Holstein Arms.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Holstein (; nds, label= Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (german: Grafschaft Holstein, links=no; 811–1474), the later Duchy of Holstein (german: Herzogtum Holstein, links=no; 1474–1866), and was the northernmost territory of the Holy Roman Empire. The history of Holstein is closely intertwined with the history of the
Holstein (; nds, label= Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (german: Grafschaft Holstein, links=no; 811–1474), the later Duchy of Holstein (german: Herzogtum Holstein, links=no; 1474–1866), and was the northernmost territory of the Holy Roman Empire. The history of Holstein is closely intertwined with the history of the 
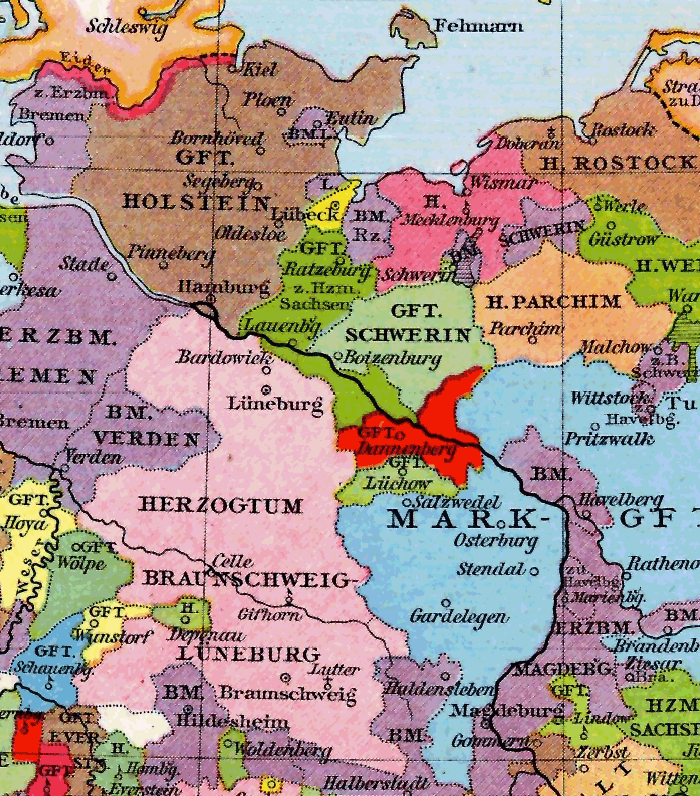 The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the Duchy of Saxony, then of the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg, and finally of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. With the establishment of the new territorial unit, expansion to the East began and the Wagrians were finally defeated in 1138.
The County of Holstein was ruled by the House of Schaumburg; the first count was Adolf I, Count of Holstein. Holstein was temporarily occupied by Denmark after the Battle of Stellau (1201), but was reconquered by the Count of Schauenburg and his allies in the Battle of Bornhöved (1227).
The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the Duchy of Saxony, then of the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg, and finally of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. With the establishment of the new territorial unit, expansion to the East began and the Wagrians were finally defeated in 1138.
The County of Holstein was ruled by the House of Schaumburg; the first count was Adolf I, Count of Holstein. Holstein was temporarily occupied by Denmark after the Battle of Stellau (1201), but was reconquered by the Count of Schauenburg and his allies in the Battle of Bornhöved (1227).

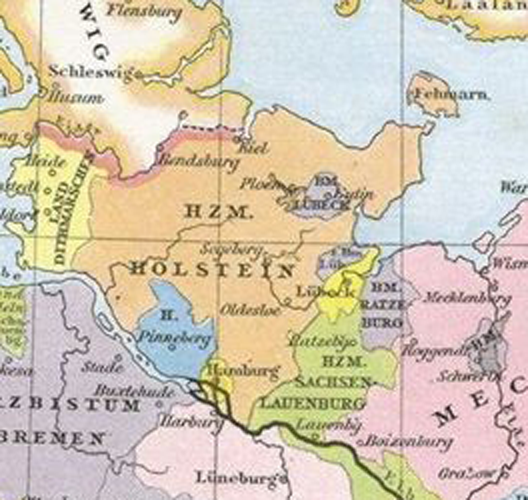 In 1474 Lauenburg's
In 1474 Lauenburg's
 Following the death of King
Following the death of King 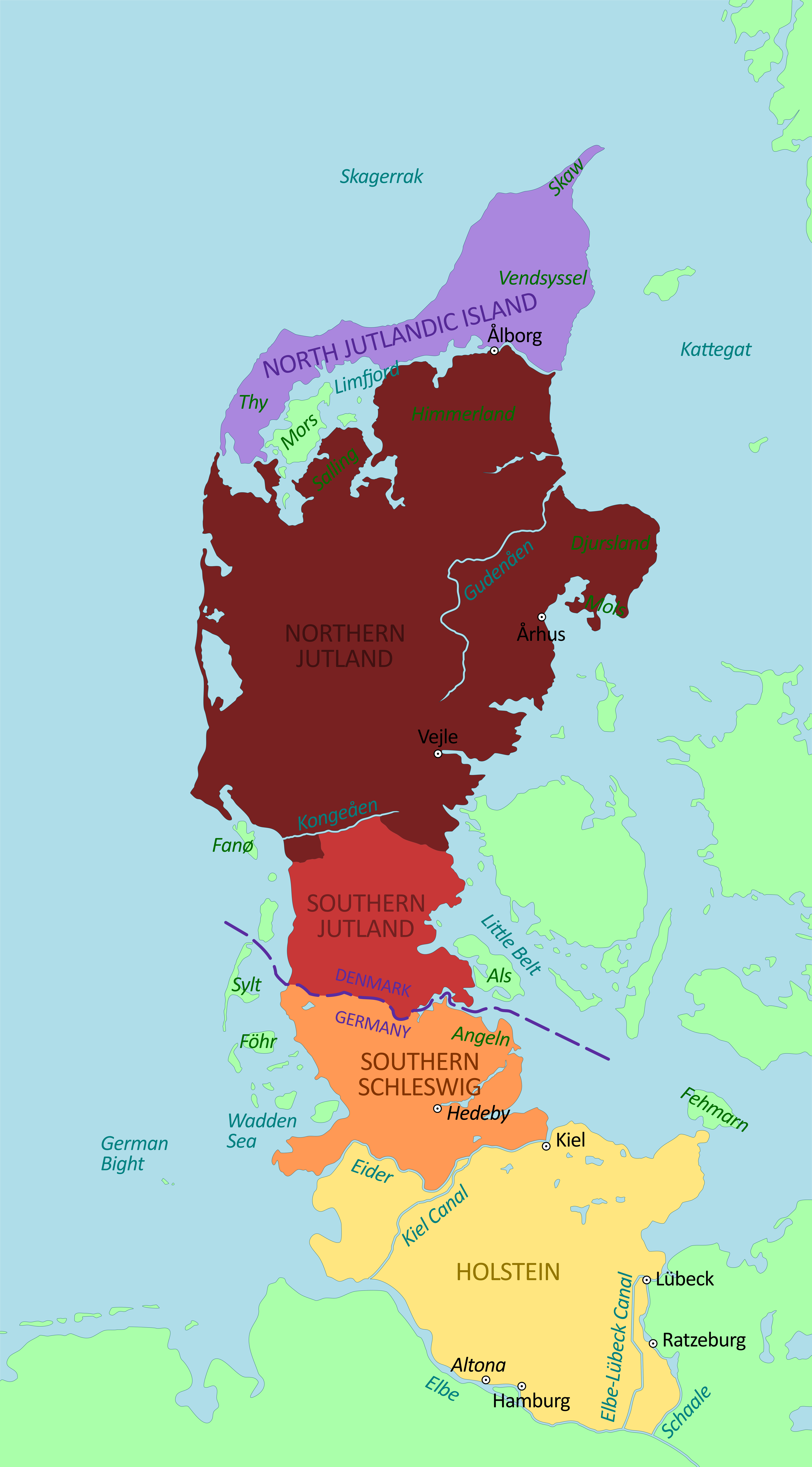 For a list of rulers, see ''
For a list of rulers, see ''
Map of Schleswig-Holstein in 1730
{{Coord, 54.1667, N, 9.66667, E, source:kolossus-nowiki, display=title History of Schleswig-Holstein Counties of the Holy Roman Empire States and territories established in 1474 Regions of Schleswig-Holstein
Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
Duchy of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km ( ...
( da, Slesvig, links=no). The capital of Holstein is Kiel.
Holstein's name comes from the Holcetae, a Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
tribe mentioned by Adam of Bremen as living on the north bank of the Elbe, to the west of Hamburg. The name means "dwellers in the wood" (Northern Low Saxon: ; german: Holzsassen, links=no).

History
Origins
After theMigration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
of the Early Middle Ages, Holstein was adjacent to the Obotrites on the coast of the Baltic Sea and the land of the Danes in Jutland.
With the conquest of Old Saxony
"Old Saxony" is the original homeland of the Saxons. It corresponds roughly to the modern German states of Lower Saxony, eastern part of modern North Rhine-Westphalia state (Westphalia), Nordalbingia (Holstein, southern part of Schleswig-Holstein ...
by Charlemagne ''circa'' 800, he granted the land north of the Eider River
The Eider (german: Die Eider; da, Ejderen; Latin: ''Egdor'' or ''Eidora'') is the longest river in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The river starts near Bordesholm and reaches the southwestern outskirts of Kiel on the shores of the Balt ...
(Schleswig) to the Danes
Danes ( da, danskere, ) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
Danes generally regard t ...
by the Treaty of Heiligen signed in 811. The ownership of what would late become eastern Holstein (districts of Plön and Ostholstein) was given to the Obotrites, namely the Wagrians, and the Saxon elite was deported to various areas of the empire. After 814, however, the Saxons were restored to Western Holstein. The Wagrians were pushed out of the Limes Saxoniae - the new border running from the Elbe River near Boizenburg northwards along the Bille River to the mouth of the Schwentine at the Kiel Fjord and the Baltic Sea. For the following 300 years, Holstein continued to be a part of Saxony.
The County of Holstein
 The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the Duchy of Saxony, then of the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg, and finally of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. With the establishment of the new territorial unit, expansion to the East began and the Wagrians were finally defeated in 1138.
The County of Holstein was ruled by the House of Schaumburg; the first count was Adolf I, Count of Holstein. Holstein was temporarily occupied by Denmark after the Battle of Stellau (1201), but was reconquered by the Count of Schauenburg and his allies in the Battle of Bornhöved (1227).
The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the Duchy of Saxony, then of the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg, and finally of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. With the establishment of the new territorial unit, expansion to the East began and the Wagrians were finally defeated in 1138.
The County of Holstein was ruled by the House of Schaumburg; the first count was Adolf I, Count of Holstein. Holstein was temporarily occupied by Denmark after the Battle of Stellau (1201), but was reconquered by the Count of Schauenburg and his allies in the Battle of Bornhöved (1227).
Partitions of the County of Holstein (1111–1474)
TheCounts of Schauenburg and Holstein
The Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein were titles of the Frankish Empire. The dynastic family came from the County of Schauenburg near Rinteln (district Schaumburg) on the Weser in Germany. Together with its ancestral possessions in Bückeburg ...
partitioned Holstein several times among the inheriting sons into up to six lines, named after their towns of residence:
* Holstein-Itzehoe
Holstein-Itzehoe was a county that was formed from Schauenburg and Holstein by the division of Holstein between Gerhard and John in 1261.
Gerhard of Holstein-Itzehoe was the only regent. After his death in 1290 Holstein-Itzehoe was divided up b ...
, branch county between 1261 and 1290, partitioned from Holstein, repartitioned into Holstein-Pinneberg, Holstein-Plön and Holstein-Rendsburg
* Holstein-Kiel
The imperial county of Holstein-Kiel was a line of the House of Schauenburg and Holstein from 1261 to 1390.
History
The County of Holstein was ruled until 1238 by Adolphus IV of Schauenburg and Holstein. When he retired, his sons John I and Ger ...
, branch county between 1261 and 1390, partitioned from Holstein, in 1273 Holstein-Segeberg (first) was partitioned from Holstein-Kiel, but reverted in 1308, but then lost to Holstein-Pinneberg, Holstein-Plön and Holstein-Rendsburg in 1316; Holstein-Kiel acquired Holstein-Plön in 1350, and merged itself into Holstein-Rendsburg
* Holstein-Pinneberg, branch county between 1290 and 1640, partitioned from Holstein-Itzehoe, acquired a share of Holstein-Segeberg in 1316, merged into the Duchy of Holstein
* Holstein-Plön, branch county between 1290 and 1390, partitioned from Holstein-Itzehoe, acquired a share of Holstein-Segeberg in 1316, merged into Holstein-Kiel
* Holstein-Rendsburg, branch county between 1290 and 1474, partitioned from Holstein-Itzehoe, acquired a share of Holstein-Segeberg (first) in 1316, and Holstein-Kiel in 1390, in 1381/1384 Holstein-Segeberg (second) was partitioned from Holstein-Rendsburg, but reverted in 1403, elevated to ducal rank in 1474
* Holstein- Segeberg (first), branch county between 1273 and 1308, partitioned from and reverted to Holstein-Kiel, but seized by allied Holstein-Pinneberg, Holstein-Plön, and Holstein-Rendsburg, partitioning Segeberg in three shares, each merged into one of the lines in 1316
* Holstein-Segeberg (second), branch county between 1381/1384 and 1403, partitioned from and reverted to Holstein-Rendsburg
In 1386 King Oluf II of Denmark and his mother-regent, Queen Margaret I, enfeoffed in Nyborg Gerhard VI, Count of Holstein-Rendsburg and his cognatic successors with the Duchy of Schleswig. He thus became as Gerhard II duke of Schleswig. Until 1390 the Rendsburg branch united by inheritance all branches except of that of Holstein-Pinneberg.
When the Holstein-Rendsburg line of the Schauenburg counts became extinct with the death of Adolf VIII of Holstein-Rendsburg (and in personal union as Adolf I Duke of Schleswig) in 1459, Christian I of Denmark inherited – from his maternal uncle Adolf I – the Duchy of Schleswig, a Danish fief. Through the Treaty of Ribe (1460) Christian was elected Count of Holstein-Rendsburg, then still a Saxe-Lauenburgian subfief within the Holy Roman Empire.
The Duchy of Holstein

 In 1474 Lauenburg's
In 1474 Lauenburg's liege lord
Homage (from Medieval Latin , lit. "pertaining to a man") in the Middle Ages was the ceremony in which a feudal tenant or vassal pledged reverence and submission to his feudal lord, receiving in exchange the symbolic title to his new position (inv ...
, the German Emperor Frederick III, elevated Christian I as Count of Holstein-Rendsburg to Duke of Holstein, thus becoming an immediate imperial (''reichsunmittelbar
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular prin ...
'') vassal (see imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular prin ...
). The Duchy of Holstein retained that status until the dissolution of the Empire in 1806.
Partitions of the Duchy of Holstein (1474–1866)
In 1490, the Duchy of Holstein was divided into Holstein-Segeberg and Holstein-Gottorp. Holstein-Segeberg remained with the Danish king and was also known as Royal Holstein; later it came to be known as Holstein-Glückstadt. Holstein-Gottorp, also known as Ducal Holstein, was given to a cadet branch of the House of Oldenburg, to which the kings of Denmark belonged. Between 1533 and 1544 KingChristian III of Denmark
Christian III (12 August 1503 – 1 January 1559) reigned as King of Denmark from 1534 and King of Norway from 1537 until his death in 1559. During his reign, Christian formed close ties between the church and the crown. He established ...
ruled the entire Duchies of Holstein and of Schleswig also in the name of his then still minor half-brothers John the Elder and Adolf. In 1544 they partitioned the Duchies of Holstein (a fief of the Holy Roman Empire) and of Schleswig (a Danish fief) in an unusual way, following negotiations between the brothers and the Estates of the Realm of the duchies, which had constituted in 1460 by the Treaty of Ribe and strictly opposed a factual partition. The elder three brothers determined their youngest brother Frederick for a career as Lutheran administrator of an ecclesiastical state within the Holy Roman Empire.
So the revenues of the duchies were divided in three equal shares by assigning the revenues of particular areas and landed estates to each of the elder brothers, while other general revenues, such as taxes from towns and customs dues, were levied together but then shared among the brothers. The estates, whose revenues were assigned to the parties, made Holstein and Schleswig look like patchworks, technically inhibiting the emergence of separate new duchies, as intended by the estates of the duchies. The secular rule in the fiscally divided duchies thus became a condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership structure whereby a building is divided into several units that are each separately owned, surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned. The term can be applied to the building or complex ...
of the parties. As dukes of Holstein and Schleswig the rulers of both houses bore the formal title of "Duke of Schleswig, Holstein, Ditmarsh and Stormarn". The three shares are usually called:
* Gottorp ducal share in Holstein and Schleswig, partitioned from ducal Holstein in 1544, acquired half of Haderslev share in 1581 (thus thereafter simply called ducal share), merged into the royal share in 1773 with its ruler receiving in return the prior Danish-held County of Oldenburg.
* Haderslev ducal share in Holstein and Schleswig, partitioned from ducal Holstein in 1544, halved between Gottorp and royal share in 1581
* Royal share in Holstein and Schleswig, acquired half of Haderslev share in 1581, the County of Holstein-Pinneberg in 1640 and the Gottorp share in 1713 (northern part) and 1773 (southern part), thus then comprising all of Holstein. Between 1648 and 1773 the royal share used to be called Holstein-Glückstadt after its capital Glückstadt. Parts of the former County of Holstein-Pinneberg were transformed 1649/50 into the Imperial County of Rantzau
The Imperial County of Rantzau (german: Reichsgrafschaft Rantzau) was an immediate state of the Holy Roman Empire. Its territory is more or less congruent with the present ''Amt'' Rantzau.
In 1649, Frederick III, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp, sold ...
, which fell back to the Danish Crown in 1726.
The dynastic name Holstein-Gottorp comes as convenient usage from the technically more correct Duke of Schleswig and Holstein at Gottorp. Adolf, the third son of Duke and King Frederick I and the second youngest half-brother of King Christian III, founded the dynastic branch called House of Holstein-Gottorp, which is a cadet branch of the then royal Danish House of Oldenburg. The Danish monarchs and the Dukes of Holstein-Gottorp ruled both duchies together as to general government, however, collected their revenues in their separate estates. John the Elder conveniently called Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Haderslev produced no issue, so no branch emerged from his side.
Similar to the above-mentioned agreement Christian III's youngest son John the Younger gained for him and his heirs a share in Holstein's and Schleswig's revenues in 1564, comprising a third of the royal share, thus a ninth of Holstein and Schleswig as to the fiscal point of view. John the Younger and his heirs, however, had no share in the condominial rule, so they were not ruling but mere titular dukes.
The share of John the Elder, who died in 1581, was halved between Adolf and Frederick II, thus increasing again the royal share by a fiscal sixth of Holstein and Schleswig.Cf. Carsten Porskrog Rasmussen, "Die dänischen Könige als Herzöge von Schleswig und Holstein", Frauke Witte and Marion Hartwig (trls.), in: ''Die Fürsten des Landes: Herzöge und Grafen von Schleswig, Holstein und Lauenburg'' e slevigske hertuger; German
E, or e, is the fifth Letter (alphabet), letter and the second vowel#Written vowels, vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worl ...
Carsten Porskrog Rasmussen (ed.) on behalf of the Gesellschaft für Schleswig-Holsteinische Geschichte, Neumünster: Wachholtz, 2008, pp. 73–109, here pp. 87seq. As an effect the complicated fiscal division of both separate duchies, Holstein and Schleswig, with shares of each party scattered in both duchies, provided them with a condominial government binding both together, partially superseding their legally different affiliation as Holy Roman and Danish fiefs.
The County of Holstein-Pinneberg, which had remained a separately ruled territory in Holstein until its line was extinct in 1640, was merged into the then royal share of the Duchy of Holstein. The Duke of Holstein-Gottorp became emperor of Russia in 1762 as Peter III Peter III may refer to:
Politics
* Peter III of Bulgaria (ruled in 1072)
* Peter III of Aragon (1239–1285)
* Peter III of Arborea (died 1347)
* Peter III Aaron (died 1467)
* Pedro III of Kongo (ruler in 1669)
* Peter III of Russia (1728–1762)
* ...
and was planning an attack on Denmark to recover the Holstein-Gottorp lands possessions in Schleswig, which were seized by the Danish king in 1713. Although Peter was soon overthrown by his wife, Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
, the Danes determined to rid themselves of this problem. In 1773, they exchanged the County of Oldenburg for the Gottorp lands in Holstein, bringing all of Holstein under their control. Thus, Holstein was again united in one state.
The territory of Holstein was enlarged by the conquest of the independent Republic of Dithmarschen in 1559, which was divided among the three ducal houses. After 1581 the southern part remained to the Danish Crown, the northern part was ruled by the House of Gottorp until 1773.
United Holstein
With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 Holstein's imperial vassal status turned void. It thus became a sovereign state. Because of its personal union with Denmark, the Duchy of Holstein did not come under French occupation during the Napoleonic era (however, the neighboring duchy of Lauenburg was annexed by France in 1811 and became a part ofBouches-de-l'Elbe
Bouches-de-l'Elbe (; "Mouths of the Elbe", ) was a departments of France, department of the First French Empire in present-day Germany that survived for three years. It was named after the mouth of the river Elbe. It was formed in 1811, when the r ...
). From 1815 to 1864 it was a member of the German Confederation, though still in personal union with Denmark (the King of Denmark being also Duke of Holstein).
 Following the death of King
Following the death of King Frederick VII of Denmark
Frederick VII (Frederik Carl Christian; 6 October 1808 – 15 November 1863) was King of Denmark from 1848 to 1863. He was the last Danish monarch of the older Royal branch of the House of Oldenburg and the last king of Denmark to rule as an ...
( House of Oldenburg) in 1863, the inheritance of Schleswig and Holstein was disputed. The new king, Christian IX ( House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg, a cadet branch of the House of Oldenburg), made his claim to the Danish throne through a female line. The Duke of Augustenborg
The House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Augustenburg () was a branch of the dukes of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg of the House of Oldenburg. The line descended from Alexander, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg. Like all of the secondary ...
, a minor scion from another cadet line of the House of Oldenburg, claimed the Duchies, and soon the German Confederation, led by Prussia and Austria, went to the Second Schleswig War with Denmark, quickly defeating it in 1864 and forcing it to cede the duchies.
However, the duchies were not given to the Duke of Augustenborg. In 1865 an arrangement was worked out between Prussia and Austria where the Austrians occupied and administered Holstein, while the Prussians did the same in Schleswig. This arrangement came to an end with the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
of 1866, which resulted in Schleswig and Holstein both being incorporated into Prussia as the Province of Schleswig-Holstein. Holstein, meanwhile including former Saxe-Lauenburg (as of 1876) and the former Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck
Free may refer to:
Concept
* Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything
* Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism
* Emancipate, to proc ...
and Region of Lübeck (both as of 1937) regained statehood, now united with Schleswig, in 1946, when the British occupation government elevated the province to the State of Schleswig-Holstein, followed by the official dissolution of Prussia in 1947.
Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein
The Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein were titles of the Frankish Empire. The dynastic family came from the County of Schauenburg near Rinteln (district Schaumburg) on the Weser in Germany. Together with its ancestral possessions in Bückeburg ...
'' and '' List of rulers of Schleswig-Holstein''.
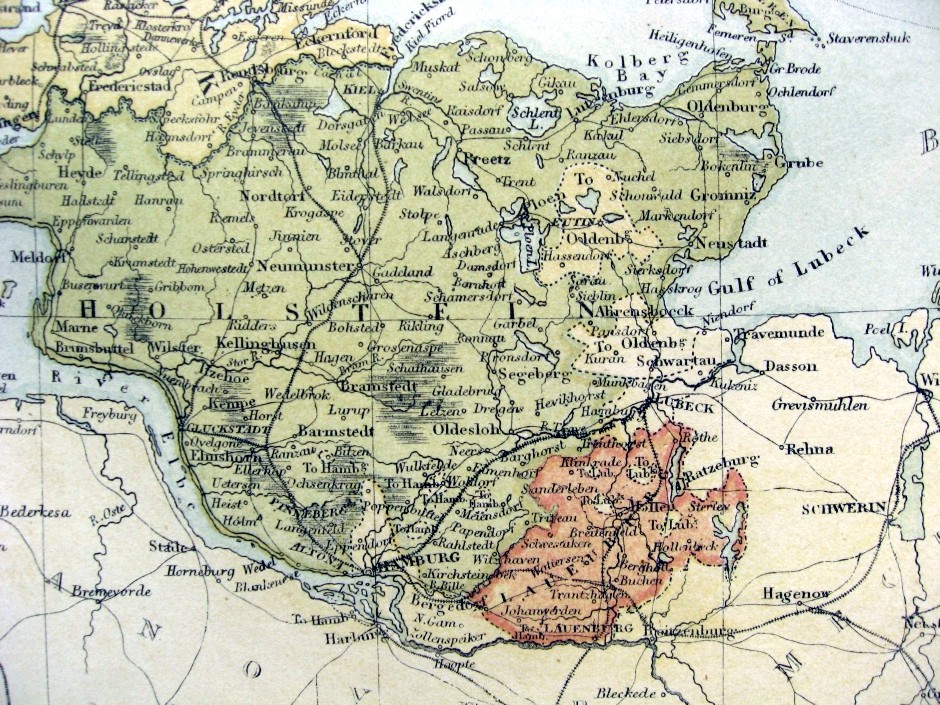
Geography
As of 1864, Holstein bordered Denmark in the north, the Principality of Lübeck (formerly the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, an exclave of the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg), theFree and Hanseatic City of Lübeck
Free may refer to:
Concept
* Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything
* Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism
* Emancipate, to proc ...
, and the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg in the east, and the Kingdom of Hanover and the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
in the south. It also borders the North Sea in the west and the Baltic Sea in the east. Its only major island is Fehmarn
Fehmarn (, da, Femern; from Old Wagrian Slavic "''Fe More''", meaning "''In the Sea''") is an island in the Baltic Sea, off the eastern coast of Germany's northernmost state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is Germany's third-largest island, after Rüg ...
, originally a part of the Duchy of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km ( ...
until 1867.
Cities in Holstein included Kiel, Altona, Glückstadt, Rendsburg
Rendsburg ( da, Rendsborg, also ''Rensborg'', nds, Rendsborg, also ''Rensborg'') is a town on the River Eider and the Kiel Canal in the central part of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) of Rendsburg-Ecke ...
, Segeberg, Heiligenhafen
Heiligenhafen (; Holsatian: ''Hilligenhaven'') is a town in the district of Ostholstein, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated on the Baltic Sea coast, opposite the island Fehmarn, approx. 60 km northeast of Lübeck, and 55 km e ...
, Oldenburg in Holstein, and Plön. It had an area of 8,385 km2.
Notes
References
External links
Map of Schleswig-Holstein in 1730
{{Coord, 54.1667, N, 9.66667, E, source:kolossus-nowiki, display=title History of Schleswig-Holstein Counties of the Holy Roman Empire States and territories established in 1474 Regions of Schleswig-Holstein