Gallipoli peninsula from space.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the
vi. 36
Xenophon, ibid.; Pseudo-Scylax, ''
PDF
or about , but the length of the peninsula from this wall to its southern extremity, Cape Mastusia, was 420 stadia or about .
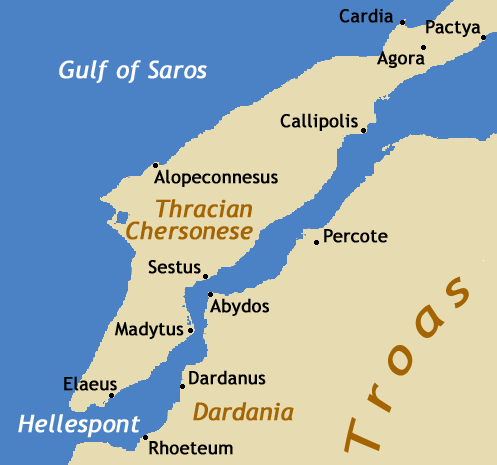 In ancient times, the Gallipoli Peninsula was known as the Thracian Chersonesus (from
In ancient times, the Gallipoli Peninsula was known as the Thracian Chersonesus (from
vi. 34
Nepos, Cornelius, ''Lives of Eminent Commanders'', "Miltiades"
1
/ref> The The Thracian Chersonese was part of the
The Thracian Chersonese was part of the
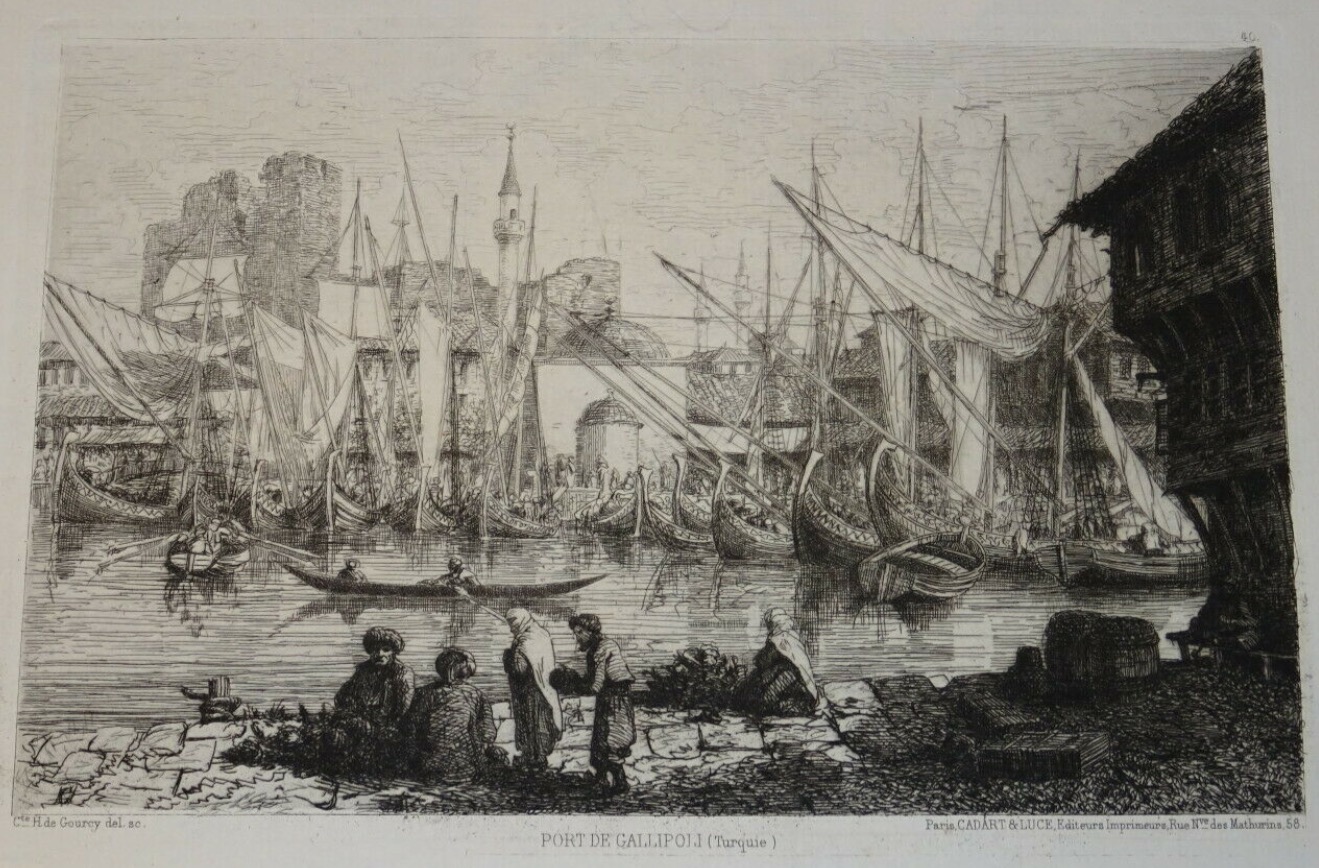 Gallipoli became a major military camp, encampment for British and French forces in 1854 during the Crimean War, and the harbour was also a stopping-off point between the western Mediterranean and Istanbul (formerly Constantinople).
In March 1854 British and French engineers constructed an line of defence to protect the peninsula from a possible Russian attack and so secure control of the route to the Mediterranean Sea.
Gallipoli became a major military camp, encampment for British and French forces in 1854 during the Crimean War, and the harbour was also a stopping-off point between the western Mediterranean and Istanbul (formerly Constantinople).
In March 1854 British and French engineers constructed an line of defence to protect the peninsula from a possible Russian attack and so secure control of the route to the Mediterranean Sea.
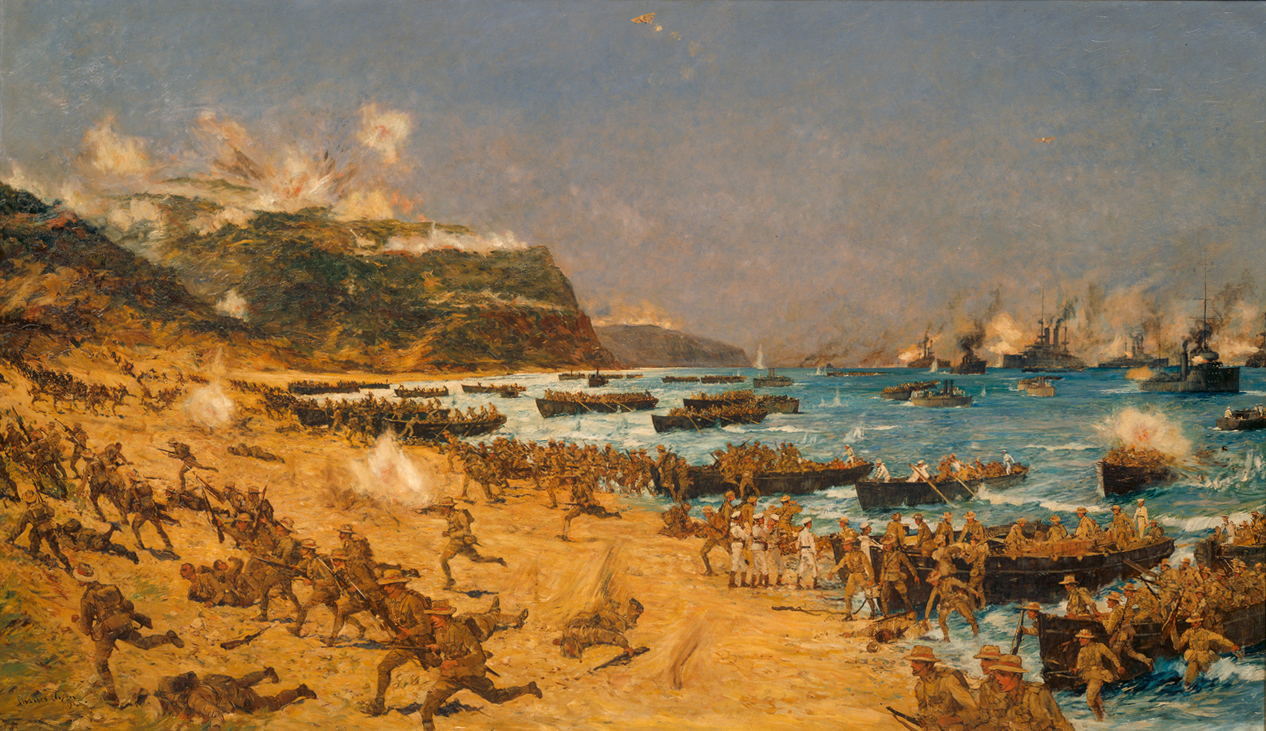
 During World War I (1914-1918), French, British and allied forces (Australian, New Zealand, Newfoundland, Irish and Indian) fought the Gallipoli campaign (1915-1916) in and near the peninsula, seeking to secure a sea route to relieve their eastern ally, Imperial Russia, Russia. The Ottomans set up defensive fortifications along the peninsula and contained the invading forces.
In early 1915, attempting to seize a strategic advantage in World War I by capturing Istanbul (formerly Constantinople), the British authorised an attack on the peninsula by French, British and British Empire forces. The first Australian troops landed at ANZAC Cove early in the morning of 25 April 1915. After eight months of heavy fighting the last Allied soldiers withdrew by 9 January 1916.
The campaign, one of the greatest Ottoman Empire, Ottoman victories during the war, is considered by historians as a major Allies of World War I, Allied failure. Turkey, Turks regard it as a defining moment in their nation's history: a final surge in the defence of the motherland as the Ottoman Empire crumbled. The struggle formed the basis for the Turkish War of Independence and the founding of the Republic of Turkey eight years later under President Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, who first rose to prominence as a commander at Gallipoli.
The Ottoman Empire instituted the Gallipoli Star (Ottoman Empire), Gallipoli Star as a military decoration in 1915 and awarded it throughout the rest of World War I.
The campaign was the first major military action of Australia and New Zealand (or Australian and New Zealand Army Corps, Anzacs) as independent dominions. The date of the landing, 25 April, is known as "Anzac Day". It remains the most significant commemoration of military casualties and veteran, "returned soldiers" in Australia and New Zealand.
On the Allied side one of the promoters of the expedition was Britain's First Lord of the Admiralty, Winston Churchill, whose bullish optimism caused damage to his reputation that took years to repair.
Whilst the underlying strategic concept of the campaign was sound the military forces of the WW1 lacked the logistical, technological and tactical capabilities to undertake an operation of this scope against a determined, well equipped defender.
The all arms coordination and logistical capabilities required to successfully prosecute such a campaign would only be achieved three decades later, during the successful Allied amphibious invasions of Europe and the Pacific during WW2.
Prior to the Allied landings in April 1915, the Ottoman Empire deported Ottoman Greeks, Greek residents from Gallipoli and surrounding region and from the islands in the sea of Marmara, to the interior where they were at the mercy of hostile Turks. The Greeks had little time to pack and the Ottoman authorities permitted them to take only some bedding and the rest was handed over to the Government. The Turks then plundered the houses and properties. A testimony of a deportee described how the deportees were forced onto crowded steamers, standing-room only then on disembarking, men of military age were removed (for forced labour in the labour Battalions (Ottoman Empire), labour battalions of the Ottoman army.) The rest were "scattered… among the farms like ownerless cattle.
The Metropolitan of Gallipoli wrote on 17 July 1915 that the extermination of the Christian refugees was methodical. He also mentions that "The Turks, like beasts of prey, immediately plundered all the Christians' property and carried it off. The inhabitants and refugees of my district are entirely without shelter, awaiting to be sent no one knows where ...". Many Greeks died from hunger and there were frequent cases of rape among women and young girls, as well as their forced conversion to Islam. In some cases, Muhacirs appeared in the villages even before the Greek inhabitants deported and stoned the houses and threatened the inhabitants that they would kill them if they did not leave.
During World War I (1914-1918), French, British and allied forces (Australian, New Zealand, Newfoundland, Irish and Indian) fought the Gallipoli campaign (1915-1916) in and near the peninsula, seeking to secure a sea route to relieve their eastern ally, Imperial Russia, Russia. The Ottomans set up defensive fortifications along the peninsula and contained the invading forces.
In early 1915, attempting to seize a strategic advantage in World War I by capturing Istanbul (formerly Constantinople), the British authorised an attack on the peninsula by French, British and British Empire forces. The first Australian troops landed at ANZAC Cove early in the morning of 25 April 1915. After eight months of heavy fighting the last Allied soldiers withdrew by 9 January 1916.
The campaign, one of the greatest Ottoman Empire, Ottoman victories during the war, is considered by historians as a major Allies of World War I, Allied failure. Turkey, Turks regard it as a defining moment in their nation's history: a final surge in the defence of the motherland as the Ottoman Empire crumbled. The struggle formed the basis for the Turkish War of Independence and the founding of the Republic of Turkey eight years later under President Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, who first rose to prominence as a commander at Gallipoli.
The Ottoman Empire instituted the Gallipoli Star (Ottoman Empire), Gallipoli Star as a military decoration in 1915 and awarded it throughout the rest of World War I.
The campaign was the first major military action of Australia and New Zealand (or Australian and New Zealand Army Corps, Anzacs) as independent dominions. The date of the landing, 25 April, is known as "Anzac Day". It remains the most significant commemoration of military casualties and veteran, "returned soldiers" in Australia and New Zealand.
On the Allied side one of the promoters of the expedition was Britain's First Lord of the Admiralty, Winston Churchill, whose bullish optimism caused damage to his reputation that took years to repair.
Whilst the underlying strategic concept of the campaign was sound the military forces of the WW1 lacked the logistical, technological and tactical capabilities to undertake an operation of this scope against a determined, well equipped defender.
The all arms coordination and logistical capabilities required to successfully prosecute such a campaign would only be achieved three decades later, during the successful Allied amphibious invasions of Europe and the Pacific during WW2.
Prior to the Allied landings in April 1915, the Ottoman Empire deported Ottoman Greeks, Greek residents from Gallipoli and surrounding region and from the islands in the sea of Marmara, to the interior where they were at the mercy of hostile Turks. The Greeks had little time to pack and the Ottoman authorities permitted them to take only some bedding and the rest was handed over to the Government. The Turks then plundered the houses and properties. A testimony of a deportee described how the deportees were forced onto crowded steamers, standing-room only then on disembarking, men of military age were removed (for forced labour in the labour Battalions (Ottoman Empire), labour battalions of the Ottoman army.) The rest were "scattered… among the farms like ownerless cattle.
The Metropolitan of Gallipoli wrote on 17 July 1915 that the extermination of the Christian refugees was methodical. He also mentions that "The Turks, like beasts of prey, immediately plundered all the Christians' property and carried it off. The inhabitants and refugees of my district are entirely without shelter, awaiting to be sent no one knows where ...". Many Greeks died from hunger and there were frequent cases of rape among women and young girls, as well as their forced conversion to Islam. In some cases, Muhacirs appeared in the villages even before the Greek inhabitants deported and stoned the houses and threatened the inhabitants that they would kill them if they did not leave.
Gallipoli Peninsula Historical National Park photos with info
Tours of Gallipoli
Australia's role in the Gallipoli Campaign – Website (ABC and Dept of Veteran's Affairs)
{{Coord, 40, 21, N, 26, 28, E, source:cawiki_region:TR_scale:1000000, display=title Gallipoli Peninsula, Dardanelles Geography of Thrace Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Landforms of Çanakkale Province Headlands of Turkey, Gelibolu Peninsulas of Turkey Tourist attractions in Çanakkale Province Territories of the Republic of Venice World Heritage Tentative List for Turkey Places of the Greek genocide
 The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
an part of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, with the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
to the west and the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
strait to the east.
Gallipoli is the Italian form of the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
name (), meaning 'beautiful city', the original name of the modern town of Gelibolu
Gelibolu, also known as Gallipoli (from el, Καλλίπολις, ''Kallipolis'', "Beautiful City"), is the name of a town and a district in Çanakkale Province of the Marmara Region, located in Eastern Thrace in the European part of Turkey on t ...
. In antiquity, the peninsula was known as the Thracian Chersonese ( grc, Θρακικὴ Χερσόνησος, ; la, Chersonesus Thracica).
The peninsula runs in a south-westerly direction into the Aegean Sea, between the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
(formerly known as the Hellespont), and the Gulf of Saros (formerly the bay of Melas). In antiquity, it was protected by the Long Wall, a defensive structure built across the narrowest part of the peninsula near the ancient city of Agora. The isthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus ...
traversed by the wall was only 36 stadia
Stadia may refer to:
* One of the plurals of stadium, along with "stadiums"
* The plural of stadion, an ancient Greek unit of distance, which equals to 600 Greek feet (''podes'').
* Stadia (Caria), a town of ancient Caria, now in Turkey
* Stadi ...
in breadthHerodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
, ''The Histories''vi. 36
Xenophon, ibid.; Pseudo-Scylax, ''
Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax
The ''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' is an ancient Greek periplus (περίπλους ''períplous'', 'circumnavigation') describing the sea route around the Mediterranean and Black Sea. It probably dates from the mid-4th century BC, specifically ...
'', 67or about , but the length of the peninsula from this wall to its southern extremity, Cape Mastusia, was 420 stadia or about .
History
Antiquity and Middle Ages
 In ancient times, the Gallipoli Peninsula was known as the Thracian Chersonesus (from
In ancient times, the Gallipoli Peninsula was known as the Thracian Chersonesus (from Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, 'peninsula') to the Greeks and later the Romans. It was the location of several prominent towns, including Cardia, Pactya
Pactya or Paktye ( grc, Πακτύη) was an ancient Greek city located in ancient Thrace, on the Thracian Chersonesus. It is cited in the ''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'', in its recitation of the towns of the Thracian Chersonesus, along with Aegosp ...
, Callipolis (Gallipoli), Alopeconnesus (), Sestos, Madytos
Madytos ( el, Μάδυτος) is a former municipality in the Thessaloniki regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volvi, of which it is a municipal unit. Its population was 2,460 in 2011. The ...
, and Elaeus
Elaeus ( grc, Ἐλαιοῦς ''Elaious'', later ''Elaeus''), the “Olive City”, was an ancient Greek city located in Thrace, on the Thracian Chersonese. Elaeus was located at the southern end of the Hellespont (now the Dardanelles) near th ...
. The peninsula was renowned for its wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
. It also benefited from its strategic importance on the main route between Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
, as well as from its control of the shipping route from Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
. The city of Sestos was the main crossing-point on the Hellespont.
According to Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
, the Thracian tribe of Dolonci Dolonci or Dolonki ( el, Δόλογκοι) is the name of a Thracian tribe in Thracian Chersonese. They are mentioned by Herodotus.
References
See also
*List of Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴ ...
() (or 'barbarians' according to Cornelius Nepos) held possession of the peninsula before the Greek colonization. Then, settlers from Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
, mainly of Ionian and Aeolian stock, founded about 12 cities on the peninsula in the 7th century BC.Herodotusvi. 34
Nepos, Cornelius, ''Lives of Eminent Commanders'', "Miltiades"
1
/ref> The
Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
statesman Miltiades the Elder
Miltiades the Elder (ca. 590 – 525 BC) was an Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seve ...
founded a major Athenian colony there around 560 BC. He took authority over the entire peninsula, augmenting its defences against incursions from the mainland. It eventually passed to his nephew, the more famous Miltiades the Younger
Miltiades (; grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon C ...
, about 524 BC. The peninsula was abandoned to the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
in 493 BC after the beginning of the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of t ...
(499–478 BC).
The Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
were eventually expelled, after which the peninsula was for a time ruled by Athens, which enrolled it into the Delian League in 478 BC. The Athenians established a number of cleruchies on the Thracian Chersonese and sent an additional 1,000 settlers around 448 BC. Sparta gained control after the decisive battle of Aegospotami
Aegospotami ( grc, Αἰγὸς Ποταμοί, ''Aigos Potamoi'') or AegospotamosMish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “Aegospotami.” '' Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985. , (in ...
in 404 BC, but the peninsula subsequently reverted to the Athenians. During the 4th century BC, the Thracian Chersonese became the focus of a bitter territorial dispute between Athens and Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an Classical antiquity, ancient monarchy, kingdom on the periphery of Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. Th ...
, whose king Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
sought possession. It was eventually ceded to Philip in 338 BC.
After the death of Philip's son Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 323 BC, the Thracian Chersonese became the object of contention among Alexander's successors. Lysimachus established his capital Lysimachia
''Lysimachia'' () is a genus consisting of 193 accepted species of flowering plants traditionally classified in the family Primulaceae. Based on a molecular phylogenetic study it was transferred to the family Myrsinaceae, before this family wa ...
here. In 278 BC, Celtic tribes from Galatia in Asia Minor settled in the area. In 196 BC, the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
king Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r ...
seized the peninsula. This alarmed the Greeks and prompted them to seek the aid of the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, who conquered the Thracian Chersonese, which they gave to their ally Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης Σωτήρ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus ...
of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
in 188 BC. At the extinction of the Attalid dynasty
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; grc-x-koine, Δυναστ ...
in 133 BC it passed again to the Romans, who from 129 BC administered it in the Roman province of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
. It was subsequently made a state-owned territory () and during the reign of the emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
it was imperial property.
 The Thracian Chersonese was part of the
The Thracian Chersonese was part of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
from its foundation in 330 AD. In 443 AD, Attila the Hun invaded the Gallipoli Peninsula during one of the last stages of his grand campaign that year. He captured both Callipolis and Sestus. Aside from a brief period from 1204 to 1235, when it was controlled by the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
ruled the territory until 1356. During the night between 1 and 2 March 1354, a strong earthquake destroyed the city of Gallipoli and its city walls, weakening its defenses.
Ottoman era
Ottoman conquest
Within a month after the devastating 1354 earthquake the Ottomans besieged and captured the town of Gallipoli, making it the first Ottoman stronghold in Europe and the staging area for Ottoman expansion across theBalkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. The Savoyard Crusade recaptured Gallipoli for Byzantium in 1366, but the beleaguered Byzantines were forced to hand it back in September 1376. The Greeks living there were allowed to continue their everyday activities. In the 19th century, Gallipoli ( ota, گلیبولو, ) was a district () in the Vilayet of Adrianople, with about thirty thousand inhabitants: comprising Greeks, Turks, Armenians and Jews.
Crimean War (1853–1856)
First Balkan War (1912–1913)
During the First Balkan War, the 1913 Battle of Bulair and several minor skirmishes took place where the Ottoman army "destroyed, looted, and burned all the Greek villages near Gallipoli". The Report of the International Commission on the Balkan Wars mention destruction and massacres in the area by the Ottoman army against Greek and Bulgarian population. The Ottoman Government, under the pretext that a village was within the firing line, ordered its evacuation within three hours. The residents abandoned everything they possessed, left their village and went to Gelibolu, Gallipoli. Seven of the Greek villagers who stayed two minutes later than the three-hour limit allowed for the evacuation were shot by the soldiers. After the end of the Balkan War the exiles were allowed to return. But as the Government allowed only the Turks to rebuild their houses and furnish them, the exiled Greeks were compelled to remain in Gallipoli.World War I: Gallipoli Campaign (1914–1918)

Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)
Greek troops occupied Gallipoli on 4 August 1920 during the Greco-Turkish War (1919–22), Greco-Turkish War of 1919–22, considered part of the Turkish War of Independence. After the Armistice of Mudros of 30 October 1918 it became a Greek prefecture centre as ''Kallipolis''. However, Greece was forced to withdraw from Eastern Thrace after the Armistice of Mudanya of October 1922. Gallipoli was briefly handed over to British troops on 20 October 1922, but finally returned to Turkish rule on 26 November 1922. In 1920, after the defeat of the White movement, Russian White army of General Pyotr Wrangel, a significant number of White émigré, émigré soldiers and their families evacuated to Gallipoli from the Crimean Peninsula. From there, many went to European countries, such as Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia, where they found refuge. There are now many list of war cemeteries and memorials on the Gallipoli Peninsula, cemeteries and war memorials on the Gallipoli peninsula.Turkish Republic
Between 1923 and 1926 Gallipoli became the centre of Gelibolu Province, comprising the districts of Gelibolu, Eceabat, Keşan and Şarköy. After the dissolution of the province, it became a district centre in Çanakkale Province.Notable people
* Ahmed Bican (1398 – ), author * Piri Reis (1465/70 – 1553), admiral, geographer and cartographer * Mustafa Âlî (1541–1600), Ottoman historian, politician and writer * Sofia Vembo (1910–1978), Greek singer and actressReferences
External links
*Gallipoli Peninsula Historical National Park photos with info
Tours of Gallipoli
Australia's role in the Gallipoli Campaign – Website (ABC and Dept of Veteran's Affairs)
{{Coord, 40, 21, N, 26, 28, E, source:cawiki_region:TR_scale:1000000, display=title Gallipoli Peninsula, Dardanelles Geography of Thrace Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Landforms of Çanakkale Province Headlands of Turkey, Gelibolu Peninsulas of Turkey Tourist attractions in Çanakkale Province Territories of the Republic of Venice World Heritage Tentative List for Turkey Places of the Greek genocide