Kenilworth club entrance.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kenilworth ( ) is a market town and civil parish in the Warwick District in Warwickshire, England, south-west of Coventry, north of Warwick and north-west of London. It lies on

 A settlement existed at Kenilworth by the time of the 1086 Domesday Book, which records it as ''Chinewrde''.
Geoffrey de Clinton (died 1134) initiated the building of an
A settlement existed at Kenilworth by the time of the 1086 Domesday Book, which records it as ''Chinewrde''.
Geoffrey de Clinton (died 1134) initiated the building of an  During the Middle Ages, Kenilworth played a significant role in the history of England: Between June and December
During the Middle Ages, Kenilworth played a significant role in the history of England: Between June and December  Elizabeth I visited
Elizabeth I visited
 The town's growth occasioned the addition of a second
The town's growth occasioned the addition of a second
 Kenilworth is close to the University of Warwick at Gibbet Hill in Coventry to the north. Kenilworth has several suburbs, which include Borrowell, Castle Green, Crackley, Ladyes Hill, Mill End, Park Hill, St Johns, Whitemoor and Windy Arbour. The town has good transport links to Coventry, Warwick,
Kenilworth is close to the University of Warwick at Gibbet Hill in Coventry to the north. Kenilworth has several suburbs, which include Borrowell, Castle Green, Crackley, Ladyes Hill, Mill End, Park Hill, St Johns, Whitemoor and Windy Arbour. The town has good transport links to Coventry, Warwick, 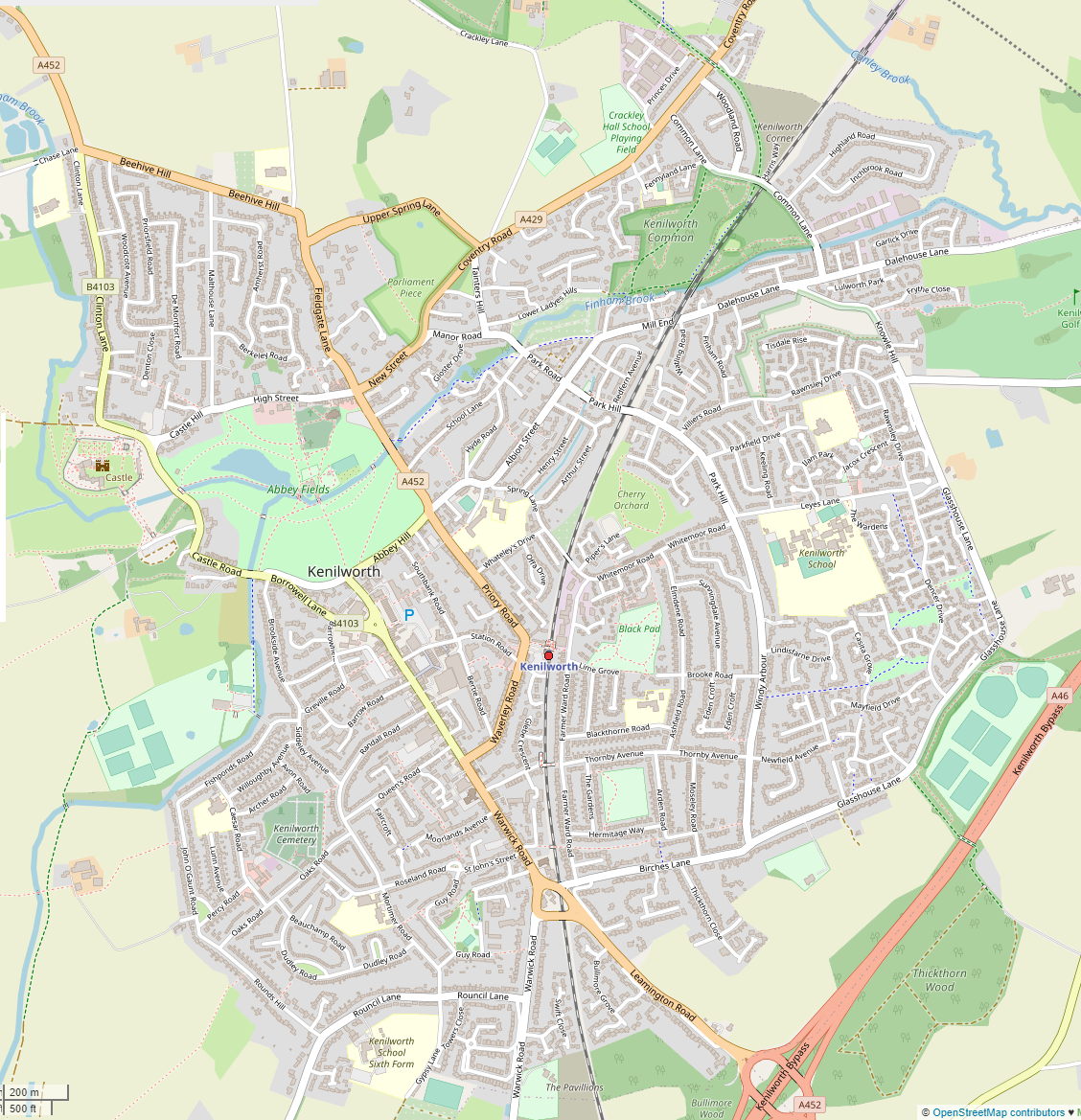 The principal shopping area of Kenilworth is around Warwick Street, Abbey End and Talisman Square; a 1960s shopping precinct. In 2008 the square was modernised and partly redeveloped to include a new Waitrose supermarket. Kenilworth has been a Fairtrade Town since 2007. The town's public library underwent a renovation in 2021. ''The Cross'', a local pub-restaurant, received a
The principal shopping area of Kenilworth is around Warwick Street, Abbey End and Talisman Square; a 1960s shopping precinct. In 2008 the square was modernised and partly redeveloped to include a new Waitrose supermarket. Kenilworth has been a Fairtrade Town since 2007. The town's public library underwent a renovation in 2021. ''The Cross'', a local pub-restaurant, received a

at www.encyclopedia-titanica.org *
Retrieved 18 April 2014.
/ref>
One World Link (OWL)
* Uyogo, Tanzania
Kenilworth Town CouncilKenilworth The Best Kept Secret in Warwickshire
— official Kenilworth town centre website
Kenilworth Chamber of TradeGeograph photos of Kenilworth and surrounding areaKenilworth local history articles and booksKenilworth in the Second World WarCatalogue of the Kenilworth Urban District Council archives
held at the
Warwickshire Geological Conservation Group (WGCG) is based in KenilworthKenilworth archives
- Our Warwickshire {{authority control Towns in Warwickshire
Finham Brook
The Finham Brook is a lower tributary of the River Sowe, it flows through Kenilworth and Warwickshire, England, to join the Sowe near Finham. Its principal tributaries include the Canley Brook, which drains the Tile Hill and Canley areas of Cove ...
, a tributary of the River Sowe
The River Sowe is a river in Warwickshire and West Midlands, England. It is a tributary of the River Avon, and flows into it just south of Stoneleigh about 5 miles (8 km) south of Coventry. It is about long.
The Sowe rises in Bedworth ...
, which joins the River Avon north-east of the town. At the 2021 Census, the population was 22,538. The town is home to the ruins of Kenilworth Castle and Kenilworth Abbey.
History
Medieval and Tudor

Augustinian priory
Augustinians are members of Christian religious orders that follow the Rule of Saint Augustine, written in about 400 AD by Augustine of Hippo. There are two distinct types of Augustinians in Catholic religious orders dating back to the 12th–13 ...
in 1122, which coincided with his initiation of Kenilworth Castle. The priory was raised to the rank of an abbey in 1450 and suppressed with the Dissolution of the Monasteries in the 1530s. Thereafter, the abbey grounds next to the castle were made common land in exchange for what Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester
Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester, (24 June 1532 – 4 September 1588) was an English statesman and the favourite of Elizabeth I from her accession until his death. He was a suitor for the queen's hand for many years.
Dudley's youth was ov ...
used to enlarge the castle. Only a few walls and a storage barn of the original abbey survive.
 During the Middle Ages, Kenilworth played a significant role in the history of England: Between June and December
During the Middle Ages, Kenilworth played a significant role in the history of England: Between June and December 1266
Year 1266 ( MCCLXVI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Europe
* January 2 – Siege of Murcia: King James I of Aragon (the Conqueror) marches with h ...
, as part of the Second Barons' War, Kenilworth Castle underwent a six-month siege, when baronial forces allied to Simon de Montfort, were besieged in the castle by the Royalist forces led by Prince Edward, this is thought to be the longest siege in Medieval English history. Despite numerous efforts at taking the castle, its defences proved impregnable. Whilst the siege was ongoing King Henry III held a Parliament at Kenilworth in August that year, which resulted in the Dictum of Kenilworth
The Dictum of Kenilworth, issued on 31 October 1266, was a pronouncement designed to reconcile the rebels of the Second Barons' War with the royal government of England. After the baronial victory at the Battle of Lewes in 1264, Simon de Montfor ...
; a concillatory document which set out peace terms to end the conflict between the barons and the monarchy. The barons initially refused to accept, but hunger and disease eventually forced them to surrender, and accept the terms of the Dictum.
During the Wars of the Roses in the 15th century
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD).
In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period.
M ...
, Kenilworth Castle served as an important Lancastrian base in the Midlands: The Lancastrian King Henry VI and his wife, Margaret of Anjou
Margaret of Anjou (french: link=no, Marguerite; 23 March 1430 – 25 August 1482) was Queen of England and nominally Queen of France by marriage to King Henry VI from 1445 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471. Born in the Duchy of Lorrain ...
spent much time here.
 Elizabeth I visited
Elizabeth I visited Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester
Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester, (24 June 1532 – 4 September 1588) was an English statesman and the favourite of Elizabeth I from her accession until his death. He was a suitor for the queen's hand for many years.
Dudley's youth was ov ...
at Kenilworth Castle several times, the last in 1575. Dudley entertained the Queen with pageants and banquets costing some £1,000 per day that surpassed anything seen in England before. These included fireworks.
Near the castle there is a group of thatched cottages called 'Little Virginia': According to local legend they gained this name because the first potatoes brought to England by Sir Walter Raleigh from the New World were planted and grown here in the 16th century. Modern historians however consider this unlikely, and have suggested that the name may have originated from early colonists to America returning to England from Virginia.
17th and 18th centuries
During the English Civil War, Kenilworth Castle, was occupied by Parliamentarians, after the Royalist garrison was withdrawn. After the end of the war, the castle's defences were slighted on the orders of Parliament in 1649, after which the castle became a ruin. In 1778 Kenilworth windmill was built. In 1884, it was converted into a water tower, by the addition of a large water tank on the top of the tower in the place of the sails. It continued to be the town's main water supply until 1939, and finally became disused in 1960. It is still a local landmark, but is now a private home.19th century to present
With the demise of the defensive role of the castle, Kenilworth had ceased to be a place of national significance, but Sir Walter Scott's 1821 novel '' Kenilworth'' brought it back to public attention, and helped establish the ruins of the castle as a major tourist attraction. In the early 19th century Kenilworth was known for its horncomb
A comb is a tool consisting of a shaft that holds a row of teeth for pulling through the hair to clean, untangle, or style it. Combs have been used since prehistoric times, having been discovered in very refined forms from settlements dating ba ...
making industry, which peaked in the 1830s.
Kenilworth was revolutionised by the arrival in 1844 of the railway to the town, when the London and Birmingham Railway opened the Coventry to Leamington Line, including Kenilworth railway station
Kenilworth railway station is a railway station in Kenilworth, Warwickshire, England on the Coventry to Leamington Line. The original Kenilworth station opened in 1844 before being rebuilt in 1884 and closed in 1965. In 2013 it was announced t ...
. The station was rebuilt in 1884 and a new link line was opened between Kenilworth and to bypass . This closed to all traffic on 3 March 1969. The railway in the 19th century brought industrialists from Birmingham and Coventry, to develop a residential area around the town's railway station, thus moving the focus of the town to the south. In the 19th century the town had some fine large mansion
A mansion is a large dwelling house. The word itself derives through Old French from the Latin word ''mansio'' "dwelling", an abstract noun derived from the verb ''manere'' "to dwell". The English word '' manse'' originally defined a property l ...
s with landscaped gardens; these were demolished after the First World War and Second World War for housing developments. The railway also brought a number of new industries to Kenilworth, such as tanning, brick
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured cons ...
making, and chemicals, and also caused substantial growth in Kenilworth's market gardening; which became known for producing crops such as tomatoes and strawberries.
 The town's growth occasioned the addition of a second
The town's growth occasioned the addition of a second Church of England parish church
A parish church in the Church of England is the church which acts as the religious centre for the people within each Church of England parish (the smallest and most basic Church of England administrative unit; since the 19th century sometimes ca ...
, St John's, which is on Warwick Road in Knights Meadow. It was designed by Ewan Christian and built in 1851–1852 as a Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
building with a south-west bell tower
A bell tower is a tower that contains one or more bells, or that is designed to hold bells even if it has none. Such a tower commonly serves as part of a Christian church, and will contain church bells, but there are also many secular bell tower ...
and broach spire
A broach spire is a type of spire (tall pyramidal structure), which usually sits atop a tower or turret of a church. It starts on a square base and is carried up to a tapering octagonal spire by means of triangular faces.
File:Leicester Cathedral ...
. By the 1870s Kenilworth's population had exceeded 4,000.
During The Blitz in World War II on the night of 21 November 1940, a German aircraft dropped two parachute mines on Kenilworth, the large explosions in the Abbey End area demolished a number of buildings, killing 25 people, and injuring 70 more. The bomb damaged area of the town was redeveloped in the 1960s.
In May 1961, the Kenilworth Society was formed over concerns about a group of 17th-century listed cottages adjacent to Finham Brook in Bridge Street. It sets out to promote awareness of Kenilworth's character and encourage its preservation.
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British rai ...
withdrew passenger services from the Coventry to Leamington Line and closed Kenilworth Station in January 1965 in line with ''The Reshaping of British Railways
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the M ...
'' report. In May 1977, British Rail reinstated passenger services, but did not reopen Kenilworth station, which became derelict and was eventually demolished. In 2011 Warwick Council granted John Laing plc planning permission to build a new station, It finally reopened in 2018.
In the early 1980s, the town's name was used by one of the first generation of computer retailers, a company called Kenilworth Computers based near the Clock Tower, for its repackaging of the Nascom microcomputer with the selling point that it was robust enough to be used by agriculture.
Kenilworth was struck by an F0/T1 tornado on 23 November 1981, as part of the record-breaking nationwide outbreak on that day.
Modern Kenilworth
 Kenilworth is close to the University of Warwick at Gibbet Hill in Coventry to the north. Kenilworth has several suburbs, which include Borrowell, Castle Green, Crackley, Ladyes Hill, Mill End, Park Hill, St Johns, Whitemoor and Windy Arbour. The town has good transport links to Coventry, Warwick,
Kenilworth is close to the University of Warwick at Gibbet Hill in Coventry to the north. Kenilworth has several suburbs, which include Borrowell, Castle Green, Crackley, Ladyes Hill, Mill End, Park Hill, St Johns, Whitemoor and Windy Arbour. The town has good transport links to Coventry, Warwick, Leamington Spa
Royal Leamington Spa, commonly known as Leamington Spa or simply Leamington (), is a spa town and civil parish in Warwickshire, England. Originally a small village called Leamington Priors, it grew into a spa town in the 18th century following ...
and Birmingham.OS Explorer Map 221, ''Coventry & Warwick''
 The principal shopping area of Kenilworth is around Warwick Street, Abbey End and Talisman Square; a 1960s shopping precinct. In 2008 the square was modernised and partly redeveloped to include a new Waitrose supermarket. Kenilworth has been a Fairtrade Town since 2007. The town's public library underwent a renovation in 2021. ''The Cross'', a local pub-restaurant, received a
The principal shopping area of Kenilworth is around Warwick Street, Abbey End and Talisman Square; a 1960s shopping precinct. In 2008 the square was modernised and partly redeveloped to include a new Waitrose supermarket. Kenilworth has been a Fairtrade Town since 2007. The town's public library underwent a renovation in 2021. ''The Cross'', a local pub-restaurant, received a Michelin star
The Michelin Guides ( ) are a series of guide books that have been published by the French tyre company Michelin since 1900. The Guide awards up to three Michelin stars for excellence to a select few establishments. The acquisition or loss of a ...
in 2015.
Near the centre of Kenilworth is Abbey Fields, a public park
A park is an area of natural, semi-natural or planted space set aside for human enjoyment and recreation or for the protection of wildlife or natural habitats. Urban parks are urban green space, green spaces set aside for recreation inside t ...
which covers , within the valley of Finham Brook
The Finham Brook is a lower tributary of the River Sowe, it flows through Kenilworth and Warwickshire, England, to join the Sowe near Finham. Its principal tributaries include the Canley Brook, which drains the Tile Hill and Canley areas of Cove ...
. Abbey Fields contains the ruins of the historic Kenilworth Abbey as well as St Nicholas church. It contains public amenities such as a swimming pool, a lake, a children's play area, and heritage trails. There are several further public open spaces in Kenilworth; firstly Kenilworth Common, an area of historic common land covering . Secondly, Parliament Piece, a field and nature reserve covering , which according to legend, was where King Henry III held a Parliament in 1266. Knowle Hill Nature Reserve, managed by the Warwickshire Wildlife Trust, is found near The Common and covers .
In the centre of Kenilworth stands a Kugel ball water feature, called the Millennium Globe.
Kenilworth's clock tower (pictured at top of article) is an important local landmark. It was first built in 1906–1907 by a notable local benefactor George Marshall Turner, as a memorial for his late wife. It stands in a roundabout in the town centre. The top part of the tower was severely damaged in 1940 by World War II bombing and had to be pulled down, it was fully restored in the 1970s. The clock tower is locally listed as a heritage asset by Warwick District Council
Warwick ( ) is a market town, civil parish and the county town of Warwickshire in the Warwick District in England, adjacent to the River Avon. It is south of Coventry, and south-east of Birmingham. It is adjoined with Leamington Spa and Whit ...
.
Politics and government
Kenilworth gained a local board of health in 1877, which was converted into an Urban District Council in 1894. Under local government reforms in1974
Major events in 1974 include the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis and the resignation of United States President Richard Nixon following the Watergate scandal. In the Middle East, the aftermath of the 1973 Yom Kippur War determined politics; f ...
Kenilworth Urban District was merged into the new Warwick District along with Warwick and Leamington Spa
Royal Leamington Spa, commonly known as Leamington Spa or simply Leamington (), is a spa town and civil parish in Warwickshire, England. Originally a small village called Leamington Priors, it grew into a spa town in the 18th century following ...
. The former urban district of Kenilworth was then reconstituted as a successor parish with a Town (parish) Council.
Since 2010 Kenilworth has been part of the Parliamentary constituency of Kenilworth and Southam
Kenilworth and Southam is a constituency in Warwickshire, England represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2010 by Jeremy Wright, a Conservative who served as Culture Secretary until 24 July 2019, having previously serv ...
, prior to that it was part of Rugby and Kenilworth.Transport
The A46 bypass opened in June 1974. Both Birmingham Airport and the M6, M42 and M40 motorways are within of the town.
The railway station
''The Railway Station'' is an 1862 genre painting by the British artist William Powell Frith. It depicts a scene at the busy Paddington Station railway terminus of the Great Western in London. Frith had developed a reputation for producing cro ...
at Kenilworth is on the Coventry to Leamington Spa line, it was closed in 1965 and reopened in April 2018. it has direct services operated by West Midlands Trains to , and . station is 11–14 minutes' drive away.
Sport
*Kenilworth Town FC, located in Gypsy Lane in the south of the town, played in theMidland Combination
The Midland Football Combination was an English football league covering parts of the West Midlands. It comprised five divisions, a Premier Division, Divisions One and Two and two Reserves Divisions. The league was one of three official feeder le ...
until June 2011, when it resigned, preferring to spend money on ground improvements rather than fielding a team. It re-entered the English football pyramid
The English football league system, also known as the football pyramid, is a series of interconnected leagues for men's association football clubs in England, with five teams from Wales, one from Guernsey, one from Jersey and one from the Isl ...
in the 2013–14 season and was placed in the Midland Football League Division 3, the 12th highest tier in the English league system. The stay, however, was brief; the first team again resigned shortly afterwards. The Gypsy Lane ground was purchased in 2018 by Coventry Plumbing F.C., which demolished the clubhouse and built a new one, before starting the 2019–20 season there.
*Kenilworth Wardens FC
Kenilworth ( ) is a market town and civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and ...
is based at Kenilworth Wardens, a Community Amateur Sports Club in Glasshouse Lane to the east of the town.
*Kenilworth RFC is the town's rugby union club. It fields three senior sides and hosts a large minis, juniors and colts section. The ground is also located in Glasshouse Lane.
*Kenilworth Tennis, Squash and Croquet Club, in Crackley Lane, has nine tennis courts, five squash and racketball courts and two croquet lawns.
*Kenilworth has two cricket clubs: Kenilworth Wardens in Glasshouse Lane fields five senior teams and a juniors section starting from seven years old; Kenilworth Cricket Club fields three senior teams and plays at the Warwick Road ground.
*Kenilworth Runners meets at the Wardens. It caters for runners of all ages and abilities.
*Octavian Droobers is the local orienteering club, using maps of Abbey Fields and Kenilworth Common on which to stage events.
*Kenilworth Wheelers meets all the year round on Saturday and Sunday morning for a road ride. During the summer months, regular evening training rides cater for all abilities from novice to racer.
*Abbey Fields Swimming Pool is in Abbey Fields. It has a 25 m by 10 m indoor pool and an outdoor pool open from May to September. It is home to Kenilworth Swimming Club and Kenilworth Masters Swimming Club.
*Kenilworth Golf Club features a mature 18-hole parkland course, plus a small six-hole par 3 course.Two Castles Run
The Two Castles Run began in 1983 as a fun run between Warwick Castle and Kenilworth Castle. It has grown into an English Athletics-licensed run with 3,000 entrants in 2010. In 2010 and 2011 it held the Warwickshire Amateur Athletic Association 10 Kilometre Championship. In 2012 all 4,000 places were sold within 25 hours. The race is organised each June by Kenilworth Rotary Club in conjunction with the Leamington Cycling and Athletic Club.Arts
Theatres
The Talisman Theatre, founded as Talisman Players in 1942, moved to its current 156-seat premises in Barrow Road in 1969. It won eight NODA awards between 2004 and 2014. The Priory Theatre, founded in 1932 as the Kenilworth Players, uses the former Unitarian/ Christadelphian chapel, a Gothic Revival building dating from 1816, which was converted into a 119-seat theatre building in 1945–1946. It was gutted by fire in 1976, but restored and reopened in September 1978.Kenilworth Arts Festival
The first Kenilworth Festival was held in 1935. After a 70-year interval, it was revived locally in 2005. Between 2005 and 2015, events were held almost every year, with varying success. The company became a social enterprise in 2010. In 2015–16, a new team oversaw a change in direction, with a new name, branding and mission statement, as 'Kenilworth Arts Festival'. Kenilworth Arts Festival took place again on 19–28 September 2019.Bonfire Night Fireworks Display
Kenilworth Castle hosts an annual firework display, known as one of the best Bonfire Night firework displays in the UK.Education
The principal secondary school in Kenilworth is the Kenilworth School and Sixth Form, based at two different sites in the town. There are also a number of schools for primary age children.Notable people
In order of birth: * Henry III of England (1207–1272) commissioned theDictum of Kenilworth
The Dictum of Kenilworth, issued on 31 October 1266, was a pronouncement designed to reconcile the rebels of the Second Barons' War with the royal government of England. After the baronial victory at the Battle of Lewes in 1264, Simon de Montfor ...
, which was made public on 31 October 1266.
* Edward II of England (1284–1327) was held prisoner in Kenilworth Castle in 1326–1327.
*Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester
Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester, (24 June 1532 – 4 September 1588) was an English statesman and the favourite of Elizabeth I from her accession until his death. He was a suitor for the queen's hand for many years.
Dudley's youth was ov ...
(1532 or 1533–1588) lived at Kenilworth Castle.
*Thomas Underhill
Thomas Underhill (1545–1591) served as Keeper of the Wardrobe of Kenilworth Castle and had charge of its contents after the castle was given by Queen Elizabeth I to her favourite Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester in 1563.
Thomas Underhill w ...
(1545–1591) was keeper of the wardrobe at Kenilworth Castle.
* Thomas Hearne (1744–1817), landscape artist, painted ''The Priory Gate at Kenilworth'' in 1784.
* William Field (1768–1851), Unitarian minister and local historian, served the Old Meeting House at Kenilworth from about 1830 to 1850.
*Sir Walter Scott's (1771–1832) novel ''Kenilworth. A Romance'' appeared anonymously in 1821.
* Samuel Butler (1774–1839), classical scholar and bishop, became the incumbent of Kenilworth in 1802.
* John Sumner (1780–1862), Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justi ...
, was born in Kenilworth.
* Charles Sumner (1790–1874), religious writer and bishop, was born in Kenilworth.
* William Gresley (1801–1876), religious writer and cleric, was born in Kenilworth.
* Samuel Carter MP (1805–1878), inherited property in Kenilworth and is buried in the graveyard of St Nicholas.
* Anna Russell (1807–1876), botanist, lived in Kenilworth.
* Samuel Hawksley Burbury (1831–1911), mathematician, was born in Kenilworth.
* Isabel, Lady Burton (née Arundell, 1831–1896), religious writer and wife of the scholar Richard Francis Burton, was born in Kenilworth.
* George Potter (1832–1893), trade unionist, first president of the Trades Union Congress of England and Wales, was born in Kenilworth.
*Sir Arthur Sullivan
Sir Arthur Seymour Sullivan (13 May 1842 – 22 November 1900) was an English composer. He is best known for 14 comic opera, operatic Gilbert and Sullivan, collaborations with the dramatist W. S. Gilbert, including ''H.M.S. Pinaf ...
's (1842–1900) long association with vocal music began with a cantata
A cantata (; ; literally "sung", past participle feminine singular of the Italian verb ''cantare'', "to sing") is a vocal composition with an instrumental accompaniment, typically in several movements, often involving a choir.
The meaning of ...
, ''The Masque at Kenilworth'', in 1864.
*Jack Burns
John Francis Burns (November 15, 1933 – January 27, 2020) was an American comedian, actor, voice actor, writer, and producer. During the 1960s, he was part of two comedy partnerships, first with George Carlin and later with Avery Schreiber. ...
(1859–1927), Scottish champion golfer, was instrumental in creating the Kenilworth course in 1890.
*Oliver Bodington
Oliver Eaton Bodington (1859 – 1936), barrister at law of the Inner Temple, Licensee en Droit, University of Paris, Member of the United States Federal Bar and President of the British Chamber of Commerce, was born March 6, 1859, in Kingsfor ...
(1859–1936), Paris-based international lawyer and marriage broker, was baptised in Kenilworth.
*Edith Emma Cooper (1862–1913) was one half of Michael Field, known as a poet, dramatist and diarist.
*Edgar Jepson
Edgar Alfred Jepson (28 November 1863 – 12 April 1938) was an English author. He largely wrote mainstream adventure and detective fiction, but also supernatural and fantasy stories. He sometimes used the pseudonym R. Edison Page.
Early life
E ...
(1863–1938), writer of crime, adventure and fantasy novels, was born in Kenilworth.
* John Siddeley, Lord Kenilworth (1866–1953), motor and aero engineering pioneer, moved to Crackley Hall, Kenilworth, in 1918.
*Reginald Lee
Reginald Lee (19 May 1870 – 6 August 1913) was a lookout stationed in the crow's nest of the RMS ''Titanic'' when the ship collided with an iceberg at 23:40 on 14 April 1912.
Biography
Born in Benson, England, Lee served in the Royal Navy as ...
(1870–1913), surviving crew member of the RMS ''Titanic'', died in Kenilworth.Mr Reginald Robinson Lee – Titanic Biography – Encyclopedia Titanicaat www.encyclopedia-titanica.org *
Walter Ritchie
Walter Ritchie (1919–1997) was a British sculptor.
Biography
Ritchie was one of the last living pupil of Eric Gill at Pigotts near High Wycombe before the Second World War Eric Gill died in 1940. Many of his public works were in stone, wood, m ...
(1919–1991), sculptor, lived and worked in Kenilworth.
* Basil Heatley (1933-2019) was a marathon runner and Olympic silver medallist born in Kenilworth.
* Andrew Davies (born 1936), is novelist and screenwriter who lives in Kenilworth (the 1995 BBC ''Pride and Prejudice'').
*Julia Slingo
Dame Julia Mary Slingo (''née'' Walker; born 13 December 1950) is a British meteorologist and climate scientist. She was Chief Scientist at the Met Office from 2009 until 2016. She is also a Visiting Professor in the Department of Meteorol ...
(born 1950), climate scientist and Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire, was born in Kenilworth.
* Peter Marlow (1952–2016) was a photojournalist and photographer.
* Tim Flowers (born 1967 in Kenilworth) is an Association football goalkeeper, notably for Southampton and Blackburn Rovers. He was capped 11 times by England.
*Rebecca Probert
Rebecca Jane Probert, (born 1973) is a British legal historian and academic.
Born in Rugby, Warwickshire, she lives in Exeter with her husband, the travel writer Liam D'Arcy-Brown. She studied for an undergraduate degree in Jurisprudence at O ...
(born 1973), legal historian and expert on marriage law, lives in Kenilworth with her travel-writer husband Liam D'Arcy Brown
Liam James D'Arcy-Brown (born 1970) is a British sinologist and travel writer. Born in Lewisham, London, he grew up in York and now lives in Exeter, Devon with his wife, legal historian Rebecca Probert. He studied Chinese at St Anne's College, ...
.
* Kelvin Langmead (born 1985), professional football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
player for Shrewsbury Town and Northampton Town, was educated at Kenilworth School.
*Sarah-Jane Perry
Sarah-Jane Perry (born 15 May 1990 in Birmingham) is a professional squash player who represents England and Great Britain. She reached a career-high world ranking of World No. 5 in July 2020.
Education
Perry was educated at Kenilworth School ...
(born 1990), professional international squash player, was educated at Kenilworth School.SquashinfoRetrieved 18 April 2014.
/ref>
Twin towns
Kenilworth is twinned with: *Bourg-la-Reine
Bourg-la-Reine () is a commune in the southern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris.
History
In 1792, during the French Revolution, Bourg-la-Reine (meaning "Town of the Queen") was renamed Bourg-l'Égalité (meani ...
, Hauts-de-Seine
Hauts-de-Seine (; ) is a Departments of France, département in the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, Northern France. It covers Paris's western inner Banlieue, suburbs. It is bordered by Paris, Seine-Saint-Denis and Val-de-Marne to the e ...
, France
* Eppstein, Hesse, Germany.
Kenilworth also has friendship links with:
* Roccalumera
Roccalumera is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina in the Italian region Sicily, located about east of Palermo and about southwest of Messina.
Roccalumera borders the following municipalities: Fiumedinisi, Furci S ...
, Italy
* Bo, Sierra Leone, througOne World Link (OWL)
* Uyogo, Tanzania
References
Sources
* *External links
Kenilworth Town Council
— official Kenilworth town centre website
Kenilworth Chamber of Trade
held at the
Modern Records Centre, University of Warwick
The Modern Records Centre (MRC) is the specialist archive service of the University of Warwick in Coventry, England, located adjacent to the Central Campus Library. It was established in October 1973 and holds the world's largest archive collecti ...
Warwickshire Geological Conservation Group (WGCG) is based in Kenilworth
- Our Warwickshire {{authority control Towns in Warwickshire