Flag of the Philippines (vertical display).svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The national flag of the

 The shade of blue used in the flag has varied over time, beginning with the original color described as ''Azul Oscuro'' (Spanish, "dark blue"). The exact nature of this shade is debated, but a likely candidate is the blue on the
The shade of blue used in the flag has varied over time, beginning with the original color described as ''Azul Oscuro'' (Spanish, "dark blue"). The exact nature of this shade is debated, but a likely candidate is the blue on the
 It has been common since the 1960s to trace the development of the Philippine flag to the various war standards of the individual leaders of the
It has been common since the 1960s to trace the development of the Philippine flag to the various war standards of the individual leaders of the

 The Philippine National Flag was designed by Emilio Aguinaldo It was first displayed in the
The Philippine National Flag was designed by Emilio Aguinaldo It was first displayed in the  The flag was formally unfurled during the proclamation of independence on June 12, 1898, in
The flag was formally unfurled during the proclamation of independence on June 12, 1898, in
 Proposals to add a ninth ray to the sun of the Philippine flag dates as early as 1969, when the Ninth Ray historical reform movement started at the
Proposals to add a ninth ray to the sun of the Philippine flag dates as early as 1969, when the Ninth Ray historical reform movement started at the
 Emmanuel L. Osorio, one of the founders of the Ninth Ray movement, also came up with a proposal adding not only a ninth ray to the flag's sun but adding a fourth star to the flag, representing North Borneo (present-day
Emmanuel L. Osorio, one of the founders of the Ninth Ray movement, also came up with a proposal adding not only a ninth ray to the flag's sun but adding a fourth star to the flag, representing North Borneo (present-day
 The flag may be flown at
The flag may be flown at
 The Philippines does not utilize a separate
The Philippines does not utilize a separate
 According to Republic Act 8491 itself, it shall be prohibited:
:a) To mutilate, deface, defile, trample on or cast contempt or commit any act or omission casting dishonor or ridicule upon the flag or over its surface;
:b) To dip the flag to any person or object by way of compliment or salute;
:c) To use the flag:
::1) As a drapery, festoon, tablecloth;
::2) As covering for ceilings, walls, statues or other objects;
::3) As a pennant in the hood, side, back and top of motor vehicles;
::4) As a staff or whip;
::5) For unveiling monuments or statues; and
::6) As trademarks, or for industrial, commercial or agricultural labels or designs.
:d) To display the flag:
::1) Under any painting or picture;
::2) Horizontally face-up. It shall always be hoisted aloft and be allowed to fall freely;
::3) Below any platform; or
::4) In discothèques, cockpits, night and day clubs, casinos, gambling joints and places of vice or where frivolity prevails.
:e) To wear the flag in whole or in part as a costume or uniform;
:f) To add any word, figure, mark, picture, design, drawings, advertisement, or imprint of any nature on the flag;
:g) To print, paint or attach representation of the flag on handkerchiefs, napkins, cushions, and other articles of merchandise;
:h) To display in public any foreign flag, except in embassies and other diplomatic establishments, and in offices of international organizations;
:i) To use, display or be part of any advertisement or infomercial; and
:j) To display the flag in front of buildings or offices occupied by aliens.
The Act mandates that violators shall, upon conviction, be punished by fine or imprisonment.
According to Republic Act 8491 itself, it shall be prohibited:
:a) To mutilate, deface, defile, trample on or cast contempt or commit any act or omission casting dishonor or ridicule upon the flag or over its surface;
:b) To dip the flag to any person or object by way of compliment or salute;
:c) To use the flag:
::1) As a drapery, festoon, tablecloth;
::2) As covering for ceilings, walls, statues or other objects;
::3) As a pennant in the hood, side, back and top of motor vehicles;
::4) As a staff or whip;
::5) For unveiling monuments or statues; and
::6) As trademarks, or for industrial, commercial or agricultural labels or designs.
:d) To display the flag:
::1) Under any painting or picture;
::2) Horizontally face-up. It shall always be hoisted aloft and be allowed to fall freely;
::3) Below any platform; or
::4) In discothèques, cockpits, night and day clubs, casinos, gambling joints and places of vice or where frivolity prevails.
:e) To wear the flag in whole or in part as a costume or uniform;
:f) To add any word, figure, mark, picture, design, drawings, advertisement, or imprint of any nature on the flag;
:g) To print, paint or attach representation of the flag on handkerchiefs, napkins, cushions, and other articles of merchandise;
:h) To display in public any foreign flag, except in embassies and other diplomatic establishments, and in offices of international organizations;
:i) To use, display or be part of any advertisement or infomercial; and
:j) To display the flag in front of buildings or offices occupied by aliens.
The Act mandates that violators shall, upon conviction, be punished by fine or imprisonment.

 The Pledge of Allegiance to the Philippine flag (distinct from the Patriotic Oath of Allegiance) should be recited while standing with the right hand with palm open raised shoulder high. Individuals whose faith or religious beliefs prohibit them from making such pledge are permitted to excuse themselves, but are required by law to show full respect when the pledge is being rendered by standing at attention.
The law makes no statement regarding the language in which the pledge must be recited, but the pledge is written (and therefore recited) in the
The Pledge of Allegiance to the Philippine flag (distinct from the Patriotic Oath of Allegiance) should be recited while standing with the right hand with palm open raised shoulder high. Individuals whose faith or religious beliefs prohibit them from making such pledge are permitted to excuse themselves, but are required by law to show full respect when the pledge is being rendered by standing at attention.
The law makes no statement regarding the language in which the pledge must be recited, but the pledge is written (and therefore recited) in the
The Official Website of the Republic of the Philippines
* *
How to properly display the Philippine flag.
* History of the Philippine Flag:
flagspot.net
Filipino Flag – Learn NowFilipinoFlag.net
(archived fro
the original
on 2012-06-23)
Watawat – Flags and Symbols of the Pearl of the Orient Seas
History of the Philippine Flag
Philippines Presidential Museum and Library
Origin of the Symbols of our National Flag
, Philippines Presidential Museum and Library
Flags and Banners of the Colonial Era in the Philippines
Philippines Presidential Museum and Library. {{DEFAULTSORT:Flag Of The Philippines National symbols of the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
( tgl, Pambansang watawat ng Pilipinas; ilo, Nailian a bandera ti Filipinas; ceb, Nasudnong bandila ng Pilipinas; es, Bandera Nacional de Filipinas) is a horizontal bicolor flag with equal bands of royal blue
Royal blue is a deep and vivid shade of blue. It is said to have been created by clothiers in Rode, Somerset, a consortium of whom won a competition to make a dress for Queen Charlotte, consort of King George III.
Brightness
The ''Oxford E ...
and crimson red, with a white, equilateral triangle at the hoist. In the center of the triangle is a golden-yellow sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
with eight primary rays, each representing a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
. At each vertex of the triangle is a five-pointed, golden-yellow star, each of which representing one of the country's three main island groups—Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as ...
, Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, ...
(though originally referring to the island of Panay) and Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
. The white triangle at the flag represents liberty
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word freedom.
In modern politics, liberty is understood as the state of being free within society fr ...
, equality
Equality may refer to:
Society
* Political equality, in which all members of a society are of equal standing
** Consociationalism, in which an ethnically, religiously, or linguistically divided state functions by cooperation of each group's elit ...
, and fraternity. A unique feature of this flag is its usage to indicate a state of war if it is displayed with the red side on top, which is effectively achieved by flipping the flag upside-down.
Design
Construction
The flag's length is twice its width, giving it an aspect ratio of 1:2. The length of all the sides of the white triangle are equal to the width of the flag. Each star is oriented in such manner that one of its tips points towards the vertex at which it is located.. Moreover, the gap-angle between two neighbors of the 8 ray-bundles is as large as the angle of one ray-bundle (so 22.5°), with each major ray having double the thickness of its two minor rays. The golden sun is not exactly in the center of the triangle but shifted slightly to the right.Color
 The shade of blue used in the flag has varied over time, beginning with the original color described as ''Azul Oscuro'' (Spanish, "dark blue"). The exact nature of this shade is debated, but a likely candidate is the blue on the
The shade of blue used in the flag has varied over time, beginning with the original color described as ''Azul Oscuro'' (Spanish, "dark blue"). The exact nature of this shade is debated, but a likely candidate is the blue on the Cuban flag
The national flag of Cuba ( es, link=yes, Bandera de Cuba) consists of five alternating stripes (three blue and two white) and a red equilateral triangle at the hoist, within which is a white five-pointed star. It was designed in 1849 and offici ...
, which a theory says influenced the Philippine flag's design. The colors of the flag were first standardized by President Ramón Magsaysay
Ramon del Fierro Magsaysay Sr. (August 31, 1907 – March 17, 1957) was a Filipino statesman who served as the seventh president of the Philippines, from December 30, 1953, until his death in an aircraft disaster on March 17, 1957. An automo ...
, upon the recommendation of the Philippine Heraldry Committee (PHC) dated January 24, 1955. Specifically, the colors adopted were Old Glory Red (Cable No. 70180), National Flag Blue (Cable No. 70077), Spanish Yellow (Cable No. 70068), and White (70001) by the Reference Guide of the Textile Color Card Association of the United States. In 1985, President Ferdinand E. Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. ( , , ; September 11, 1917 – September 28, 1989) was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial ...
through Executive Order No. 1010, s. 1985 instructed the National Historical Institute
The National Historical Commission of the Philippines ( fil, Pambansang Komisyong Pangkasaysayan ng Pilipinas, abbreviated NHCP) is a government agency of the Philippines. Its mission is "the promotion of Philippine history and cultural heritag ...
"to take the necessary steps to restore the original color of the First Philippine Flag". In late May, the NHI adopted Oriental Blue (Cable No. 80176) for the new national flag, but this was later rescinded by President Corazon C. Aquino
Maria Corazon "Cory" Sumulong Cojuangco-Aquino (; ; January 25, 1933 – August 1, 2009) was a Filipina politician who served as the 11th president of the Philippines from 1986 to 1992. She was the most prominent figure of the 1986 People P ...
after the 1986 People Power Revolution
The People Power Revolution, also known as the EDSA Revolution or the February Revolution, was a series of popular demonstrations in the Philippines, mostly in Metro Manila, from February 22 to 25, 1986. There was a sustained campaign of c ...
that removed him from power in favor of pre-1985 National Flag Blue. For the 1998 centennial
{{other uses, Centennial (disambiguation), Centenary (disambiguation)
A centennial, or centenary in British English, is a 100th anniversary or otherwise relates to a century, a period of 100 years.
Notable events
Notable centennial events at ...
celebration of Philippine independence, the Flag and Heraldic Code of the Philippines (Republic Act. 8491, s. 1998) was passed, designating Royal Blue (Cable No. 80173) as the official variant to be used from 1998 to present.
The flag's colors are specified and codified under Republic Act
This article contains a partial list of Philippine laws.
Sources of Philippine laws
;Notes
: *Customs may be considered as supplementary source of law, however, customs which are contrary to law, public order or public policy shall not be ...
8491, s. 1998 signed on February 12, 1998, in terms of their cable number in the system developed by the Color Association of the United States
The Color Association of the United States (CAUS), known until 1955 as the Textile Color Card Association of the United States (TCCA), is an independent color trend forecasting and color consulting service to the business community, known for its ...
. The official colors and their approximations in other color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represen ...
s are listed below:
Symbolism
In the 1850s, bothManila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
and Iloilo
Iloilo (), officially the Province of Iloilo ( hil, Kapuoran sang Iloilo; krj, Kapuoran kang Iloilo; tl, Lalawigan ng Iloilo), is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the City of Iloilo, the ...
, the islands' largest ports, had maritime flags used for navigation in the Philippine seas. Both maritime flags were swallowtail flags with red and blue stripes, respectively, which are now both part of the Philippine flag. The Philippine national flag has a rectangular design that consists of a white equilateral triangle, symbolizing liberty, equality and fraternity; a horizontal blue stripe for peace, truth, and justice; and a horizontal red stripe for patriotism and valor
Valor, valour, or valorous may mean:
* Courage, a similar meaning
* Virtue ethics, roughly "courage in defense of a noble cause"
Entertainment
* Valor (band), a Christian gospel music group
* Valor Kand, a member of the band Christian Death
* ' ...
. In the center of the white triangle is an eight-rayed golden sun symbolizing unity, freedom, people's democracy, and sovereignty. Each ray represents a province with significant involvement in the 1896 Philippine Revolution against Spain; these provinces are Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
, Bulacan
Bulacan, officially the Province of Bulacan ( tl, Lalawigan ng Bulacan), is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is the city of Malolos. Bulacan was established on August 15, 1578, and part of the Me ...
, Cavite
Cavite, officially the Province of Cavite ( tl, Lalawigan ng Kabite; Chavacano: ''Provincia de Cavite''), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region in Luzon. Located on the southern shores of Manila Bay and southwest ...
, Pampanga
Pampanga, officially the Province of Pampanga ( pam, Lalawigan ning Pampanga; tl, Lalawigan ng Pampanga ), is a province in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. Lying on the northern shore of Manila Bay, Pampanga is bordered by Tarlac ...
, Morong (modern-day province of Rizal), Laguna, Batangas
Batangas, officially the Province of Batangas ( tl, Lalawigan ng Batangas ), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region on Luzon. Its capital is the city of Batangas, and is bordered by the provinces of Cavite and La ...
, and Nueva Ecija
Nueva Ecija, officially the Province of Nueva Ecija ( tgl, Lalawigan ng Nueva Ecija , also ; ilo, Probinsia ti Nueva Ecija; pag, Luyag/Probinsia na Nueva Ecija; Kapampangan: ''Lalawigan/Probinsia ning Nueva Ecija''), is a landlocked province ...
(some sources specify other provinces as alternatives to some of these).Philippine Declaration of Independence
The Philippine Declaration of Independence ( fil, Pagpapahayag ng Kasarinlan ng Pilipinas; es, Declaración de Independencia de Filipinas); es, Acta de la proclamación de independencia del pueblo Filipino, link=no) was proclaimed by Fili ...
However, according to the Declaration of Independence and a research by Ateneo de Manila University
, mottoeng = Light in the Lord
, type = Private, research, non-profit, coeducational basic and higher education institution
, established = December 10, 1859
, religious_affiliation = Roman Catholic ( Jesuits)
, academic ...
Professor Ambeth Ocampo, the rays of the sun symbolized the first eight provinces of the Philippines which was declared under martial law during the Philippine Revolution (Batangas
Batangas, officially the Province of Batangas ( tl, Lalawigan ng Batangas ), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region on Luzon. Its capital is the city of Batangas, and is bordered by the provinces of Cavite and La ...
, Bulacan
Bulacan, officially the Province of Bulacan ( tl, Lalawigan ng Bulacan), is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is the city of Malolos. Bulacan was established on August 15, 1578, and part of the Me ...
, Cavite
Cavite, officially the Province of Cavite ( tl, Lalawigan ng Kabite; Chavacano: ''Provincia de Cavite''), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region in Luzon. Located on the southern shores of Manila Bay and southwest ...
, Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
, Laguna, Nueva Ecija
Nueva Ecija, officially the Province of Nueva Ecija ( tgl, Lalawigan ng Nueva Ecija , also ; ilo, Probinsia ti Nueva Ecija; pag, Luyag/Probinsia na Nueva Ecija; Kapampangan: ''Lalawigan/Probinsia ning Nueva Ecija''), is a landlocked province ...
, Pampanga
Pampanga, officially the Province of Pampanga ( pam, Lalawigan ning Pampanga; tl, Lalawigan ng Pampanga ), is a province in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. Lying on the northern shore of Manila Bay, Pampanga is bordered by Tarlac ...
and Tarlac
Tarlac, officially the Province of Tarlac ( pam, Lalawigan ning Tarlac; pag, Luyag/Probinsia na Tarlac; ilo, Probinsia ti Tarlac; tgl, Lalawigan ng Tarlac; ), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. It ...
). Three five-pointed stars, one at each of the triangle's points, stand for the three major island groups: Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as ...
, Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, ...
(originally referring to Panay Island
Panay is the sixth-largest and fourth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of and has a total population of 4,542,926 as of 2020 census. Panay comprises 4.4 percent of the entire population of the country. The City ...
) and Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
.
The flag's original symbolism is enumerated in the text of the independence proclamation, which makes reference to an attached drawing, though no record of the drawing has surfaced. The proclamation explains the flag as follows:
The symbolism given in the 1898 Proclamation of Philippine Independence differs from the current official explanation. According to the document, the white triangle signifies the emblem of the Katipunan
The Katipunan, officially known as the Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan or Kataastaasan Kagalang-galang na Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan (KKK; en, Supreme and Honorable Association of the Children of the Nation ...
, the secret society that opposed Spanish rule. It says the flag's colors commemorate the flag of the United States as a manifestation of gratitude for American aid against the Spanish during the Philippine Revolution. It also says that one of the three stars represents the island of Panay, which recent historical interpretations say was "representative of the entire Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, ...
region".
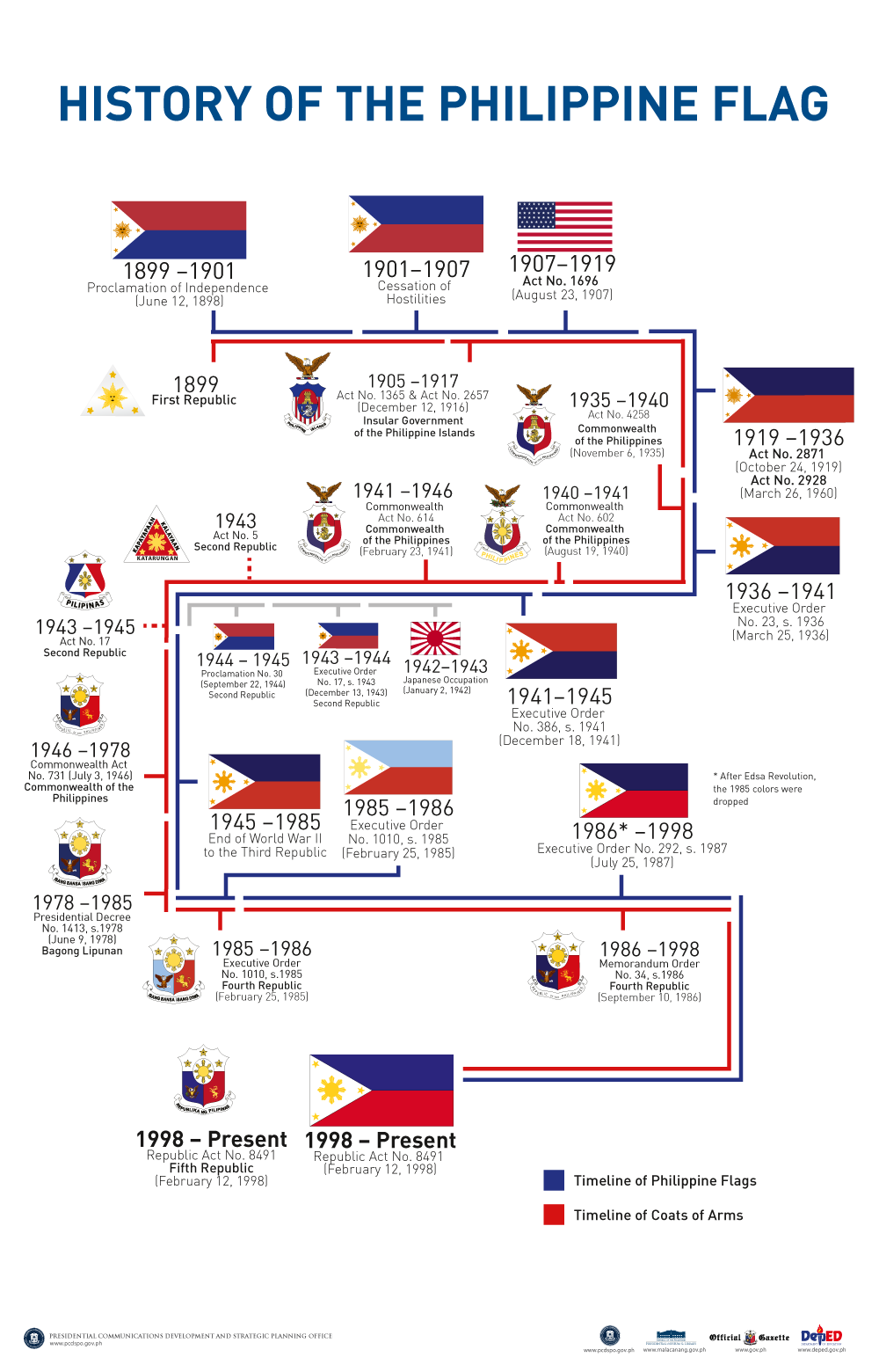
History
Historical flags of the Philippine Revolution
 It has been common since the 1960s to trace the development of the Philippine flag to the various war standards of the individual leaders of the
It has been common since the 1960s to trace the development of the Philippine flag to the various war standards of the individual leaders of the Katipunan
The Katipunan, officially known as the Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan or Kataastaasan Kagalang-galang na Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan (KKK; en, Supreme and Honorable Association of the Children of the Nation ...
, a pseudo-masonic
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
revolutionary movement that opposed Spanish rule in the Philippines and led the Philippine Revolution. However, while some symbols common to the Katipunan flags would be adopted into the iconography of the Revolution, it is inconclusive whether these war standards can be considered precursors to the present Philippine flag.
The first flag of the Katipunan was a red rectangular flag with a horizontal alignment of three white Ks (an acronym for the Katipunan's full name, ''Kataas-taasang Kagalang-galangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan'' – Supreme and Venerable Society of the Sons of the Nation). The flag's red field symbolized blood, as members of the Katipunan signed their membership papers in their own blood.
The various leaders of the Katipunan, such as Andrés Bonifacio, Mariano Llanera, and Pío del Pilar, also had individual war standards.
Current flag

 The Philippine National Flag was designed by Emilio Aguinaldo It was first displayed in the
The Philippine National Flag was designed by Emilio Aguinaldo It was first displayed in the Battle of Alapan
The Battle of Alapan ( fil, Labanan sa Alapan, es, Batalla de Alapan) was fought on May 28, 1898, and was the first military victory of the Filipino Revolutionaries led by Emilio Aguinaldo after his return to the Philippines from Hong Kong. Afte ...
on May 28, 1898, after the Spaniards were defeated and surrendered to Aguinaldo.
 The flag was formally unfurled during the proclamation of independence on June 12, 1898, in
The flag was formally unfurled during the proclamation of independence on June 12, 1898, in Kawit
Kawit, officially the Municipality of Kawit ( tgl, Bayan ng Kawit), is a first-class municipality in the province of Cavite, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 107,535. It is one of the notable places that had ...
, Cavite
Cavite, officially the Province of Cavite ( tl, Lalawigan ng Kabite; Chavacano: ''Provincia de Cavite''), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region in Luzon. Located on the southern shores of Manila Bay and southwest ...
. However, a Manila Times
''The Manila Times'' is the oldest extant English-language newspaper in the Philippines. It is published daily by The Manila Times Publishing Corp. (formerly La Vanguardia Publishing Corporation) with editorial and administrative offices at 2/F ...
article by Augusto de Viana, Chief History Researcher, National Historical Institute, mentions assertions in history textbooks and commemorative rites that the flag was first raised in Alapan, Imus
Imus, officially the City of Imus ( fil, Lungsod ng Imus), is a 3rd class component city and ''de jure'' capital of the province of Cavite, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 496,794 people.
It is the ''de jure ...
, Cavite
Cavite, officially the Province of Cavite ( tl, Lalawigan ng Kabite; Chavacano: ''Provincia de Cavite''), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region in Luzon. Located on the southern shores of Manila Bay and southwest ...
, on May 28, 1898, citing Presidential Proclamation No. 374, issued by then-President Diosdado Macapagal on March 6, 1965. The article goes on to claim that historical records indicate that the first display of the Philippine flag took place in Cavite City
Cavite City, officially the City of Cavite ( fil, Lungsod ng Kabite, Spanish and cbk, Ciudad de Cavite), is a 4th class component city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 100,674 people.
The city was the ...
, when General Aguinaldo displayed it during the first fight of the Philippine Revolution.
The original design of the flag adopted a mythical sun with a face influenced by The Republics of the Rio de la Plata, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
and Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
, which in turn represent Inti
INTI International University & Colleges are private university colleges located in Malaysia. The main campus was initially known as INTI University College until 31 May 2010 when the Higher Education Ministry announced its upgrade to universi ...
the Incan Sun-god; a triangle, representing the Katipunan which inspired by the Eye of Providence in the Great Seal of the United States and the Masonic Triangle and which enshrined Liberté, Égalité, Fraternité of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
; the stripes and colors derived from the American flag
The national flag of the United States of America, often referred to as the ''American flag'' or the ''U.S. flag'', consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the ca ...
. The particular shade of blue of the original flag has been a source of controversy. Based on anecdotal evidence and the few surviving flags from the era, historians argue that the colors of the original flag was influenced by the flags of Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
.
During the session of the Malolos Congress
The Malolos Congress (also known as the Revolutionary Congress), formally known as the National Assembly, was the legislative body of the Revolutionary Government of the Philippines. Members were chosen in the elections held from June 23 to Septe ...
, Aguinaldo presented the symbolism of the official flag to the members, delegates and representatives of the assembly as follows:
The original flag that was first hoisted on May 28, 1898, and unfurled during the Declaration of independence on June 12, 1898, is being preserved at the Gen. Emilio Aguinaldo Museum in Baguio
Baguio ( ,
), officially the City of Baguio ( ilo, Siudad ti Baguio; fil, Lungsod ng Baguio), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Cordillera Administrative Region, Philippines. It is known as the "Summer Capital of the Philippines", ...
. There were plans to restore the flag by replacing the worn-out portion but the idea was abandoned because matching threads could not be found. The flag is more elaborate than the flag which is currently in use. It bears the embroidered words, ''Libertad, Justicia and Igualdad'' (Liberty, Justice, and Equality) on one side of the flag and ''Fuerzas Expedicionarias del Norte de Luzon'' (Expeditionary forces of Northern Luzon) on the other
Hostilities broke out between the Philippines and the United States in 1899. The flag was first flown with the red field up on February 4, 1899, to show that a state of war existed. Aguinaldo was captured by the Americans two years later, and swore allegiance to the United States.
With the defeat of the Philippine Republic, the Philippines was placed under American colonial rule and the display of the Philippine flag and other flags and banners associated with the Katipunan were declared illegal by the Flag Act of 1907. This law was repealed on October 24, 1919.. With the legalization of display of the Philippine flag, the cloth available in most stores was the red and blue of the flag of the United States, so the flag from 1919 onwards adopted the "National Flag blue" color. On March 26, 1920, the Philippine Legislature
The Philippine Legislature was the legislature of the Philippines from 1907 to 1935, during the American colonial period, and predecessor of the current Congress of the Philippines. It was bicameral and the legislative branch of the Insular G ...
passed Act. No 2928 on March 26, 1920, which legally adopted the Philippine flag as the official flag of the Philippine Islands. Up until the eve of World War II, Flag Day was celebrated on annually on October 30, commemorating the date the ban on the flag was lifted.
The Commonwealth of the Philippines was inaugurated in 1935. On March 25, 1936, President Manuel L. Quezon
Manuel Luis Quezon y Molina, (; 19 August 1878 – 1 August 1944), also known by his initials MLQ, was a Filipino lawyer, statesman, soldier and politician who served as president of the Commonwealth of the Philippines from 1935 until his de ...
issued Executive Order No. 23 which provided for the technical description and specifications of the flag. Among the provisions of the order was the definition of the triangle at the hoist as an equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
, the definition of the aspect ratio at 1:2, the precise angles of the stars, the geometric and aesthetic design of the sun, and the formal elimination of the mythical face on the sun. The exact shades of colors, however, were not precisely defined. These specifications have remained unchanged and in effect to the present. In 1941, Flag Day was officially moved to June 12, commemorating the date that Philippine independence was proclaimed in 1898.
The flag was once again banned with the Japanese invasion and occupation of the Philippines beginning in December 1941, to be hoisted again with the establishment of the Second Republic of the Philippines, a client state of Japan. In ceremonies held in October 1943, Emilio Aguinaldo hoisted the flag with the original Cuban blue and red colors restored. The flag was initially flown with the blue stripe up, until President José P. Laurel proclaimed the existence of a state of war with the Allied Powers in 1944. The Commonwealth government-in-exile in Washington, D.C. continued to use the flag with the American colors, and had flown it with the red stripe up since the initial invasion of the Japanese. With the combined forces of the Filipino & American soldiers and the liberation of the Philippines in 1944 to 1945, the flag with the American colors was restored, and it was this flag that was hoisted upon the granting of Philippine independence from the United States on July 4, 1946.
Chronology
Proposals
Ninth ray for the flag's sun
University of the Philippines
The University of the Philippines (UP; fil, Pamantasan ng Pilipinas Unibersidad ng Pilipinas) is a state university system in the Philippines. It is the country's national university, as mandated by Republic Act No. 9500 (UP Charter of 20 ...
in Diliman, Quezon City. The symbolism of the ninth ray varies by proponent.
As representative of a ninth province
Prior to the 1998 independence centennial celebrations, the provincial government ofZambales
Zambales, officially the Province of Zambales ( fil, Lalawigan ng Zambales; ilo, Probinsia ti Zambales; Pangasinan: ''Luyag/Probinsia na Zambales''; xsb, Probinsya nin Zambales), is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon re ...
lobbied that the sunburst design accommodate a ninth ray, reasoning that their province was also in a state of rebellion in 1896. The Centennial Commission however refuted this change, based on research by the National Historical Institute. In August 2003, then Foreign Affairs Secretary Blas Ople
Blas Fajardo Ople (February 3, 1927 – December 14, 2003) was a Filipino journalist and politician who held several high-ranking positions in the executive and legislative branches of the Philippine government, including as Senate President fr ...
also lobbied for a ninth ray, saying that Quezon
Quezon, officially the Province of Quezon ( tl, Lalawigan ng Quezon), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region on Luzon. Kalilayan was the first known name of the province. It was later renamed Tayabas. In honor of the ...
should be added. He reasons that the first uprising against the Spaniards happened at the foot of Mount Banahaw which was led by Hermano Pule
Apolinario de la Cruz (July 22, 1815 – November 4, 1841), better known as Hermano Pule (, Spanish for "Brother Pule"; also spelled Hermano Puli), was a Filipino religious leader who founded and led the ''Cofradía de San José'' (Confratern ...
in 1841.
As representative of an ethnic group
In December 1987, congressman Alawadin Bandon Jr. ofTawi-Tawi
Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi ( tl, Lalawigan ng Tawi-Tawi; Tausug: ''Wilaya' sin Tawi-Tawi''; Sinama: ''Jawi Jawi/Jauih Jauih''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim ...
proposed the addition of a ninth ray to the Philippine flag's sun to represent "Muslim participation" in the Philippine Revolution, arguing that "As a Muslim I am assaulted by a feeling of alienation in being excluded from the symbolic narration of the great history of the country."
In 2008, Senator Richard Gordon filed Senate Bill No. 2590 which aimed to amend the Flag and Heraldic Code of the Philippines. This measure was later superseded by Senate Bill No. 3307 which was sponsored by Senator Francis Escudero and approved in September 2009. The bill was sent to the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
for concurrence with House Bill 6424. Both S.B. No. 3307 and H.B. 6424 was reconciled by the Bicameral Conference Committee in September 2009. President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo, however, vetoed the measure.
, a proposal from the Ninth Ray movement intends the additional ray to represent the Muslim and indigenous people of the country, including the Moro people
The Moro people or Bangsamoro people are the 13 Muslim-majority ethnolinguistic Austronesian groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro (lit. ''Moro nation'' or ''Moro country''). As Muslim-majorit ...
, who kept colonizers away from their lands.
In June 2018, Gordon renewed his campaign to get his proposal passed into law.
Fourth star
Sabah
Sabah () is a state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indonesia to the south. The Federal Territory o ...
), a territory claimed by the Philippines but currently under Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
n sovereignty. The flag's triangle is changed into a rectangle to accommodate the fourth star. According to Osorio, the star representing Sabah in his proposed flag was added "in principle" and said the flag proposal seeks to express the Ninth Ray movement's view that "if we get Sabah, then it could be represented by the star".
Crescent moon
There was a proposal to add a crescent moon during the administration of PresidentFidel V. Ramos
Fidel Valdez Ramos (, ; March 18, 1928 – July 31, 2022), popularly known as FVR and Eddie Ramos, was a Filipino general and politician who served as the 12th president of the Philippines from 1992 to 1998. He was the only career military ...
in a lead up to the 1998 Philippine Centennial. Ramos directed Education Secretary Ricardo Gloria in 1995 to form a commission of scholars to research on the possible modification of the flag. The crescent is meant to represent the Moro community.
Usage
Display
The flag should be displayed in all government buildings,official residence
An official residence is the residence of a head of state, head of government, governor, religious leader, leaders of international organizations, or other senior figure. It may be the same place where they conduct their work-related functions. ...
s, public plazas, and schools every day throughout the year. All other places as may be designated by the National Historical Commission as such. The days of May 28 (National Flag Day) and June 12 (Independence Day) are designated as flag days, during which all offices, agencies and instrumentalities of government, business establishments, institutions of learning and private homes are enjoined to display the flag. But in recent years, the flag days are now from May 28 to June 30 yearly to promote patriotism and to celebrate the nation's independence.
The display of the Philippine flag in cockpit arenas, casinos, disco venues, night and day clubs, gambling joints and "places of vice or where frivolity prevails" is illegal.
When displaying the Philippine flag with another flag in a crossed position, the former should hang on the left side of the observer and its staff should be displayed over the staff of the second flag. The display of two crossed Philippine flags is not permissible. In the case of the Philippine flag's display on a stage or platform such as in a speech, the flag's staff should be positioned on the right side and in front of the speaker and all other secondary flags displayed on the speaker's left.
Permanent display
=Original named sites
= By law, the Philippine flag must be permanently hoisted and illuminated at night at the following locations:=Additional sites
= The National Historical Commission of the Philippines (formerly the National Historical Institute) as per Republic Act. 8491 can also designate additional sites where the Philippine flag should be displayed permanently.Half-mast
 The flag may be flown at
The flag may be flown at half-mast
Half-mast or half-staff (American English) refers to a flag flying below the summit of a ship mast, a pole on land, or a pole on a building. In many countries this is seen as a symbol of respect, mourning, distress, or, in some cases, a salut ...
as a sign of mourning. Upon the official announcement of the death of the president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
or a former president, the flag should be flown at half-mast for ten days. The flag should be flown at half-mast for seven days following the death of the vice president
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on ...
, the chief justice, the president of the Senate or the speaker of the House of Representatives.
The flag may also be required to fly at half-mast upon the death of other persons to be determined by the National Historical Institute, for a period less than seven days. The flag shall be flown at half-mast on all the buildings and places where the decedent was holding office, on the day of death until the day of interment of an incumbent member of the Supreme Court, the Cabinet, the Senate or the House of Representatives, and such other persons as may be determined by the National Historical Commission.
When flown at half-mast, the flag should be first hoisted to the peak for a moment then lowered to the half-mast position. It should be raised to the peak again before it is lowered for the day.
A bill was filed in 2014, to mandate the flying of the flag at half-mast as a tribute to public school teachers. Under the proposal the flag shall be flown at half-mast for at least five days at the school or district office the deceased teacher was assigned.
In wakes and burials
The flag may also be used to cover the caskets of the dead of thetanod
A barangay tanod, also known as a barangay police officer – and sometimes as BPSO (which can stand for barangay public safety officer, barangay peacekeeping and security officer, or barangay police safety officer) – is the lowest level of ...
, military and police, civil uniformed services, fire fighter, traffic enforcer, supreme court judge, Filipino governance servants, veterans of previous wars, national artists, uniformed rescuers, PNP SWAT and outstanding civilians as determined by the local government. In such cases, the flag must be placed such that the white triangle is at the head and the blue portion covers the right side of the casket. The flag should not be lowered to the grave or allowed to touch the ground, but should be solemnly folded and handed to the heirs of the deceased.
As a war ensign
 The Philippines does not utilize a separate
The Philippines does not utilize a separate war flag
A war flag, also known as a military flag, battle flag, or standard, is a variant of a national flag for use by a country's military forces when on land. The nautical equivalent is a naval ensign. Under the strictest sense of the term, few count ...
; instead, the national flag itself is used for this purpose. To indicate a state of war, the red field is flown upwards and is placed on the right (i.e., the observer's left) when hung vertically. In times of peace, however, the blue area is the superior field. On this case, the Philippine flag is the only official country flag in the world that can be flipped when the country is at war. The red side-up orientation of the flag was used by the First Philippine Republic
The Philippine Republic ( es, República Filipina), now officially known as the First Philippine Republic, also referred to by historians as the Malolos Republic, was established in Malolos, Bulacan during the Philippine Revolution against ...
during the Philippine–American War from 1899 to 1901, by the Philippine Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of the Philippines ( es, Commonwealth de Filipinas or ; tl, Komonwelt ng Pilipinas) was the administrative body that governed the Philippines from 1935 to 1946, aside from a period of exile in the Second World War from 1942 ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
from 1941 to 1945, by the Japanese-sponsored Philippine Republic The term "Philippine Republic" or "Republic of the Philippines" refers to a succession of republics during and after the Philippine Revolution in the Philippines.
The current government of the Philippines recognizes five "Philippine republics" in ...
when it declared war against the United Kingdom and the United States in 1944, by soldiers and civilians during the attempted coups d'états against President Corazon Aquino's administration, and by militants and rallyists during EDSA III
The May 1 riots, or EDSA III (pronounced as ''EDSA Three'' or ''EDSA Tres'', the Spanish word for "three"), were protests sparked by the arrest of newly deposed president Joseph Estrada of the Philippines from April 25 to May 1, 2001. The p ...
.
Subdivision insignia
The usage of the Philippine flag as an element of a local government unit's (LGU; provinces, cities, and municipalities) seal is discouraged as per Memorandum Circular 92-30 of the Department of the Interior and Local Government. The usage of the flag is permissible if the flag itself has been part of the LGU's history such as in the case of Kawit, Cavite which is the site of the declaration of Philippine independence.In intellectual property
The Philippine Flag itself is not eligible to betrademarked
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression that identifies products or services from a particular source and distinguishes them from others. ...
according to the Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines
The Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines shortened as IPOPHL, is a government agency attached to the Department of Trade and Industry in charge of registration of intellectual property and conflict resolution of intellectual property ...
(IPOPHIL) since the flag is "owned by the public" in line with prohibitions on the flag's usage stated in Republic Act 8491. The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property
The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, signed in Paris, France, on 20 March 1883, was one of the first intellectual property treaties. It established a Union for the protection of industrial property. The convention is c ...
, which the Philippines is a member of, also prohibits the registration of the state flags of its members as trademark. However both small and large businesses in the Philippines have used elements of the Philippine flag for their intellectual property. When it comes to this concern, the IPOPHIL has allowed businesses to use elements of the flag to invoke the national symbol as long as the intellectual property is neither a "true representation" of the Philippine flag nor a "modification that would amount to defacement of the flag".
Prohibited acts
Relevant customs
Pledge

 The Pledge of Allegiance to the Philippine flag (distinct from the Patriotic Oath of Allegiance) should be recited while standing with the right hand with palm open raised shoulder high. Individuals whose faith or religious beliefs prohibit them from making such pledge are permitted to excuse themselves, but are required by law to show full respect when the pledge is being rendered by standing at attention.
The law makes no statement regarding the language in which the pledge must be recited, but the pledge is written (and therefore recited) in the
The Pledge of Allegiance to the Philippine flag (distinct from the Patriotic Oath of Allegiance) should be recited while standing with the right hand with palm open raised shoulder high. Individuals whose faith or religious beliefs prohibit them from making such pledge are permitted to excuse themselves, but are required by law to show full respect when the pledge is being rendered by standing at attention.
The law makes no statement regarding the language in which the pledge must be recited, but the pledge is written (and therefore recited) in the Filipino language
Filipino (; , ) is an Austronesian language. It is the national language ( / ) of the Philippines, and one of the two official languages of the country, with English. It is a standardized variety of Tagalog based on the native dialect, sp ...
.
Flag anthem
Spanish, Tagalog and English versions of the national anthem have been given official status throughout Philippine history. However, only the most recent and current "Filipino" version is officially recognized by law. The Flag and Heraldic Code, approved on February 12, 1998, specifies, ''Lupang Hinirang'', "The National Anthem shall always be sung in the national language within or without the country"; violation of the law is punishable by a fine and imprisonment.National Flag Day
The National Flag Day in the Philippines is celebrated every May 28, the very day of the 1898Battle of Alapan
The Battle of Alapan ( fil, Labanan sa Alapan, es, Batalla de Alapan) was fought on May 28, 1898, and was the first military victory of the Filipino Revolutionaries led by Emilio Aguinaldo after his return to the Philippines from Hong Kong. Afte ...
. The official National Flag flying period starts from May 28 and ends on Independence Day, June 12, every year, although the flying period for the flag in homes, businesses and public establishments may start on a specified day of May (to be given by the National Historical Commission of the Philippines) and may last until June 30.
See also
*Coat of arms of the Philippines
The coat of arms of the Philippines ( fil, Sagisag ng Pilipinas; es, Escudo de Filipinas) features the eight-rayed sun of the Philippines with each ray representing the eight provinces (Batangas, Bulacan, Cavite, Manila, Laguna, Nueva Ecija ...
* List of flags of the Philippines
* Philippine coastwise emblem
Notes
References
External links
*The Official Website of the Republic of the Philippines
* *
How to properly display the Philippine flag.
* History of the Philippine Flag:
flagspot.net
Filipino Flag – Learn Now
(archived fro
the original
on 2012-06-23)
Watawat – Flags and Symbols of the Pearl of the Orient Seas
History of the Philippine Flag
Philippines Presidential Museum and Library
Origin of the Symbols of our National Flag
, Philippines Presidential Museum and Library
Flags and Banners of the Colonial Era in the Philippines
Philippines Presidential Museum and Library. {{DEFAULTSORT:Flag Of The Philippines National symbols of the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...