Genghis Khan empire-en.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Chinggis Khaan''
Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr /> Mongol script:
''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan'' , birth_name = Tem√ľjin , successor = Tolui (as regent)
√Ėgedei Khan , spouse = , issue = , house =
(presumptively
Mongolia: a guide to economic and political developments
.'' Taylor & Francis. pp. 5‚Äď7. . Many medieval chroniclers and modern historians describe Genghis Khan's conquests as wholesale destruction on an unprecedented scale that led to drastic population declines in some regions as a result of both mass exterminations and
‚ÄĒ Big Russian Encyclopedia, 2010 When

 Tem√ľjin was born the first son of Hoelun, second wife of his father Yes√ľgei, who was the chief of the
Tem√ľjin was born the first son of Hoelun, second wife of his father Yes√ľgei, who was the chief of the
 In the early 12th century, the Central Asian plateau north of China was divided into several prominent tribal confederations, including Naimans, Merkits, Tatars, Khamag Mongols, and
In the early 12th century, the Central Asian plateau north of China was divided into several prominent tribal confederations, including Naimans, Merkits, Tatars, Khamag Mongols, and
 In his rule and his conquest of rival tribes, Tem√ľjin broke with Mongol tradition in a few crucial ways. He delegated authority based on merit and loyalty, rather than family ties. As an incentive for absolute obedience and the Yassa code of law, Tem√ľjin promised civilians and soldiers wealth from future war spoils. When he defeated rival tribes, he did not drive away their soldiers and abandon their civilians. Instead, he took the conquered tribe under his protection and integrated its members into his own tribe. He would even have his mother adopt orphans from the conquered tribe, bringing them into his family. These political innovations inspired great loyalty among the conquered people, making Tem√ľjin stronger with each victory.
In his rule and his conquest of rival tribes, Tem√ľjin broke with Mongol tradition in a few crucial ways. He delegated authority based on merit and loyalty, rather than family ties. As an incentive for absolute obedience and the Yassa code of law, Tem√ľjin promised civilians and soldiers wealth from future war spoils. When he defeated rival tribes, he did not drive away their soldiers and abandon their civilians. Instead, he took the conquered tribe under his protection and integrated its members into his own tribe. He would even have his mother adopt orphans from the conquered tribe, bringing them into his family. These political innovations inspired great loyalty among the conquered people, making Tem√ľjin stronger with each victory.
 One of the later ruptures between Tem√ľjin and Toghrul was Toghrul's refusal to give his daughter in marriage to Jochi, Tem√ľjin's first son. This was disrespectful in Mongolian culture and led to a war. Toghrul allied with
One of the later ruptures between Tem√ľjin and Toghrul was Toghrul's refusal to give his daughter in marriage to Jochi, Tem√ľjin's first son. This was disrespectful in Mongolian culture and led to a war. Toghrul allied with

 The part of the Merkit clan that sided with the Naimans were defeated by
The part of the Merkit clan that sided with the Naimans were defeated by

 Using his rival Nilga Senggum's temporary refuge in Western Xia as a pretext, Tem√ľjin launched a raid against the state in 1205 in the Edsin region. The next year, in 1206, Tem√ľjin was formally proclaimed Genghis Khan, ruler of all the Mongols, marking the official start of the Mongol Empire, and the same year Emperor Huanzong of the Western Xia was deposed by
Using his rival Nilga Senggum's temporary refuge in Western Xia as a pretext, Tem√ľjin launched a raid against the state in 1205 in the Edsin region. The next year, in 1206, Tem√ľjin was formally proclaimed Genghis Khan, ruler of all the Mongols, marking the official start of the Mongol Empire, and the same year Emperor Huanzong of the Western Xia was deposed by
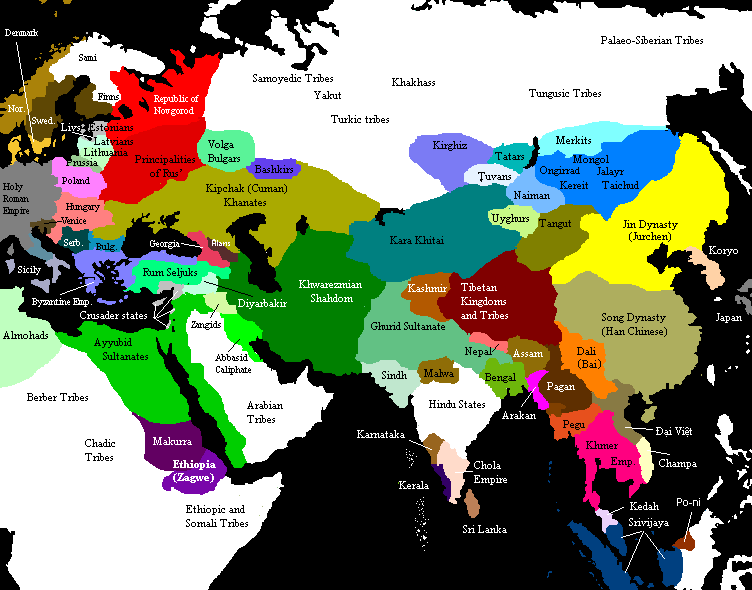 In the early 13th century, the Khwarazmian dynasty was governed by Shah Ala ad-Din Muhammad. Genghis Khan saw the potential advantage in Khwarazmia as a commercial trading partner using the
In the early 13th century, the Khwarazmian dynasty was governed by Shah Ala ad-Din Muhammad. Genghis Khan saw the potential advantage in Khwarazmia as a commercial trading partner using the  The Mongol army under Genghis Khan, generals and his sons crossed the Tien Shan mountains by entering the area controlled by the Khwarazmian Empire. After compiling intelligence from many sources Genghis Khan carefully prepared his army, which was divided into three groups. His son Jochi led the first division into the northeast of Khwarazmia. The second division under Jebe marched secretly to the southeast part of Khwarazmia to form, with the first division, a pincer attack on
The Mongol army under Genghis Khan, generals and his sons crossed the Tien Shan mountains by entering the area controlled by the Khwarazmian Empire. After compiling intelligence from many sources Genghis Khan carefully prepared his army, which was divided into three groups. His son Jochi led the first division into the northeast of Khwarazmia. The second division under Jebe marched secretly to the southeast part of Khwarazmia to form, with the first division, a pincer attack on  With the capture of Bukhara, the way was clear for the Mongols to advance on the capital of
With the capture of Bukhara, the way was clear for the Mongols to advance on the capital of
How Stuff Works. Retrieved April 27, 2021 According to widely circulated but unverified stories, the severed heads were then erected in separate piles for the men, women and children. Near to the end of the battle for
 After the defeat of the Khwarazmian Empire in 1220, Genghis Khan gathered his forces in Persia and Armenia to return to the Mongolian steppes. Under the suggestion of
After the defeat of the Khwarazmian Empire in 1220, Genghis Khan gathered his forces in Persia and Armenia to return to the Mongolian steppes. Under the suggestion of
 The vassal emperor of the Tanguts (Western Xia) had earlier refused to take part in the Mongol war against the Khwarezmid Empire. Western Xia and the defeated Jin dynasty formed a coalition to resist the Mongols, counting on the campaign against the Khwarazmians to preclude the Mongols from responding effectively.
In 1226, immediately after returning from the west, Genghis Khan began a retaliatory attack on the Tanguts. His armies quickly took Heisui,
The vassal emperor of the Tanguts (Western Xia) had earlier refused to take part in the Mongol war against the Khwarezmid Empire. Western Xia and the defeated Jin dynasty formed a coalition to resist the Mongols, counting on the campaign against the Khwarazmians to preclude the Mongols from responding effectively.
In 1226, immediately after returning from the west, Genghis Khan began a retaliatory attack on the Tanguts. His armies quickly took Heisui,
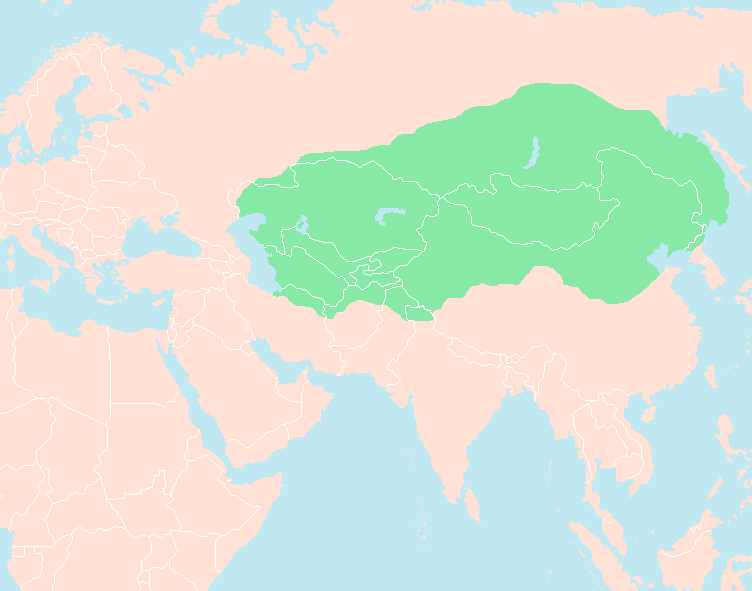 Genghis Khan died within eight days of setting off for his final campaign against the Western Xia on 18 August 1227, according to the official ''History of Yuan'' commissioned during China's Ming dynasty. The date of his death is therefore said to have fallen on 25 August 1227, during the fall of Yinchuan. The exact cause of his death remains a mystery, and is variously attributed to illness, being killed in action or from wounds sustained in hunting or battle. According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', Genghis Khan fell from his horse while hunting and died because of the injury. The '' Galician‚ÄďVolhynian Chronicle'' alleges he was killed by the Western Xia in battle, while
Genghis Khan died within eight days of setting off for his final campaign against the Western Xia on 18 August 1227, according to the official ''History of Yuan'' commissioned during China's Ming dynasty. The date of his death is therefore said to have fallen on 25 August 1227, during the fall of Yinchuan. The exact cause of his death remains a mystery, and is variously attributed to illness, being killed in action or from wounds sustained in hunting or battle. According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', Genghis Khan fell from his horse while hunting and died because of the injury. The '' Galician‚ÄďVolhynian Chronicle'' alleges he was killed by the Western Xia in battle, while  Years before his death, Genghis Khan asked to be buried without markings, according to the customs of his tribe. After he died, his body was returned to Mongolia and presumably to his birthplace in Khentii Aimag, where many assume he is buried somewhere close to the Onon River and the Burkhan Khaldun mountain (part of the Khentii mountain range). According to legend, the funeral escort killed anyone and anything across their path to conceal where he was finally buried. The Genghis Khan Mausoleum, constructed many years after his death, is his memorial, but not his burial site.
Before Genghis Khan died, he assigned √Ėgedei Khan as his successor. Genghis Khan left behind an army of more than 129,000 men; 28,000 were given to his various brothers and his sons. Tolui, his youngest son, inherited more than 100,000 men. This force contained the bulk of the elite Mongolian
Years before his death, Genghis Khan asked to be buried without markings, according to the customs of his tribe. After he died, his body was returned to Mongolia and presumably to his birthplace in Khentii Aimag, where many assume he is buried somewhere close to the Onon River and the Burkhan Khaldun mountain (part of the Khentii mountain range). According to legend, the funeral escort killed anyone and anything across their path to conceal where he was finally buried. The Genghis Khan Mausoleum, constructed many years after his death, is his memorial, but not his burial site.
Before Genghis Khan died, he assigned √Ėgedei Khan as his successor. Genghis Khan left behind an army of more than 129,000 men; 28,000 were given to his various brothers and his sons. Tolui, his youngest son, inherited more than 100,000 men. This force contained the bulk of the elite Mongolian
 The Mongol Empire was governed by a civilian and military
The Mongol Empire was governed by a civilian and military
 Genghis Khan is credited with bringing the
Genghis Khan is credited with bringing the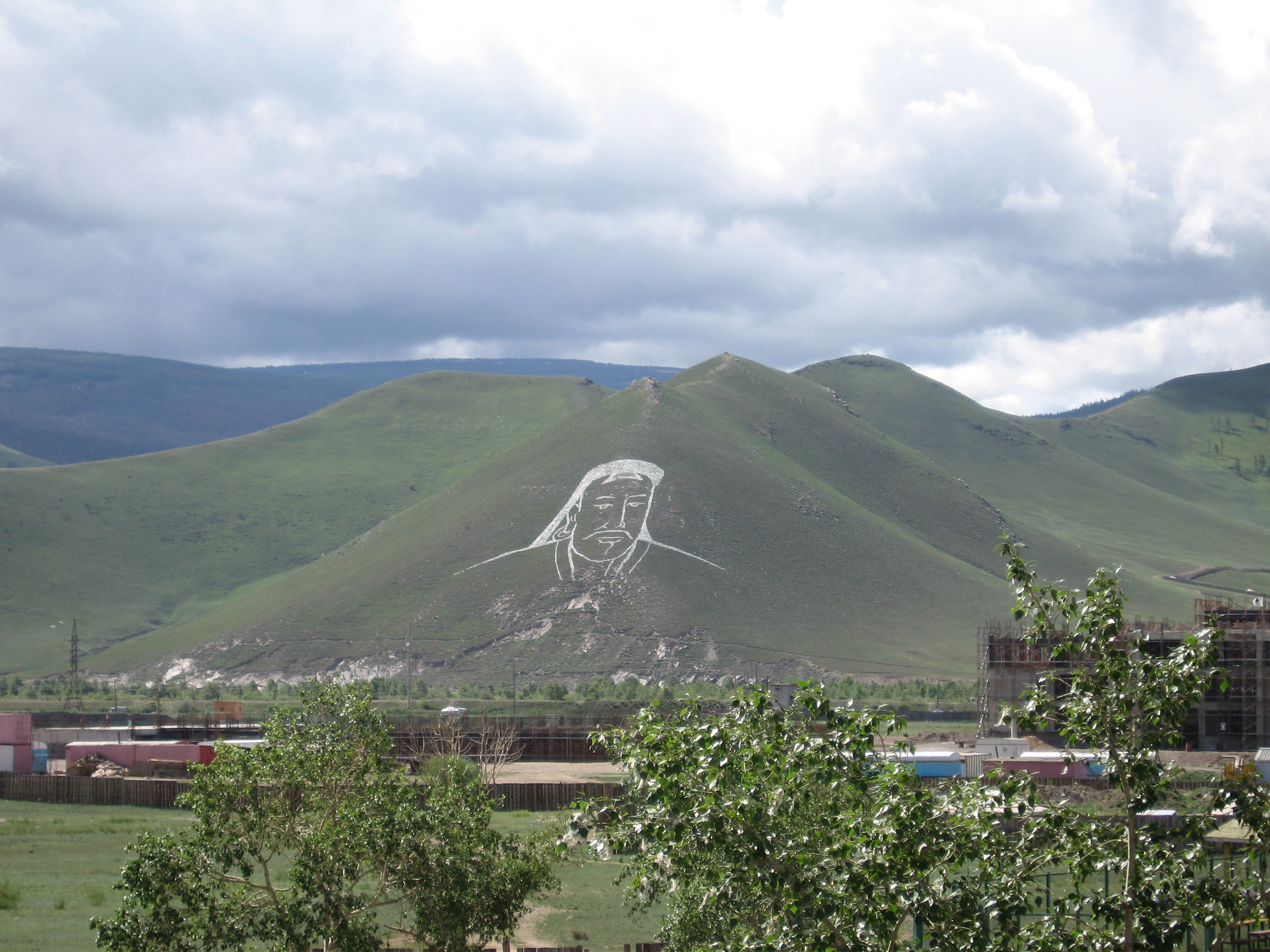  In Mongolia, Genghis Khan has meanwhile been revered for centuries by Mongols and many Turkic peoples because of his association with tribal statehood, political and military organization, and victories in war. As the principal unifying figure in Mongolian history, he remains a larger-than-life figure in Mongolian culture. He is credited with introducing the Mongolian script and creating the first written Mongolian code of law, in the form of the Yassa.
During the communist period in Mongolia, Genghis was often described by the government as a
In Mongolia, Genghis Khan has meanwhile been revered for centuries by Mongols and many Turkic peoples because of his association with tribal statehood, political and military organization, and victories in war. As the principal unifying figure in Mongolian history, he remains a larger-than-life figure in Mongolian culture. He is credited with introducing the Mongolian script and creating the first written Mongolian code of law, in the form of the Yassa.
During the communist period in Mongolia, Genghis was often described by the government as a
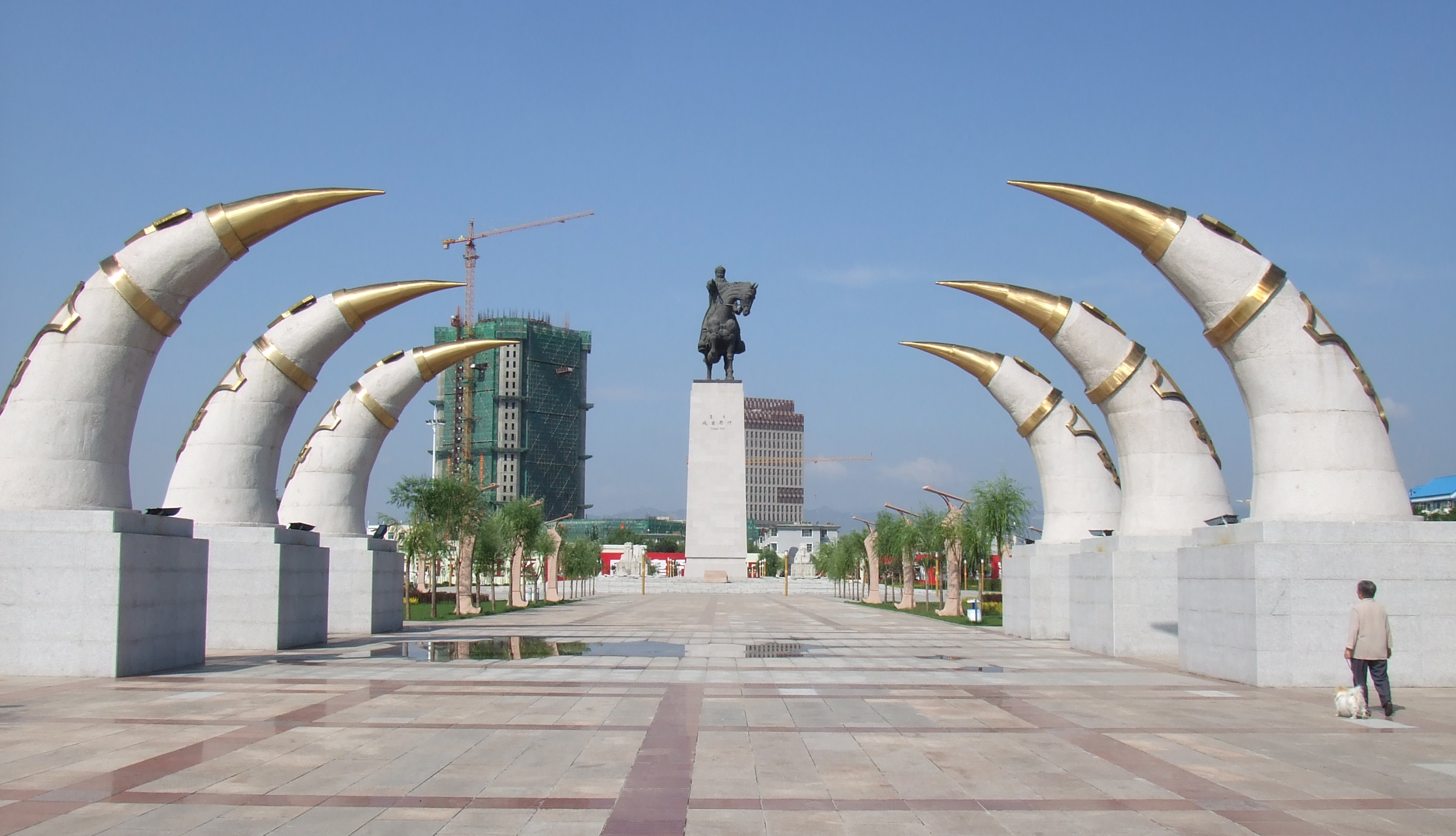 There are conflicting views of Genghis Khan in China, which suffered a drastic decline in population.William Bonner, Addison Wiggin (2006).
There are conflicting views of Genghis Khan in China, which suffered a drastic decline in population.William Bonner, Addison Wiggin (2006).
Empire of debt: the rise of an epic financial crisis
''. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 43‚Äď44. The population of north China decreased from 50 million in the 1195 census to 8.5 million in the Mongol census of 1235‚Äď36; however, many were victims of plague. In Hebei province alone, 9 out of 10 were killed by the
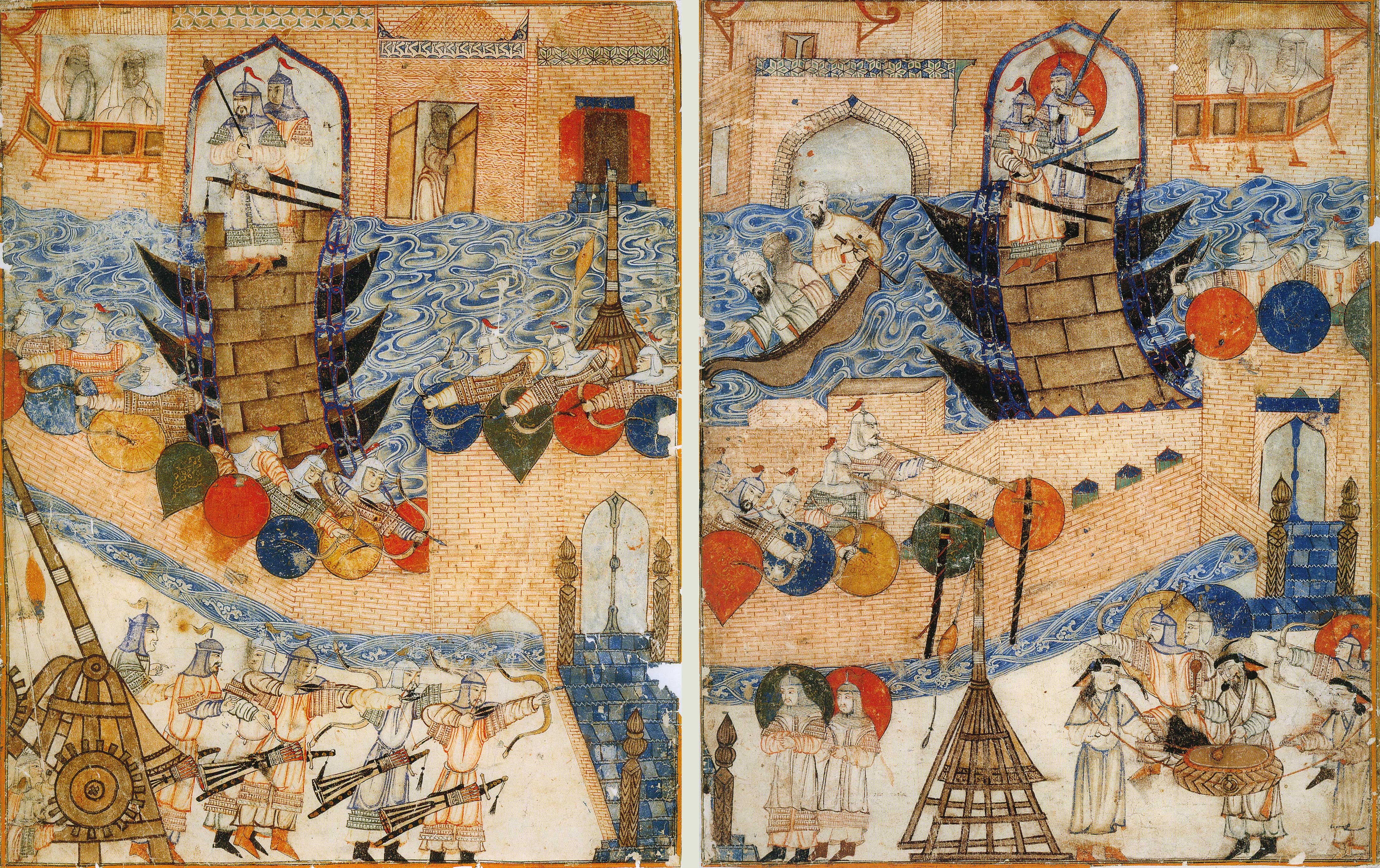 The conquests and leadership of Genghis Khan included widespread devastation and
The conquests and leadership of Genghis Khan included widespread devastation and


File:Bust of Genghis Khan in Mongolia.jpg, A bust of Genghis Khan adorns a wall in the presidential palace in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia.
File:GhinggisKhanStatue.jpg, Statue of Genghis Khan at his mausoleum, Inner Mongolia
File:GenghisKhanMonumentInHulunbuir.jpg, Monument in
Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr /> Mongol script:
''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan'' , birth_name = Tem√ľjin , successor = Tolui (as regent)
√Ėgedei Khan , spouse = , issue = , house =
Borjigin
A Borjigin, ; ; russian: –Ď–ĺ—Ä–ī–∂–ł–≥–ł–Ĺ, BordŇĺigin; English plural: Borjigins or Borjigid (from Middle Mongolian);''Histoire des campagnes de Gengis Khan'', p. 119. Manchu plural: is a member of the Mongol sub-clan, which started with Bo ...
, dynasty = Genghisid
, regnal name = Genghis Khan ()
, temple name = Taizu ()
, posthumous name = Emperor Fatian Qiyun Shengwu ()
, father = Yes√ľgei
, mother = Hoelun
, religion = Tengrism
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Khentii Mountains, Khamag Mongol
, death_date = (aged 64‚Äď65)
, death_place = Xingqing, Western Xia
, burial_place = Unknown(presumptively
Ikh Khorig
The Ikh Khorig, or Great Taboo, is a area in the Khentii Aimag (province) of Mongolia, believed by some to be the location of Genghis Khan's grave. It has been carefully guarded for most of its history, and it is only since the late 1980s that t ...
, Burkhan Khaldun, Khentii Province)
Genghis Khan (born Tem√ľjin; ; xng, Tem√ľjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin ‚Äď August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan ( Emperor) of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death. He came to power by uniting many of the nomadic tribe
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the pop ...
s of the Mongol steppe
The Mongols ( mn, –ú–ĺ–Ĺ–≥–ĺ–Ľ—á—É—É–ī, , , ; ; russian: –ú–ĺ–Ĺ–≥–ĺ–Ľ—č) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
and being proclaimed the universal ruler of the Mongols, or ''Genghis Khan''. With the tribes of Northeast Asia largely under his control, he set in motion the Mongol invasions, which ultimately witnessed the conquest of much of Eurasia, and incursions by Mongol raiding parties as far west as Legnica
Legnica (Polish: ; german: Liegnitz, szl, Lignica, cz, Lehnice, la, Lignitium) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River (left tributary of the Oder) and the Czarna Woda (Kaczawa), Czarna Woda ...
in western Poland
Poland ( pl, Polska) is a country that extends across the North European Plain from the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south to the sandy beaches of the Baltic Sea in the north. Poland is the fifth-most populous country of the Europe ...
and as far south as Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip Lebanon
* Ghazzeh, a village in ...
. He launched campaigns against the Qara Khitai, Khwarezmia, the Western Xia and Jin dynasty during his life, and his generals raided into medieval Georgia
The nation of Georgia ( ka, ŠÉ°ŠÉźŠÉ•ŠÉźŠÉ†ŠÉóŠÉēŠÉĒŠÉöŠÉĚ ''sakartvelo'') was first unified as a kingdom under the Bagrationi dynasty by the King Bagrat III of Georgia in the early 11th century, arising from a number of predecessor states of ...
, Circassia, the Kievan Rus', and Volga Bulgaria.
His exceptional military successes made Genghis Khan one of the most important conquerors of all time, and by the end of the Great Khan's life, the Mongol Empire occupied a substantial portion of Central Asia and present-day China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Genghis Khan and his story of conquest have a fearsome reputation in local histories.Ian Jeffries (2007). Mongolia: a guide to economic and political developments
.'' Taylor & Francis. pp. 5‚Äď7. . Many medieval chroniclers and modern historians describe Genghis Khan's conquests as wholesale destruction on an unprecedented scale that led to drastic population declines in some regions as a result of both mass exterminations and
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
. Estimates of the number of people who died as a consequence of Genghis Khan's military campaigns range from about four million in the most conservative estimates to up to sixty million in the most sweeping historical accounts. On the other hand, Genghis Khan was also portrayed positively by medieval European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
authors, out of respect for the great spread of culture, technology and ideas along the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
under the Mongol Empire.
Beyond his military successes, Genghis Khan's civil achievements included the establishment of Mongol law and the adoption of the Uyghur script as a writing system across his vast territories. He also practiced meritocracy
Meritocracy (''merit'', from Latin , and ''-cracy'', from Ancient Greek 'strength, power') is the notion of a political system in which economic goods and/or political power are vested in individual people based on talent, effort, and achiev ...
and religious tolerance. Present-day Mongolians regard him as the founding father of Mongolia for unifying the nomadic tribes of Northeast Asia. By bringing the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
under one cohesive political environment, he also considerably eased communication and trade between Northeast Asia, Muslim
Muslims ( ar, ōßŔĄŔÖō≥ŔĄŔÖŔąŔÜ, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
Southwest Asia, and Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christ√≥s'' (őßŌĀőĻ ...
Europe, boosting global commerce and expanding the cultural horizons of all the Eurasian civilizations of the day.
Names and titles
According to '' The Secret History of the Mongols'', Genghis Khan's birth name ''Tem√ľjin'' () came from the Tatar chief Tem√ľjin-√ľge whom his father had just captured. The name Tem√ľjin is also equated with the Turco-Mongol ''tem√ľrńći(n)'', " blacksmith", and there existed a tradition that viewed Genghis Khan as a smith, according to Paul Pelliot, which, though unfounded, was well established by the middle of the 13th century. ''Genghis Khan'' is an honorary title meaning "universal ruler" that represents an aggrandization of the pre-existing title of ''Khan'' that is used to denote a clan chief in Mongolian. The appellation of "Genghis" to the term is thought to derive from theTurkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
word "''tengiz''", meaning sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
, making the honorary title literally "oceanic ruler", but understood more broadly as a metaphor for the universality or totality of Tem√ľjin's rule from a Mongol perspective.–ß–ė–Ě–ď–ė–°–•–źŐĀ–Ě‚ÄĒ Big Russian Encyclopedia, 2010 When
Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 ‚Äď 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of th ...
established the Yuan dynasty in 1271, he had his grandfather Genghis Khan placed in official records and accorded him the temple name ''Taizu'' () and the posthumous name ''Emperor Shengwu'' (). Genghis Khan is thus also referred to as ''Yuan Taizu'' (Emperor Taizu of Yuan; ) in Chinese historiography
Chinese historiography is the study of the techniques and sources used by historians to develop the recorded history of China.
Overview of Chinese history
The recording of events in Chinese history dates back to the Shang dynasty (c. 1600‚Äď1046 ...
. K√ľl√ľg Khan later expanded Genghis Khan's title to ''Emperor Fatian Qiyun Shengwu'' ().
Early life
Lineage and birth

 Tem√ľjin was born the first son of Hoelun, second wife of his father Yes√ľgei, who was the chief of the
Tem√ľjin was born the first son of Hoelun, second wife of his father Yes√ľgei, who was the chief of the Borjigin
A Borjigin, ; ; russian: –Ď–ĺ—Ä–ī–∂–ł–≥–ł–Ĺ, BordŇĺigin; English plural: Borjigins or Borjigid (from Middle Mongolian);''Histoire des campagnes de Gengis Khan'', p. 119. Manchu plural: is a member of the Mongol sub-clan, which started with Bo ...
clan in the nomadic Khamag Mongol confederation, nephew to Ambaghai and Hotula Khan, and an ally of Toghrul of the Keraite tribe. Tem√ľjin was related on his father's side to Khabul Khan, Ambaghai, and Hotula Khan, who had headed the Khamag Mongol confederation and were descendants of Bodonchar Munkhag
Bodonchar Munkhag (Mongol: –Ď–ĺ–ī–ĺ–Ĺ—á–į—Ä –ú”©–Ĺ—Ö, ; died 10th Century CE.) was a renowned Mongol warlord and a direct ancestor of Genghis Khan as well as of the Barlas Mongols, the tribe of the Central Asian warlord Timur.
According to the ...
( 900), while his mother Hoelun was from the Olkhunut
Olkhunut ( Mongolian: –ě–Ľ—Ö—É–Ĺ–ĺ—É–ī, –ě–Ľ—Ö–ĺ–Ĺ—É—É–ī, –ě–Ľ–≥–ĺ–Ĺ—É—É–ī, Olhonuud; ) was the clan of Hoelun, the mother of Genghis Khan. They helped Genghis to defeat the Naimans. The Olkhunut people were very closely related to the Hongirad t ...
sub-lineage of the Khongirad
The Khongirad ( Mongolian: Š†¨Š†£Š†©Š†≠Š†ĘŠ†∑Š††Š†≥; –•–ĺ–Ĺ–≥–ł—Ä–į–ī; Khonghirad; ), also known as Qongirat (QoŇčńüńĪrat/“ö–ĺ“£“ď—č—Ä–į—ā), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Q ...
tribe. Tem√ľjin's noble background made it easier for him, later in life, to solicit help from and eventually consolidate the other Mongol tribes.
There is considerable uncertainty surrounding both the date and location of Tem√ľjin's birth, with historical accounts assigning dates of birth ranging from 1155 to 1182 and a wide variety of possible birth locations. The Arab historian Rashid al-Din asserted that Tem√ľjin was born in 1155, while the '' History of Yuan'' records his year of birth as 1162 and Tibetan sources implausibly present 1182 as the correct date. Modern historical studies have largely attested the 1162 date presented by the Chinese history as the most realistic, given the significant problems associated with how either the 1155 or 1182 dates would reflect on other event's in Tem√ľjin's timeline. Accepting a birth in 1155, for instance, would render Tem√ľjin a father at the age of 30 and would imply that he personally commanded the expedition against the Tanguts
The Tangut people ( Tangut: , ''mj…® njaŐĪ'' or , ''mji dzjwo''; ; ; mn, –Ę–į–Ĺ–≥—É–ī) were a Tibeto-Burman tribal union that founded and inhabited the Western Xia dynasty. The group initially lived under Tuyuhun authority, but later submitted t ...
at the age of 72. ''The Secret History of the Mongols'' relates that Tem√ľjin was an infant during the attack by the Merkits, when a birth date of 1155 would have made him 18 years old. The 1162 date has meanwhile been attested by various sources, including a 1992 study of the Mongol calendar commissioned by UNESCO that suggested the specific date of 1 May 1162.
The location of Tem√ľjin's birth largely shrouded in mystery, with a wide range of locations proposed, many in the vicinity of the mountain Burkhan Khaldun. One such location is Del√ľ√ľn Boldog
Dul√ľ√ľn-Boldog, or Delun-Boldog, is a tourist attraction located in Dadal, Khentii, in Onon-Balj National Park, Mongolia. It is one of several locations that is considered to be the birthplace of Genghis Khan (Tem√ľjin), in the year 1162 ...
, which lies near the rivers Onon and Kherlen
Kherlen River (also known as Kern or Ker√ľlen; ; ) is a 1,254 km river in Mongolia and China.
Course
The river originates in the south slopes of the Khentii mountains, near the Burkhan Khaldun mountain in the Khan Khentii Strictly Protecte ...
.
Tribal upbringing
Tem√ľjin grew up with three brothers, Qasar, Hachiun, and Tem√ľge; one sister,Tem√ľlen
Tem√ľl√ľn (‚Äď?) was the youngest full sibling and only sister of Genghis Khan (born Tem√ľjin), the famed founder and Khagan, Great Khan of the Mongol Empire. Her parents were Yesugei, Yes√ľgei, chief of the Borjigin clan in the Khamag Mongol conf ...
; and two half-brothers, Behter and Belgutei
Belgutei ( ‚Äď ) was the son of Yesugei and Sochigel and half-brother to Genghis Khan. He also became general to Genghis Khan. Belgutei was considered a wise counselor and skilled diplomat, and was often used as a messenger by Genghis Khan. With ...
. As was common to nomads in Mongolia, Tem√ľjin's early life was marked by difficulties.
At age nine, his father arranged a marriage for him and delivered him to the family of his future wife Börte of the tribe Khongirad
The Khongirad ( Mongolian: Š†¨Š†£Š†©Š†≠Š†ĘŠ†∑Š††Š†≥; –•–ĺ–Ĺ–≥–ł—Ä–į–ī; Khonghirad; ), also known as Qongirat (QoŇčńüńĪrat/“ö–ĺ“£“ď—č—Ä–į—ā), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Q ...
. Tem√ľjin was to live there serving the head of the household Dai Setsen until the marriageable age
Marriageable age (or marriage age) is the general age, as a legal age or as the minimum age subject to parental, religious or other forms of social approval, at which a person is legitimately allowed for marriage. Age and other prerequisites to ...
of 12. While heading home, his father ran into the neighboring Tatars, who had long been Mongol enemies, and they offered his father food under the guise of hospitality, but instead poisoned him. Upon learning this, Tem√ľjin returned home to claim his father's position as chief, but the tribe refused him and abandoned the family, leaving it without protection.
For the next several years, the family lived in poverty, surviving mostly on wild fruits, ox carcasses, marmots, and other small game killed by Tem√ľjin and his brothers. During this time, Tem√ľjin's mother, Hoelun, taught him about Mongol politics, including the lack of unity between the different clans and the need for arranged marriages to solidify temporary alliances, and strong alliances to ultimately ensure the stability of Mongolia. Indeed, he was later successful, in part, because of his mother's role as a warrior in battle.
Over time, Tem√ľjin's older half-brother Behter began to exercise power as the eldest male in the family, creating tension in the family that boiled over during one hunting excursion by the men of the family and resulted in the death of Behter at the hands of Tem√ľjin and his brother Qasar.
Later, in a raid around 1177, Tem√ľjin was captured by his father's former allies, the Tayichi'ud, enslaved, and, reportedly humiliated by being shacked in a cangue
A cangue () or tcha is a device that was used for public humiliation and corporal punishment in East AsiaJamyang NorbuFrom Darkness to Dawn, site ''Phayul.com'', May 19, 2009. and some other parts of Southeast Asia until the early years of the t ...
(a form of portable stocks). With the help of a sympathetic guard, he escaped from the ger (yurt) at night by hiding in a river crevice. The escape earned Tem√ľjin a reputation. Soon, Jelme and Bo'orchu Bo'orchu ( mn, –Ď–ĺ–ĺ—Ä—á–ł, ''Boorchi'') was one of the first and most loyal of Genghis Khan's friends and allies. He first met Genghis Khan as a boy. At that time, Genghis Khan (then Temujin) was looking for his stolen horses. Bo'orchu helped to ...
joined forces with him, and they and the guard's son Chilaun eventually became generals of Genghis Khan.
Wives and concubines
As was common for powerful Mongol men, Tem√ľjin had many wives and concubines. These women were often queens or princesses that were taken captive from the territories he conquered or gifted to him by allies, vassals, or other tribal acquaintances. His principal or most famous wives and concubines included: B√∂rte, Yesugen,Yesui
Yesui was one of the wives of Genghis Khan, the founder of the Mongol Empire. She was of Tatar ancestry.
Like the other wives of Genghis Khan, she had her own ''ordo'', or court and to her was assigned the Tuul River. Her sister Yesugen was al ...
, Khulan Khatun
Khulan ( mn, Š†¨Š†§Š†ĮŠ††Š†®, Ppp=qulan; ; ‚Äď ) was an empress consort of Genghis Khan and head of the second Court of Genghis Khan. Her status in the Mongol Empire was second only to Grand Empress B√∂rte.
Biography
Khulan was a daughter of ...
, Möge Khatun, Juerbiesu, and Ibaqa Beki.
He gave several of his high-status wives their own ''ordos'' or camps to live in and manage. Each camp also contained junior wives, concubines, and children. It was the job of the Kheshig (Mongol imperial guard) to protect the yurts of Tem√ľjin's wives. The guards had to pay particular attention to the individual yurt and camp in which Tem√ľjin slept, which could change every night as he visited different wives. When he set out on his military conquests, he usually took one wife with him and left the rest of his wives and concubines to manage the empire in his absence.
Uniting the Mongol confederations, 1184‚Äď1206
 In the early 12th century, the Central Asian plateau north of China was divided into several prominent tribal confederations, including Naimans, Merkits, Tatars, Khamag Mongols, and
In the early 12th century, the Central Asian plateau north of China was divided into several prominent tribal confederations, including Naimans, Merkits, Tatars, Khamag Mongols, and Keraites
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid''; ; ) were one of the five dominant Mongol or Turkic tribal confederations (khanates) in the Altai-Sayan region during the 12th century. They had converted to the Church of the East (Nestorianism) i ...
, that were often unfriendly towards each other, as evidenced by random raids, revenge attacks, and plundering
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
.
Early attempts at power
Tem√ľjin began his ascent to power by offering himself as an ally (or, according to other sources, a vassal) to his father's ''anda'' (sworn brother or blood brother) Toghrul, who wasKhan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
of the Keraites
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid''; ; ) were one of the five dominant Mongol or Turkic tribal confederations (khanates) in the Altai-Sayan region during the 12th century. They had converted to the Church of the East (Nestorianism) i ...
. This relationship was first reinforced when B√∂rte was kidnapped by Merkits in around 1184. To win her back, Tem√ľjin called on the support of Toghrul, who offered 20,000 of his Keraite warriors and suggested that Tem√ľjin involve his childhood friend Jamukha
Jamukha ( mn, –Ė–į–ľ—É—Ö–į; ) was a Mongol military and political leader and the chief rival to Tem√ľjin (later Genghis Khan) in the unification of the Mongol tribes.
Biography
Jamukha was born in the Jadaran, a sub-tribe of the Khamag Mongol co ...
, who was Khan of his own tribe, the Jadaran.
Rift with Jamukha and defeat
AsJamukha
Jamukha ( mn, –Ė–į–ľ—É—Ö–į; ) was a Mongol military and political leader and the chief rival to Tem√ľjin (later Genghis Khan) in the unification of the Mongol tribes.
Biography
Jamukha was born in the Jadaran, a sub-tribe of the Khamag Mongol co ...
and Tem√ľjin drifted apart in their friendship, each began consolidating power and they became rivals. Jamukha supported the traditional Mongolian aristocracy, while Tem√ľjin followed a meritocratic method, and attracted a broader range and lower class of followers. Following his earlier defeat of the Merkits, and a proclamation by the shaman Kokochu that the Eternal Blue Sky had set aside the world for Tem√ľjin, Tem√ľjin began rising to power. In 1186, Tem√ľjin was elected khan of the Mongols. Threatened by this rise, Jamukha attacked Temujin in 1187 with an army of 30,000 troops. Tem√ľjin gathered his followers to defend against the attack, but was decisively beaten in the Battle of Dalan Balzhut
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
. However, Jamukha horrified and alienated potential followers by boiling 70 young male captives alive in cauldrons. Toghrul, as Tem√ľjin's patron, was exiled to the Qara Khitai. The life of Tem√ľjin for the next 10 years is unclear, as historical records are mostly silent on that period.
Return to power
Around the year 1197, the Jin initiated an attack against their formal vassal, the Tatars, with help from theKeraites
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid''; ; ) were one of the five dominant Mongol or Turkic tribal confederations (khanates) in the Altai-Sayan region during the 12th century. They had converted to the Church of the East (Nestorianism) i ...
and Mongols. Tem√ľjin commanded part of this attack, and after victory, he and Toghrul were restored by the Jin to positions of power. The Jin bestowed Toghrul with the honorable title of Ong Khan, and Tem√ľjin with a lesser title of ''j'aut quri''.
Around 1200, the main rivals of the Mongol confederation (traditionally the "Mongols") were the Naimans to the west, the Merkits to the north, the Tanguts
The Tangut people ( Tangut: , ''mj…® njaŐĪ'' or , ''mji dzjwo''; ; ; mn, –Ę–į–Ĺ–≥—É–ī) were a Tibeto-Burman tribal union that founded and inhabited the Western Xia dynasty. The group initially lived under Tuyuhun authority, but later submitted t ...
to the south, and the Jin to the east.
 In his rule and his conquest of rival tribes, Tem√ľjin broke with Mongol tradition in a few crucial ways. He delegated authority based on merit and loyalty, rather than family ties. As an incentive for absolute obedience and the Yassa code of law, Tem√ľjin promised civilians and soldiers wealth from future war spoils. When he defeated rival tribes, he did not drive away their soldiers and abandon their civilians. Instead, he took the conquered tribe under his protection and integrated its members into his own tribe. He would even have his mother adopt orphans from the conquered tribe, bringing them into his family. These political innovations inspired great loyalty among the conquered people, making Tem√ľjin stronger with each victory.
In his rule and his conquest of rival tribes, Tem√ľjin broke with Mongol tradition in a few crucial ways. He delegated authority based on merit and loyalty, rather than family ties. As an incentive for absolute obedience and the Yassa code of law, Tem√ľjin promised civilians and soldiers wealth from future war spoils. When he defeated rival tribes, he did not drive away their soldiers and abandon their civilians. Instead, he took the conquered tribe under his protection and integrated its members into his own tribe. He would even have his mother adopt orphans from the conquered tribe, bringing them into his family. These political innovations inspired great loyalty among the conquered people, making Tem√ľjin stronger with each victory.
Rift with Toghrul
Senggum, son of Toghrul (Wang Khan), envied Tem√ľjin's growing power and affinity with his father. He allegedly planned to assassinate Tem√ľjin. Although Toghrul was allegedly saved on multiple occasions by Tem√ľjin, he gave in to his son and became uncooperative with Tem√ľjin. Tem√ľjin learned of Senggum's intentions and eventually defeated him and his loyalists. One of the later ruptures between Tem√ľjin and Toghrul was Toghrul's refusal to give his daughter in marriage to Jochi, Tem√ľjin's first son. This was disrespectful in Mongolian culture and led to a war. Toghrul allied with
One of the later ruptures between Tem√ľjin and Toghrul was Toghrul's refusal to give his daughter in marriage to Jochi, Tem√ľjin's first son. This was disrespectful in Mongolian culture and led to a war. Toghrul allied with Jamukha
Jamukha ( mn, –Ė–į–ľ—É—Ö–į; ) was a Mongol military and political leader and the chief rival to Tem√ľjin (later Genghis Khan) in the unification of the Mongol tribes.
Biography
Jamukha was born in the Jadaran, a sub-tribe of the Khamag Mongol co ...
, who already opposed Tem√ľjin's forces. However, the dispute between Toghrul and Jamukha, plus the desertion of a number of their allies to Tem√ľjin, led to Toghrul's defeat. Jamukha escaped during the conflict. This defeat was a catalyst for the fall and eventual dissolution of the Keraite tribe.
After conquering his way steadily through the Alchi Tatars, Keraites, and Uhaz Merkits and acquiring at least one wife each time, Tem√ľjin turned to the next threat on the steppe, the Turkic Naimans under the leadership of Tayang Khan with whom Jamukha and his followers took refuge. The Naimans did not surrender, although enough sectors again voluntarily sided with Tem√ľjin.
In 1201, a Khuruldai elected Jamukha
Jamukha ( mn, –Ė–į–ľ—É—Ö–į; ) was a Mongol military and political leader and the chief rival to Tem√ľjin (later Genghis Khan) in the unification of the Mongol tribes.
Biography
Jamukha was born in the Jadaran, a sub-tribe of the Khamag Mongol co ...
as G√ľr Khan, "universal ruler", a title used by the rulers of the Qara Khitai. Jamukha's assumption of this title was the final breach with Tem√ľjin, and Jamukha formed a coalition of tribes to oppose him. Before the conflict, several generals abandoned Jamukha, including Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''S√ľb√ľg√§t√§i'' or ''S√ľb√ľ'√§t√§i''; Modern Mongolian: –°“Į–Ī—ć—ć–ī—ć–Ļ, ''S√ľbeedei''. ; ; c. 1175‚Äď1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and √Ėgedei Khan. He directed m ...
, Jelme's well-known younger brother. After several battles, Jamukha was turned over to Tem√ľjin by his own men in 1205.
According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', Tem√ľjin again offered his friendship to Jamukha
Jamukha ( mn, –Ė–į–ľ—É—Ö–į; ) was a Mongol military and political leader and the chief rival to Tem√ľjin (later Genghis Khan) in the unification of the Mongol tribes.
Biography
Jamukha was born in the Jadaran, a sub-tribe of the Khamag Mongol co ...
. Tem√ľjin had killed the men who betrayed Jamukha, stating that he did not want disloyal men in his army. Jamukha refused the offer, saying that there can only be one sun in the sky, and he asked for a noble death. The custom was to die without spilling blood, specifically by having one's back broken. Jamukha requested this form of death, although he was known to have boiled his opponents' generals alive.
Sole ruler of the Mongol plains

 The part of the Merkit clan that sided with the Naimans were defeated by
The part of the Merkit clan that sided with the Naimans were defeated by Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''S√ľb√ľg√§t√§i'' or ''S√ľb√ľ'√§t√§i''; Modern Mongolian: –°“Į–Ī—ć—ć–ī—ć–Ļ, ''S√ľbeedei''. ; ; c. 1175‚Äď1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and √Ėgedei Khan. He directed m ...
, who was by then a member of Tem√ľjin's personal guard and later became one of Tem√ľjin's most successful commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain.
...
s. The Naimans' defeat left Tem√ľjin as the sole ruler of the Mongol steppe
The Mongols ( mn, –ú–ĺ–Ĺ–≥–ĺ–Ľ—á—É—É–ī, , , ; ; russian: –ú–ĺ–Ĺ–≥–ĺ–Ľ—č) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
‚Äď all the prominent confederations fell or united under his Mongol confederation.
Accounts of Tem√ľjin's life are marked by claims of a series of betrayals and conspiracies. These include rifts with his early allies such as Jamukha (who also wanted to be a ruler of Mongol tribes) and Wang Khan (his and his father's ally), his son Jochi, and problems with the most important shaman, who allegedly tried to drive a wedge between him and his loyal brother Khasar. His military strategies
Military strategy is a set of ideas implemented by military organizations to pursue desired strategic goals. Derived from the Greek word '' strategos'', the term strategy, when it appeared in use during the 18th century, was seen in its narrow s ...
showed a deep interest in gathering intelligence and understanding the motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-dire ...
s of his rivals, exemplified by his extensive spy network and Yam
Yam or YAM may refer to:
Plants and foods
*Yam (vegetable), common name for members of ''Dioscorea''
* Taro, known in Malaysia and Singapore as yam
* Sweet potato, specifically its orange-fleshed cultivars, often referred to as yams in North Amer ...
route systems. He seemed to be a quick student, adopting new technologies and ideas that he encountered, such as siege warfare from the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
. He was also ruthless, demonstrated by his tactic of measuring against the linchpin
Measuring against the linchpin was a method of determining which enemy civilians would be beheaded, used by the Mongols and other tribes that lived in the Mongolian plateau.
Genghis Khan used this method against Jamukha's coalition of tribes in 1 ...
, used against the tribes led by Jamukha.
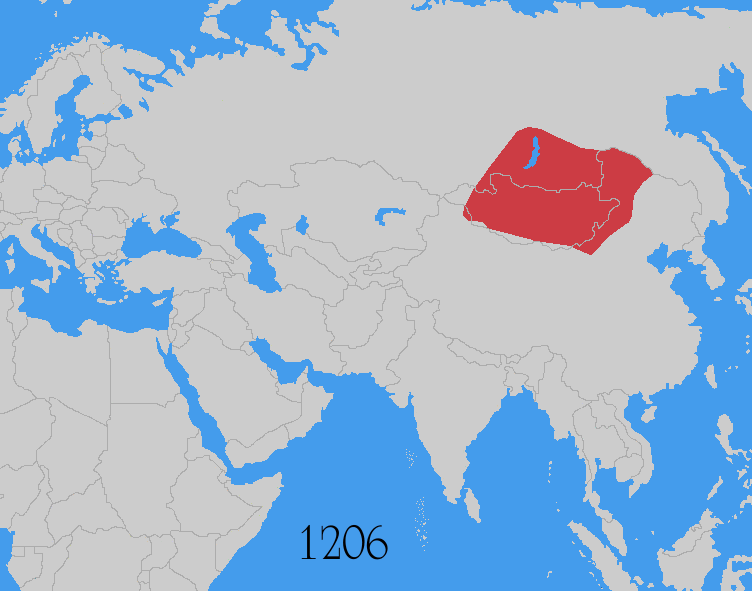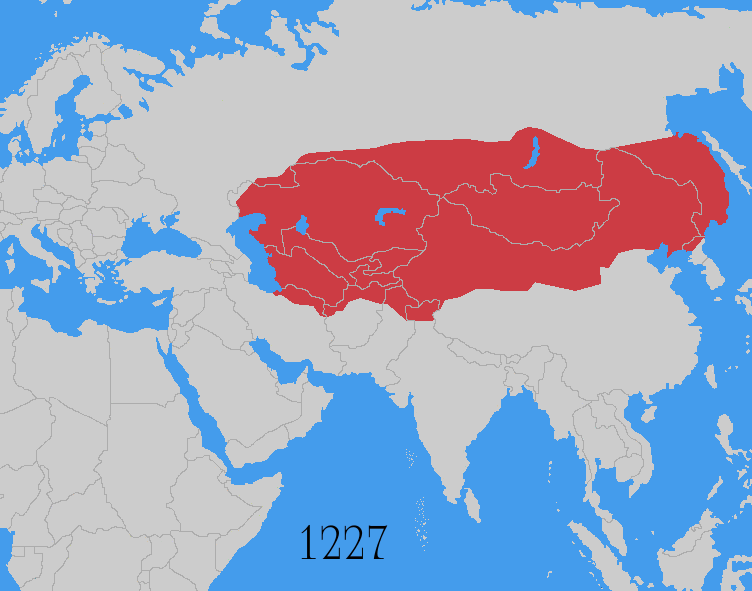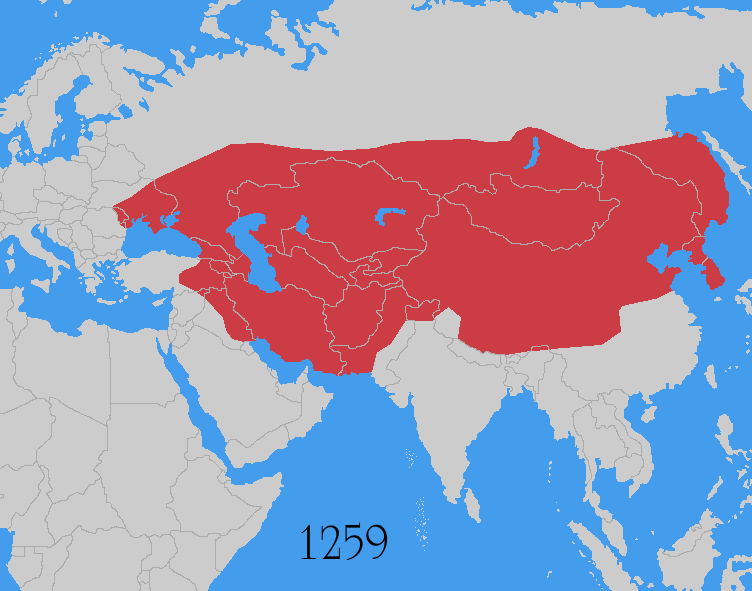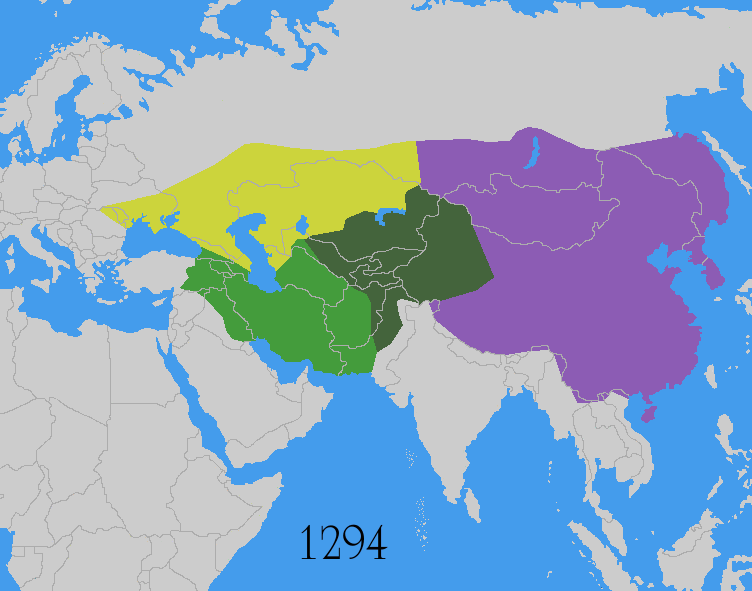
As a result, by 1206, Tem√ľjin had managed to unite or subdue the Merkits, Naimans, Mongols, Keraites, Tatars, Uyghurs, and other disparate smaller tribes under his rule. This was a monumental feat. It resulted in peace between previously warring tribes, and a single political and military force. The union became known as the Mongols. At a '' Khuruldai'', a council of Mongol chiefs, Tem√ľjin was acknowledged as Khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
of the consolidated tribes and took the new title "Genghis Khan". The title Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, ūźįīūźįćūźį£ ), or , tr, Kańüan or ; ug, ŔāōßōļōßŔÜ, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, ōģōßŔāōßŔÜ ''KhńĀqńĀn'', alternatively spelled Kańüan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
was conferred posthumously by his son and successor √Ėgedei who took the title for himself (as he was also to be posthumously declared the founder of the Yuan dynasty).
According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', the chieftains of the conquered tribes pledged to Genghis Khan by proclaiming:"We will make you Khan; you shall ride at our head, against our foes. We will throw ourselves like lightning on your enemies. We will bring you their finest women and girls, their rich tents like palaces."
Military campaigns, 1207‚Äď1227
Western Xia dynasty
During the 1206 political rise of Genghis Khan, the Mongol Empire and its allies shared their western borders with the Tangut Western Xia dynasty. To the east and south of the Western Xia dynasty was the militarily superior Jin dynasty, founded by theManchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616‚Äď1636) and ...
rian Jurchens, who ruled northern China as well as being the traditional overlords of the Mongolian tribes for centuries.May 2012, pg. 1211
Though militarily inferior to the neighboring Jin, the Western Xia still exerted a significant influence upon the adjacent northern steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
s. Following the death of the Keraites
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid''; ; ) were one of the five dominant Mongol or Turkic tribal confederations (khanates) in the Altai-Sayan region during the 12th century. They had converted to the Church of the East (Nestorianism) i ...
leader Ong Khan to Tem√ľjin's emerging Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
in 1203, Keriat leader Nilqa Senggum led a small band of followers into Western Xia before later being expelled from Western Xia territory.

 Using his rival Nilga Senggum's temporary refuge in Western Xia as a pretext, Tem√ľjin launched a raid against the state in 1205 in the Edsin region. The next year, in 1206, Tem√ľjin was formally proclaimed Genghis Khan, ruler of all the Mongols, marking the official start of the Mongol Empire, and the same year Emperor Huanzong of the Western Xia was deposed by
Using his rival Nilga Senggum's temporary refuge in Western Xia as a pretext, Tem√ľjin launched a raid against the state in 1205 in the Edsin region. The next year, in 1206, Tem√ľjin was formally proclaimed Genghis Khan, ruler of all the Mongols, marking the official start of the Mongol Empire, and the same year Emperor Huanzong of the Western Xia was deposed by Li Anquan
Emperor Xiangzong of Western Xia (1170‚Äď1211), born Li Anquan (), was the seventh emperor of the Tangut-led Western Xia dynasty
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known ...
in a ''coup d'état''. In 1207, Genghis led another raid into Western Xia, invading the Ordos region and sacking Wuhai, the main garrison along the Yellow River, before withdrawing in 1208. Genghis then began preparing for a full-scale invasion, organizing his people, army and state to first prepare for war.
By invading Western Xia, Genghis Khan would gain a tribute-paying vassal, and also would take control of caravan routes along the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
and provide the Mongols with valuable revenue.Kohn 2007, pg. 205 Furthermore, from Western Xia he could launch raids into the even more wealthy Jin dynasty. He correctly believed that the more powerful young ruler of the Jin dynasty would not come to the aid of the Western Xia. When the Tanguts requested help from the Jin dynasty, they were refused. Despite initial difficulties in capturing Western Xia cities, Genghis Khan managed to force Emperor Renzong to submit to vassal status.
Jin dynasty
In 1211, after the conquest of Western Xia, Genghis Khan planned again to conquer the Jin dynasty. Luckily for the Mongols, Wanyan Jiujin, the field commander of the Jin army, made several tactical mistakes, including avoiding attacking the Mongols at the first opportunity using his overwhelming numerical superiority, and instead initially fortifying behind the Great wall. At the subsequent Battle of Yehuling, which the Jin commander later committed to in the hope of using the mountainous terrain to his advantage against the Mongols, the general's emissary Ming'an defected to the Mongol side and instead handed over intelligence on the movements of the Jin army, which was subsequently outmanoeuvred, resulting in hundreds of thousands of Jin casualties. So many, in fact, that decades later, when the Daoist sage Qiu Chuji was passing through this pass to meet Genghis Khan, he was stunned to still see the bones of so many people scattered in the pass. On his way back, he camped close to this pass for three days and prayed for the departed souls. In 1215, Genghis besieged the Jin capital of Zhongdu (modern-day Beijing). According toIvar Lissner
Ivar Arthur Nicolai Lissner (23 April 1909 ‚Äď 4 September 1967) was a German journalist and author, and a Nazi spy during World War II.
Early life and education
Born to a German-Jewish father, Robert Lissner, and mother Charlotte Lissner (n√ ...
, the inhabitants resorted to firing gold and silver cannon shot on the Mongols with their muzzle-loading cannons when their supply of metal for ammunition ran out. The city was captured and sacked. This forced the Jin ruler, Emperor Xuanzong, to move his capital south to Kaifeng, abandoning the northern half of his empire to the Mongols. Between 1232 and 1233, Kaifeng fell to the Mongols under the reign of Genghis's third son and successor, √Ėgedei Khan. The Jin dynasty collapsed in 1234, after the siege of Caizhou
The siege of Caizhou between 1233 and 1234 was fought between the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty and the allied forces of the Mongol Empire and Southern Song dynasty. It was the last major battle in the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty.
Backgroun ...
.
Qara Khitai
Kuchlug, the deposedKhan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
of the Naiman confederation that Genghis Khan defeated and folded into his Mongol Empire, fled west and usurped the khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
Mong ...
of Qara Khitai (also known as the Western Liao, as it was originally established as remnants of the Liao dynasty). Genghis Khan decided to conquer the Qara Khitai and defeat Kuchlug, possibly to take him out of power. By this time the Mongol army was exhausted from ten years of continuous campaigning in China against the Western Xia and Jin dynasty. Therefore, Genghis sent only two ''tumen'' (20,000 soldiers) against Kuchlug, under his younger general, Jebe, known as "The Arrow".
With such a small force, the invading Mongols were forced to change strategies and resort to inciting internal revolt among Kuchlug's supporters, leaving the Qara Khitai more vulnerable to Mongol conquest. As a result, Kuchlug's army was defeated west of Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, ŔāŘēōīŔāŘēōĪ, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=ŚĖÄšĽÄ) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
. Kuchlug fled again, but was soon hunted down by Jebe's army and executed. By 1218, as a result of the defeat of Qara Khitai, the Mongol Empire and its control extended as far west as Lake Balkhash, which bordered Khwarazmia, a Muslim state that reached the Caspian Sea to the west and Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea to the south.
Khwarazmian Empire
 In the early 13th century, the Khwarazmian dynasty was governed by Shah Ala ad-Din Muhammad. Genghis Khan saw the potential advantage in Khwarazmia as a commercial trading partner using the
In the early 13th century, the Khwarazmian dynasty was governed by Shah Ala ad-Din Muhammad. Genghis Khan saw the potential advantage in Khwarazmia as a commercial trading partner using the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
, and he initially sent a 500-man caravan
Caravan or caravans may refer to:
Transport and travel
*Caravan (travellers), a group of travellers journeying together
**Caravanserai, a place where a caravan could stop
*Camel train, a convoy using camels as pack animals
*Convoy, a group of veh ...
to establish official trade ties with the empire. Genghis Khan and his family and commanders invested
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing i ...
in the caravan gold, silver, silk, various kinds of textiles and fabrics and pelts to trade with the Muslim traders in the Khwarazmian lands. However, Inalchuq Inalchuq (or Inalchuk) (died 1219) was governor of Otrar in the Khwarezmian Empire
The Khwarazmian or Khwarezmian Empire) or the Khwarazmshahs ( fa, ōģŔąōßōĪō≤ŔÖōīōßŔáŘĆōßŔÜ, KhwńĀrazmshńĀhiyńĀn) () was a Turko-Persian Sunni Muslim empire t ...
, the governor of the Khwarazmian city of Otrar, attacked the caravan, claiming that the caravan contained spies and therefore was a conspiracy against Khwarazmia. The situation became further complicated because the governor later refused to make repayments for the looting of the caravans and hand over the perpetrators. Genghis Khan then sent a second group of three ambassadors (two Mongols and a Muslim) to meet the Shah himself, instead of the governor Inalchuq. The Shah had all the men shaved and the Muslim beheaded and sent his head back with the two remaining ambassadors. Outraged, Genghis Khan planned one of his largest invasion campaigns by organizing together around 100,000 soldiers (10 tumens
Tumen, or t√ľmen ("unit of ten thousand";
Old Turkic: t√ľm√§n; mn, –Ę“Į–ľ—ć–Ĺ, ''t√ľmen''; tr , t√ľmen; hu , t√∂m√©ny), was a decimal unit of measurement used by the Turkic and Mongol peoples to quantify and organize their societies in group ...
), his most capable generals and some of his sons. He left a commander and number of troops in China, designated his successors to be his family members and likely appointed √Ėgedei to be his immediate successor and then went out to Khwarazmia.
 The Mongol army under Genghis Khan, generals and his sons crossed the Tien Shan mountains by entering the area controlled by the Khwarazmian Empire. After compiling intelligence from many sources Genghis Khan carefully prepared his army, which was divided into three groups. His son Jochi led the first division into the northeast of Khwarazmia. The second division under Jebe marched secretly to the southeast part of Khwarazmia to form, with the first division, a pincer attack on
The Mongol army under Genghis Khan, generals and his sons crossed the Tien Shan mountains by entering the area controlled by the Khwarazmian Empire. After compiling intelligence from many sources Genghis Khan carefully prepared his army, which was divided into three groups. His son Jochi led the first division into the northeast of Khwarazmia. The second division under Jebe marched secretly to the southeast part of Khwarazmia to form, with the first division, a pincer attack on Samarkand
fa, ō≥ŔÖōĪŔāŔÜōĮ
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
. The third division under Genghis Khan and Tolui marched to the northwest and attacked Khwarazmia from that direction.
The Shah's army was split by diverse internecine feuds and by the Shah's decision to divide his army into small groups concentrated in various cities. This fragmentation was decisive in Khwarazmia's defeats, as it allowed the Mongols, although exhausted from the long journey, to immediately set about defeating small fractions of the Khwarazmian forces instead of facing a unified defense. The Mongol army quickly seized the town of Otrar, relying on superior strategy and tactics. Genghis Khan ordered the wholesale massacre of many of the civilians, enslaved the rest of the population and executed Inalchuq by pouring molten silver into his ears and eyes, as retribution for his actions.
Next, Genghis Khan besieged the city of Bukhara. Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, –Ď—É—Ö–ĺ—Ä–ĺ, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
was not heavily fortified, with just a moat and a single wall, and the citadel typical of Khwarazmian cities. The city leaders opened the gates to the Mongols, though a unit of Turkish defenders held the city's citadel for another twelve days. The survivors from the citadel were executed, artisans and craftsmen were sent back to Mongolia, young men who had not fought were drafted into the Mongolian army and the rest of the population was sent into slavery. After the surrender of Bukhara, Genghis Khan also took the unprecedented step of personally entering the city, after which he had the city's aristocrats and elites brought to the mosque, where, through interpreters, he lectured them on their misdeeds, saying: "If you had not committed great sins, God would not have sent a punishment like me upon you."
Samarkand
fa, ō≥ŔÖōĪŔāŔÜōĮ
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, which possessed significantly better fortifications and a larger garrison compared to Bukhara. To overcome the city, the Mongols engaged in intensive psychological warfare, including the use of captured Khwarazmian prisoners as body shields. After several days only a few remaining soldiers, loyal supporters of the Shah, held out in the citadel. After the fortress fell, Genghis executed every soldier that had taken arms against him. According to the Persian historian Ata-Malik Juvayni, the people of Samarkand were then ordered to evacuate and assemble in a plain outside the city, where they were killed and pyramids of severed heads raised as a symbol of victory. Similarly, Juvayni wrote that in the city Termez, to the south of Samarkand
fa, ō≥ŔÖōĪŔāŔÜōĮ
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, "all the people, both men and women, were driven out onto the plain, and divided in accordance with their usual custom, then they were all slain".
Juvayni's account of mass killings at these sites is not corroborated by modern archaeology. Instead of killing local populations, the Mongols tended to enslave the conquered and either send them to Mongolia to act as menial labor or retain them for use in the war effort. The effect was still mass depopulation. The piling of a "pyramid of severed heads" happened not at Samarkand
fa, ō≥ŔÖōĪŔāŔÜōĮ
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
but at Nishapur
Nishapur or officially Romanized as Neyshabur ( fa, ;Or also "ŔÜŘĆōīōßŔĺŔąōĪ" which is closer to its original and historic meaning though it is less commonly used by modern native Persian speakers. In Persian poetry, the name of this city is wr ...
, where Genghis Khan's son-in-law Toquchar was killed by an arrow shot from the city walls after the residents revolted. The Khan then allowed his widowed daughter, who was pregnant at the time, to decide the fate of the city, and she decreed that the entire population be killed. She also supposedly ordered that every dog, cat and any other animals in the city by slaughtered, "so that no living thing would survive the murder of her husband". The sentence was duly carried out by the Khan's youngest son Tolui.The Truth About NishapurHow Stuff Works. Retrieved April 27, 2021 According to widely circulated but unverified stories, the severed heads were then erected in separate piles for the men, women and children. Near to the end of the battle for
Samarkand
fa, ō≥ŔÖōĪŔāŔÜōĮ
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, the Shah fled rather than surrender. Genghis Khan subsequently ordered two of his generals, Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''S√ľb√ľg√§t√§i'' or ''S√ľb√ľ'√§t√§i''; Modern Mongolian: –°“Į–Ī—ć—ć–ī—ć–Ļ, ''S√ľbeedei''. ; ; c. 1175‚Äď1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and √Ėgedei Khan. He directed m ...
and Jebe, to destroy the remnants of the Khwarazmian Empire, giving them 20,000 men and two years to do this. The Shah died under mysterious circumstances on a small island in the Caspian Sea that he had retreated to with his remaining loyal forces.
Meanwhile, the wealthy trading city of Urgench was still in the hands of Khwarazmian forces. The assault on Urgench proved to be the most difficult battle of the Mongol invasion and the city fell only after the defenders put up a stout defense, fighting block for block. Mongolian casualties were higher than normal, due to the unaccustomed difficulty of adapting Mongolian tactics to city fighting.
As usual, the artisans were sent back to Mongolia, young women and children were given to the Mongol soldiers as slaves, and the rest of the population was massacred. The Persian scholar Juvayni Juvayni ( fa, ō¨ŔąŘĆŔÜŘĆ), also spelled in English as Juwayni, Juvaini, or Joveini, is a Persian last name, meaning from the city of Juvayn in Khorasan, Iran. In the historical context, it may refer to these persons:
* Al-Juwayni (c. 1028‚Äď1085) ...
states that 50,000 Mongol soldiers were given the task of executing twenty-four Urgench citizens each, which would mean that 1.2 million people were killed. These numbers are considered logistically implausible by modern scholars, but the sacking of Urgench was no doubt a bloody affair.
Georgia, Crimea, Kievan Rus and Volga Bulgaria
 After the defeat of the Khwarazmian Empire in 1220, Genghis Khan gathered his forces in Persia and Armenia to return to the Mongolian steppes. Under the suggestion of
After the defeat of the Khwarazmian Empire in 1220, Genghis Khan gathered his forces in Persia and Armenia to return to the Mongolian steppes. Under the suggestion of Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''S√ľb√ľg√§t√§i'' or ''S√ľb√ľ'√§t√§i''; Modern Mongolian: –°“Į–Ī—ć—ć–ī—ć–Ļ, ''S√ľbeedei''. ; ; c. 1175‚Äď1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and √Ėgedei Khan. He directed m ...
, the Mongol army was split into two forces. Genghis Khan led the main army on a raid through Afghanistan and northern India towards Mongolia, while another 20,000 (two tumen) contingent marched through the Caucasus and into Russia under generals Jebe and Subutai. They pushed deep into Armenia and Azerbaijan. The Mongols defeated the kingdom of Georgia, sacked the Genoese trade-fortress of Caffa in Crimea and overwintered near the Black Sea. Heading home, Subutai's forces attacked the allied forces of the Cuman‚ÄďKipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the Se ...
and the poorly coordinated 80,000 Kievan Rus' troops led by Mstislav the Bold of Halych and Mstislav III of Kiev
Mstislav Romanovich the Old ( uk, –ú—Ā—ā–ł—Ā–Ľ–į–≤ –†–ĺ–ľ–į–Ĺ–ĺ–≤–ł—á –°—ā–į—Ä–ł–Ļ; russian: –ú—Ā—ā–ł—Ā–Ľ–į–≤ –†–ĺ–ľ–į–Ĺ–ĺ–≤–ł—á –°—ā–į—Ä—č–Ļ) (died 1223) was Prince of Pskov (1179‚Äď?), Smolensk (1197‚Äď?), Belgorod (1206), Halych (?‚Äď?) and Gran ...
who went out to stop the Mongols' actions in the area. Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''S√ľb√ľg√§t√§i'' or ''S√ľb√ľ'√§t√§i''; Modern Mongolian: –°“Į–Ī—ć—ć–ī—ć–Ļ, ''S√ľbeedei''. ; ; c. 1175‚Äď1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and √Ėgedei Khan. He directed m ...
sent emissaries to the Slavic princes calling for a separate peace, but the emissaries were executed. At the Battle of Kalka River in 1223, Subutai's forces defeated the larger Kievan force. They may have been defeated by the neighbouring Volga Bulgars at the Battle of Samara Bend. There is no historical record except a short account by the Arab historian Ibn al-Athir, writing in Mosul some away from the event.John Chambers, ''The Devil's Horsemen: The Mongol Invasion of Europe'', Atheneum, 1979. p. 31 Various historical secondary sources ‚Äď Morgan, Chambers, Grousset ‚Äď state that the Mongols actually defeated the Bulgars, Chambers even going so far as to say that the Bulgars had made up stories to tell the (recently crushed) Russians that they had beaten the Mongols and driven them from their territory. The Russian princes then sued for peace. Subutai agreed but was in no mood to pardon the princes. Not only had the Rus put up strong resistance, but also Jebe ‚Äď with whom Subutai had campaigned for years ‚Äď had been killed just prior to the Battle of Kalka River. As was customary in Mongol society for nobility, the Russian princes were given a bloodless death. Subutai had a large wooden platform constructed on which he ate his meals along with his other generals. Six Russian princes, including Mstislav III of Kiev
Mstislav Romanovich the Old ( uk, –ú—Ā—ā–ł—Ā–Ľ–į–≤ –†–ĺ–ľ–į–Ĺ–ĺ–≤–ł—á –°—ā–į—Ä–ł–Ļ; russian: –ú—Ā—ā–ł—Ā–Ľ–į–≤ –†–ĺ–ľ–į–Ĺ–ĺ–≤–ł—á –°—ā–į—Ä—č–Ļ) (died 1223) was Prince of Pskov (1179‚Äď?), Smolensk (1197‚Äď?), Belgorod (1206), Halych (?‚Äď?) and Gran ...
, were put under this platform and crushed to death.
The Mongols learned from captives of the abundant green pastures beyond the Bulgar territory, allowing for the planning for conquest of Hungary and Europe. Genghis Khan recalled Subutai back to Mongolia soon afterwards. The famous cavalry expedition led by Subutai and Jebe, in which they encircled the entire Caspian Sea defeating all armies in their path, remains unparalleled to this day, and word of the Mongol triumphs began to trickle to other nations, particularly in Europe. These two campaigns are generally regarded as reconnaissance campaigns that tried to get the feel of the political and cultural elements of the regions. In 1225 both divisions returned to Mongolia. These invasions added Transoxiana and Persia to an already formidable empire while destroying any resistance along the way. Later under Genghis Khan's grandson Batu and the Golden Horde, the Mongols returned to conquer Volga Bulgaria and Kievan Rus' in 1237, concluding the campaign in 1240.
Western Xia and Jin dynasty
 The vassal emperor of the Tanguts (Western Xia) had earlier refused to take part in the Mongol war against the Khwarezmid Empire. Western Xia and the defeated Jin dynasty formed a coalition to resist the Mongols, counting on the campaign against the Khwarazmians to preclude the Mongols from responding effectively.
In 1226, immediately after returning from the west, Genghis Khan began a retaliatory attack on the Tanguts. His armies quickly took Heisui,
The vassal emperor of the Tanguts (Western Xia) had earlier refused to take part in the Mongol war against the Khwarezmid Empire. Western Xia and the defeated Jin dynasty formed a coalition to resist the Mongols, counting on the campaign against the Khwarazmians to preclude the Mongols from responding effectively.
In 1226, immediately after returning from the west, Genghis Khan began a retaliatory attack on the Tanguts. His armies quickly took Heisui, Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
, and Suzhou (not the Suzhou in Jiangsu province), and in the autumn he took Xiliang-fu. One of the Tangut generals challenged the Mongols to a battle near Helan Mountains but was defeated. In November, Genghis laid siege to the Tangut city Lingzhou and crossed the Yellow River, defeating the Tangut relief army. According to legend, it was here that Genghis Khan reportedly saw a line of five stars arranged in the sky and interpreted it as an omen of his victory.
In 1227, Genghis Khan's army attacked and destroyed the Tangut capital of Ning Hia and continued to advance, seizing Lintiao-fu, Xining province, Xindu-fu, and Deshun province in quick succession in the spring. At Deshun, the Tangut general Ma Jianlong put up a fierce resistance for several days and personally led charges against the invaders outside the city gate. Ma Jianlong later died from wounds received from arrows in battle. Genghis Khan, after conquering Deshun, went to Liupanshan (Qingshui County
Qingshui County () is a county in Gansu province of the People's Republic of China, bordering Shaanxi province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Tianshui. In 2014 its population was 324,300 people, of whi ...
, Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
Province) to escape the severe summer. The new Tangut emperor quickly surrendered to the Mongols, and the rest of the Tanguts officially surrendered soon after. Not happy with their betrayal and resistance, Genghis Khan ordered the entire imperial family to be executed, effectively ending the Tangut royal lineage.
Death and succession
 Genghis Khan died within eight days of setting off for his final campaign against the Western Xia on 18 August 1227, according to the official ''History of Yuan'' commissioned during China's Ming dynasty. The date of his death is therefore said to have fallen on 25 August 1227, during the fall of Yinchuan. The exact cause of his death remains a mystery, and is variously attributed to illness, being killed in action or from wounds sustained in hunting or battle. According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', Genghis Khan fell from his horse while hunting and died because of the injury. The '' Galician‚ÄďVolhynian Chronicle'' alleges he was killed by the Western Xia in battle, while
Genghis Khan died within eight days of setting off for his final campaign against the Western Xia on 18 August 1227, according to the official ''History of Yuan'' commissioned during China's Ming dynasty. The date of his death is therefore said to have fallen on 25 August 1227, during the fall of Yinchuan. The exact cause of his death remains a mystery, and is variously attributed to illness, being killed in action or from wounds sustained in hunting or battle. According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', Genghis Khan fell from his horse while hunting and died because of the injury. The '' Galician‚ÄďVolhynian Chronicle'' alleges he was killed by the Western Xia in battle, while Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
wrote that he died after the infection of an arrow wound he received during his final campaign. Later Mongol chronicles connect Genghis's death with a Western Xia princess taken as war booty. One chronicle from the early 17th century even relates the legend that the princess hid a small dagger and stabbed or castrated him. All of these legends were invented well after Genghis Khan's death, however. In contrast, a 2021 study found that the great leader likely died from bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well a ...
, after investigating reports of the clinical signs exhibited by both the Khan and his army, which in turn matched the symptoms associated with the strain of plague present in Western Xia at that time.
 Years before his death, Genghis Khan asked to be buried without markings, according to the customs of his tribe. After he died, his body was returned to Mongolia and presumably to his birthplace in Khentii Aimag, where many assume he is buried somewhere close to the Onon River and the Burkhan Khaldun mountain (part of the Khentii mountain range). According to legend, the funeral escort killed anyone and anything across their path to conceal where he was finally buried. The Genghis Khan Mausoleum, constructed many years after his death, is his memorial, but not his burial site.
Before Genghis Khan died, he assigned √Ėgedei Khan as his successor. Genghis Khan left behind an army of more than 129,000 men; 28,000 were given to his various brothers and his sons. Tolui, his youngest son, inherited more than 100,000 men. This force contained the bulk of the elite Mongolian
Years before his death, Genghis Khan asked to be buried without markings, according to the customs of his tribe. After he died, his body was returned to Mongolia and presumably to his birthplace in Khentii Aimag, where many assume he is buried somewhere close to the Onon River and the Burkhan Khaldun mountain (part of the Khentii mountain range). According to legend, the funeral escort killed anyone and anything across their path to conceal where he was finally buried. The Genghis Khan Mausoleum, constructed many years after his death, is his memorial, but not his burial site.
Before Genghis Khan died, he assigned √Ėgedei Khan as his successor. Genghis Khan left behind an army of more than 129,000 men; 28,000 were given to his various brothers and his sons. Tolui, his youngest son, inherited more than 100,000 men. This force contained the bulk of the elite Mongolian cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
. By tradition, the youngest son inherits his father's property. Jochi, Chagatai, √Ėgedei Khan, and Kulan's son Gelejian received armies of 4,000 men each. His mother and the descendants of his three brothers received 3,000 men each. The title of Great Khan passed to √Ėgedei, the third son of Genghis Khan, making him the second Great Khan (Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, ūźįīūźįćūźį£ ), or , tr, Kańüan or ; ug, ŔāōßōļōßŔÜ, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, ōģōßŔāōßŔÜ ''KhńĀqńĀn'', alternatively spelled Kańüan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
) of the Mongol Empire. Genghis Khan's eldest son, Jochi, died in 1226, during his father's lifetime. Chagatai, Genghis Khan's second son was meanwhile passed over, according to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', over a row just before the invasion of the Khwarezmid Empire in which Chagatai declared before his father and brothers that he would never accept Jochi as Genghis Khan's successor due to questions about his elder brother's parentage. In response to this tension and possibly for other reasons, √Ėgedei was appointed as successor.
Later, his grandsons split his empire into khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
Mong ...
s. His descendants extended the Mongol Empire across most of Eurasia by conquering or creating vassal states in all of modern-day China, Korea, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and substantial portions of Eastern Europe and Southwest Asia. Many of these invasions repeated the earlier large-scale slaughters of local populations.
Organizational philosophy
Politics and economics
 The Mongol Empire was governed by a civilian and military
The Mongol Empire was governed by a civilian and military code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information‚ÄĒsuch as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture‚ÄĒinto another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communication ...
, called the Yassa, created by Genghis Khan. The Mongol Empire did not emphasize the importance of ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
and race in the administrative realm, instead adopting an approach grounded in meritocracy
Meritocracy (''merit'', from Latin , and ''-cracy'', from Ancient Greek 'strength, power') is the notion of a political system in which economic goods and/or political power are vested in individual people based on talent, effort, and achiev ...
. The Mongol Empire was one of the most ethnically and culturally diverse empires in history, as befitted its size. Many of the empire's nomadic inhabitants considered themselves ''Mongols'' in military and civilian life, including the Mongol people, Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
peoples, and others. There were Khans
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
of various non-Mongolian ethnicities such as Muhammad Khan.
There were tax exemptions for religious figures and, to some extent, teachers and doctors. The Mongol Empire practiced religious tolerance because Mongol tradition had long held that religion was a personal concept, and not subject to law or interference. Genghis Khan was a Tengrist
Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is an ethnic and old state Turko- Mongolic religion originating in the Eurasian steppes, based on folk shamanism, animism and generally centered around the titular sky god Tengri. ...
, but was religiously tolerant and interested in learning philosophical and moral lessons from other religions. He consulted Buddhist monks (including the Zen monk Haiyun), Muslims, Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christ√≥s'' (őßŌĀőĻ ...
missionaries, and the Daoist monk Qiu Chuji. Sometime before the rise of Genghis Khan, Ong Khan, his mentor and eventual rival, had converted to Nestorian Christianity. Various Mongol tribes were Shamanist, Buddhist or Christian. Religious tolerance was thus a well established concept on the Asian steppe.
Modern Mongolian historians say that towards the end of his life, Genghis Khan attempted to create a civil state under the Great Yassa that would have established the legal equality of all individuals, including women. However, there is no evidence of this, or of the lifting of discriminatory policies towards sedentary peoples such as the Chinese. Women played a relatively important role in the Mongol Empire and in the family, for example Töregene Khatun was briefly in charge of the Mongol Empire while the next male leader Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, ūźįīūźįćūźį£ ), or , tr, Kańüan or ; ug, ŔāōßōļōßŔÜ, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, ōģōßŔāōßŔÜ ''KhńĀqńĀn'', alternatively spelled Kańüan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
was being chosen. Modern scholars refer to the alleged policy of encouraging trade and communication as the Pax Mongolica (Mongol Peace).
Genghis Khan realised that he needed people who could govern cities and states conquered by him. He also realised that such administrators could not be found among his Mongol people because they were nomads and thus had no experience governing cities. For this purpose Genghis Khan invited a Khitan prince, Chu'Tsai, who worked for the Jin and had been captured by the Mongol army after the Jin dynasty was defeated. Jin had risen to power by displacing the Khitan people. Genghis told Chu'Tsai, who was a lineal descendant of Khitan rulers, that he had avenged Chu'Tsai's forefathers. Chu'Tsai responded that his father served the Jin dynasty honestly and so did he; also he did not consider his own father his enemy, so the question of revenge did not apply. This reply impressed Genghis Khan. Chu'Tsai administered parts of the Mongol Empire and became a confidant of the successive Mongol Khans.
Military
Genghis Khan put absolute trust in his generals, such as Muqali, Jebe, andSubutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''S√ľb√ľg√§t√§i'' or ''S√ľb√ľ'√§t√§i''; Modern Mongolian: –°“Į–Ī—ć—ć–ī—ć–Ļ, ''S√ľbeedei''. ; ; c. 1175‚Äď1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and √Ėgedei Khan. He directed m ...
, and regarded them as close advisors, often extending them the same privileges and trust normally reserved for close family members. He allowed them to make decisions on their own when they embarked on campaigns far from the Mongol Empire capital Karakorum. Muqali, a trusted lieutenant, was given command of the Mongol forces against the Jin dynasty while Genghis Khan was fighting in Central Asia, and Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''S√ľb√ľg√§t√§i'' or ''S√ľb√ľ'√§t√§i''; Modern Mongolian: –°“Į–Ī—ć—ć–ī—ć–Ļ, ''S√ľbeedei''. ; ; c. 1175‚Äď1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and √Ėgedei Khan. He directed m ...
and Jebe were allowed to pursue the Great Raid into the Caucasus and Kievan Rus', an idea they had presented to the Khagan on their own initiative. While granting his generals a great deal of autonomy in making command decisions, Genghis Khan also expected unwavering loyalty from them.
The Mongol military was also successful in siege warfare, cutting off resources for cities and towns by diverting certain rivers, taking enemy prisoners and driving them in front of the army, and adopting new ideas, techniques and tools from the people they conquered, particularly in employing Muslim and Chinese siege engines and engineers to aid the Mongol cavalry in capturing cities. Another standard tactic
Tactic(s) or Tactical may refer to:
* Tactic (method), a conceptual action implemented as one or more specific tasks
** Military tactics, the disposition and maneuver of units on a particular sea or battlefield
** Chess tactics
** Political tact ...
of the Mongol military was the commonly practiced feigned retreat to break enemy formations and to lure small enemy groups away from the larger group and defended position for ambush and counterattack
A counterattack is a tactic employed in response to an attack, with the term originating in "war games". The general objective is to negate or thwart the advantage gained by the enemy during attack, while the specific objectives typically seek ...
.
Another important aspect of the military organization of Genghis Khan was the communications and supply route or ''Yam
Yam or YAM may refer to:
Plants and foods
*Yam (vegetable), common name for members of ''Dioscorea''
* Taro, known in Malaysia and Singapore as yam
* Sweet potato, specifically its orange-fleshed cultivars, often referred to as yams in North Amer ...
'', adapted from previous Chinese models. Genghis Khan dedicated special attention to this in order to speed up the gathering of military intelligence and official communications. To this end, Yam waystations were established all over the empire.
Impressions
Positive
 Genghis Khan is credited with bringing the
Genghis Khan is credited with bringing the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
under one cohesive political environment. This allowed increased communication and trade between the West, Middle East and Asia, thus expanding the horizons of all three cultural areas. Some historians have noted that Genghis Khan instituted certain levels of meritocracy
Meritocracy (''merit'', from Latin , and ''-cracy'', from Ancient Greek 'strength, power') is the notion of a political system in which economic goods and/or political power are vested in individual people based on talent, effort, and achiev ...
in his rule, was tolerant of religions and explained his policies clearly to all his soldiers. Genghis Khan had a notably positive reputation among some western European authors in the Middle Ages, who knew little concrete information about his empire in Asia. The Italian explorer Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
said that Genghis Khan "was a man of great worth, and of great ability, and valor", while philosopher and inventor Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiri ...
applauded the scientific and philosophical vigor of Genghis Khan's empire, and the famed writer Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer (; ‚Äď 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He wa ...
wrote concerning :
reactionary
In political science, a reactionary or a reactionist is a person who holds political views that favor a return to the ''status quo ante'', the previous political state of society, which that person believes possessed positive characteristics abse ...
figure, and positive statements about him were avoided. In 1962, the erection of a monument at his birthplace and a conference held in commemoration of his 800th birthday led to criticism from the Soviet Union and the dismissal of secretary Tömör-Ochir of the ruling Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party Central Committee
Central committee is the common designation of a standing administrative body of Communist party, communist parties, analogous to a board of directors, of both ruling and nonruling parties of former and existing socialist states. In such party org ...
.
In the early 1990s, the memory of Genghis Khan underwent a powerful revival, partly in reaction to its suppression during the Mongolian People's Republic period. Genghis Khan became a symbol of national identity for many younger Mongolians, who maintain that the historical records written by non-Mongolians are unfairly biased against Genghis Khan and that his butchery is exaggerated, while his positive role is underrated.
Mixed
 There are conflicting views of Genghis Khan in China, which suffered a drastic decline in population.William Bonner, Addison Wiggin (2006).
There are conflicting views of Genghis Khan in China, which suffered a drastic decline in population.William Bonner, Addison Wiggin (2006). Empire of debt: the rise of an epic financial crisis
''. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 43‚Äď44. The population of north China decreased from 50 million in the 1195 census to 8.5 million in the Mongol census of 1235‚Äď36; however, many were victims of plague. In Hebei province alone, 9 out of 10 were killed by the
Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
when Toghon Tem√ľr was enthroned in 1333. Northern China was also struck by floods and famine long after the war in northern China was over in 1234 and not killed by Mongols. The Black Death also contributed. By 1351, two out of three people in China had died of the plague, helping to spur armed rebellion, most notably in the form of the Red Turban Rebellions
The Red Turban Rebellions () were uprisings against the Yuan dynasty between 1351 and 1368, eventually leading to its collapse. Remnants of the Yuan imperial court retreated northwards and is thereafter known as the Northern Yuan in historiogr ...
. However according to Richard von Glahn, a historian of Chinese economics, China's population only fell by 15% to 33% from 1340 to 1370 and there is "a conspicuous lack of evidence for pandemic disease on the scale of the Black Death in China at this time." An unknown number of people also migrated to Southern China in this period, including under the preceding Southern Song dynasty.
The Mongols also spared many cities from massacre and sacking if they surrendered, including Kaifeng, Yangzhou, and Hangzhou. Ethnic Han and Khitan soldiers defected en masse to Genghis Khan against the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty. Equally, while Genghis never conquered all of China, his grandson Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 ‚Äď 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of th ...
, by completing that conquest and establishing the Yuan dynasty, is often credited with re-uniting China, and there is a great deal of Chinese artwork and literature praising Genghis as a military leader and political genius. The Yuan dynasty left an indelible imprint on Chinese political and social structures and a cultural legacy that outshone the preceding Jin dynasty.
Negative
 The conquests and leadership of Genghis Khan included widespread devastation and
The conquests and leadership of Genghis Khan included widespread devastation and mass murder
Mass murder is the act of murdering a number of people, typically simultaneously or over a relatively short period of time and in close geographic proximity. The United States Congress defines mass killings as the killings of three or more pe ...
. The targets of campaigns that refused to surrender would often be subject to reprisals in the form of enslavement and wholesale slaughter. The second campaign against Western Xia, the final military action led by Genghis Khan, and during which he died, involved an intentional and systematic destruction of Western Xia cities and culture. According to John Man
John Man (1512‚Äď1569) was an English churchman, college head, and a diplomat.
Life
He was born at Lacock or Winterbourne Stoke, in Wiltshire. He was educated at Winchester College from 1523, and New College, Oxford, where he graduated B.A. in ...
, because of this policy of total obliteration, Western Xia is little known to anyone other than experts in the field because so little record is left of that society. He states that "There is a case to be made that this was the first ever recorded example of attempted genocide. It was certainly very successful '' ethnocide''." In the conquest of Khwarezmia under Genghis Khan, the Mongols razed the cities of Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, –Ď—É—Ö–ĺ—Ä–ĺ, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, Samarkand
fa, ō≥ŔÖōĪŔāŔÜōĮ
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, HerńĀt
HerńĀt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safńďd ...
, ŠĻ¨Ňęs
Tus ( Persian: ō™Ŕąō≥ Tus), also spelled as Tous or Toos, is an ancient city in Razavi Khorasan Province in Iran near Mashhad. To the ancient Greeks, it was known as Susia ( grc, ő£őŅŌćŌÉőĻőĪ). It was also known as Tusa. Tus was divided int ...
, and NeyshńĀbŇęr and killed the respective urban populations. His invasions are considered the beginning of a 200-year period known in Iran and other Islamic societies as the "Mongol catastrophe." Ibn al-Athir, Ata-Malik Juvaini, Seraj al-Din Jozjani, and Rashid al-Din Fazl-Allah Hamedani, Iranian historians from the time of Mongol occupation, describe the Mongol invasions as a catastrophe never before seen. A number of present-day Iranian historians, including Zabih Allah Safa, have likewise viewed the period initiated by Genghis Khan as a uniquely catastrophic era. Steven R. Ward writes that the Mongol violence and depredations in the Iranian Plateau "killed up to three-fourths of the population... possibly 10 to 15 million people. Some historians have estimated that Iran's population did not again reach its pre-Mongol levels until the mid-20th century."
Although the famous Mughal emperors were proud descendants of Genghis Khan and particularly Timur, they clearly distanced themselves from the Mongol atrocities committed against the Khwarizim Shahs, Turks, Persians, the citizens of Baghdad and Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, Nishapur
Nishapur or officially Romanized as Neyshabur ( fa, ;Or also "ŔÜŘĆōīōßŔĺŔąōĪ" which is closer to its original and historic meaning though it is less commonly used by modern native Persian speakers. In Persian poetry, the name of this city is wr ...
, Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, –Ď—É—Ö–ĺ—Ä–ĺ, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
and historical figures such as Attar of Nishapur and many other notable Muslims. However, Mughal Emperors directly patronized the legacies of Genghis Khan and Timur; together their names were synonymous with the names of other distinguished personalities particularly among the Muslim populations of South Asia.
Depictions


Medieval
Unlike most emperors, Genghis Khan never allowed his image to be portrayed in paintings or sculptures. The earliest known images of Genghis Khan were produced half a century after his death, including the famousNational Palace Museum
The National Palace Museum (; PhaŐćk-fa-sŠĻ≥: Kwet-liŐćp k√Ļ-kiung pok-vuŐćt-y√®n), is a museum in Taipei, Republic of China (Taiwan). It has a permanent collection of nearly 700,000 pieces of Chinese artifacts and artworks, many of which wer ...
portrait in Taiwan. The portrait portrays Genghis Khan wearing white robes, a leather warming cap and his hair tied in braids, much like a similar depiction of Kublai Khan. This portrait is often considered to represent the closest resemblance to what Genghis Khan actually looked like, though it, like all others renderings, suffers from the same limitation of being, at best, a facial composite
A facial composite is a graphical representation of one or more eyewitnesses' memories of a face, as recorded by a composite artist. Facial composites are used mainly by police in their investigation of (usually serious) crimes. These images a ...
. Like many of the earliest images of Genghis Khan, the Chinese-style portrait presents the Great Khan in a manner more akin to a Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
sage than a Mongol warrior. Other portrayals of Genghis Khan from other cultures likewise characterized him according to their particular image of him: in Persia he was portrayed as a Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
sultan and in Europe he was pictured as an ugly barbarian with a fierce face and cruel eyes. According to sinologist Herbert Allen Giles, a Mongol painter known as Ho-li-hosun (also known as Khorisun or Qooriqosun) was commissioned by Kublai Khan in 1278 to paint the National Palace Museum portrait. The story goes that Kublai Khan ordered Khorisun, along with the other entrusted remaining followers of Genghis Khan, to ensure the portrait reflected the Great Khan's true image.
The only individuals to have recorded Genghis Khan's physical appearance during his lifetime were the Persian chronicler Minhaj al-Siraj Juzjani and Chinese diplomat Zhao Hong. Minhaj al-Siraj described Genghis Khan as "a man of tall stature, of vigorous build, robust in body, the hair of his face scanty and turned white, with cats’ eyes, possessed of dedicated energy, discernment, genius, and understanding, awe-striking...". The chronicler had also previously commented on Genghis Khan's height, powerful build, with cat's eyes and lack of grey hair, based on the evidence of eyes witnesses in 1220, which saw Genghis Khan fighting in the Khorasan (modern day northwest Persia). According to Paul Ratchnevsky, the Song dynasty envoy Zhao Hong who visited the Mongols in 1221, described Genghis Khan as "of tall and majestic stature, his brow is broad and his beard is long".
Other descriptions of Genghis Khan come from 14th century texts. The Persian historian Rashid-al-Din in ''Jami' al-tawarikh
The ''JńĀmi Ņ al-tawńĀrńękh'' (Persian/Arabic: , ) is a work of literature and history, produced in the Mongol Ilkhanate. Written by Rashid al-Din Hamadani (1247‚Äď1318 AD) at the start of the 14th century, the breadth of coverage of the work h ...
'', written in the beginning of the 14th century, stated that most Borjigin ancestors of Genghis Khan were "tall, long-bearded, red-haired, and bluish green-eyed," features which Genghis Khan himself had. The factual nature of this statement is considered controversial. In the Georgian Chronicles, in a passage written in the 14th century, Genghis Khan is similarly described as a large, good-looking man, with red hair. However, according to John Andrew Boyle
John Andrew Boyle (1916‚ąí1978), was a British orientalist and historian.
Life and career
He was born at Worcester Park, Surrey, England, on 10 March 1916. He graduated with first class honours in German at Birmingham University. He later purs ...
, Rashid al-Din's text of red hair referred to ruddy skin complexion, and that Genghis Khan was of ruddy complexion like most of his children except for Kublai Khan who was swarthy. He translated the text as ‚ÄúIt chanced that he was born 2 months before M√∂ge, and when Chingiz-Khan's eye fell upon him he said: ‚Äúall our children are of a ruddy complexion, but this child is swarthy like his maternal uncles. Tell Sorqoqtani Beki to give him to a good nurse to be reared‚ÄĚ. 14th century Arabic historian Shihab al-Umari also disputed Rashid al-Din's translation and claimed Alan Gua
Alan Gua ( mn, –ź–Ľ—É–Ĺ –≥—É–į, ''Alun gua'', ''lit. "Alun the Beauty"''. ''Gua'' or ''Guva/Quwa'' means ''beauty'' in Mongolian) is a mythical figure from ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', eleven generations after the grey wolf and the whit ...
falsified the origin of her clan. Some Historians such as Denise Aigle claimed that Rashid al-Din mythicized the origin of Genghis Khan ancestors (the Borjigin clan) through his own interpretations of ''The Secret History of the Mongols''. Italian historian Igor de Rachewiltz claimed that the Mongol origins of the early ancestors of Genghis Khan were animals born from the blue eye wolf (Borte Chino) and the fallow doe (Qo'ai Maral) that was described in the early legends, that their ancestors were animals.
Modern
In Mongolia today, Genghis Khan's name and likeness appear on products, streets, buildings, and other places. His face can be found on everyday commodities, from liquor bottles to candy, and on the largest denominations of 500, 1,000, 5,000, 10,000, and 20,000 Mongolian t√∂gr√∂g (‚āģ). Mongolia's main international airport in Ulaanbaatar is namedChinggis Khaan International Airport
Chinggis Khaan International Airport,, also referred to as New Ulaanbaatar International Airport, , is an international airport located in the Khöshig Valley of Sergelen, Töv, Mongolia, 52 km south of the capital Ulaanbaatar and 20& ...
, and there is a 40m-high equestrian statue of Genghis Khan
The Genghis Khan Equestrian Statue, part of the Genghis Khan Statue Complex, is a tall, stainless steel statue of Genghis Khan on horseback and the world's tallest equestrian statue. It is located on the bank of the Tuul River at ''Tsonjin Boldog ...
east of the Mongolian capital. There has been talk about regulating the use of his name and image to avoid trivialization.
Genghis Khan's birthday, on the first day of winter (according to the Mongolian lunar calendar), is a national holiday.
Outside of Mongolia, there have been numerous works of literature, films and other adaptation works based on the Mongolian ruler and his legacy.
Hulunbuir
Hulunbuir or Hulun Buir ( mn, , ''K√∂l√ľn buyir'', Mongolian Cyrillic: –•”©–Ľ”©–Ĺ–Ī—É–Ļ—Ä, ''Kh√∂l√∂nbuir''; zh, s=ŚĎľšľ¶ŤīĚŚįĒ, ''HŇęl√ļnb√®i'ńõr'') is a region that is governed as a prefecture-level city in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. ...
, Inner Mongolia
File:Lenoir - The Actor LeKain in the Role of Gengis Khan.jpg, The actor LeKain in the role of Genghis Khan
Literature
* "The Squire's Tale
"The Squire's Tale" is a tale in Geoffrey Chaucer's ''The Canterbury Tales''. It is unfinished, because it is interrupted by the next story-teller, the Franklin, who then continues with his own prologue and tale. The Squire is the Knight's son, a ...
", one of ''The Canterbury Tales
''The Canterbury Tales'' ( enm, Tales of Caunterbury) is a collection of twenty-four stories that runs to over 17,000 lines written in Middle English by Geoffrey Chaucer between 1387 and 1400. It is widely regarded as Chaucer's ''Masterpiece, ...
'' by Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer (; ‚Äď 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He wa ...
, is set at the court of Genghis Khan.
* ''Genghis Khan'' by Vasily Yan, 1939‚ÄĒfirst installment of an epic trilogy about the conquests of the Mongols.
* ''The End of Genghis'', a poem by F. L. Lucas
Frank Laurence Lucas (28 December 1894 ‚Äď 1 June 1967) was an English classical scholar, literary critic, poet, novelist, playwright, political polemicist, Fellow of King's College, Cambridge, and intelligence officer at Bletchley Park during ...
, in which the dying Khan, attended by his Khitan counsellor Yel√ľ Chucai, looks back on his life.
* '' The Conqueror'' series of novels by Conn Iggulden
* ''Steppe'' by Piers Anthony
* ''Genghis Khan'' (Last incarnation) in Metro 2033 by Dmitry Glukhovsky
Dmitry Alekseyevich Glukhovsky (russian: –Ē–ľ–łŐĀ—ā—Ä–ł–Ļ –ź–Ľ–Ķ–ļ—Ā–ĶŐĀ–Ķ–≤–ł—á –ď–Ľ—É—Ö–ĺŐĀ–≤—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ, born 12 June 1979) is a Russian author and journalist best known for the science fiction novel ''Metro 2033'' and its sequels. As a journal ...
* ''White cloud of Genghis Khan'' by Chingiz Aitmatov
Chingiz Mustafayev ( az, Çingiz Mustafayev; born 11 March 1991) is an Azerbaijani singer, songwriter, and guitarist. He Azerbaijan in the Eurovision Song Contest 2019, represented Azerbaijan in the Eurovision Song Contest 2019 with the song "Tru ...
* ''The Private Life of Genghis Khan
"The Private Life of Genghis Khan" is a short story written by Douglas Adams and Graham Chapman. It is based in part on a sketch devised by Graham Chapman, and written by Chapman and Adams for the 1975 TV show pilot ''Out of the Trees''. It appea ...
'' by Douglas Adams and Graham Chapman
Films
* ''Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem√ľjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)√Ėgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
'', a 1950 Philippine film directed by Manuel Conde.
* '' The Conqueror'', released in 1956 and starring John Wayne
Marion Robert Morrison (May 26, 1907 ‚Äď June 11, 1979), known professionally as John Wayne and nicknamed The Duke or Duke Wayne, was an American actor who became a popular icon through his starring roles in films made during Hollywood's Gol ...
as Tem√ľjin and Susan Hayward
Susan Hayward (born Edythe Marrenner; June 30, 1917 ‚Äď March 14, 1975) was an American film actress, best known for her film portrayals of women that were based on true stories.
After working as a fashion model for the Walter Thornton Model A ...
as Börte.
* ''Changez Khan'', a 1957 Indian Hindi-language film directed by Kedar Kapoor, starring Sheikh Mukhtar as the emperor along with Bina Rai
Bina Rai (13 July 1931 ‚Äď 6 December 2009), sometimes referred to as Beena Rai, was an Indian actress, primarily of the black and white era of Hindi cinema. She is most known for her roles in classics such as ''Anarkali'' (1953), '' Ghunghat' ...
and Prem Nath in the lead roles.
* ''Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem√ľjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)√Ėgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
'', a 1965 film starring Omar Sharif
Omar Sharif ( ar, ōĻŔÖōĪ ōßŔĄōīōĪŔäŔĀ ; born Michel Yusef Dimitri Chalhoub , 10 April 193210 July 2015) was an Egyptian actor, generally regarded as one of his country's greatest male film stars. He began his career in his native country in the ...
.
* ''Under the Eternal Blue Sky'', a Mongolian film directed by Baljinnyam, which was released in 1990. Starring Agvaantserengiin Enkhtaivan as Tem√ľjin.
* ''Genghis Khan'', an unfinished 1992 film starring Richard Tyson, Charlton Heston
Charlton Heston (born John Charles Carter; October 4, 1923April 5, 2008) was an American actor and political activist.
As a Hollywood star, he appeared in almost 100 films over the course of 60 years. He played Moses in the epic film ''The Ten C ...
and Pat Morita.
* ''Genghis Khan ‚Äď A Proud Son Of Heaven'', a 1998 film made in Mongolian, with English subtitles.
* '' Genghis Khan: To the Ends of the Earth and Sea'', also known as ''The Descendant of Gray Wolf'', a Japanese-Mongolian film released in 2007.
* '' Mongol'', a 2007 film directed by Sergei Bodrov, starring Tadanobu Asano. ( Academy Award nominee for Best Foreign Language Film).
* ''No Right to Die ‚Äď Chinggis Khaan
''No Right to Die ‚Äď Chinggis Khaan'' ( mn, “ģ—Ö—ć–∂ “Į–Ľ –Ī–ĺ–Ľ–Ĺ–ĺ, –ß–ł–Ĺ–≥–ł—Ā –•–į–į–Ĺ) is a 2008 film directed by L Erdenebulgan based on the life of Tem√ľjin, the young Genghis Khan and his unification of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mong ...
'', a Mongolian film released in 2008.
* ''Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem√ľjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)√Ėgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
'', a Chinese film released in 2018.
Television series
* ''Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem√ľjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)√Ėgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
'', a 1987 Hong Kong television series produced by TVB, starring Alex Man
Alex Man Chi-leung () is a Golden Horse Award-winning Hong Kong actor. Born in Hong Kong to Hakka parents, Alex Man became a television actor for ATV in the 1970s. He joined TVB
Television Broadcasts Limited (TVB) is a television bro ...
.
* ''Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem√ľjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)√Ėgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
'', a 1987 Hong Kong television series produced by ATV
ATV may refer to:
Broadcasting
* Amateur television
*Analog television
Television stations and companies
* Ràdio i Televisió d'Andorra
* ATV (Armenia)
* ATV (Aruba), NBC affiliate
* ATV (Australian TV station), Melbourne
* ATV (Austria)
* AT ...
, starring Tony Liu.
* ''Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem√ľjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)√Ėgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
'', a 2004 Chinese-Mongolian co-produced television series, starring Batdorj-in Baasanjab, who is a descendant of Genghis Khan's second son Chagatai.
*"Aaakhri Chattan", a 1978 Pakistani drama series having Zahoor Ahmed as Genghis Khan.
Music
* West German pop band Dschinghis Khan took its name from the German-language spelling of Genghis Khan. They participated in theEurovision Song Contest 1979
The Eurovision Song Contest 1979 was the 24th edition of the annual Eurovision Song Contest. It took place in Jerusalem, Israel, following the country's victory at the with the song "A-Ba-Ni-Bi" by Izhar Cohen and the Alphabeta. Organised by the ...
with their song of the same name.
* Heavy metal band Iron Maiden released an all-instrumental track titled "Genghis Khan" on their 1981 sophomore album '' Killers''.
* The band Miike Snow released the song "Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' Õ° É įiŇč…°…™s xaňźŇčbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Tem√ľjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)√Ėgedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
" in 2017.
* Mongolian Folk-Rock band The Hu released a song called ''The Great Chinggis Khaan'' in August 2019.
Video games
* '' Tem√ľjin (video game)'', a 1997 computer game. * ''Aoki ŇĆkami to Shiroki Mejika
is a turn-based strategy video game series developed and published by Japanese video game company Koei. The series is set in Yuan Dynasty of China (12th - 14th century), and based on the first Emperor of Yuan Dynasty - Genghis Khan. The game ...
'', Genghis Khan-themed Japanese game series.
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * Incorrect source cite: ** Cite based on title and URL: . ** Cite based on ISBN * * * * * * * * * ; Primary sources * ** * * * **Further reading
* * This Elibron Classics book is a facsimile reprint of an 1888 edition by Tr√ľbner & Co., London. * * * * * * * (summary in English) * * * * * * * * * * * , - , - {{Authority control 1160s births 1227 deaths People from Khentii Province Great Khans of the Mongol Empire 13th-century Mongol rulers 12th-century Mongol rulers 13th-century Chinese monarchs Year of birth uncertain Deaths by horse-riding accident Genocide perpetrators Mongol Empire people Medieval military leaders Medieval slaves Founding monarchs Tengrist monarchs