Kunming (; ), also known as Yunnan-Fu, is the capital and largest city of
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
province,
China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The headquarters of many of Yunnan's large businesses are in Kunming. It was important during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
as a Chinese military center,
American air base, and transport terminus for the
Burma Road
The Burma Road () was a road linking Burma (now known as Myanmar) with southwest China. Its terminals were Kunming, Yunnan, and Lashio, Burma. It was built while Burma was a British colony to convey supplies to China during the Second Sino ...
. In the middle of the
Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau
The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau () is a highland region located in southwest China. The region is primarily spread over the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou. In the southwest, the Yungui is a true plateau with relatively flatter ...
, Kunming is at an altitude of
above sea level and a
latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
just north of the
Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted tow ...
. As of 2020 census, Kunming had a total population of 8,460,088 inhabitants, of whom 5,604,310 lived in its built-up (or metro) area made of all urban districts but Jinning, not conurbated yet. It is at the northern edge of
Dian Lake
Dianchi Lake (), also known as Lake Dian and Kunming Lake (), is a large lake located on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau close to Kunming, Yunnan, China. Its nickname is the "Sparkling Pearl Embedded in a Highland" () and it was the model for the Ku ...
, surrounded by temples and lake-and-
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
hill landscapes.
Kunming consists of an old, previously walled city, a modern commercial district, residential zones and university areas. It is also one of the top 200
cities in the world by scientific research output. The city has an
astronomical observatory, and its
institutions of higher learning include
Yunnan University
Yunnan University (, Acronym: YNU) is a national key university in Yunnan Province, China. Its main campuses are located in the provincial capital city of Kunming.
Founded in December 1922, Yunnan University started to enroll in April 1923. It ...
,
Kunming University of Science and Technology
Kunming University of Science and Technology (KUST) () is in Kunming, the capital city of Yunnan Province, Southwestern China.
As the goal by 2010, KUST was to become a National Key Universities, key university with a strong science and engineerin ...
,
Yunnan University of Finance and Economics,
Kunming Medical University,
Yunnan Normal University
Yunnan Normal University (; YNNU) is in Kunming, the capital city of Yunnan province.
Yunnan Normal University (YNNU) is a key university of Yunnan province, with a long history and a great tradition.
It is a higher institution co-funded by the ...
,
Yunnan Agricultural University and
Southwest Forestry University. On the northeast mountainous outskirt is a
bronze temple dating from the Ming dynasty, the largest of its kind in China.
Kunming's economic importance derives from its geographical position. It is near the border with
Southeastern Asian countries, serving as a
transportation hub
A transport hub is a place where passengers and cargo are exchanged between vehicles and/or between transport modes. Public transport hubs include railway stations, rapid transit stations, bus stops, tram stops, airports and ferry slips. F ...
in
Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China.
Geography
Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (东南丘陵) and ...
, linking by rail to
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and by road to
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
,
Laos and
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
. This positioning also makes it an important trade center in the region. As a gateway to
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, the
Kunming Changshui International Airport
Kunming Changshui International Airport is the primary airport serving Kunming, the capital of Yunnan Province, China. The airport is located northeast of the city center in a graded mountainous area about above sea level. The airport opene ...
is one of the top 40th-
busiest airports in the world. Kunming also houses some manufacturing, chiefly the processing of copper, as well as various chemicals, machinery, textiles, paper and cement. Kunming has a nearly 2,400-year history, but its modern prosperity dates only to 1910, when the railway from
Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is ...
was built. The city has continued to develop rapidly under China's modernization efforts. Kunming's streets have widened while office buildings and housing projects develop at a fast pace. Kunming has been designated a special tourism center and as such sports a proliferation of
high-rises and
luxury hotel
A hotel is an establishment that provides paid lodging on a short-term basis. Facilities provided inside a hotel room may range from a modest-quality mattress in a small room to large suites with bigger, higher-quality beds, a dresser, a ref ...
s.
Etymology
The name "Kunming" evolved from an ancient ethnicity named ''
Kunming Yi
Kunming (; ), also known as Yunnan-Fu, is the capital and largest city of Yunnan province, China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The headquar ...
'' or ''Kunming Barbarian'' (), which was a branch of
Di-
Qiang. The ''Kunming Yi'' lived in the neighbouring region of
Erhai Lake
Erhai or Er Lake (), is an alpine fault lake in Yunnan province, China. Erhai was also known as Yeyuze () or Kunming Lake () in ancient times.
Etymology
The character "洱" (er) does not have the same meaning as ear (耳). During the Han to Tan ...
during the
Western Han
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a war ...
dynasty. The Han dynasty incorporated the territory of the Dian Kingdom and set a division called
Yizhou Commandery Yi Prefecture or Yizhou may refer to:
* Yizhou (Southwest China) (), a historical province of China covering Southwest China
* Yi Prefecture (Shandong) (), active between the 7th and 18th centuries
* Yi Prefecture (Guangxi) (), active between th ...
in 109 BC; the Han dynasty also incorporated the ''Kunming Yi'' into Yizhou Commandery soon after. Therefore, ''Kunming Yi'' expanded east to the
Lake Dian
Dianchi Lake (), also known as Lake Dian and Kunming Lake (), is a large lake located on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau close to Kunming, Yunnan, China. Its nickname is the "Sparkling Pearl Embedded in a Highland" () and it was the model for the Ku ...
area later. "Kunming" has acted as a place name since the
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the West ...
period, but the reference was not clear because this ethnicity occupied a large region. In the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fift ...
, the central government set "Kunming County" in modern Kunming; the name "Kunming" has continued to this day.
Some modern research states that the name "Kunming" of ''Kunming Yi'' is a
cognate word of "
Khmer" and "
Khmu" that originally meant "people".
History
Early history
Kunming long profited from its position on the caravan roads through to
South-East Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, India and
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
. Early townships in the southern edge of
Lake Dian
Dianchi Lake (), also known as Lake Dian and Kunming Lake (), is a large lake located on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau close to Kunming, Yunnan, China. Its nickname is the "Sparkling Pearl Embedded in a Highland" () and it was the model for the Ku ...
(outside the contemporary city perimeter) can be dated back to 279 BC, although they have been long lost to history. Early settlements in the area around
Lake Dian
Dianchi Lake (), also known as Lake Dian and Kunming Lake (), is a large lake located on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau close to Kunming, Yunnan, China. Its nickname is the "Sparkling Pearl Embedded in a Highland" () and it was the model for the Ku ...
date back to
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
times. The
Dian Kingdom
Dian () was an ancient kingdom established by the Dian people, a non-Han Chinese metalworking civilization that inhabited around the Dian Lake plateau of central northern Yunnan, China from the late Spring and Autumn period until the Eastern Han d ...
, whose original language was likely related to
Tibeto-Burman language
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spe ...
s was also established near the area.
Dian was subjugated by the Chinese
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
under the reign of
Emperor Wu of Han in 109 BC. The Han dynasty incorporated the territory of the Dian Kingdom into their
Yizhou Commandery Yi Prefecture or Yizhou may refer to:
* Yizhou (Southwest China) (), a historical province of China covering Southwest China
* Yi Prefecture (Shandong) (), active between the 7th and 18th centuries
* Yi Prefecture (Guangxi) (), active between th ...
, but left the King of Dian as the local ruler.
The
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
(205 BC–AD 220), seeking control over the
Southern Silk Road running to Burma and India, brought small parts of Yunnan into China's orbit, though subsequent dynasties could do little to tame what was then a remote and wild
border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
land. During the
Sui dynasty (581–618), two military expeditions were launched against the area, and it was renamed ''Kunzhou'' in Chinese sources.
Medieval China
Founded in 765, Kunming was known to the Chinese as ''Tuodong'' () city in the
Kingdom of Nanzhao
Nanzhao (, also spelled Nanchao, ) was a dynastic kingdom that flourished in what is now southern China and northern Southeast Asia during the 8th and 9th centuries. It was centered on present-day Yunnan in China.
History
Origins
Nanzha ...
(737–902) during the 8th and 9th centuries.
Tuodong later became part of the successor
Kingdom of Dali
The Dali Kingdom, also known as the Dali State (; Bai: Dablit Guaif), was a state situated in modern Yunnan province, China from 937 until 1253. In 1253, it was conquered by the Mongols but members of its former ruling dynasty continued to a ...
(937–1253). The possession of Tuodong changed hands when the city came under the control of the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fift ...
invasion of the southwest in 1252–1253. During the reign of provincial governor
Ajall Shams al-Din Omar, a "Chinese Style" city named Zhongjing Chen was founded where modern Kunming is today. Shams al-Din ordered the construction of Buddhist temple, a Confucian temple, and two mosques in the city. The Confucian temple, doubling as a school, was the first of its kind in Yunnan, attracting students from minority groups across the province. Coupled with his promotion of Confucian ceremonies and customs, Shams al-Din has been largely credited with the
sinicization
Sinicization, sinofication, sinification, or sinonization (from the prefix , 'Chinese, relating to China') is the process by which non-Chinese societies come under the influence of Chinese culture, particularly the language, societal norms, cul ...
of the region. The city grew as a trading center between the southwest and the rest of China. It is considered by scholars to have been the city of Yachi Fu (Duck Pond Town) where people had used
cowries
Cowrie or cowry () is the common name for a group of small to large sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries.
The term '' porcelain'' derives from the old Italian term for the cowrie shell (''porcellana' ...
as cash and ate their meat raw, as described by the 13th-century Venetian traveler
Marco Polo.
Ming and Qing dynasties

In the 14th century, Kunming was retaken from Khan Mongolian control when the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
defeated the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fift ...
, later building a
wall
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or, is decorative. There are many kinds of walls, including:
* Walls in buildings that form a fundamental part of the sup ...
surrounding present-day Kunming. 300 years later, Ming General
Wu Sangui defected to Manchu invaders and held the city until his death in 1678, long after the rest of China had fallen under
Manchu rule. During the beginning of Qing rule, the entirety of Yunnan and Guizhou were ruled from Kunming and Wu. During the
Revolt of the Three Feudatories
The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, () also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion in China lasting from 1673 to 1681, during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722) of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). The revolt was ...
, the seat of Wu's newly declared Zhou dynasty was moved to Hengzhou, Hunan. Later in 1678 when Wu died, his grandson
Wu Shifan
Wu Shifan ( Chinese: 吳世璠), 1663–1681, was the grandson of Wu Sangui and his successor as emperor of the Zhou dynasty during the Revolt of the Three Feudatories. He was declared the ''taisun'' (太孫, lit. 'Imperial Eldest Grandson'). He w ...
resisted the Qing for two more months before committing suicide, thereby reverting control of the city back into Qing hands. During the Ming and
Qing dynasties, it was the seat of the
superior prefecture of Yunnan.
The area was first dubbed Kunming in the period towards the decline of the Yuan dynasty and later still in 1832, the beginnings of a real city were acknowledged within the city walls and significant structures within their confines. Founding of the city can, therefore be said to have been a predominantly 19th century affair. It was also in this century that the city grew to become the major market and transport centre for the region. Many of the city's inhabitants were displaced as a result of the
1833 Kunming earthquake.
The rebel leader
Du Wenxiu
Du Wenxiu (, Xiao'erjing: ) (1823 to 1872) was the Chinese Muslim leader of the Panthay Rebellion, an anti-Qing revolt in China during the Qing dynasty. Du had ethnic Hui ancestry.
Early life and background
Born in Yongchang (now Baoshan, Y ...
, the Muslim Han Sultan of
Dali, attacked and besieged the city several times between 1858 and 1868. Many of the city's wealth did not survived the 1856
Panthay Rebellion
The Panthay Rebellion (1856–1873), also known as the Du Wenxiu Rebellion (Tu Wen-hsiu Rebellion), was a rebellion of the Muslim Hui people and other (Muslim as well as non-Muslim) ethnic groups against the Manchu-led Qing dynasty in southwe ...
, when most of the Buddhist sites in the capital were bad damaged, converted to mosques or razed. Decades later, Kunming began to be influenced by the West, especially from the
French Empire. In the 1890s, an uprising against working conditions on the Kunming–Haiphong rail line saw many laborers executed after France shipped in weapons to suppress the revolt. The meter-gauge rail line, only completed by around 1911, was designed by the French so that they could tap Yunnan's mineral resources for their colonies in Indochina.
Kunming was a
communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
center
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
*Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentrici ...
in early times and a junction of two major trading routes, one westward via
Dali and
Tengchong County
Tengchong () is a county-level city of Baoshan City, western Yunnan province, People's Republic of China. It is well known for its volcanic activity. The city is named after the town of Tengchong which serves as its political center, previously kn ...
into
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, the other southward through
Mengzi County
Mengzi (; Hani: ) is a city in the southeast of Yunnan Province, China. Administratively, it is a county-level city and the prefectural capital of the Honghe Hani and Yi Autonomous Prefecture, located about southeast from Kunming, and 400 kilome ...
to the
Red River in
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
. Eastward, a difficult mountain route led to
Guiyang in Guizhou province and thence to
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
province. To the northeast was a well-established trade trail to
Yibin
Yibin (; Sichuanese Pinyin: nyi2bin1; Sichuanese pronunciation: ) is a prefecture-level city in the southeastern part of Sichuan province, China, located at the junction of the Min and Yangtze Rivers. Its population was 4,588,804 inhabitants, a ...
in Sichuan province on the
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
. But these trails were all extremely difficult, passable only by mule trains or pack-carrying porters.

After Qing dynasty
"In the late 1800s, the French started to build the Kunming-Haiphong railway for trade and shipping of weapons".
Kunming reverted to county status in 1912, under the name Kunming, and became a municipality in 1935. The opening of the Kunming area began in earnest with the completion in 1906–1910 of the
Yunnan-Vietnam Railway to
Haiphong
Haiphong ( vi, Hải Phòng, ), or Hải Phòng, is a major industrial city and the third-largest in Vietnam. Hai Phong is also the center of technology, economy, culture, medicine, education, science and trade in the Red River delta.
Haiphong wa ...
in north
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
(part of
French Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
).
Kunming became a
treaty port
Treaty ports (; ja, 条約港) were the port cities in China and Japan that were opened to foreign trade mainly by the unequal treaties forced upon them by Western powers, as well as cities in Korea opened up similarly by the Japanese Empire.
...
opening to foreign trade in 1908 and soon became a commercial center.
A
university
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States ...
was set up in 1922. In the 1930s the first highways were built, linking Kunming with
Chongqing in Sichuan and
Guiyang in Guizhou to the east.
The local warlord General
Tang Jiyao established the
Wujiaba Aerodrome in 1922; an additional 23 airports would be established in Yunnan from 1922 to 1929.

Second World War (1937-1945)
Kunming was transformed into a modern city as a result of fighting of the
Second Sino-Japanese War/World War II in 1937 with the outbreak of the
Battle of Shanghai
The Battle of Shanghai () was the first of the twenty-two major engagements fought between the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Republic of China (ROC) and the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) of the Empire of Japan
The also ...
,
Nanking
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
and
Taiyuan, forcing a great movement of refugees from the north and eastern coastal regions of China, bringing much commerce and industry into the southwest of China, including Kunming. They brought with them dismantled industrial plants, which were then re-erected beyond the range of Japanese bombers. In addition, a number of
universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, ...
and institutes of higher education were evacuated there. The increased trade and expertise quickly established Kunming as an industrial and manufacturing base for the wartime government in
Chongqing.
As the battles of Shanghai, Taiyuan and
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
were lost by the end of 1937, and with the
Battle of Wuhan falling into Japanese occupation by the end of 1938, many more of China's military forces and civilians retreated to cities outside the reach of the Japanese military ground forces a year prior to the outbreak of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
in Europe in 1939, including the relocation of the
Chinese Air Force Academy from
Jianqiao Airbase to Kunming's
Wujiaba Airbase, where the airfield was vastly expanded, becoming the new training hub for the battered but regrouped
Chinese Air Force
The People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF; ), also known as the Chinese Air Force (中国空军) or the People's Air Force (人民空军), is an aerial service branch of the People's Liberation Army, the regular armed forces of the Peo ...
in which Lieutenant General
Claire Lee Chennault
Claire Lee Chennault (September 6, 1893 – July 27, 1958) was an American military aviator best known for his leadership of the "Flying Tigers" and the Chinese Air Force in World War II.
Chennault was a fierce advocate of "pursuit" or fighte ...
took command of cadet training duties in the summer of 1938. The Chinese Air Force command established the 41st Pursuit Squadron based in Kunming, also known as the French Volunteer Group squadron in June 1938, and with them they brought
Dewoitine D.510 fighters, with the intention of securing the sale of the planes to the Chinese Air Force; the French participated in some combat engagements against Japanese raids, including dogfights against Mitsubishi A5M fighters with Chinese Curtiss BF2C Goshawk, ''Hawk III'' fighters over Nanchang, but after several setbacks, including a fighter pilot ''Killed in action, KIA'', the group was disbanded in October 1938.
Although the Empire of Japan was focusing on ending the Chinese ''war of resistance'' at the Bombing of Chongqing, Battle of Chonqing and Chengdu, Kunming was not out of the reach of Japanese air raids, and faced attacks by Imperial Japanese Army Air Service, IJAAF and Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service, IJNAF bombers; military assets and infrastructure were under regular attack, while the Development of Chinese Nationalist air force (1937–1945), RoCAF 18th Fighter Squadron and units of the Air Force Academy at Wujiaba were tasked with aerial defense of Kunming. The city of Kunming was prepared as an alternate National Redoubt in case the temporary capital in
Chongqing fell, with an elaborate system of caves to serve as offices, barracks and factories, but never utilised. Kunming was to have served again in this role during the ensuing Chinese Civil War, but the Kuomintang, Nationalist garrison there switched sides and joined the Communists. Instead Taiwan would become the last redoubt and home of the Republic of China government; a role it fulfills to this day.
When the city of Nanning fell to the Japanese during the Battle of South Guangxi, China's sea-access was cut off, however, the Chinese victory at the Battle of Kunlun Pass kept the Burma Road open. When the Japanese began occupying French Indochina in 1940, the Burma Road that linked Kunming and the outside-world with unoccupied China grew increasingly vital as much of the essential support and materials were imported through
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, and the start of the Pacific War in December 1941, Kunming acted as an Allied military command center, which grouped the Chinese, American, British and French forces together for operations in Southeast Asia. Kunming became the northern and easternmost terminus of the vital war-supply line into China known as "''The Hump. The Office of Strategic Services' Service Unit Detachment 101 (predecessor to the 1st Special Forces Group) was also headquartered in Kunming and whose mission was to divert and disrupt Japanese combat operations in Burma.

Kunming was increasingly targeted by the IJAAF when the Burma Road was lost to the Japanese, and the 1st American Volunteer Group, known as the "Flying Tigers", based in Kunming, and tasked with defense of ''The Hump'' supply-line that stretched over the Himalayas between the British bases in India to port-of-entry Kunming against Japanese aerial interceptions; China's primary lifeline to the outside world, which had included the Burma Road and the Ledo Road, all with Kunming as the northern terminus.
Industry became important in Kunming during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. The large state-owned Central Machine Works was transferred there from
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
, while the manufacture of electrical products, copper, cement, steel, paper, and textiles expanded.
After World War II
Until 1952, Kunming was a walled city. The city government in 1952 ordered hundreds of young people to tear down the wall and use its bricks to make a new road running north–south. To show its appreciation for the young people that demolished the east wall, the city government named the new street after them. Their existence still echoes today in place names like Xiao Ximen () and Beimen Jie (). There are also less obvious connections to the wall, such as Qingnian Lu (), which was once Kunming's east wall.
After 1949, Kunming developed rapidly into an Metropolitan Regions of China, industrial metropolis with the construction of large iron and steel and chemical complexes, along with
Chongqing, Chengdu and
Guiyang in the Southwest China, southwest. A Yunnan Institute for Nationalities, Minorities' Institute was set up in the 1950s to promote mutual understanding and access to university education among Yunnan's multiethnic population. The city consolidated its position as a supply depot during the Vietnam War and subsequent Sino-Vietnamese War, border clashes. Until Mao Zedong's death, Kunming was still generally thought in much of the rest of the country as a remote frontier settlement and so it acted as a place up to then for the government to exile people who had fallen politically out of favor, especially during the Cultural Revolution.
In 1957, Kunming's rail link to Hanoi was re-opened (after being cut during World War II). It was cut again in 1979.

Since the Economic reform in the People's Republic of China, economic reforms of the mid-1980s, Kunming has enjoyed increased Tourism in China, tourism and Economy of China, foreign investment, for instance investors from
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
trace their ancestries back to Yunnan. Several Thai Chinese banks have offices in Kunming, for example, Kasikorn Bank and Krung Thai Bank. Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn of Thailand has visited Kunming many times to study Chinese culture and promote friendly relations.
Rail link to Vietnam re-opened again in 1996.
In July 2005, the second Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) Summit was held in Kunming, with government leaders from China, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam participating. There, China agreed to lend its neighbors more than $1 billion for a series of projects. China was then promoting GMS cooperation as a first step toward building an eventual China-ASEAN Free Trade Area.
Infrastructure improvements have been underway to improve links between Kunming and Southeast Asia in time for the 2010 China-ASEAN Free Trade Area. The FTA is expected to make Kunming a trade and financial center for Southeast Asia. In addition to physical improvements to enhance Kunming's trade with Southeast Asia, the central and provincial governments have made financial preparations to assist the city's emergence. At the end of 2004, the central government approved Kunming to be one of the 18 mainland cities in which foreign banks could conduct business in renminbi.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the city center was rebuilt, with Swiss help, in its current 'modern' style to impress visitors attending the 1999 World Horticultural Exposition. It was primarily during 1997 and 1998 that much of the city's roads, bridges and high rises were built.

The World Horticultural Expo was widely regarded as a public relations success for Kunming. Today the after-effects of the Expo are apparent in more than just the physical improvements to the city—it was the Expo that made the outside world take notice of Kunming, which was relatively unknown at the time.
In July 2006, talks at the ASEAN Regional Forum, China, Bangladesh and Myanmar (Burma) agreed to construct a highway from Kunming to Chittagong through Mandalay for trade and development.
On 1 March 2014, 29 people were killed, and more than 130 were injured at Kunming Railway Station in 2014 Kunming attack, a terrorist attack.
Geography




Kunming is located in east-central
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
province. It is located between north latitude 24°23' and 26°22' N, and east longitude 102°10' and 103°40' E, with a total area of . Its widest stretch from the east to the west amounts to and its largest expansion from the north to the south amounts to .
Situated in a fertile lake basin on the northern shore of the
Lake Dian
Dianchi Lake (), also known as Lake Dian and Kunming Lake (), is a large lake located on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau close to Kunming, Yunnan, China. Its nickname is the "Sparkling Pearl Embedded in a Highland" () and it was the model for the Ku ...
and surrounded by mountains to the north, west, and east, Kunming has always played a pivotal role in the Communications in the People's Republic of China, communications of southwestern China. Lake Dian, known as "the Pearl of the Plateau", is the largest lake in Yunnan and the sixth largest fresh water lake in China. It has an area of approximately . Kunming's highest point is Mazong Ridge of the Jiaozi Mountain in Luquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County, Luquan with an elevation of , and its lowest point is the joint of the Xiao River and the Jinsha River in Dongchuan District, with an elevation of . Its downtown area is above sea level.
About southeast of the city centre is the Stone Forest in Shilin County, a karst formation developed as a tourist attraction consisting of rock caves, arches, and pavilions. It is part of the larger karst-based landscape of the area.
Climate
Located at an elevation of on the
Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau
The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau () is a highland region located in southwest China. The region is primarily spread over the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou. In the southwest, the Yungui is a true plateau with relatively flatter ...
with low latitude and high elevation, Kunming has one of the mildest climates in China, characterized by short, cool dry winters with mild days and crisp nights, and long, balmy and humid summers. With its perpetual spring-like weather which provides the ideal climate for plants and flowers, Kunming is known as the "City of Eternal Spring". The weather has seldom reached high temperatures in summer, only exceeding on a handful of occasions. However, freak snowfalls occur in occasional winters. Controlled by a subtropical highland climate (Köppen climate classification, Köppen ''Cwb''), the monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from in January to in June, with daily high temperatures reaching their lowest point and peak in December and May, respectively. The city is covered with blossoms and lush vegetation all-year round. The period from May to October is the monsoon season and the rest of the year is dry. The city has an annual mean temperature of , rainfall of (nearly three-fifths occurring from June to August) and a frost-free period of 230 days. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 30% in July to 69 percent in February and March, the city receives 2,198 hours of bright sunshine annually. Extreme temperatures in the city have ranged from .
Natural resources
Mineral resources include phosphorus, salt, magnesium, titanium, coal, quartz sand, clay, silica, copper. Phosphorus and salt mines are the most plentiful. Kunyang Phosphorus Mine is one of the three major phosphorus mines in the country. Rock salt reserves are and mirabilite reserves are . Dongchuan is a major copper production base.
Proven reserves of Coal bed gas is about , equal to of standard coal. Geothermal resources are widely distributed.
Environment and horticulture
Kunming has of lawns, trees and flowers, averaging per capita and a green space rate of 21.7 percent. The city's smoke control area is and noise control area .
Kunming is a significant horticultural center in China, providing products such as grain, wheat, horsebeans, corn, potato and fruit such as peaches, apples, oranges, grapes and chestnuts. Kunming is world-famous for its flowers and flower-growing exports. More than 400 types of flowers are commonly grown in Kunming. The camellia, Yulan magnolia, azalea, fairy primrose, lily and orchid are known as the six famous flowers of the city.
The camellia was confirmed by the Municipality of Kunming as its city flower in 1983.
The Kunming city government plans to create an environmental trial court to deal with environment-related lawsuits. It is to be part of the city's intermediate Local people's court, people's court and will have jurisdiction over appeals by companies that have been found guilty of violating environmental laws in cities throughout Yunnan.
Demographics
Of the more than five million people registered as residents in Kunming in 2006, around four million are Han Chinese, Han. The Yi people are the most prominent minority in the city, with more than 400,000 residents. The least-represented ethnic minority in Kunming were the 75 Dulong people living in the city.
Registered ethnic populations of Kunming :
* Han Chinese, Han: 4,383,500
* Yi people, Yi: 400,200
* Hui people, Hui: 149,000
* Bai people, Bai: 73,200
* Miao people, Miao: 46,100
* Lisu people, Lisu: 17,700
* Zhuang people, Zhuang: 14,000
* Dai people, Dai: 13,200
* Hani people, Hani: 11,000
* Nakhi, Naxi: 8,400
*
Manchu: 4,800
* Buyei: 3,400
* Mongols, Mongol: 2,500
* Lahu people, Lahu: 1,700
* Tibetan people, Tibetan: 1,500
* Yao people, Yao: 1,100
* Jingpo people, Jingpo: 1,100
* Va people, Va: 1,000
* Blang people, Blang: 441
* Primi: 421
* Sui people, Sui: 294
* Achang: 263
* Nu people, Nu: 156
* Jino: 135
* Derung: 75
Cityscape
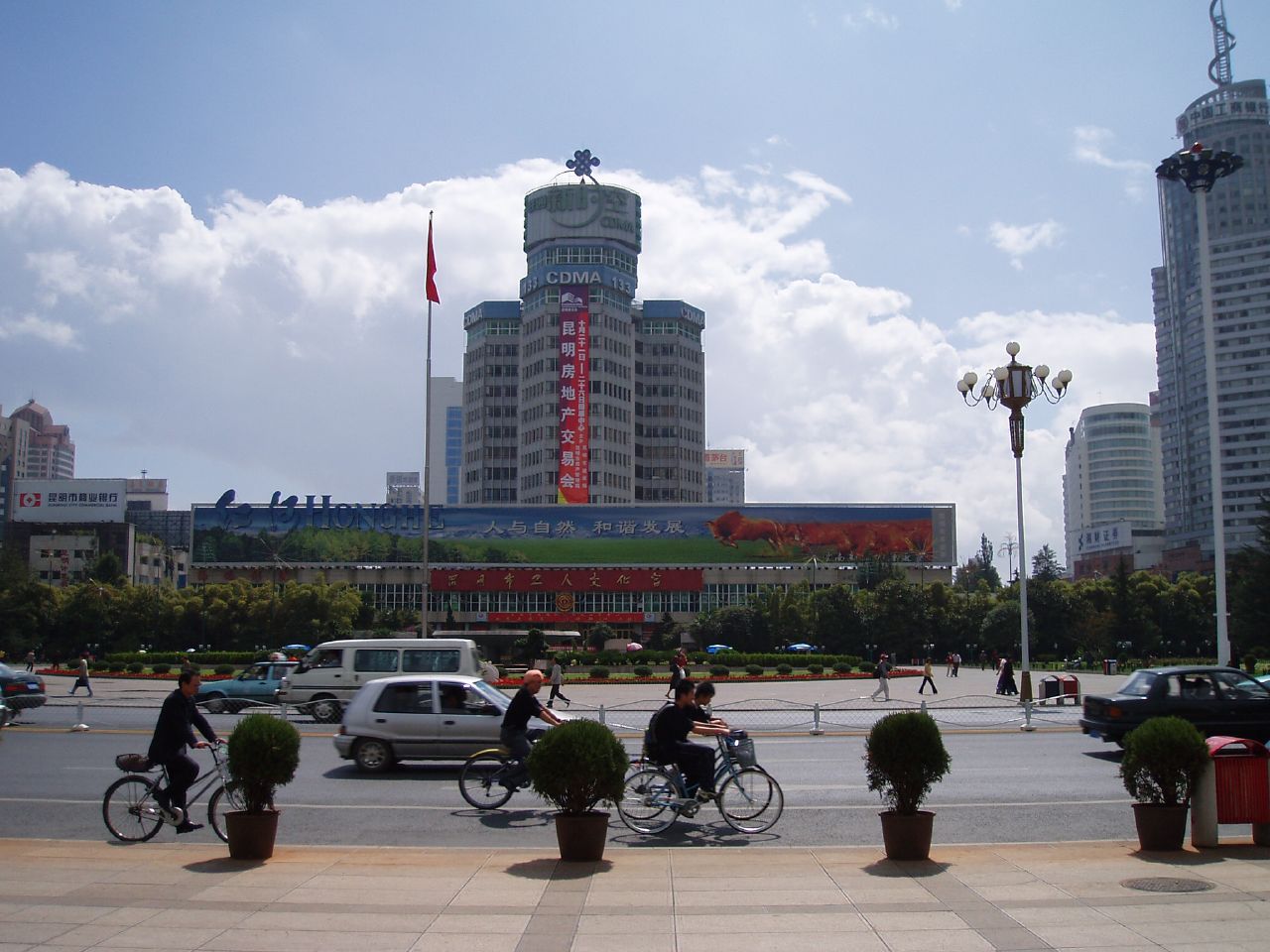

The city center has three major squares and five major streets: Jinma Biji Square, Nanping Square and Dongfeng Square along with Nanping Jie, Jinbi Lu, Renmin Lu, Zhengyi Lu and Jingxin Jie. Qingnian Lu, Zhengyi Lu, and Renmin Lu are the main commercial areas in Kunming; the most popular pedestrian streets are Nanping Jie, Jingxing Birds-Flowers' Market, and Jinma Biji Fang.
Kunming's public focus is the huge square outside the now-demolished Workers' Cultural Hall at the Beijing Lu-Dongfeng Lu intersection, where in the mornings there are crowds doing taijiquan and playing badminton. Weekend amateur theatre are also performed in the square. Rapidly being modernized, the city's true center is west of the square across the adjacent Panlong River (now more of a canal), outside the Kunming Department Store at the Nanping Lu/Zhengyi Lu crossroads, a densely crowded shopping precinct packed with clothing and electronics stores. The river receives sewage and wastewater from surrounding pipes. Surrounding the area are plenty of new high-rises.
The center is an area of importance to Kunming's Hui people, Hui population, with Shuncheng Jie, one of the last old streets in the center of the city, previously forming a Muslim quarter. Until shortly before 2005, this street was full of wind-dried beef and mutton carcasses, pitta bread and raisin sellers, and huge woks of roasting coffee beans being stirred with shovels. Under Kunming's rapid modernisation, however, the street has been demolished to make way for apartments and shopping centers. Rising behind a supermarket one block north off Zhengyi Lu, Nancheng Qingzhen Si is the city's new mosque, its green dome and chevron-patterned minaret visible from afar and built on the site of an earlier
Qing edifice.
Running west off Zhengyi Jie just past the mosque, Jingxing Jie leads into one of the more bizarre corners of the city, with Kunming's huge Bird and Flower Market convening daily in the streets connecting it with the northerly, parallel Guanghua Jie. The market offers many plants such as orchids that have been collected and farmed across the province. In the small grounds of Wen Miao, a now vanished Confucian temple off the western end of Changchun Lu, there is an avenue of pines, an ancient pond and pavilion, and beds of bamboo, azaleas and potted palms.
Jinbi Lu runs roughly parallel to and south of Dongfeng Lu, reached from Beijing Lu. Two large Chinese pagodas rise in the vicinity, each a solid thirteen stories of whitewashed brick crowned with four iron cockerels. The West Pagoda was built between 824 and 859, during the Tang dynasty; its original counterpart, the East Pagoda, was built at the same time, but was destroyed by 1833 Kunming earthquake, an earthquake in 1833 and rebuilt in the same Tang style in 1882. South down Dongsi Jie, past another mosque, the entrance to the Eastern and Western Pagodas, West Pagoda is along a narrow lane on the right. In the tiny surrounding courtyard, sociable idlers while away sunny afternoons playing cards and sipping tea in the peaceful, ramshackle surroundings. The Eastern and Western Pagodas, East Pagoda is a more cosmetic, slightly tilted duplicate standing in an ornamental garden a few minutes' walk east on Shulin Jie. The temples associated with both pagodas are closed to the public.

Parks

Cuihu Park (Green Lake Park) is one of Kunming's major parks and is predominately a lake surrounded by greenery. Located in the west side of the park is the statue of one of Yunnan's most famous patriots—Nie Er, the composer of China's March of the Volunteers, national anthem. Now it is open to public for free.
Daguan Park lies on Dian Chi in Kunming's southwestern limits. Originally laid out by the Kangxi Emperor in the Qing dynasty, it has been modified over the years to include a noisy funfair, food stalls and emporiums, and is a favourite haunt of Kunming's youth.
Kunming's zoo, founded in 1950, is adjoined to Yuantong Park. The zoo houses 5,000 animals from 140 species and receives 3 million visitors a year.
Other parks in Kunming include Heilongtan (Kunming), Black Dragon Pool, and the Kunming Botanical Gardens in the north, and Wenmiao Tea Garden in Wuhua District.
Landmarks
The "World Horti-Expo Garden, Garden of the World Horticultural Exposition", located in the northern suburbs of Kunming, is from central Kunming. From 1 May to 31 October 1999, Kunming held the 1999 World Horticulture Exposition, with the theme of "Man and Nature—Marching Toward the 21st Century".
The "Golden Hall Scenic Zone", located on the Mingfeng Hill in the northern suburbs of Kunming, is from central Kunming. Constructed in 1602 (the 30th year of the Wanli Emperor, Wanli reign period of the Ming dynasty), all of its beams, pillars, arches, doors, windows, tiles, Buddhist statues, and horizontal inscribed boards are made of copper, weighing more than 200 tons. It is the largest copper building in China.
Notable museums in Kunming:
* Yunnan Provincial Museum
* Kunming City Museum (redeveloped in 2014)
* Kunming Natural History Museum of Zoology (opened in November 2006)
* Yunnan Ethnology Museum (opened 1995)

Yuantong Si is Kunming's major Buddhist temple. It is Kunming's largest and most famous temple with the original structure being first constructed more than 1,200 years ago during the Tang dynasty. The temple sits in a depression on the southern side of Yuantong Park. Northwest about from the city center is the Qiongzhu Si (Bamboo Temple) built in 639 and rebuilt in 1422 to 1428. Numerous Buddhist temples line the road to the Dragon Gate () in the Western Mountains.
Administrative divisions
The prefecture-level city of Kunming has jurisdiction over 14 subdivisions; seven districts, one county-level city, three counties and three autonomous counties.
Kunming is bounded by Qujing City to the east, Honghe Hani and Yi Autonomous Prefecture to the southeast and Yuxi City to the southwest, Chuxiong Yi Autonomous Prefecture to the west and Zhaotong City to the northeast. Kunming also borders with Panzhihua prefecture level city and Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture of Sichuan province.
Kunming plans to add two new districts to its existing four urban districts (Panlong, Wuhua, Guandu, Xishan) over the next few years.
Society and culture
Leisure and entertainment
Within Kunming, the entertainment district has its focus around Kundu Square, with many cinemas, bars, clubs and restaurants. Food aside, one feature of less formal Yunnanese cuisine, Yunnanese restaurants is that they often have a communal bamboo water pipe and tobacco for their customers. There are plenty of student bars and clubs. The city has several operatic troupes and indigenous entertainments which include ''huadeng'', a lantern dance. Although indoor performances are lacking, there are often informal shows at the weekend outside the Workers' Cultural Hall and in Cuihu Park. There are similar shows at the Yunnan Arts Theater on Dongfeng Xi Lu. Kunming's main cinema house is on the south side of the Dongfeng Lu/Zhengyi Lu intersection. The other main multiplex, the XJS, at the junction of Wenlin Jie and Dongfeng Xi Lu.
Language
The Kunming dialect is very similar to that of Sichuan and Guizhou but uses the third tone much less than standard Chinese. Many terms are used only in Kunming dialect, such as "" meaning 'terrific'.
The pronunciations of certain Chinese characters are very different from Mandarin Chinese. For example, " (fish)" would be pronounced as "yi" in Kunming dialect instead of "yu" in Mandarin Chinese; " (street)" would be pronounced as "gai" instead of "jie".
When someone speaks Mandarin Chinese with a strong Kunming accent, it'll be called Mapu (), short for Majie (, a place in Kunming) Mandarin Chinese.
The Kunming Dialect is slowly dying due to it being 'informal' and is being replaced by Mandarin Chinese. Sometimes this is called dirt language or slum language (土话)
Tourism

Kunming attracts domestic and foreign tourists year-round. At the center of Yunnan and as its capital, Kunming is also a transport hub for tourists heading to other parts of Yunnan such as Dali, Yunnan, Dali, Lijiang City, Lijiang and Shangri-La County, Shangrila.
Conference and exhibition venues in Kunming include the Kunming International Convention and Exhibition Center and the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Hall.
Kingdom of the Little People, a theme park featuring performers with dwarfism, is also located near Kunming.
Other famous attractions include Stone Forest and Yunnan's Ethnic Village.
Sports
Every year, many Chinese and international athletes come to Kunming for high-altitude training. The city has been China's national high-elevation training base for more than 30 years. There are two major training complexes, Hongta Sports Center and Haigeng National Training Center.
Hongta Sports Center was built in 2000 by Hongta (Red Pagoda) cigarette company, at a cost of US$58 million. Located near Haigeng Park, the complex is mostly used by professional athletes, but also acts as a sports club for the general public. Every weekend, it hosts amateur football matches. Aside from about 10 football pitches, including one surrounded by a running track, Hongta also has a swimming pool, a badminton gymnasium, tennis courts and a basketball court. It also has one of China's few ice hockey rinks, and a workout room with treadmills and weightlifting machines. There are also game rooms for air hockey; also pool tables and a basement bowling alley. The complex comes complete with a 101-room hotel and restaurant.
Haigeng National Training Center is located ten minutes away from Hongta on Dianchi (Lake Dian) near Kunming's award-winning Lakeview Golf Club and new condominium developments. This complex dates from the late 1970s and was built by the government specifically to specialize in high-altitude training.
Golf
Golf is a major attraction in Kunming. There are four golf courses within an hour's drive of downtown. For the last six years , Spring City Golf and Lake Resort in nearby Yiliang County has reigned as the best golf course in China and Hong Kong according to ''US Golf Digest''. In 2004, it was named Asia's best golf resort by ''Asian Golf Monthly''.
[Spring City Blooming](_blank)
It hosts the Kunming Leg of the Omega China Tour.
Kunming has attracted foreign investment in golf course development. "Spring City" Golf Resort is a US$600 million project that began as an investment led by Singapore's Keppel Land Group in 1992. Jack Nicklaus and course designer Robert Trent Jones, Jr designed the two courses.
Sport facilities
Major sports facilities include:
* Tuodong Sports Center, a multi-purpose venue
* Golf: Spring City Golf and Lake Resort, its 'Mountain Course' was designed by Jack Nicklaus
* Lakeview Golf Villa
* Cuihu Park tennis courts
* Kunming Municipal Athletic Center
* Kunming Gymnasium
* Yunnan Provincial Stadium, home to Hongta Yunnan Football Club
* Wuhua District Stadium
Economy

Kunming has three economic advantages over other cities in southwest China: significant natural resources, a large consumer market and a mild climate. Due to its position at the center of Yunnan, one of China's largest producers of agricultural products, minerals and hydroelectricity, Kunming is the main commercial hub for most of the province's resources.
Kunming's chief industries are copper, lead and zinc production. Its iron and steel industry has been expanded. Salt and phosphate mines around Kunming are some of the largest in China. Yunnan Copper Company Limited, based in Kunming, is one of Yunnan's largest mining corporations. From the late 1970s, Kunming's main industries also came to include food and tobacco processing and the manufacture of construction equipment and machines.
In May 1995, the State Council of the People's Republic of China, State Council approved Kunming as an Open City. By the end of 1995, the city had approved 929 overseas-funded enterprises with a total investment of $2.3 billion including $1.1 billion of foreign capital. More than 40 projects each had an investment of more than $9 million.
Kunming is a center of engineering and the manufacture of machine tools, electrical machinery, electrical equipment, equipment and automobiles (including heavy goods vehicles). It has a chemical industry, and plastics, cement works and textile factories. Its processing plants, which include tanneries, woodworking and papermaking factories, use Agriculture in China, local agricultural products. In 1997, Yunnan Tire Co. opened a tire plant in Kunming, with a capacity to produce two million tires per year.
Development zones
Kunming has two major development zones, Kunming High-tech Industrial Development Zone (biological medicine, new materials, electronic information, photoelectron, agriculture) and Kunming Economic and Technology Development Zone (mechanical equipment production, biological science and food industry, information industry, software).
Industrial parks
There are 30 key industrial parks promulgated and recognized by National Development and Reform Commission in Yunnan Province.
The largest include:
* Chenggong Industrial Park
* Anning Industrial Park
* Songming Yanglin Industrial Development Zone
* Dongchuan Special Industrial Park
* Xundian Special Industrial Park
* Kunming Haikou Industrial Park.
Companies
, Kunming is home to 65 of the Top 100 Enterprises in Yunnan Province. The top 100 enterprises were based on their revenues for 2007. Hongta Group, with revenues of some Renminbi, RMB39.88 billion for 2007 topped the list. The tobacco sector remains the largest sector in the province.
Flower industry
Yunnan has developed into the largest flower export base in Asia, with many Dutch experts having transferred technology to the area. The Dounan Flower Market, located in suburban Kunming, is the largest in China with daily sales of 2.5 million yuan (US$300,000) from the 2 million sprays of flowers (). The provincial government agency, the Yunnan Flower Association, regulates the industry.
Logistics
Kunming East Station is at present Yunnan province's only container handling depot, with direct links to only three provinces; Guangdong, Guizhou and Sichuan. It also has direct access to the metropolitan district of
Chongqing.
The Jiaying Depot is connected with the new system of highways built linking Yunnan to the increasingly important markets of
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, facilitating cheap Chinese exports to the region and granting resource-poor China greater access to the region's massive raw material resources. Yunnan has thereby become a progressively important area in the Southwestern China, Southwest's rail logistics both in terms of national and international logistics.
Solar energy

In July 2008, Kunming began to implement a program to transform the city's solar energy industry into a US$8.8 billion industrial base in China by 2013. Kunming receives an annual average sunshine of more than 2,400 hours. Each 1 kW PV system has the potential to generate 1500 kilowatt-hours of electricity a year from solar energy.
, the Kunming Economic Committee listed about 130 solar energy enterprises in the city. Of these, 118 enterprises produce solar lamps and solar water heaters, with a combined total production value of about US$43.8 million, and 10 enterprises are engaged in solar photovoltaic cells manufacturing, with a total production value of about US$51.2 million.
Suntech Power announced in December 2008 that it was jointly constructing a solar energy project with Yunnan Provincial Power Investment and other investors. The 1MW first-phase of the Shilin Yi Autonomous County, Shilin 66MW on-grid solar power station began generating power on 28 December 2009. The initial phase of the 66MW project was originally scheduled to start production in first half of 2010 while the 20MW second phase and 36 MW third phase were under construction.
Transport

Kunming is situated on the
Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau
The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau () is a highland region located in southwest China. The region is primarily spread over the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou. In the southwest, the Yungui is a true plateau with relatively flatter ...
. Rail and air are the main two methods to travel to or from Kunming from outside Yunnan.
Air transport
Kunming has air connections with several Chinese and
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
n cities. Kunming is served by
Kunming Changshui International Airport
Kunming Changshui International Airport is the primary airport serving Kunming, the capital of Yunnan Province, China. The airport is located northeast of the city center in a graded mountainous area about above sea level. The airport opene ...
(KMG), which opened in June 2012, replacing the older Kunming Wujiaba International Airport, international airport, which was located southeast of central Kunming.
The now defunct Yunnan Airlines was headquartered in Kunming until it was acquired by China Eastern Airlines. China Southwest Airlines used to operate routes to and from Kunming, until it was merged with Air China.
Lucky Air is a budget airline based in Kunming and operates scheduled services from Dali City, Yunnan, Dali to Kunming and Xishuangbanna, and plans to expand to other areas of China.
Currently, the longest non-stop flight from Kunming is to Paris, France, operated by China Eastern Airlines since 18 December 2014.
Highway

China National Highways China National Highway 108, 108, China National Highway 213, 213 and China National Highway 320, 320 intersect in Kunming. Highways link Kunming to
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
,
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and
Laos, and provide Yunnan province access to seaports of
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
.
Rail
Kunming is the main rail hub of Yunnan province. The Chengdu–Kunming railway from Sichuan, Shanghai–Kunming railway from Guizhou, and Nanning–Kunming railway from Guangxi converge in Kunming from the north, northeast and east. The Yunnan–Vietnam Railway runs from Kunming southeast to Hekou Yao Autonomous County, Hekou and Lao Cai on the Sino-Vietnamese border and then on to
Haiphong
Haiphong ( vi, Hải Phòng, ), or Hải Phòng, is a major industrial city and the third-largest in Vietnam. Hai Phong is also the center of technology, economy, culture, medicine, education, science and trade in the Red River delta.
Haiphong wa ...
The Kunming–Yuxi railway runs south to Yuxi, where a second rail line to Vietnam is being planned and built. To the west of Kunming, the Guangtong–Dali railway extends off the Chengdu–Kunming Line to Dali City, Dali (Xiaguan Town).
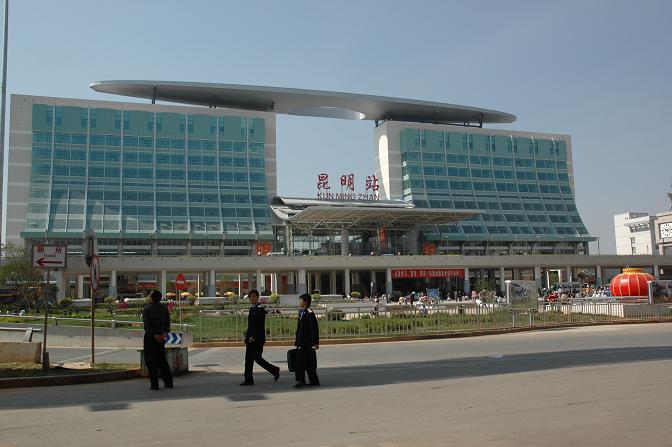
Kunming has three major railway stations:
*Kunming railway station is at the southern end of Beijing Xi Lu. Compared with the other railway station (North Railway Station), Kunming Railway Station services most of the "conventional" (not high-speed) trains to places to other provinces of China. Trains run north to Chengdu, southeast via Xingyi to Baise and Nanning in Guangxi, and east through Guizhou, via Liupanshui, Anshun,
Guiyang, into the rest of the country.
*Kunming South railway station, opened at the end of 2016, is located in Chenggong District, many miles southeast from the historical city center. It is the western terminal of the Shanghai–Kunming high-speed railway and the Guangzhou–Nanning–Kunming high-speed railway, and has high-speed service to destinations along these lines and elsewhere on the nation's high-speed network.
*Kunming North railway station (serviced by the No. 23 Bus) is on the heritage Kunming–Hai Phong Railway, which runs to Hekou Yao Autonomous County, Hekou and
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
. Most of the station has been converted into a museum. Due to the deterioration of the railway line, the long distance narrow-gauge service has been cancelled; however, , some local narrow gauge service still operates at Kunming North Railway Station, in particular two daily trains to Shizui () Station on the western outskirts of Kunming, and to Wangjiaying () east of the city.
As of 2017, railway development projects continue to proceed in the Kunming metropolitan area. In February 2017, the railway authorities announced that a connector between the new Kunming South railway station and the old Kunming railway station (also known as the Nanyao Station; ) will open by the end of 2017, making it possible for some high-speed train to serve Kunming railway station as well.
Urban rail plan
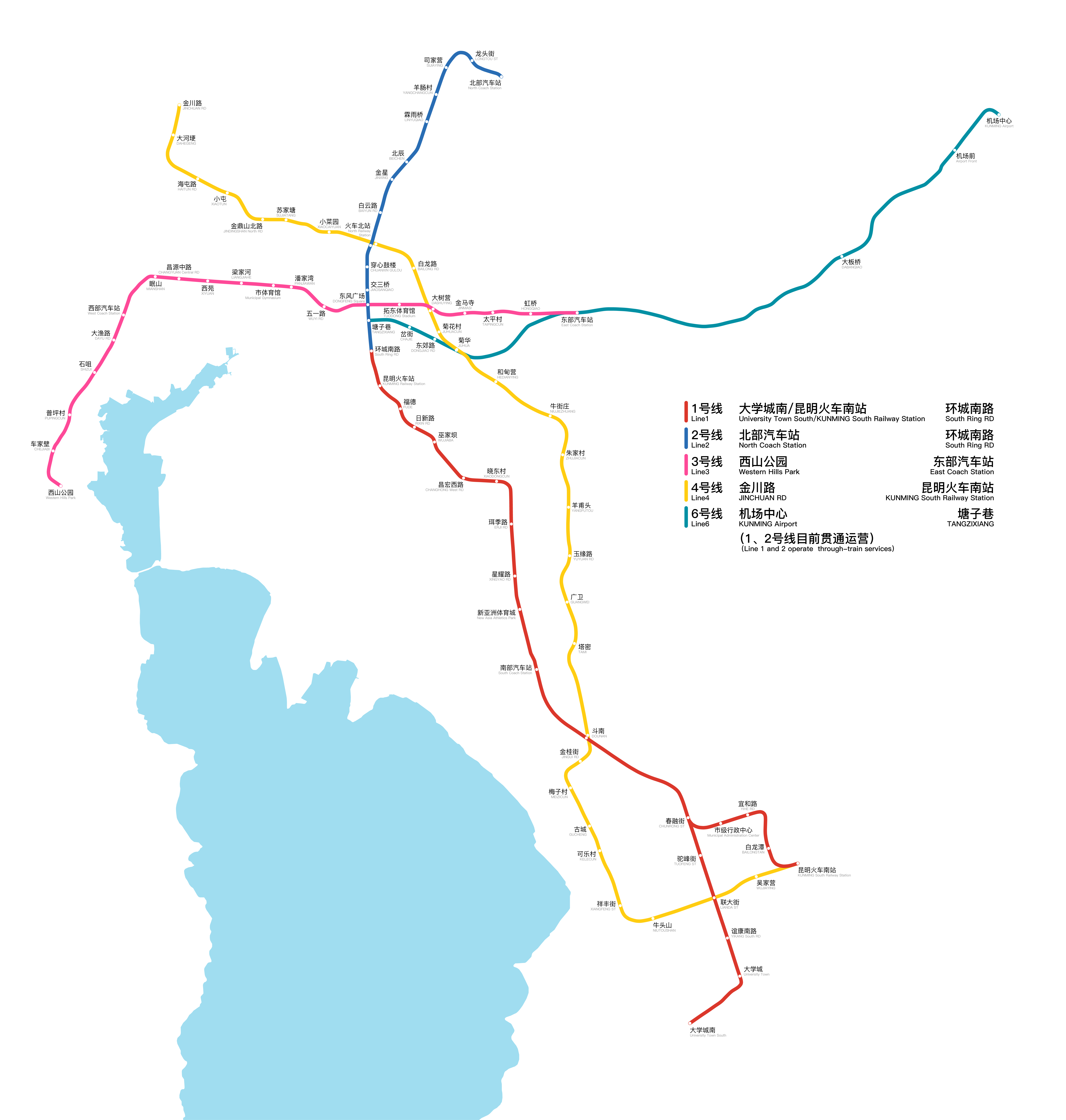
In May 2010, Kunming began construction on its first urban rail lines, line 1 and 2 of the Kunming Metro. An elevated test section had been under construction since 2009. Parts of lines 1 and 2 opened in April 2014. Construction on line 3 began in August 2010 and the Phase 1 was completed in 2018. The entire system consisting of 6 lines and covering a total of is estimated to be complete by 2018.
High-speed rail plan
Kunming will be the hub and terminus for the "Kunming–Singapore Railway, Pan Asia High Speed Network" using high-speed trains to connect China, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore.
Completed but under trial high-speed railways:
# Shanghai–Kunming High-Speed Railway, Kunming–Shanghai. The construction completed on 16 June 2016. It goes through 6 provincial capital cities: Shanghai, Hangzhou, Nanchang, Changsha, Guiyang and Kunming. The overall length is . As estimated it would take 3 hours from Shanghai to Nanchang, 2.5 hours from Hangzhou to Nanchang, 4 hours from Kunming to Changsha, 8 hours from Kunming to Hangzhou and 9 hours from Shanghai to Kunming. It is expected to start operating on 30 December 2016.
Construction is underway for the following high-speed railways:
# Shanghai–Kunming High-Speed Railway, Kunming–Shanghai. The speed will be .
# Kunming–Nanning. The speed will be . Later the speed may be improved to or 156 miles/h.
# Kunming–Vietnam via Honghe Prefecture.
# Kunming–Singapore Railway, Kunming–Singapore via
Laos,
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, and Malaysia.
Study or planning is being done for the following railways:
# Kunming–Chengdu. The speed will be .
# Kunming–
Chongqing. The speed will be .
# Intercity rail will connect three neighboring cities: Qujing, Chuxiong City, Chuxiong, and Yuxi. The line to Chuxiong will then be extended to Dali City, Dali. The speed will be .
# Kunming to Kolkata, India via Myanmar
# Kunming to Kyaukphyu, Myanmar.

Road and transit

Yunnan has built a comprehensive highway system with roads reaching almost all the major cities or towns in the region. Bus travel across the region is extensive. Buses head from Kunming to destinations such as Dali, Yunnan, Dali and Lijiang City, Lijiang several times a day.
There are four major long-distance bus stations in Kunming with the South Bus Station and Railway Square Bus Station being the most primary.
* South Bus Station faces the Kunming Railway Station in Beijing Xi Lu, with standard, luxury, express and sleeper buses departing for all over Yunnan and neighboring provinces.
* Railway Square Bus Station is smaller than SBS and the majority of the buses depart from the station are private-run. Usually no fixed schedules are available and buses will leave when they are full. There are standard and sleeper services to Dali, Jinghong and elsewhere in Yunnan.
Leaving China by road into
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and
Laos is also possible through the respective crossings at Hekou in southeastern Yunnan or Bian Mao Zhan in Xishuangbanna.
The Kunming–Bangkok Expressway is the first Expressways of China, expressway from China to Bangkok via Laos. The long Kunming–Bangkok Expressway begins at Kunming going down to Ban Houayxay in Laos; it then crosses the Mekong River to Chiangkhong in
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and eventually reaches Bangkok.
At the 14th Greater Mekong Subregion Ministerial Conference in July 2007, China, Laos and Thailand signed an agreement on the construction of a new bridge over the Mekong River to connect Chiangkhong in Thailand and Ban Houayxay in Laos, to the Kunming–Bangkok Highway. The completion of the new bridge over the Mekong River will help connect China's southeast provinces with Bangkok. With capital investments from both China and Thailand, the bridge is expected to be completed in 2011 and will be the last link in the highway system that winds through the Mekong River region.
Local transit
Public buses and taxis are the two main means of transport within the city. A metro system is currently under construction (see Kunming Metro).
Nearly two hundred public bus lines crisscross the city center, covering the whole prefecture.
Cycling is common, and many hotels around the Kunming Railway Station provide bicycle rental services.
Conscious of its growing traffic issues, the city is currently renovating a pedestrian-friendly city centre.
Central Kunming
The city hangs off two main thoroughfares: Beijing Lu forms the north–south axis, passing just east of the center as it runs for between the city's two trains stations; while Dongfeng Lu crosses it halfway along, divided into east (Dongfeng Dong Lu), middle (Dongfeng Zhong Lu) and west (Dongfeng Xi Lu) sections as it cuts right through the business center. The far end runs out of the city as Renmin Xi Lu, the first leg of the
Burma Road
The Burma Road () was a road linking Burma (now known as Myanmar) with southwest China. Its terminals were Kunming, Yunnan, and Lashio, Burma. It was built while Burma was a British colony to convey supplies to China during the Second Sino ...
. Most of the city's famous hotels and foreign consulates lies along Dongfeng Dong Lu and the southern half of Beijing Lu, while the majority of specific landmarks and shopping district are north and west of the center around Dongfeng Xi Lu and Green Lake (Kunming), Cuihu Park (Green Lake Park). Circling most of this is the city's first highway ring road, Huancheng Lu, though others are planned.
Education and research
Kunming remains a major educational and cultural center in the Southwest China, southwest region of China, with universities, medical and teacher-training colleges, technical schools, and scientific research institutes.
Colleges and universities
*
Kunming Medical University
* Kunming Metallurgy College
* Kunming University
*
Kunming University of Science and Technology
Kunming University of Science and Technology (KUST) () is in Kunming, the capital city of Yunnan Province, Southwestern China.
As the goal by 2010, KUST was to become a National Key Universities, key university with a strong science and engineerin ...
(1925)
*
Southwest Forestry University
*
Yunnan Agricultural University
* Yunnan Arts University
*
Yunnan Normal University
Yunnan Normal University (; YNNU) is in Kunming, the capital city of Yunnan province.
Yunnan Normal University (YNNU) is a key university of Yunnan province, with a long history and a great tradition.
It is a higher institution co-funded by the ...
* Yunnan Normal University Business School
*
Yunnan University
Yunnan University (, Acronym: YNU) is a national key university in Yunnan Province, China. Its main campuses are located in the provincial capital city of Kunming.
Founded in December 1922, Yunnan University started to enroll in April 1923. It ...
(1922)
*
Yunnan University of Finance and Economics
* Yunnan Nationalities University
* Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Yunnan University
Yunnan University (), located in Kunming, is one of the largest and the most prestigious universities in China and is the only university in Yunnan province which has been developed into a "National Key University". It was founded in 1922, as "University of the Eastern Land". Its name has been changed six times subsequently. The institution has 17 schools on the local campus and 3 independent schools located in other cities. It claims the largest and best law school in Yunnan province.
Yunnan Normal University
Yunnan Normal University () was founded in 1938 as the National Normal College of Southwestern Union University. In 1946, when some faculties returned to the north of China, it changed its name to National Kunming Normal College. It now as 6 campuses in Kunming itself and other cities. With 22 schools, it has an enrollment of some 33000 undergraduate students.
Kunming University of Science and Technology
Kunming University of Science and Technology () was established in 1954 and was given "key university" status in 2010. In 2017, it had 3 campuses in Kunming housing 24 schools and had an enrollment of 27000 undergraduates.
Yunnan Nationalities University
Yunnan Nationalities University was founded in 1951 as Yunnan Nationalities College. It is now one of six "key" universities in the province. It has established cooperative relations with 26 foreign universities including University of Bergen in Norway, La Trobe University in Australia, and University of Virginia in the United States. The university has a Nationalities Museum, which contains more than 20000 rare exhibits. There are more than 23000 undergraduates on campus.
Huayang Academy
Huayang Academy is a specialist Chinese language training centre considered unique for offering training Kunming dialect as well as standard Mandarin. Its locality is a popular centre of Western culture in Kunming, attracting numerous foreign-owned businesses.
Management training
The Shanghai-based China Europe International Business School, aka CEIBS, will launch in 2009 its Business Development Certificate Programme in Kunming. With the Business Development Certificate Programme, CEIBS and program partner Frankfurt School of Finance & Management aim to train approximately 500 Chinese managers in the coming four years, with the first phase of the program beginning in 2008 in Hefei, the capital of Anhui province. Kunming and Harbin will be the focus of the program's expansion in 2009. The program is part of a two million Euro umbrella project funded by the EU, which also includes another program that provides scholarships for MBA students from China's less-developed regions.
Research institutes
* Solar Energy Research Institute of Yunnan Normal University
* Kunming Municipal Planning and Design Research Institute
Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Kunming Branch of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) was established in 1957. It was formerly known as Kunming Office of CAS and was promoted and renamed into a branch in 1958. In 1962, Yunnan Branch combined with Sichuan Branch and Guizhou Branch to establish Southwest China Branch of CAS in Chengdu. In October 1978, Kunming Branch was reestablished at the approval of the State Council.
As a working department of CAS, Kunming Branch now administers five research institutes:
* Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
* Kunming Institute of Medical Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
* Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
* Kunming Primate Research Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences
* Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Gardens in Menglun, Mengla County, Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture, far southern Yunnan.
At present, it has a total staff of 1,160, of whom 808 are professional researchers, seven are academicians and 343 are senior researchers. There are also 447 PhD degree students and 530 master's degree students. The retired staff is 1,090. The Branch has set up three national key open labs, two CAS key open labs, five key labs set up by CAS and local province, three engineering centers, five doctoral sites, five post doctoral stations and national famous plant herbariums and halls of wildlife specimens and has a series of up-to-date research instruments and apparatus, computer networks and biodiversity information systems. The Branch has become an advanced comprehensive science research base in astronomy, geology and biology.
Libraries
* Yunnan Provincial Library
Twin towns and sister cities
Kunming currently maintains sister city agreements with the following foreign cities.
Health
Currently, there are 2,774 medical institutes of various kinds and 33,600 medical professionals in the city. The 170 medical service institutes based on communities cover a population of 1.86 million. China Health Management Corp (CNHC) is the main Health insurance, private healthcare provider in the city. It has been predicted that private hospitals will provide 70 percent of total medical health care services by 2012 within Kunming City.
Hospitals in Kunming include:
Yunnan Provincial Red Cross Hospital and Emergency Center is the main general hospital in Kunming.
Yunnan Provincial First People's HospitalFirst Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical College* Kunming Mental Hospital, founded in 1955, houses over 400 patients.
* Kunming Physical Rehabilitation Center
HIV/AIDS
In late 2006, China's first provincial-level HIV/AIDS treatment center was built. The US$17.5 million center is located from downtown Kunming. The center has six main departments: clinical treatment, technical consulting, research and development, international exchange and cooperation, clinical treatment training and psychological therapy.
Yunnan, with a population of more than 45 million, leads China in HIV/AIDS infections: primarily spread through intravenous drug use and unsafe sex, often involving the sex industry. According to official statistics, by the end of 2005, Yunnan was home to more than 48,000 HIV-infected patients, 3,900 patients with AIDS and a death toll of 1,768.
Military
Kunming is headquarters of the 14th Army (People's Republic of China), 14th Group Army of the People's Liberation Army, one of the two group armies that comprise the Chengdu Military Region responsible for the defense of China's southwestern borders with India and
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, as well as security in
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
.
Public security and crime
The headquarters of the Kunming Municipal Public Security Bureau is on Beijing Lu. Its foreign affairs department, located on Jinxing Huayuan, Jinxing Xiao Lu in the northeast of the city, handles immigration and travel visas.
Drug trafficking
Kunming has a pivotal role as a major conduit point in international drug trafficking as it is the closest major Chinese city to the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle in
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
. The Kunming Municipal Public Security Bureau Narcotics Squad is the specialist counter-narcotics police service.
Police confiscated at least three tons of drugs in Yunnan in 2005. Yunnan province seized 10 tons of illegal drugs in 2006, accounting for 80 percent of the total drugs confiscated nationwide during the period, according to Sun Dahong, then deputy director of Yunnan's provincial Public Security Bureau. The total is more than double the amount seized in the province in 2005.
Heroin and methamphetamine seem to be the main targets of the 30,000+ strong anti-drug police in Yunnan. The majority of heroin coming into China from the Golden Triangle passes through Dali City, Yunnan, Dali from where it is then distributed to the rest of China and internationally via China's coastal cities.
Kunming Municipal Compulsory Rehabilitation Center in Kunming is the main rehabilitation center for drug addicts, mostly recovering from heroin addiction. International drug rings have used Yunnan and Kunming to channel new synthetic drugs (like methamphetamine) as well as traditional drugs like heroin.
Opium was until recently in widespread medicinal use by many of the minority peoples of the province; however, after the Opium War the Chinese government has made growing the poppy illegal, and all but stamped out its production within the borders of Yunnan.
International relations
The following countries have a List of diplomatic missions in the People's Republic of China, diplomatic mission in Kunming:
* Consulates:
** Diplomatic missions of Bangladesh, Bangladesh
** Diplomatic missions of Cambodia, Cambodia
** Diplomatic missions of Burma, Myanmar (Burma)
** Diplomatic missions of Laos, Laos
** Diplomatic missions of Malaysia, Malaysia
** Diplomatic missions of Thailand, Thailand
** Diplomatic missions of Vietnam, Vietnam
* Trade offices:
** Australia
** Netherlands
Notable residents
Notable people from Kunming include:
* Benedict Anderson, scholar (born in Kunming)
* Cai Xitao, botanist
* Chih-Kung Jen, physicist
* Wang Xiji, aerospace engineer and recipient of the "Two Bombs, One Satellite" Meritorious Award
* Pierre Jean Marie Delavay, 19th-century French missionary, lived and died in Kunming
* Lamu Gatusa, professor and writer
* He Yunchang, Chinese performance artist born in Kunming whose early, seminal works were also performed there
* Li Weiwei (handballer), Li Weiwei, Olympics handball player
* Liu Fang, pipa player
* Maran Brang Seng, Burmese politician (died in Kunming)
* Ma Yashu, actress
* Nie Er, composer (born in Kunming)
* Frank Shu, Chinese-American astrophysicist, born in Kunming
* Xing Ruan, Chinese-Australian author and architect, born in Kunming
* Song Wencong, aerospace engineer and aircraft designer
*
Tang Jiyao, general and warlord of Yunnan, died in Kunming
* Tong Yao, actress
* Tu Wei-ming, ethicist (born in Kunming)
* Wang Hongni, triathlete and Asian Games gold medallist
* Wen Yiduo, poet and scholar, (lived and assassinated in Kunming)
* Anthony Zee, physicist
* Zhang Xiaogang, artist, born in Kunming
* Zheng He,
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
explorer
* Zhu De, military leader (studied in Kunming)
* Zhu Youlang (Ming dynasty emperor), (fought and was executed in Kunming)
Diplomats:
* Auguste François, French consul in south China
* George Soulié de Morant, French diplomat
* John S. Service, American diplomat served in Kunming for two years
National Southwestern Associated University:
* Chen Ning Yang, physicist
* Chen Yinke, linguist
* Feng Youlan, philosopher
* Shiing-Shen Chern, mathematician
* Ta-You Wu, physicist
* Tsung-Dao Lee, physicist
* Wang Yuan (mathematician), Wang Yuan, mathematician
* Wu Ningkun, professor emeritus
* Zhang Boling, founder of Nankai University
See also
* 2008 Kunming bus bombings
* 3650 Kunming, an asteroid
* :Films set in Kunming
* Zheng He
* List of cities in the People's Republic of China
* List of twin towns and sister cities in China
References
Further reading
* ''Kunming Statistical Yearbook-2007'' China Statistics Pres
*
*
Sustainable Urban Development – the Case Study of Kunming, China Willy Schmid, Markus Eggenberger, 1997.NSL – Network City and Landscape– contains Kunming sustainable development papers
*
*
*
*
* Chin, K. and Zhang, S.
. American Society of Criminology (ASC) 2008-06-26
Social Development Division, United Nations ESCAP
* Kobusingye KA
''Int Conf AIDS''. 2004 Jul 11–16; 15: abstract no. WePeC5999.
Kunming Journal. Nicholas D. Kristof. 30 May 1991
* Book about Kunming's regional cooperation with Southeast Asia: ''ASEAN-China Relations: Realities and Prospects'' (2005) Saw Swee Hock, Lijun Sheng, Sheng Lijun, Kin Wah Chin, Chin Kin Wah. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies (ISEAS)
* Wei Xing. "Prevalence of ethnic intermarriage in Kunming: Social exchange or insignificance of ethnicity?" ''Asian Ethnicity'', Volume 8, Issue 2 June 2007, pages 165–179
* Jianli Li; Mary Francis Marx.
''Journal of Southern Academic and Special Librarianship'' (2000)
External links
Official Kunming Municipal Government Website
Official Kunming Website
{{Authority control
Kunming,
765 establishments
8th-century establishments in China
Cities in Yunnan
National Forest Cities in China
Populated places established in the 8th century
Provincial capitals in China
Tourism in Yunnan
 In the 14th century, Kunming was retaken from Khan Mongolian control when the
In the 14th century, Kunming was retaken from Khan Mongolian control when the 

 Kunming was increasingly targeted by the IJAAF when the Burma Road was lost to the Japanese, and the 1st American Volunteer Group, known as the "Flying Tigers", based in Kunming, and tasked with defense of ''The Hump'' supply-line that stretched over the Himalayas between the British bases in India to port-of-entry Kunming against Japanese aerial interceptions; China's primary lifeline to the outside world, which had included the Burma Road and the Ledo Road, all with Kunming as the northern terminus.
Industry became important in Kunming during
Kunming was increasingly targeted by the IJAAF when the Burma Road was lost to the Japanese, and the 1st American Volunteer Group, known as the "Flying Tigers", based in Kunming, and tasked with defense of ''The Hump'' supply-line that stretched over the Himalayas between the British bases in India to port-of-entry Kunming against Japanese aerial interceptions; China's primary lifeline to the outside world, which had included the Burma Road and the Ledo Road, all with Kunming as the northern terminus.
Industry became important in Kunming during  Since the Economic reform in the People's Republic of China, economic reforms of the mid-1980s, Kunming has enjoyed increased Tourism in China, tourism and Economy of China, foreign investment, for instance investors from
Since the Economic reform in the People's Republic of China, economic reforms of the mid-1980s, Kunming has enjoyed increased Tourism in China, tourism and Economy of China, foreign investment, for instance investors from  The World Horticultural Expo was widely regarded as a public relations success for Kunming. Today the after-effects of the Expo are apparent in more than just the physical improvements to the city—it was the Expo that made the outside world take notice of Kunming, which was relatively unknown at the time.
In July 2006, talks at the ASEAN Regional Forum, China, Bangladesh and Myanmar (Burma) agreed to construct a highway from Kunming to Chittagong through Mandalay for trade and development.
On 1 March 2014, 29 people were killed, and more than 130 were injured at Kunming Railway Station in 2014 Kunming attack, a terrorist attack.
The World Horticultural Expo was widely regarded as a public relations success for Kunming. Today the after-effects of the Expo are apparent in more than just the physical improvements to the city—it was the Expo that made the outside world take notice of Kunming, which was relatively unknown at the time.
In July 2006, talks at the ASEAN Regional Forum, China, Bangladesh and Myanmar (Burma) agreed to construct a highway from Kunming to Chittagong through Mandalay for trade and development.
On 1 March 2014, 29 people were killed, and more than 130 were injured at Kunming Railway Station in 2014 Kunming attack, a terrorist attack.



 Kunming is located in east-central
Kunming is located in east-central  The city center has three major squares and five major streets: Jinma Biji Square, Nanping Square and Dongfeng Square along with Nanping Jie, Jinbi Lu, Renmin Lu, Zhengyi Lu and Jingxin Jie. Qingnian Lu, Zhengyi Lu, and Renmin Lu are the main commercial areas in Kunming; the most popular pedestrian streets are Nanping Jie, Jingxing Birds-Flowers' Market, and Jinma Biji Fang.
Kunming's public focus is the huge square outside the now-demolished Workers' Cultural Hall at the Beijing Lu-Dongfeng Lu intersection, where in the mornings there are crowds doing taijiquan and playing badminton. Weekend amateur theatre are also performed in the square. Rapidly being modernized, the city's true center is west of the square across the adjacent Panlong River (now more of a canal), outside the Kunming Department Store at the Nanping Lu/Zhengyi Lu crossroads, a densely crowded shopping precinct packed with clothing and electronics stores. The river receives sewage and wastewater from surrounding pipes. Surrounding the area are plenty of new high-rises.
The center is an area of importance to Kunming's Hui people, Hui population, with Shuncheng Jie, one of the last old streets in the center of the city, previously forming a Muslim quarter. Until shortly before 2005, this street was full of wind-dried beef and mutton carcasses, pitta bread and raisin sellers, and huge woks of roasting coffee beans being stirred with shovels. Under Kunming's rapid modernisation, however, the street has been demolished to make way for apartments and shopping centers. Rising behind a supermarket one block north off Zhengyi Lu, Nancheng Qingzhen Si is the city's new mosque, its green dome and chevron-patterned minaret visible from afar and built on the site of an earlier Qing edifice.
Running west off Zhengyi Jie just past the mosque, Jingxing Jie leads into one of the more bizarre corners of the city, with Kunming's huge Bird and Flower Market convening daily in the streets connecting it with the northerly, parallel Guanghua Jie. The market offers many plants such as orchids that have been collected and farmed across the province. In the small grounds of Wen Miao, a now vanished Confucian temple off the western end of Changchun Lu, there is an avenue of pines, an ancient pond and pavilion, and beds of bamboo, azaleas and potted palms.
Jinbi Lu runs roughly parallel to and south of Dongfeng Lu, reached from Beijing Lu. Two large Chinese pagodas rise in the vicinity, each a solid thirteen stories of whitewashed brick crowned with four iron cockerels. The West Pagoda was built between 824 and 859, during the Tang dynasty; its original counterpart, the East Pagoda, was built at the same time, but was destroyed by 1833 Kunming earthquake, an earthquake in 1833 and rebuilt in the same Tang style in 1882. South down Dongsi Jie, past another mosque, the entrance to the Eastern and Western Pagodas, West Pagoda is along a narrow lane on the right. In the tiny surrounding courtyard, sociable idlers while away sunny afternoons playing cards and sipping tea in the peaceful, ramshackle surroundings. The Eastern and Western Pagodas, East Pagoda is a more cosmetic, slightly tilted duplicate standing in an ornamental garden a few minutes' walk east on Shulin Jie. The temples associated with both pagodas are closed to the public.
The city center has three major squares and five major streets: Jinma Biji Square, Nanping Square and Dongfeng Square along with Nanping Jie, Jinbi Lu, Renmin Lu, Zhengyi Lu and Jingxin Jie. Qingnian Lu, Zhengyi Lu, and Renmin Lu are the main commercial areas in Kunming; the most popular pedestrian streets are Nanping Jie, Jingxing Birds-Flowers' Market, and Jinma Biji Fang.
Kunming's public focus is the huge square outside the now-demolished Workers' Cultural Hall at the Beijing Lu-Dongfeng Lu intersection, where in the mornings there are crowds doing taijiquan and playing badminton. Weekend amateur theatre are also performed in the square. Rapidly being modernized, the city's true center is west of the square across the adjacent Panlong River (now more of a canal), outside the Kunming Department Store at the Nanping Lu/Zhengyi Lu crossroads, a densely crowded shopping precinct packed with clothing and electronics stores. The river receives sewage and wastewater from surrounding pipes. Surrounding the area are plenty of new high-rises.
The center is an area of importance to Kunming's Hui people, Hui population, with Shuncheng Jie, one of the last old streets in the center of the city, previously forming a Muslim quarter. Until shortly before 2005, this street was full of wind-dried beef and mutton carcasses, pitta bread and raisin sellers, and huge woks of roasting coffee beans being stirred with shovels. Under Kunming's rapid modernisation, however, the street has been demolished to make way for apartments and shopping centers. Rising behind a supermarket one block north off Zhengyi Lu, Nancheng Qingzhen Si is the city's new mosque, its green dome and chevron-patterned minaret visible from afar and built on the site of an earlier Qing edifice.
Running west off Zhengyi Jie just past the mosque, Jingxing Jie leads into one of the more bizarre corners of the city, with Kunming's huge Bird and Flower Market convening daily in the streets connecting it with the northerly, parallel Guanghua Jie. The market offers many plants such as orchids that have been collected and farmed across the province. In the small grounds of Wen Miao, a now vanished Confucian temple off the western end of Changchun Lu, there is an avenue of pines, an ancient pond and pavilion, and beds of bamboo, azaleas and potted palms.
Jinbi Lu runs roughly parallel to and south of Dongfeng Lu, reached from Beijing Lu. Two large Chinese pagodas rise in the vicinity, each a solid thirteen stories of whitewashed brick crowned with four iron cockerels. The West Pagoda was built between 824 and 859, during the Tang dynasty; its original counterpart, the East Pagoda, was built at the same time, but was destroyed by 1833 Kunming earthquake, an earthquake in 1833 and rebuilt in the same Tang style in 1882. South down Dongsi Jie, past another mosque, the entrance to the Eastern and Western Pagodas, West Pagoda is along a narrow lane on the right. In the tiny surrounding courtyard, sociable idlers while away sunny afternoons playing cards and sipping tea in the peaceful, ramshackle surroundings. The Eastern and Western Pagodas, East Pagoda is a more cosmetic, slightly tilted duplicate standing in an ornamental garden a few minutes' walk east on Shulin Jie. The temples associated with both pagodas are closed to the public.
 Cuihu Park (Green Lake Park) is one of Kunming's major parks and is predominately a lake surrounded by greenery. Located in the west side of the park is the statue of one of Yunnan's most famous patriots—Nie Er, the composer of China's March of the Volunteers, national anthem. Now it is open to public for free.
Daguan Park lies on Dian Chi in Kunming's southwestern limits. Originally laid out by the Kangxi Emperor in the Qing dynasty, it has been modified over the years to include a noisy funfair, food stalls and emporiums, and is a favourite haunt of Kunming's youth.
Kunming's zoo, founded in 1950, is adjoined to Yuantong Park. The zoo houses 5,000 animals from 140 species and receives 3 million visitors a year.
Other parks in Kunming include Heilongtan (Kunming), Black Dragon Pool, and the Kunming Botanical Gardens in the north, and Wenmiao Tea Garden in Wuhua District.
Cuihu Park (Green Lake Park) is one of Kunming's major parks and is predominately a lake surrounded by greenery. Located in the west side of the park is the statue of one of Yunnan's most famous patriots—Nie Er, the composer of China's March of the Volunteers, national anthem. Now it is open to public for free.
Daguan Park lies on Dian Chi in Kunming's southwestern limits. Originally laid out by the Kangxi Emperor in the Qing dynasty, it has been modified over the years to include a noisy funfair, food stalls and emporiums, and is a favourite haunt of Kunming's youth.
Kunming's zoo, founded in 1950, is adjoined to Yuantong Park. The zoo houses 5,000 animals from 140 species and receives 3 million visitors a year.
Other parks in Kunming include Heilongtan (Kunming), Black Dragon Pool, and the Kunming Botanical Gardens in the north, and Wenmiao Tea Garden in Wuhua District.
 Yuantong Si is Kunming's major Buddhist temple. It is Kunming's largest and most famous temple with the original structure being first constructed more than 1,200 years ago during the Tang dynasty. The temple sits in a depression on the southern side of Yuantong Park. Northwest about from the city center is the Qiongzhu Si (Bamboo Temple) built in 639 and rebuilt in 1422 to 1428. Numerous Buddhist temples line the road to the Dragon Gate () in the Western Mountains.
Yuantong Si is Kunming's major Buddhist temple. It is Kunming's largest and most famous temple with the original structure being first constructed more than 1,200 years ago during the Tang dynasty. The temple sits in a depression on the southern side of Yuantong Park. Northwest about from the city center is the Qiongzhu Si (Bamboo Temple) built in 639 and rebuilt in 1422 to 1428. Numerous Buddhist temples line the road to the Dragon Gate () in the Western Mountains.
 Kunming attracts domestic and foreign tourists year-round. At the center of Yunnan and as its capital, Kunming is also a transport hub for tourists heading to other parts of Yunnan such as Dali, Yunnan, Dali, Lijiang City, Lijiang and Shangri-La County, Shangrila.
Conference and exhibition venues in Kunming include the Kunming International Convention and Exhibition Center and the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Hall.
Kingdom of the Little People, a theme park featuring performers with dwarfism, is also located near Kunming.
Other famous attractions include Stone Forest and Yunnan's Ethnic Village.
Kunming attracts domestic and foreign tourists year-round. At the center of Yunnan and as its capital, Kunming is also a transport hub for tourists heading to other parts of Yunnan such as Dali, Yunnan, Dali, Lijiang City, Lijiang and Shangri-La County, Shangrila.
Conference and exhibition venues in Kunming include the Kunming International Convention and Exhibition Center and the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Hall.
Kingdom of the Little People, a theme park featuring performers with dwarfism, is also located near Kunming.
Other famous attractions include Stone Forest and Yunnan's Ethnic Village.
 Kunming has three economic advantages over other cities in southwest China: significant natural resources, a large consumer market and a mild climate. Due to its position at the center of Yunnan, one of China's largest producers of agricultural products, minerals and hydroelectricity, Kunming is the main commercial hub for most of the province's resources.
Kunming's chief industries are copper, lead and zinc production. Its iron and steel industry has been expanded. Salt and phosphate mines around Kunming are some of the largest in China. Yunnan Copper Company Limited, based in Kunming, is one of Yunnan's largest mining corporations. From the late 1970s, Kunming's main industries also came to include food and tobacco processing and the manufacture of construction equipment and machines.
In May 1995, the State Council of the People's Republic of China, State Council approved Kunming as an Open City. By the end of 1995, the city had approved 929 overseas-funded enterprises with a total investment of $2.3 billion including $1.1 billion of foreign capital. More than 40 projects each had an investment of more than $9 million.
Kunming is a center of engineering and the manufacture of machine tools, electrical machinery, electrical equipment, equipment and automobiles (including heavy goods vehicles). It has a chemical industry, and plastics, cement works and textile factories. Its processing plants, which include tanneries, woodworking and papermaking factories, use Agriculture in China, local agricultural products. In 1997, Yunnan Tire Co. opened a tire plant in Kunming, with a capacity to produce two million tires per year.
Kunming has three economic advantages over other cities in southwest China: significant natural resources, a large consumer market and a mild climate. Due to its position at the center of Yunnan, one of China's largest producers of agricultural products, minerals and hydroelectricity, Kunming is the main commercial hub for most of the province's resources.
Kunming's chief industries are copper, lead and zinc production. Its iron and steel industry has been expanded. Salt and phosphate mines around Kunming are some of the largest in China. Yunnan Copper Company Limited, based in Kunming, is one of Yunnan's largest mining corporations. From the late 1970s, Kunming's main industries also came to include food and tobacco processing and the manufacture of construction equipment and machines.
In May 1995, the State Council of the People's Republic of China, State Council approved Kunming as an Open City. By the end of 1995, the city had approved 929 overseas-funded enterprises with a total investment of $2.3 billion including $1.1 billion of foreign capital. More than 40 projects each had an investment of more than $9 million.
Kunming is a center of engineering and the manufacture of machine tools, electrical machinery, electrical equipment, equipment and automobiles (including heavy goods vehicles). It has a chemical industry, and plastics, cement works and textile factories. Its processing plants, which include tanneries, woodworking and papermaking factories, use Agriculture in China, local agricultural products. In 1997, Yunnan Tire Co. opened a tire plant in Kunming, with a capacity to produce two million tires per year.
 In July 2008, Kunming began to implement a program to transform the city's solar energy industry into a US$8.8 billion industrial base in China by 2013. Kunming receives an annual average sunshine of more than 2,400 hours. Each 1 kW PV system has the potential to generate 1500 kilowatt-hours of electricity a year from solar energy.
, the Kunming Economic Committee listed about 130 solar energy enterprises in the city. Of these, 118 enterprises produce solar lamps and solar water heaters, with a combined total production value of about US$43.8 million, and 10 enterprises are engaged in solar photovoltaic cells manufacturing, with a total production value of about US$51.2 million.
Suntech Power announced in December 2008 that it was jointly constructing a solar energy project with Yunnan Provincial Power Investment and other investors. The 1MW first-phase of the Shilin Yi Autonomous County, Shilin 66MW on-grid solar power station began generating power on 28 December 2009. The initial phase of the 66MW project was originally scheduled to start production in first half of 2010 while the 20MW second phase and 36 MW third phase were under construction.
In July 2008, Kunming began to implement a program to transform the city's solar energy industry into a US$8.8 billion industrial base in China by 2013. Kunming receives an annual average sunshine of more than 2,400 hours. Each 1 kW PV system has the potential to generate 1500 kilowatt-hours of electricity a year from solar energy.
, the Kunming Economic Committee listed about 130 solar energy enterprises in the city. Of these, 118 enterprises produce solar lamps and solar water heaters, with a combined total production value of about US$43.8 million, and 10 enterprises are engaged in solar photovoltaic cells manufacturing, with a total production value of about US$51.2 million.
Suntech Power announced in December 2008 that it was jointly constructing a solar energy project with Yunnan Provincial Power Investment and other investors. The 1MW first-phase of the Shilin Yi Autonomous County, Shilin 66MW on-grid solar power station began generating power on 28 December 2009. The initial phase of the 66MW project was originally scheduled to start production in first half of 2010 while the 20MW second phase and 36 MW third phase were under construction.
 Kunming is situated on the
Kunming is situated on the  China National Highways China National Highway 108, 108, China National Highway 213, 213 and China National Highway 320, 320 intersect in Kunming. Highways link Kunming to
China National Highways China National Highway 108, 108, China National Highway 213, 213 and China National Highway 320, 320 intersect in Kunming. Highways link Kunming to  In May 2010, Kunming began construction on its first urban rail lines, line 1 and 2 of the Kunming Metro. An elevated test section had been under construction since 2009. Parts of lines 1 and 2 opened in April 2014. Construction on line 3 began in August 2010 and the Phase 1 was completed in 2018. The entire system consisting of 6 lines and covering a total of is estimated to be complete by 2018.
In May 2010, Kunming began construction on its first urban rail lines, line 1 and 2 of the Kunming Metro. An elevated test section had been under construction since 2009. Parts of lines 1 and 2 opened in April 2014. Construction on line 3 began in August 2010 and the Phase 1 was completed in 2018. The entire system consisting of 6 lines and covering a total of is estimated to be complete by 2018.

 Yunnan has built a comprehensive highway system with roads reaching almost all the major cities or towns in the region. Bus travel across the region is extensive. Buses head from Kunming to destinations such as Dali, Yunnan, Dali and Lijiang City, Lijiang several times a day.
There are four major long-distance bus stations in Kunming with the South Bus Station and Railway Square Bus Station being the most primary.
* South Bus Station faces the Kunming Railway Station in Beijing Xi Lu, with standard, luxury, express and sleeper buses departing for all over Yunnan and neighboring provinces.
* Railway Square Bus Station is smaller than SBS and the majority of the buses depart from the station are private-run. Usually no fixed schedules are available and buses will leave when they are full. There are standard and sleeper services to Dali, Jinghong and elsewhere in Yunnan.
Leaving China by road into
Yunnan has built a comprehensive highway system with roads reaching almost all the major cities or towns in the region. Bus travel across the region is extensive. Buses head from Kunming to destinations such as Dali, Yunnan, Dali and Lijiang City, Lijiang several times a day.
There are four major long-distance bus stations in Kunming with the South Bus Station and Railway Square Bus Station being the most primary.
* South Bus Station faces the Kunming Railway Station in Beijing Xi Lu, with standard, luxury, express and sleeper buses departing for all over Yunnan and neighboring provinces.
* Railway Square Bus Station is smaller than SBS and the majority of the buses depart from the station are private-run. Usually no fixed schedules are available and buses will leave when they are full. There are standard and sleeper services to Dali, Jinghong and elsewhere in Yunnan.
Leaving China by road into