Lymphocyte activation simple.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the

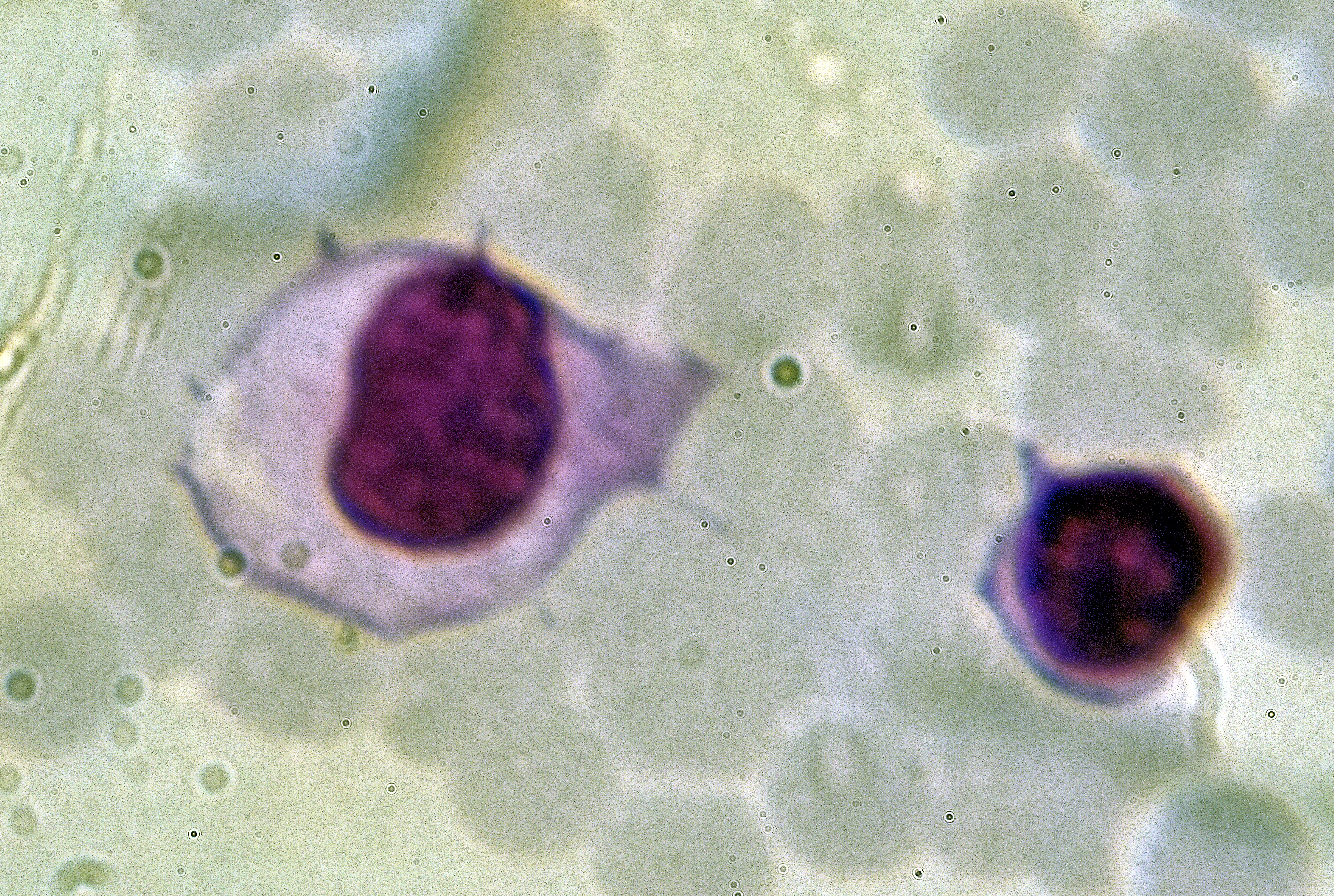 The three major types of lymphocyte are
The three major types of lymphocyte are
 A lymphocyte count is usually part of a peripheral
A lymphocyte count is usually part of a peripheral
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splint ...
of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
), T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
), and B cells (for humoral
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it invo ...
, antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
-driven adaptive immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
). They are the main type of cell found in lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells.
Types

 The three major types of lymphocyte are
The three major types of lymphocyte are T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s, B cells and natural killer
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represen ...
(NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus.
T cells and B cells
T cells (thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity
Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines in ...
, whereas B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (relating to antibodies). The function of T cells and B cells is to recognize specific "non-self" antigens, during a process known as antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, n ...
. Once they have identified an invader, the cells generate specific responses that are tailored maximally to eliminate specific pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s or pathogen-infected cells. B cells respond to pathogens by producing large quantities of antibodies which then neutralize foreign objects like bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
and virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es. In response to pathogens some T cells, called ''T helper cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are consider ...
s'', produce cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s that direct the immune response, while other T cells, called '' cytotoxic T cells'', produce toxic granules that contain powerful enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s which induce the death of pathogen-infected cells. Following activation, B cells and T cells leave a lasting legacy of the antigens they have encountered, in the form of ''memory cells''. Throughout the lifetime of an animal, these memory cells will "remember" each specific pathogen encountered, and are able to mount a strong and rapid response if the same pathogen is detected again; this is known as acquired immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity desc ...
.
Natural killer cells
NK cells are a part of the innate immune system and play a major role in defending the host fromtumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s and virally infected cells. NK cells modulate the functions of other cells, including macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
and T cells, and distinguish infected cells and tumors from normal and uninfected cells by recognizing changes of a surface molecule called MHC ( major histocompatibility complex) class I. NK cells are activated in response to a family of cytokines called interferons. Activated NK cells release cytotoxic (cell-killing) granules which then destroy the altered cells. They are named "natural killer cells" because they do not require prior activation in order to kill cells which are missing MHC class I.
Dual expresser lymphocyte – X cell
The X lymphocyte is a reported cell type expressing both aB-cell receptor
The B cell receptor (BCR) is a transmembrane protein on the surface of a B cell. A B cell receptor is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin molecule and a signal transduction moiety. The former forms a type 1 transmembrane receptor protein, ...
and T-cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding b ...
and is hypothesized to be implicated in type 1 diabetes. Its existence as a cell type has been challenged by two studies. However, the authors of original article pointed to the fact that the two studies have detected X cells by imaging microscopy and FACS as described. Additional studies are obviously required to determine the nature and properties of X cells (also called dual expressers).
Development
Mammalian stem cells differentiate into several kinds of blood cell within the bone marrow. This process is calledhaematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cell ...
. All lymphocytes originate, during this process, from a common lymphoid progenitor before differentiating into their distinct lymphocyte types. The differentiation of lymphocytes follows various pathways in a hierarchical fashion as well as in a more plastic fashion. The formation of lymphocytes is known as lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, which are one of the five types of white blood cells (WBCs). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.
Disruption in lymphopoiesis can lead t ...
. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s. In bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius In birds, the bursa of Fabricius (Latin: ''bursa cloacalis'' or ''bursa fabricii'') is the site of hematopoiesis. It is a specialized organ that, as first demonstrated by Bruce Glick and later by Max Dale Cooper and Robert Good, is necessary fo ...
, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, (B for bursa) and not from bone marrow as commonly believed. T cells migrate to the blood stream and mature in a distinct primary organ, called the thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
. Following maturation, the lymphocytes enter the circulation and peripheral lymphoid organs
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid ...
(e.g. the spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
and lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
) where they survey for invading pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s and/or tumor cells.
The lymphocytes involved in adaptive immunity (i.e. B and T cells) differentiate further after exposure to an antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
; they form effector and memory lymphocytes. Effector lymphocytes function to eliminate the antigen, either by releasing antibodies (in the case of B cells), cytotoxic granules ( cytotoxic T cells) or by signaling to other cells of the immune system (helper T cells
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
). Memory T cells
Memory T cells are a subset of T lymphocytes that might have some of the same functions as memory B cells. Their lineage is unclear.
Function
Antigen-specific memory T cells specific to viruses or other microbial molecules can be found in both ...
remain in the peripheral tissues and circulation for an extended time ready to respond to the same antigen upon future exposure; they live weeks to several years, which is very long compared to other leukocytes.
Characteristics
Microscopically, in aWright's stain
Wright's stain is a hematologic stain that facilitates the differentiation of blood cell types. It is classically a mixture of eosin (red) and methylene blue dyes. It is used primarily to stain peripheral blood smears, urine samples, and bone m ...
ed peripheral blood smear
A blood smear, peripheral blood smear or blood film is a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass microscope slide and then stained in such a way as to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically. Blood smears are examined in the ...
, a normal lymphocyte has a large, dark-staining nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
with little to no eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye.
Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''E ...
cytoplasm. In normal situations, the coarse, dense nucleus of a lymphocyte is approximately the size of a red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
(about 7 μm in diameter). Some lymphocytes show a clear perinuclear zone (or halo) around the nucleus or could exhibit a small clear zone to one side of the nucleus. Polyribosomes
A polyribosome (or polysome or ergosome) is a group of ribosomes bound to an mRNA molecule like “beads” on a “thread”. It consists of a complex of an mRNA molecule and two or more ribosomes that act to translate mRNA instructions into pol ...
are a prominent feature in the lymphocytes and can be viewed with an electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
. The ribosomes
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
are involved in protein synthesis, allowing the generation of large quantities of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s and immunoglobulins by these cells.
It is impossible to distinguish between T cells and B cells in a peripheral blood smear. Normally, flow cytometry testing is used for specific lymphocyte population counts. This can be used to determine the percentage of lymphocytes that contain a particular combination of specific cell surface proteins, such as immunoglobulins or cluster of differentiation
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophen ...
(CD) markers or that produce particular proteins (for example, cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s using intracellular cytokine staining (ICCS)). In order to study the function of a lymphocyte by virtue of the proteins it generates, other scientific techniques like the ELISPOT
The enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot (ELISpot) is a type of assay that focuses on quantitatively measuring the frequency of cytokine secretion for a single cell. The ELISpot Assay is also a form of immunostaining since it is classified as a tec ...
or secretion assay Secretion assay is a process used in cell biology to identify cells that are secretion, secreting a particular protein (usually a cytokine). It was first developed by ''Manz et al.'' in 1995.
Usually, a cell that is secreting the protein of interes ...
techniques can be used.
:
In the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, they move from lymph node to lymph node. This contrasts with macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, which are rather stationary in the nodes.
Lymphocytes and disease
 A lymphocyte count is usually part of a peripheral
A lymphocyte count is usually part of a peripheral complete blood cell count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cell ...
and is expressed as the percentage of lymphocytes to the total number of white blood cells counted.
A general increase in the number of lymphocytes is known as lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood. Absolute lymphocytosis is the condition where there is an increase in the lymphocyte count beyond the normal range while relative lymphocytosis refers to the cond ...
, whereas a decrease is known as lymphocytopenia
Lymphocytopenia is the condition of having an abnormally low level of lymphocytes in the blood. Lymphocytes are a white blood cell with important functions in the immune system. It is also called lymphopenia. The opposite is lymphocytosis, which r ...
.
High
An increase in lymphocyte concentration is usually a sign of aviral infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Structural Characteristics
Basic structural characteristics, ...
(in some rare case, leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
s are found through an abnormally raised lymphocyte count in an otherwise normal person). A high lymphocyte count with a low neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
count might be caused by lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enla ...
. Pertussis toxin
Pertussis toxin (PT) is a protein-based AB5-type exotoxin produced by the bacterium ''Bordetella pertussis'', which causes whooping cough. PT is involved in the colonization of the respiratory tract and the establishment of infection. Rese ...
(PTx) of ''Bordetella pertussis
''Bordetella pertussis'' is a Gram-negative, aerobic, pathogenic, encapsulated coccobacillus of the genus ''Bordetella'', and the causative agent of pertussis or whooping cough. Like '' B. bronchiseptica'', ''B. pertussis'' is motile and expre ...
'', formerly known as lymphocytosis-promoting factor, causes a decrease in the entry of lymphocytes into lymph nodes, which can lead to a condition known as lymphocytosis, with a complete lymphocyte count of over 4000 per μl in adults or over 8000 per μl in children. This is unique in that many bacterial infections illustrate neutrophil-predominance instead.
Low
A low normal to low absolute lymphocyte concentration is associated with increased rates of infection after surgery or trauma. One basis for low T cell lymphocytes occurs when thehuman immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immun ...
(HIV) infects and destroys T cells (specifically, the CD4+ subgroup of T lymphocytes, which become helper T cells). Without the key defense that these T cells provide, the body becomes susceptible to opportunistic infections that otherwise would not affect healthy people. The extent of HIV progression is typically determined by measuring the percentage of CD4+ T cells in the patient's blood – HIV ultimately progresses to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). The effects of other virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es or lymphocyte disorders can also often be estimated by counting the numbers of lymphocytes present in the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
.
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
In some cancers, such as melanoma and colorectal cancer, lymphocytes can migrate into and attack thetumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
. This can sometimes lead to regression of the primary tumor.
Lymphocyte-variant hypereosinophilia
Blood content
History
See also
*Addressin
Mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (MAdCAM-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MADCAM1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule that interacts preferentially with the leukoc ...
* Anergy
In immunology, anergy is a lack of reaction by the body's defense mechanisms to foreign substances, and consists of a direct induction of peripheral lymphocyte tolerance. An individual in a state of anergy often indicates that the immune syste ...
* Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and pl ...
* Cytotoxicity
* Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
* Innate lymphoid cell
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secretion of signalling mo ...
* Lymphocystivirus
''Lymphocystivirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Iridoviridae''. Fish serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: tumor-like growths on the skin.
Hosts
''Lymphocystivirus ...
* Lymphoproliferative disorders
Lymphoproliferative disorders (LPDs) refer to a specific class of diagnoses, comprising a group of several conditions, in which lymphocytes are produced in excessive quantities. These disorders primarily present in patients who have a compromised i ...
* Reactive lymphocyte
* Secretion assay Secretion assay is a process used in cell biology to identify cells that are secretion, secreting a particular protein (usually a cytokine). It was first developed by ''Manz et al.'' in 1995.
Usually, a cell that is secreting the protein of interes ...
* Trogocytosis
*
*
Notes
References
External links
* * * {{Authority control Lymph fluid Lymphatic tissue Lymphatic system Immune system