Garcinia indica rinds being dried.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Garcinia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family (biology), family Clusiaceae native to Asia, America, Australia, tropical and southern Africa, and Polynesia. The number of species is disputed; Plants of the World Online (POWO) recognise up to 400. Commonly, the plants in this genus are called saptrees, mangosteens (which may also refer specifically to ''Garcinia mangostana''), garcinias, or monkey fruit.
Many species are threatened by habitat destruction, and at least one species, ''Garcinia cadelliana, G. cadelliana'', from South Andaman Island, is almost or even completely extinct already.
The fruits are a food source for several animals, such as the Archduke (butterfly), archduke butterflies (''Lexias'' spp.) of tropical eastern Asia which relish the sap of overripe mangosteens.
The genus is named after French botanist Laurent Garcin (1683–1751).
 The fruit of most species of ''Garcinia'' are eaten locally; some species' fruits are highly esteemed in one region, but unknown just a few hundred kilometres away. The best-known species is ''Garcinia mangostana'', which is now cultivated throughout Southeast Asia and other tropical countries, having become established in the late 20th century. Less well-known, but still of international importance, are kandis (''G. forbesii'') with small round red fruits with subacid taste and melting flesh, the Garcinia intermedia, lemon drop mangosteen (''G. intermedia'') with yellow fruit that look like a wrinkled lemon, and the thin-skinned orange button mangosteen (''G. prainiana'').
In addition, mangosteen rind (exocarp) extract is used as a spice. It figures prominently in Kodava people, Kodava culture, and ''Garcinia multiflora, G. multiflora'' is used to flavour and colour the famous ''bún riêu'' soup of Vietnam, where this plant is known as ''hạt điều màu''. ''Garcinia gummi-gutta'' yields a spice widely used in South Asia, in particular in Kerala, where it is called ''kodumpulli''.
Most species in Garcinia are known for their Gum (botany), gum resin, brownish-yellow from xanthonoids such as mangostin, and used as purgative or cathartic, but most frequently – at least in former times – as a pigment. The colour term gamboge refers to this pigment.
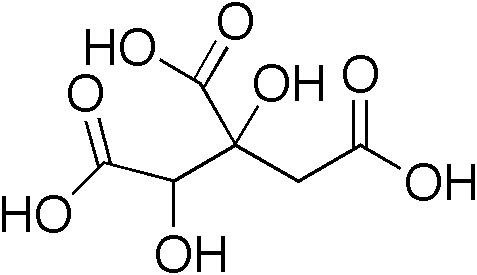
Extracts of the exocarp of certain species – typically Garcinia gummi-gutta, ''G. gummi-gutta'', but also ''G. mangostana'' – are often contained in appetite suppressants, but their effectiveness at normal consumption levels is unproven, while at least one case of severe acidosis caused by long-term consumption of such products has been documented. Furthermore, they may contain significant amounts of hydroxycitric acid, which is somewhat toxic and might even destroy the testicles after prolonged use.
Bitter kola (Garcinia kola, ''G. kola'') seeds are used in folk medicine. ''Garcinia mannii, G. mannii'' is popular as a chew stick in western Africa, freshening the breath and cleaning the teeth.
''Garcinia subelliptica, G. subelliptica'', called ''fukugi'' in Japanese (language), Japanese, is the floral emblem of Motobu, Okinawa, Mobuto and Tarama, Okinawa, Tarama on Okinawa. The Malaysian town of Beruas – often spelled "Bruas" – derives its name from the seashore mangosteen (''Garcinia hombroniana, G. hombroniana''), known locally as ''pokok bruas''. It has been used for many years by certain African tribes as a tonic believed to increase 'energy levels' and to possess digestive and fat-busting properties.
The fruit of most species of ''Garcinia'' are eaten locally; some species' fruits are highly esteemed in one region, but unknown just a few hundred kilometres away. The best-known species is ''Garcinia mangostana'', which is now cultivated throughout Southeast Asia and other tropical countries, having become established in the late 20th century. Less well-known, but still of international importance, are kandis (''G. forbesii'') with small round red fruits with subacid taste and melting flesh, the Garcinia intermedia, lemon drop mangosteen (''G. intermedia'') with yellow fruit that look like a wrinkled lemon, and the thin-skinned orange button mangosteen (''G. prainiana'').
In addition, mangosteen rind (exocarp) extract is used as a spice. It figures prominently in Kodava people, Kodava culture, and ''Garcinia multiflora, G. multiflora'' is used to flavour and colour the famous ''bún riêu'' soup of Vietnam, where this plant is known as ''hạt điều màu''. ''Garcinia gummi-gutta'' yields a spice widely used in South Asia, in particular in Kerala, where it is called ''kodumpulli''.
Most species in Garcinia are known for their Gum (botany), gum resin, brownish-yellow from xanthonoids such as mangostin, and used as purgative or cathartic, but most frequently – at least in former times – as a pigment. The colour term gamboge refers to this pigment.
Extracts of the exocarp of certain species – typically Garcinia gummi-gutta, ''G. gummi-gutta'', but also ''G. mangostana'' – are often contained in appetite suppressants, but their effectiveness at normal consumption levels is unproven, while at least one case of severe acidosis caused by long-term consumption of such products has been documented. Furthermore, they may contain significant amounts of hydroxycitric acid, which is somewhat toxic and might even destroy the testicles after prolonged use.
Bitter kola (Garcinia kola, ''G. kola'') seeds are used in folk medicine. ''Garcinia mannii, G. mannii'' is popular as a chew stick in western Africa, freshening the breath and cleaning the teeth.
''Garcinia subelliptica, G. subelliptica'', called ''fukugi'' in Japanese (language), Japanese, is the floral emblem of Motobu, Okinawa, Mobuto and Tarama, Okinawa, Tarama on Okinawa. The Malaysian town of Beruas – often spelled "Bruas" – derives its name from the seashore mangosteen (''Garcinia hombroniana, G. hombroniana''), known locally as ''pokok bruas''. It has been used for many years by certain African tribes as a tonic believed to increase 'energy levels' and to possess digestive and fat-busting properties.

 , Kew's Plants of the World Online lists nearly 400 accepted species. Selected species include:
)
* ''Garcinia macrophylla'' – ''pungara''
* ''Garcinia madruno'' (Kunth) Hammel – ''charichuelo''
* ''Garcinia magnifolia'' – ''bebasajo''
* ''Garcinia maingayi''
* ''Garcinia mangostana'' – purple mangosteen
* ''Garcinia microcarpa''
* ''Garcinia minutiflora''
* ''Garcinia monantha''
* ''Garcinia montana''
* ''Garcinia morella'' – ''ireevalsinni'' (Tamil)
* ''Garcinia multiflora'' Champ. – ''dọc'' (Vietnamese (language), Vietnamese)
* ''Garcinia murtonii''
* ''Garcinia nigrolineata'' Planch. ex T.Anderson
* ''Garcinia nitida''
* ''Garcinia oliveri''
* ''Garcinia opaca''
* ''Garcinia parvifolia'' - Kundong, Brunei cherry, Asam aur aur
* ''Garcinia paucinervis''
* ''Garcinia pedunculata''
* ''Garcinia prainiana'' – button mangosteen, ''cherapu''
* ''Garcinia pseudoguttifera'' - mo'onia tree
* ''Garcinia pushpangadaniana''
* ''Garcinia pyrifera''
* ''Garcinia quaesita''
* ''Garcinia rubro-echinata''
* ''Garcinia scortechinii''
* ''Garcinia semseii''
* ''Garcinia sessilis'' Seem. – ''heilala'' (Tongan), ''seilala'' (Samoan)
* ''Garcinia spicata'' - bitter garcinia
* ''Garcinia staudtii''
* ''Garcinia subelliptica'' - fukugi tree
* ''Garcinia terpnophylla''
* ''Garcinia thwaitesii''
* ''Garcinia travancorica''
* ''Garcinia uniflora''
* ''Garcinia warrenii'' F.Muell.
* ''Garcinia wightii''
* ''Garcinia xanthochymus'' – yellow mangosteen, ''gamboge''
* ''Garcinia zeylanica''
, Kew's Plants of the World Online lists nearly 400 accepted species. Selected species include:
)
* ''Garcinia macrophylla'' – ''pungara''
* ''Garcinia madruno'' (Kunth) Hammel – ''charichuelo''
* ''Garcinia magnifolia'' – ''bebasajo''
* ''Garcinia maingayi''
* ''Garcinia mangostana'' – purple mangosteen
* ''Garcinia microcarpa''
* ''Garcinia minutiflora''
* ''Garcinia monantha''
* ''Garcinia montana''
* ''Garcinia morella'' – ''ireevalsinni'' (Tamil)
* ''Garcinia multiflora'' Champ. – ''dọc'' (Vietnamese (language), Vietnamese)
* ''Garcinia murtonii''
* ''Garcinia nigrolineata'' Planch. ex T.Anderson
* ''Garcinia nitida''
* ''Garcinia oliveri''
* ''Garcinia opaca''
* ''Garcinia parvifolia'' - Kundong, Brunei cherry, Asam aur aur
* ''Garcinia paucinervis''
* ''Garcinia pedunculata''
* ''Garcinia prainiana'' – button mangosteen, ''cherapu''
* ''Garcinia pseudoguttifera'' - mo'onia tree
* ''Garcinia pushpangadaniana''
* ''Garcinia pyrifera''
* ''Garcinia quaesita''
* ''Garcinia rubro-echinata''
* ''Garcinia scortechinii''
* ''Garcinia semseii''
* ''Garcinia sessilis'' Seem. – ''heilala'' (Tongan), ''seilala'' (Samoan)
* ''Garcinia spicata'' - bitter garcinia
* ''Garcinia staudtii''
* ''Garcinia subelliptica'' - fukugi tree
* ''Garcinia terpnophylla''
* ''Garcinia thwaitesii''
* ''Garcinia travancorica''
* ''Garcinia uniflora''
* ''Garcinia warrenii'' F.Muell.
* ''Garcinia wightii''
* ''Garcinia xanthochymus'' – yellow mangosteen, ''gamboge''
* ''Garcinia zeylanica''
Description
''Garcinia'' species are evergreen trees and shrubs, dioecious and in several cases apomictic. The fruit is a berry with fleshy endocarp, which in several species is delicious. Among neotropical ''Garcinia'' several species are dioecious (G. leptophylla, G. macrophylla and G. magnifolia), although female trees have often been observed to have some degree of self-fertility.Uses
 The fruit of most species of ''Garcinia'' are eaten locally; some species' fruits are highly esteemed in one region, but unknown just a few hundred kilometres away. The best-known species is ''Garcinia mangostana'', which is now cultivated throughout Southeast Asia and other tropical countries, having become established in the late 20th century. Less well-known, but still of international importance, are kandis (''G. forbesii'') with small round red fruits with subacid taste and melting flesh, the Garcinia intermedia, lemon drop mangosteen (''G. intermedia'') with yellow fruit that look like a wrinkled lemon, and the thin-skinned orange button mangosteen (''G. prainiana'').
In addition, mangosteen rind (exocarp) extract is used as a spice. It figures prominently in Kodava people, Kodava culture, and ''Garcinia multiflora, G. multiflora'' is used to flavour and colour the famous ''bún riêu'' soup of Vietnam, where this plant is known as ''hạt điều màu''. ''Garcinia gummi-gutta'' yields a spice widely used in South Asia, in particular in Kerala, where it is called ''kodumpulli''.
Most species in Garcinia are known for their Gum (botany), gum resin, brownish-yellow from xanthonoids such as mangostin, and used as purgative or cathartic, but most frequently – at least in former times – as a pigment. The colour term gamboge refers to this pigment.
Extracts of the exocarp of certain species – typically Garcinia gummi-gutta, ''G. gummi-gutta'', but also ''G. mangostana'' – are often contained in appetite suppressants, but their effectiveness at normal consumption levels is unproven, while at least one case of severe acidosis caused by long-term consumption of such products has been documented. Furthermore, they may contain significant amounts of hydroxycitric acid, which is somewhat toxic and might even destroy the testicles after prolonged use.
Bitter kola (Garcinia kola, ''G. kola'') seeds are used in folk medicine. ''Garcinia mannii, G. mannii'' is popular as a chew stick in western Africa, freshening the breath and cleaning the teeth.
''Garcinia subelliptica, G. subelliptica'', called ''fukugi'' in Japanese (language), Japanese, is the floral emblem of Motobu, Okinawa, Mobuto and Tarama, Okinawa, Tarama on Okinawa. The Malaysian town of Beruas – often spelled "Bruas" – derives its name from the seashore mangosteen (''Garcinia hombroniana, G. hombroniana''), known locally as ''pokok bruas''. It has been used for many years by certain African tribes as a tonic believed to increase 'energy levels' and to possess digestive and fat-busting properties.
The fruit of most species of ''Garcinia'' are eaten locally; some species' fruits are highly esteemed in one region, but unknown just a few hundred kilometres away. The best-known species is ''Garcinia mangostana'', which is now cultivated throughout Southeast Asia and other tropical countries, having become established in the late 20th century. Less well-known, but still of international importance, are kandis (''G. forbesii'') with small round red fruits with subacid taste and melting flesh, the Garcinia intermedia, lemon drop mangosteen (''G. intermedia'') with yellow fruit that look like a wrinkled lemon, and the thin-skinned orange button mangosteen (''G. prainiana'').
In addition, mangosteen rind (exocarp) extract is used as a spice. It figures prominently in Kodava people, Kodava culture, and ''Garcinia multiflora, G. multiflora'' is used to flavour and colour the famous ''bún riêu'' soup of Vietnam, where this plant is known as ''hạt điều màu''. ''Garcinia gummi-gutta'' yields a spice widely used in South Asia, in particular in Kerala, where it is called ''kodumpulli''.
Most species in Garcinia are known for their Gum (botany), gum resin, brownish-yellow from xanthonoids such as mangostin, and used as purgative or cathartic, but most frequently – at least in former times – as a pigment. The colour term gamboge refers to this pigment.
Extracts of the exocarp of certain species – typically Garcinia gummi-gutta, ''G. gummi-gutta'', but also ''G. mangostana'' – are often contained in appetite suppressants, but their effectiveness at normal consumption levels is unproven, while at least one case of severe acidosis caused by long-term consumption of such products has been documented. Furthermore, they may contain significant amounts of hydroxycitric acid, which is somewhat toxic and might even destroy the testicles after prolonged use.
Bitter kola (Garcinia kola, ''G. kola'') seeds are used in folk medicine. ''Garcinia mannii, G. mannii'' is popular as a chew stick in western Africa, freshening the breath and cleaning the teeth.
''Garcinia subelliptica, G. subelliptica'', called ''fukugi'' in Japanese (language), Japanese, is the floral emblem of Motobu, Okinawa, Mobuto and Tarama, Okinawa, Tarama on Okinawa. The Malaysian town of Beruas – often spelled "Bruas" – derives its name from the seashore mangosteen (''Garcinia hombroniana, G. hombroniana''), known locally as ''pokok bruas''. It has been used for many years by certain African tribes as a tonic believed to increase 'energy levels' and to possess digestive and fat-busting properties.
Species

 , Kew's Plants of the World Online lists nearly 400 accepted species. Selected species include:
)
* ''Garcinia macrophylla'' – ''pungara''
* ''Garcinia madruno'' (Kunth) Hammel – ''charichuelo''
* ''Garcinia magnifolia'' – ''bebasajo''
* ''Garcinia maingayi''
* ''Garcinia mangostana'' – purple mangosteen
* ''Garcinia microcarpa''
* ''Garcinia minutiflora''
* ''Garcinia monantha''
* ''Garcinia montana''
* ''Garcinia morella'' – ''ireevalsinni'' (Tamil)
* ''Garcinia multiflora'' Champ. – ''dọc'' (Vietnamese (language), Vietnamese)
* ''Garcinia murtonii''
* ''Garcinia nigrolineata'' Planch. ex T.Anderson
* ''Garcinia nitida''
* ''Garcinia oliveri''
* ''Garcinia opaca''
* ''Garcinia parvifolia'' - Kundong, Brunei cherry, Asam aur aur
* ''Garcinia paucinervis''
* ''Garcinia pedunculata''
* ''Garcinia prainiana'' – button mangosteen, ''cherapu''
* ''Garcinia pseudoguttifera'' - mo'onia tree
* ''Garcinia pushpangadaniana''
* ''Garcinia pyrifera''
* ''Garcinia quaesita''
* ''Garcinia rubro-echinata''
* ''Garcinia scortechinii''
* ''Garcinia semseii''
* ''Garcinia sessilis'' Seem. – ''heilala'' (Tongan), ''seilala'' (Samoan)
* ''Garcinia spicata'' - bitter garcinia
* ''Garcinia staudtii''
* ''Garcinia subelliptica'' - fukugi tree
* ''Garcinia terpnophylla''
* ''Garcinia thwaitesii''
* ''Garcinia travancorica''
* ''Garcinia uniflora''
* ''Garcinia warrenii'' F.Muell.
* ''Garcinia wightii''
* ''Garcinia xanthochymus'' – yellow mangosteen, ''gamboge''
* ''Garcinia zeylanica''
, Kew's Plants of the World Online lists nearly 400 accepted species. Selected species include:
)
* ''Garcinia macrophylla'' – ''pungara''
* ''Garcinia madruno'' (Kunth) Hammel – ''charichuelo''
* ''Garcinia magnifolia'' – ''bebasajo''
* ''Garcinia maingayi''
* ''Garcinia mangostana'' – purple mangosteen
* ''Garcinia microcarpa''
* ''Garcinia minutiflora''
* ''Garcinia monantha''
* ''Garcinia montana''
* ''Garcinia morella'' – ''ireevalsinni'' (Tamil)
* ''Garcinia multiflora'' Champ. – ''dọc'' (Vietnamese (language), Vietnamese)
* ''Garcinia murtonii''
* ''Garcinia nigrolineata'' Planch. ex T.Anderson
* ''Garcinia nitida''
* ''Garcinia oliveri''
* ''Garcinia opaca''
* ''Garcinia parvifolia'' - Kundong, Brunei cherry, Asam aur aur
* ''Garcinia paucinervis''
* ''Garcinia pedunculata''
* ''Garcinia prainiana'' – button mangosteen, ''cherapu''
* ''Garcinia pseudoguttifera'' - mo'onia tree
* ''Garcinia pushpangadaniana''
* ''Garcinia pyrifera''
* ''Garcinia quaesita''
* ''Garcinia rubro-echinata''
* ''Garcinia scortechinii''
* ''Garcinia semseii''
* ''Garcinia sessilis'' Seem. – ''heilala'' (Tongan), ''seilala'' (Samoan)
* ''Garcinia spicata'' - bitter garcinia
* ''Garcinia staudtii''
* ''Garcinia subelliptica'' - fukugi tree
* ''Garcinia terpnophylla''
* ''Garcinia thwaitesii''
* ''Garcinia travancorica''
* ''Garcinia uniflora''
* ''Garcinia warrenii'' F.Muell.
* ''Garcinia wightii''
* ''Garcinia xanthochymus'' – yellow mangosteen, ''gamboge''
* ''Garcinia zeylanica''
Genetic Diversity
The genetic diversity of 22 Garcinia accessions was analyzed using peroxidase, RAPD markers, and gene sequence-specific amplification polymorphism (GSSAP). Genetic diversity assessment revealed low genetic variation among them. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that Garcinia species clustered into five groups at a mean similarity coefficient of 0.54. This study showed that the ''G. magostana'' accessions can be clearly distinguished by combined peroxidase, RAPD, and gene sequence-specific amplification polymorphism.References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q311454 Garcinia, Malpighiales genera Dioecious plants Medicinal plants