Kraków dzielnica XVIII Nowa Huta.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in
 Kraków's early history begins with evidence of a Stone Age settlement on the present site of the Wawel Hill. A legend attributes Kraków's founding to the mythical ruler
Kraków's early history begins with evidence of a Stone Age settlement on the present site of the Wawel Hill. A legend attributes Kraków's founding to the mythical ruler
Rocznica lokacji Krakowa (750-year anniversary of the Kraków Location Act).
See also
translated from Latin by Bożena Wyrozumsk
Retrieved 21 December 2012. based on new location act and incorporated in 1257 by the high duke In 1335, King
In 1335, King
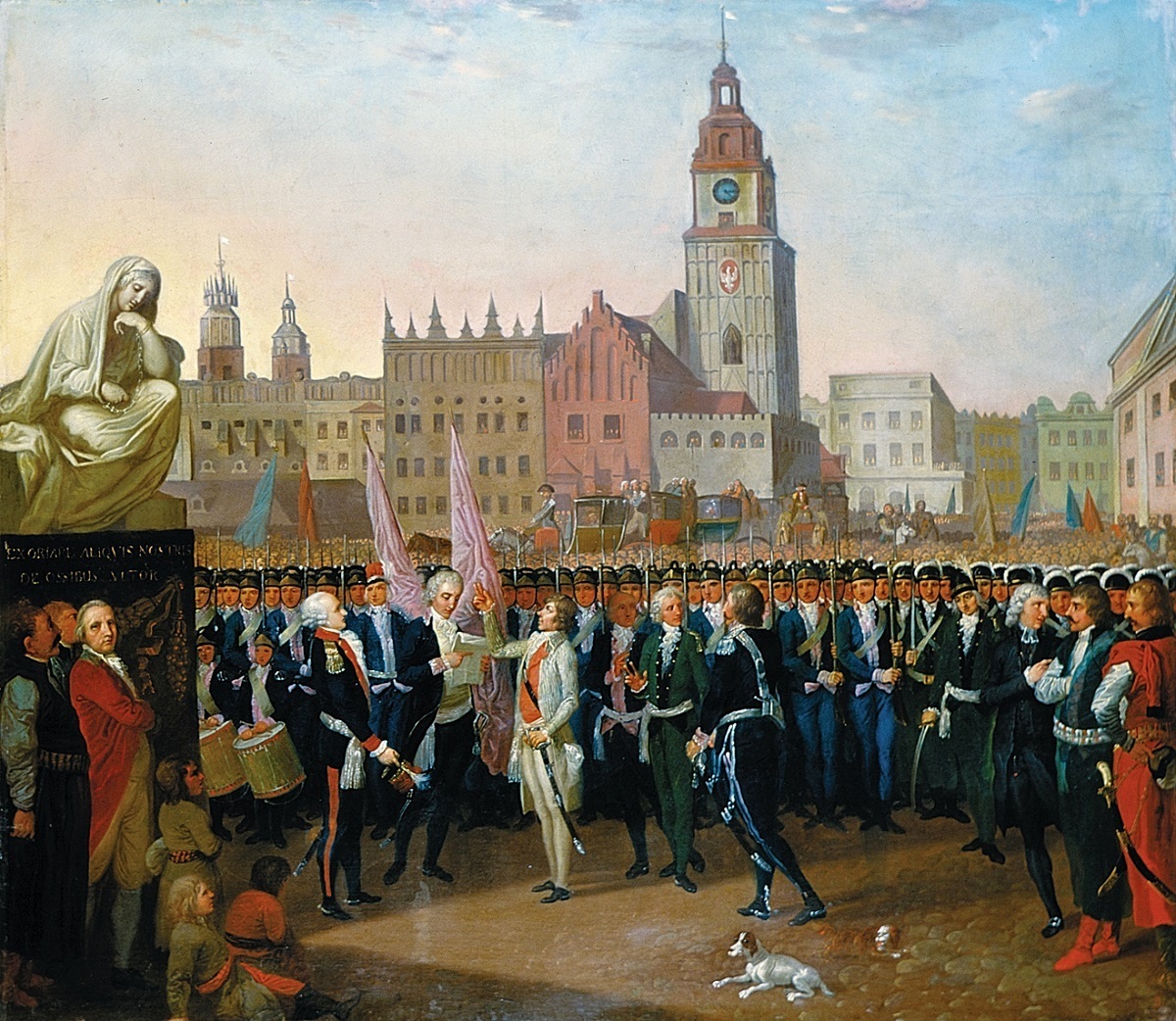 Already weakened during the 18th century, by the mid-1790s the
Already weakened during the 18th century, by the mid-1790s the  At the outbreak of
At the outbreak of
 Following the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918, Kraków resumed its role as a major Polish academic and cultural centre, with the establishment of new universities such as the
Following the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918, Kraków resumed its role as a major Polish academic and cultural centre, with the establishment of new universities such as the  After the war, under the
After the war, under the
 Kraków lies in the southern part of Poland, on the
Kraków lies in the southern part of Poland, on the
 In addition to the old town, the city's district of
In addition to the old town, the city's district of  By the 1930s, Kraków had 120 officially registered synagogues and prayer houses that spanned across the old city. Much of Jewish intellectual life had moved to new centres like
By the 1930s, Kraków had 120 officially registered synagogues and prayer houses that spanned across the old city. Much of Jewish intellectual life had moved to new centres like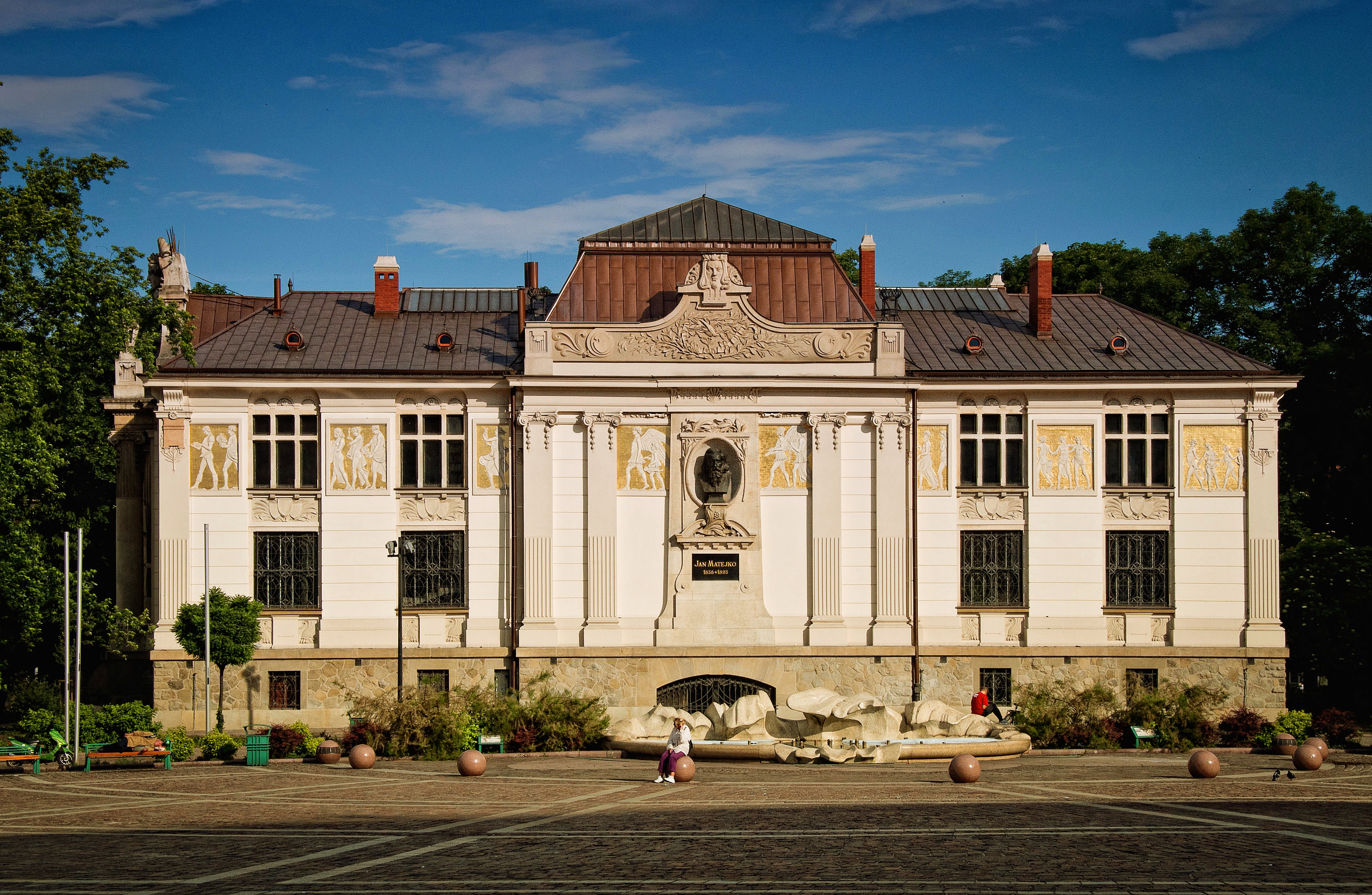  As the city of Kraków began to expand further under the rule of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the new architectural styles also developed. Key buildings from the 19th and early 20th centuries in Kraków include the Jan Matejko Academy of Fine Arts, the directorate of the Polish State Railways as well as the original complex of Kraków Główny railway station and the city's Academy of Economics. It was also at around that time that Kraków's first radial boulevards began to appear, with the city undergoing a large-scale program aimed at transforming the ancient Polish capital into a sophisticated regional centre of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. New representative government buildings and multi-story tenement houses were built at around that time. Much of the urban-planning beyond the walls of the Old Town was done by Polish architects and engineers trained in
As the city of Kraków began to expand further under the rule of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the new architectural styles also developed. Key buildings from the 19th and early 20th centuries in Kraków include the Jan Matejko Academy of Fine Arts, the directorate of the Polish State Railways as well as the original complex of Kraków Główny railway station and the city's Academy of Economics. It was also at around that time that Kraków's first radial boulevards began to appear, with the city undergoing a large-scale program aimed at transforming the ancient Polish capital into a sophisticated regional centre of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. New representative government buildings and multi-story tenement houses were built at around that time. Much of the urban-planning beyond the walls of the Old Town was done by Polish architects and engineers trained in  With Poland's regained independence came the major change in the fortunes of Kraków—now the second most important city of a sovereign nation. The state began to make new plans for the city development and commissioned a number of representative buildings. The predominant style for new projects was modernism with various interpretations of the art-deco style. Important buildings constructed in the style of Polish modernism include the Feniks 'LOT' building on Basztowa Street, the Feniks department store on the Main Square and the Municipal Savings Bank on Szczepański Square. The Józef Piłsudski house is also of note as a particularly good example of interwar architecture in the city.
After the Second World War, new government turned toward Soviet influence and the Stalinist monumentalism. The doctrine of
With Poland's regained independence came the major change in the fortunes of Kraków—now the second most important city of a sovereign nation. The state began to make new plans for the city development and commissioned a number of representative buildings. The predominant style for new projects was modernism with various interpretations of the art-deco style. Important buildings constructed in the style of Polish modernism include the Feniks 'LOT' building on Basztowa Street, the Feniks department store on the Main Square and the Municipal Savings Bank on Szczepański Square. The Józef Piłsudski house is also of note as a particularly good example of interwar architecture in the city.
After the Second World War, new government turned toward Soviet influence and the Stalinist monumentalism. The doctrine of  Since the style of the
Since the style of the

 There are about 40 parks in Kraków including dozens of gardens and forests. Several, like the
There are about 40 parks in Kraków including dozens of gardens and forests. Several, like the
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. Situated on the Vistula River
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, economic, cultural and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Old Town with Wawel Royal Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established on ...
was declared a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 1978, one of the first 12 sites granted the status.
The city has grown from a Stone Age settlement to Poland's second-most-important city. It began as a hamlet on Wawel Hill
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established o ...
and was reported by Ibrahim Ibn Yakoub, a merchant from Cordoba, as a busy trading centre of Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
in 985. With the establishment of new universities and cultural venues at the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918 and throughout the 20th century, Kraków reaffirmed its role as a major national academic and artistic centre. As of 2022, the city has a population of 800,653, with approximately 8 million additional people living within a radius of its main square.
After the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
at the start of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the newly defined Distrikt Krakau (Kraków District) became the capital of Germany's General Government. The Jewish population of the city was forced into a walled zone known as the Kraków Ghetto
The Kraków Ghetto was one of five major metropolitan Nazi ghettos created by Germany in the new General Government territory during the German occupation of Poland in World War II. It was established for the purpose of exploitation, terror, and ...
, from where they were sent to Nazi extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s such as the nearby Auschwitz, and Nazi concentration camps
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps, (officially) or (more commonly). The Nazi concentration camps are distinguished from other types of Nazi camps such as forced-labor camps, as well as con ...
like Płaszów
Płaszów is a suburb of Kraków, Poland, now part of Podgórze district. Formerly a separate village, it became a part of the Greater Kraków in 1911 under the Austrian Partition of Poland as the 21st cadastral district of the city. During World ...
. However, the city was spared from destruction and major bombing.
In 1978, Karol Wojtyła, archbishop of Kraków
The Archbishop of Kraków is the head of the archdiocese of Kraków. A bishop of Kraków first came into existence when the diocese was created in 1000; it was promoted to an archdiocese on 28 October 1925. Due to Kraków's role as Poland's politic ...
, was elevated to the papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
as Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
—the first non-Italian pope in 455 years. Also that year, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
approved Kraków's entire Old Town and historic centre as its first World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
alongside Quito. Kraków is classified as a global city with the ranking of "high sufficiency" by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network
The Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) is a think tank that studies the relationships between world cities in the context of globalization. It is based in the geography department of Loughborough University in Leicestershire ...
. Its extensive cultural heritage across the epochs of Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
, Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
and Baroque architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means t ...
includes Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral ( pl, Katedra Wawelska), formally titled the Royal Archcathedral Basilica of Saints Stanislaus and Wenceslaus, is a Roman Catholic cathedral situated on Wawel Hill in Kraków, Poland. Nearly 1000 years old, it is part of the ...
and Wawel Royal Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established on ...
on the banks of the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
, St. Mary's Basilica, Saints Peter and Paul Church and the largest medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
market square in Europe, Rynek Główny
Rynek may refer to the following places:
* Rynek, Lesser Poland Voivodeship (south Poland)
* Rynek, Masovian Voivodeship (east-central Poland)
*Rynek, Subcarpathian Voivodeship
Rynek is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Grębów ...
. Kraków is home to Jagiellonian University, one of the oldest universities in the world and traditionally Poland's most reputable institution of higher learning. The city also hosts a number of institutions of national significance such as the National Museum,
Kraków Opera, Juliusz Słowacki Theatre
Juliusz Słowacki Theatre ( pl, Teatr im. Juliusza Słowackiego w Krakowie) is a 19th-century Eclectic theatre-opera house in the heart of Kraków, Poland, and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Erected in 1893, it was modeled after some of the best ...
, National Stary Theatre
The Helena Modrzejewska National Stary Theater in Kraków (Polish: ''Narodowy Stary Teatr im. Heleny Modrzejewskiej'') is one of the oldest public stages in Poland and a national institution of culture, first opened in 1781. It was named after re ...
and the Jagiellonian Library
Jagiellonian Library ( pl, Biblioteka Jagiellońska, popular nickname ''Jagiellonka'') is the library of the Jagiellonian University in Kraków and with almost 6.7 million volumes, one of the largest libraries in Poland, serving as a public libra ...
. The city is served by John Paul II International Airport
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
, the country's second busiest airport and the most important international airport for the inhabitants of south-eastern Poland.
In 2000, Kraków was named European Capital of Culture. In 2013, Kraków was officially approved as a UNESCO City of Literature
UNESCO's City of Literature programme is part of the wider Creative Cities Network.
The ''Network'' was launched in 2004, and now has member cities in seven creative fields. The other creative fields are: Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gas ...
. The city hosted World Youth Day
World Youth Day (WYD) is an event for young people organized by the Catholic Church that was initiated by Pope John Paul II in 1985, sometimes nicknamed in later years as the "Catholic Woodstock". Its concept has been influenced by the Light-L ...
in July 2016. In 2023, the third edition of the European Games
The European Games is a continental multi-sport event in the Olympic tradition contested by athletes from European nations and several transcontinental countries. The Games were envisioned and are governed by the European Olympic Committees ...
will be held by Kraków and the Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
region.
Etymology
The name of Kraków is traditionally derived fromKrakus
Krakus, Krak or Grakch was a legendary Polish prince, king and founder of Kraków, the ruler of the Lechitic tribe of Vistulans. Krakus is also credited with building Wawel Castle and slaying the Wawel Dragon by feeding it a dead sheep full ...
(Krak, Grakch), the legendary founder of Kraków and a ruler of the tribe of Lechitians. In Polish, is an archaic possessive form of ''Krak'' and essentially means "Krak's (town)". The true origin of the name is highly disputed among historians, with many theories in existence and no unanimous consensus. The first recorded mention of Prince Krakus (then written as ''Grakch'') dates back to 1190, although the town existed as early as the seventh century, when it was inhabited by the tribe of Vistulans
The Vistulans, or Vistulanians ( pl, Wiślanie), were an early medieval Lechitic tribe inhabiting the western part of modern Lesser Poland."The main tribe inhabiting the reaches of the Upper Vistula and its tributaries was the Vislane (Wislanie) ...
. It is possible that the name of the city is derived from the word " kruk", meaning crow or raven.
The city's full official name is , which can be translated as " Royal Capital City of Kraków". In English, a person born or living in Kraków is a Cracovian ( pl, krakowianin or ''krakus''). Up through the 1990s the English version of the name was often written as Cracow, but now the most widespread modern English version is Krakow.
History
 Kraków's early history begins with evidence of a Stone Age settlement on the present site of the Wawel Hill. A legend attributes Kraków's founding to the mythical ruler
Kraków's early history begins with evidence of a Stone Age settlement on the present site of the Wawel Hill. A legend attributes Kraków's founding to the mythical ruler Krakus
Krakus, Krak or Grakch was a legendary Polish prince, king and founder of Kraków, the ruler of the Lechitic tribe of Vistulans. Krakus is also credited with building Wawel Castle and slaying the Wawel Dragon by feeding it a dead sheep full ...
, who built it above a cave occupied by a dragon, Smok Wawelski
''Smok'' (meaning "dragon" in Polish) is an extinct genus of large carnivorous archosaur. It lived during the latest Triassic period (latest Norian to early Rhaetian stage, between 205–200 Ma). Its remains have been found in Lisowice, ...
. The first written record of the city's name dates back to 965, when Kraków was described as a notable commercial centre controlled first by Moravia (876–879), but captured by a Bohemian duke Boleslaus I in 955. The first acclaimed ruler of Poland, Mieszko I, took Kraków from the Bohemians and incorporated it into the holdings of the Piast dynasty towards the end of his reign.
In 1038, Kraków became the seat of the Polish government. By the end of the tenth century, the city was a leading centre of trade. Brick buildings were constructed, including the Royal Wawel Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established o ...
with St. Felix and Adaukt Rotunda, Romanesque churches such as St. Andrew's Church, a cathedral, and a basilica. The city was sacked and burned during the Mongol invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
of 1241. It was rebuilt practically identical,Polska Agencja Prasowa. Nauka w Polsce (June 2007)Rocznica lokacji Krakowa (750-year anniversary of the Kraków Location Act).
See also
translated from Latin by Bożena Wyrozumsk
Retrieved 21 December 2012. based on new location act and incorporated in 1257 by the high duke
Bolesław V the Chaste
Bolesław V the Chaste ( pl, Bolesław Wstydliwy; 21 June 1226 – 7 December 1279) was Duke of Sandomierz in Lesser Poland from 1232 and High Duke of Poland from 1243 until his death, as the last male representative of the Lesser Polish branch o ...
who following the example of Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
, introduced city rights modelled on the Magdeburg law
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within ...
allowing for tax benefits and new trade privileges for the citizens. In 1259, the city was again ravaged by the Mongols. A third attack in 1287 was repelled thanks in part to the newly built fortifications.
 In 1335, King
In 1335, King Casimir III the Great
Casimir III the Great ( pl, Kazimierz III Wielki; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, and fought to retain the title in the Galicia-Volhynia Wars. He ...
(Kazimierz in Polish) declared the two western suburbs to be a new city named after him, Kazimierz
Kazimierz (; la, Casimiria; yi, קוזמיר, Kuzimyr) is a historical district of Kraków and Kraków Old Town, Poland. From its inception in the 14th century to the early 19th century, Kazimierz was an independent city, a royal city of the ...
(''Casimiria'' in Latin). The defensive walls were erected around the central section of Kazimierz in 1362, and a plot was set aside for the Augustinian Augustinian may refer to:
*Augustinians, members of religious orders following the Rule of St Augustine
*Augustinianism, the teachings of Augustine of Hippo and his intellectual heirs
*Someone who follows Augustine of Hippo
* Canons Regular of Sain ...
order next to Skałka
Saint Michael the Archangel and Saint Stanislaus the Bishop and Martyr Basilica, also known as Skałka, which means "a small rock" in Polish, is a small outcrop in Kraków atop of which a Pauline monastery is located, a place where the Bish ...
. The city rose to prominence in 1364, when Casimir founded the University of Kraków
The Jagiellonian University ( Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
, the second oldest university in central Europe after the Charles University in Prague
)
, image_name = Carolinum_Logo.svg
, image_size = 200px
, established =
, type = Public, Ancient
, budget = 8.9 billion CZK
, rector = Milena Králíčková
, faculty = 4,057
, administrative_staff = 4,026
, students = 51,438
, undergr ...
. Casimir also began work on a campus for the academy in Kazimierz, but he died in 1370 and the campus was never completed.
The city continued to grow under the joint Lithuanian-Polish Jagiellon dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
. As the capital of the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
and a member of the Hanseatic League, the city attracted many craftsmen from abroad, businesses, and guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s as science and the arts began to flourish. The royal chancery and the university ensured a first flourishing of Polish literary culture in the city.
Kraków's "Golden Age"
The 15th and 16th centuries were known as Poland's ''Złoty Wiek'' orGolden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the '' Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the G ...
. Many works of Polish Renaissance
The Renaissance in Poland ( pl, Renesans, Odrodzenie; literally: the Rebirth) lasted from the late 15th to the late 16th century and is widely considered to have been the Golden Age of Polish culture. Ruled by the Jagiellonian dynasty, the Crown ...
art and architecture were created, including ancient synagogues in Kraków's Jewish quarter located in the north-eastern part of Kazimierz, such as the Old Synagogue. During the reign of Casimir IV, various artists came to work and live in Kraków, and Johann Haller
Johann Haller or Jan Haller (1463–1525) is considered one of the first commercial printers in Poland.
Early life
Haller was born in Rothenburg,
Franconia, Germany. After his studies at the Kraków Academy, Haller became a merchant in wine, c ...
established a printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
in the city after Kasper Straube had printed the Calendarium Cracoviense, the first work printed in Poland, in 1473.
In 1520, the most famous church bell
A church bell in Christian architecture is a bell which is rung in a church for a variety of religious purposes, and can be heard outside the building. Traditionally they are used to call worshippers to the church for a communal service, and to ...
in Poland, named '' Zygmunt'' after Sigismund I of Poland
Sigismund I the Old ( pl, Zygmunt I Stary, lt, Žygimantas II Senasis; 1 January 1467 – 1 April 1548) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until his death in 1548. Sigismund I was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty, the ...
, was cast by Hans Behem. At that time, Hans Dürer, a younger brother of artist and thinker Albrecht Dürer, was Sigismund's court painter
A court painter was an artist who painted for the members of a royal or princely family, sometimes on a fixed salary and on an exclusive basis where the artist was not supposed to undertake other work. Painters were the most common, but the cour ...
. Hans von Kulmbach
Hans Suess, known as Hans von Kulmbach, was a German artist. He was born around 1480 in Kulmbach, Franconia and died prior to 3 December 1522 in Nuremberg.John Denison Champlin, Charles CallahanCyclopedia of Painters and PaintingsNew York, Pub ...
made altarpieces for several churches. In 1553, the Kazimierz district council gave the Jewish Qahal
The ''qahal'' ( he, קהל) was a theocratic organizational structure in ancient Israelite society according to the Hebrew Bible. See column345-6 The Ashkenazi Jewish system of a self-governing community or kehila from medieval Christian Europe ...
a licence for the right to build their own interior walls across the western section of the already existing defensive walls. The walls were expanded again in 1608 due to the growth of the community and influx of Jews from Bohemia. In 1572, King Sigismund II
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first rule ...
, the last of the Jagiellons, died childless. The Polish throne passed to Henry III of France and then to other foreign-based rulers in rapid succession, causing a decline in the city's importance that was worsened by pillaging during the Swedish invasion and by an outbreak of bubonic plague that left 20,000 of the city's residents dead. In 1596, Sigismund III of the House of Vasa moved the administrative capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
from Kraków to Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
.
19th century
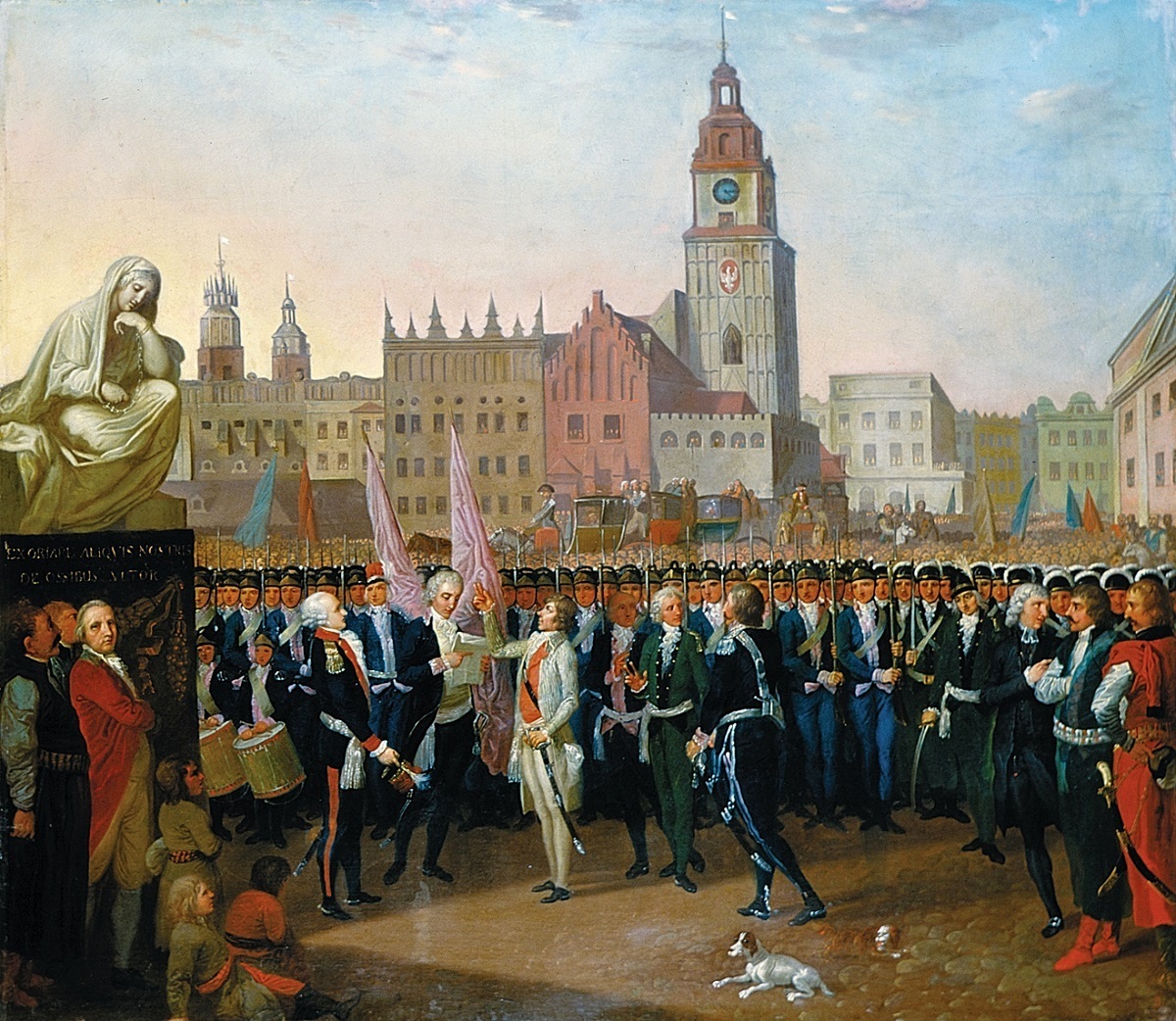 Already weakened during the 18th century, by the mid-1790s the
Already weakened during the 18th century, by the mid-1790s the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
had twice been partitioned by its neighbors: Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, the Habsburg empire
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
. In 1791, the Austrian and Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II
Joseph II (German: Josef Benedikt Anton Michael Adam; English: ''Joseph Benedict Anthony Michael Adam''; 13 March 1741 – 20 February 1790) was Holy Roman Emperor from August 1765 and sole ruler of the Habsburg lands from November 29, 1780 un ...
changed the status of Kazimierz as a separate city and made it into a district of Kraków. The richer Jewish families began to move out. However, because of the injunction against travel on the Sabbath, most Jewish families stayed relatively close to the historic synagogues. In 1794, Tadeusz Kościuszko
Andrzej Tadeusz Bonawentura Kościuszko ( be, Andréj Tadévuš Banavientúra Kasciúška, en, Andrew Thaddeus Bonaventure Kosciuszko; 4 or 12 February 174615 October 1817) was a Polish military engineer, statesman, and military leader who ...
initiated an unsuccessful insurrection
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
in the town's Main Square which, in spite of his victorious Battle of Racławice against a numerically superior Russian army
The Russian Ground Forces (russian: Сухопутные войска �ВSukhoputnyye voyska V}), also known as the Russian Army (, ), are the land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
The primary responsibilities of the Russian Ground Force ...
, resulted in the third and final partition of Poland. In 1809, Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
captured former Polish territories from Austria and made the town part of the Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
. Following Napoleon's defeat, the 1815 Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
restored the pre-war boundaries but also created the partially independent Free City of Kraków
Free may refer to:
Concept
* Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything
* Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism
* Emancipate, to procure ...
. An insurrection in 1846 failed, resulting in the city being annexed by Austria under the name the Grand Duchy of Kraków
The Grand Duchy of Kraków (german: Großherzogtum Krakau; pl, Wielkie Księstwo Krakowskie) was created after the incorporation of the Free City of Cracow into Austria on November 16, 1846. From 1846 to 1918 the title, Grand Duke of Kraków, w ...
( pl, Wielkie Księstwo Krakowskie, german: Großherzogtum Krakau).
In 1866, Austria granted a degree of autonomy to Galicia after its own defeat in the Austro-Prussian War. Politically freer Kraków became a Polish national symbol and a centre of culture and art, known frequently as the "Polish Athens" ('). Many leading Polish artists of the period resided in Kraków, among them the seminal painter Jan Matejko, laid to rest at Rakowicki Cemetery
Rakowicki Cemetery (English: ; pl, Cmentarz Rakowicki) is a historic necropolis and a cultural heritage monument located on 26 Rakowicka Street in the centre of Kraków, Poland. It lies within the Administrative District No. 1 ''Stare Miasto'' ...
, and the founder of modern Polish drama, Stanisław Wyspiański
Stanisław Mateusz Ignacy Wyspiański (; 15 January 1869 – 28 November 1907) was a Polish playwright, painter and poet, as well as interior and furniture designer. A patriotic writer, he created a series of symbolic, national dramas withi ...
. Fin de siècle
() is a French term meaning "end of century,” a phrase which typically encompasses both the meaning of the similar English idiom "turn of the century" and also makes reference to the closing of one era and onset of another. Without context, ...
Kraków evolved into a modern metropolis; running water
Tap water (also known as faucet water, running water, or municipal water) is water supplied through a tap, a water dispenser valve. In many countries, tap water usually has the quality of drinking water. Tap water is commonly used for drinkin ...
and electric streetcars were introduced in 1901, and between 1910 and 1915, Kraków and its surrounding suburban communities were gradually combined into a single administrative unit called Greater Kraków (').
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
on 3 August 1914, Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
formed a small cadre military unit, the First Cadre Company—the predecessor of the Polish Legions—which set out from Kraków to fight for the liberation of Poland. The city was briefly besieged by Russian troops in November 1914. Austrian rule in Kraków ended in 1918 when the Polish Liquidation Committee assumed power.
20th century to the present
 Following the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918, Kraków resumed its role as a major Polish academic and cultural centre, with the establishment of new universities such as the
Following the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918, Kraków resumed its role as a major Polish academic and cultural centre, with the establishment of new universities such as the AGH University of Science and Technology
AGH University of Science and Technology in Kraków, (abbreviated as ''AGH UST'') is a public university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1913, its inauguration took place in 1919. The university focuses on innovative technologies, its research p ...
and the Jan Matejko Academy of Fine Arts
The Jan Matejko Academy of Fine Arts in Kraków ( pl, Akademia Sztuk Pięknych im. Jana Matejki w Krakowie, usually abbreviated to ''ASP''), is a public institution of higher education located in the centre of Kraków, Poland. It is the oldest Pol ...
, including a number of new and essential vocational schools. The city became an important cultural centre for Polish Jews
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the l ...
, including both Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
and Bundist groups. Kraków was also an influential centre of Jewish spiritual life, with all its manifestations of religious observance - from Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pa ...
to Hasidic and Reform Judaism
Reform Judaism, also known as Liberal Judaism or Progressive Judaism, is a major Jewish denomination that emphasizes the evolving nature of Judaism, the superiority of its ethical aspects to its ceremonial ones, and belief in a continuous sear ...
- flourishing side by side.
Following the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
by Nazi Germany in September 1939, the city of Kraków became part of the General Government, a separate administrative region of the Third Reich
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. On 26 October 1939, the Nazi régime set up Distrikt Krakau, one of a total of four districts within the General Government. On the same day, the city of Kraków also became the capital of the administration. The General Government was ruled by Governor-General Hans Frank
Hans Michael Frank (23 May 1900 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and lawyer who served as head of the General Government in Nazi-occupied Poland during the Second World War.
Frank was an early member of the German Workers' Party ...
, who was based in the city's Wawel Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established o ...
. The Nazis envisioned turning Kraków into a completely Germanised city; after removal of all the Jews and Poles, renaming of locations and streets into the German language, and sponsorship of propaganda trying to portray it as a historically German city. On 28 November 1939 Hans Frank set up ''Judenräte'' (Jewish Councils) to be run by Jewish citizens for the purpose of carrying out orders for the Nazis. These orders included the registration of all Jewish people living in each area, the collection of taxes, and the formation of forced-labour groups. The Polish Home Army
The Home Army ( pl, Armia Krajowa, abbreviated AK; ) was the dominant resistance movement in German-occupied Poland during World War II. The Home Army was formed in February 1942 from the earlier Związek Walki Zbrojnej (Armed Resistance) est ...
maintained a parallel underground administrative system.
On the eve of World War II some 56,000 Jews resided in Krakow, almost one-quarter of a total population of about 250,000. By November 1939, the Jewish population of Krakow had grown to approximately 70,000. According to German statistics from 1940, over 200,000 Jews lived within the entire Kraków District, comprising more than 5 percent of the total population in the district. These statistics, however, probably underestimate the situation.
In November 1939, during an operation known as "", the Germans arrested more than 180 university professors and academics and sent them to the Sachsenhausen
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners ...
and Dachau concentration camps
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
, though the survivors were later released on the request of prominent Italians.
Before the formation of ghettos, which began in the Distrikt in December 1939, Jews were encouraged to flee the city. For those who remained the German authorities decided in March 1941 to allocate a then suburban neighborhood, Podgórze District, to become Kraków's ghetto - there many Jews would die of illness or starvation. Initially, most ghettos were open and Jews were allowed to enter and exit freely. However, with time ghettos were generally closed and security became tighter. From autumn 1941, the SS developed the policy of Extermination through labour
Extermination through labour (or "extermination through work", german: Vernichtung durch Arbeit) is a term that was adopted to describe forced labor in Nazi concentration camps in light of the high mortality rate and poor conditions; in some ...
, which further worsened the already bleak conditions for Jews. The ghetto inhabitants were later murdered or sent to German Extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s, including Bełżec and Auschwitz, and to Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp
Płaszów () or Kraków-Płaszów was a Nazi concentration camp operated by the SS in Płaszów, a southern suburb of Kraków, in the General Governorate of German-occupied Poland. Most of the prisoners were Polish Jews who were targeted for de ...
. The largest deportations within the Distrikt occurred from June to September 1942. More specifically, the Kraków ghetto deportation occurred in the first week of June 1942, and in March 1943 the ghetto was definitely liquidated.
Roman Polanski
Raymond Roman Thierry Polański , group=lower-alpha, name=note_a ( né Liebling; 18 August 1933) is a French-Polish film director, producer, screenwriter, and actor. He is the recipient of numerous accolades, including an Academy Award, tw ...
, the film director, survived the Kraków ghetto. Oskar Schindler
Oskar Schindler (; 28 April 1908 – 9 October 1974) was a German industrialist, humanitarian and a member of the Nazi Party who is credited with saving the lives of 1,200 Jews during the Holocaust by employing them in his enamelware and ...
selected employees from the ghetto to work in his enamelware factory ' (' for short), saving them from the camps. Similarly, many men capable of physical labor were saved from the deportations to extermination camps and instead sent to labor camps across the General Government.
By September 1943, the last of the Jews from the Kraków ghetto had been deported. Although looted by occupational authorities, Kraków remained relatively undamaged at the end of World War II, with most of the city's historical and architectural legacy spared. Soviet forces under the command of Marshal Ivan Konev
Ivan Stepanovich Konev ( rus, link=no, Ива́н Степа́нович Ко́нев, p=ɪˈvan sʲtʲɪˈpanəvʲɪtɕ ˈkonʲɪf; – 21 May 1973) was a Soviet general and Marshal of the Soviet Union who led Red Army forces on the ...
entered the city on 18 January 1945, and began arresting Poles loyal to the Polish government-in-exile
The Polish government-in-exile, officially known as the Government of the Republic of Poland in exile ( pl, Rząd Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej na uchodźstwie), was the government in exile of Poland formed in the aftermath of the Invasion of Pola ...
or those who had served in the Home Army.
Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million ne ...
(officially declared in 1952), the intellectual and academic community of Kraków came under complete political control. The universities were soon deprived of printing rights and autonomy. The Stalinist government of Poland ordered the construction of the country's largest steel mill in the newly created suburb of Nowa Huta
Nowa Huta (, literally "The New Steel Mill") is the easternmost district of Kraków, Poland. With more than 200,000 inhabitants, it is one of the most populous areas of the city. Until 1990, the neighbouring districts were considered expansions o ...
. The creation of the giant Lenin Steelworks (now Sendzimir Steelworks owned by Mittal) sealed Kraków's transformation from a university city into an industrial centre. The new working-class population, drawn by the industrialization of Kraków, contributed to rapid growth.
In an effort that spanned two decades, Karol Wojtyła
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
, cardinal archbishop of Kraków from 1964 to 1978, successfully lobbied for permission to build the first churches in the newly-industrial suburbs. In 1978 the Catholic Church elevated Wojtyła to the papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
as John Paul II
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
, the first non-Italian pope in 455 years. In the same year, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
, following the application of local authorities, placed Kraków Old Town on the first-ever list of World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s.
Geography
Vistula River
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
, in a valley at the foot of the Carpathian Mountains, above sea level; halfway between the Jurassic Rock Upland ( pl, Jura Krakowsko-Częstochowska) to the north, and the Tatra Mountains
The Tatra Mountains (), Tatras, or Tatra (''Tatry'' either in Slovak () or in Polish () - '' plurale tantum''), are a series of mountains within the Western Carpathians that form a natural border between Slovakia and Poland. They are the hi ...
to the south, constituting the natural border with Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
and the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
; west from the border with Ukraine.
There are five nature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
s in Kraków, with a combined area of ca. . Due to their ecological value, these areas are legally protected. The western part of the city, along its northern and north-western side, borders an area of international significance known as the Jurassic Bielany
Bielany () is a district in Warsaw located in the north-western part of the city.
Initially a part of Żoliborz, Bielany has been an independent district since 1994. Bielany borders Żoliborz to the south-east, and Bemowo to the south-west. It ...
-Tyniec
Tyniec is a historic village in Poland on the Vistula river, since 1973 a part of the city of Kraków (currently in the district of Dębniki). Tyniec is notable for its Benedictine abbey founded by King Casimir the Restorer in 1044.
Etymology
T ...
refuge. The main motives for the protection of this area include plant and animal wildlife and the area's geomorphological features and landscape. Another part of the city is located within the ecological 'corridor' of the Vistula River valley. This corridor is also assessed as being of international significance as part of the Pan-European ecological network. The city centre is situated on the left (northern) bank of the river.
Climate
Officially, Kraków has atemperate oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
, denoted by Köppen classification Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author an ...
as ''Cfb'', best defined as a semicontinental climate. In older reference periods it was classified as a warm summer continental climate (''Dfb''). By classification of Wincenty Okołowicz
Wincenty Okołowicz (26 June 1906 – 3 September 1979) was a Polish geographer and an expert in geomorphology and climatology. He is best known as the author of the 1965 major Polish classification of world's climates, ''Climatic Zones of the ...
, it has a warm temperate climate in the centre of continental Europe with the "fusion" of different features.
Due to its geographic location, the city may be under marine influence, sometimes Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
influence, but without direct influence, giving the city variable meteorological conditions over short spaces of time.
Being towards Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
and a relatively considerable distance from the sea, Krakow has significant temperature differences according to the progress of different air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and humidity. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adapt to the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to l ...
es, having four defined seasons of the year. Average temperatures in summer range from and in winter from . The average annual temperature is . In summer temperatures often exceed , even reaching , while in winter temperatures drop to at night and about during the day. During very cold nights the temperature can drop to . The city lies near the Tatra Mountains
The Tatra Mountains (), Tatras, or Tatra (''Tatry'' either in Slovak () or in Polish () - '' plurale tantum''), are a series of mountains within the Western Carpathians that form a natural border between Slovakia and Poland. They are the hi ...
, there are often occurrences of halny
Halny is a foehn wind that blows in southern Poland and in Slovakia in the Tatra Mountains of the Carpathians. The most turbulent halny blows in Podhale region of southern Poland, coming from the south, down the slopes of the Tatra Mountains; in S ...
blowing (a foehn wind
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range.
It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of ...
), causing temperatures to rise rapidly, and even in winter reach up to .
In relation to Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, temperatures are very similar for most of the year, except that in the colder months southern Poland has a larger daily temperature range, more moderate winds, generally more rainy days and with greater chances of clear skies on average, especially in winter. The higher sun angle also allows for a longer growing season. In addition, for older data there was less sun than the capital of the country, about 30 minutes daily per year, but both have small differences in relative humidity and the direction of the winds is northeast.
The climate table below presents weather data from 2000 to 2012, although the official Köppen reference period was from 1981 to 2010 (therefore not being technically a climatological normal). According to ongoing measurements, the temperature has increased during these years as compared with the last series. This increase averages about over all months. Warming is most pronounced during the winter months, with an increase of more than in January.
Cityscape
Developed over many centuries, Kraków provides a showcase setting for many historic styles of architecture. As the city expanded, so too did the architectural achievements of its builders. It is for this reason that the variations in style and urban planning are so easily recognisable. Built from its earliest nucleus outward, and having escaped much of the destruction endured by Poland during the 20th-century wars, Kraków's many architectural monuments can typically be seen in historical order by walking from the city centre out, towards its later districts. Kraków is one of the few medieval towns in Poland that does not have a historicRatusz
A ''Ratusz'' () (german: Rathaus; russian: Ратуша, ''Ratusha''; lt, Rotušė) is a historic administrative building in countries that adopted the Magdeburg rights such as the Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and others ...
town hall in its Main Square, because it has not survived the Partitions of Poland.
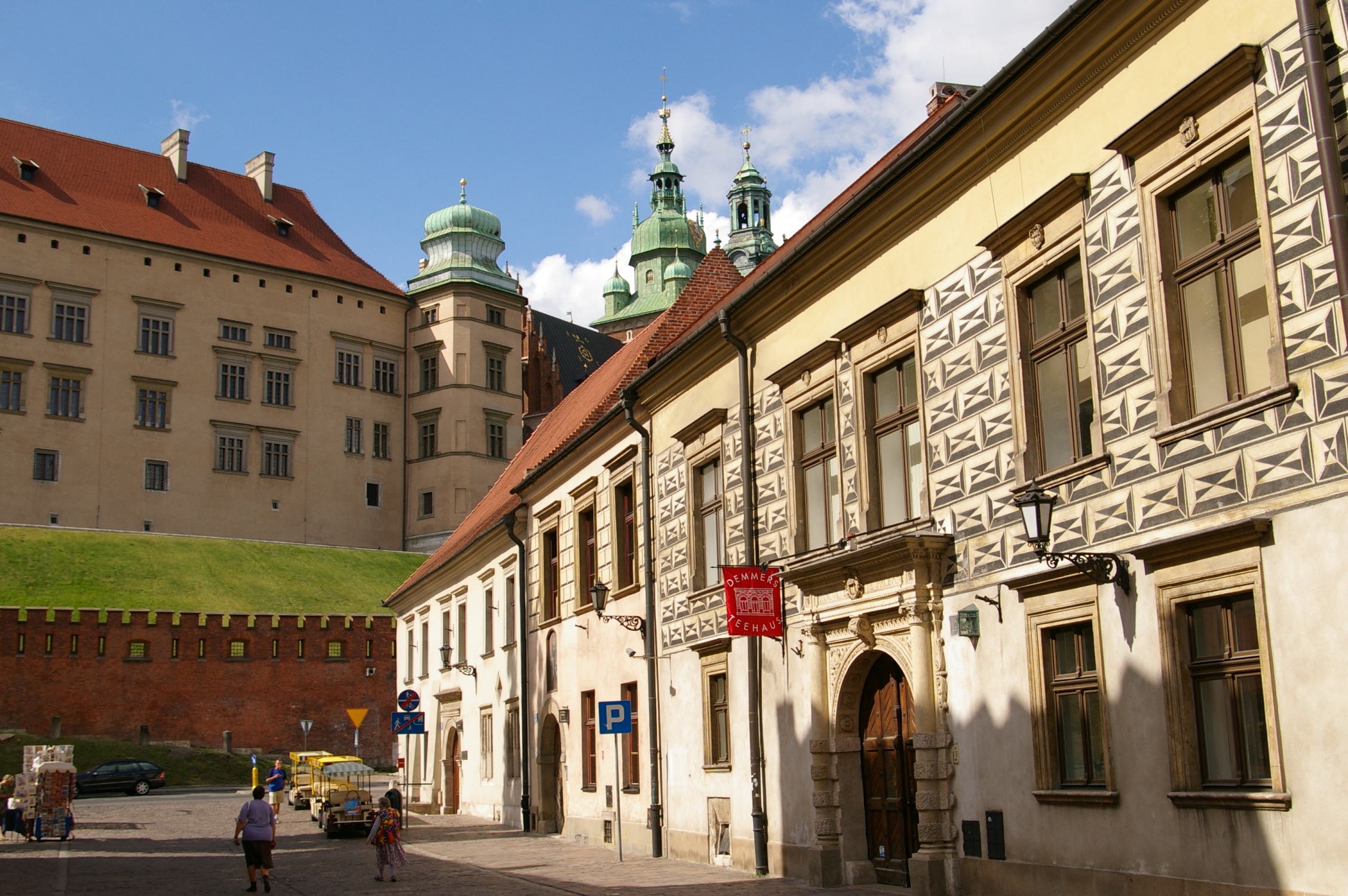
Kraków's historic centre, which includes the Old Town, Kazimierz
Kazimierz (; la, Casimiria; yi, קוזמיר, Kuzimyr) is a historical district of Kraków and Kraków Old Town, Poland. From its inception in the 14th century to the early 19th century, Kazimierz was an independent city, a royal city of the ...
and the Wawel Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established o ...
, was included as the first of its kind on the list of UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s in 1978. The ''Stare Miasto'' is the most prominent example of an old town in the country. For many centuries Kraków was the royal
''The Royal'' is a British period medical drama, produced by Yorkshire Television (later part of ITV Studios), and broadcast on ITV1 from 2003 until its cancellation in 2011. The series is set in the 1960s and focuses on the lives of the ...
capital of Poland, until Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa ( pl, Zygmunt III Waza, lt, Žygimantas Vaza; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632
N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden and Grand Duke of Finland from 1592 to ...
relocated the court to Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
in 1596. The whole district is bisected by the Royal Road
''The Royal Road'' is a 2015 documentary film directed by Jenni Olson. The film premiered in the New Frontier section of the 2015 Sundance Film Festival. In the film's voiceover, Olson reflects on her butch identity and experiences of unrequited ...
, the coronation route traversed by the Kings of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th ...
. The Route begins at St. Florian's Church outside the northern flank of the old city-walls in the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
suburb of Kleparz; passes the Barbican of Kraków (''Barbakan'') built in 1499, and enters ''Stare Miasto'' through the Florian Gate
St. Florian's Gate or Florian Gate ( pl, Brama Floriańska) in Kraków, Poland, is one of the best-known Polish Gothic towers, and a focal point of Kraków's Old Town. It was built about the 14th century as a rectangular Gothic tower of "wild sto ...
. It leads down Floriańska Street through the Main Square, and up Grodzka to Wawel
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established o ...
, the former seat of Polish royalty, overlooking the Vistula river
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
. Old Town attracts visitors from all over the World. Kraków historic centre is one of the 13 places in Poland that are included in the UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s. The architectural design of the district had survived all cataclysms of the past and retained its original form coming from the medieval times.
 In addition to the old town, the city's district of
In addition to the old town, the city's district of Kazimierz
Kazimierz (; la, Casimiria; yi, קוזמיר, Kuzimyr) is a historical district of Kraków and Kraków Old Town, Poland. From its inception in the 14th century to the early 19th century, Kazimierz was an independent city, a royal city of the ...
is particularly notable for its many renaissance buildings and picturesque streets, as well as the historic Jewish quarter located in the north-eastern part of Kazimierz. Kazimierz was founded in the 14th century to the south-east of the city centre and soon became a wealthy, well-populated area where construction of imposing properties became commonplace. Perhaps the most important feature of medieval Kazimierz was the only major, permanent bridge (''Pons Regalis'') across the northern arm of the Vistula. This natural barrier used to separate Kazimierz from the Old Town for several centuries, while the bridge connected Kraków to the Wieliczka Salt Mine
The Wieliczka Salt Mine ( pl, Kopalnia soli Wieliczka) is a salt mine in the town of Wieliczka, near Kraków in southern Poland.
From Neolithic times, sodium chloride (table salt) was produced there from the upwelling brine. The Wieliczka sa ...
and the lucrative Hungarian trade route. The last structure at this location (at the end of modern Stradom Street) was dismantled in 1880 when the northern arm of the river was filled in with earth and rock, and subsequently built over.
 By the 1930s, Kraków had 120 officially registered synagogues and prayer houses that spanned across the old city. Much of Jewish intellectual life had moved to new centres like
By the 1930s, Kraków had 120 officially registered synagogues and prayer houses that spanned across the old city. Much of Jewish intellectual life had moved to new centres like Podgórze
Podgórze is a district of Kraków, Poland, situated on the right (southern) bank of the Vistula River, at the foot of Lasota Hill. The district was subdivided in 1990 into six new districts, see present-day districts of Kraków for more details. ...
. This in turn, led to the redevelopment and renovation of much of Kazimierz and the development of new districts in Kraków. Most historic buildings in central Kazimierz today are preserved in their original form. Some old buildings, however, were not repaired after the devastation brought by the Second World War, and have remained empty. Most recent efforts at restoring the historic neighborhoods gained new impetus around 1993. Kazimierz is now a well-visited area, seeing a booming growth in Jewish-themed restaurants, bars, bookstores and souvenir shops.
 As the city of Kraków began to expand further under the rule of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the new architectural styles also developed. Key buildings from the 19th and early 20th centuries in Kraków include the Jan Matejko Academy of Fine Arts, the directorate of the Polish State Railways as well as the original complex of Kraków Główny railway station and the city's Academy of Economics. It was also at around that time that Kraków's first radial boulevards began to appear, with the city undergoing a large-scale program aimed at transforming the ancient Polish capital into a sophisticated regional centre of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. New representative government buildings and multi-story tenement houses were built at around that time. Much of the urban-planning beyond the walls of the Old Town was done by Polish architects and engineers trained in
As the city of Kraków began to expand further under the rule of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the new architectural styles also developed. Key buildings from the 19th and early 20th centuries in Kraków include the Jan Matejko Academy of Fine Arts, the directorate of the Polish State Railways as well as the original complex of Kraków Główny railway station and the city's Academy of Economics. It was also at around that time that Kraków's first radial boulevards began to appear, with the city undergoing a large-scale program aimed at transforming the ancient Polish capital into a sophisticated regional centre of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. New representative government buildings and multi-story tenement houses were built at around that time. Much of the urban-planning beyond the walls of the Old Town was done by Polish architects and engineers trained in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
. Some major projects of the era include the development of the Jagiellonian University's new premises and the building of the Collegium Novum
The ''Collegium Novum'' (Latin: "New College") is the Neo-Gothic main building of the Jagiellonian University in Kraków, Poland, originally built between the year 1363 and 1365 and after its destruction, rebuilt in between 1873-1887. Based on ...
just west of the Old Town. The imperial style planning of the city's further development continued until the return of Poland's independence, following the First World War. Early modernist style in Kraków is represented by such masterpieces as the Palace of Art
"The Palace of Art" is an 1832 (revised 1842) poem by Alfred Tennyson. In the poem a man constructs a palace of art for his soul with any amount of art. The art of the palace and its gardens deals with sacred, secular and irreligious themes, the mo ...
by Franciszek Mączyński and the 'House under the Globe'. Secession style architecture, which had arrived in Kraków from Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, became popular towards the end of the Partitions.
 With Poland's regained independence came the major change in the fortunes of Kraków—now the second most important city of a sovereign nation. The state began to make new plans for the city development and commissioned a number of representative buildings. The predominant style for new projects was modernism with various interpretations of the art-deco style. Important buildings constructed in the style of Polish modernism include the Feniks 'LOT' building on Basztowa Street, the Feniks department store on the Main Square and the Municipal Savings Bank on Szczepański Square. The Józef Piłsudski house is also of note as a particularly good example of interwar architecture in the city.
After the Second World War, new government turned toward Soviet influence and the Stalinist monumentalism. The doctrine of
With Poland's regained independence came the major change in the fortunes of Kraków—now the second most important city of a sovereign nation. The state began to make new plans for the city development and commissioned a number of representative buildings. The predominant style for new projects was modernism with various interpretations of the art-deco style. Important buildings constructed in the style of Polish modernism include the Feniks 'LOT' building on Basztowa Street, the Feniks department store on the Main Square and the Municipal Savings Bank on Szczepański Square. The Józef Piłsudski house is also of note as a particularly good example of interwar architecture in the city.
After the Second World War, new government turned toward Soviet influence and the Stalinist monumentalism. The doctrine of Socialist realism in Poland
Socialist realism in Poland ( pl, socrealizm) was a socio-political and aesthetic doctrine enforced by the pro-Soviet communist government in the process of Stalinization of the post-war Polish People’s Republic. The official policy was introduce ...
, as in other countries of the People's Republic
People's republic is an official title, usually used by some currently or formerly communist or left-wing states. It is mainly associated with soviet republics, socialist states following people's democracy, sovereign states with a democratic- ...
s, was enforced from 1949 to 1956. It involved all domains of art, but its most spectacular achievements were made in the field of urban design. The guidelines for this new trend were spelled-out in a 1949 resolution of the National Council of Party Architects. Architecture was to become a weapon in establishing the new social order by the communists. The ideological impact of urban design was valued more than aesthetics. It aimed at expressing persistence and power. This form of architecture was implemented in the new industrial district of Nowa Huta with apartment blocks constructed according to a Stalinist blueprint, with repetitious courtyards and wide, tree-lined avenues.
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
was generally regarded as the most revered in old Polish architecture, it was also used for augmenting Poland's Socialist national format. However, in the course of incorporating the principles of Socialist realism, there were quite a few deviations introduced by the communists. One of these was to more closely reflect Soviet architecture, which resulted in the majority of works blending into one another. From 1953, critical opinions in the Party were increasingly frequent, and the doctrine was given up in 1956 marking the end of Stalinism. The soc-realist centre of Nowa Huta is considered to be a meritorious monument of the times. This period in postwar architecture was followed by the mass-construction of large Panel System apartment blocks, most of which were built outside the city centre and thus do not encroach upon the beauty of the old or new towns. Some examples of the new style (e.g., Hotel Cracovia) recently listed as heritage monuments were built during the latter half of the 20th century in Kraków.
After the Revolutions of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Nat ...
and the birth of the Third Republic in the latter half of the 20th century, a number of new architectural projects were completed, including the construction of large business parks and commercial facilities such as the Galeria Krakowska, or infrastructure investments like the Kraków Fast Tram
Kraków Fast Tram ( pl, Krakowski Szybki Tramwaj) is a light rail network being developed in Kraków.
It consists of several modernized or purpose-built tram tracks with radio-controlled absolute priority on crossings, a long tunnel under Kr ...
. A good example of this would be the Manggha Museum of Japanese Art and Technology designed by Arata Isozaki
Arata Isozaki (磯崎 新, ''Isozaki Arata''; born 23 July 1931) is a Japanese architect, urban designer, and theorist from Ōita. He was awarded the RIBA Gold Medal in 1986 and the Pritzker Architecture Prize in 2019.
Biography
Isozaki was ...
, the 2007-built ''Pawilon Wyspiański 2000'', which is used as a multi-purpose information and exhibition space, or the Małopolski Garden of Arts ('' Małopolski Ogród Sztuki''), a multi-purpose exhibition and theatre complex located in the historic Old Town.
Parks and gardens

Planty Park Planty may refer to:
* Planty Park Planty may refer to:
* Planty Park, a city park in Kraków, Poland
* Planty, Podlaskie Voivodeship (north-east Poland)
* Planty, Aube, France
{{geodis
City counties of Poland
Cities and towns in Lesser Poland Voivodeship
Former capitals of Poland
Kraków Voivodeship (14th century – 1795)
Free City of Kraków
Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria
Kraków Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Historic Jewish communities
World Heritage Sites in Poland
Members of the Hanseatic League
Magdeburg rights
Holocaust locations in Poland