Hoof quoted.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate
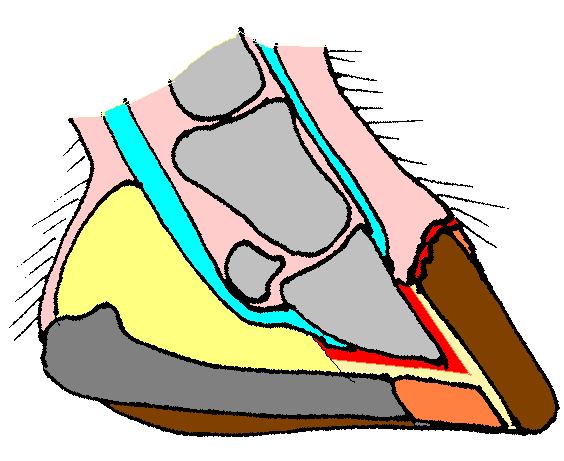 The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the
The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the
 Hooves grow continuously. In nature, wild animals are capable of wearing down the hoof as it continuously grows, but captive domesticated species often must undergo specific hoof care for a healthy, functional hoof. Proper care improves biomechanical efficiency and prevents lameness. If not worn down enough by use, such as in the dairy industry, hooves may need to be trimmed. However, too much wear can result in damage of the hooves, and for this reason,
Hooves grow continuously. In nature, wild animals are capable of wearing down the hoof as it continuously grows, but captive domesticated species often must undergo specific hoof care for a healthy, functional hoof. Proper care improves biomechanical efficiency and prevents lameness. If not worn down enough by use, such as in the dairy industry, hooves may need to be trimmed. However, too much wear can result in damage of the hooves, and for this reason,
 A cow hoof is cloven, or divided, into two approximately equal parts, usually called claws. Approximately 95% of lameness in dairy cattle occurs in the feet. Lameness in dairy cows can reduce milk production and fertility, and cause reproductive problems and suffering. For dairy farm profitability, lameness, behind only infertility and mastitis, is the third most important cow health issue.
Hoof trimmers trim and care for bovine hooves, usually
A cow hoof is cloven, or divided, into two approximately equal parts, usually called claws. Approximately 95% of lameness in dairy cattle occurs in the feet. Lameness in dairy cows can reduce milk production and fertility, and cause reproductive problems and suffering. For dairy farm profitability, lameness, behind only infertility and mastitis, is the third most important cow health issue.
Hoof trimmers trim and care for bovine hooves, usually
File:Masai Giraffe right-rear foot.jpg, Rear foot of a
mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the ruminants with two digits, are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis ...
, deer, bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
, cattle, goat, and sheep. The feet of perissodactyl mammals have an odd number of toes, e.g. the horse, the rhinoceros, and the tapir. Hooves are limb structures restricted to placental mammals, which have long pregnancies; however, the marsupial '' Chaeropus'' had hooves.
Description
 The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the
The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the distal phalanx
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones.
...
, and the navicular bone. The hoof consists of the hoof wall
The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the rumi ...
, the bars of the hoof, the sole and frog and soft tissue shock absorption structures. The weight of the animal is normally borne by both the sole and the edge of the hoof wall. Hooves perform many functions, including supporting the weight of the animal, dissipating the energy impact as the hooves strike the ground or surface, protecting the tissues and bone within the hoof capsule, and providing traction for the animal. Numerous factors can affect hoof structure and health, including genetics, hoof conformation, environmental influences, and athletic performance of the animal. The ideal hoof has a parallel hoof-pastern axis, a thick hoof wall, adequate sole depth, a solid heel base and growth rings of equal size under the coronary band.
There are four layers within the exterior wall of the hoof. From the outside, a hoof is made up of the stratum externum, the stratum medium, the stratum internum and the dermis parietis. The stratum externum and the stratum medium are difficult to distinguish, the stratum externum is thin and the stratum medium is what makes up the bulk of the hoof wall. Inside the hoof wall is a laminar junction, a soft tissue structure that allows the hoof to withstand the demands of force transmission it undergoes. This tissue structure binds the inner surface of the hoof wall, the dermis parietis and the outer surface of the third phalanx.
Most even-toed ungulates (such as sheep, goats, deer, cattle, bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
and pigs) have two main hooves on each foot, together called a cloven hoof.The term "cloven hoof" therefore being a technical misnomer as nothing is actually "cloven". Most of these cloven-hooved animals also have two smaller hooves called '' dewclaws'' a little further up the leg – these are not normally used for walking, but in some species with larger dewclaws (such as deer and pigs) they may touch the ground when running or jumping, or if the ground is soft. In the mountain goat, the dewclaw serves to provide extra traction when descending rocky slopes as well as additional drag on loose or slippery surfaces made of ice, dirt, or snow. Other cloven-hooved animals (such as giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis ...
s and pronghorns) have no dewclaws.
In some so-called "cloven-hooved" animals, such as camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. C ...
s, the "hoof" is not properly a hoof – it is not a hard or rubbery sole with a hard wall formed by a thick nail – instead it is a soft toe with little more than a nail merely having an appearance of a hoof.
Some odd-toed ungulates (equid
Equidae (sometimes known as the horse family) is the taxonomic family of horses and related animals, including the extant horses, asses, and zebras, and many other species known only from fossils. All extant species are in the genus '' Equus'', w ...
s) have one hoof on each foot; others have (or had) three distinct hooved or heavily nailed toes, or one hoof and two dewclaws. The tapir is a special case, having three toes on each hind foot and four toes on each front foot.
Management
 Hooves grow continuously. In nature, wild animals are capable of wearing down the hoof as it continuously grows, but captive domesticated species often must undergo specific hoof care for a healthy, functional hoof. Proper care improves biomechanical efficiency and prevents lameness. If not worn down enough by use, such as in the dairy industry, hooves may need to be trimmed. However, too much wear can result in damage of the hooves, and for this reason,
Hooves grow continuously. In nature, wild animals are capable of wearing down the hoof as it continuously grows, but captive domesticated species often must undergo specific hoof care for a healthy, functional hoof. Proper care improves biomechanical efficiency and prevents lameness. If not worn down enough by use, such as in the dairy industry, hooves may need to be trimmed. However, too much wear can result in damage of the hooves, and for this reason, horseshoe
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toen ...
s and oxshoes are used by animals that routinely walk on hard surfaces and carry heavy weight.
Horses
Within the equine world, the expression, "no foot, no horse" emphasizes the importance of hoof health. Hoof care is important in theequine industry
The horse industry, or equine industry, is the economic activity associated with horses. This includes core agribusiness activities related to the use, possession or ownership of horses, as well as leisure activities and related economic activity ...
. Problems that can arise with poor horse hoof care include hoof cracks, thrush, abscesses and laminitis.
Cattle
 A cow hoof is cloven, or divided, into two approximately equal parts, usually called claws. Approximately 95% of lameness in dairy cattle occurs in the feet. Lameness in dairy cows can reduce milk production and fertility, and cause reproductive problems and suffering. For dairy farm profitability, lameness, behind only infertility and mastitis, is the third most important cow health issue.
Hoof trimmers trim and care for bovine hooves, usually
A cow hoof is cloven, or divided, into two approximately equal parts, usually called claws. Approximately 95% of lameness in dairy cattle occurs in the feet. Lameness in dairy cows can reduce milk production and fertility, and cause reproductive problems and suffering. For dairy farm profitability, lameness, behind only infertility and mastitis, is the third most important cow health issue.
Hoof trimmers trim and care for bovine hooves, usually dairy cows
Dairy cattle (also called dairy cows) are cattle bred for the ability to produce large quantities of milk, from which dairy products are made. Dairy cattle generally are of the species ''Bos taurus''.
Historically, little distinction was mad ...
. Hooves can be trimmed with a sharp knife while the cow is restrained and positioned with ropes. Professional hoof-trimming tend to use angle grinders and of some type of hoof trimming crush to make the process quicker and less physically demanding on the hoof trimmer. A hoof trimmer using modern machinery may trim the hooves of more than 10,000 cows per year. The trimmer shapes the hooves to provide the optimal weight bearing surface. A freshly trimmed hoof may be treated with copper sulfate pentahydrate to prevent foot rot.
Gallery
giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis ...
(no dewclaws)
File:Horse rear hooves.jpg, Rear hooves of a horse
File:Tapir hooves.jpg, Malayan tapir hooves: front with four toes, back with three toes
In culture
Hooves have historical significance in ceremonies and games. They have been used in burial ceremonies.See also
* Claw *Hoof glue Hoof glue is a form of animal glue made by boiling down the hooves of ungulates into partially hydrolyzed keratin. It is not to be confused with hide glue.
History
Hoof glue applications include stiffening bow strings, adhering fabric to wood, ...
* Horse hoof
* Nail (anatomy)
Notes
References
{{Authority control Mammal anatomy