Loess landscape china.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly
Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly
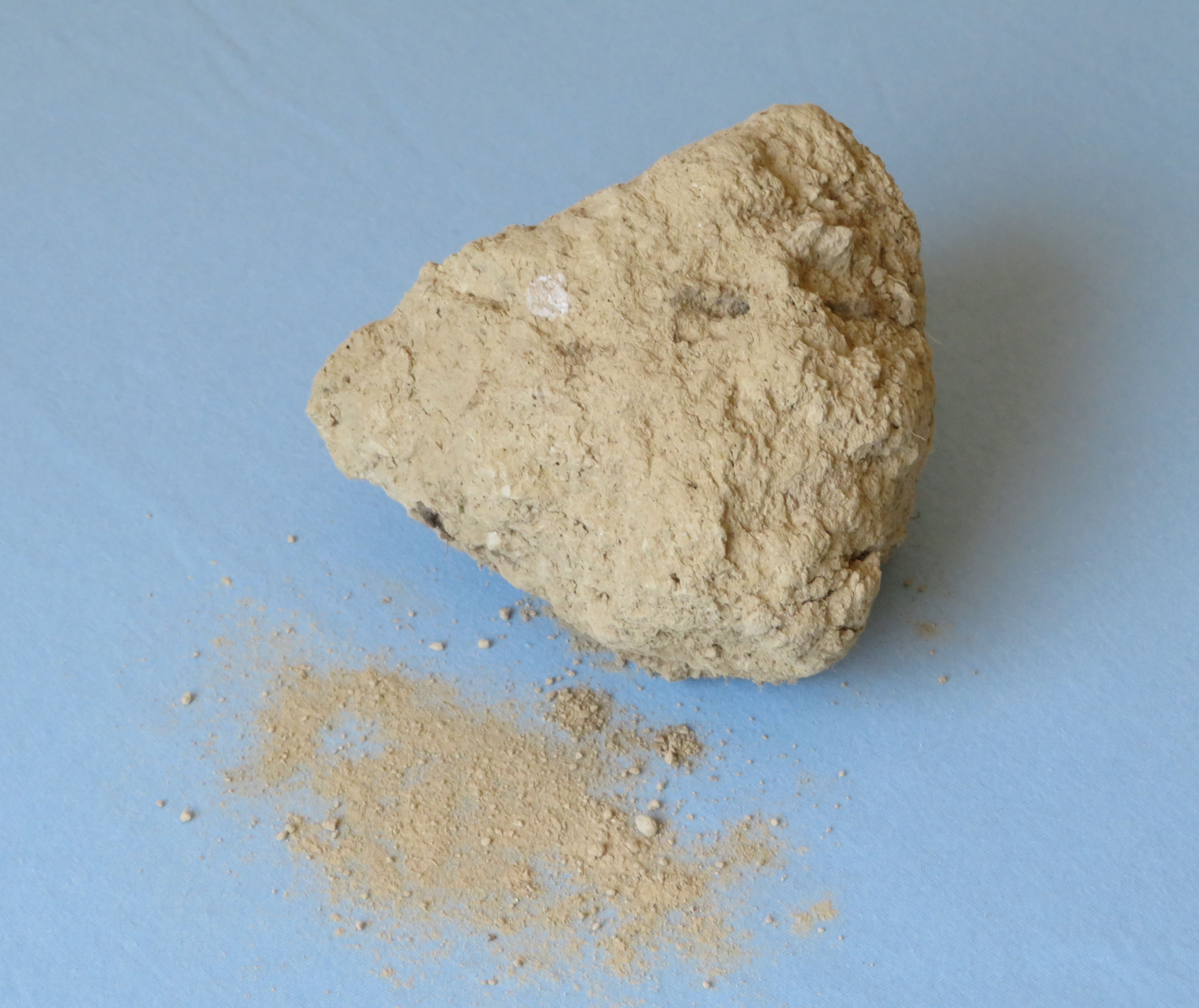
 Loess is homogeneous,
Loess is homogeneous,
 According to Pye (1995), four fundamental requirements are necessary for the formation of loess: a dust source, adequate wind energy to transport the dust, a suitable accumulation area, and a sufficient amount of time.
According to Pye (1995), four fundamental requirements are necessary for the formation of loess: a dust source, adequate wind energy to transport the dust, a suitable accumulation area, and a sufficient amount of time.
 The
The
''Loesses in Louisiana and at Vicksburg, Mississippi. Guidebook, Friends of the Pleistocene Field Trip, 12-14 April, 1985.''
LA Agricultural Experimental Station,
 Much of Argentina is covered by loess. Two areas of loess are usually distinguished in Argentina: the neotropical loess north of latitude 30° S and the pampean loess.
The neotropical loess is made of silt or silty clay. Relative to the pampean loess the neotropical loess is poor in
Much of Argentina is covered by loess. Two areas of loess are usually distinguished in Argentina: the neotropical loess north of latitude 30° S and the pampean loess.
The neotropical loess is made of silt or silty clay. Relative to the pampean loess the neotropical loess is poor in
''The Secret of China’s Vast Loess Plateau''
Suburban Emergency Management Project, Chicago, Illinois. * 2007
''New European Loess Map.''
''Glacial Deposits: Loess and Till.''
''Loess Thickness Map (of Illinois).''
Illinois State Geological Survey,
''Loess map of Louisiana.''
Public Information Series. no. 12,
''The Loess Hills: A Geologic View.''
Iowa Geological Survey,
''Geology of the Loess Hills, Iowa''
*
''Eolian History of North America''
Why is loess important to study?
''The Loess Hills of Roztocze in Poland''
{{Authority control Pedology Glaciology Sedimentary rocks Sediments Types of soil Aeolian landforms
 Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly
Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
-sized sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ho ...
. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loess or similar deposits
A deposit account is a bank account maintained by a financial institution in which a customer can deposit and withdraw money. Deposit accounts can be savings accounts, current accounts or any of several other types of accounts explained below.
...
.
Loess is a periglacial
Periglaciation (adjective: "periglacial", also referring to places at the edges of glacial areas) describes geomorphic processes that result from seasonal thawing of snow in areas of permafrost, the runoff from which refreezes in ice wedges and o ...
or aeolian (windborne) sediment, defined as an accumulation of 20% or less of clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
and a balance of roughly equal parts sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
and silt (with a typical grain size from 20 to 50 micrometers), often loosely cemented by calcium carbonate. It is usually homogeneous and highly porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
and is traversed by vertical capillaries that permit the sediment to fracture and form vertical bluffs.
Properties

 Loess is homogeneous,
Loess is homogeneous, porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
, friable
Friability ( ), the condition of being friable, describes the tendency of a solid substance to break into smaller pieces under duress or contact, especially by rubbing. The opposite of friable is indurate.
Substances that are designated hazardous, ...
, pale yellow or buff
Buff or BUFF may refer to:
People
* Buff (surname), a list of people
* Buff (nickname), a list of people
* Johnny Buff, ring name of American world champion boxer John Lisky (1888–1955)
* Buff Bagwell, a ring name of American professional ...
, slightly coherent
Coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
Physics
* Coherence (physics), an ideal property of waves that enables stationary (i.e. temporally and spatially constant) interference
* Coherence (units of measurement), a deri ...
, typically non- stratified and often calcareous
Calcareous () is an adjective meaning "mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate", in other words, containing lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of scientific disciplines.
In zoology
''Calcareous'' is used as an ad ...
. Loess grains are angular, with little polishing or rounding, and composed of crystals of quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
, feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) felds ...
, mica and other mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s. Loess can be described as a rich, dust-like soil.
Loess deposits may become very thick, more than a hundred meters in areas of Northwestern China and tens of meters in parts of the Midwestern United States. Loess generally occurs as a blanket deposit that covers areas of hundreds of square kilometers. The deposits are often tens of meters thick. Loess often stands in either steep or vertical faces. Because the grains are angular, loess will often stand in banks for many years without slumping. This soil has a characteristic called vertical cleavage which makes it easily excavated to form cave dwellings, a popular method of making human habitations in some parts of China. Loess will erode very readily.
In several areas of the world, loess ridges have formed that are aligned with the prevailing wind
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point o ...
s during the last glacial maximum
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
. These are called " paha ridges" in America and "greda ridges" in Europe. The form of these loess dunes has been explained by a combination of wind and tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
conditions.
Etymology
The word ''loess'', with connotations of origin by wind-deposited accumulation, came into English fromGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
''Löss'', which can be traced back to Swiss German and is cognate with the English word ''loose'' and the German word ''los''. It was first applied to Rhine River valley loess about 1821.
History of research
The term "Löß" was first described inCentral Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
by Karl Cäsar von Leonhard
Karl Cäsar von Leonhard (12 September 1779 in Rumpenheim – 23 January 1862 in Heidelberg) was a German mineralogist and geologist. His son, Gustav von Leonhard, was also a mineralogist.
From 1797 he studied at the universities of Marburg and ...
(1823–1824) who reported yellowish brown, silty deposits along the Rhine valley near Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914 ...
. Charles Lyell (1834) brought this term into widespread usage by observing similarities between loess and loess derivatives along the loess bluffs in the Rhine and Mississippi. At that time it was thought that the yellowish brown silt-rich sediment was of fluvial origin being deposited by the large rivers. It was not until the end of the 19th century that the aeolian origin of loess was recognized (Virlet D'Aoust 1857), especially the convincing observations of loess in China by Ferdinand von Richthofen (1878). A tremendous number of papers have been published since then, focusing on the formation of loess and on loess/paleosol
In the geosciences, paleosol (''palaeosol'' in Great Britain and Australia) is an ancient soil that formed in the past. The precise definition of the term in geology and paleontology is slightly different from its use in soil science.
In geolo ...
(older soil buried under deposits) sequences as archives of climate and environment change. These water conservation works were carried out extensively in China and the research of loess in China has been continued since 1954. (Liu TS, Loess and the environment)
Much effort was put into the setting up of regional and local loess stratigraphies and their correlation (Kukla 1970, 1975, 1977). But even the chronostratigraphical position of the last interglacial soil correlating to marine isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numb ...
substage 5e has been a matter of debate, owing to the lack of robust and reliable numerical dating, as summarized for example in Zöller et al. (1994) and Frechen, Horváth & Gábris (1997) for the Austrian and Hungarian loess stratigraphy, respectively.
Since the 1980s, thermoluminescence
Thermoluminescence is a form of luminescence that is exhibited by certain crystalline materials, such as some minerals, when previously absorbed energy from electromagnetic radiation or other ionizing radiation is re-emitted as light upon he ...
(TL), optically stimulated luminescence
In physics, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) is a method for measuring doses from ionizing radiation. It is used in at least two applications:
* Luminescence dating of ancient materials: mainly geological sediments and sometimes fired pott ...
(OSL) and infrared stimulated luminescence (IRSL) dating are available providing the possibility for dating the time of loess (dust) deposition, i.e. the time elapsed since the last exposure of the mineral grains to daylight. During the past decade, luminescence dating
Luminescence dating refers to a group of methods of determining how long ago mineral grains were last exposed to sunlight or sufficient heating. It is useful to geologists and archaeologists who want to know when such an event occurred. It uses var ...
has significantly improved by new methodological improvements, especially the development of single aliquot
Aliquot ( la, a few, some, not many) may refer to:
Mathematics
* Aliquot part, a proper divisor of an integer
*Aliquot sum, the sum of the aliquot parts of an integer
*Aliquot sequence, a sequence of integers in which each number is the aliquot su ...
regenerative (SAR) protocols (Murray & Wintle 2000) resulting in reliable ages (or age estimates) with an accuracy of up to 5 and 10% for the last glacial record. More recently, luminescence dating has also become a robust dating technique for penultimate and antepenultimate glacial loess (e.g. Thiel et al. 2011, Schmidt et al. 2011) allowing for a reliable correlation of loess/palaeosol sequences for at least the last two interglacial/glacial cycles throughout Europe and the Northern Hemisphere (Frechen 2011). Furthermore, the numerical dating provides the basis for quantitative loess research applying more sophisticated methods to determine and understand high-resolution proxy data, such as the palaeodust content of the atmosphere, variations of the atmospheric circulation patterns and wind systems, palaeoprecipitation and palaeotemperature.
Besides luminescence dating methods, the use of radiocarbon dating in loess has increased during the past decades. Advances in methods of analyses, instrumentation and refinements to the radiocarbon calibration curve have enabled to obtain reliable ages from loess deposits for the last 40-45 ka. However, the use of this method relies on finding suitable in situ organic material in deposits such as charcoal, seeds, earthworm granules or snail shells.
Formation
 According to Pye (1995), four fundamental requirements are necessary for the formation of loess: a dust source, adequate wind energy to transport the dust, a suitable accumulation area, and a sufficient amount of time.
According to Pye (1995), four fundamental requirements are necessary for the formation of loess: a dust source, adequate wind energy to transport the dust, a suitable accumulation area, and a sufficient amount of time.
Periglacial loess
Periglacial
Periglaciation (adjective: "periglacial", also referring to places at the edges of glacial areas) describes geomorphic processes that result from seasonal thawing of snow in areas of permafrost, the runoff from which refreezes in ice wedges and o ...
(glacial) loess is derived from the floodplains of glacial
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betwe ...
braided rivers that carried large volumes of glacial meltwater and sediments from the annual melting of continental icesheets and mountain icecaps during the spring and summer. During the autumn and winter, when melting of the icesheets and icecaps ceased, the flow of meltwater down these rivers either ceased or was greatly reduced. As a consequence, large parts of the formerly submerged and unvegetated floodplains of these braided rivers dried out and were exposed to the wind. Because these floodplains consist of sediment containing a high content of glacially ground flour-like silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
, they were highly susceptible to winnowing of their silts and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
s by the wind. Once entrained by the wind, particles were then deposited downwind. The loess deposits found along both sides of the Mississippi River Alluvial Valley are a classic example of periglacial loess.
During the Quaternary, loess and loess-like sediments were formed in periglacial environments on mid-continental shield areas in Europe and Siberia, on the margins of high mountain ranges like in Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
and on semi-arid margins of some lowland deserts like in China.
In England, periglacial loess is also known as brickearth
Brickearth is a term originally used to describe superficial windblown deposits found in southern England. The term has been employed in English-speaking regions to describe similar deposits.
Brickearths are periglacial loess, a wind-b ...
.
Non-glacial
Non-glacial loess can originate from deserts,dune field
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, fl ...
s, playa lake
Playa (plural playas) may refer to:
Landforms
* Endorheic basin, also known as a sink, alkali flat or sabkha, a desert basin with no outlet which periodically fills with water to form a temporary lake
* Dry lake, often called a ''playa'' in the so ...
s, and volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
.
Some types of nonglacial loess are:
* Desert loess produced by aeolian attrition of quartz grains;
* Volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
loess in Ecuador and Argentina;
* Tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
loess in Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay;
* Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
loess in Spain;
* Trade wind
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
loess in Venezuela and Brazil;
* Anticyclonic
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from abov ...
loess in Argentina.
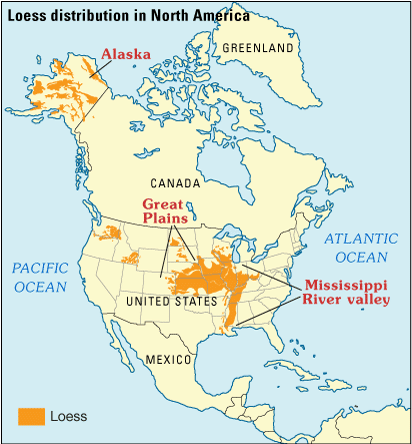
The thick Chinese loess deposits are non-glacial loess having been blown in from deserts in northern China. The loess covering the Great Plains of Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, and Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
is considered to be non-glacial desert loess. Non-glacial desert loess is also found in Australia and Africa.
Fertility
Loess tends to develop into very rich soils. Under appropriate climatic conditions, it is some of the most agriculturally productive terrain in the world. Soils underlain by loess tend to be excessively drained. The fine grainsweather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmos ...
rapidly due to their large surface area, making soils derived from loess rich. One theory states that the fertility of loess soils is due largely to cation exchange capacity
Cation-exchange capacity (CEC) is a measure of how many cations can be retained on soil particle surfaces. Negative charges on the surfaces of soil particles bind positively-charged atoms or molecules (cations), but allow these to exchange with ot ...
(the ability of plants to absorb nutrients from the soil) and porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measur ...
(the air-filled space in the soil). The fertility of loess is not due to organic matter content, which tends to be rather low, unlike tropical soils which derive their fertility almost wholly from organic matter.
Even well managed loess farmland
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with bo ...
can experience dramatic erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
of well over 2.5 kg /m2 per year. In China the loess deposits which give the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
its color have been farmed and have produced phenomenal yields for over one thousand years. Winds pick up loess particles, contributing to the Asian Dust pollution problem. The largest deposit of loess in the United States, the Loess Hills
The Loess Hills are a formation of wind-deposited loess soil in the westernmost parts of Iowa and Missouri, and the easternmost parts of Nebraska and Kansas, along the Missouri River.
Geology
The Loess (, , or ) Hills are generally located bet ...
along the border of Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
and Nebraska, has survived intensive farming
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ...
and poor farming practices. For almost 150 years, this loess deposit was farmed with mouldboard plough
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
s and fall tilled, both intensely erosive. At times it suffered erosion rates of over 10 kilograms per square meter per year. Today this loess deposit is worked as low till or no till
No-till farming (also known as zero tillage or direct drilling) is an agricultural technique for growing crops or pasture without disturbing the soil through tillage. No-till farming decreases the amount of soil erosion tillage causes in certa ...
in all areas and is aggressively terraced
In agriculture, a terrace is a piece of sloped plane that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces or platforms, which resemble steps, for the purposes of more effective farming. This type of landscaping is therefore ...
.
Large areas of loess deposits and soils
Central Asia
From southernTajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
up to Almaty, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, spans an area of multiple loess deposits.
East Asia
China
TheLoess Plateau
The Chinese Loess Plateau, or simply the Loess Plateau, is a plateau in north-central China formed of loess, a clastic silt-like sediment formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. It is located southeast of the Gobi Desert and is surrounde ...
(), also known as the Huangtu Plateau, is a plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
that covers an area of some 640,000 km2 around the upper and middle reaches of China's Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
. The Yellow River was so named because the loess forming its banks gave a yellowish tint to the water. The soil of this region has been called the "most highly erodible soil on earth". The Loess Plateau and its dusty soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debri ...
cover almost all of Shanxi, Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
, and Gansu provinces, the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1 ...
, and parts of others.
Europe
Loess deposits of varying thickness (decimeter to several tens of meters) are widely distributed over the European continent. The northern European loess belt stretches from southern England and northern France to Germany, Poland and the southern Ukraine and deposits are characterized by strong influences ofperiglacial
Periglaciation (adjective: "periglacial", also referring to places at the edges of glacial areas) describes geomorphic processes that result from seasonal thawing of snow in areas of permafrost, the runoff from which refreezes in ice wedges and o ...
conditions. South-eastern European loess is mainly deposited in plateau-like situations in the Danube basin
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
s, likely derived from the Danube River system. In south-western Europe, relocated loess derivatives are mostly restricted to the Ebro Valley
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
and central Spain.
North America
United States
 The
The Loess Hills
The Loess Hills are a formation of wind-deposited loess soil in the westernmost parts of Iowa and Missouri, and the easternmost parts of Nebraska and Kansas, along the Missouri River.
Geology
The Loess (, , or ) Hills are generally located bet ...
of Iowa owe their fertility to the prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
topsoil
Topsoil is the upper layer of soil. It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs.
Description
Topsoil is composed of mineral particles and organic matt ...
s built by 10,000 years of post-glacial accumulation of organic-rich humus as a consequence of a persistent grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ...
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
. When the valuable A-horizon topsoil is eroded or degraded, the underlying loess soil is infertile, and requires the addition of fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
in order to support agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
.
The loess along the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
near Vicksburg, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
, consist of three layers. The ''Peoria Loess'', ''Sicily Island Loess'', and ''Crowley's Ridge Loess'' accumulated at different periods of time during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
. Ancient soils, called paleosol
In the geosciences, paleosol (''palaeosol'' in Great Britain and Australia) is an ancient soil that formed in the past. The precise definition of the term in geology and paleontology is slightly different from its use in soil science.
In geolo ...
s, have developed in the top of the Sicily Island Loess and Crowley's Ridge
Crowley's Ridge (also Crowleys Ridge) is a geological formation that rises 250 to above the alluvial plain of the Mississippi embayment in a line from southeastern Missouri to the Mississippi River near Helena, Arkansas. It is the most pro ...
Loess. The lowermost loess, the Crowley's Ridge Loess, accumulated during the late Illinoian Stage
The Illinoian Stage is the name used by Quaternary geologists in North America to designate the period c.191,000 to c.130,000 years ago, during the middle Pleistocene, when sediments comprising the Illinoian Glacial Lobe were deposited. It precedes ...
. The middle loess, Sicily Island Loess, accumulated during early Wisconsin Stage. The uppermost loess, the Peoria Loess, in which the modern soil has developed, accumulated during the late Wisconsin Stage. Animal remains include terrestrial gastropods and mastodon
A mastodon ( 'breast' + 'tooth') is any proboscidean belonging to the extinct genus ''Mammut'' (family Mammutidae). Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene up to their extinction at the end of th ...
s.Miller, B.J., G.C. Lewis, J.J. Alford, and W.J. Day, 1985''Loesses in Louisiana and at Vicksburg, Mississippi. Guidebook, Friends of the Pleistocene Field Trip, 12-14 April, 1985.''
LA Agricultural Experimental Station,
Louisiana State University
Louisiana State University (officially Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, commonly referred to as LSU) is a public land-grant research university in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. The university was founded in 1860 nea ...
, Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
. 126 pp.
Oceania
New Zealand
Extensive areas of loess occur in New Zealand including theCanterbury Plains
The Canterbury Plains () are an area in New Zealand centred in the Mid Canterbury, to the south of the city of Christchurch in the Canterbury region. Their northern extremes are at the foot of the Hundalee Hills in the Hurunui District, and in t ...
and on the Banks Peninsula. The basis of loess stratigraphy was introduced by John Hardcastle in 1890.*Hardcastle, J. 1890. On the Timaru loess as a climate register. Transcations & Proceedings of the New Zealand Institute 23, 324-332 (on line: Royal Society of New Zealand http://rsnz.natlib.govt.nz; reproduced in Loess Letter supplement 23, November 1988).
South America
Argentina
quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
and calcium carbonate. The source region for this loess is thought by some scientists to be areas of fluvio-glacial
Fluvio refers to things related to rivers and glacial refers to something that is of ice. Fluvio-glacial refers to the meltwater created when a glacier melts. Fluvio-glacial processes can occur on the surface and within the glacier. The deposits t ...
deposits the Andean foothills formed by the Patagonian Ice Sheet
upright=1.4, Map showing the extent of the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the Strait of Magellan area during the last glacial period. Selected modern settlements are shown with yellow dots. Sea level was much lower than shown here.
The Patagonian Ice S ...
. Other researchers stress the importance of volcanic material
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Ear ...
in the neotropical loess.
The pampean loess is sandy or made of silty sand.
See also
* – North German loess regions * – South German loess regions *References
; Attribution This article incorporates CC-BY-3.0 text from the reference "Loess in Europe: Guest Editorial".Further reading
* Smalley, I. J. (editor) 1975. ''Loess Lithology & Genesis''. Benchmark Geology 26. Dowden, Hutchinson & Ross 454pp. * Smalley, I. J. 1980. ''Loess: A Partial Bibliography''. Geobooks/Elsevier. . 103pp. * Rozycki, S. Z. 1991. ''Loess and Loess-like Deposits''. Ossolineum Wroclaw . 187pp.External links
* 2006''The Secret of China’s Vast Loess Plateau''
Suburban Emergency Management Project, Chicago, Illinois. * 2007
''New European Loess Map.''
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research
The work of the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research – UFZ (prior to 28 November 2006 UFZ-Umweltforschungszentrum Leipzig-Halle GmbH) covers both basic research and applied research.
The UFZ was established on 12 December 1991. The Cent ...
, Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
, Germany.
''Glacial Deposits: Loess and Till.''
Illinois State Museum
The Illinois State Museum features the life, land, people and art of the State of Illinois. The headquarters museum is located on Spring and Edwards Streets, one block southwest of the Illinois State Capitol, in Springfield. There are three satell ...
, Springfield, Illinois.
* Briedis. C.A., 2006''Loess Thickness Map (of Illinois).''
Illinois State Geological Survey,
Champaign, Illinois
Champaign ( ) is a city in Champaign County, Illinois, United States. The population was 88,302 at the 2020 census. It is the tenth-most populous municipality in Illinois and the fourth most populous city in Illinois outside the Chicago metro ...
.
* Heinrich, P.V., 2008''Loess map of Louisiana.''
Public Information Series. no. 12,
Louisiana Geological Survey The Louisiana Geological Survey is a state geological survey established by the Louisiana legislature by Act 131 in 1934 to serve the citizens Louisiana by collecting, preserving, and disseminating impartial information on the geomorphology, hydrog ...
, Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
.
* Prior, J.C., and D.J. Quade, nd''The Loess Hills: A Geologic View.''
Iowa Geological Survey,
Department of Natural Resources
This article lists subnational environmental agencies in the United States, by state. Agencies with a variety of titles and responsibilities are included, e.g. Department of Environment, Department of Environmental Conservation, Department of E ...
, Iowa City, Iowa.
* U.S. Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
, 1999''Geology of the Loess Hills, Iowa''
*
U.S. Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
, 2006''Eolian History of North America''
Why is loess important to study?
''The Loess Hills of Roztocze in Poland''
{{Authority control Pedology Glaciology Sedimentary rocks Sediments Types of soil Aeolian landforms