Fujian Expwy S10 sign no name.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a
 After Liu's death, the circuit was briefly ruled by his biological nephew/adoptive son Liu Shaozi, who was then overthrown by the officers
After Liu's death, the circuit was briefly ruled by his biological nephew/adoptive son Liu Shaozi, who was then overthrown by the officers

 The province is mostly mountainous and is traditionally said to be "eight parts mountain, one part water, and one part farmland" (). The northwest is higher in altitude, with the
The province is mostly mountainous and is traditionally said to be "eight parts mountain, one part water, and one part farmland" (). The northwest is higher in altitude, with the
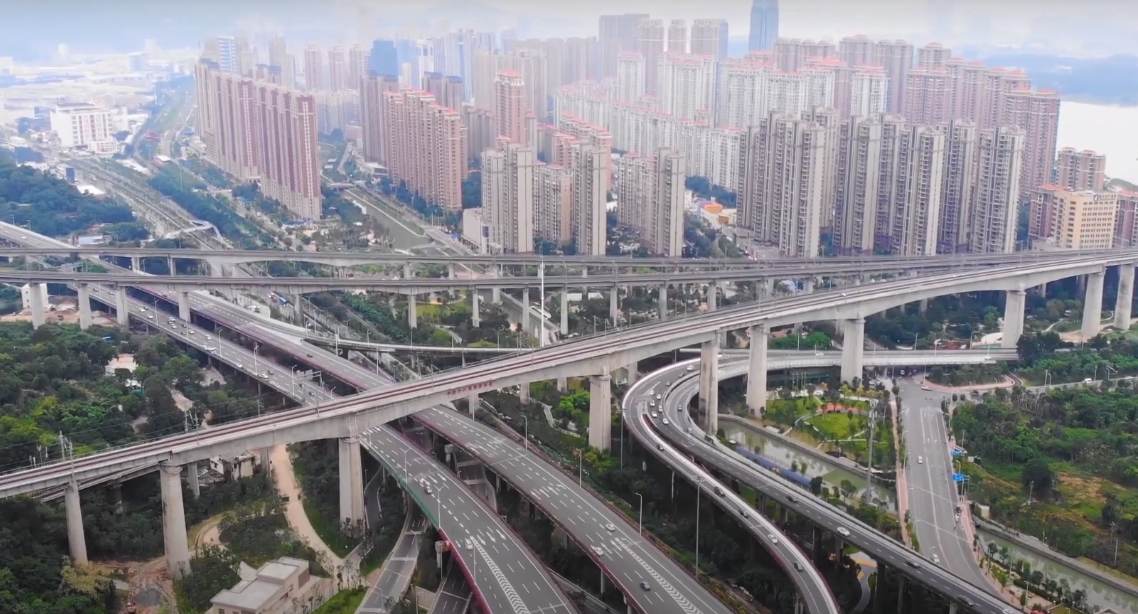 , there are of highways in Fujian, including of expressways. The top infrastructure projects in recent years have been the Zhangzhou-Zhaoan Expressway (US$624 million) and the Sanmingshi-Fuzhou expressway (US$1.40 billion). The 12th Five-Year Plan, covering the period from 2011 to 2015, aims to double the length of the province's expressways to .
, there are of highways in Fujian, including of expressways. The top infrastructure projects in recent years have been the Zhangzhou-Zhaoan Expressway (US$624 million) and the Sanmingshi-Fuzhou expressway (US$1.40 billion). The 12th Five-Year Plan, covering the period from 2011 to 2015, aims to double the length of the province's expressways to .
 Due to Fujian's mountainous terrain and traditional reliance on maritime transportation, railways came to the province comparatively late. The first rail links to neighboring
Due to Fujian's mountainous terrain and traditional reliance on maritime transportation, railways came to the province comparatively late. The first rail links to neighboring
 Fujian is one of the more affluent provinces with many industries spanning tea production, clothing, and sports manufacturers such as Anta, 361 Degrees,
Fujian is one of the more affluent provinces with many industries spanning tea production, clothing, and sports manufacturers such as Anta, 361 Degrees,
 *Dongshan Economic and Technology Development Zone
* Fuzhou Economic & Technical Development Zone
* Fuzhou Free Trade Zone
* Fuzhou Hi-Tech Park
* Fuzhou Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
* Jimei Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
*
*Dongshan Economic and Technology Development Zone
* Fuzhou Economic & Technical Development Zone
* Fuzhou Free Trade Zone
* Fuzhou Hi-Tech Park
* Fuzhou Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
* Jimei Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
*
 As of 1832, the province was described as having an estimated "population of fourteen millions."
Fujianese who are legally classified as
As of 1832, the province was described as having an estimated "population of fourteen millions."
Fujianese who are legally classified as

 Because of its mountainous nature and waves of migration from central China and assimilation of numerous foreign ethnic groups such as maritime traders in the course of history, Fujian is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse places in China. Local dialects can become unintelligible within , and the regional cultures and ethnic composition can be completely different from each other as well. This is reflected in the expression that "if you drive five miles in Fujian the culture changes, and if you drive ten miles, the language does".French, Howard W.
Because of its mountainous nature and waves of migration from central China and assimilation of numerous foreign ethnic groups such as maritime traders in the course of history, Fujian is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse places in China. Local dialects can become unintelligible within , and the regional cultures and ethnic composition can be completely different from each other as well. This is reflected in the expression that "if you drive five miles in Fujian the culture changes, and if you drive ten miles, the language does".French, Howard W.
Uniting China to Speak Mandarin, the One Official Language: Easier Said Than Done
." ''

 Fujian is home to several tourist attractions, including four UNESCO World Heritage Sites, one of the highest in China.
In the capital of Fuzhou is the Yongquan Temple, a Buddhist temple built during the
Fujian is home to several tourist attractions, including four UNESCO World Heritage Sites, one of the highest in China.
In the capital of Fuzhou is the Yongquan Temple, a Buddhist temple built during the
Economic profile for Fujian
Complete Map of the Seven Coastal Provinces
from 1821 to 1850 {{Authority control Provinces of the People's Republic of China East China
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
to the north, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
to the west, Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
to the south, and the Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait is a -wide strait separating the island of Taiwan and continental Asia. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. The narrowest part is wide.
The Taiwan Strait is itself a ...
to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou, while its largest city by population is Quanzhou, both located near the coast of the Taiwan Strait in the east of the province.
While its population is predominantly of Chinese ethnicity, it is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse provinces in China. The dialects of the language group Min Chinese were most commonly spoken within the province, including the Fuzhou dialect
Fuzhou (; , Fuzhounese: Hokchew, ''Hók-ciŭ''), alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute ...
of northeastern Fujian and various Hokkien
The Hokkien () variety of Chinese is a Southern Min language native to and originating from the Minnan region, where it is widely spoken in the south-eastern part of Fujian in southeastern mainland China. It is one of the national languages ...
dialects of southeastern Fujian. Hakka Chinese
Hakka (, , ) forms a language group of varieties of Chinese, spoken natively by the Hakka people throughout Southern China and Taiwan and throughout the diaspora areas of East Asia, Southeast Asia and in overseas Chinese communities aroun ...
is also spoken, by the Hakka people
The Hakka (), sometimes also referred to as Hakka Han, or Hakka Chinese, or Hakkas are a Han Chinese subgroup whose ancestral homes are chiefly in the Hakka-speaking provincial areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hunan, Zhej ...
in Fujian. Min dialects, Hakka and Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language ...
are mutually unintelligible. Due to emigration, a sizable amount of the ethnic Chinese populations of Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Philippines speak Southern Min (or Hokkien).
With a population of 41.5 million, Fujian ranks 15th in population among Chinese provinces. As of 2021, Fujian's GDP (nominal)
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
reached 768 billion US dollars ( CNY 4.88 trillion), ranking 4th in East China
East China () is a geographical and a loosely defined cultural region that covers the eastern coastal area of China.
A concept abolished in 1978, for economical purposes the region was defined from 1949 to 1961 by the Chinese Central Govern ...
region and 8th
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ...
nationwide in GDP. Fujian's GDP per capita is above the national average, at CN¥117,500 (approx.US$28,658 in PPP), the second highest GDP per capita of all Chinese provinces after Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its ca ...
. It has benefited from its geographical proximity with Taiwan. As a result of the Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on m ...
, a small proportion of Historical Fujian is now within the Republic of China (ROC, Taiwan). The Fujian province of the ROC consist of three offshore archipelagos namely the Kinmen Islands, the Matsu Islands
The Matsu Islands ( or , ; Foochow Romanized: Mā-cū liĕk-dō̤), officially Lienchiang County (, ; Foochow Romanized: Lièng-gŏng-gâing), are an archipelago of 36 islands and islets in the East China Sea governed by the Republic of China ( ...
and the Wuqiu Islands.
Fujian is considered one of China's leading provinces in education and research. As of 2022, two major cities ranked in the top 65 cities in the world (Fuzhou 50th and Xiamen 63rd) by scientific research output, as tracked by the Nature Index The Nature Index is a database that tracks institutions and countries and their scientific output since its introduction in November, 2014. Each year, Nature Index ranks the leading institutions (which can be companies, universities, government agen ...
.
Name
The name ''Fujian'' (福建) originated from the combination of the city names of Fuzhou (福州) and nearby Jianzhou (建州 present-dayNanping
Nanping (), historically known as Yanping (), is a third-tier prefecture-level city in northwestern Fujian Province, People's Republic of China. It borders Ningde to the east, Sanming to the south, and the provinces of Zhejiang and Jiangxi to ...
(南平)).
History
Prehistoric Fujian
Recent archaeological discoveries in 2011 demonstrate that Fujian had entered theNeolithic Age
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
by the middle of the 6th millennium BC. From the Keqiutou site (7450–5590 BP), an early Neolithic site in Pingtan Island
Pingtan Island or Haitan Island is an island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be c ...
located about southeast of Fuzhou, numerous tools made of stones, shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
s, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s, jades, and ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
s (including wheel-made ceramics) have been unearthed, together with spinning wheel
A spinning wheel is a device for spinning thread or yarn from fibres. It was fundamental to the cotton textile industry prior to the Industrial Revolution. It laid the foundations for later machinery such as the spinning jenny and spinning f ...
s, which is definitive evidence of weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal ...
.
The Tanshishan () site (5500–4000 BP) in suburban Fuzhou spans the Neolithic and Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
Age where semi-underground circular buildings were found in the lower level. The Huangtulun () site (ca.1325 BC), also in suburban Fuzhou, was of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
in character.
Tianlong Jiao (2013)Jiao, Tianlong. 2013. "The Neolithic Archaeology of Southeast China." In Underhill, Anne P., et al. ''A Companion to Chinese Archaeology'', 599-611. Wiley-Blackwell. notes that the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
appeared on the coast of Fujian around 6,000 B.P. During the Neolithic, the coast of Fujian had a low population density, with the population depending on mostly on fishing and hunting, along with limited agriculture.
There were four major Neolithic cultures in coastal Fujian, with the earliest Neolithic cultures originating from the north in coastal Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
.
*Keqiutou culture (; c. 6000–5500 BP, or c. 4050–3550 BC)
*Tanshishan culture (; c. 5000–4300 BP, or c. 3050–2350 BC)
*Damaoshan culture (; c. 5000–4300 BP)
*Huangguashan culture (; c. 4300–3500 BP, or c. 2350–1550 BC)
There were two major Neolithic cultures in inland Fujian, which were highly distinct from the coastal Fujian Neolithic cultures. These are the Niubishan culture () from 5000 to 4000 years ago, and the Hulushan culture () from 2050 to 1550 BC.
Minyue kingdom
Fujian was also where the kingdom ofMinyue
Minyue () was an ancient kingdom in what is now the Fujian province in southern China. It was a contemporary of the Han dynasty, and was later annexed by the Han empire as the dynasty expanded southward. The kingdom existed approximately from ...
was located. The word "Mǐnyuè" was derived by combining "Mǐn" (), which is perhaps an ethnic name (), and " Yuè", after the State of Yue
Yue (, Old Chinese: ''*''), also known as Yuyue (), was a state in ancient China which existed during the first millennium BC the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods of China's Zhou dynasty in the modern provinces of Zhejiang, Sha ...
, a Spring and Autumn period kingdom in Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
to the north. This is because the royal family of Yuè fled to Fujian after its kingdom was annexed by the State of Chu in 306 BC. Mǐn is also the name of the main river
Main rivers () are a statutory type of watercourse in England and Wales, usually larger streams and rivers, but also some smaller watercourses. A main river is designated by being marked as such on a main river map, and can include any structure o ...
in this area, but the ethnonym is probably older.
Qin dynasty
The Qin deposed the King of Minyue, establishing instead a paramilitary province there called Minzhong Commandery. Minyue was a ''de facto'' kingdom until one of the emperors of theQin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), ...
, the first unified imperial Chinese state, abolished its status.Britannica
Han dynasty
In the aftermath of the Qin dynasty's fall,civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
broke out between two warlords, Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, –202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: 霸王, ''Bà Wáng'') of Western Chu during the Chu–Han Contention period (206–202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dyna ...
and Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Empe ...
. The Minyue king Wuzhu sent his troops to fight with Liu and his gamble paid off. Liu was victorious and founded the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
. In 202 BC, he restored Minyue's status as a tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drai ...
independent kingdom. Thus Wuzhu was allowed to construct his fortified city in Fuzhou as well as a few locations in the Wuyi Mountains
The Wuyi Mountains or Wuyishan (; formerly known as Bohea Hills in early Western documents) are a mountain range located in the prefecture of Nanping, in northern Fujian province near the border with Jiangxi province, China. The highest peak in ...
, which have been excavated in recent years. His kingdom extended beyond the borders of contemporary Fujian into eastern Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
, eastern Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
, and southern Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
.
After Wuzhu's death, Minyue maintained its militant tradition and launched several expeditions against its neighboring kingdoms in Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
, and Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
, primarily in the 2nd century BC. This was stopped by the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
as it expanded southward. The Han emperor eventually decided to get rid of the potential threat by launching a military campaign against Minyue. Large forces approached Minyue simultaneously from four directions via land and sea in 111 BC. The rulers in Fuzhou surrendered to avoid a futile fight and destruction and the first kingdom in Fujian history came to an abrupt end.
Fujian was part of the much larger Yang Province
Yangzhou, Yangchow or Yang Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China mentioned in historical texts such as the ''Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'' and '' Rites of Zhou''.
Name
There are four different theories regarding the origin of t ...
(Yangzhou), whose provincial capital was designated in Liyang (歷陽; present-day He County, Anhui).
The Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
collapsed at the end of the 2nd century AD, paving the way for the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the West ...
era. Sun Quan, the founder of the Kingdom of Wu, spent nearly 20 years subduing the Shan Yue people, the branch of the Yue living in mountains.
Jin era
The first wave ofimmigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
of the noble class arrived in the province in the early 4th century when the Western Jin dynasty
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that i ...
collapsed and the north was torn apart by invasions by nomadic peoples from the north, as well as a civil war. These immigrants were primarily from eight families in central China
Central China () is a geographical and a loosely defined cultural region that includes the provinces of Henan, Hubei and Hunan. Jiangxi is sometimes also regarded to be part of this region. Central China is now officially part of South Centra ...
:
Nevertheless, isolation from nearby areas owing to rugged terrain contributed to Fujian's relatively undeveloped economy and level of development, despite major population boosts from northern China during the "barbarian" invasions. The population density in Fujian remained low compared to the rest of China. Only two commanderies and sixteen counties were established by the Western Jin dynasty. Like other southern provinces such as Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
, Guangxi, Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
, and Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, Fujian often served as a destination for exiled prisoners and dissidents at that time.
During the Southern and Northern Dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered as ...
era, the Southern Dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered as ...
(Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern Dynasty (南朝宋) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. ...
, Southern Qi, Liang ( Western Liang), and Chen) reigned south of the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
, including Fujian.
Sui and Tang dynasties
During the Sui andTang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) b ...
eras a large influx of migrants settled in Fujian.
During the Sui dynasty, Fujian was again part of Yang Province
Yangzhou, Yangchow or Yang Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China mentioned in historical texts such as the ''Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'' and '' Rites of Zhou''.
Name
There are four different theories regarding the origin of t ...
.
During the Tang, Fujian was part of the larger Jiangnan East Circuit
The Tang dynasty of China administered territory using a hierarchical system of three descending divisions: circuits (''dào'' 道), prefectures (''zhōu'' 州), and counties (''xiàn'' 縣). Prefectures have been called ''jùn'' (郡) as well ...
, whose capital was at Suzhou. Modern-day Fujian was composed of around 5 prefectures and 25 counties.
The Tang dynasty (618–907) oversaw the next golden age of China, which contributed to a boom in Fujian's culture and economy. Fuzhou's economic and cultural institutions grew and developed. The later years of the Tang dynasty saw several political upheavals in the Chinese heartland, prompting even larger waves of northerners to immigrate to the northern part of Fujian.
Five Dynasties Ten Kingdoms
As the Tang dynasty ended, China was torn apart in the period of theFive Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concu ...
. During this time, a second major wave of immigration arrived in the safe haven of Fujian, led by General Wang, who set up an independent Kingdom of Min with its capital in Fuzhou. After the death of the founding king, however, the kingdom suffered from internal strife, and was soon absorbed by Southern Tang
Southern Tang () was a state in Southern China that existed during Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, which proclaimed itself to be the successor of the former Tang dynasty. The capital was located at Nanjing in present-day Jiangsu Province. ...
, another southern kingdom.
Parts of northern Fujian were conquered by the Wuyue Kingdom to the north as well, including the Min capital Fuzhou.
Quanzhou city was blooming into a seaport under the reign of the Min Kingdom
Min () was one of the Ten Kingdoms which was in existence between the years of 909 and 945. It existed in a mountainous region of modern-day Fujian province of China and had a history of quasi-independent rule. Its capital was Fuzhou. It was fou ...
and was the largest seaport in the world. For a long period its population was also greater than Fuzhou.
''Qingyuan Jiedushi
''Qingyuan Jiedushi'' () (i.e., the ''Jiedushi'' of Qingyuan Circuit) was a military/governance administrative unit ( circuit) late in China's Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, later renamed to ''Pinghai Jiedushi'' (). It was an office cre ...
'' was a military/governance office created in 949 by Southern Tang
Southern Tang () was a state in Southern China that existed during Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, which proclaimed itself to be the successor of the former Tang dynasty. The capital was located at Nanjing in present-day Jiangsu Province. ...
's second emperor Li Jing for the warlord Liu Congxiao Liu Congxiao (; 906-962), formally the Prince of Jinjiang (), was a general of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period state Min. After Min's fall, he initially submitted to Southern Tang (which had conquered Min), but eventually, takin ...
, who nominally submitted to him but controlled Quan (, in modern Quanzhou, Fujian) and Zhang (, in modern Zhangzhou
Zhangzhou (), alternately romanized as Changchow, is a prefecture-level city in Fujian Province, China. The prefecture around the city proper comprises the southeast corner of the province, facing the Taiwan Strait and surrounding the prefect ...
, Fujian) Prefectures in ''de facto'' independence from the Southern Tang state.''Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song (960–1127), Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959&n ...
'', vol. 288. (Zhang Prefecture was, at times during the circuit's existence, also known as Nan Prefecture ().)'' History of Song'', vol. 483. Starting in 960, in addition to being nominally submissive to Southern Tang, Qingyuan Circuit was also nominally submissive to Song
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetit ...
, which had itself become Southern Tang's nominal overlord.''Xu Zizhi Tongjian
''Xu Zizhi Tongjian'' (續資治通鑑; "Continuation to ''Zizhi Tongjian''") was a book chronicling Chinese history of the Song dynasty between 960 and 1279 and the Yuan dynasty between 1279 and 1370. Credited to Bi Yuan (畢沅; 1730–1797), a ...
'', vol. 1.
 After Liu's death, the circuit was briefly ruled by his biological nephew/adoptive son Liu Shaozi, who was then overthrown by the officers
After Liu's death, the circuit was briefly ruled by his biological nephew/adoptive son Liu Shaozi, who was then overthrown by the officers Zhang Hansi Zhang Hansi (張漢思) was a military officer of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period state Min (Ten Kingdoms), Min. After Min's fall, he served under Liu Congxiao, who controlled Qingyuan Jiedushi, Qingyuan Circuit (headquartered in ...
and Chen Hongjin. Zhang then ruled the circuit briefly, before Chen deposed him and took over. In 978, with Song's determination to unify Chinese lands in full order, Chen decided that he could not stay ''de facto'' independent, and offered the control of the circuit to Song's Emperor Taizong, ending Qingyuan Circuit as a ''de facto'' independent entity.''Xu Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 9.
Song dynasty
The area was reorganized into theFujian Circuit
Fujian Circuit, also translated as Fujian Province, was one of the major circuits during the Tang and Song dynasties of imperial China. Its administrative area corresponds to roughly the modern Chinese province of Fujian.
History
The Tang-era ...
in 985, which was the first time the name "Fujian" was used for an administrative region.
Vietnam
Many Chinese migrated from Fujian's major ports to Vietnam'sRed River Delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
. The settlers then created Trần port and Vân Đồn. Fujian and Guangdong Chinese moved to the Vân Đồn coastal port to engage in commerce.
During the Lý and Trần dynasties, many Chinese ethnic groups with the surname Trần (陳) migrated to Vietnam from what is now Fujian or Guangxi. They settled along the coast of Vietnam and the capital's southeastern area. The Vietnamese Trần clan traces their ancestry to Trần Tự Minh (227 BC). He was a Qin General during the Warring state period who belonged to the indigenous Mân, a Baiyue ethnic group of Southern China and Northern Vietnam. Tự Minh also served under King An Dương Vương of Âu Lạc
Âu Lạc ( Hán tự: 甌貉 (Peripheral Records/Volume 1:6a): "王既併文郎國,改國號曰甌貉國。""The King then annexed the Văn Lang nation, changed the nation's name to Âu Lạc nation."/甌駱; (Volume 113): "且南方卑濕, ...
kingdom in resisting Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (秦), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (秦), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (大秦), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
's conquest of Âu Lạc. Their genealogy also included Trần Tự Viễn (582 - 637) of Giao Châu and Trần Tự An (1010 - 1077) of Đại Việt. Near the end of the 11th century the descendants of a fisherman named Trần Kinh, whose hometown was in Tức Mạc village in Đại Việt (Modern day Vietnam), would marry the royal Lý clan, which was then founded the Vietnam Tran Dynasty in the year 1225.
In Vietnam, the Trần served as officials. The surnames are found in the Trần and Lý dynasty Imperial exam records. Chinese ethnic groups are recorded in Trần and Lý dynasty records of officials. Clothing, food, and languages were fused with the local Vietnamese in Vân Đồn district where the Chinese ethnic groups had moved after leaving their home province of what is now Fujian, Guangxi, and Guangdong.
In 1172, Fujian was attacked by Pi-she-ye pirates from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
or the Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, ...
, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
.
Yuan dynasty
After the establishment of theYuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fift ...
, Fujian became part of Jiangzhe province
Jiangzhe province () or Chiangche was a province of the Yuan dynasty established in 1276. It included the southern portion of Jiangsu south of the Yangtze River, Zhejiang, Fujian, modern-day Penghu of Taiwan Province and part of northern Guangdo ...
, whose capital was at Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
. From 1357 to 1366 Muslims in Quanzhou participated in the Ispah Rebellion
The Ispah rebellion () were a series of civil wars in the middle of 14th century in Fujian during the Yuan dynasty. The term Ispah might derive from the Persian word "سپاه" (''sepâh''), meaning "army" or " Sepoy". Thus, the rebellion is also ...
, advancing northward and even capturing Putian and Fuzhou before the rebellion was crushed by the Yuan. Afterward, Quanzhou city lost foreign interest in trading and its formerly welcoming international image as the foreigners were all massacred or deported.
Yuan dynasty General Chen Youding, who had put down the Ispah Rebellion, continued to rule over the Fujian area even after the outbreak of the Red Turban Rebellion. Forces loyal to the eventual Ming dynasty founder Zhu Yuanzhang
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328 – 24 June 1398), personal name Zhu Yuanzhang (), courtesy name Guorui (), was the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty of China, reigning from 1368 to 1398.
As famine, plagues and peasant revolts i ...
(Hongwu Emperor) defeated Chen in 1367.
Ming dynasty
After the establishment of theMing dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
, Fujian became a province, with its capital at Fuzhou. In the early Ming era, Fuzhou Changle was the staging area and supply depot of Zheng He
Zheng He (; 1371–1433 or 1435) was a Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat, fleet admiral, and court eunuch during China's early Ming dynasty. He was originally born as Ma He in a Muslim family and later adopted the surname Zheng conferr ...
's naval expeditions. Further development was severely hampered by the sea trade ban, and the area was superseded by nearby ports of Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
, Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
, Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
and Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
despite the lifting of the ban in 1550. Large-scale piracy by Wokou
''Wokou'' (; Japanese: ''Wakō''; Korean: 왜구 ''Waegu''), which literally translates to "Japanese pirates" or "dwarf pirates", were pirates who raided the coastlines of China and Korea from the 13th century to the 16th century.
was eventually wiped out by the Chinese military.
An account of the Ming dynasty Fujian was written by No In (Lu Ren ).
The Pisheya appear in Quanzhou Ming era records.
Qing dynasty
The late Ming and earlyQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
symbolized an era of a large influx of refugees and another 20 years of sea trade ban under the Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to ...
, a measure intended to counter the refuge Ming government of Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
in the island of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country located in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, formerly known in the Western political circles, press and literature as Formosa, makes up 99% of the land area of the territori ...
.
The sea ban implemented by the Qing forced many people to evacuate the coast to deprive Koxinga's Ming loyalists of resources. This has led to the myth that it was because Manchus were "afraid of water".
Incoming refugees did not translate into a major labor force, owing to their re-migration into prosperous regions of Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
. In 1683, the Qing dynasty conquered Taiwan in the Battle of Penghu
The Battle of Penghu () was a naval battle fought in 1683 between the Qing dynasty and the Kingdom of Tungning. The Qing admiral Shi Lang led a fleet to attack the Tungning forces in Penghu. Each side possessed more than 200 warships. The Tungn ...
and annexed it into the Fujian province, as Taiwan Prefecture
Taiwan Prefecture or Taiwanfu was a prefecture of Taiwan during the Qing dynasty. The prefecture was established by the Qing government in 1684, after the island came under Qing dynasty rule in 1683 following its conquest of the Kingdom of Tungnin ...
. Many more Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
then settled in Taiwan. Today, most Taiwanese are descendants of Hokkien people
The Hoklo people or Hokkien people () are a Han Chinese (also Han Taiwanese) subgroup who speak Hokkien, a Southern Min language, or trace their ancestry to Southeastern Fujian, China and known by various endonyms or other related terms such a ...
from Southern Fujian. Fujian and Taiwan were originally treated as one province (Fujian-Taiwan-Province
Taiwan Province (; PFS: ''Thòi-vàn-sén'' or ''Thòi-vân-sén'') is a nominal administrative division of the Republic of China (ROC). Its definition has remained part of the Constitution of the Republic of China, but the province is no lon ...
), but starting in 1885, they split into two separate provinces.
In the 1890s, the Qing ceded Taiwan to Japan via the Treaty of Shimonoseki
The , also known as the Treaty of Maguan () in China and in the period before and during World War II in Japan, was a treaty signed at the , Shimonoseki, Japan on April 17, 1895, between the Empire of Japan and Qing China, ending the Firs ...
after the First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the ...
. In 1905-1907 Japan made overtures to enlarge its sphere of influence to include Fujian. Japan was trying to obtain French loans and also avoid the Open Door Policy
The Open Door Policy () is the United States diplomatic policy established in the late 19th and early 20th century that called for a system of equal trade and investment and to guarantee the territorial integrity of Qing China. The policy wa ...
. Paris provided loans on condition that Japan respects the Open Door principles and does not violate China's territorial integrity.
Republic of China
TheXinhai revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a ...
overthrew the Qing dynasty and brought the province into the rule of the Republic of China.
Fujian briefly established the independent Fujian People's Government
The Fujian People's Government (or spelled as the Fukien People's Government) is the common name for the People's Revolutionary Government of the Republic of China (1933–1934) (), also known as the Fujian People's Government (), was a s ...
in 1933. It was re-controlled by the Republic of China in 1934.
Fujian came under a Japanese sea blockade during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
People's Republic of China
After theChinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on m ...
, the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
unified the country and took over most of Fujian, excluding the Quemoy
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), off the southeastern coast of mainland China. It lies roughly east of the city of Xiamen in Fujian, from which it is separate ...
and Matsu Islands.
In its early days, Fujian's development was relatively slow in comparison to other coastal provinces due to potential conflicts with Kuomintang-controlled Taiwan. Today, the province has the highest forest coverage rate while enjoying a high growth rate in the economy. The GDP per capita in Fujian is ranked 4-6th place among provinces of China in recent years.
Development has been accompanied by a large influx of population from the overpopulated areas to Fujian's north and west, and much of the farmland and forest, as well as cultural heritage sites such as the temples of king Wuzhu, have given way to ubiquitous high-rise buildings. Fujian faces challenges to sustain development while at the same time preserving Fujian's natural and cultural heritage.
Geography

Wuyi Mountains
The Wuyi Mountains or Wuyishan (; formerly known as Bohea Hills in early Western documents) are a mountain range located in the prefecture of Nanping, in northern Fujian province near the border with Jiangxi province, China. The highest peak in ...
forming the border between Fujian and Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
. It is the most forested provincial-level administrative region in China, with a 62.96% forest coverage rate in 2009. Fujian's highest point is Mount Huanggang
Mount Huanggang () is the highest peak in the UNESCO designated Wuyi Mountains, China. It separates and is the highest point of both Fujian and Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in th ...
in the Wuyi Mountains, with an altitude of .
Fujian faces East China Sea to the east, South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phi ...
to the south, and the Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait is a -wide strait separating the island of Taiwan and continental Asia. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. The narrowest part is wide.
The Taiwan Strait is itself a ...
to the southeast. The coastline is rugged and has many bays and islands. Major islands include Quemoy
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), off the southeastern coast of mainland China. It lies roughly east of the city of Xiamen in Fujian, from which it is separate ...
(also known as Kinmen, controlled by the Republic of China), Haitan Island, and Nanri Island
Nanri Island (Chinese: ), Nanjisü, Nanjih, historically known as Nanni Shan () and Nanri Shan (), is a small island off the coast of China. Nanri Town () is an administrative unit of Xiuyu District, Putian, Fujian, People's Republic of China whi ...
. Meizhou Island
Meizhou Island (; Pu-Xian Min: ''Mî-ciu-doh''), Meichow; Meichou, is a small island close to the coast of China. Meizhou Town () is an administrative unit of Xiuyu District, Putian, Fujian, China. It is known for being the birthplace of the go ...
occupies a central place in the cult of the goddess Matsu, the patron deity of Chinese sailors.
The Min River and its tributaries cut through much of northern and central Fujian. Other rivers include the Jin and the Jiulong. Due to its uneven topography, Fujian has many cliffs and rapids.
Fujian is separated from Taiwan by the -wide Taiwan Strait. Some of the small islands in the Taiwan Strait are also part of the province. The islands of Kinmen
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), off the southeastern coast of mainland China. It lies roughly east of the city of Xiamen in Fujian, from which it is separat ...
and Matsu are under the administration of the Republic of China.
Fujian contains several faults, the result of a collision between the Asiatic Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate
The Philippine Sea Plate or the Philippine Plate is a tectonic plate comprising oceanic lithosphere that lies beneath the Philippine Sea, to the east of the Philippines. Most segments of the Philippines, including northern Luzon, are part o ...
. The Changle-Naoao and Longan-Jinjiang fault zones in this area have annual displacement rates of 3–5 mm. They could cause major earthquakes in the future.
Fujian has a subtropical climate, with mild winters. In January, the coastal regions average around while the hills average . In the summer, temperatures are high, and the province is threatened by typhoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
s coming in from the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
. Average annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
is .
Transportation
Roads
 , there are of highways in Fujian, including of expressways. The top infrastructure projects in recent years have been the Zhangzhou-Zhaoan Expressway (US$624 million) and the Sanmingshi-Fuzhou expressway (US$1.40 billion). The 12th Five-Year Plan, covering the period from 2011 to 2015, aims to double the length of the province's expressways to .
, there are of highways in Fujian, including of expressways. The top infrastructure projects in recent years have been the Zhangzhou-Zhaoan Expressway (US$624 million) and the Sanmingshi-Fuzhou expressway (US$1.40 billion). The 12th Five-Year Plan, covering the period from 2011 to 2015, aims to double the length of the province's expressways to .
Railways
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
, Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
, and Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
Province, opened respectively, in 1959, 2000, and 2009. As of October 2013, Fujian has four rail links with Jiangxi to the northwest: the Yingtan–Xiamen Railway (opened 1957), the Hengfeng–Nanping Railway (1998), Ganzhou–Longyan Railway
The Ganzhou–Longyan railway or Ganlong railway () is a railway connecting Jiangxi and Fujian Provinces, in southeastern China. The line is named after its two terminal cities Ganzhou and Longyan, and has a total length of . Construction bega ...
(2005) and the high-speed Xiangtang–Putian Railway (2013). Fujian's lone rail link to Guangdong to the west, the Zhangping–Longchuan Railway (2000), will be joined with the high-speed Xiamen–Shenzhen Railway (Xiashen Line) in late 2013. The Xiashen Line forms the southernmost section of China's Southeast Coast High-Speed Rail Corridor
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
. The Wenzhou–Fuzhou and Fuzhou–Xiamen sections of this corridor entered operation in 2009 and link Fujian with Zhejiang with trains running at speeds of up to .
Within Fujian, coastal and interior cities are linked by the Nanping–Fuzhou (1959), Zhangping–Quanzhou–Xiaocuo (2007) and Longyan–Xiamen Railway
The Longyan–Xiamen railway () is a dual-track, electrified, high-speed rail line in Fujian Province, China. The line, also known as the Longxia railway, is named after its two terminal cities Longyan and Xiamen, and has a total length of .
s, (2012). To attract Taiwanese investment, the province intends to increase its rail length by 50 percent to .
Air
The major airports areFuzhou Changle International Airport
Fuzhou Changle International Airport is an international airport serving Fuzhou, the capital of Fujian province, China. The airport was inaugurated on 23 June 1997, after being approved to start constructing in 1992. The current handling ca ...
, Xiamen Gaoqi International Airport
Xiamen Gaoqi International Airport is the airport serving the city of Xiamen in Fujian Province, China. It is the main base of XiamenAir and TAECO, an aircraft maintenance provider. The airport is located on the north side of Xiamen Island ...
, Quanzhou Jinjiang International Airport
Quanzhou Jinjiang International Airport is a dual-use military and public airport serving the city of Quanzhou in Fujian, China. It is located 12 kilometers south of the city center, in the county-level city of Jinjiang, which is under the adm ...
, Nanping Wuyishan Airport
Nanping (), historically known as Yanping (), is a third-tier prefecture-level city in northwestern Fujian Province, People's Republic of China. It borders Ningde to the east, Sanming to the south, and the provinces of Zhejiang and Jiangxi to t ...
, Longyan Guanzhishan Airport and Sanming Shaxian Airport
Sanming Shaxian Airport is an airport serving the city of Sanming in Fujian Province, China. It is located in Fenggang Subdistrict of Shaxian District. The airport was opened on 7 March 2016.
History
Construction of Sanming Airport was first ...
. Xiamen is capable of handling 15.75 million passengers as of 2011. Fuzhou is capable of handling 6.5 million passengers annually with a cargo capacity of more than 200,000 tons. The airport offers direct links to 45 destinations including international routes to Japan, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, and Hong Kong.
Administrative divisions
ThePeople's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
controls most of the province and divides it into nine prefecture-level division
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there a ...
s: all prefecture-level cities
A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure.
During the Republican era, many of China' ...
(including a sub-provincial city):
All of the prefecture-level cities except Nanping, Sanming, and Longyan are found along the coast.
These nine prefecture-level cities are subdivided into 85 county-level division
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there ...
s (28 district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
s, 13 county-level cities
A county-level municipality (), county-level city or county city, formerly known as prefecture-controlled city (1949–1970: ; 1970–1983: ), is a county-level administrative division of the People's Republic of China. County-level ...
, and 44 counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
). Those are in turn divided into 1,107 township-level divisions
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there ...
(605 town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
s, 328 township
A township is a kind of human settlement or administrative subdivision, with its meaning varying in different countries.
Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, that tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, C ...
s, 18 ethnic township
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often voc ...
s, and 156 subdistricts).
The People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
claims five of the six townships of Kinmen County, Republic of China (Taiwan) as a county of the prefecture-level city of Quanzhou.
The PRC claims Wuqiu Township, Kinmen County, Republic of China (Taiwan) as part of Xiuyu District
Xiuyu District () is a district of the city of Putian, Fujian, People's Republic of China. The district executive, legislature and judiciary are in Hushi Town (), together with the CPC and PSB branches.
History
In October 1952, PRC and ROC fo ...
of the prefecture-level city of Putian.
Finally, the PRC claims Lienchiang County
The Matsu Islands ( or , ; Foochow Romanized: Mā-cū liĕk-dō̤), officially Lienchiang County (, ; Foochow Romanized: Lièng-gŏng-gâing), are an archipelago of 36 islands and islets in the East China Sea governed by the Republic of China ( ...
(Matsu Islands), Republic of China (Taiwan) as a township of its Lianjiang County
Lianjiang (; BUC: Lièng-gŏng) is a county on the eastern coast in Fuzhou prefecture-level city, the provincial capital of Fujian Province, China. Most of the county is administered by the People's Republic of China (PRC), while a number of ...
, which is part of the prefecture-level city of Fuzhou.
Together, these three groups of islands make up the Republic of China's Fujian Province.
Urban areas
Politics
List of provincial-level leaders
CCP Party Secretaries
#Zhang Dingcheng
Zhang Dingcheng (; December 1898 – December 16, 1981) was a politician of the People's Republic of China, Procurator–General of the Supreme People's Procuratorate from 1954 to 1975.
(): 1949-1954
#Ye Fei
Ye Fei (; 7 May 1914 – 18 April 1999) was a Philippine-born Chinese military general and politician of the People's Republic of China. Born Sixto Mercado Tiongco in the Philippines to a Chinese father and a Filipino mother, he joined the Ch ...
(): 1954-1958
#Jiang Yizhen
Jiang Yizhen (; March 1915 – March 24, 1994) was a People's Republic of China politician. He was born in Liancheng County, Fujian. He was Chinese Communist Party Committee Secretary and Governor of his home province. He was People's Congres ...
(): 1958-1970
#Han Xianchu
Han Xianchu (; 1913–1986) was a general of the Chinese Communist Party. Han participated in many military campaigns and battles such as Battle of Pingxingguan, Liaoshen Campaign, Pingjin Campaign, Hainan Campaign, and the Korean War. In 195 ...
(): 1971-1973
# Liao Zhigao (): 1974-1982
# Xiang Nan (): 1982-1986
#Chen Guangyi
Chen Guangyi (; born August 1933) was a Chinese politician. He served as Governor of Gansu Province, Communist Party Secretary of Fujian Province, and Director of the Civil Aviation Administration of China. Under his leadership, Fujian achieved ...
(): 1986-1993
#Jia Qinglin
Jia Qinglin (; born 13 March 1940) is a retired senior leader of the People's Republic of China and of the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP). He was a member of the CCP's Politburo Standing Committee, the party's highest ruling organ, between ...
(): 1993-1996
# Chen Mingyi (): 1996-2000
# Song Defu (): 2000-2004
#Lu Zhangong
Lu Zhangong (; born May 1952) is a Chinese politician. He is, since 2013, a Vice Chairman of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, and previously served as the Communist Party Secretary of Fujian and Henan provinces, and Gover ...
(): 2004-2009
# Sun Chunlan (): 2009-2012
#You Quan
You Quan (; born January 1954) is a Chinese politician who is the former director of the United Front Work Department and a former secretary of the Secretariat of the Chinese Communist Party. He previously served as Communist Party Secretary of F ...
(): 2012-2017
# Yu Weiguo (): 2017-2020
# Yin Li (): 2020-2022
#Zhou Zuyi
Zhou Zuyi (; born January 1965) is a Chinese politician who is the current Communist Party Secretary of Fujian and the Minister of Human Resources and Social Security. He is a member of the 20th Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party. ...
(): 2022-present
Chairpersons of Fujian People's Congress
# Liao Zhigao (): 1979-1982 #Hu Hong (): 1982-1985 #Cheng Xu (): 1985-1993 #Chen Guangyi
Chen Guangyi (; born August 1933) was a Chinese politician. He served as Governor of Gansu Province, Communist Party Secretary of Fujian Province, and Director of the Civil Aviation Administration of China. Under his leadership, Fujian achieved ...
(): 1993-1994
#Jia Qinglin
Jia Qinglin (; born 13 March 1940) is a retired senior leader of the People's Republic of China and of the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP). He was a member of the CCP's Politburo Standing Committee, the party's highest ruling organ, between ...
(): 1994-1998
# Yuan Qitong (): 1998-2002
# Song Defu (): 2002-2005
#Lu Zhangong
Lu Zhangong (; born May 1952) is a Chinese politician. He is, since 2013, a Vice Chairman of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, and previously served as the Communist Party Secretary of Fujian and Henan provinces, and Gover ...
(): 2005-2010
# Sun Chunlan (): 2010-2013
#You Quan
You Quan (; born January 1954) is a Chinese politician who is the former director of the United Front Work Department and a former secretary of the Secretariat of the Chinese Communist Party. He previously served as Communist Party Secretary of F ...
(): 2013-2018
# Yu Weiguo (): 2018-2021
# Yin Li (): 2021-present
Governors
#Zhang Dingcheng
Zhang Dingcheng (; December 1898 – December 16, 1981) was a politician of the People's Republic of China, Procurator–General of the Supreme People's Procuratorate from 1954 to 1975.
(): 1949-1954
#Ye Fei
Ye Fei (; 7 May 1914 – 18 April 1999) was a Philippine-born Chinese military general and politician of the People's Republic of China. Born Sixto Mercado Tiongco in the Philippines to a Chinese father and a Filipino mother, he joined the Ch ...
(): 1954-1959
#Jiang Yizhen
Jiang Yizhen (; March 1915 – March 24, 1994) was a People's Republic of China politician. He was born in Liancheng County, Fujian. He was Chinese Communist Party Committee Secretary and Governor of his home province. He was People's Congres ...
(): 1959
#Wu Hongxiang (): acting: 1960-1962
#Jiang Yizhen
Jiang Yizhen (; March 1915 – March 24, 1994) was a People's Republic of China politician. He was born in Liancheng County, Fujian. He was Chinese Communist Party Committee Secretary and Governor of his home province. He was People's Congres ...
(): 1962
#Wei Jinshui
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (衛, 1040–209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (魏, 403–225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
(): 1962-1967
#Han Xianchu
Han Xianchu (; 1913–1986) was a general of the Chinese Communist Party. Han participated in many military campaigns and battles such as Battle of Pingxingguan, Liaoshen Campaign, Pingjin Campaign, Hainan Campaign, and the Korean War. In 195 ...
(): 1967-1973
# Liao Zhigao (): 1974-1979
# Ma Xingyuan (): 1979-1983
#Hu Ping
Hu Ping (胡萍) (1910-?) was a Chinese actress, screenwriter and filmmaker from Hunan, China, born in Changsha. She started acting in Shanghai, in the theater industry and was a household name in Shanghai in the 1930s. She joined the Friends Fil ...
(): 1983-1987
#Wang Zhaoguo
Wang Zhaoguo (; born 14 July 1941) is a retired Chinese politician who came to prominence during the era of Deng Xiaoping. An automobile factory technician by trade, Wang had a long and varied political career, known for having acquired a minist ...
(): 1987–1990
#Jia Qinglin
Jia Qinglin (; born 13 March 1940) is a retired senior leader of the People's Republic of China and of the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP). He was a member of the CCP's Politburo Standing Committee, the party's highest ruling organ, between ...
(): 1990–1994
# Chen Mingyi (): 1994–1996
#He Guoqiang
He Guoqiang (; born October 1. 1943) is a retired senior leader of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Between 2007 and 2012, He was a member of the Politburo Standing Committee (PSC), China's highest ruling council, and the Secretary of the Cent ...
(): 1996–1999
#Xi Jinping
Xi Jinping ( ; ; ; born 15 June 1953) is a Chinese politician who has served as the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and chairman of the Central Military Commission (CMC), and thus as the paramount leader of China, ...
(): 1999–2002
#Lu Zhangong
Lu Zhangong (; born May 1952) is a Chinese politician. He is, since 2013, a Vice Chairman of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, and previously served as the Communist Party Secretary of Fujian and Henan provinces, and Gover ...
(): 2002–2004
#Huang Xiaojing
Huang Xiaojing (; February 1946 - ) is a politician of the People's Republic of China and a former governor of Fujian Province.
A native of Fuzhou, Fujian, Huang started working in September 1969, and joined the Chinese Communist Party in Decem ...
(): 2004–2011
#Su Shulin
Su Shulin (; born 14 March 1962) is a Chinese oil and gas executive and former politician. Between 2011 and 2015, he served as Governor of Fujian province, on China's eastern coast. Before beginning his political career, Su served as the Vice-Pr ...
(): 2011–2015
# Yu Weiguo (): 2015–2018
#Tang Dengjie
Tang Dengjie (; born June 1964) is a Chinese politician and business executive, serving since February 2022 as Minister of Civil Affairs of the People's Republic of China. Previously he served as deputy minister in charge of the National Develop ...
(): 2018–2020
# Wang Ning (): 2020–2021
#Zhao Long
Zhao Long (; born September 1967) is a Chinese politician who is the current governor of Fujian, in office since 22 October 2021.
Biography
Zhao was born in Panjin, Liaoning, in September 1967. He joined the Chinese Communist Party in Decembe ...
(): 2021–present
Economy
 Fujian is one of the more affluent provinces with many industries spanning tea production, clothing, and sports manufacturers such as Anta, 361 Degrees,
Fujian is one of the more affluent provinces with many industries spanning tea production, clothing, and sports manufacturers such as Anta, 361 Degrees, Xtep
Xtep International Holdings Limited (SEHK stock code: 1368) is a Chinese manufacturing company of sports equipment based in Kowloon Bay, Hong Kong. Established in 2001, the company was listed on the Main Board of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange on ...
, Peak Sport Products
Peak Sport Products Co., Limited () is a Chinese manufacturing company of sportswear and footwear based in Quanzhou. Founded in 1989 as a shoe manufacturer, the company was listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 2009, however due to low per ...
and Septwolves. Many foreign firms have operations in Fujian. They include Boeing, Dell, GE, Kodak, Nokia, Siemens, Swire, TDK, and Panasonic.
As of 2021, Fujian's nominal GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
was CNY 4.88 trillion (US$ 768 billion), ranking 8th in GDP nationwide and appearing in the world's top 20 largest sub-national economies with its GDP (Purchasing Power Parity) being over US$1.19 trillion. Along with its coastal neighbours Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
and Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
, Fujian's GDP per capita is above the national average, at CN¥117,500 (approx.US$18,217 in nominal value
In economics, nominal value is measured in terms of money, whereas real value is measured against goods or services. A real value is one which has been adjusted for inflation, enabling comparison of quantities as if the prices of goods had not c ...
and US$28,658 in Purchasing Power Parity), the second highest GDP per capita of all Chinese provinces after Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its ca ...
.
As of 2021, Fujian's nominal GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
exceeded that of Poland with a GDP of US$ 674 billion, the 21st largesRice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
is the main crop, supplemented by sweet potatoes and wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
and barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
. Cash crops include sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
and rapeseed
Rapeseed (''Brassica napus ''subsp.'' napus''), also known as rape, or oilseed rape, is a bright-yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae (mustard or cabbage family), cultivated mainly for its oil-rich seed, which naturally contains a ...
. Fujian leads the provinces of China in longan
''Dimocarpus longan'', commonly known as the longan () and dragon's eye, is a tropical tree species that produces edible fruit. It is one of the better-known tropical members of the soapberry family Sapindaceae, to which the lychee and rambu ...
production, and is also a major producer of lychee
Lychee (US: ; UK: ; ''Litchi chinensis''; ) is a monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus ''Litchi'' in the soapberry family, ''Sapindaceae''.
It is a tropical tree native to Southeast and Southwest China (the Guangdong, Fujian, Yun ...
s and tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
. Seafood is another important product, with shellfish production especially prominent.
Because of its geographic location with Taiwan, Fujian has been considered the battlefield frontline in a potential war between mainland China and Taiwan. Hence, it received much less investment from the Chinese central government and developed much slower than the rest of China before 1978. Since 1978, when China opened to the world, Fujian has received significant investment from overseas Fujianese around the world, Taiwanese and foreign investment.
Minnan Golden Triangle which includes Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an ...
, Quanzhou, and Zhangzhou
Zhangzhou (), alternately romanized as Changchow, is a prefecture-level city in Fujian Province, China. The prefecture around the city proper comprises the southeast corner of the province, facing the Taiwan Strait and surrounding the prefect ...
accounts for 40 percent of the GDP of Fujian province.
Fujian province will be the major economic beneficiary of the opening up of direct transport with Taiwan which commenced on December 15, 2008. This includes direct flights from Taiwan to major Fujian cities such as Xiamen and Fuzhou. In addition, ports in Xiamen, Quanzhou, and Fuzhou will upgrade their port infrastructure for increased economic trade with Taiwan.
Fujian is the host of China International Fair for Investment and Trade
The China International Fair for Investment and Trade (CIFIT, simplified chinese:中国国际投资贸易洽谈会, traditional chinese:中國國際投資貿易洽談會), approved by the State Council of the People's Republic of China, takes pla ...
annually. It is held in Xiamen to promote foreign investment for all of China.
Economic and Technological Development Zones
Meizhou Island
Meizhou Island (; Pu-Xian Min: ''Mî-ciu-doh''), Meichow; Meichou, is a small island close to the coast of China. Meizhou Town () is an administrative unit of Xiuyu District, Putian, Fujian, China. It is known for being the birthplace of the go ...
National Tourist Holiday Resort
* Wuyi Mountain National Tourist Holiday Resort
* Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an ...
Export Processing Zone
* Xiamen Free Trade Zone
* Xiamen Haicang Economic and Technological Development Zone
* Xiamen Torch New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone (Chinese version)
* Xinglin Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
Demographics
 As of 1832, the province was described as having an estimated "population of fourteen millions."
Fujianese who are legally classified as
As of 1832, the province was described as having an estimated "population of fourteen millions."
Fujianese who are legally classified as Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
make up 98% of the population. Various Min Chinese speakers make up the largest subgroups classified as Han Chinese in Fujian such as Hoklo people, Fuzhounese people, Putian people
The Putian people or Xinghua people, ( Chinese: 莆田人, pinyin: ''Pútiánrén''; Puxian Min: 莆仙儂, Hinghwa Romanized: ) are people from Putian, east Fujian, China. They are also known as Xinghua or Henghua people ( zh, s=兴化, t=興化 ...
and Fuzhou Tanka.
Hakka
The Hakka (), sometimes also referred to as Hakka Han, or Hakka Chinese, or Hakkas are a Han Chinese subgroup whose ancestral homes are chiefly in the Hakka-speaking provincial areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hunan, Zhej ...
, a Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
people with their own distinct identity, live in the central and southwestern parts of Fujian. The She
She most commonly refers to:
*She (pronoun), the third person singular, feminine, nominative case pronoun in modern English.
She or S.H.E. may also refer to:
Literature and films
*'' She: A History of Adventure'', an 1887 novel by H. Rider Hagga ...
, scattered over mountainous regions in the north, is the largest minority ethnic group of the province.
Many ethnic Chinese around the world, especially in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, trace their ancestries to the Fujianese branches of Hoklo people and Teochew people
The Teochew people or Chaoshan people (rendered Têo-Swa in romanized Teoswa and Chaoshan in Standard Chinese also known as Teo-Swa in mainland China due to a change in place names) is anyone native to the historical Chaoshan region in south ...
. Descendants of Southern Min speaking emigrants make up the predominant majority ethnic Chinese populations of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, Australia, Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by t ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. While Eastern Min
Eastern Min or Min Dong (, Foochow Romanized: Mìng-dĕ̤ng-ngṳ̄), is a branch of the Min group of Sinitic languages of China. The prestige form and most-cited representative form is the Fuzhou dialect, the speech of the capital of Fujian.
G ...
speaking people, especially Fuzhounese people, are one of the major sources of China immigrants in the United States, especially since the 1990s.
Religion
The predominant religions in Fujian areChinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion, also known as Chinese popular religion comprehends a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. Vivienne Wee described it as "an empty bowl, which can variously be filled ...
s, Taoist traditions, and Chinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism which has shaped Chinese culture in a wide variety of areas including art, politics, literature, philosophy, ...
. According to surveys conducted in 2007 and 2009, 31.31% of the population believes and is involved in Chinese ancestral religion
Chinese ancestor veneration, also called Chinese ancestor worship, is an aspect of the Chinese traditional religion which revolves around the ritual celebration of the deified ancestors and tutelary deities of people with the same surname or ...
, while 3.5% of the population identifies as Christian. The reports did not give figures for other types of religion; 65.19% of the population may be either irreligious or involved in Chinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion, also known as Chinese popular religion comprehends a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. Vivienne Wee described it as "an empty bowl, which can variously be filled ...
, Buddhism, Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a ...
, Taoism, folk religious sects, and small minorities of Muslims.
In 2010, there are 115.978 Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
in Fujian
Culture

Uniting China to Speak Mandarin, the One Official Language: Easier Said Than Done
." ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
''. July 10, 2005. Retrieved June 13, 2008. Most varieties spoken in Fujian are assigned to a broad Min
Min or MIN may refer to:
Places
* Fujian, also called Mǐn, a province of China
** Min Kingdom (909–945), a state in Fujian
* Min County, a county of Dingxi, Gansu province, China
* Min River (Fujian)
* Min River (Sichuan)
* Mineola (Am ...
category. Recent classifications subdivide Min into
* Eastern Min
Eastern Min or Min Dong (, Foochow Romanized: Mìng-dĕ̤ng-ngṳ̄), is a branch of the Min group of Sinitic languages of China. The prestige form and most-cited representative form is the Fuzhou dialect, the speech of the capital of Fujian.
G ...
(the former Northern group), including the Fuzhou dialect
Fuzhou (; , Fuzhounese: Hokchew, ''Hók-ciŭ''), alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute ...
* Northern Min, spoken in inland northern areas
* Pu-Xian, spoken in central coastal areas
* Central Min, spoken in the west of the province
* Shao-Jiang, spoken in the northwest
* Southern Min, including the Amoy dialect
The Amoy dialect or Xiamen dialect (), also known as Amoynese, Amoy Hokkien, Xiamenese or Xiamen Hokkien, is a dialect of Hokkien spoken in the city of Xiamen (historically known as "Amoy") and its surrounding metropolitan area, in the souther ...
and Taiwanese
The seventh subdivision of Min, Qiong Wen, is not spoken in Fujian. Hakka
The Hakka (), sometimes also referred to as Hakka Han, or Hakka Chinese, or Hakkas are a Han Chinese subgroup whose ancestral homes are chiefly in the Hakka-speaking provincial areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hunan, Zhej ...
, another subdivision of spoken Chinese, is spoken around Longyan
Longyan (; Hakka: ''Liùng-ngàm''; Longyan dialect: ''Lengngia'') is a prefecture-level city in south-western Fujian Province, China, bordering Guangdong to the south and Jiangxi to the west.
History
In 736 AD, (the Tang dynasty), the prefec ...
by the Hakka people
The Hakka (), sometimes also referred to as Hakka Han, or Hakka Chinese, or Hakkas are a Han Chinese subgroup whose ancestral homes are chiefly in the Hakka-speaking provincial areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hunan, Zhej ...
who live there.
As is true of other provinces, the official language in Fujian is Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
, which is used for communication between people of different localities, although native Fujian peoples still converse in their native languages and dialects respectively.
Several regions of Fujian have their own form of Chinese opera. Min opera
Min opera (; Foochow Romanized: Mìng-kiŏk), also called Fuzhou drama (; Foochow Romanized: Hók-ciŭ-hié), is one of the major traditional opera forms in Fujian Province. It enjoys a good popularity in Fuzhou, Middle Fujian, East Fujian and Nort ...
is popular around Fuzhou; Gaojiaxi around Jinjiang and Quanzhou; Xiangju around Zhangzhou
Zhangzhou (), alternately romanized as Changchow, is a prefecture-level city in Fujian Province, China. The prefecture around the city proper comprises the southeast corner of the province, facing the Taiwan Strait and surrounding the prefect ...
; Fujian Nanqu throughout the south, and Puxianxi around Putian and Xianyou County
Xianyou (; Puxian Min: ) is a county in the municipal region of Putian, in eastern Fujian province, People's Republic of China.
Administration
The county seat is in Licheng Subdistrict ().
Towns (镇, ''zhen'')
* Linan, Xianyou
Linan () is a ...
.
Fujian cuisine, with an emphasis on seafood, is one of the eight great traditions of Chinese cuisine
Chinese cuisine encompasses the numerous cuisines originating from China, as well as overseas cuisines created by the Chinese diaspora. Because of the Chinese diaspora and historical power of the country, Chinese cuisine has influenced many o ...
. It is composed of traditions from various regions, including Fuzhou cuisine and Min Nan cuisine. The most prestigious dish is Fotiaoqiang (literally " Buddha jumps over the wall"), a complex dish making use of many ingredients, including shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
fin
A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foils that produce lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while traveling in water, air, or other fluids. Fin ...
, sea cucumber, abalone and Shaoxing wine
Shaoxing wine (''Shaohsing'', ''Hsiaohsing'', ''Shaoshing''), also called "yellow wine", is a traditional Chinese wine made by fermenting glutinous rice, water and wheat-based yeast.
It must be produced in Shaoxing, in the Zhejiang province of ...
(a type of Chinese alcoholic beverage
There is a long history of alcoholic drinks in China. They include rice and grape wine, beer, whisky and various liquors including ''baijiu'', the most-consumed distilled spirit in the world.
Name
(''jiǔ'') is the Chinese character referring ...
).
Many well-known tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
s originate from Fujian, including oolong, Wuyi Yancha, Lapsang souchong
Lapsang souchong (; ) or Zhengshan xiaozhong () is a black tea consisting of leaves that are smoke-dried over a pinewood fire. This smoking is accomplished either as a cold smoke of the raw leaves as they are processed or as a hot smoke of pr ...
and Fuzhou jasmine tea. Indeed, the tea processing
Tea processing is the method in which the leaves from the tea plant ''Camellia sinensis'' are transformed into the dried leaves for brewing tea.
The categories of tea are distinguished by the processing they undergo. In its most general form, t ...
techniques for three major classes of tea, namely, oolong, white tea
White tea may refer to one of several styles of tea which generally feature young or minimally processed leaves of the ''Camellia sinensis'' plant.
Currently there is no generally accepted definition of white tea and very little internationa ...
, and black tea
Black tea, also translated to red tea in various East Asian languages, is a type of tea that is more oxidized than oolong, yellow, white and green teas. Black tea is generally stronger in flavour than other teas. All five types are made from ...
were all developed in the province. Fujian tea ceremony is an elaborate way of preparing and serving tea. The English word "tea" is borrowed from Hokkien
The Hokkien () variety of Chinese is a Southern Min language native to and originating from the Minnan region, where it is widely spoken in the south-eastern part of Fujian in southeastern mainland China. It is one of the national languages ...
of the Min Nan
Southern Min (), Minnan ( Mandarin pronunciation: ) or Banlam (), is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages that form a branch of Min Chinese spoken in Fujian (especially the Minnan region), most of Taiwan ...
languages. Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
and Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
pronounce the word ''chá''.
Nanyin is a popular form of music of Fujian.
Fuzhou bodiless lacquer ware, a noted type of lacquer ware, is noted for using a body of clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
and/or plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
to form its shape; the body later removed. Fuzhou is also known for Shoushan stone carvings.
Tourism

Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
.
The Wuyi Mountains
The Wuyi Mountains or Wuyishan (; formerly known as Bohea Hills in early Western documents) are a mountain range located in the prefecture of Nanping, in northern Fujian province near the border with Jiangxi province, China. The highest peak in ...
was the first location in Fujian to be listed by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
as one of the World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s in 1999. They are a mountain range in the prefecture of Nanping
Nanping (), historically known as Yanping (), is a third-tier prefecture-level city in northwestern Fujian Province, People's Republic of China. It borders Ningde to the east, Sanming to the south, and the provinces of Zhejiang and Jiangxi to ...
and contain the highest peak in Fujian, Mount Huanggang
Mount Huanggang () is the highest peak in the UNESCO designated Wuyi Mountains, China. It separates and is the highest point of both Fujian and Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in th ...
. It is famous as a natural landscape garden and a summer resort in China.
The Fujian Tulou are Chinese rural dwellings unique to the Hakka in southwest Fujian. They were listed by the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
as one of the World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s in 2008.
Gulangyu Island
The Gulangyu, Gulang Island or Kulangsu is a pedestrian-only island off the coast of Xiamen, Fujian Province in southeastern China. A UNESCO World Cultural Heritage Site, the island is about in area, and is reached by an 8-minute ferry ride fro ...
, Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an ...
, is notable for its beaches, winding lanes, and rich architecture. The island is on China's list of National Scenic Spots and is classified as a 5A tourist attraction by the China National Tourism Administration
The China National Tourism Administration (CNTA; ) was a Chinese government authority responsible for the development of tourism in the country. The CNTA was subordinate to the State Council. Its headquarters are in Beijing, with regional branch ...
(CNTA). It was listed by the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
as one of the World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 2017. Also in Xiamen is the South Putuo Temple
South Putuo or Nanputuo () is a famous Buddhist temple founded in the Tang dynasty in the Chinese city of Xiamen. It is so named because it is south of the Buddhist holy site Mount Putuo in Zhejiang Province.
Location
The South Putuo Temple i ...
.
The Guanghua Temple is a Buddhist temple in Putian. It was built in the penultimate year of the Southern Chen Dynasty. Located in the northern half of the mouth of Meizhou Bay, it is about 1.8 nautical miles from the mainland and faces the Strait of Taiwan to the southeast. Covering an area of six square miles, the island is swathed in luxuriant green foliage. The coastline is indented with over 12 miles of the beach area. Another Buddhist temple, Nanshan Temple is located in Zhangzhou
Zhangzhou (), alternately romanized as Changchow, is a prefecture-level city in Fujian Province, China. The prefecture around the city proper comprises the southeast corner of the province, facing the Taiwan Strait and surrounding the prefect ...
.
Around Meizhou Islands is the Matsu pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
.
The Kaiyuan Temple, is a Buddhist temple in West Street, Quanzhou, the largest in Fujian province with an area of ."Kaiyuan Temple". Chinaculture.org. Retrieved 31 January 2012. Although it is known as both a Hindu and Buddhist temple, on account of added Tamil-Hindu influences, the main statue in the most important hall is that of Vairocana Buddha, the main Buddha according to Huayan Buddhism.
Mount Taimu
Mount Taimu () is a mountain in Ningde, Fujian, China. It is located 46km south of the county-level city of Fuding.
Mythology
In Chinese mythology, the mountain was considered a gathering point for deities from the East China Sea.
Tourism
Si ...
is a mountain and a scenic resort in Fuding
() is a county-level city in northeastern Ningde prefecture-level city, on Fujian's border with Zhejiang province.
History
Fuding county was established during the Qing Dynasty in 1739 AD.
On December 15, 1950, the Matsu Administrative Office ( ...
. It offers a grand view of mountains and sea and is famous for its natural scenery including granite caves, odd-shaped stones, cliffs, clear streams, cascading waterfalls, and cultural attractions such as ancient temples and cliff Inscriptions.
The Danxia landform
The Danxia landform () refers to various landscapes found in southeast, southwest and northwest China that "consist of a red bed characterized by steep cliffs". It is a unique type of petrographic geomorphology found in China. Danxia landform ...
in Taining was listed by the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
as one of the World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s in 2010. It is a unique type of petrographic
Petrography is a branch of petrology that focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. Someone who studies petrography is called a petrographer. The mineral content and the textural relationships within the rock are described in detail. The class ...
geomorphology found in China. Danxia landform is formed from red-coloured sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
s and conglomerates of largely Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
age. The landforms look very much like karst topography that forms in areas underlain by limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
s, but since the rocks that form danxia are sandstones and conglomerates, they have been called "pseudo-karst" landforms. They were formed by endogenous forces (including uplift) and exogenous forces (including weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement) ...
and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
).
Notable individuals
The province and its diaspora abroad also have a tradition of educational achievement and have produced many important scholars, statesmen, and other notable people. These include people whose ancestral home (祖籍) is Fujian (their ancestors originated from Fujian). In addition to the below list, many notable individuals of Han Chinese descent in Taiwan, Southeast Asia, and elsewhere have ancestry that can be traced to Fujian. Some notable individuals include (in rough chronological order): Han, Tang, and Song dynasties * Baizhang Huaihai (720–814), an influential master of Chan Buddhism during the Tang Dynasty *Huangbo Xiyun
Huángbò Xīyùn (, ja, Ōbaku Kiun) (died 850) was an influential master of Zen Buddhism during the Tang dynasty.
Huángbò was a disciple of Baizhang Huaihai (720–840), and the teacher of Linji Yixuan (died 866) (Wade–Giles: Lin-chi I- ...
(died 850), an influential master of Chan Buddhism during the Tang Dynasty
* Chen Yan (849-892), Tang dynasty governor of Fujian
* Liu Yong (987–1053), a famous poet
*Cai Jing
Cai Jing (1047–1126), courtesy name Yuanchang (), was a Chinese calligrapher and politician who lived during the Northern Song dynasty of China. He is also fictionalised as one of the primary antagonists in ''Water Margin'', one of the Four G ...
(1047–1126), government official and calligrapher who lived during the Northern Song dynasty
* Li Gang (1083–1140), Song dynasty politician and military leader (ancestral home is Shaowu
Shaowu () is a county-level city in northwestern Fujian province, People's Republic of China, located in the central part of the Wuyi Mountains and bordering Jiangxi province to the west. It has more than 100,000 inhabitants. The local dialect ...
)
*Zhu Xi
Zhu Xi (; ; October 18, 1130 – April 23, 1200), formerly romanized Chu Hsi, was a Chinese calligrapher, historian, philosopher, poet, and politician during the Song dynasty. Zhu was influential in the development of Neo-Confucianism. He con ...
(1130–1200), Confucian philosopher
*Zhen Dexiu
Zhen Dexiu (; 1178 – 1235) was a Chinese politician and philosopher during the Southern Song dynasty. His Neo-Confucianist views were influential at court and together with his colleague Wei Liaoweng he was instrumental in making Neo-Confucian ...
(1178–1235), Song dynasty politician and philosopher
* Yan Yu (1191–1241), a poetry theorist and poet of the Southern Song dynasty
* Chen Wenlong (1232–1277), a scholar-general in the last years of the Southern Song dynasty
*Pu Shougeng Pu Shougeng (; fl. c. 1250–1281) was a Muslim merchant and administrator in China under the Song and Yuan dynasties.
The name Pu probably comes from Arabic '' Abū'' (father). Pu's family background is unknown. According to one theory, his fam ...
(1250–1281), a Muslim merchant and administrator in the last years of the Southern Song dynasty
Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties
* Chen Youding (1330–1368), Yuan dynasty military leader
*Gao Bing Gao Bing (高棅, 1350 to 1423), was a Chinese poetry anthologist and writer. A native of Fuzhou, he flourished during the newly established Ming Dynasty (1368–1644) as an author and poetry theorist. Gao Bing collected and arranged Tang poetry-era ...
(1350–1423), an author and poetry theorist during Ming Dynasty
*Huang Senping Ong Sum Ping () is a legendary figure. Identified as Pengiran Maharaja Lela of Brunei. The Hokkien name implies that Ong Sum Ping was a native of Fujian, China.
Career and personal life
According to Wen Xiongfei 温雄飞 in the 《南洋华侨史� ...
(14th–15th century), royal son-in-law of Sultan Muhammad Shah of Brunei
Muhammad Shah (born Awang Alak Betatar) established the Sultanate of Brunei and was its first sultan, possibly from 1363 to 1402. The genealogy of Muhammad Shah is unclear, and is based on several historical sources and legends.
Biography
Th ...
* Zhang Jing (1492–1555), Ming dynasty politician and general
*Yu Dayou
Yu Dayou (1503–1579), courtesy name Zhifu, art name Xujiang, was a Chinese general and martial artist best known for countering the ''wokou'' pirates along China's southeastern coast during the reign of the Jiajing Emperor in the Ming dynasty. ...
(1503–1579), Ming dynasty general and martial artist
*Chen Di
Chen Di / Chʻen Ti () (1541–1617), courtesy name: Jili (), was a Chinese philologist, strategist, and traveler of the Ming dynasty. A native of Lianjiang County, Fuzhou, Fujian, China, he was versed in both pen and sword. As a strategist, he s ...
(1541–1617), Ming dynasty philologist, strategist, and traveler
*Huang Daozhou
Huang Daozhou (, 1585–1646) was a Chinese calligrapher, scholar and official of the Ming dynasty.
Huang obtained the degree of Jinshi in 1622. He subsequently held various government positions, including Minister for Education. He was known f ...
(1585–1646), Ming dynasty politician, calligrapher, and scholar
* Ingen (1592–1673), well-known Buddhist monk, poet, and calligrapher who lived during Ming Dynasty
*Hong Chengchou
Hong Chengchou (; 1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining t ...
(1593–1665), Ming dynasty official
* Shi Lang (1621–1696), Qing dynasty admiral
*Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
(1624–1662), Ming dynasty general who expelled the Dutch from Taiwan
* Huang Shen (1687–1772), a painter during the Qing dynasty
*Lin Zexu
Lin Zexu (30 August 1785 – 22 November 1850), courtesy name Yuanfu, was a Chinese political philosopher and politician. He was the head of states (Viceroy), Governor General, scholar-official, and under the Daoguang Emperor of the Qing dynas ...
(1785–1850), Qing dynasty scholar and official
* Chen Baochen (1848–1935), imperial preceptor
The Imperial Preceptor, or Dishi (, lit. "Teacher of the Emperor") was a high title and powerful post created by Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty. It was established as part of Mongol patronage of Tibetan Buddhism and the Yuan administra ...
of Qing dynasty
* Zhan Shi Chai (1840s–1893), entertainer as "Chang the Chinese giant"
* Huang Naishang (1849–1924), scholar, and revolutionary, discovered the town of Sibu
Sibu (; Hokchew Romanized: ''Sĭ-bŭ'') is a landlocked city in the central region of Sarawak. It is the capital of Sibu District in Sibu Division, Sarawak, Malaysia. The city is located on the island of Borneo and covers an area of . It i ...
in Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the Malaysian state of Sabah to the northeast, ...
, east Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
in 1901
* Lin Shu (1852–1924), translator, who introduced the western classics into Chinese.
*Yan Fu
Yan Fu (, IPA: ; courtesy name: Ji Dao, ; 8 January 1854 — 27 October 1921) was a Chinese military officer, newspaper editor, translator, and writer. He was most famous for introducing western ideas, including Darwin's "natural selection", ...
(1854–1921), scholar and translator
* Sa Zhenbing (1859–1952), high-ranking naval officer of Mongolian origin
*Zheng Xiaoxu
Zheng Xiaoxu (Cheng Hsiao-hsu; ; Hepburn: ''Tei Kōsho'') (2 April 1860 – 28 March 1938) was a Chinese statesman, diplomat and calligrapher. He served as the first Prime Minister of Manchukuo.
Early life and diplomatic career
Although Zhe ...
(1860–1938), statesman, diplomat, and calligrapher
*Qiu Jin
Qiu Jin (; 8 November 1875 – 15 July 1907) was a Chinese revolutionary, feminist, and writer. Her courtesy names are Xuanqing () and Jingxiong (). Her sobriquet name is Jianhu Nüxia (). Qiu was executed after a failed uprising against the Qi ...
(1875–1907), revolutionary and writer
*Lin Changmin () (1876—1925), a high-rank governor in the Beiyang Government
*Liang Hongzhi
Liang Hongzhi; (; Wade-Giles: ''Liang Hung-chih''; Hepburn: ''Ryō Koushi'', 1882 - November 6, 1946) was a leading official in the Anhui clique of the Beiyang Government, later noted for his role as in the collaborationist Reformed Governmen ...
(1882–1946), a high-rank governor in the Beiyang Government
*Lin Juemin
Lin Juemin (; 1887–1911) was a late Qing dynasty revolutionary.
Biography
In 1907, Lin traveled to Japan to study at Keio University, where he joined Dr. Sun Yat-sen's revolutionary group, the Tongmenghui. Lin attempted to begin a popular revo ...
(1887–1911), one of 72 Revolutionary Martyrs at Huanghuagang, Guangzhou
* Chen Shaokuan (1889–1969), Fleet Admiral who served as the senior commander of naval forces of the National Revolutionary Army
* Huang Jun (1890–1937), writer
* Hsien Wu (1893–1959), protein scientist
*Lin Yutang
Lin Yutang ( ; October 10, 1895 – March 26, 1976) was a Chinese inventor, linguist, novelist, philosopher, and translator. His informal but polished style in both Chinese and English made him one of the most influential writers of his generati ...
(1894–1976), writer
*Zou Taofen
Zou Taofen (; November 5, 1895 – July 24, 1944) was a Chinese journalist, media entrepreneur, and political activist. Zou was known for developing ''Shenghuo Zhoukan'' (Life Magazine) into a pioneering journal of political reporting and social ...
(1895–1944), journalist, media entrepreneur, and political activist
*Zheng Zhenduo
Zheng Zhenduo (Cheng Chen-to; December 19, 1898 – October 17, 1958), courtesy name Xidi, was a Chinese journalist, writer, archaeologist and scholar. His pen names were Baofen (寶芬), Guo Yuanxin (郭源新) and CT.
He made a significant con ...
(1898–1958), literary historian
* Lu Yin (1899–1934), writer
20th-21st century
*Bing Xin
Xie Wanying (; October 5, 1900 – February 28, 1999), better known by her pen name Bing Xin () or Xie Bingxin, was one of the most prolific Chinese women writers of the 20th century. Many of her works were written for young readers. She ...
(1900–1999), writer
* Shu Chun Teng (1902–1970), scientist, researcher, and lecturer
*Zhang Yuzhe
Zhang Yuzhe (; 16 February 1902 – 21 July 1986), also known as Yu-Che Chang, was a Chinese astronomer and director of the Purple Mountain Observatory who is widely regarded as the father of modern Chinese astronomy. accessed 3 October 2006 H ...
(1902–1986), astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either ...
and director of the Purple Mountain Observatory
The Purple Mountain Observatory (), also known as Zijinshan Astronomical Observatory is an astronomical observatory located on the Purple Mountain in the east of Nanjing.
Description
The Purple Mountain Observatory was established in 1934 f ...
*Hu Yepin
Hu Yepin (; 4 May 1903 – 7 February 1931) was a Chinese writer, poet, and playwright. A prominent member of the League of Left-Wing Writers, he was one of the Five Martyrs of the Left League executed in February 1931 by the Kuomintang governmen ...
(1903–1931), writer
*Lin Huiyin
Lin Huiyin (; known as Phyllis Lin or Lin Whei-yin when in the United States; 10 June 1904 – 1 April 1955) was a Chinese architect and writer. She is known to be the first female architect in modern China and her husband the famed "Father of M ...
(1904–1955), architect and writer
*Go Seigen
Wu Quan (), courtesy name Wu Qingyuan ()His courtesy name was created based on his real name (''Quan'' means "spring, fountain" and ''Qing Yuan'' means "clear and pure source of water"). (June 12, 1914 – November 30, 2014), better known by ...
(1914–2014), pseudonym
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person or group assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individua ...
of Go champion Wú Qīngyuán
*Lin Jiaqiao
Chia-Chiao Lin (; 7 July 1916 – 13 January 2013) was a Chinese-born American applied mathematician and Institute Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Lin made major contributions to the theory of hydrodynamic stabili ...
(1916-2013), a well-known mathematician
*Wang Shizhen Wang Shizhen is the name of:
*Wang Shizhen (Tang dynasty) (759–809), Tang dynasty warlord, de facto ruler of Chengde
* Wang Shizhen (Ming dynasty) (1526–1590), Ming dynasty poet, writer, artist and litterateur.
*Wang Shizhen (Beiyang government ...
(1916-2016), nuclear medicine physician
* Liem Sioe Liong (1916–2012), a Chinese-born Indonesian businessman of Fuqing
(; Foochow Romanized: Hók-chiăng; also romanized as Hokchia) is a county-level city of Fujian Province, China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Fuzhou.
Geography
Fuqing is located in the north-central part ...
origin, founder of Salim Group
* Zheng Min (1920–2022), a scholar and poet
* Ray Wu (1928–2008), geneticist
* Chih-Tang Sah (born 1932), well-known electronics engineer of Mongolian origin
* Chen Jingrun (1933-1996), a widely known mathematician who invented the Chen's theorem and Chen prime
A prime number ''p'' is called a Chen prime if ''p'' + 2 is either a prime or a product of two primes (also called a semiprime). The even number 2''p'' + 2 therefore satisfies Chen's theorem.
The Chen primes are named after Chen Jingru ...
*Wang Wen-hsing
Wang Wen-hsing () was born in Fuzhou, Fujian, in 1939 and grew up in Taiwan. He obtained a BA in Foreign Languages and Literatures from National Taiwan University and an MFA in Creative Writing from the Iowa Writers' Workshop
The Iowa Writers' ...
(born 1939), writer
* Liu Yingming (1940–2016), a mathematician and academician
* Sun Shensu (born 1943), a geochemist and Ph.D. holder from the Columbian University
, mottoeng = "God is Our Trust"
, established =
, type = Private federally chartered research university
, academic_affiliations =
, endowment = $2.8 billion (2022)
, presid ...
(ancestral home is Fuzhou)
*Chen Kaige
Chen Kaige (; born 12 August 1952) is a Chinese film director and a leading figure of the fifth generation of Chinese cinema.Berry, Michael (2002). "Chen Kaige: Historical Revolution and Cinematic Rebellion" in Speaking in Images: Interviews wi ...
(born 1952), film director (ancestral home is Fuzhou)
*Chen Zhangliang
Chen Zhangliang (; born February 3, 1961, Fuqing, Fujian) graduated from the South China College of Tropical Crops (now Hainan University) in 1983, and then was sent to study in the United States by the Chinese Government. He finished his Ph.D. in ...
(born 1961), a Chinese biologist, elected as vice-governor of Guangxi in 2007
* Liu Yudong (born 1970), a professional basketball player
* Shi Zhiyong (born 1980), professional weightlifter
*Zhang Jingchu
Zhang Jingchu (, born 2 February 1980) is a Chinese film actress. Zhang is best known for winning the China Film Media Award Best Actress award for the 2005 film ''Peacock'', which was shown at the Berlin International Film Festival.
Early l ...
(born 1980), actress
*Lin Dan
Lin Dan (born 14 October 1983) is a Chinese former professional badminton player. He is a two-time Olympic champion, five-time World champion, as well as a six-time All England champion. Widely regarded as the greatest badminton player of a ...
(born 1983), professional badminton player
*Jony J
Xiao Jia (), known professionally as Jony J, is a Chinese rapper and songwriter. Born and raised in Fuzhou, China, he debuted his rapping career through releasing a mixtape in 2013. In 2016, he founded his record label Shooc Studio and release ...
(born 1989), rapper and songwriter
*Xu Bin
Xu Bin (; born 19 February 1989) is a Chinese actor based in Singapore. He is managed under NoonTalk Media and was named as one of the 8 Dukes of Caldecott Hill.
Life and career
Xu was born in Fuzhou, China, and moved to Singapore to pursue ...
(born 1989), actor and singer
*Tian Houwei
Tian Houwei (; born 11 January 1992) is a badminton player from China. He was the 2009 World and Asian Junior Champions in the boys' singles event. Tian was part of the Chinese national team that won the silver medals at the 2013 Summer Univer ...
(born 1992), professional badminton player
*Oho Ou
Oho Ou or Ou Hao (, born 13 October 1992) is a Chinese actor and singer. He is best known for his role as Zhang Yang in '' The Left Ear'' (2015).
Career
In 2012, Ou released his first single "Fake Movement", which won him the "Outstanding Newco ...
(born 1992), actor and singer
*Wang Zhelin
Wang Zhelin (, pronounced ; born January 20, 1994) is a Chinese basketball player for the Shanghai Sharks in the Chinese Basketball Association. He was drafted in Round 2 (Number 57 overall) in the 2016 NBA Draft by the Memphis Grizzlies.
Pro ...
(born 1994), professional basketball player
*Qian Kun
NCT (; an acronym for Neo Culture Technology) is a South Korean boy band formed by SM Entertainment and introduced in January 2016. The group consists of 23 members and divided into four different sub-units: NCT U, NCT 127, NCT Dream, and WayV. I ...
(born 1996), singer and songwriter
*Zhang Yiming
Zhang Yiming (; born April 1, 1983 in Longyan, Fujian) is a Chinese internet entrepreneur. He founded ByteDance in 2012 and developed the news aggregator Toutiao and the video sharing platform TikTok (Douyin/抖音), formerly known as Musical.l ...
(born 1983), Internet entrepreneur, founder of ByteDance
ByteDance Ltd. () is a Chinese internet technology company headquartered in Beijing and incorporated in the Cayman Islands.
Founded by Zhang Yiming, Liang Rubo and a team of others in 2012, ByteDance developed the video-sharing social network ...
, TikTok
TikTok, known in China as Douyin (), is a short-form video hosting service owned by the Chinese company ByteDance. It hosts user-submitted videos, which can range in duration from 15 seconds to 10 minutes.
TikTok is an international version o ...
's parent company.
*Wang Xing
Wang Xing (; born 18 February 1979) is a Chinese billionaire businessman and the CEO of Meituan-Dianping. ''Fortune'' listed Wang as number three on its 2018 "40 under 40" list. ''Forbes'' estimates his net worth at US$8.9 billion as of Novemb ...
(born 1979), Internet entrepreneur, founder of Meituan-Dianping
Meituan (, literally "beautiful group"), formerly Meituan-Dianping, is a Chinese shopping platform for locally found consumer products and retail services including entertainment, dining, delivery, travel and other services. The company is headqu ...
.
*Robin Zeng
Zeng Yuqun, also known as Robin Zeng, is a Chinese billionaire entrepreneur. He is the founder and chairman of the battery manufacturer Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL).
Early life and education
Zeng is from Fujian Province. He holds ...
(born 1968), Tech entrepreneur, founder of Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL).
Sports
Fujian includes professional sports teams in both theChinese Basketball Association
The Chinese Basketball Association (), often abbreviated as the CBA, is the first-tier professional men's basketball league in China.
The league is commonly known by fans as the CBA, and this acronym is even used in Chinese on a regular basis ...
and the Chinese League One
The Chinese Football Association China League (), also known as China League One or Chinese Jia League (中甲联赛), is the second level of professional football in China. Above League One is the Chinese Super League.
Prior to the formation of ...
.
The representative of the province in the Chinese Basketball Association
The Chinese Basketball Association (), often abbreviated as the CBA, is the first-tier professional men's basketball league in China.
The league is commonly known by fans as the CBA, and this acronym is even used in Chinese on a regular basis ...
is the Fujian Sturgeons
Fujian SBS Xunxing Sturgeons (Simplified Chinese: 福建SBS浔兴鲟) or Fujian Xunxing or Fujian SBS are a Chinese professional men's basketball team in the Chinese Basketball Association, based in Jinjiang, Quanzhou, Fujian. The "SBS" reflects c ...
, who are based in Jinjiang, Quanzhou. The Fujian Sturgeons made their debut in the 2004–2005 season, and finished in seventh and last place in the South Division, out of the playoffs. In the 2005–2006 season, they tied for fifth, just one win away from making the playoffs
The playoffs, play-offs, postseason or finals of a sports league are a competition played after the regular season by the top competitors to determine the league champion or a similar accolade. Depending on the league, the playoffs may be eit ...
.
The Xiamen Blue Lions formerly represented Fujian in the Chinese Super League
The Chinese Football Association Super League, commonly known as Chinese Super League or CSL, currently known as the China Ping An Chinese Football Association Super League for sponsorship reasons, is the highest tier of professional association ...
, before the team's closure in 2007. Today the province is represented by Fujian Tianxin F.C., who play in the China League Two
The Chinese Football Association Division Two League (Simplified Chinese: 中国足球协会乙级联赛), or China League Two, is the third tier league of the People's Republic of China. The league is under the auspices of the Chinese Football As ...
, and the Fujian Broncos.
Education and research
Fujian is considered one of China's leading provinces in education and research. As of 2022, two major cities ranked in the top 65 cities in the world (Fuzhou 50th and Xiamen 63th) by scientific research output, as tracked by theNature Index The Nature Index is a database that tracks institutions and countries and their scientific output since its introduction in November, 2014. Each year, Nature Index ranks the leading institutions (which can be companies, universities, government agen ...
.
High schools
* Fuzhou Gezhi High School * Fuzhou No.1 Middle School * Fuzhou No.3 Middle School * Quanzhou No.5 Middle School * Xiamen Shuangshi High School * Xiamen No.1 Middle School *Xiamen Foreign Language School
Xiamen Foreign Language School () is a secondary and senior high school in Xiamen, Fujian, China,
Facilities
The school has two campuses that cover 112,707 m2 with four buildings of 65,222 m2. The school hosts three classroom buildings, two labo ...
Colleges and universities
National
*Xiamen University
Xiamen University (; Southern Min: ''Ē-mn̂g-toā-o̍h''), colloquially known as Xia Da (; Southern Min: ''Hā-tāi''), is a national public research university in Xiamen, Fujian, China.
Founded in 1921 by Tan Kah Kee, a Chinese patriotic e ...
(founded 1921, also known as University of Amoy, "985 project
Project 985 () was a terminated project that was first announced by General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party Jiang Zemin at the 100th anniversary of Peking University on May 4, 1998, to promote the development and reputation of the Ch ...
", "211 project
Project 211 () was an abolished project of developing comprehensive universities and colleges initiated in 1995 by the Ministry of Education of China, with the intent of raising the research standards of comprehensive universities and cultiva ...
") (Xiamen)
* Huaqiao University (Quanzhou and Xiamen)
Provincial
*Fuzhou University
Fuzhou University (FZU ) is a university located in Fuzhou, Fujian, China. Split into two campuses by the Min River, Fuzhou University's Old Campus is located on the north bank of the river in the western part of Fuzhou City, while the New Campu ...
(founded 1958, one of "211 project
Project 211 () was an abolished project of developing comprehensive universities and colleges initiated in 1995 by the Ministry of Education of China, with the intent of raising the research standards of comprehensive universities and cultiva ...
" key Universities) (Fuzhou)
*Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University
Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (FAFU) is a leading higher education institution in Fujian Province, jointly supported by the Ministry of Agriculture, the State Forestry Administration and the Fujian Provincial Government in China. Rat ...
(Fuzhou)
* Fujian College of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Fuzhou)
*Fujian Medical University
Fujian Medical University () is a university located in Fuzhou, Fujian, China. Fujian Medical University was founded in 1937, named Fujian Provincial Medical Vocational School at that time. The name of the school was changed to Fujian Provincial ...
(Fuzhou)
*Fujian Normal University
Fujian Normal University () is a public university in Fuzhou, Fujian, China. FNU has been hailed as the province's "Cradle of teachers."
History
Tracing its origin back to Fujian Superior Normal School, founded in 1907, Fujian Normal University ...
(founded 1907) (Fuzhou)
*Fujian University of Technology
Fujian University of Technology () is a public university located in Fuzhou, Fujian, China.
The Chinese Ministry of Education established the university in 2002 by merging Fujian College of Architecture and Civil Engineering and Fujian Institute o ...
(Fuzhou)
*Xiamen University
Xiamen University (; Southern Min: ''Ē-mn̂g-toā-o̍h''), colloquially known as Xia Da (; Southern Min: ''Hā-tāi''), is a national public research university in Xiamen, Fujian, China.
Founded in 1921 by Tan Kah Kee, a Chinese patriotic e ...
(Xiamen)
*Jimei University
Jimei University (JMU) (, Pinyin: , POJ: ), colloquially known as "Jídà" (), is a public university in Xiamen, Fujian, People's Republic of China.It offers doctorate degree programs. It is authorized to enroll postgraduate candidates exempt from ...
(Xiamen)
* Xiamen University of Technology (Xiamen)
* Longyan University (Longyan)
* Minnan Normal University (Zhangzhou)
*Minjiang University
Minjiang University () is a public university located in Minhou County, Fuzhou, Fujian, China. The university is a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary university accredited by the Chinese Education Ministry the right to confer undergraduate degrees ...
(Fuzhou)
*Putian University
Putian University () is a public university located in Putian, Fujian, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most popul ...
(Putian)
* Quanzhou Normal College (Quanzhou)
* Wuyi University (Wuyishan)
Private
* Yang-En University (Quanzhou)See also
*Major national historical and cultural sites in Fujian
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicator ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
; Economic dataEconomic profile for Fujian
External links
* * *Complete Map of the Seven Coastal Provinces
from 1821 to 1850 {{Authority control Provinces of the People's Republic of China East China