Hurling sport - Taking a swing.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Hurling ( ga, iománaíocht, ') is an outdoor team game of ancient Gaelic Irish origin, played by men. One of Ireland's native Gaelic games, it shares a number of features with Gaelic football, such as the field and goals, the number of players and much
Hurling ( ga, iománaíocht, ') is an outdoor team game of ancient Gaelic Irish origin, played by men. One of Ireland's native Gaelic games, it shares a number of features with Gaelic football, such as the field and goals, the number of players and much
 A hurling pitch is similar in some respects to a
A hurling pitch is similar in some respects to a
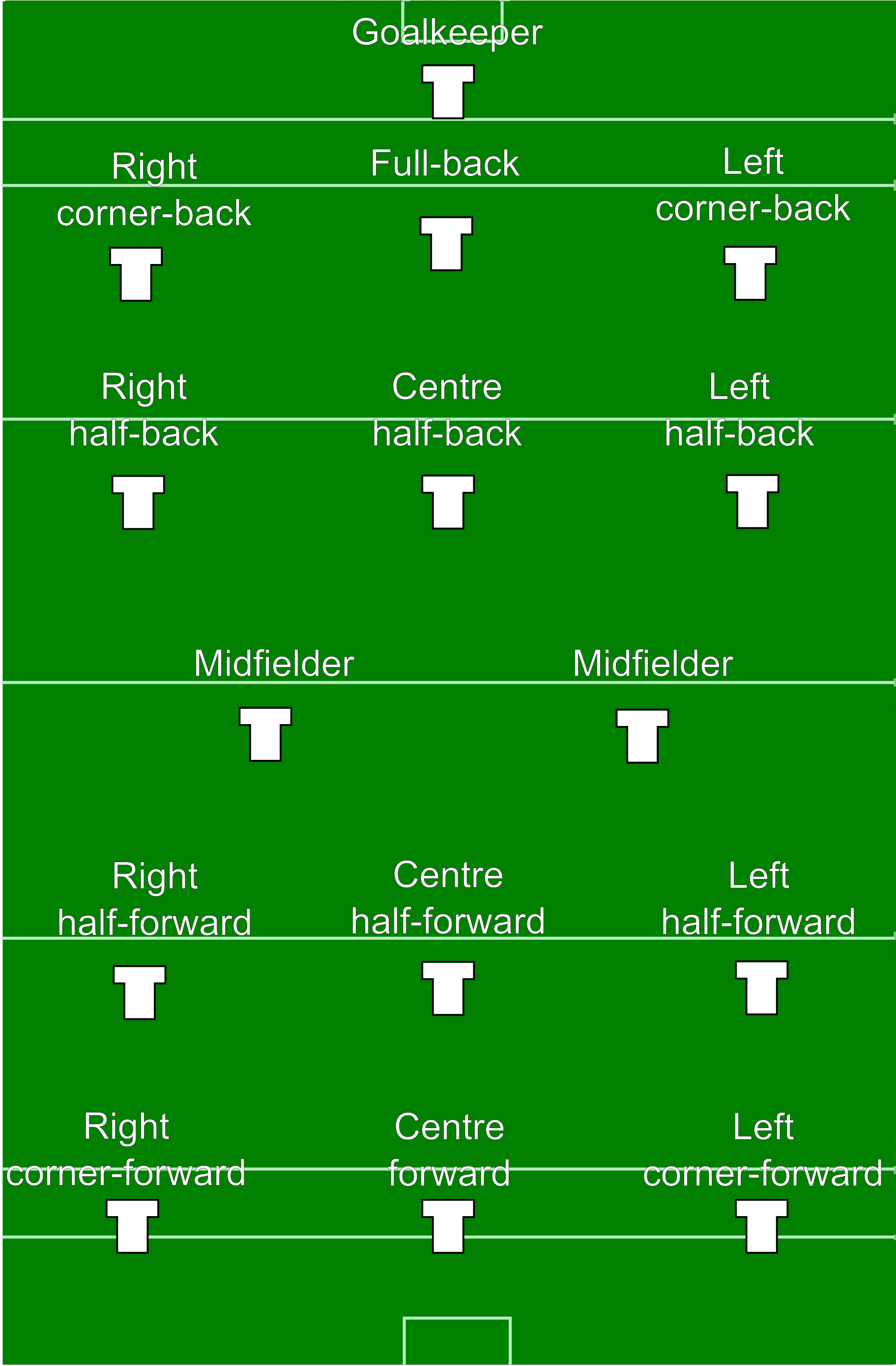 Teams consist of fifteen players: a goalkeeper, three full backs, three half backs, two midfielders, three half forwards and three full forwards (see diagram). The panel is made up of 24–30 players and five substitutions are allowed per game. An exception can now be made in the case of a blood substitute being necessary. Blood substitutes are a result of one player needing medical treatment for a laceration, usually stitches, and another coming on as a temporary replacement while the injured player is tended to.
Teams consist of fifteen players: a goalkeeper, three full backs, three half backs, two midfielders, three half forwards and three full forwards (see diagram). The panel is made up of 24–30 players and five substitutions are allowed per game. An exception can now be made in the case of a blood substitute being necessary. Blood substitutes are a result of one player needing medical treatment for a laceration, usually stitches, and another coming on as a temporary replacement while the injured player is tended to.
 From 1 January 2010, the wearing of helmets with faceguards became compulsory for hurlers at all levels. This saw senior players follow the regulations already introduced in 2009 at minor and under 21 grades. The GAA hopes to significantly reduce the number of injuries by introducing the compulsory wearing of helmets with full faceguards, both in training and matches. Hurlers of all ages, including those at nursery clubs when holding a hurley in their hand, must wear a helmet and faceguard at all times. Match officials will be obliged to stop play if any player at any level appears on the field of play without the necessary standard of equipment.
From 1 January 2010, the wearing of helmets with faceguards became compulsory for hurlers at all levels. This saw senior players follow the regulations already introduced in 2009 at minor and under 21 grades. The GAA hopes to significantly reduce the number of injuries by introducing the compulsory wearing of helmets with full faceguards, both in training and matches. Hurlers of all ages, including those at nursery clubs when holding a hurley in their hand, must wear a helmet and faceguard at all times. Match officials will be obliged to stop play if any player at any level appears on the field of play without the necessary standard of equipment.
 Scoring is achieved by sending the ''sliotar'' between the opposition's goal posts. The posts, which are at each end of the field, are ''H'' posts as in
Scoring is achieved by sending the ''sliotar'' between the opposition's goal posts. The posts, which are at each end of the field, are ''H'' posts as in 
 * The match begins with the referee throwing the ''sliotar'' in between the four midfielders on the halfway line
* After an attacker has scored or put the ball wide of the goals, the goalkeeper may take a "puckout" from the hand at the edge of the small square. All players must be beyond the 20 m line.
* After a defender has put the ball wide of the goals, an attacker may take a "65" from the 65 m line level with where the ball went wide. It must be taken by lifting and striking. However, the ball must not be taken into the hand but struck whilst the ball is lifted.
* After a player has put the ball over the sideline, the other team may take a 'sideline cut' at the point where the ball left the pitch. It must be taken from the ground.
* After a player has committed a foul, the other team may take a 'free' at the point where the foul was committed. It must be taken by lifting and striking in the same style as the "65".
* After a defender has committed a foul inside the square (large rectangle), the other team may take a "penalty" from the ground from behind the 20 m line. Only the goalkeeper may guard the goals. It must be taken by lifting and striking and the ''sliotar'' must be struck on or behind the 20m line (The penalty rule was amended in 2015 due to safety concerns. Before this the ball merely had to start at the 20m line but could be struck beyond it. To balance this advantage the two additional defenders previously allowed on the line have been removed).
* If many players are struggling for the ball and no side is able to capitalize or gain control of it the referee may choose to throw the ball in between two opposing players. This is also known as a "throw in".
* The match begins with the referee throwing the ''sliotar'' in between the four midfielders on the halfway line
* After an attacker has scored or put the ball wide of the goals, the goalkeeper may take a "puckout" from the hand at the edge of the small square. All players must be beyond the 20 m line.
* After a defender has put the ball wide of the goals, an attacker may take a "65" from the 65 m line level with where the ball went wide. It must be taken by lifting and striking. However, the ball must not be taken into the hand but struck whilst the ball is lifted.
* After a player has put the ball over the sideline, the other team may take a 'sideline cut' at the point where the ball left the pitch. It must be taken from the ground.
* After a player has committed a foul, the other team may take a 'free' at the point where the foul was committed. It must be taken by lifting and striking in the same style as the "65".
* After a defender has committed a foul inside the square (large rectangle), the other team may take a "penalty" from the ground from behind the 20 m line. Only the goalkeeper may guard the goals. It must be taken by lifting and striking and the ''sliotar'' must be struck on or behind the 20m line (The penalty rule was amended in 2015 due to safety concerns. Before this the ball merely had to start at the 20m line but could be struck beyond it. To balance this advantage the two additional defenders previously allowed on the line have been removed).
* If many players are struggling for the ball and no side is able to capitalize or gain control of it the referee may choose to throw the ball in between two opposing players. This is also known as a "throw in".

 Hurling is older than the recorded history of Ireland. It is thought to predate Christianity, having come to Ireland with the Celts. The earliest written references to the sport in
Hurling is older than the recorded history of Ireland. It is thought to predate Christianity, having come to Ireland with the Celts. The earliest written references to the sport in
 References to hurling on the North American continent date from the 1780s in modern-day Canada concerning immigrants from County Waterford and County Kilkenny, and also, in New York City. After the end of the
References to hurling on the North American continent date from the 1780s in modern-day Canada concerning immigrants from County Waterford and County Kilkenny, and also, in New York City. After the end of the
 * All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship
** Connacht Senior Hurling Championship
** Leinster Senior Hurling Championship
** Munster Senior Hurling Championship
** Ulster Senior Hurling Championship
* National Hurling League
* Christy Ring Cup
*
* All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship
** Connacht Senior Hurling Championship
** Leinster Senior Hurling Championship
** Munster Senior Hurling Championship
** Ulster Senior Hurling Championship
* National Hurling League
* Christy Ring Cup
*
Hurling
at the GAA website {{Authority control Hurling, Gaelic games Hurlers Stick sports Sports originating in Ireland Team sports

 Hurling ( ga, iománaíocht, ') is an outdoor team game of ancient Gaelic Irish origin, played by men. One of Ireland's native Gaelic games, it shares a number of features with Gaelic football, such as the field and goals, the number of players and much
Hurling ( ga, iománaíocht, ') is an outdoor team game of ancient Gaelic Irish origin, played by men. One of Ireland's native Gaelic games, it shares a number of features with Gaelic football, such as the field and goals, the number of players and much terminology
Terminology is a group of specialized words and respective meanings in a particular field, and also the study of such terms and their use; the latter meaning is also known as terminology science. A ''term'' is a word, compound word, or multi-wo ...
. The same game played by women is called camogie ('), which shares a common Gaelic root.
The objective of the game is for players to use an ash wood
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of flowering plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae. It contains 45–65 species of usually medium to large trees, mostly deciduous, though a number of subtropical species are evergreen ...
stick called a hurley (in Irish a ', pronounced or ) to hit a small ball called a ' between the opponent's goalposts either over the crossbar for one point or under the crossbar into a net guarded by a goalkeeper
In many team sports which involve scoring goals, the goalkeeper (sometimes termed goaltender, netminder, GK, goalie or keeper) is a designated player charged with directly preventing the opposing team from scoring by blocking or intercepting o ...
for three points. The ' can be caught in the hand and carried for not more than four steps, struck in the air or struck on the ground with the hurley. It can be kicked, or slapped with an open hand (the hand pass), for short-range passing. A player who wants to carry the ball for more than four steps has to bounce or balance the ' on the end of the stick, and the ball can only be handled twice while in the player’s possession.
Provided that a player has at least one foot on the ground, he may make a shoulder-to-shoulder charge on an opponent who is in possession of the ball or is playing the ball, or when both players are moving in the direction of the ball.
No protective padding is worn by players. A plastic protective helmet with a faceguard is mandatory for all age groups as of 2010. The game has been described as "a bastion of humility", with player names absent from jerseys and a player's number decided by his position on the field.
Hurling is administered by the Gaelic Athletic Association
The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA; ga, Cumann Lúthchleas Gael ; CLG) is an Irish international amateur sports, amateur sporting and cultural organisation, focused primarily on promoting indigenous Gaelic games and pastimes, which include t ...
(GAA). It is played throughout the world and is popular among members of the Irish diaspora in North America, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Argentina and South Korea. In many parts of Ireland, however, hurling is a fixture of life. It has featured regularly in art forms such as film, music and literature. The final of the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship was listed in second place by CNN
CNN (Cable News Network) is a multinational cable news channel headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable news channel, and presently owned by ...
in its "10 sporting events you have to see live", after the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a vari ...
and ahead of both the FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
and UEFA European Championship
The UEFA European Football Championship, less formally the European Championship and informally the Euro, is the primary association football tournament organised by the Union of European Football Associations ( UEFA). The competition is conte ...
. After covering the 1959 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final between Kilkenny and Waterford
"Waterford remains the untaken city"
, mapsize = 220px
, pushpin_map = Ireland#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption = Location within Ireland##Location within Europe
, pushpin_relief = 1
, coordinates ...
for BBC Television, English football commentator Kenneth Wolstenholme
Kenneth Wolstenholme, DFC & Bar (17 July 1920 – 25 March 2002) was an English football commentator for BBC television in the 1950s and 1960s. He is best remembered for his commentary during the 1966 FIFA World Cup Final; in the closing minu ...
was moved to describe hurling as his second favourite sport in the world. Alex Ferguson used footage of an All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship final in an attempt to motivate his players during his time as manager of Premier League
The Premier League (legal name: The Football Association Premier League Limited) is the highest level of the men's English football league system. Contested by 20 clubs, it operates on a system of promotion and relegation with the English Fo ...
football club Manchester United. The players winced at the standard of physicality and intensity in which the hurlers engaged. In 2007, ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also r ...
'' magazine described the media attention and population multiplication of Thurles
Thurles (; ''Durlas Éile'') is a town in County Tipperary, Ireland. It is located in the civil parish of the same name in the barony of Eliogarty and in the ecclesiastical parish of Thurles. The cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Arc ...
town ahead of one of the game's annual provincial hurling finals as being "the rough equivalent of 30 million Americans watching a regional lacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensiv ...
game". ''Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and published digitally that focuses on business and economic current affairs. Based in London, England, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Ni ...
'' columnist Simon Kuper
Simon Kuper is a South African-British author. He writes about sports "from an anthropologic perspective."
Kuper was born in Uganda of South African parents, and moved to Leiden in the Netherlands as a child, where his father, Adam Kuper, was ...
wrote after Stephen Bennett's performance in the 2020 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final
The 2020 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final, the 133rd event of its kind and the culmination of the 2020 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, was played at Croke Park in Dublin on 13 December 2020.
The match was televised live on ...
that hurling was "the best sport ever and if the Irish had colonised the world, nobody would ever have heard of football".
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
lists hurling as an element of Intangible cultural heritage.
Statistics
* A team comprises 15 players, or "hurlers" * The hurl is generally in length * The ball, known as a '' sliotar'', has a cork centre and a leather cover; it is between in diameter, and weighs between * The goalkeeper's hurl usually has a ''bas'' (the flattened, curved end) twice the size of other players' hurleys to provide some advantage against the fast moving ''sliotar'' * A good strike with a hurl can propel the ball over in speed and in distance. * A ball hit over the bar is worth one point. A ball that is hit under the bar is called a ''goal'' and is worth three points. * As of 2010, all players must wear helmets.Rules
Playing field
rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
pitch but larger. The grass pitch is rectangular, stretching long and wide. There are ''H''-shaped goalposts at each end, formed by two posts, which are usually high, set apart, and connected above the ground by a crossbar. A net extending behind the goal is attached to the crossbar and lower goal posts. The same pitch is used for Gaelic football; the GAA, which organises both sports, decided this to facilitate dual usage. Lines are marked at distances of 14 yards, 21 yards and 65 yards (45 yards for Gaelic football) from each end-line. Shorter pitches and smaller goals are used by youth teams.
Teams
 Teams consist of fifteen players: a goalkeeper, three full backs, three half backs, two midfielders, three half forwards and three full forwards (see diagram). The panel is made up of 24–30 players and five substitutions are allowed per game. An exception can now be made in the case of a blood substitute being necessary. Blood substitutes are a result of one player needing medical treatment for a laceration, usually stitches, and another coming on as a temporary replacement while the injured player is tended to.
Teams consist of fifteen players: a goalkeeper, three full backs, three half backs, two midfielders, three half forwards and three full forwards (see diagram). The panel is made up of 24–30 players and five substitutions are allowed per game. An exception can now be made in the case of a blood substitute being necessary. Blood substitutes are a result of one player needing medical treatment for a laceration, usually stitches, and another coming on as a temporary replacement while the injured player is tended to.
Helmets
 From 1 January 2010, the wearing of helmets with faceguards became compulsory for hurlers at all levels. This saw senior players follow the regulations already introduced in 2009 at minor and under 21 grades. The GAA hopes to significantly reduce the number of injuries by introducing the compulsory wearing of helmets with full faceguards, both in training and matches. Hurlers of all ages, including those at nursery clubs when holding a hurley in their hand, must wear a helmet and faceguard at all times. Match officials will be obliged to stop play if any player at any level appears on the field of play without the necessary standard of equipment.
From 1 January 2010, the wearing of helmets with faceguards became compulsory for hurlers at all levels. This saw senior players follow the regulations already introduced in 2009 at minor and under 21 grades. The GAA hopes to significantly reduce the number of injuries by introducing the compulsory wearing of helmets with full faceguards, both in training and matches. Hurlers of all ages, including those at nursery clubs when holding a hurley in their hand, must wear a helmet and faceguard at all times. Match officials will be obliged to stop play if any player at any level appears on the field of play without the necessary standard of equipment.
Duration, extra time, replays
Senior inter-county matches last 70 minutes (35 minutes per half). All other matches last 60 minutes (30 minutes per half). For teams under-13 and lower, games may be shortened to 50 minutes. Timekeeping is at the discretion of the referee who adds on stoppage time at the end of each half. In 2020, water breaks were brought in after the first 15 minutes in each half. There are various solutions for knockout games that end in a draw, such as a replay, or what the rules refer to as "Winner on the Day" measures such as extra time (20 minutes), further extra time (10 more minutes), or a shoot-out. The application and details of these measures vary according to the importance of the match and the difficulty of scheduling possible replays, and can change from year to year. The general trend is that the GAA have been trying to reduce the need for replays, to ease scheduling.Technical fouls
The following are considered technical fouls ("fouling the ball"): * Picking the ball directly off the ground (instead it must be flicked up with the hurley) * Throwing the ball (instead it must be "hand-passed": slapped with the open hand) * Going more than four steps with the ball in the hand (it may be carried indefinitely on the hurley) * Catching the ball three times in a row without it touching the ground (touching the hurley does not count) * Putting the ball from one hand to the other * Hand-passing a goal * "Chopping" slashing downwards on another player's hurl *Deliberately dropping the Hurley or throwing it away. *A 'square ball', entering the opponent's small rectangle prior to the ball entering it *To cover or shield the ball by lying down on it. *To deliberately throw the ball up and catch it again (the ball must touch a hurl or other body part) *Carrying the ball over the opponent's goal lineAggressive fouls
Can be deliberate or accidental, oftentimes accompanied by a card. They are as follows: * Pulling down an opponent. * Using the hurl in an uncontrolled or reckless way. * Tripping an opponent up * Using threatening and/or abusive language to an opposing player, a teammate or an official * Throwing the hurl in a dangerous manner * Attempts to strike any player or official with a hurl, elbow, fist, head or kick * Spitting at an opponent * Any form of racial, sectarian or homophobic abuseScoring
 Scoring is achieved by sending the ''sliotar'' between the opposition's goal posts. The posts, which are at each end of the field, are ''H'' posts as in
Scoring is achieved by sending the ''sliotar'' between the opposition's goal posts. The posts, which are at each end of the field, are ''H'' posts as in rugby football
Rugby football is the collective name for the team sports of rugby union and rugby league.
Canadian football and, to a lesser extent, American football were once considered forms of rugby football, but are seldom now referred to as such. The ...
but with a net under the crossbar as in football. The posts are 6.4 m apart and the crossbar is 2.44 m above the ground.
If the ball goes over the crossbar, a ''point'' is scored and a white flag is raised by an umpire. If the ball goes below the crossbar, a ''goal'', worth three points, is scored, and a green flag is raised by an umpire. A goal must be scored by either a striking motion or by directly soloing the ball into the net. The goal is guarded by a goalkeeper. Scores are recorded in the format – . For example, the 1997 All-Ireland
All-Ireland (sometimes All-Island) refers to all of Ireland, as opposed to the separate jurisdictions of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. "All-Ireland" is most frequently used to refer to sporting teams or events for the entire islan ...
final finished: Clare 0–20 Tipperary
Tipperary is the name of:
Places
*County Tipperary, a county in Ireland
**North Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Nenagh
**South Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Clonmel
*Tipperary (town), County Tipperary's na ...
2–13. Thus Clare won by one point (2–13 being worth nineteen points).
In speech, a score consisting of at least one goal and one point is read as simply the two numbers, so Tipperary's 2–13 is read "two thirteen"; the words "goals" and "points" invariably omitted. Goals are never "converted" into points; it is incorrect to describe a score of 2–13 as "nineteen". 2–0 would be referred to as "two goals", never "two zero". Likewise, 0–10 would be referred to as "ten points", never "zero ten". 0–0 is said "no score". So the Clare/Tipperary match score would be read as "Clare twenty points, Tipperary two thirteen".

Tackling
Players may be tackled but not struck by a one-handed slash of the stick; exceptions are two-handed jabs and strikes. Jersey-pulling, wrestling, pushing and tripping are all forbidden. There are several forms of acceptable tackling, the most popular being: * the "block", where one player attempts to smother an opposing player's strike by trapping the ball between his hurley and the opponent's swinging hurl * the "hook", where a player approaches another player from a rear angle and attempts to catch the opponent's hurley with his own at the top of the swing * the "side pull", where two players running together for the ''sliotar'' will collide at the shoulders and swing together to win the tackle and "pull" (name given to swing the hurley) with extreme force *The "shoulder barge" where one player attackes the other player by shoving them with their shoulder contacting the other players shoulderRestarting play
 * The match begins with the referee throwing the ''sliotar'' in between the four midfielders on the halfway line
* After an attacker has scored or put the ball wide of the goals, the goalkeeper may take a "puckout" from the hand at the edge of the small square. All players must be beyond the 20 m line.
* After a defender has put the ball wide of the goals, an attacker may take a "65" from the 65 m line level with where the ball went wide. It must be taken by lifting and striking. However, the ball must not be taken into the hand but struck whilst the ball is lifted.
* After a player has put the ball over the sideline, the other team may take a 'sideline cut' at the point where the ball left the pitch. It must be taken from the ground.
* After a player has committed a foul, the other team may take a 'free' at the point where the foul was committed. It must be taken by lifting and striking in the same style as the "65".
* After a defender has committed a foul inside the square (large rectangle), the other team may take a "penalty" from the ground from behind the 20 m line. Only the goalkeeper may guard the goals. It must be taken by lifting and striking and the ''sliotar'' must be struck on or behind the 20m line (The penalty rule was amended in 2015 due to safety concerns. Before this the ball merely had to start at the 20m line but could be struck beyond it. To balance this advantage the two additional defenders previously allowed on the line have been removed).
* If many players are struggling for the ball and no side is able to capitalize or gain control of it the referee may choose to throw the ball in between two opposing players. This is also known as a "throw in".
* The match begins with the referee throwing the ''sliotar'' in between the four midfielders on the halfway line
* After an attacker has scored or put the ball wide of the goals, the goalkeeper may take a "puckout" from the hand at the edge of the small square. All players must be beyond the 20 m line.
* After a defender has put the ball wide of the goals, an attacker may take a "65" from the 65 m line level with where the ball went wide. It must be taken by lifting and striking. However, the ball must not be taken into the hand but struck whilst the ball is lifted.
* After a player has put the ball over the sideline, the other team may take a 'sideline cut' at the point where the ball left the pitch. It must be taken from the ground.
* After a player has committed a foul, the other team may take a 'free' at the point where the foul was committed. It must be taken by lifting and striking in the same style as the "65".
* After a defender has committed a foul inside the square (large rectangle), the other team may take a "penalty" from the ground from behind the 20 m line. Only the goalkeeper may guard the goals. It must be taken by lifting and striking and the ''sliotar'' must be struck on or behind the 20m line (The penalty rule was amended in 2015 due to safety concerns. Before this the ball merely had to start at the 20m line but could be struck beyond it. To balance this advantage the two additional defenders previously allowed on the line have been removed).
* If many players are struggling for the ball and no side is able to capitalize or gain control of it the referee may choose to throw the ball in between two opposing players. This is also known as a "throw in".
Officials
A hurling match is watched over by eight officials: * The referee (on field) * Two linesmen (sideline) * Sideline official/standby linesman (inter-county games only) * Four umpires (two at each end) *Hawkeye Video technology for some scoring situations in Croke Park and Semple Stadium (inter-county games only) The referee is responsible for starting and stopping play, recording the score, awarding frees, noting infractions, and issuing yellow (caution) and red (order off) penalty cards to players after offences. A second yellow card at the same game leads to a red card, and therefore to a dismissal. Linesmen are responsible for indicating the direction of line balls to the referee and also for conferring with the referee. The fourth official is responsible for overseeing substitutions, and also indicating the amount of stoppage time (signalled to him by the referee) and the players substituted using an electronic board. The umpires are responsible for judging the scoring. They indicate to the referee whether a shot was: wide (spread both arms), a 65 m puck (raise one arm), a point (wave white flag), or a goal (wave green flag). Contrary to popular belief within the association, all officials are not obliged to indicate "any misdemeanours" to the referee, but are in fact permitted to inform the referee only of violent conduct they have witnessed which has occurred without the referee's knowledge. A linesman or umpire is not permitted to inform the referee of technical fouls such as a "third time in the hand", where a player catches the ball for a third time in succession after soloing or an illegal pick up of the ball. Such decisions can only be made at the discretion of the referee.Injury risk
Blunt injury to the larynx is an infrequent consequence of contact sports despite protective equipment and stringent rules. Hurling, one of the two national sporting games of Ireland, is seen as one of the fastest field sports on earth and only played with a facemask and helmet as protection, making injury an unavoidable feature of the game without further padding. The two most common sites of injury in hurling are the fingers and the hamstrings. Hurling is also considered to have, "...a notable proportion of blunt scrotal trauma."History


 Hurling is older than the recorded history of Ireland. It is thought to predate Christianity, having come to Ireland with the Celts. The earliest written references to the sport in
Hurling is older than the recorded history of Ireland. It is thought to predate Christianity, having come to Ireland with the Celts. The earliest written references to the sport in Brehon law
Early Irish law, historically referred to as (English: Freeman-ism) or (English: Law of Freemen), also called Brehon law, comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norma ...
date from the 5th century. Seamus King's book ''A History of Hurling'' references oral history going back as far as 1200 BCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
of the game being played in Tara, County Meath. Hurling is related to the games of shinty that is played primarily in Scotland, cammag
Cammag () is a team sport originating on the Isle of Man. It is closely related to the Scottish game of shinty and is similar to the Irish game of hurling. Once the most widespread sport on Man, it ceased to be played around 1900 after the introd ...
on the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
and bando
Bando ( my, ဗန်တို, ) is a defensive unarmed martial art from Myanmar. Bando is sometimes mistakenly used as a generic word for all Burmese martial arts, but it is only one martial art; Burmese fighting systems collectively are ref ...
which was played formerly in England and Wales. The tale of the '' Táin Bó Cuailnge'' (drawing on earlier legends) describes the hero Cúchulainn playing hurling at Emain Macha
Navan Fort ( sga, Emain Macha ; ga, Eamhain Mhacha, label= Modern Irish ) is an ancient ceremonial monument near Armagh, Northern Ireland. According to tradition it was one of the great royal sites of pre-Christian Gaelic Ireland and the cap ...
. Similar tales are told about Fionn Mac Cumhail
Fionn mac Cumhaill ( ; Old and mga, Find or ''mac Cumail'' or ''mac Umaill''), often anglicized Finn McCool or MacCool, is a hero in Irish mythology, as well as in later Scottish and Manx folklore. He is leader of the '' Fianna'' bands of ...
and the Fianna
''Fianna'' ( , ; singular ''Fian''; gd, Fèinne ) were small warrior-hunter bands in Gaelic Ireland during the Iron Age and early Middle Ages. A ''fian'' was made up of freeborn young males, often aristocrats, "who had left fosterage but had ...
, his legendary warrior band. Recorded references to hurling appear in many places such as the fourteenth century Statutes of Kilkenny
The Statutes of Kilkenny were a series of thirty-five acts enacted by the Parliament of Ireland at Kilkenny in 1366, aiming to curb the decline of the Hiberno-Norman Lordship of Ireland.
Background to the Statutes
By the middle decades of the ...
and a fifteenth-century grave slab survives in Inishowen
Inishowen () is a peninsula in the north of County Donegal in Ireland. Inishowen is the largest peninsula on the island of Ireland.
The Inishowen peninsula includes Ireland's most northerly point, Malin Head. The Grianan of Aileach, a ringfort ...
, County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconn ...
.
The eighteenth century is frequently referred to as "The Golden Age of Hurling". This was when members of the Anglo-Irish landed gentry kept teams of players on their estates and challenged each other's teams to matches for the amusement of their tenants.
One of the first modern attempts to standardise the game with a formal, written set of rules came with the foundation of the Irish Hurling Union at Trinity College Dublin
, name_Latin = Collegium Sanctae et Individuae Trinitatis Reginae Elizabethae juxta Dublin
, motto = ''Perpetuis futuris temporibus duraturam'' (Latin)
, motto_lang = la
, motto_English = It will last i ...
in 1879. It aimed "to draw up a code of rules for all clubs in the union and to foster that manly and noble game of hurling in this, its native country".
The founding of the Gaelic Athletic Association
The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA; ga, Cumann Lúthchleas Gael ; CLG) is an Irish international amateur sports, amateur sporting and cultural organisation, focused primarily on promoting indigenous Gaelic games and pastimes, which include t ...
(GAA) in 1884 in Hayes Hotel, Thurles, Co Tipperary, ended decline by organising the game around a common set of written rules. In 1888, Tipperary represented by Thurles Blues beat Meelick of Galway to win the first All-Ireland Championship. However, the twentieth century saw Cork, Kilkenny as well as Tipperary
Tipperary is the name of:
Places
*County Tipperary, a county in Ireland
**North Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Nenagh
**South Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Clonmel
*Tipperary (town), County Tipperary's na ...
dominate hurling with each of these counties winning more than 20 All-Ireland titles each. Wexford
Wexford () is the county town of County Wexford, Ireland. Wexford lies on the south side of Wexford Harbour, the estuary of the River Slaney near the southeastern corner of the island of Ireland. The town is linked to Dublin by the M11/N11 ...
, Waterford
"Waterford remains the untaken city"
, mapsize = 220px
, pushpin_map = Ireland#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption = Location within Ireland##Location within Europe
, pushpin_relief = 1
, coordinates ...
, Clare, Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
, Offaly
County Offaly (; ga, Contae Uíbh Fhailí) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in h ...
, Antrim, Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
, and Galway
Galway ( ; ga, Gaillimh, ) is a city in the West of Ireland, in the province of Connacht, which is the county town of County Galway. It lies on the River Corrib between Lough Corrib and Galway Bay, and is the sixth most populous city on ...
were also strong hurling counties during the twentieth century.
As hurling entered the new millennium, it has remained Ireland's second most popular sport. An extended qualifier system resulted in a longer All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. Pay-for-play remains controversial and the Gaelic Players Association continues to grow in strength. The inauguration of the Christy Ring Cup and Nicky Rackard Cup
The Nicky Rackard Cup (; often referred to as the Rackard Cup) is the fourth tier of the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. Each year, the champion team in the Nicky Rackard Cup is promoted to the Christy Ring Cup, and the lowest finishing ...
gave new championships and an opportunity to play in Croke Park to the weaker county teams. Further dissemination of the championship structure was completed in 2009 with the addition of the Lory Meagher Cup
The Lory Meagher Cup (; often referred to as the Meagher Cup) is the fifth-highest inter-county senior championship in hurling. Each year, the champion team in the Lory Meagher Cup is promoted to the Nicky Rackard Cup.
The Lory Meagher Cup, w ...
to make it a four tier championship.
Hurling at the Olympic Games
Hurling was an unofficial sport at the 1904 Summer Olympics inSt. Louis, Missouri
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
, in the United States. In the final, Fenian F.C. (Chicago) USA beat Innisfails (St. Louis). This was the only time hurling was in the Olympics
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a vari ...
.
International
Although many hurling clubs exist worldwide, only Ireland has a national team (although it includes only players from weaker counties in order to ensure matches are competitive). It and the Scotland shinty team have played for many years with modified match rules (as withInternational Rules Football
International rules football ( ga, Peil na rialacha idirnáisiunta; also known as international rules in Australia and compromise rules or Aussie rules in Ireland) is a team sport consisting of a hybrid of football codes, which was developed ...
). The match is the only such international competition. However, competition at club level has been going on around the world since the late nineteenth century thanks to emigration from Ireland, and the strength of the game has ebbed and flowed along with emigration trends. Nowadays, growth in hurling is noted in Continental Europe, Australia, and North America.
Argentina
Irish immigrants began arriving inArgentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
in the 19th century.
The earliest reference to hurling in Argentina dates from the late 1880s in Mercedes, Buenos Aires. However, the game was not actively promoted until 1900, when it came to the attention of author and newspaperman William Bulfin. Under Bulfin's patronage, the Argentine Hurling Club
Hurling Club is an Argentine sports club, located in Hurlingham, Buenos Aires. As its name implies, the club was established in 1922 as a hurling team. Other disciplines hosted by Hurling are field hockey, Gaelic football, rugby union and tennis. ...
was formed on 15 July 1900, leading to teams being established in different neighborhoods of Buenos Aires and the surrounding farming communities.
Games of hurling were played every weekend until 1914 and received frequent coverage from Argentina's Spanish language newspapers, such as ''La Nación''. After the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, it became almost impossible to obtain hurleys from Ireland. An attempt was made to use native Argentine mountain ash, but it proved too heavy and lacking in pliability. Although the game was revived after the end of the war, the golden age of Argentine hurling had passed. World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
finally brought the era to its close.
In the aftermath of the Second World War, immigration from Ireland slowed to a trickle. In addition, native born Irish-Argentines assimilated into the local community. The last time that hurling was played in Argentina was in 1980, when the Aer Lingus Hurling Club conducted a three-week tour of the country and played matches at several locations. Since 2009, with the realization of several Summers Camps and the visit of the All Stars in December, hurling returned to be a frequent activity at the Hurling Club, where many boys and young men have since been trained and taught to play. Even the Hurling Club are invited to participate Hurling Festival is organized within The Gathering events organized by Aer Lingus
Aer Lingus ( ; an anglicisation of the Irish , meaning "air fleet" compare Welsh 'llynges awyr') is the flag carrier of Ireland. Founded by the Irish Government, it was privatised between 2006 and 2015 and it is now a wholly owned subsidiary ...
. This team was present in September 2013 in the city of Galway. The team consists of 21 players from Hockey and Rugby teams. Many have contributed to the return of hurling as an activity in the club. As an example we can name Alejandro Yoyo Wade, Johnny Wade, Barbie, Cecilia and Irene Scally, David Ganly, Dickie Mac Allister, Eduardo Cabrera Punter, Hernan Magrini Scally. Several Irish have participated in many opportunities to work with the skills and education: Jonathan Lynch, Kevin O'Connors and Michael Connery, who currently works with the team's training to participate in the Aer Lingus International Hurling Festival.
Australia
The earliest reference to hurling in Australia is related in the book "Sketches of Garryowen." On 12 July 1844, a match took place at Batman's Hill inMelbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
as a counterpoint to a march by the Orange Order. Reportedly, the hurling match attracted a crowd of five hundred Irish immigrants, while the Orange march shivered out of existence.
Several hurling clubs existed in Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
in the 1870s including Melbourne, Collingwood, Upper Yarra, Richmond and Geelong.
In 1885, a game between two Sydney based teams took place before a crowd of over ten thousand spectators. Reportedly, the contest was greatly enjoyed despite the fact that one newspaper dubbed the game "Two Degrees Safer Than War."
Arden Street Oval in North Melbourne
North Melbourne is an inner-city suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, north-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Melbourne local government area. North Melbourne recorded a population of 14,953 at ...
was used by Irish immigrants during the 1920s.
The game in Australasia is administered by Australasia GAA
The Australasia County Board of the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA), or Australasian GAA, or Gaelic Football & Hurling Association of Australasia is one of the county boards of the GAA outside Ireland, and is responsible for Gaelic games all a ...
.
Great Britain
Hurling was brought to Great Britain in the 19th century. The game is administered byBritish GAA
The British Council of the Gaelic Athletic Association ( ga, Cumann Lúthchleas Gael na Breataine) or Britain GAA is the only provincial council of the Gaelic Athletic Association outside the island of Ireland (however, the Headquarters of Uls ...
. Warwickshire
Warwickshire (; abbreviated Warks) is a county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, and the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare at Stratford-upon-Av ...
and Lancashire compete at inter-county level in the Lory Meagher Cup
The Lory Meagher Cup (; often referred to as the Meagher Cup) is the fifth-highest inter-county senior championship in hurling. Each year, the champion team in the Lory Meagher Cup is promoted to the Nicky Rackard Cup.
The Lory Meagher Cup, w ...
, competing against other counties in Ireland. London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
is the only non-Irish team to have won the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship (having captured the title in 1901
Events
January
* January 1 – The British colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia federate as the Commonwealth of Australia; Edmund Barton becomes the first Prime Minist ...
), and after winning the 2012 Christy Ring Cup gained the right to contest the Liam MacCarthy Cup in 2013.
The first ever hurling game played in the Scottish Highlands was played at Easter 2012 between CLG Micheal Breathnach and Fir Uladh, an Ulster select of Gaeiligoiri, as part of the Iomain Cholmcille festival, na Breathnaich coming out victorious.
Wales has its own club, St. Colmilles in Cardiff.
South Africa
Soldiers who served in the Irish Brigade during theAnglo-Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
are believed to have played the game on the veld
Veld ( or ), also spelled veldt, is a type of wide open rural landscape in :Southern Africa. Particularly, it is a flat area covered in grass or low scrub, especially in the countries of South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zimbabwe and Bot ...
t. Immigrants from County Wicklow who had arrived to work in the explosives factory in Umbogintwini, KwaZulu-Natal formed a team c. 1915–16. A major burst of immigration in the 1920s led to the foundation of the ''Transvaal Hurling Association'' in Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Dem ...
in 1928. Games were traditionally played in a pitch on the site of the modern day Johannesburg Central Railway Station every Easter Sunday
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the ''Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel P ...
after Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
.
In 1932, a South African hurling team sailed to Ireland to compete in the Tailteann Games, where they carried a banner donated by a convent of Irish nuns in Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. On their arrival, they were personally received by the Taoiseach
The Taoiseach is the head of government, or prime minister, of Ireland. The office is appointed by the president of Ireland upon the nomination of Dáil Éireann (the lower house of the Oireachtas, Ireland's national legislature) and the o ...
(Prime Minister) at the time, Éamon de Valera
Éamon de Valera (, ; first registered as George de Valero; changed some time before 1901 to Edward de Valera; 14 October 1882 – 29 August 1975) was a prominent Irish statesman and political leader. He served several terms as head of govern ...
.
South African hurling continued to prosper until the outbreak of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, which caused immigration from Ireland to cease and made it impossible to import equipment. Games of hurling and Gaelic football were occasionally sponsored by the Christian Brothers schools in Boksburg
Boksburg is a city on the East Rand of Gauteng province of South Africa. Gold was discovered in Boksburg in 1887. Boksburg was named after the State Secretary of the South African Republic, W. Eduard Bok. The Main Reef Road linked Boksburg ...
and Pretoria
Pretoria () is South Africa's administrative capital, serving as the seat of the executive branch of government, and as the host to all foreign embassies to South Africa.
Pretoria straddles the Apies River and extends eastward into the foot ...
well into the 1950s. Both games have all but ceased to be played.
North America
 References to hurling on the North American continent date from the 1780s in modern-day Canada concerning immigrants from County Waterford and County Kilkenny, and also, in New York City. After the end of the
References to hurling on the North American continent date from the 1780s in modern-day Canada concerning immigrants from County Waterford and County Kilkenny, and also, in New York City. After the end of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, references to hurling cease in American newspapers until the aftermath of the Great Famine when Irish people moved to America in huge numbers, bringing the game with them. Newspaper reports from the 1850s refer to occasional matches played in San Francisco, Hoboken
Hoboken ( ; Unami: ') is a city in Hudson County in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the city's population was 60,417. The Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated that the city's population was 58,69 ...
and New York City. The first game of hurling played under GAA rules outside Ireland was played on Boston Common
The Boston Common (also known as the Common) is a public park in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest city park in the United States. Boston Common consists of of land bounded by Tremont Street (139 Tremont St.), Park Street, Beac ...
in June 1886.
In 1888, there was an American tour by fifty Gaelic athletes from Ireland, known as the 'American Invasion'. This created enough interest among Irish Americans
, image = Irish ancestry in the USA 2018; Where Irish eyes are Smiling.png
, image_caption = Irish Americans, % of population by state
, caption = Notable Irish Americans
, population =
36,115,472 (10.9%) alone ...
to lay the groundwork for the North American GAA. By the end of 1889, almost a dozen GAA clubs existed in America, many of them in and around New York City, Philadelphia and Chicago. Later, clubs were formed in Boston, Cleveland, and many other centers of Irish America. Concord, New Hampshire has its state's only hurling team, New Hampshire Wolves, sponsored by Litherman's Limited Craft Brewery.
In 1910, twenty-two hurlers, composed of an equal number from Chicago and New York, conducted a tour of Ireland, where they played against the County teams from County Kilkenny, Kilkenny, County Tipperary, Tipperary, County Limerick, Limerick, County Dublin, Dublin and County Wexford, Wexford.Traditionally, hurling was a game played by Irish immigrants and discarded by their children. Many American hurling teams took to raising money to import players directly from Ireland. In recent years, this has changed considerably with the advent of the Internet and increased travel. The Barley House Wolves hurling team from New Hampshire was formed when U.S. soldiers returning from Iraq saw a hurling game on the television in Shannon Airport as their plane refuelled. Outside of the traditional North American GAA cities of New York, Boston, Chicago and San Francisco, clubs are springing up in other places where they consist of predominantly American-born players who bring a new dimension to the game and actively seek to promote it as a mainstream sport, especially Joe Maher, a leading expert at the sport in Boston. Currently, the Milwaukee Hurling Club, with 300 members, is the largest Hurling club in the world outside Ireland, which is made of all Americans and very few Irish immigrants. The St. Louis Gaelic Athletic Club was established in 2002 and has expanded its organization to an eight team hurling league in the spring and six team Gaelic football league in the fall. They also have a 30-member camogie league. Saint Louis has won two National Championships in Jr C Hurling (2004 and 2011), as well as two National Championships in Jr D Gaelic Football (2005, and 2013). The Indianapolis Hurling Club began in 2002, then reformed in 2005. In 2008, the Indy Hurling Club won the Junior C National Championship. In 2011, Indy had 7 club teams and sent a Junior B, Junior C and Camogie team to nationals. Hurling continues to grow in popularity with teams now in Knoxville, TN, Charleston, SC, Orlando, FL, Tampa, FL, Augusta, GA, Greenville, SC, Indianapolis, IN, Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester, MA, Corvallis, OR, Akron, OH, Raleigh, NC, Concord, NH, Portland, Maine, Providence, RI, Twin Cities, MN, Madison, WI, Milwaukee, WI, Washington, DC, Hampton Roads, VA, Rochester NY, Nashville, TN, Richmond, VA, Hartford, CT, Missoula, MT, Butte, MT and Seattle, WA.
The GAA have also begun to invest in American college students with university teams springing up at University of Connecticut, Stanford University, University of California, Berkeley, UC Berkeley, Purdue University, Indiana University, University of Montana and other schools. On 31 January 2009, the first ever US collegiate hurling match was held between UC Berkeley and Stanford University, organized by the newly formed California Collegiate Gaelic Athletic Association. UC Berkeley won the challenge match by one point, while Stanford won the next two CCGAA matches to win the first collegiate cup competition in the U.S. On Memorial Day Weekend of 2011, the first ever National Collegiate GAA championship was played. The Indiana University Hurling Club won all matches of the tournament, and won by four points in the championship final to be crowned the first ever National U.S. Collegiate Hurling Champions, U.S. National Collegiate Champions.
Major hurling competitions
Nicky Rackard Cup
The Nicky Rackard Cup (; often referred to as the Rackard Cup) is the fourth tier of the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. Each year, the champion team in the Nicky Rackard Cup is promoted to the Christy Ring Cup, and the lowest finishing ...
* All-Ireland Senior Club Hurling Championship
** Leinster Senior Club Hurling Championship
* All-Ireland Under-21 Hurling Championship
** Leinster Under-21 Hurling Championship
* All-Ireland Minor Hurling Championship
* Poc Fada
* Féile na nGael
* Composite rules shinty–hurling (usually internationals between Scotland and Ireland)
Popular culture
See also
* Camogie * Field Hockey * Bando (sport) * Shinty * Women's shinty * LacrosseReferences
Further reading
* *External links
Hurling
at the GAA website {{Authority control Hurling, Gaelic games Hurlers Stick sports Sports originating in Ireland Team sports