Magadha kingdom coin Circa 350 BC AR Karshapana.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn,




 The territory of the Magadha kingdom proper before its expansion was bounded to the north, west, and east respectively by the Gaṅgā,
The territory of the Magadha kingdom proper before its expansion was bounded to the north, west, and east respectively by the Gaṅgā,
Rigvedic history: poets, chieftains, and polities
" in ''The Indo-Aryans of Ancient South Asia: Language, Material Culture and Ethnicity.'' ed. G. Erdosy (Walter de Gruyer, 1995), p. 333 The earliest reference to the Magadha people occurs in the ''

 According to Indologist
According to Indologist
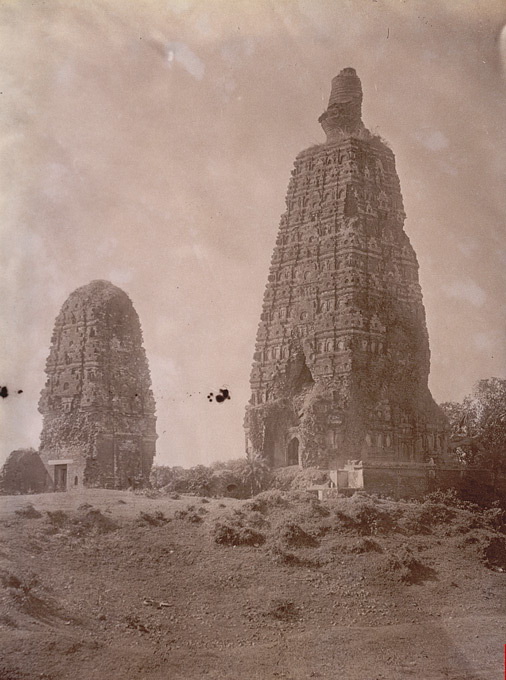 Among the Buddhist sites currently found in the Magadha region include two UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Mahabodhi temple at
Among the Buddhist sites currently found in the Magadha region include two UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Mahabodhi temple at
Mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and '' janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urban ...
, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled by Brihadratha dynasty, Pradyota dynasty (682–544 BCE), Haryanka dynasty (544–413 BCE), the Shaishunaga dynasty (413–345 BCE) and the Mauryan dynasty by the end of it. Villages had their own assemblies under their local chiefs called ''Gramakas''. Their administrations were divided into executive, judicial, and military functions.
Magadha played an important role in the development of Jainism and Buddhism. It was succeeded by four of northern India's greatest empires, the Nanda Empire
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
(c. 345–322 BCE), Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
(c. 322–185 BCE), Shunga Empire
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra Shunga, Pushyamitra, after taking ...
(c. 185–78 BCE) and Gupta Empire (c. 319–550 CE). The Pala Empire also ruled over Magadha and maintained a royal camp in Pataliputra.
The Pithipatis of Bodh Gaya
The Pīṭhīpatis of Bodh Gaya (also known as the Pithis) were the rulers of the area around Bodh Gaya from roughly the 11th to 13th centuries in the Magadha region of what is now Bihar in India. Pithi refers to the diamond throne where the Bud ...
referred to themselves as ''Magadhādipati'' and ruled in parts of Magadha until the 13th century.
Geography





 The territory of the Magadha kingdom proper before its expansion was bounded to the north, west, and east respectively by the Gaṅgā,
The territory of the Magadha kingdom proper before its expansion was bounded to the north, west, and east respectively by the Gaṅgā, Son
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some current c ...
, and Campā rivers, and the eastern spurs of the Vindhya mountains
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.
Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the ...
formed its southern border. The territory of the initial Magadha kingdom thus corresponded to the modern-day Patna and Gaya
Gaya may refer to:
Geography Czech Republic
*Gaya (German and Latin), Kyjov (Hodonín District), a town
Guinea
* Gaya or Gayah, a town
India
*Gaya, India, a city in Bihar
**Gaya Airport
*Bodh Gaya, a town in Bihar near Gaya
*Gaya district, Bi ...
districts of the Indian state of Bihar.
The region of Greater Magadha also included neighbouring regions in the eastern Gangetic plains and had a distinct culture and belief. Much of the Second Urbanisation took place here from (c. 500 BCE) onwards and it was here that Jainism and Buddhism arose.
History
Some scholars have identified the Kīkaṭa tribe—mentioned in the Rigveda (3.53.14) with their ruler Pramaganda—as the forefathers ofMagadhas
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
because Kikata is used as synonym for Magadha in the later texts; Like the Magadhas in the Atharvaveda, the Rigveda speaks of the Kikatas as a hostile tribe, living on the borders of Brahmanical India, who did not perform Vedic rituals.M. Witzel.Rigvedic history: poets, chieftains, and polities
" in ''The Indo-Aryans of Ancient South Asia: Language, Material Culture and Ethnicity.'' ed. G. Erdosy (Walter de Gruyer, 1995), p. 333 The earliest reference to the Magadha people occurs in the ''
Atharvaveda
The Atharva Veda (, ' from ' and ''veda'', meaning "knowledge") is the "knowledge storehouse of ''atharvāṇas'', the procedures for everyday life".Laurie Patton (2004), Veda and Upanishad, in ''The Hindu World'' (Editors: Sushil Mittal and G ...
'', where they are found listed along with the Angas, Gandharis and Mujavats. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganges; its first capital was Rajagriha (modern day Rajgir), then Pataliputra (modern Patna). Rajagriha was initially known as 'Girivrijja' and later came to be known as so during the reign of Ajatashatru. Magadha expanded to include most of Bihar and Bengal with the conquest of Vajjika League and Anga, respectively. The kingdom of Magadha eventually came to encompass Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, West Bengal, eastern Uttar Pradesh, and the areas that are today the nations of Bangladesh and Nepal.
The ancient kingdom of Magadha is heavily mentioned in Jain and Buddhist texts
Buddhist texts are those religious texts which belong to the Buddhist tradition. The earliest Buddhist texts were not committed to writing until some centuries after the death of Gautama Buddha. The oldest surviving Buddhist manuscripts a ...
. It is also mentioned in the '' Ramayana'', the '' Mahabharata'' and the Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
.
There is little certain information available on the early rulers of Magadha. The most important sources are the Buddhist '' Pāli Canon'', the ''Jain Agamas
Jain literature (Sanskrit: जैन साहित्य) refers to the literature of the Jain religion. It is a vast and ancient literary tradition, which was initially transmitted orally. The oldest surviving material is contained in the ca ...
'' and the Hindu ''Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
''. Based on these sources, it appears that Magadha was ruled by the Haryanka dynasty for some 200 years, c. 543 to 413 BCE.
Gautama Buddha, the founder of Buddhism, lived much of his life in the kingdom of Magadha. He attained enlightenment in Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gaya is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple Complex in Gaya district in the Indian state of Bihar. It is famous as it is the place where Gautama Buddha is said to have attained Enlightenment ( pi, ...
, gave his first sermon in Sarnath and the first Buddhist council
__NOTOC__
The First Buddhist council was a gathering of senior monks of the Buddhist order convened just after Gautama Buddha's death, which according to Buddhist tradition was c. 483 BCE, though most modern scholars place it around 400 BCE. T ...
was held in Rajgriha
Rajgir, meaning "The City of Kings," is a historic town in the district of Nalanda in Bihar, India. As the ancient seat and capital of the Haryanka dynasty, the Pradyota dynasty, the Brihadratha dynasty and the Mauryan Empire, as well as the ...
.
The Hindu '' Mahabharata'' calls Brihadratha the first ruler of Magadha. Ripunjaya, last king of Brihadratha dynasty, was killed by his minister Pulika, who established his son Pradyota as the new king. Pradyota dynasty was succeeded by Haryanka dynasty founded by Bimbisara. Bimbisara led an active and expansive policy, conquering the Kingdom of Anga in what is now West Bengal. King Bimbisara was killed by his son, Ajatashatru. Pasenadi, king of neighbouring Kosala
The Kingdom of Kosala (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indian kingdom with a rich culture, corresponding to the area within the region of Awadh in present-day Uttar Pradesh to Western Odisha. It emerged as a janapada, small state during the late Ve ...
and brother-in-law of Bimbisara, promptly reconquered the Kashi province.
Accounts differ slightly as to the cause of King Ajatashatru's war with the Licchavi, a powerful tribe north of the river Ganges. It appears that Ajatashatru sent a minister to the area who worked for three years to undermine the unity of the Licchavis. To launch his attack across the Ganges River, Ajatashatru built a fort at the town of Pataliputra. Torn by disagreements, the Licchavis fought with Ajatashatru. It took fifteen years for Ajatashatru to defeat them. Jain texts tell how Ajatashatru used two new weapons: a catapult, and a covered chariot with swinging mace that has been compared to a modern tank. Pataliputra began to grow as a centre of commerce and became the capital of Magadha after Ajatashatru's death.
The Haryanka dynasty was overthrown by the Shishunaga dynasty. The last Shishunaga ruler, Mahanandin, was assassinated by Mahapadma Nanda in 345 BCE, the first of the so-called "Nine Nandas", i. e. Mahapadma and his eight sons, last being Dhana Nanda.
In 326 BCE, the army of Alexander approached the western boundaries of Magadha. The army, exhausted and frightened at the prospect of facing another giant Indian army at the Ganges, mutinied at the Hyphasis (the modern Beas River) and refused to march further east. Alexander, after the meeting with his officer Coenus, was persuaded that it was better to return and turned south, conquering his way down the Indus to the Ocean.
Around 321 BCE, the Nanda Dynasty ended with the defeat of Dhana Nanda at the hands of Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empi ...
who became the first king of the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
with the help of his mentor Chanakya. The Empire later extended over most of India under King Ashoka The Great, who was at first known as 'Ashoka the Cruel' but later became a disciple of Buddhism and became known as 'Dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for '' ...
Ashoka'. Later, the Mauryan Empire ended, as did the Shunga and Khārabēḷa empires, to be replaced by the Gupta Empire. The capital of the Gupta Empire remained Pataliputra in Magadha.
During the Pala-period in Magadha from the 11th to 13th century CE, a local Buddhist dynasty known as the Pithipatis of Bodh Gaya
The Pīṭhīpatis of Bodh Gaya (also known as the Pithis) were the rulers of the area around Bodh Gaya from roughly the 11th to 13th centuries in the Magadha region of what is now Bihar in India. Pithi refers to the diamond throne where the Bud ...
ruled as tributaries to Pala Empire.
Buddhism and Jainism
Several Śramaṇic movements have existed before the 6th century BCE, and these influenced both theāstika and nāstika
''Āstika'' and ''nāstika'' are concepts that have been used to classify Indian philosophies by modern scholars, as well as some Hindu, Buddhist and Jain texts. The various definitions for ''āstika'' and ''nāstika'' philosophies have bee ...
traditions of Indian philosophy. The Śramaṇa movement gave rise to diverse range of heterodox beliefs, ranging from accepting or denying the concept of soul, atomism, antinomian ethics, materialism, atheism, agnosticism, fatalism to free will, idealization of extreme asceticism to that of family life, strict ahimsa
Ahimsa (, IAST: ''ahiṃsā'', ) is the ancient Indian principle of nonviolence which applies to all living beings. It is a key virtue in most Indian religions: Jainism, Buddhism, and Hinduism.Bajpai, Shiva (2011). The History of India � ...
(non-violence) and vegetarianism to the permissibility of violence and meat-eating. Magadha kingdom was the nerve centre of this revolution.
Jainism was revived and re-established after Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6t ...
, the last and the 24th '' Tirthankara'', who synthesised and revived the philosophies and promulgations of the ancient Śramaṇic traditions laid down by the first Jain tirthankara Rishabhanatha
Rishabhanatha, also ( sa, ऋषभदेव), Rishabhadeva, or Ikshvaku is the first (Supreme preacher) of Jainism and establisher of Ikshvaku dynasty. He was the first of twenty-four teachers in the present half-cycle of time in Jain c ...
millions of years ago. Buddha founded Buddhism which received royal patronage in the kingdom.

 According to Indologist
According to Indologist Johannes Bronkhorst
Johannes Bronkhorst (born 17 July 1946, Schiedam) is a Dutch Orientalist and Indologist, specializing in Buddhist studies and early Buddhism. He is emeritus professor at the University of Lausanne.
Life
After studying Mathematics, Physics, and ...
, the culture of Magadha was in fundamental ways different from the Vedic kingdoms of the Indo-Aryans. According to Bronkhorst, the śramana culture arose in " Greater Magadha," which was Indo-Aryan, but not Vedic. In this culture, Kshatriyas were placed higher than Brahmins, and it rejected Vedic authority and rituals. He argues for a cultural area termed " Greater Magadha", defined as roughly the geographical area in which the Buddha and Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6t ...
lived and taught. Suggestive of this distinction, in some Vedic and post-Vedic rituals, a "Magadha man" represents the canonical non-Vedic "Barbarian", the Magadhan standing in for the presence of any and all non-Vedic peoples or the ritually impure.
With regard to the Buddha, this area stretched by and large from Śrāvastī, the capital of Kosala
The Kingdom of Kosala (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indian kingdom with a rich culture, corresponding to the area within the region of Awadh in present-day Uttar Pradesh to Western Odisha. It emerged as a janapada, small state during the late Ve ...
, in the north-west to Rājagṛha, the capital of Magadha, in the south-east". According to Bronkhorst "there was indeed a culture of Greater Magadha which remained recognizably distinct from Vedic culture until the time of the grammarian Patañjali (ca. 150 BCE) and beyond". Vedic texts such as the Satapatha Brahmana demonize the inhabitants of this area as demonic and as speaking a barbarous speech. The Buddhologist Alexander Wynne writes that there is an "overwhelming amount of evidence" to suggest that this rival culture to the Vedic Aryans dominated the eastern Gangetic plain during the early Buddhist period. Orthodox Vedic Brahmins were, therefore, a minority in Magadha during this early period.
The Magadhan religions are termed the sramana traditions and include Jainism, Buddhism and Ājīvika. Buddhism and Jainism were the religions promoted by the early Magadhan kings, such as Srenika, Bimbisara and Ajatashatru, and the Nanda Dynasty
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
(345–321 BCE) that followed was mostly Jain. These Sramana religions did not worship the Vedic deities, practised some form of asceticism
Asceticism (; from the el, ἄσκησις, áskesis, exercise', 'training) is a lifestyle characterized by abstinence from sensual pleasures, often for the purpose of pursuing spiritual goals. Ascetics may withdraw from the world for their p ...
and meditation ( jhana) and tended to construct round burial mounds (called stupas in Buddhism). These religions also sought some type of liberation from the cyclic rounds of rebirth and karmic retribution through spiritual knowledge.
Religious sites in Magadha
 Among the Buddhist sites currently found in the Magadha region include two UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Mahabodhi temple at
Among the Buddhist sites currently found in the Magadha region include two UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Mahabodhi temple at Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gaya is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple Complex in Gaya district in the Indian state of Bihar. It is famous as it is the place where Gautama Buddha is said to have attained Enlightenment ( pi, ...
and the Nalanda
Nalanda (, ) was a renowned ''mahavihara'' (Buddhist monastic university) in ancient Magadha (modern-day Bihar), India. The Mahabodhi temple is one of the most important places of pilgrimage in the Buddhist world and is said to mark the site where the Buddha attained enlightenment.
 Important people from the ancient region of Magadha include:
*
Important people from the ancient region of Magadha include:
*
Language
Beginning in the Theravada commentaries, the Pali language has been identified withMagahi
The Magahi language (), also known as Magadhi (), is a language spoken in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal states of eastern India, and in the Terai of Nepal. Magadhi Prakrit was the ancestor of Magahi, from which the latter's name derives. ...
, the language of the kingdom of Magadha, and this was taken to also be the language that the Buddha used during his life. In the 19th century, the British Orientalist Robert Caesar Childers argued that the true or geographical name of the Pali language was Magadhi Prakrit
Magadhi Prakrit (''Māgadhī'') is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali and Sanskrit. It was a vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan language, replacing earlier Vedic Sanskrit.
Hist ...
, and that because ''pāḷi'' means "line, row, series", the early Buddhists extended the meaning of the term to mean "a series of books", so ''pāḷibhāsā'' means "language of the texts". Nonetheless, Pali does retain some eastern features that have been referred to as ''Māgadhisms''.
Magadhi Prakrit was one of the three dramatic prakrits to emerge following the decline of Sanskrit. It was spoken in Magadha and neighbouring regions and later evolved into modern eastern Indo-Aryan languages like Magahi
The Magahi language (), also known as Magadhi (), is a language spoken in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal states of eastern India, and in the Terai of Nepal. Magadhi Prakrit was the ancestor of Magahi, from which the latter's name derives. ...
, Maithili and .
Rulers
Two notable rulers of Magadha were Bimbisara (also known as ''Shrenika'') and his son Ajatashatru (also known as ''Kunika''), who are mentioned in Buddhist and Jain literature as contemporaries of the Buddha and Mahavira. Later, the throne of Magadha was usurped by Mahapadma Nanda, the founder of theNanda Dynasty
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
(c. 345–322 BCE), which conquered much of north India. The Nanda dynasty was overthrown by Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empi ...
, the founder of the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
(c. 322–185 BCE).
There is much uncertainty about the succession of kings and the precise chronology of Magadha prior to Mahapadma Nanda; the accounts of various ancient texts (all of which were written many centuries later than the era in question) contradict each other on many points.
Furthermore, there is a "Long Chronology" and a contrasting "Short Chronology" preferred by some scholars, an issue that is inextricably linked to the uncertain chronology of the Buddha and Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6t ...
.
According to historian John Keay, a proponent of the "Short Chronology," Bimbisara must have been reigning in the late 5th century BCE, and Ajatashatru in the early 4th century BCE. Keay states that there is great uncertainty about the royal succession after Ajatashatru's death, probably because there was a period of "court intrigues and murders," during which "evidently the throne changed hands frequently, perhaps with more than one incumbent claiming to occupy it at the same time" until Mahapadma Nanda was able to secure the throne.
List of rulers
The following "Long Chronology" is according to the Buddhist Mahavamsa: ; Haryanka dynasty (c. 544 – 413 BCE) ; Shishunaga dynasty (c. 413 – 345 BCE) ;Nanda Empire
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
(c. 345 – 322 BCE)
Other lists
; Puranic list TheHindu Literature
Hindu texts are manuscripts and voluminous historical literature which are related to any of the diverse traditions within Hinduism. A few of these texts are shared across these traditions and they are broadly considered Hindu scriptures. These ...
mostly Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
give a different sequence:
*Shishunaga dynasty (360 years)
** Shishunaga (reigned for 40 years)
** Kakavarna (36 years)
** Kshemadharman (20 years)
** Kshatraujas (29 years)
** Bimbisara (28 years)
** Ajatashatru (25 years)
** Darbhaka or Darshaka or Harshaka (25 years)
** Udayin (33 years)
** Nandivardhana (42 years)
** Mahanandin (43 years)
*Nanda dynasty (100 years)
;List by Jain literature
A shorter list appears in the Jain tradition, which simply lists Shrenika (Bimbisara), Kunika (Ajatashatru), Udayin, followed by the Nanda dynasty.
Historical figures from Magadha
 Important people from the ancient region of Magadha include:
*
Important people from the ancient region of Magadha include:
* Śāriputra
Śāriputra ( sa, शारिपुत्र; Tibetan: ཤཱ་རིའི་བུ་, Pali: ''Sāriputta'', lit. "the son of Śāri", born Upatiṣya, Pali: ''Upatissa'') was one of the top disciples of the Buddha. He is considered the fir ...
– born to a wealthy '' Brahmin'' in a village located near Rājagaha
Rajgir, meaning "The City of Kings," is a historic town in the district of Nalanda in Bihar, India. As the ancient seat and capital of the Haryanka dynasty, the Pradyota dynasty, the Brihadratha dynasty and the Mauryan Empire, as well as the d ...
in Magadha. He is considered the first of the Buddha's two chief male disciples, together with Maudgalyāyana.
* Maudgalyāyana – born in the village of Kolita in Magadha. He was one of the Buddha's two main disciples. In his youth, he was a spiritual wanderer before meeting the Buddha.
* Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6t ...
– the 24th Tirthankara of Jainism. Born into a royal kshatriya family in what is now Vaishali district of Bihar. He abandoned all worldly possessions at the age of 30 and became an ascetic. He is considered a slightly older contemporary of the Buddha.
* Maitripada
Maitrīpāda ( 1007–1085, also known as Maitreyanātha, Advayavajra, and, to Tibetans, Maitrīpa), was a prominent Indian Buddhist Mahasiddha associated with the Mahāmudrā transmission of tantric Buddhism.Roberts, Peter Alan, Mahamudra an ...
– an 11th-century Indian Buddhist Mahasiddha associated with the Mahāmudrā
Mahāmudrā (Sanskrit: महामुद्रा, , contraction of ) literally means "great seal" or "great imprint" and refers to the fact that "all phenomena inevitably are stamped by the fact of wisdom and emptiness inseparable". Mahāmudr ...
transmission. Born in the village of Jhatakarani in Magadha. Also associated with the monasteries of Nalanda
Nalanda (, ) was a renowned ''mahavihara'' (Buddhist monastic university) in ancient Magadha (modern-day Bihar), India.Vikramashila.
See also
*Mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and '' janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urban ...
* History of India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
* Magadha-Vajji war
* Magadha-Anga war
* Avanti-Magadhan Wars
* List of Indian monarchs
The following list of Indian monarchs is one of several lists of incumbents. It includes those said to have ruled a portion of the Indian subcontinent, including Sri Lanka.
The earliest Indian rulers are known from epigraphical sources fo ...
* Timeline of Indian history
* Magahi Culture
* Magahi Languages
References
Sources
* * * * {{Historical regions of North India, state=expanded Ancient India Empires and kingdoms of India History of Bihar Iron Age cultures of South Asia Mahajanapadas Jain empires and kingdoms Regions of Bihar Kingdoms of Bihar 4th-century BC disestablishments in India Magahi language Ancient Indian cities Empires and kingdoms of Nepal Former kingdoms