Freemasons begin their journey in the "craft" by being progressively "initiated", "passed" and "raised" into the three degrees of Craft, or Blue Lodge Masonry. During these three rituals, the candidate is progressively taught the Masonic symbols, and entrusted with grips or tokens, signs, and words to signify to other Masons which degrees he has taken. The dramatic allegorical ceremonies include explanatory lectures, and revolve around the construction of the Temple of Solomon, and the artistry and death of the chief architect, Hiram Abiff. The degrees are those of "Entered apprentice", "Fellowcraft" and "Master Mason". While many different versions of these rituals exist, with various lodge layouts and versions of the Hiramic legend, each version is recognizable to any Freemason from any jurisdiction.
In some jurisdictions, the main themes of each degree are illustrated by tracing boards. These painted depictions of Masonic themes are exhibited in the lodge according to which degree is being worked, and are explained to the candidate to illustrate the legend and symbolism of each degree.
The idea of Masonic brotherhood probably descends from a 16th-century legal definition of a "brother" as one who has taken an oath of mutual support to another. Accordingly, Masons swear at each degree to keep the contents of that degree secret, and to support and protect their brethren unless they have broken the law. In most Lodges, the oath or obligation is taken on a ''Volume of Sacred Law'', whichever book of divine revelation is appropriate to the religious beliefs of the individual brother (usually the Bible in the Anglo-American tradition). In ''Progressive'' continental Freemasonry, books other than scripture are permissible, a cause of rupture between Grand Lodges.
History
Origins
 Since the middle of the 19th century, Masonic historians have sought the origins of the movement in a series of similar documents known as the Old Charges, dating from the Regius Poem in about 1425 to the beginning of the 18th century. Alluding to the membership of a lodge of operative masons, they relate it to a mythologised history of the craft, the duties of its grades, and the manner in which oaths of fidelity are to be taken on joining. The 15th century also sees the first evidence of ceremonial regalia.
There is no clear mechanism by which these local trade organisations became today's Masonic Lodges. The earliest rituals and passwords known, from operative lodges around the turn of the 17th–18th centuries, show continuity with the rituals developed in the later 18th century by accepted or speculative Masons, as those members who did not practice the physical craft gradually came to be known. The minutes of the Lodge of Edinburgh (Mary's Chapel) No. 1 in Scotland show a continuity from an operative lodge in 1598 to a modern speculative Lodge. It is reputed to be the oldest Masonic Lodge in the world.
Since the middle of the 19th century, Masonic historians have sought the origins of the movement in a series of similar documents known as the Old Charges, dating from the Regius Poem in about 1425 to the beginning of the 18th century. Alluding to the membership of a lodge of operative masons, they relate it to a mythologised history of the craft, the duties of its grades, and the manner in which oaths of fidelity are to be taken on joining. The 15th century also sees the first evidence of ceremonial regalia.
There is no clear mechanism by which these local trade organisations became today's Masonic Lodges. The earliest rituals and passwords known, from operative lodges around the turn of the 17th–18th centuries, show continuity with the rituals developed in the later 18th century by accepted or speculative Masons, as those members who did not practice the physical craft gradually came to be known. The minutes of the Lodge of Edinburgh (Mary's Chapel) No. 1 in Scotland show a continuity from an operative lodge in 1598 to a modern speculative Lodge. It is reputed to be the oldest Masonic Lodge in the world.
 Alternatively, Thomas De Quincey in his work titled ''Rosicrucians and Freemasonry'' put forward the theory that suggested that Freemasonry may have been an outgrowth of Rosicrucianism. The theory had also been postulated in 1803 by German professor; J. G. Buhle.
The first Grand Lodge, the Grand Lodge of London and Westminster, later called the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Grand Lodge of England, was founded on St John's Day, 24 June 1717, when four existing London Lodges met for a joint dinner. Over the next decade, most of the existing Lodges in England joined the new regulatory body, which itself entered a period of self-publicity and expansion. New lodges were created and the fraternity began to grow.
During the course of the 18th century, as aristocrats and artists crowded out the craftsmen originally associated with the organization, Freemasonry became fashionable throughout Europe and the European colonization of the Americas, American colonies.
Between 1730 and 1750, the Grand Lodge endorsed several significant changes that some Lodges could not endorse. A rival Grand Lodge was formed on 17 July 1751, which called itself the "Antient Grand Lodge of England” to signify that these lodges were maintaining older traditions, and rejected changes that “modern” Lodges had adopted (historians still use these terms - “Ancients” and “Moderns” - to differentiate the two bodies). These two Grand Lodges vied for supremacy until the Moderns promised to return to the ancient ritual. They united on 27 December 1813 to form the United Grand Lodge of England.I. R. Clarke, "The Formation of the Grand Lodge of the Antients"
Alternatively, Thomas De Quincey in his work titled ''Rosicrucians and Freemasonry'' put forward the theory that suggested that Freemasonry may have been an outgrowth of Rosicrucianism. The theory had also been postulated in 1803 by German professor; J. G. Buhle.
The first Grand Lodge, the Grand Lodge of London and Westminster, later called the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Grand Lodge of England, was founded on St John's Day, 24 June 1717, when four existing London Lodges met for a joint dinner. Over the next decade, most of the existing Lodges in England joined the new regulatory body, which itself entered a period of self-publicity and expansion. New lodges were created and the fraternity began to grow.
During the course of the 18th century, as aristocrats and artists crowded out the craftsmen originally associated with the organization, Freemasonry became fashionable throughout Europe and the European colonization of the Americas, American colonies.
Between 1730 and 1750, the Grand Lodge endorsed several significant changes that some Lodges could not endorse. A rival Grand Lodge was formed on 17 July 1751, which called itself the "Antient Grand Lodge of England” to signify that these lodges were maintaining older traditions, and rejected changes that “modern” Lodges had adopted (historians still use these terms - “Ancients” and “Moderns” - to differentiate the two bodies). These two Grand Lodges vied for supremacy until the Moderns promised to return to the ancient ritual. They united on 27 December 1813 to form the United Grand Lodge of England.I. R. Clarke, "The Formation of the Grand Lodge of the Antients"Ars Quatuor Coronatorum, vol 79 (1966), p. 270-73, ''Grand Lodge of British Columbia and Yukon'', retrieved 28 June 2012 The Grand Lodge of Ireland and the Grand Lodge of Scotland were formed in 1725 and 1736, respectively, although neither persuaded all of the existing lodges in their countries to join for many years.
North America
The earliest known American lodges were in Pennsylvania. The Collector for the port of Pennsylvania, John Moore, wrote of attending lodges there in 1715, two years before the putative formation of the first Grand Lodge in London. The Premier Grand Lodge of England, Grand Lodge of England appointed a Provincial Grand Master for North America in 1731, based in Pennsylvania, leading to the creation of the Grand Lodge of Pennsylvania. In Canada, Erasmus James Philipps became a Freemason while working on a commission to resolve boundaries in New England and, in 1739, he became provincial Grand Master for Nova Scotia; Philipps founded the first Masonic lodge in Canada at Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia. Other lodges in the colony of Pennsylvania obtained authorisations from the later Antient Grand Lodge of England, the Grand Lodge of Scotland, and the Grand Lodge of Ireland, which was particularly well represented in the travelling lodges of the British Army. Many lodges came into existence with no warrant from any Grand Lodge, applying and paying for their authorisation only after they were confident of their own survival. After the American Revolution, independent U.S. Grand Lodges developed within each state. Some thought was briefly given to organising an overarching "Grand Lodge of the United States," with George Washington, who was a member of a Virginian lodge, as the first Grand Master, but the idea was short-lived. The various state Grand Lodges did not wish to diminish their own authority by agreeing to such a body.Jamaican Freemasonry
Freemasonry was imported to Jamaica by British immigrants who colonized the island for over 300 years. In 1908, there were eleven recorded Masonic Lodges, which included three Grand Lodges, two Craft Lodges, and two Rose Croix Chapters. During slavery, the Lodges were open to all "freeborn" men. According to the Jamaican 1834 census, that potentially included 5,000 free black men and 40,000 free people of colour (mixed race). After the Slavery Abolition Act 1833, full abolition of slavery in 1838, the Lodges were open to all Jamaican men of any race. Jamaica also kept close relationships with Masons from other countries. Jamaican Freemasonry historian Jackie Ranston, noted that: On 25 May 2017, Masons around the world celebrated the 300th anniversary of the fraternity. Jamaica hosted one of the regional gatherings for this celebration.Prince Hall Freemasonry
Prince Hall Freemasonry exists because of the refusal of early American lodges to admit African Americans. In 1775, an African American named Prince Hall, along with 14 other African-American men, was initiated into a British military lodge with a warrant from the Grand Lodge of Ireland, having failed to obtain admission from the other lodges in Boston. When the British military Lodge left North America after the end of the Revolution, those 15 men were given the authority to meet as a Lodge, but not to initiate Masons. In 1784, these individuals obtained a Warrant from the Grand Lodge of England (Moderns) and formed African Lodge No. 459, African Lodge, Number 459. When the two English grand lodges united in 1813, all U.S.-based Lodges were stricken from their rolls – largely because of the War of 1812. Thus, separated from both English jurisdiction and any concordantly recognised U.S. Grand Lodge, African Lodge retitled itself as the African Lodge, Number 1 – and became a ''de facto'' Grand Lodge. (This lodge is not to be confused with the various Grand Lodges in Africa.) As with the rest of U.S. Freemasonry, Prince Hall Freemasonry soon grew and organised on a Grand Lodge system for each state. Widespread racial segregation in 19th- and early 20th-century North America made it difficult for African Americans to join Lodges outside of Prince Hall jurisdictions – and impossible for inter-jurisdiction recognition between the parallel U.S. Masonic authorities. By the 1980s, such discrimination was a thing of the past. Today most U.S. Grand Lodges recognise their Prince Hall counterparts, and the authorities of both traditions are working towards full recognition. The United Grand Lodge of England has no problem with recognising Prince Hall Grand Lodges. While celebrating their heritage as lodges of African-Americans, Prince Hall is open to all men regardless of race or religion.Emergence of Continental Freemasonry
 English Freemasonry spread to France in the 1720s, first as lodges of expatriates and exiled Jacobitism, Jacobites, and then as distinctively French lodges that still follow the ritual of the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Moderns. From France and England, Freemasonry spread to most of Continental Europe during the course of the 18th century. The Grande Loge de France formed under the Grand Mastership of the Duke of Clermont, who exercised only nominal authority. His successor, the Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, Duke of Orléans, reconstituted the central body as the Grand Orient de France in 1773. Briefly eclipsed during the French Revolution, French Freemasonry continued to grow in the next century, at first under the leadership of Alexandre Francois Auguste de Grasse, Comte de Grassy-Tilly. A career Army officer, he lived with his family in Charleston, South Carolina from 1793 to the early 1800s, after leaving Saint-Domingue, now Haiti, during the years of the Haitian Revolution.
English Freemasonry spread to France in the 1720s, first as lodges of expatriates and exiled Jacobitism, Jacobites, and then as distinctively French lodges that still follow the ritual of the Premier Grand Lodge of England, Moderns. From France and England, Freemasonry spread to most of Continental Europe during the course of the 18th century. The Grande Loge de France formed under the Grand Mastership of the Duke of Clermont, who exercised only nominal authority. His successor, the Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, Duke of Orléans, reconstituted the central body as the Grand Orient de France in 1773. Briefly eclipsed during the French Revolution, French Freemasonry continued to grow in the next century, at first under the leadership of Alexandre Francois Auguste de Grasse, Comte de Grassy-Tilly. A career Army officer, he lived with his family in Charleston, South Carolina from 1793 to the early 1800s, after leaving Saint-Domingue, now Haiti, during the years of the Haitian Revolution.
Freemasonry in the Middle East
After the failure of the Revolutions of 1830#In Italy, 1830 Italian revolution, a number of Italians, Italian Freemasons were forced to flee. They secretly set up an approved chapter of Scottish Rite in Alexandria, a town already inhabited by a large Italian community. Meanwhile, the French people, French freemasons publicly organised a local chapter in Alexandria in 1845. During the 19th and 20th century Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire, Masonic lodges operated widely across all parts of the empire and numerous Tariqa, Sufi orders shared a close relationship with them. Many Young Turks affiliated with the Bektashi Order, Bektashi order were members and patrons of freemasonry. They were also closely allied against European imperialism. Many Ottoman intellectuals believed that Sufism and Freemasonry shared close similarities in doctrines, spiritual outlook and mysticism.Schism
The ritual form on which the Grand Orient of France was based was abolished in England in the events leading to the formation of the United Grand Lodge of England in 1813. However the two jurisdictions continued in amity, or mutual recognition, until events of the 1860s and 1870s drove a seemingly permanent wedge between them. In 1868 the ''Supreme Council of the Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite of the State of Louisiana'' appeared in the jurisdiction of the Grand Lodge of Louisiana, recognised by the Grand Orient de France, but regarded by the older body as an invasion of their jurisdiction. The new Scottish Rite body admitted black people. The resolution of the Grand Orient the following year that neither colour, race, nor religion could disqualify a man from Masonry prompted the Grand Lodge to withdraw recognition, and it persuaded other American Grand Lodges to do the same. A dispute during the Lausanne Congress of Supreme Councils of 1875 prompted the Grand Orient de France to commission a report by a Protestant pastor, which concluded that, as Freemasonry was not a religion, it should not require a religious belief. The new constitutions read, "Its principles are absolute liberty of conscience and human solidarity", the existence of God and the immortality of the soul being struck out. It is possible that the immediate objections of the United Grand Lodge of England were at least partly motivated by the political tension between France and Britain at the time. The result was the withdrawal of recognition of the Grand Orient of France by the United Grand Lodge of England, a situation that continues today. Not all French lodges agreed with the new wording. In 1894, lodges favouring the compulsory recognition of the Great Architect of the Universe formed the Grande Loge de France. In 1913, the United Grand Lodge of England recognised a new Grand Lodge of Regular Freemasons, a Grand Lodge that follows a similar rite to Anglo-American Freemasonry with a mandatory belief in a deity. There are now three strands of Freemasonry in France, which extend into the rest of Continental Europe:- * Liberal, also called adogmatic or progressive – Principles of liberty of conscience, and laicity, particularly the separation of the Church and State. * Traditional – Old French ritual with a requirement for a belief in a Supreme Being. (This strand is typified by the Grande Loge de France). * Regular – Standard Anglo-American ritual, mandatory belief in Supreme Being. The term Continental Freemasonry was used in Mackey's 1873 ''Encyclopedia of Freemasonry'' to "designate the Lodges on the Continent of Europe which retain many usages which have either been abandoned by, or never were observed in, the Lodges of England, Ireland, and Scotland, as well as the United States of America". Today, it is frequently used to refer to only the Liberal jurisdictions typified by the Grand Orient de France. The majority of Freemasonry considers the Liberal (Continental) strand to be Irregular, and thus withhold recognition. The Continental lodges, however, did not want to sever masonic ties. In 1961, an umbrella organisation, Centre de Liaison et d'Information des Puissances maçonniques Signataires de l'Appel de Strasbourg (CLIPSAS) was set up, which today provides a forum for most of these Grand Lodges and Grand Orients worldwide. Included in the list of over 70 Grand Lodges and Grand Orients are representatives of all three of the above categories, including mixed and women's organisations. The United Grand Lodge of England does not communicate with any of these jurisdictions, and expects its allies to follow suit. This creates the distinction between Anglo-American and Continental Freemasonry.Freemasonry and women
The status of women in the old guilds and corporations of medieval masons remains uncertain. The principle of "femme sole" allowed a widow to continue the trade of her husband, but its application had wide local variations, such as full membership of a trade body or limited trade by deputation or approved members of that body. In masonry, the small available evidence points to the less empowered end of the scale. At the dawn of the History of Freemasonry#Early Grand Lodge period, Grand Lodge era, during the 1720s, James Anderson (Freemason), James Anderson composed the Anderson's Constitutions, first printed constitutions for Freemasons, the basis for most subsequent constitutions, which specifically excluded women from Freemasonry. As Freemasonry spread, women began to be added to the Rite of Adoption, Lodges of Adoption by their husbands who were continental masons, which worked three degrees with the same names as the men's but different content. The French officially abandoned the experiment in the early 19th century.Barbara L. Thames, "A History of Women's Masonry"''Phoenix Masonry'', retrieved 5 March 2013 Later organisations with a similar aim emerged in the United States, but distinguished the names of the degrees from those of male masonry. Maria Deraismes was initiated into Freemasonry in 1882, then resigned to allow her lodge to rejoin their Grand Lodge. Having failed to achieve acceptance from any masonic governing body, she and Georges Martin (freemason), Georges Martin started a mixed masonic lodge that worked masonic ritual. Annie Besant spread the phenomenon to the English-speaking world. Disagreements over ritual led to the formation of exclusively female bodies of Freemasons in England, which spread to other countries. Meanwhile, the French had re-invented Adoption as an all-female lodge in 1901, only to cast it aside again in 1935. The lodges, however, continued to meet, which gave rise, in 1959, to a body of women practising continental Freemasonry. In general, Continental Freemasonry is sympathetic to Freemasonry amongst women, dating from the 1890s when French lodges assisted the emergent co-masonic movement by promoting enough of their members to the 33rd degree of the Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite to allow them, in 1899, to form their own grand council, recognised by the other Continental Grand Councils of that Rite."Histoire du Droit Humain"
''Droit Humain'', retrieved 12 August 2013 The United Grand Lodge of England issued a statement in 1999 recognising the two women's grand lodges there, The Order of Women Freemasons and The Honourable Fraternity of Ancient Freemasons, to be regular in all but the participants. While they were not, therefore, recognised as regular, they were part of Freemasonry "in general". The attitude of most regular Anglo-American grand lodges remains that women Freemasons are not legitimate Masons. In 2018, guidance was released by the United Grand Lodge of England stating that, in regard to transgender women, "A Freemason who after initiation ceases to be a man does not cease to be a Freemason". The guidance also states that transgender men are allowed to apply to become Freemasons.
Political activity
18th century Enlightenment
 During the Age of the Enlightenment in the 18th century, Freemasons comprised an international network of like-minded men, often meeting in secret in ritualistic programs at their lodges. They promoted the ideals of the Enlightenment, and helped diffuse these values across Britain and France and other places. British Freemasonry offered a systematic creed with its own myths, values and set of rituals. It fostered new codes of conduct – including a communal understanding of liberty and equality inherited from guild sociability – "liberty, fraternity, and equality" Scottish soldiers and Jacobite Scots brought to the Continent ideals of fraternity which reflected not the local system of Scottish customs but the institutions and ideals originating in the English Revolution against royal absolutism. Freemasonry was particularly prevalent in France – by 1789, there were between 50,000 and 100,000 French Masons, making Freemasonry the most popular of all Enlightenment associations.
Jacob argues that Masonic lodges probably had an effect on society as a whole, for they “reconstituted the polity and established a constitutional form of self-government, complete with constitutions and laws, elections and representatives”. In other words, the micro-society set up within the lodges constituted a normative model for society as a whole. This was especially true on the Continent: when the first lodges began to appear in the 1730s, their embodiment of British values was often seen as threatening by state authorities. For example, the Parisian lodge that met in the mid 1720s was composed of English Jacobitism, Jacobite exiles. Furthermore, freemasons all across Europe made reference to the Enlightenment in general in the 18th century. In French lodges, for example, the line “As the means to be enlightened I search for the enlightened” was a part of their initiation rites. British lodges assigned themselves the duty to “initiate the unenlightened”. Many lodges praised the Grand Architect, the masonic terminology for the divine being who created a scientifically ordered universe.
On the other hand, historian Robert Roswell Palmer noted that lodges operated separately and Masons politically did not act together as a group. American historians, while noting that Benjamin Franklin and George Washington were leading Masons, have downplayed the group's importance in the era of the American Revolution. Daniel Roche contests freemasonry’s claims for egalitarianism, writing that “the real equality of the lodges was elitist”, only attracting men of similar social backgrounds.
In long-term historical perspective, Norman Davies has argued that Freemasonry was a powerful force in Europe, from about 1700 to the twentieth century. It expanded rapidly during the Age of Enlightenment, reaching practically every country in Europe, as well as the European colonies in the New World and Asia. Davies states, "In the nineteenth century and beyond it would be strongly associated with the cause of Liberalism." In Catholic lands it was anti-clerical and came under heavy attack from the Catholic Church. In the 20th century it was suppressed by Fascist and Communist regimes. It was especially attractive to royalty, aristocrats and politicians and businessmen, as well as intellectuals, artists and political activists. Davies notes that prominent members included Montesquieu, Voltaire, Robert Walpole, Sir Robert Walpole, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Benjamin Franklin, and George Washington. Steven Bullock notes that in the late 18th century, English lodges were headed by the Prince of Wales, Prussian lodges by king Frederick the Great, and French lodges by royal princes. Emperor Napoleon selected as Grand Master of France his own brother.
During the Age of the Enlightenment in the 18th century, Freemasons comprised an international network of like-minded men, often meeting in secret in ritualistic programs at their lodges. They promoted the ideals of the Enlightenment, and helped diffuse these values across Britain and France and other places. British Freemasonry offered a systematic creed with its own myths, values and set of rituals. It fostered new codes of conduct – including a communal understanding of liberty and equality inherited from guild sociability – "liberty, fraternity, and equality" Scottish soldiers and Jacobite Scots brought to the Continent ideals of fraternity which reflected not the local system of Scottish customs but the institutions and ideals originating in the English Revolution against royal absolutism. Freemasonry was particularly prevalent in France – by 1789, there were between 50,000 and 100,000 French Masons, making Freemasonry the most popular of all Enlightenment associations.
Jacob argues that Masonic lodges probably had an effect on society as a whole, for they “reconstituted the polity and established a constitutional form of self-government, complete with constitutions and laws, elections and representatives”. In other words, the micro-society set up within the lodges constituted a normative model for society as a whole. This was especially true on the Continent: when the first lodges began to appear in the 1730s, their embodiment of British values was often seen as threatening by state authorities. For example, the Parisian lodge that met in the mid 1720s was composed of English Jacobitism, Jacobite exiles. Furthermore, freemasons all across Europe made reference to the Enlightenment in general in the 18th century. In French lodges, for example, the line “As the means to be enlightened I search for the enlightened” was a part of their initiation rites. British lodges assigned themselves the duty to “initiate the unenlightened”. Many lodges praised the Grand Architect, the masonic terminology for the divine being who created a scientifically ordered universe.
On the other hand, historian Robert Roswell Palmer noted that lodges operated separately and Masons politically did not act together as a group. American historians, while noting that Benjamin Franklin and George Washington were leading Masons, have downplayed the group's importance in the era of the American Revolution. Daniel Roche contests freemasonry’s claims for egalitarianism, writing that “the real equality of the lodges was elitist”, only attracting men of similar social backgrounds.
In long-term historical perspective, Norman Davies has argued that Freemasonry was a powerful force in Europe, from about 1700 to the twentieth century. It expanded rapidly during the Age of Enlightenment, reaching practically every country in Europe, as well as the European colonies in the New World and Asia. Davies states, "In the nineteenth century and beyond it would be strongly associated with the cause of Liberalism." In Catholic lands it was anti-clerical and came under heavy attack from the Catholic Church. In the 20th century it was suppressed by Fascist and Communist regimes. It was especially attractive to royalty, aristocrats and politicians and businessmen, as well as intellectuals, artists and political activists. Davies notes that prominent members included Montesquieu, Voltaire, Robert Walpole, Sir Robert Walpole, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Benjamin Franklin, and George Washington. Steven Bullock notes that in the late 18th century, English lodges were headed by the Prince of Wales, Prussian lodges by king Frederick the Great, and French lodges by royal princes. Emperor Napoleon selected as Grand Master of France his own brother.
France
In the 18th century liberal French politicians met together in Masonic lodges to develop some of the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment ideas that dominated the French Revolution of 1789. Avner Halpern has traced French Freemasonry's major role in building France's first modern political party in 1901, Radical Party (France), the Radical Party. It used two Masonic devices: the "civil leadership model," which Freemasonry developed in the late 19th century France, and the local Masonic congresses of the Grand Orient of France federations.Russia
Freemasons had been active in Russia in the 18th century, working to introduce Russian Enlightenment, Enlightenment ideas. However they were increasingly suppressed by the government. According to Ludwick Hass, Freemasonry was officially illegal in Tsarist Russia. However it was introduced by exiles who returned after the 1905 revolution. They had been active Masons in Paris where lodges were politically active in the new Radical Party. In Russia the Freemasons supported constitutional liberalism. They maintained ties with France but simplified many of the ceremonial rituals. Their secret meetings became a locus of progressive ideas, attracting politicians and activists. The lodges at first supported World War I, promoting close ties with France. Alexander Kerensky was an important Masonic activist, who came to political power with the overthrow of the czars in 1917. The organization collapsed as the Bolsheviks took power and was again outlawed.Italy
According to Adrian Lyttelton, in the early 20th century Freemasonry was an influential semi-secret force in Italian politics with a strong presence among professionals and the middle class across Italy, as well as among the leadership of the parliament, public administration, and the army. The two main organisations were the Grand Orient and the Grand Lodge of Italy. They had 25,000 members in some 500 lodges. Freemasons typically espoused anticlericalism and promoted unification. The Catholic Church was a vigorous opponent of unification and of the Freemasons. The various national governments went back and forth between the anticlerical side and the Church side. Politically, they promoted Italian nationalism focused on unification, and undermining the power of the Catholic Church. Freemasons took on the challenge of mobilizing the press, public opinion and the leading political parties in support of Italian entry into World War I, Italy's joining the Allies of the First World War in 1914–1915. In 1919 they favoured a League of Nations to promote a new post-war universal order based upon the peaceful coexistence of independent and democratic nations. In the early 1920s many of Mussolini's collaborators, especially the leaders in organizing the March on Rome, were now Masons. The lodges hailed Fascism as the savior of Italy from Bolshevism. However Mussolini decided he needed to come to terms with the Catholic Church in the mid 1920s, and he outlawed Freemasonry.Latin America
The Spanish government outlawed Freemasonry in its overseas empire in the mid-18th century, and energetically enforced the ban., Nevertheless many Freemasons were active in planning and plotting for independence. Leaders with Freemason membership included Grand Master Francisco de Miranda, José de San Martin, Simón Bolivar, Bernardo O'Higgins, and many others. The movement was important after independence was achieved in the 1820s. In Brazil, many prominent men were Freemasons, and they played a leading role in the abolition of slavery.Mexico
Freemasons were leaders in liberalism and anti-clericalism in 19th and 20th century Mexico. Members included numerous top leaders. The Freemasons were divided regarding relations with the United States, with a pro-U.S. faction supported by the American ambassador Joel Poinsett known as the "Yorkinos." According to historian Karen Racine, Freemasons in List of heads of state of Mexico, the presidency of Mexico included: Guadalupe Victoria, Valentín Gómez Farías, Antonio López de Santa Anna, Benito Juárez, Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada, Porfirio Díaz, Francisco I. Madero, Venustiano Carranza, Plutarco Elías Calles, Lázaro Cárdenas, Emilio Portes Gil, Pascual Ortiz Rubio, Abelardo L. Rodríguez, and Miguel Alemán Valdés.Anti-Masonry
''Anti-Masonry'' (alternatively called ''Anti-Freemasonry'') has been defined as "opposition to Freemasonry", but there is no homogeneous anti-Masonic movement. Anti-Masonry consists of widely differing criticisms from diverse (and often incompatible) groups who are hostile to Freemasonry in some form. Critics have included religious groups, political groups, and conspiracy theorists, in particular, those espousing Masonic conspiracy theories or the Judeo-Masonic conspiracy theory. Certain prominent Anti-Masons, such as Nesta Helen Webster (1876–1960), have exclusively criticized "Continental Masonry" while considering "Regular Masonry" an honorable association. There have been many disclosures and exposés dating as far back as the 18th century. These often lack context, may be outdated for various reasons, or could be outright hoaxes on the part of the author, as in the case of the Taxil hoax. These hoaxes and exposés have often become the basis for criticism of Masonry, often religious or political in nature or are based on suspicion of corrupt conspiracy of some form. The political opposition that arose after the American "William Morgan (anti-Mason)#Disappearance, Morgan Affair" in 1826 gave rise to the term ''Anti-Masonry'', which is still in use in America today, both by Masons in referring to their critics and as a self-descriptor by the critics themselves.Religious opposition
Freemasonry has attracted criticism from theocracy, theocratic states and organised religions for supposed competition with religion, or supposed heterodoxy within the fraternity itself and has long been the target of Masonic conspiracy theories, conspiracy theories, which assert Freemasonry to be an occult and evil power.Christianity and Freemasonry
Although members of various faiths cite objections, certain Christian religious denomination, denominations have had high-profile negative attitudes to Masonry, banning or discouraging their members from being Freemasons. The denomination with the longest history of objection to Freemasonry is the Catholic Church. The objections raised by the Catholic Church are based on the allegation that Masonry teaches a naturalistic deistic religion which is in conflict with Church doctrine. A number of Papal pronouncements have been issued against Freemasonry. The first was Pope Clement XII's ''In eminenti apostolatus,'' 28 April 1738; the most recent was Pope Leo XIII's ''Ab apostolici,'' 15 October 1890. The ''1917 Code of Canon Law'' explicitly declared that joining Freemasonry entailed automatic excommunication, and banned books favouring Freemasonry.Canon 2335, 1917 Code of Canon Law from In 1983, the Church issued a new code of Canon law (Catholic Church), canon law. Unlike its predecessor, the ''1983 Code of Canon Law'' did not explicitly name Masonic orders among the secret societies it condemns. It states: "A person who joins an association which plots against the Church is to be punished with a just penalty; one who promotes or takes office in such an association is to be punished with an Interdict (Roman Catholic Church), interdict." This named omission of Masonic orders caused both Catholics and Freemasons to believe that the ban on Catholics becoming Freemasons may have been lifted, especially after the perceived liberalisation of Second Vatican Council, Vatican II. However, the matter was clarified when Cardinal Joseph Ratzinger (later Pope Benedict XVI), Joseph Ratzinger as Prefect of the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith, as the Prefect of the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith, issued a Declaration on Masonic Associations, which states: "... the Church's negative judgment in regard to Masonic association remains unchanged since their principles have always been considered irreconcilable with the doctrine of the Church and therefore membership in them remains forbidden. The faithful who enrol in Masonic associations are in a state of grave sin and may not receive Holy Communion." For its part, Freemasonry has never objected to Catholics joining their fraternity. Those Grand Lodges in amity with the United Grand Lodge of England deny the Church's claims, stating that "Freemasonry does not seek to replace a Mason's religion or provide a substitute for it." In contrast to Catholic allegations of rationalism and naturalism, Protestant objections are more likely to be based on allegations of mysticism, occultism, and even Satanism. Masonic scholar Albert Pike is often quoted (in some cases misquoted) by Protestant anti-Masons as an authority for the position of Masonry on these issues. However, Pike, although undoubtedly learned, was not a spokesman for Freemasonry and was also controversial among Freemasons in general. His writings represented his personal opinion only, and furthermore an opinion grounded in the attitudes and understandings of late 19th century Southern Freemasonry of the US. Notably, his book carries in the preface a form of disclaimer from his own Grand Lodge. No one voice has ever spoken for the whole of Freemasonry. Free Methodist Church founder B.T. Roberts was a vocal opponent of Freemasonry in the mid 19th century. Roberts opposed the society on moral grounds and stated, "The god of the lodge is not the God of the Bible." Roberts believed Freemasonry was a "Greco-Roman mysteries, mystery" or "alternate" religion and encouraged his church not to support ministers who were Freemasons. Freedom from secret societies is one of the "frees" upon which the Free Methodist Church was founded. Since the founding of Freemasonry, many Bishops of the Church of England have been Freemasons, such as Archbishop Geoffrey Fisher. In the past, few members of the Church of England would have seen any incongruity in concurrently adhering to Anglican Christianity and practising Freemasonry. In recent decades, however, reservations about Freemasonry have increased within Anglicanism, perhaps due to the increasing prominence of the evangelical wing of the church. The former archbishop of Canterbury, Rowan Williams, Dr Rowan Williams, appeared to harbour some reservations about Masonic ritual, whilst being anxious to avoid causing offence to Freemasons inside and outside the Church of England. In 2003 he felt it necessary to apologise to British Freemasons after he said that their beliefs were incompatible with Christianity and that he had barred the appointment of Freemasons to senior posts in his diocese when he was Bishop of Monmouth. In 1933, the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Church of Greece officially declared that being a Freemason constitutes an act of Apostasy in Christianity, apostasy and thus, until he repents, the person involved with Freemasonry cannot partake of the Eucharist. This has been generally affirmed throughout the whole Eastern Orthodox Church. The Orthodox critique of Freemasonry agrees with both the Catholic and Protestant versions: "Freemasonry cannot be at all compatible with Christianity as far as it is a secret organisation, acting and teaching in mystery and secret and deifying rationalism." Regular Freemasonry has traditionally not responded to these claims, beyond the often repeated statement that Freemasonry explicitly adheres to the principle that "Freemasonry is not a religion, nor a substitute for religion. There is no separate 'Masonic deity,' and there is no separate proper name for a deity in Freemasonry." Christian men, who were discouraged from joining the Freemasons by their Churches or who wanted a more religiocentric society, joined similar fraternal organisations, such as the Knights of Columbus and Knights of Peter Claver for Catholics, and the Orange Order, Loyal Orange Institution for Protestants, although these fraternal organisations have been "organized in part on the style of and use many symbols of Freemasonry". There are some elements of Freemasonry within the temple (Latter Day Saints), temple Endowment (Mormonism), rituals of Freemasonry and Mormonism, Mormonism.Islam and Freemasonry
Many Islamic anti-Masonic arguments are closely tied to Anti-Zionism, though other criticisms are made such as linking Freemasonry to Al-Masih ad-Dajjal (the false Messiah in Islamic Scripture). Syrians, Syrian-Egyptians, Egyptian Islamic theologian Rashid Rida, Mūhammād Rashīd Ridâ ( 1865-1935) played the crucial role in leading the opposition to Freemasonry across the Muslim world, Islamic World during the early twentieth century. Influenced by Rida, Islamic anti-Masons argue that Freemasonry promotes the interests of the Jews around the world and that one of its aims is to destroy the Temple Mount, Al-Aqsa Mosque compound in order to rebuild the Temple of Solomon in Jerusalem. Through his popular Pan-Islamism, pan-Islamic journal ''Al-Manār (magazine), Al-Manar'', Rashid Rida spread anti-Masonic ideas which would directly influence the Muslim Brotherhood and subsequent Islamist movements such as Hamas. In article 28 of its Covenant, Hamas states that Freemasonry, Rotary International, Rotary, and other similar groups "work in the interest of Zionism and according to its instructions ..." Many countries with a majority Muslim population do not allow Masonic establishments within their borders. However, countries such as Turkey and Morocco have established Grand Lodges, while in countries such as Malaysia and Lebanon there are District Grand Lodges operating under a warrant from an established Grand Lodge. In Pakistan in 1972, Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto, then Prime Minister of Pakistan, placed a ban on Freemasonry. Lodge buildings were confiscated by the government. Masonic lodges existed in Iraq as early as 1917, when the first lodge under the United Grand Lodge of England (UGLE) was opened. Nine lodges under UGLE existed by the 1950s, and a Scottish lodge was formed in 1923. However, the position changed following the revolution, and all lodges were forced to close in 1965. This position was later reinforced under Saddam Hussein; the death penalty was "prescribed" for those who "promote or acclaim Zionist principles, including freemasonry, or who associate [themselves] with Zionist organisations."Political opposition
In 1799, English Freemasonry almost came to a halt due to Parliamentary proclamation. In the wake of the French Revolution, the Unlawful Societies Act banned any meetings of groups that required their members to take an oath or obligation.Andrew Prescott, "The Unlawful Societies Act"First published in M. D. J. Scanlan, ed., ''The Social Impact of Freemasonry on the Modern Western World'', The Canonbury Papers I (London: Canonbury Masonic Research Centre, 2002), pp. 116–34, ''Pietre-Stones'' website, retrieved 9 January 2014 The Grand Masters of both the Moderns and the Antients Grand Lodges called on Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger, William Pitt (who was not a Freemason) and explained to him that Freemasonry was a supporter of the law and lawfully constituted authority and was much involved in charitable work. As a result, Freemasonry was specifically exempted from the terms of the Act, provided that each private lodge's Secretary placed with the local "Clerk of the Peace" a list of the members of his lodge once a year. This continued until 1967, when the obligation of the provision was rescinded by Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament. Freemasonry in the United States faced political pressure following the 1826 kidnapping of William Morgan (anti-Mason), William Morgan by Freemasons and his subsequent disappearance. Reports of the "Morgan Affair", together with opposition to Jacksonian democracy (Andrew Jackson was a prominent Mason), helped fuel an Anti-Masonic movement. The short-lived Anti-Masonic Party was formed, which fielded candidates for the presidential elections of 1828 and 1832.
 In Italy, Freemasonry has become linked to a scandal concerning the Propaganda Due lodge (a.k.a. P2). This lodge was chartered by the Grande Oriente d'Italia in 1877, as a lodge for visiting Masons unable to attend their own lodges. Under Licio Gelli's leadership, in the late 1970s, P2 became involved in the financial scandals that nearly bankrupted the Vatican Bank. However, by this time the lodge was operating independently and irregularly, as the Grand Orient had revoked its charter and expelled Gelli in 1976.
Conspiracy theorists have long associated Freemasonry with the New World Order (conspiracy theory), New World Order and the Illuminati, and state that Freemasonry as an organisation is either bent on world domination or already secretly in control of world politics. Historically Freemasonry has attracted criticism, and suppression from both the politically far right (e.g., Nazi Germany) and the far left (e.g. the former Communist states in Eastern Europe).
Freemasonry is viewed with distrust even in some modern democracies.Hodapp, Christopher. ''Freemasons for Dummies''. Indianapolis: Wiley, 2005. p. 86. In the UK, Masons working in the justice system, such as judges and police officers, were from 1999 to 2009 required to disclose their membership.Bright, Martin (12 June 2005).
In Italy, Freemasonry has become linked to a scandal concerning the Propaganda Due lodge (a.k.a. P2). This lodge was chartered by the Grande Oriente d'Italia in 1877, as a lodge for visiting Masons unable to attend their own lodges. Under Licio Gelli's leadership, in the late 1970s, P2 became involved in the financial scandals that nearly bankrupted the Vatican Bank. However, by this time the lodge was operating independently and irregularly, as the Grand Orient had revoked its charter and expelled Gelli in 1976.
Conspiracy theorists have long associated Freemasonry with the New World Order (conspiracy theory), New World Order and the Illuminati, and state that Freemasonry as an organisation is either bent on world domination or already secretly in control of world politics. Historically Freemasonry has attracted criticism, and suppression from both the politically far right (e.g., Nazi Germany) and the far left (e.g. the former Communist states in Eastern Europe).
Freemasonry is viewed with distrust even in some modern democracies.Hodapp, Christopher. ''Freemasons for Dummies''. Indianapolis: Wiley, 2005. p. 86. In the UK, Masons working in the justice system, such as judges and police officers, were from 1999 to 2009 required to disclose their membership.Bright, Martin (12 June 2005).MPs told to declare links to Masons
, ''The Guardian'' While a parliamentary inquiry found that there had been no evidence of wrongdoing, the government believed that Masons' potential loyalties to support fellow Masons should be transparent to the public. The policy of requiring a declaration of masonic membership by applicants for judicial office (judges and magistrates) was ended in 2009 by Secretary of State for Justice, Justice Secretary Jack Straw (who had initiated the requirement in the 1990s). Straw stated that the rule was considered disproportionate, since no impropriety or malpractice had been shown as a result of judges being Freemasons. Freemasonry is both successful and controversial in France. As of the early 21st century, membership is rising, but reporting of it in popular media is often negative. In some countries anti-Masonry is often related to antisemitism and anti-Zionism. For example, in 1980, the Iraqi Law of Iraq, legal and Iraqi Penal Code, penal code was changed by Saddam Hussein's ruling Ba'ath Party (Iraq), Ba'ath Party, making it a felony to "promote or acclaim Zionist principles, including Freemasonry, or who associate [themselves] with Zionist organisations". Professor Andrew Prescott of the University of Sheffield writes: "Since at least the time of the The Protocols of the Elders of Zion, Protocols of the Elders of Zion, antisemitism has gone hand in hand with anti-masonry, so it is not surprising that allegations that 11 September 2001 attacks, 11 September was a Zionist plot have been accompanied by suggestions that the attacks were inspired by a masonic world order".
The Holocaust
See also
* *References
Further reading
* Belton, John L., et al. ''Freemasonry in context: history, ritual, controversy'' (Lexington Books, 2004online
* Dickie, John. ''The Craft: How the Freemasons Made the Modern World'' (PublicAffairs, 2020)
excerpt
* Fozdar, Vahid. " 'That Grand Primeval and Fundamental Religion': The Transformation of Freemasonry into a British Imperial Cult." ''Journal of World History'' 22#3 (2011), pp. 493–525
online
* Hamill, John. ''The Craft: A History of English Freemasonry'' (1986) * Harland-Jacobs, Jessica L. ''Builders of Empire: Freemasons and British Imperialism, 1717-1927'' (2007) * Hoffmann, Stefan-Ludwig. ''Freemasonry and German Civil Society, 1840-1918'' (U of Michigan Press, 2007)
excerpt
see als
online review
* Jacob, Margaret C. ''Living the Enlightenment: Freemasonry and Politics in Eighteenth-Century Europe'' (1991
excerpt
* Jacob, Margaret C. ''The Origins of Freemasonry: Facts and Fictions'' (U of Pennsylvania Press, 2007). * Jacob, Margaret, and Matthew Crow. "Freemasonry and the Enlightenment." in ''Handbook of Freemasonry'' (Brill, 2014) pp. 100–116
online
* Loiselle, Kenneth. "Freemasonry and the Catholic Enlightenment in Eighteenth-Century France." ''Journal of Modern History'' 94.3 (2022): 499-536
online
* Önnerfors, Andreas. ''Freemasonry: a very short introduction'' (Oxford University Press, 2017
excerpt
* Racine, Karen. "Freemasonry" in Michael S. Werner, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Mexico: History, Society, and Culture'' (Fitzroy Dearborn, 1997) 1:538–540. * Snoek Jan A.M. and Henrik Bogdan. "The History of Freemasonry: An Overview" in Bogdan and Snoek, eds. ''Handbook of Freemasonry'' (Brill, 2014) ch. 2 pp 13–32
online
* Stevenson, David. "Four Hundred Years of Freemasonry in Scotland.” ''Scottish Historical Review,'' 90#230 (2011), pp. 280–95
online
* Stevenson, David. ''The First Freemasons. Scotland's Early Lodges and Their Members'' (1988) * Weisberger, R. William et al. '' Freemasonry on Both Sides of the Atlantic: Essays concerning the Craft in the British Isles, Europe, the United States, and Mexico'' (2002), 969pp * Weisberger, R. William. ''Speculative Freemasonry and the Enlightenment: A Study of the Craft in London, Paris, Prague and Vienna'' (Columbia University Press, 1993) 243 pp.
United States
* Bullock, Steven C. ''Revolutionary brotherhood: Freemasonry and the transformation of the American social order, 1730-1840'' (UNC Press Books, 2011). * Formisano, Ronald P., and Kathleen Smith Kutolowski. "Antimasonry and Masonry: The Genesis of Protest, 1826-1827." ''American Quarterly'' 29.2 (1977): 139-165online
* Hackett, David G. ''That Religion in Which All Men Agree : Freemasonry in American Culture'' (U of California Press, 2015
excerpt
* Hinks, Peter P. et al. ''All Men Free and Brethren: Essays on the History of African American Freemasonry '' (Cornell UP, 2013). * Kantrowitz, Stephen. " 'Intended for the Better Government of Man': The Political History of African American Freemasonry in the Era of Emancipation." ''Journal of American History'' 96#4, (2010), pp. 1001–26
online
* Weisberger, R. William et al. '' Freemasonry on Both Sides of the Atlantic: Essays concerning the Craft in the British Isles, Europe, the United States, and Mexico'' (2002), 969pp * York, Neil L. “Freemasons and the American Revolution.” ''Historian'' 55#2 (1993), pp. 315–30
online
Historiography and memory
* Jacob, Margaret. "The Radical Enlightenment and Freemasonry: where we are now." ''REHMLAC: Revista de Estudios Históricos de la Masonería Latinoamericana y Caribeña'' 1 (2013): 11–2online
External links
*Web of Hiram
at the University of Bradford. A database of donated Masonic material.
of the ''Pietre-Stones Review of Freemasonry''
''The Constitutions of the Free-Masons''
(1734), James Anderson, Benjamin Franklin, Paul Royster. Hosted by the Libraries at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln
by William Morgan, from Project Gutenberg * ,
The United Grand Lodge of England's Library and Museum of Freemasonry
, London
Articles on Judaism and Freemasonry
Anti-Masonry: Points of View
– Edward L. King's Masonic website
The International Order of Co-Freemasonry ''Le Droit Humain''
* {{Authority control Freemasonry,