Eishockey O2 World Hamburg.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a

 Stick-and-ball games date go back to the pre-Christian era in
Stick-and-ball games date go back to the pre-Christian era in
Thomas Raddall Selected Correspondence: An Electronic Edition
. From Thomas Raddall to Douglas M. Fisher, January 25, 1954. MS-2-202 41.14. ''Oochamkunutk'' was the name used by the Mi'kmaq to describe their own stick and ball game which they played on the ice while "Alchamadyk" was what the Mi'kmaq called the new the game of "Hurley on Ice" which was played by others around the province during the same period. Of particular note among influential Micmacs is Joe Cope ("Old Joe"), a Mi'kmaq elder known for his talent for carving what became one of the earliest types of ice hockey sticks used. Cope once stated, "Long before the pale faces strayed to this country, the Micmacs were playing two ball games, a field game and an ice game." Sticks made by the Mi'kmaq were used by the British for their games. Early 19th-century paintings depict
Early 19th-century paintings depict
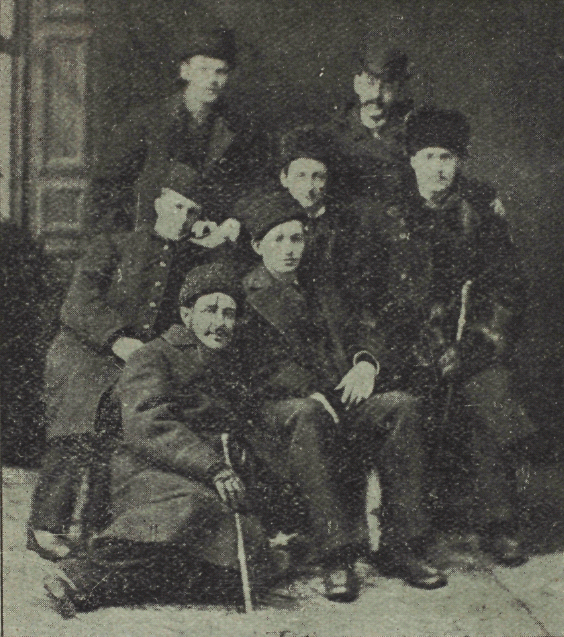 The Canadian city of
The Canadian city of 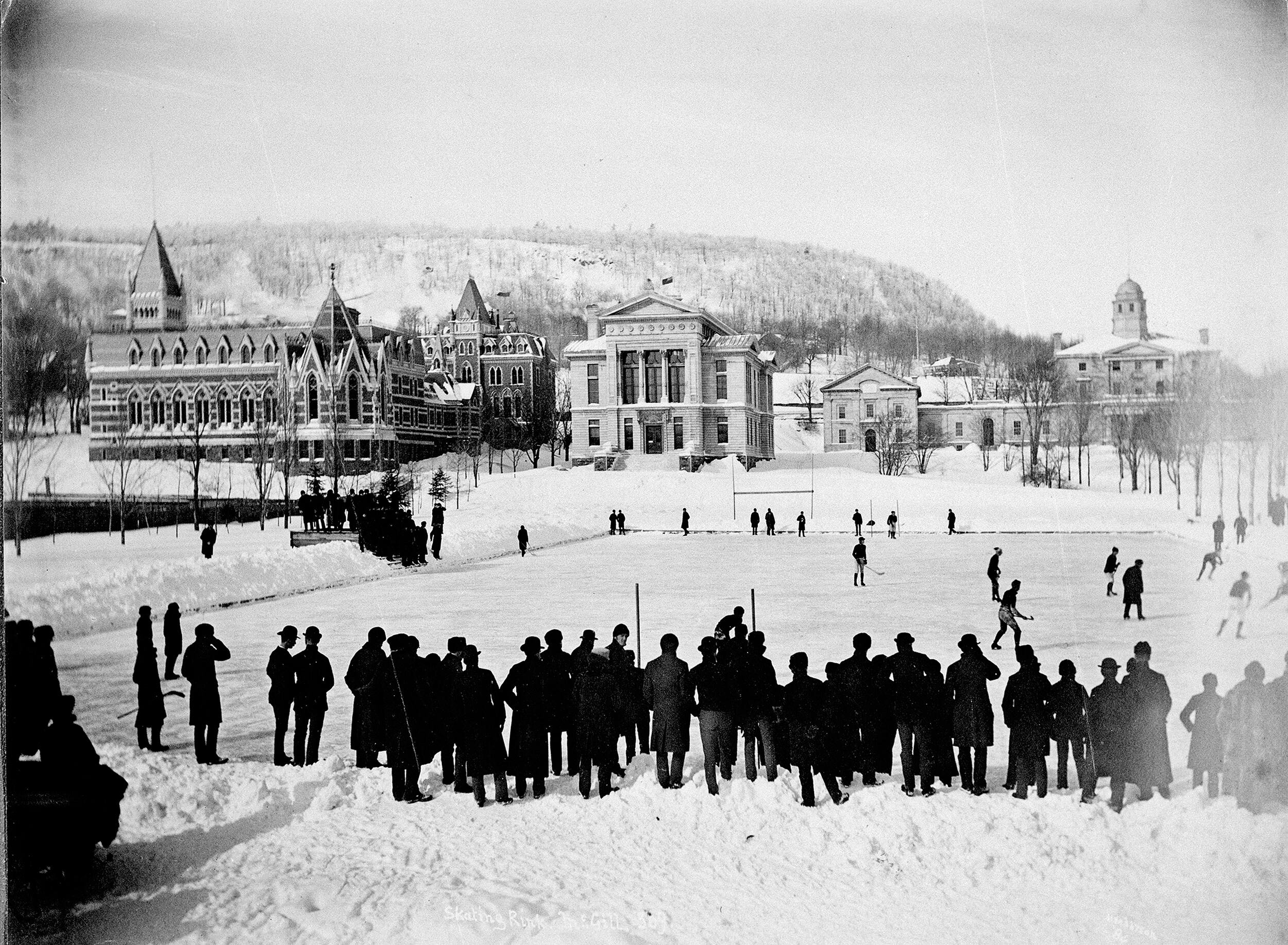 The number of teams grew, enough to hold the first "world championship" of ice hockey at Montreal's annual
The number of teams grew, enough to hold the first "world championship" of ice hockey at Montreal's annual  By 1893, there were almost a hundred teams in Montreal alone; in addition, there were leagues throughout Canada.
By 1893, there were almost a hundred teams in Montreal alone; in addition, there were leagues throughout Canada.  By 1898 the following leagues had already formed: the Amateur Hockey League of New York, the Amateur Hockey Association of Canada, and the Ontario Hockey Association. The 1898
By 1898 the following leagues had already formed: the Amateur Hockey League of New York, the Amateur Hockey Association of Canada, and the Ontario Hockey Association. The 1898
 While scattered incidents of players taking pay to play hockey occurred as early as the 1890s, those found to have done so were banned from playing in the amateur leagues which dominated the sport. By 1902, the Western Pennsylvania Hockey League (WPHL) was the first to employ professionals. The league joined with teams in Michigan and Ontario to form the first fully professional leagueŌĆöthe International Professional Hockey League (IPHL)ŌĆöin 1904. The WPHL and IPHL hired players from Canada; in response, Canadian leagues began to pay players (who played with amateur sports, amateurs). The IPHL, cut off from its largest source of players, disbanded in 1907. By then, several professional hockey leagues were operating in Canada (with leagues in Manitoba, Ontario and Quebec).
In 1910, the National Hockey Association (NHA) was formed in Montreal. The NHA would further refine the rules: dropping the rover position, dividing the game into three 20-minute periods and introducing minor and major penalties. After re-organizing as the National Hockey League in 1917, the league expanded into the United States, starting with the Boston Bruins in 1924.
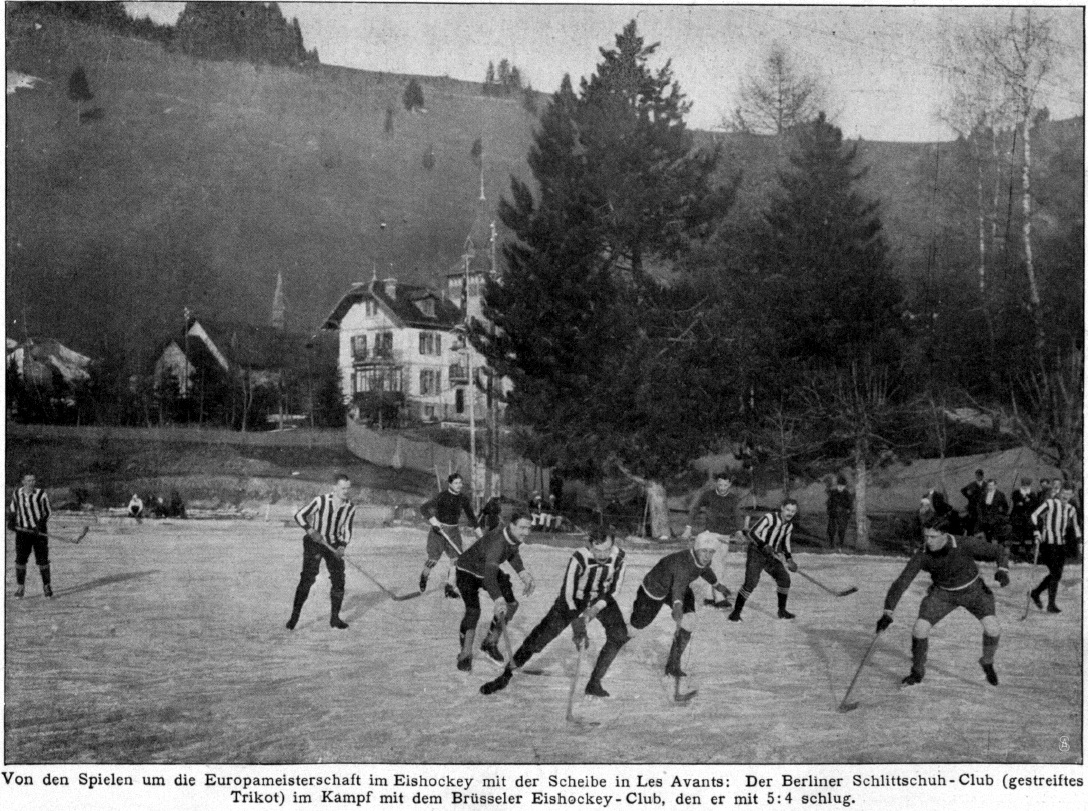
Professional hockey leagues developed later in Europe, but amateur leagues leading to national championships were in place. One of the first was the Swiss National League A, founded in 1916. Today, professional leagues have been introduced in most countries of Europe. Top European leagues include the Kontinental Hockey League, the Czech Extraliga, the Finnish Liiga and the Swedish Hockey League.
While scattered incidents of players taking pay to play hockey occurred as early as the 1890s, those found to have done so were banned from playing in the amateur leagues which dominated the sport. By 1902, the Western Pennsylvania Hockey League (WPHL) was the first to employ professionals. The league joined with teams in Michigan and Ontario to form the first fully professional leagueŌĆöthe International Professional Hockey League (IPHL)ŌĆöin 1904. The WPHL and IPHL hired players from Canada; in response, Canadian leagues began to pay players (who played with amateur sports, amateurs). The IPHL, cut off from its largest source of players, disbanded in 1907. By then, several professional hockey leagues were operating in Canada (with leagues in Manitoba, Ontario and Quebec).
In 1910, the National Hockey Association (NHA) was formed in Montreal. The NHA would further refine the rules: dropping the rover position, dividing the game into three 20-minute periods and introducing minor and major penalties. After re-organizing as the National Hockey League in 1917, the league expanded into the United States, starting with the Boston Bruins in 1924.
Professional hockey leagues developed later in Europe, but amateur leagues leading to national championships were in place. One of the first was the Swiss National League A, founded in 1916. Today, professional leagues have been introduced in most countries of Europe. Top European leagues include the Kontinental Hockey League, the Czech Extraliga, the Finnish Liiga and the Swedish Hockey League.

 While the general characteristics of the game remain constant, the exact rules depend on the particular Ice hockey rules, code of play being used. The two most important codes are those of the IIHF and the NHL. Both of these codes, and others, originated from Canadian rules of ice hockey of the early 20th century.
Ice hockey is played on a ''hockey rink''. During normal play, there are six players on ice skates on the ice per side, one of them being the goaltender. The objective of the game is to score ''goal (ice hockey), goals'' by shooting a hard Vulcanization, vulcanized rubber disc, the '' puck'', into the opponent's goal net at the opposite end of the rink. The players use their sticks to pass or shoot the puck.
With certain restrictions, players may redirect the puck with any part of their body. Players may not hold the puck in their hand and are prohibited from using their hands to pass the puck to their teammates unless they are in the defensive zone. Players however can knock a puck out of the air with their hand to themself. Players are prohibited from kicking the puck into the opponent's goal, though unintentional redirections off the skate are permitted. Players may not intentionally bat the puck into the net with their hands.
While the general characteristics of the game remain constant, the exact rules depend on the particular Ice hockey rules, code of play being used. The two most important codes are those of the IIHF and the NHL. Both of these codes, and others, originated from Canadian rules of ice hockey of the early 20th century.
Ice hockey is played on a ''hockey rink''. During normal play, there are six players on ice skates on the ice per side, one of them being the goaltender. The objective of the game is to score ''goal (ice hockey), goals'' by shooting a hard Vulcanization, vulcanized rubber disc, the '' puck'', into the opponent's goal net at the opposite end of the rink. The players use their sticks to pass or shoot the puck.
With certain restrictions, players may redirect the puck with any part of their body. Players may not hold the puck in their hand and are prohibited from using their hands to pass the puck to their teammates unless they are in the defensive zone. Players however can knock a puck out of the air with their hand to themself. Players are prohibited from kicking the puck into the opponent's goal, though unintentional redirections off the skate are permitted. Players may not intentionally bat the puck into the net with their hands.
 Hockey is an Offside (ice hockey), off-side game, meaning that forward passes are allowed, unlike in rugby. Before the 1930s, hockey was an on-side game, meaning that only backward passes were allowed. Those rules emphasized individual stick-handling to drive the puck forward. With the arrival of offside rules, the forward pass transformed hockey into a true team sport, where individual performance diminished in importance relative to team play, which could now be coordinated over the entire surface of the ice as opposed to merely rearward players.
The six players on each team are typically divided into three forwards, two defencemen, and a goaltender. The term ''skaters'' typically applies to all players except goaltenders. The ''Forward (ice hockey), forward'' positions consist of a ''Center (ice hockey), centre'' and two ''Winger (ice hockey), wingers'': a ''left wing'' and a ''right wing''. Forwards often play together as units or ''lines'', with the same three forwards always playing together. The ''Defenceman (ice hockey), defencemen'' usually stay together as a pair generally divided between left and right. Left and right side wingers or defencemen are generally positioned on the side on which they carry their stick. A substitution (sport), substitution of an entire unit at once is called a ''line change''. Teams typically employ alternate sets of forward lines and defensive pairings when ''short-handed'' or on a ''Power play (sporting term), power play''. The goaltender stands in a, usually blue, semi-circle called the ''crease'' in the defensive zone keeping pucks out of the goal. Substitutions are permitted at any time during the game, although during a stoppage of play the home team is permitted the final change. When players are substituted during play, it is called changing ''on the fly''. An NHL rule added in the 2005ŌĆō06 season prevents a team from changing their line after they ''Icing (ice hockey), ice'' the puck.
Hockey is an Offside (ice hockey), off-side game, meaning that forward passes are allowed, unlike in rugby. Before the 1930s, hockey was an on-side game, meaning that only backward passes were allowed. Those rules emphasized individual stick-handling to drive the puck forward. With the arrival of offside rules, the forward pass transformed hockey into a true team sport, where individual performance diminished in importance relative to team play, which could now be coordinated over the entire surface of the ice as opposed to merely rearward players.
The six players on each team are typically divided into three forwards, two defencemen, and a goaltender. The term ''skaters'' typically applies to all players except goaltenders. The ''Forward (ice hockey), forward'' positions consist of a ''Center (ice hockey), centre'' and two ''Winger (ice hockey), wingers'': a ''left wing'' and a ''right wing''. Forwards often play together as units or ''lines'', with the same three forwards always playing together. The ''Defenceman (ice hockey), defencemen'' usually stay together as a pair generally divided between left and right. Left and right side wingers or defencemen are generally positioned on the side on which they carry their stick. A substitution (sport), substitution of an entire unit at once is called a ''line change''. Teams typically employ alternate sets of forward lines and defensive pairings when ''short-handed'' or on a ''Power play (sporting term), power play''. The goaltender stands in a, usually blue, semi-circle called the ''crease'' in the defensive zone keeping pucks out of the goal. Substitutions are permitted at any time during the game, although during a stoppage of play the home team is permitted the final change. When players are substituted during play, it is called changing ''on the fly''. An NHL rule added in the 2005ŌĆō06 season prevents a team from changing their line after they ''Icing (ice hockey), ice'' the puck.
 The boards surrounding the ice help keep the puck in play and they can also be used as tools to play the puck. Players are permitted to bodycheck opponents into the boards to stop progress. The referees, linesmen and the outsides of the goal are "in play" and do not stop the game when the puck or players either bounce into or collide with them. Play can be stopped if the goal is knocked out of position. Play often proceeds for minutes without interruption. After a stoppage, play is restarted with a faceoff. Two players face each other and an official drops the puck to the ice, where the two players attempt to gain control of the puck. Markings (circles) on the ice indicate the locations for the faceoff and guide the positioning of players.
Three major rules of play in ice hockey limit the movement of the puck: ''offside'', ''icing'', and the puck going out of play.
*A player is offside if he enters his Hockey rink#Zones, opponent's zone before the puck itself.
*Under many situations, a player may not "ice the puck", which means shooting the puck all the way across both the centre line and the opponent's goal line.
*The puck goes out of play whenever it goes past the perimeter of the ice rink (onto the player benches, over the Plexiglas, glass, or onto the protective netting above the glass) and a stoppage of play is called by the officials using whistles. It does not matter if the puck comes back onto the ice surface from outside of the rink, because the puck is considered dead once it leaves the perimeter of the rink. The referee may also blow the whistle for a stoppage in play if the puck is jammed along the boards when 2 or more players are battling for the puck for a long time, or if the puck is stuck on the back of any of the two nets for a period of time.
Under IIHF rules, each team may carry a maximum of 20 players and two goaltenders on their roster. NHL rules restrict the total number of players per game to 18, plus two goaltenders. In the NHL, the players are usually divided into four lines of three forwards, and into three pairs of defencemen. On occasion, teams may elect to substitute an extra defenceman for a forward. The seventh defenceman may play as a substitute defenceman, spend the game on the bench, or if a team chooses to play four lines then this seventh defenceman may see ice-time on the fourth line as a forward.
The boards surrounding the ice help keep the puck in play and they can also be used as tools to play the puck. Players are permitted to bodycheck opponents into the boards to stop progress. The referees, linesmen and the outsides of the goal are "in play" and do not stop the game when the puck or players either bounce into or collide with them. Play can be stopped if the goal is knocked out of position. Play often proceeds for minutes without interruption. After a stoppage, play is restarted with a faceoff. Two players face each other and an official drops the puck to the ice, where the two players attempt to gain control of the puck. Markings (circles) on the ice indicate the locations for the faceoff and guide the positioning of players.
Three major rules of play in ice hockey limit the movement of the puck: ''offside'', ''icing'', and the puck going out of play.
*A player is offside if he enters his Hockey rink#Zones, opponent's zone before the puck itself.
*Under many situations, a player may not "ice the puck", which means shooting the puck all the way across both the centre line and the opponent's goal line.
*The puck goes out of play whenever it goes past the perimeter of the ice rink (onto the player benches, over the Plexiglas, glass, or onto the protective netting above the glass) and a stoppage of play is called by the officials using whistles. It does not matter if the puck comes back onto the ice surface from outside of the rink, because the puck is considered dead once it leaves the perimeter of the rink. The referee may also blow the whistle for a stoppage in play if the puck is jammed along the boards when 2 or more players are battling for the puck for a long time, or if the puck is stuck on the back of any of the two nets for a period of time.
Under IIHF rules, each team may carry a maximum of 20 players and two goaltenders on their roster. NHL rules restrict the total number of players per game to 18, plus two goaltenders. In the NHL, the players are usually divided into four lines of three forwards, and into three pairs of defencemen. On occasion, teams may elect to substitute an extra defenceman for a forward. The seventh defenceman may play as a substitute defenceman, spend the game on the bench, or if a team chooses to play four lines then this seventh defenceman may see ice-time on the fourth line as a forward.
 If a tie occurs in tournament play, as well as in the NHL playoffs, North Americans favour ''sudden death Overtime (ice hockey), overtime'', in which the teams continue to play twenty-minute periods until a goal is scored. Up until the 1999ŌĆō2000 season, regular-season NHL games were settled with a single five-minute sudden death period with five players (plus a goalie) per side, with both teams awarded one point in the standings in the event of a tie. With a goal, the winning team would be awarded two points and the losing team none (just as if they had lost in regulation). The total elapsed time from when the puck first drops, is about 2 hours and 20 minutes for a 60-minute game.
From the 1999ŌĆō2000 until the 2003ŌĆō04 seasons, the National Hockey League decided ties by playing a single five-minute sudden-death overtime period with each team having four skaters per side (plus the goalie). In the event of a tie, each team would still receive one point in the standings but in the event of a victory the winning team would be awarded two points in the standings and the losing team one point. The idea was to discourage teams from playing for a tie, since previously some teams might have preferred a tie and 1 point to risking a loss and zero points. The exception to this rule is if a team opts to pull their goalie in exchange for an extra skater during overtime and is subsequently scored upon (an ''empty net'' goal), in which case the losing team receives no points for the overtime loss. Since the 2015ŌĆō16 season, the single five-minute sudden-death overtime session involves three skaters on each side. Since three skaters must always be on the ice in an NHL game, the consequences of penalties are slightly different from those during regulation play; any penalty during overtime that would result in a team losing a skater during regulation instead causes the other side to add a skater. Once the penalized team's penalty ends, the penalized skater exits the penalty box and the teams continue at 4-on-4 until the next stoppage of play, at which point the teams return to three skaters per side.
If a tie occurs in tournament play, as well as in the NHL playoffs, North Americans favour ''sudden death Overtime (ice hockey), overtime'', in which the teams continue to play twenty-minute periods until a goal is scored. Up until the 1999ŌĆō2000 season, regular-season NHL games were settled with a single five-minute sudden death period with five players (plus a goalie) per side, with both teams awarded one point in the standings in the event of a tie. With a goal, the winning team would be awarded two points and the losing team none (just as if they had lost in regulation). The total elapsed time from when the puck first drops, is about 2 hours and 20 minutes for a 60-minute game.
From the 1999ŌĆō2000 until the 2003ŌĆō04 seasons, the National Hockey League decided ties by playing a single five-minute sudden-death overtime period with each team having four skaters per side (plus the goalie). In the event of a tie, each team would still receive one point in the standings but in the event of a victory the winning team would be awarded two points in the standings and the losing team one point. The idea was to discourage teams from playing for a tie, since previously some teams might have preferred a tie and 1 point to risking a loss and zero points. The exception to this rule is if a team opts to pull their goalie in exchange for an extra skater during overtime and is subsequently scored upon (an ''empty net'' goal), in which case the losing team receives no points for the overtime loss. Since the 2015ŌĆō16 season, the single five-minute sudden-death overtime session involves three skaters on each side. Since three skaters must always be on the ice in an NHL game, the consequences of penalties are slightly different from those during regulation play; any penalty during overtime that would result in a team losing a skater during regulation instead causes the other side to add a skater. Once the penalized team's penalty ends, the penalized skater exits the penalty box and the teams continue at 4-on-4 until the next stoppage of play, at which point the teams return to three skaters per side.
 International play and several North American professional leagues, including the NHL (in the regular season), now use an overtime period identical to that from 1999ŌĆō2000 to 2003ŌĆō04 followed by a Shootout (hockey), penalty shootout. If the score remains tied after an extra overtime period, the subsequent shootout consists of three players from each team taking penalty shots. After these six total shots, the team with the most goals is awarded the victory. If the score is still tied, the shootout then proceeds to ''Sudden death (sport), sudden death''. Regardless of the number of goals scored by either team during the shootout, the final score recorded will award the winning team one more goal than the score at the end of regulation time. In the NHL if a game is decided in overtime or by a shootout the winning team is awarded two points in the standings and the losing team is awarded one point. Ties no longer occur in the NHL.
Overtime in the NHL playoffs differs from the regular season. In the playoffs there are no shootouts. If a game is tied after regulation, then a 20-minute period of 5-on-5 sudden-death overtime will be added. If the game is still tied after the overtime, another period is added until a team scores, which wins the match. Since 2019, the IIHF World Championships and the gold medal game in the Olympics use the same format, but in a 3-on-3 format.
International play and several North American professional leagues, including the NHL (in the regular season), now use an overtime period identical to that from 1999ŌĆō2000 to 2003ŌĆō04 followed by a Shootout (hockey), penalty shootout. If the score remains tied after an extra overtime period, the subsequent shootout consists of three players from each team taking penalty shots. After these six total shots, the team with the most goals is awarded the victory. If the score is still tied, the shootout then proceeds to ''Sudden death (sport), sudden death''. Regardless of the number of goals scored by either team during the shootout, the final score recorded will award the winning team one more goal than the score at the end of regulation time. In the NHL if a game is decided in overtime or by a shootout the winning team is awarded two points in the standings and the losing team is awarded one point. Ties no longer occur in the NHL.
Overtime in the NHL playoffs differs from the regular season. In the playoffs there are no shootouts. If a game is tied after regulation, then a 20-minute period of 5-on-5 sudden-death overtime will be added. If the game is still tied after the overtime, another period is added until a team scores, which wins the match. Since 2019, the IIHF World Championships and the gold medal game in the Olympics use the same format, but in a 3-on-3 format.
 In ice hockey, infractions of the rules lead to a play stoppage whereby the play is restarted at a faceoff. Some infractions result in a ''penalty'' on a player or team. In the simplest case, the offending player is sent to the ''penalty box'' and their team must play with one less player on the ice for a designated time. ''Minor'' penalties last for two minutes, ''major'' penalties last for five minutes, and a ''double minor'' penalty is two ''consecutive'' penalties of two minutes duration. A single minor penalty may be extended by two minutes for causing visible injury to the victimized player. This is usually when blood is drawn during high sticking. Players may be also assessed personal extended penalties or game expulsions for misconduct in addition to the penalty or penalties their team must serve. The team that has been given a penalty is said to be playing ''short-handed'' while the opposing team is on a ''power play (sport), power play''.
A two-minute minor penalty is often charged for lesser infractions such as tripping (ice hockey), tripping, elbow (strike), elbowing, roughing, high-sticking, delay of game, delay of the game, too many men, too many players on the ice, boarding (ice hockey), boarding, illegal equipment, charging (ice hockey), charging (leaping into an opponent or body-checking him after taking more than two strides), holding, holding the stick (grabbing an opponent's stick), interference, hooking (ice hockey), hooking, slashing (ice hockey), slashing, kneeing, unsportsmanlike conduct (arguing a penalty call with referee, extremely vulgar or inappropriate verbal comments), "butt-ending" (striking an opponent with the knob of the stick), "spearing" (jabbing an opponent with the blade of the stick), or cross-checking. As of the 2005ŌĆō2006 season, a minor penalty is also assessed for diving (ice hockey), diving, where a player embellishes or simulates an offence. More egregious fouls may be penalized by a four-minute double-minor penalty, particularly those that injure the victimized player. These penalties end either when the time runs out or when the other team scores during the power play. In the case of a goal scored during the first two minutes of a double-minor, the penalty clock is set down to two minutes upon a score, effectively expiring the first minor penalty.
Five-minute major penalties are called for especially violent instances of most minor infractions that result in intentional injury to an opponent, or when a minor penalty results in visible injury (such as bleeding), as well as for fighting. Major penalties are always served in full; they do not terminate on a goal scored by the other team. Major penalties assessed for fighting are typically offsetting, meaning neither team is short-handed and the players exit the penalty box upon a stoppage of play following the expiration of their respective penalties. The foul of boarding (defined as "check[ing] an opponent in such a manner that causes the opponent to be thrown violently in the boards") is penalized either by a minor or major penalty at the discretion of the referee, based on the violent state of the hit. A minor or major penalty for boarding is often assessed when a player checks an opponent from behind and into the boards.
Some varieties of penalty do not require the offending team to play a man short. Concurrent five-minute major penalties in the NHL usually result from fighting. In the case of two players being assessed five-minute fighting majors, both the players serve five minutes without their team incurring a loss of player (both teams still have a full complement of players on the ice). This differs with two players from opposing sides getting minor penalties, at the same time or at any intersecting moment, resulting from more common infractions. In this case, both teams will have only four skating players (not counting the goaltender) until one or both penalties expire (if one penalty expires before the other, the opposing team gets a power play for the remainder of the time); this applies regardless of current pending penalties. However, in the NHL, a team always has at least three skaters on the ice. Thus, ten-minute ''misconduct'' penalties are served in full by the penalized player, but his team may immediately substitute another player on the ice ''unless'' a minor or major penalty is assessed in conjunction with the misconduct (a ''two-and-ten'' or ''five-and-ten''). In this case, the team designates another player to serve the minor or major; both players go to the penalty box, but only the designee may not be replaced, and he is released upon the expiration of the two or five minutes, at which point the ten-minute misconduct begins. In addition, ''game misconducts'' are assessed for deliberate intent to inflict severe injury on an opponent (at the officials' discretion), or for a major penalty for a stick infraction or repeated major penalties. The offending player is ejected from the game and must immediately leave the playing surface (he does not sit in the penalty box); meanwhile, if an additional minor or major penalty is assessed, a designated player must serve out of that segment of the penalty in the box (similar to the above-mentioned "two-and-ten"). In some rare cases, a player may receive up to nineteen minutes in penalties for one string of plays. This could involve receiving a four-minute double-minor penalty, getting in a fight with an opposing player who retaliates, and then receiving a game misconduct after the fight. In this case, the player is ejected and two teammates must serve the double-minor and major penalties.
In ice hockey, infractions of the rules lead to a play stoppage whereby the play is restarted at a faceoff. Some infractions result in a ''penalty'' on a player or team. In the simplest case, the offending player is sent to the ''penalty box'' and their team must play with one less player on the ice for a designated time. ''Minor'' penalties last for two minutes, ''major'' penalties last for five minutes, and a ''double minor'' penalty is two ''consecutive'' penalties of two minutes duration. A single minor penalty may be extended by two minutes for causing visible injury to the victimized player. This is usually when blood is drawn during high sticking. Players may be also assessed personal extended penalties or game expulsions for misconduct in addition to the penalty or penalties their team must serve. The team that has been given a penalty is said to be playing ''short-handed'' while the opposing team is on a ''power play (sport), power play''.
A two-minute minor penalty is often charged for lesser infractions such as tripping (ice hockey), tripping, elbow (strike), elbowing, roughing, high-sticking, delay of game, delay of the game, too many men, too many players on the ice, boarding (ice hockey), boarding, illegal equipment, charging (ice hockey), charging (leaping into an opponent or body-checking him after taking more than two strides), holding, holding the stick (grabbing an opponent's stick), interference, hooking (ice hockey), hooking, slashing (ice hockey), slashing, kneeing, unsportsmanlike conduct (arguing a penalty call with referee, extremely vulgar or inappropriate verbal comments), "butt-ending" (striking an opponent with the knob of the stick), "spearing" (jabbing an opponent with the blade of the stick), or cross-checking. As of the 2005ŌĆō2006 season, a minor penalty is also assessed for diving (ice hockey), diving, where a player embellishes or simulates an offence. More egregious fouls may be penalized by a four-minute double-minor penalty, particularly those that injure the victimized player. These penalties end either when the time runs out or when the other team scores during the power play. In the case of a goal scored during the first two minutes of a double-minor, the penalty clock is set down to two minutes upon a score, effectively expiring the first minor penalty.
Five-minute major penalties are called for especially violent instances of most minor infractions that result in intentional injury to an opponent, or when a minor penalty results in visible injury (such as bleeding), as well as for fighting. Major penalties are always served in full; they do not terminate on a goal scored by the other team. Major penalties assessed for fighting are typically offsetting, meaning neither team is short-handed and the players exit the penalty box upon a stoppage of play following the expiration of their respective penalties. The foul of boarding (defined as "check[ing] an opponent in such a manner that causes the opponent to be thrown violently in the boards") is penalized either by a minor or major penalty at the discretion of the referee, based on the violent state of the hit. A minor or major penalty for boarding is often assessed when a player checks an opponent from behind and into the boards.
Some varieties of penalty do not require the offending team to play a man short. Concurrent five-minute major penalties in the NHL usually result from fighting. In the case of two players being assessed five-minute fighting majors, both the players serve five minutes without their team incurring a loss of player (both teams still have a full complement of players on the ice). This differs with two players from opposing sides getting minor penalties, at the same time or at any intersecting moment, resulting from more common infractions. In this case, both teams will have only four skating players (not counting the goaltender) until one or both penalties expire (if one penalty expires before the other, the opposing team gets a power play for the remainder of the time); this applies regardless of current pending penalties. However, in the NHL, a team always has at least three skaters on the ice. Thus, ten-minute ''misconduct'' penalties are served in full by the penalized player, but his team may immediately substitute another player on the ice ''unless'' a minor or major penalty is assessed in conjunction with the misconduct (a ''two-and-ten'' or ''five-and-ten''). In this case, the team designates another player to serve the minor or major; both players go to the penalty box, but only the designee may not be replaced, and he is released upon the expiration of the two or five minutes, at which point the ten-minute misconduct begins. In addition, ''game misconducts'' are assessed for deliberate intent to inflict severe injury on an opponent (at the officials' discretion), or for a major penalty for a stick infraction or repeated major penalties. The offending player is ejected from the game and must immediately leave the playing surface (he does not sit in the penalty box); meanwhile, if an additional minor or major penalty is assessed, a designated player must serve out of that segment of the penalty in the box (similar to the above-mentioned "two-and-ten"). In some rare cases, a player may receive up to nineteen minutes in penalties for one string of plays. This could involve receiving a four-minute double-minor penalty, getting in a fight with an opposing player who retaliates, and then receiving a game misconduct after the fight. In this case, the player is ejected and two teammates must serve the double-minor and major penalties.
 A Penalty shot (ice hockey), penalty shot is awarded to a player when the illegal actions of another player stop a clear scoring opportunity, most commonly when the player is on a Breakaway (ice hockey), breakaway. A penalty shot allows the obstructed player to pick up the puck on the centre red-line and attempt to score on the goalie with no other players on the ice, to compensate for the earlier missed scoring opportunity. A penalty shot is also awarded for a defender other than the goaltender covering the puck in the goal crease, a goaltender intentionally displacing his own goal posts during a breakaway to avoid a goal, a defender intentionally displacing his own goal posts when there is less than two minutes to play in regulation time or at any point during overtime, or a player or coach intentionally throwing a stick or other object at the puck or the puck carrier and the throwing action disrupts a shot or pass play.
Officials also stop play for puck movement violations, such as using one's hands to pass the puck in the offensive end, but no players are penalized for these offences. The sole exceptions are deliberately falling on or gathering the puck to the body, carrying the puck in the hand, and shooting the puck out of play in one's defensive zone (all penalized two minutes for delay of game).
In the NHL, a unique penalty applies to the goalies. The goalies now are forbidden to play the puck in the "corners" of the rink near their own net. This will result in a two-minute penalty against the goalie's team. Only in the area in front of the goal line and immediately behind the net (marked by two red lines on either side of the net) can the goalie play the puck.
An additional rule that has never been a penalty, but was an infraction in the NHL before recent rules changes, is the Two-line pass, two-line offside pass. Prior to the 2005ŌĆō06 NHL season, play was stopped when a pass from inside a team's defending zone crossed the centre line, with a face-off held in the defending zone of the offending team. Now, the centre line is no longer used in the NHL to determine a two-line pass infraction, a change that the IIHF had adopted in 1998. Players are now able to pass to teammates who are more than the blue and centre ice red line away.
The NHL has taken steps to speed up the game of hockey and create a game of finesse, by reducing the number of illegal hits, fights, and "clutching and grabbing" that occurred in the past. Rules are now more strictly enforced, resulting in more penalties, which provides more protection to the players and facilitates more goals being scored. The governing body for United States' amateur hockey has implemented many new rules to reduce the number of stick-on-body occurrences, as well as other detrimental and illegal facets of the game ("zero tolerance").
In men's hockey, but not in women's, a player may use his hip or shoulder to hit another player if the player has the puck or is the last to have touched it. This use of the hip and shoulder is called '' body checking''. Not all physical contact is legalŌĆöin particular, hits from behind, hits to the head and most types of forceful stick-on-body contact are illegal.
A Penalty shot (ice hockey), penalty shot is awarded to a player when the illegal actions of another player stop a clear scoring opportunity, most commonly when the player is on a Breakaway (ice hockey), breakaway. A penalty shot allows the obstructed player to pick up the puck on the centre red-line and attempt to score on the goalie with no other players on the ice, to compensate for the earlier missed scoring opportunity. A penalty shot is also awarded for a defender other than the goaltender covering the puck in the goal crease, a goaltender intentionally displacing his own goal posts during a breakaway to avoid a goal, a defender intentionally displacing his own goal posts when there is less than two minutes to play in regulation time or at any point during overtime, or a player or coach intentionally throwing a stick or other object at the puck or the puck carrier and the throwing action disrupts a shot or pass play.
Officials also stop play for puck movement violations, such as using one's hands to pass the puck in the offensive end, but no players are penalized for these offences. The sole exceptions are deliberately falling on or gathering the puck to the body, carrying the puck in the hand, and shooting the puck out of play in one's defensive zone (all penalized two minutes for delay of game).
In the NHL, a unique penalty applies to the goalies. The goalies now are forbidden to play the puck in the "corners" of the rink near their own net. This will result in a two-minute penalty against the goalie's team. Only in the area in front of the goal line and immediately behind the net (marked by two red lines on either side of the net) can the goalie play the puck.
An additional rule that has never been a penalty, but was an infraction in the NHL before recent rules changes, is the Two-line pass, two-line offside pass. Prior to the 2005ŌĆō06 NHL season, play was stopped when a pass from inside a team's defending zone crossed the centre line, with a face-off held in the defending zone of the offending team. Now, the centre line is no longer used in the NHL to determine a two-line pass infraction, a change that the IIHF had adopted in 1998. Players are now able to pass to teammates who are more than the blue and centre ice red line away.
The NHL has taken steps to speed up the game of hockey and create a game of finesse, by reducing the number of illegal hits, fights, and "clutching and grabbing" that occurred in the past. Rules are now more strictly enforced, resulting in more penalties, which provides more protection to the players and facilitates more goals being scored. The governing body for United States' amateur hockey has implemented many new rules to reduce the number of stick-on-body occurrences, as well as other detrimental and illegal facets of the game ("zero tolerance").
In men's hockey, but not in women's, a player may use his hip or shoulder to hit another player if the player has the puck or is the last to have touched it. This use of the hip and shoulder is called '' body checking''. Not all physical contact is legalŌĆöin particular, hits from behind, hits to the head and most types of forceful stick-on-body contact are illegal.
 A ''delayed penalty call'' occurs when an offence is committed by the team that does not have possession of the puck. In this circumstance the team with possession of the puck is allowed to complete the play; that is, play continues until a goal is scored, a player on the opposing team gains control of the puck, or the team in possession commits an infraction or penalty of their own. Because the team on which the penalty was called cannot control the puck without stopping play, it is impossible for them to score a goal. In these cases, the team in possession of the puck can pull the goalie for an extra attacker without fear of being scored on. However, it is possible for the controlling team to mishandle the puck into their own net. If a delayed penalty is signalled and the team in possession scores, the penalty is still assessed to the offending player, but not served. In 2012, this rule was changed by the United States' National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) for college ice hockey, college level hockey. In college games, the penalty is still enforced even if the team in possession scores.
A ''delayed penalty call'' occurs when an offence is committed by the team that does not have possession of the puck. In this circumstance the team with possession of the puck is allowed to complete the play; that is, play continues until a goal is scored, a player on the opposing team gains control of the puck, or the team in possession commits an infraction or penalty of their own. Because the team on which the penalty was called cannot control the puck without stopping play, it is impossible for them to score a goal. In these cases, the team in possession of the puck can pull the goalie for an extra attacker without fear of being scored on. However, it is possible for the controlling team to mishandle the puck into their own net. If a delayed penalty is signalled and the team in possession scores, the penalty is still assessed to the offending player, but not served. In 2012, this rule was changed by the United States' National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) for college ice hockey, college level hockey. In college games, the penalty is still enforced even if the team in possession scores.
 The most widespread system is the "three-man system", which uses one referee and two linesmen. A less commonly used system is the two referee and one linesman system. This system is close to the regular three-man system except for a few procedure changes. Beginning with the National Hockey League, a number of leagues have implemented the "four-official system", where an additional referee is added to aid in the calling of penalties normally difficult to assess by one referee. The system is used in every NHL game since 2001, at
The most widespread system is the "three-man system", which uses one referee and two linesmen. A less commonly used system is the two referee and one linesman system. This system is close to the regular three-man system except for a few procedure changes. Beginning with the National Hockey League, a number of leagues have implemented the "four-official system", where an additional referee is added to aid in the calling of penalties normally difficult to assess by one referee. The system is used in every NHL game since 2001, at
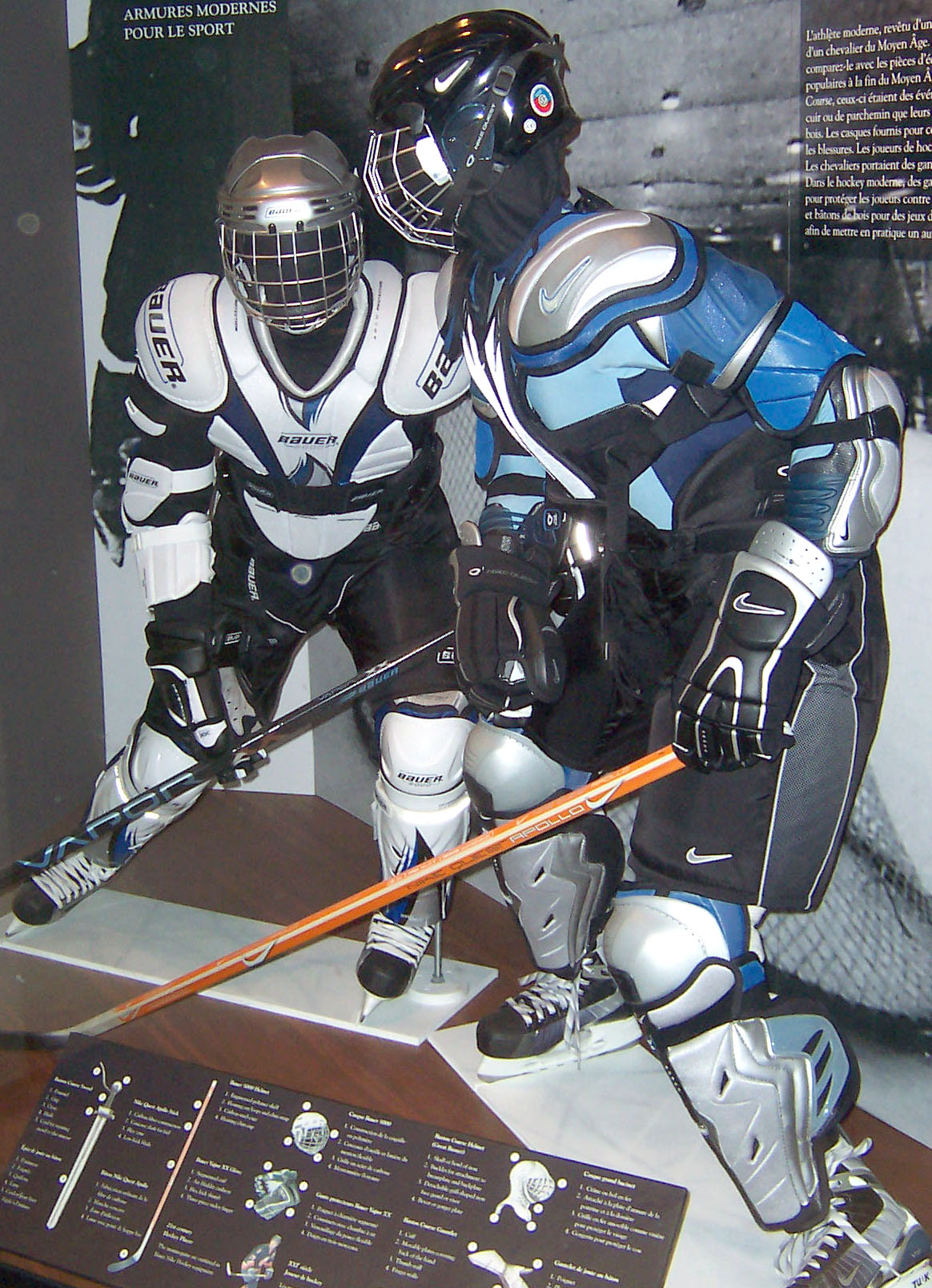 Since men's ice hockey is a full-contact sport, body checks are allowed so injuries are a common occurrence. Protective equipment is mandatory and is enforced in all competitive situations. This includes a helmet with either a visor or a full face mask, shoulder pads, elbow pads, mouth guard, protective gloves, heavily padded shorts (also known as hockey pants) or a girdle, athletic cup (also known as a jock, for males; and jill, for females), shin pads, skates, and (optionally) a neck protector.
Since men's ice hockey is a full-contact sport, body checks are allowed so injuries are a common occurrence. Protective equipment is mandatory and is enforced in all competitive situations. This includes a helmet with either a visor or a full face mask, shoulder pads, elbow pads, mouth guard, protective gloves, heavily padded shorts (also known as hockey pants) or a girdle, athletic cup (also known as a jock, for males; and jill, for females), shin pads, skates, and (optionally) a neck protector.
 An important defensive tactic is checkingŌĆöattempting to take the puck from an opponent or to remove the opponent from play. ''Stick checking'', ''sweep checking'', and ''poke checking'' are legal uses of the stick to obtain possession of the puck. The ''neutral zone trap'' is designed to isolate the puck carrier in the neutral zone preventing him from entering the offensive zone. ''Body checking'' is using one's shoulder or hip to strike an opponent who has the puck or who is the last to have touched it (the last person to have touched the puck is still legally "in possession" of it, although a penalty is generally called if he is checked more than two seconds after his last touch). Body checking is also a penalty in certain leagues in order to reduce the chance of injury to players. Often the term checking is used to refer to body checking, with its true definition generally only propagated among fans of the game.
An important defensive tactic is checkingŌĆöattempting to take the puck from an opponent or to remove the opponent from play. ''Stick checking'', ''sweep checking'', and ''poke checking'' are legal uses of the stick to obtain possession of the puck. The ''neutral zone trap'' is designed to isolate the puck carrier in the neutral zone preventing him from entering the offensive zone. ''Body checking'' is using one's shoulder or hip to strike an opponent who has the puck or who is the last to have touched it (the last person to have touched the puck is still legally "in possession" of it, although a penalty is generally called if he is checked more than two seconds after his last touch). Body checking is also a penalty in certain leagues in order to reduce the chance of injury to players. Often the term checking is used to refer to body checking, with its true definition generally only propagated among fans of the game.
 A ''deflection'' is a shot that redirects a shot or a pass towards the goal from another player, by allowing the puck to strike the stick and carom towards the goal. A ''one-timer'' is a shot struck directly off a pass, without receiving the pass and shooting in two separate actions. ''Headmanning the puck'', also known as ''breaking out'', is the tactic of rapidly passing to the player farthest down the ice. ''Loafing (ice hockey), Loafing'', also known as ''cherry picking (basketball), cherry-picking'', is when a player, usually a forward, skates behind an attacking team, instead of playing defence, in an attempt to create an easy scoring chance.
A team that is losing by one or two goals in the last few minutes of play will often elect to ''pull the goalie''; that is, remove the goaltender and replace him or her with an ''extra attacker'' on the ice in the hope of gaining enough advantage to score a goal. However, it is an act of desperation, as it sometimes leads to the opposing team extending their lead by scoring a goal in the empty net.
One of the most important strategies for a team is their ''forecheck''. Forechecking is the act of attacking the opposition in their defensive zone. Forechecking is an important part of the ''dump and chase'' strategy (i.e. shooting the puck into the offensive zone and then chasing after it). Each team will use their own unique system but the main ones are: 2-1-2 Forecheck, 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2, 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2, and 1ŌĆō4. The 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2 is the most basic forecheck system where two forwards will go in deep and pressure the opposition's defencemen, the third forward stays high and the two defencemen stay at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2 is a bit more conservative system where one forward pressures the puck carrier and the other two forwards cover the oppositions' wingers, with the two defencemen staying at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō4 is the most defensive forecheck system, referred to as the neutral zone trap, where one forward will apply pressure to the puck carrier around the oppositions' blueline and the other 4 players stand basically in a line by their blueline in hopes the opposition will skate into one of them. Another strategy is the left wing lock, which has two forwards pressure the puck and the left wing and the two defencemen stay at the blueline.
A ''deflection'' is a shot that redirects a shot or a pass towards the goal from another player, by allowing the puck to strike the stick and carom towards the goal. A ''one-timer'' is a shot struck directly off a pass, without receiving the pass and shooting in two separate actions. ''Headmanning the puck'', also known as ''breaking out'', is the tactic of rapidly passing to the player farthest down the ice. ''Loafing (ice hockey), Loafing'', also known as ''cherry picking (basketball), cherry-picking'', is when a player, usually a forward, skates behind an attacking team, instead of playing defence, in an attempt to create an easy scoring chance.
A team that is losing by one or two goals in the last few minutes of play will often elect to ''pull the goalie''; that is, remove the goaltender and replace him or her with an ''extra attacker'' on the ice in the hope of gaining enough advantage to score a goal. However, it is an act of desperation, as it sometimes leads to the opposing team extending their lead by scoring a goal in the empty net.
One of the most important strategies for a team is their ''forecheck''. Forechecking is the act of attacking the opposition in their defensive zone. Forechecking is an important part of the ''dump and chase'' strategy (i.e. shooting the puck into the offensive zone and then chasing after it). Each team will use their own unique system but the main ones are: 2-1-2 Forecheck, 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2, 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2, and 1ŌĆō4. The 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2 is the most basic forecheck system where two forwards will go in deep and pressure the opposition's defencemen, the third forward stays high and the two defencemen stay at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2 is a bit more conservative system where one forward pressures the puck carrier and the other two forwards cover the oppositions' wingers, with the two defencemen staying at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō4 is the most defensive forecheck system, referred to as the neutral zone trap, where one forward will apply pressure to the puck carrier around the oppositions' blueline and the other 4 players stand basically in a line by their blueline in hopes the opposition will skate into one of them. Another strategy is the left wing lock, which has two forwards pressure the puck and the left wing and the two defencemen stay at the blueline.
 There are many other little tactics used in the game of hockey. ''Cycling (ice hockey), Cycling'' moves the puck along the boards in the offensive zone to create a scoring chance by making defenders tired or moving them out of position. ''Pinching'' is when a defenceman pressures the opposition's winger in the offensive zone when they are breaking out, attempting to stop their attack and keep the puck in the offensive zone. A ''saucer pass'' is a pass used when an opposition's stick or body is in the passing lane. It is the act of raising the puck over the obstruction and having it land on a teammate's stick.
A deke (ice hockey), deke, short for "decoy", is a feint with the body or stick to fool a defender or the goalie. Many modern players, such as Pavel Datsyuk, Sidney Crosby and Patrick Kane, have picked up the skill of "dangling", which is fancier deking and requires more stick handling skills.
There are many other little tactics used in the game of hockey. ''Cycling (ice hockey), Cycling'' moves the puck along the boards in the offensive zone to create a scoring chance by making defenders tired or moving them out of position. ''Pinching'' is when a defenceman pressures the opposition's winger in the offensive zone when they are breaking out, attempting to stop their attack and keep the puck in the offensive zone. A ''saucer pass'' is a pass used when an opposition's stick or body is in the passing lane. It is the act of raising the puck over the obstruction and having it land on a teammate's stick.
A deke (ice hockey), deke, short for "decoy", is a feint with the body or stick to fool a defender or the goalie. Many modern players, such as Pavel Datsyuk, Sidney Crosby and Patrick Kane, have picked up the skill of "dangling", which is fancier deking and requires more stick handling skills.
 Although fighting is officially prohibited in the rules, it is not an uncommon occurrence at the professional level, and its prevalence has been both a target of criticism and a considerable draw for the sport. At the professional level in North America fights are unofficially condoned. enforcer (ice hockey), Enforcers and other players fight to demoralize the opposing players while exciting their own, as well as settling personal scores. A fight will also break out if one of the team's skilled players gets hit hard or someone receives what the team perceives as a dirty hit. The amateur game penalizes fisticuffs more harshly, as a player who receives a fighting major is also assessed at least a 10-minute misconduct penalty (NCAA and some Junior leagues) or a game misconduct penalty and suspension (punishment), suspension (high school and younger, as well as some casual adult leagues).
Although fighting is officially prohibited in the rules, it is not an uncommon occurrence at the professional level, and its prevalence has been both a target of criticism and a considerable draw for the sport. At the professional level in North America fights are unofficially condoned. enforcer (ice hockey), Enforcers and other players fight to demoralize the opposing players while exciting their own, as well as settling personal scores. A fight will also break out if one of the team's skilled players gets hit hard or someone receives what the team perceives as a dirty hit. The amateur game penalizes fisticuffs more harshly, as a player who receives a fighting major is also assessed at least a 10-minute misconduct penalty (NCAA and some Junior leagues) or a game misconduct penalty and suspension (punishment), suspension (high school and younger, as well as some casual adult leagues).
 Women began playing the game of ice hockey in the late 19th century. Several games were recorded in the 1890s in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The women of Lord Stanley's family were known to participate in the game of ice hockey on the outdoor ice rink at Rideau Hall, the residence of Canada's Governor-General.
The earliest available records of women's ice hockey were in the late 19th-century in Canada. Much like the men's game, women had previously been playing a conglomeration of stick-and-ball ice games. As with men's hockey, the women's game developed at first without an organizing body. A tournament in 1902 between
Women began playing the game of ice hockey in the late 19th century. Several games were recorded in the 1890s in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The women of Lord Stanley's family were known to participate in the game of ice hockey on the outdoor ice rink at Rideau Hall, the residence of Canada's Governor-General.
The earliest available records of women's ice hockey were in the late 19th-century in Canada. Much like the men's game, women had previously been playing a conglomeration of stick-and-ball ice games. As with men's hockey, the women's game developed at first without an organizing body. A tournament in 1902 between  Today, the women's game is played from youth through adult leagues, and the university level in North America and internationally. There are major professional women's hockey leagues: the Premier Hockey Federation, (formerly the National Women's Hockey League) with teams in the United States, Canada, and the Zhenskaya Hockey League with teams in Russia and China. In 2019, the Professional Women's Hockey Players Association was formed by over 150 players with the goal of creating a sustainable professional league for women's ice hockey in North America.
Between 1995 and 2005 the number of participants increased by 400 percent. In 2011, Canada had 85,827 women players, United States had 65,609, Finland 4,760, Sweden 3,075 and Switzerland 1,172.
Women's ice hockey was added as a medal sport eight years after the 1990 IIHF World Women's Championship, first world women's ice hockey championship in 1990 at the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Nagano, Nagano, Japan.
Today, the women's game is played from youth through adult leagues, and the university level in North America and internationally. There are major professional women's hockey leagues: the Premier Hockey Federation, (formerly the National Women's Hockey League) with teams in the United States, Canada, and the Zhenskaya Hockey League with teams in Russia and China. In 2019, the Professional Women's Hockey Players Association was formed by over 150 players with the goal of creating a sustainable professional league for women's ice hockey in North America.
Between 1995 and 2005 the number of participants increased by 400 percent. In 2011, Canada had 85,827 women players, United States had 65,609, Finland 4,760, Sweden 3,075 and Switzerland 1,172.
Women's ice hockey was added as a medal sport eight years after the 1990 IIHF World Women's Championship, first world women's ice hockey championship in 1990 at the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Nagano, Nagano, Japan.
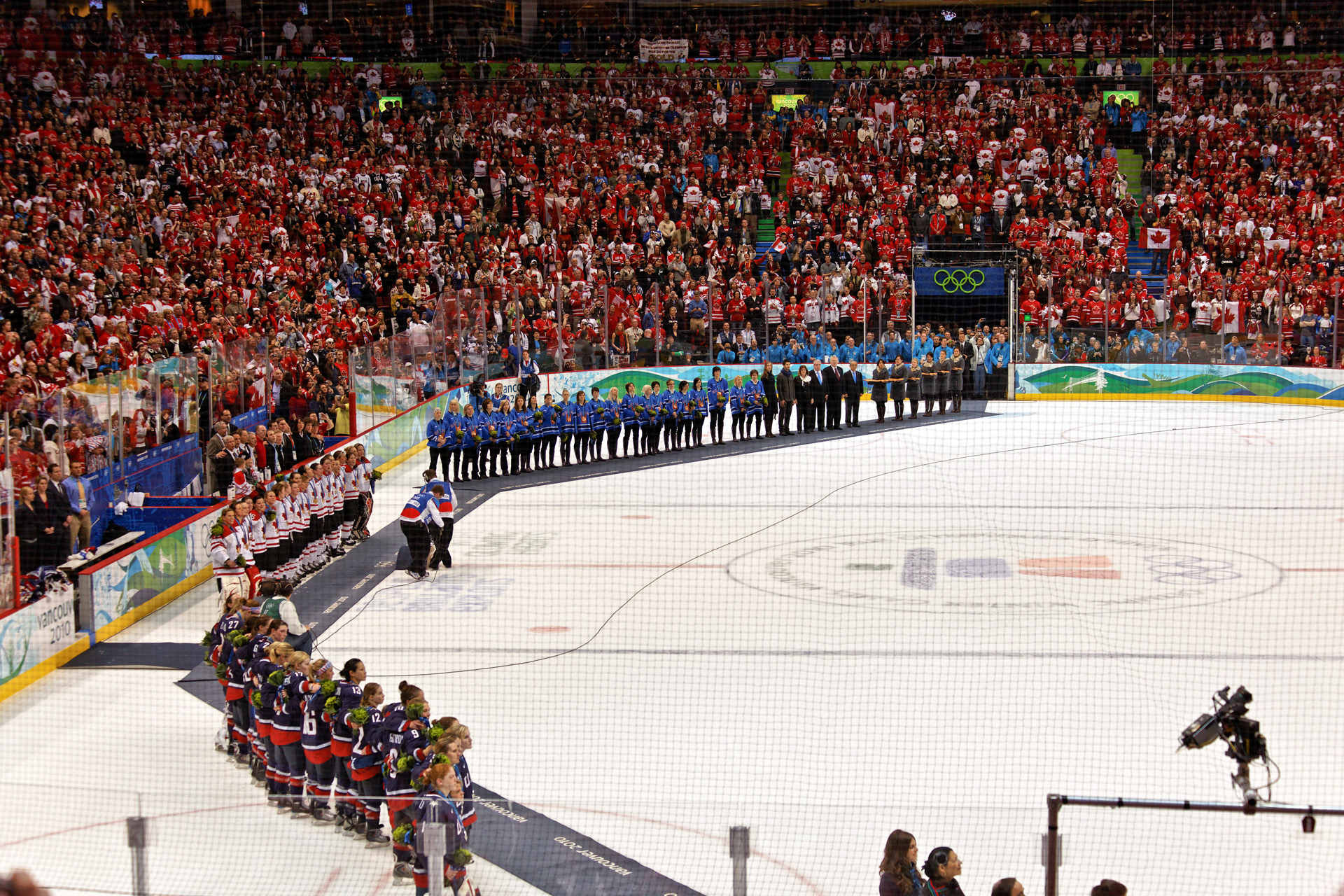 Prior to the professionalization of women's ice hockey in the 21st century, almost all professional women hockey players who played against men were goaltenders. No woman has ever played a full season in top tier men's professional ice hockey. The United States Hockey League (USHL) welcomed the first female professional ice hockey player in 1969ŌĆō70, when the Marquette Iron Rangers signed 18 yearŌĆōold, Karen Koch, a goaltender. Only one woman has ever played in the
Prior to the professionalization of women's ice hockey in the 21st century, almost all professional women hockey players who played against men were goaltenders. No woman has ever played a full season in top tier men's professional ice hockey. The United States Hockey League (USHL) welcomed the first female professional ice hockey player in 1969ŌĆō70, when the Marquette Iron Rangers signed 18 yearŌĆōold, Karen Koch, a goaltender. Only one woman has ever played in the
 The NHL is the best attended and most popular ice hockey league in the world, and is among the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada. The league's history began after Canada's National Hockey Association decided to disband in 1917; the result was the creation of the National Hockey League with four teams. The league expanded to the United States beginning in 1924 and had as many as 10 teams before contracting to six teams by 1942ŌĆō43. In 1967, the NHL doubled in size to 12 teams, undertaking one of the greatest expansions in professional sports history. A few years later, in 1972, a new 12-team league, the World Hockey Association (WHA) was formed and due to its ensuing rivalry with the NHL, it caused an escalation in players' salaries. In 1979, the 17-team NHL merged with the WHA creating a 21-team league. By 2017, the NHL had expanded to 31 teams, and after a realignment in 2013, these teams were divided into two conferences and four divisions. The league expanded to 32 teams in 2021.
The American Hockey League (AHL) is the primary developmental professional league for players aspiring to enter the NHL. It comprises 31 teams from the United States and Canada. It is run as a Farm team, farm league to the NHL, with the vast majority of AHL players under contract to an NHL team. The ECHL (called the East Coast Hockey League before the 2003ŌĆō04 season) is a mid-level minor league in the United States with a few players under contract to NHL or AHL teams.
As of 2019, there are three minor professional leagues with no NHL affiliations: the Federal Prospects Hockey League (FPHL), Ligue Nord-Am├®ricaine de Hockey (LNAH), and the Southern Professional Hockey League (SPHL).
The NHL is the best attended and most popular ice hockey league in the world, and is among the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada. The league's history began after Canada's National Hockey Association decided to disband in 1917; the result was the creation of the National Hockey League with four teams. The league expanded to the United States beginning in 1924 and had as many as 10 teams before contracting to six teams by 1942ŌĆō43. In 1967, the NHL doubled in size to 12 teams, undertaking one of the greatest expansions in professional sports history. A few years later, in 1972, a new 12-team league, the World Hockey Association (WHA) was formed and due to its ensuing rivalry with the NHL, it caused an escalation in players' salaries. In 1979, the 17-team NHL merged with the WHA creating a 21-team league. By 2017, the NHL had expanded to 31 teams, and after a realignment in 2013, these teams were divided into two conferences and four divisions. The league expanded to 32 teams in 2021.
The American Hockey League (AHL) is the primary developmental professional league for players aspiring to enter the NHL. It comprises 31 teams from the United States and Canada. It is run as a Farm team, farm league to the NHL, with the vast majority of AHL players under contract to an NHL team. The ECHL (called the East Coast Hockey League before the 2003ŌĆō04 season) is a mid-level minor league in the United States with a few players under contract to NHL or AHL teams.
As of 2019, there are three minor professional leagues with no NHL affiliations: the Federal Prospects Hockey League (FPHL), Ligue Nord-Am├®ricaine de Hockey (LNAH), and the Southern Professional Hockey League (SPHL).
 U Sports ice hockey is the highest level of play at the Canadian university level under the auspices of U Sports, Canada's governing body for university sports. As these players compete at the university level, they are obligated to follow the rule of standard eligibility of five years.
In the United States especially, college hockey is popular and the best university teams compete in the annual NCAA Men's Ice Hockey Championship. The American Collegiate Hockey Association is composed of college teams at the club level.
In Canada, the Canadian Hockey League is an umbrella organization comprising three major junior leagues: the Ontario Hockey League, the Western Hockey League, and the Quebec Major Junior Hockey League. It attracts players from Canada, the United States and Europe. The major junior players are considered amateurs as they are under 21-years-old and not paid a salary, however, they do get a stipend and play a schedule similar to a professional league. Typically, the NHL drafts many players directly from the major junior leagues.
In the United States, the United States Hockey League (USHL) is the highest junior league. Players in this league are also amateur with players required to be under 21-years old, but do not get a stipend, which allows players to retain their eligibility for participation in College ice hockey#NCAA, NCAA ice hockey.
U Sports ice hockey is the highest level of play at the Canadian university level under the auspices of U Sports, Canada's governing body for university sports. As these players compete at the university level, they are obligated to follow the rule of standard eligibility of five years.
In the United States especially, college hockey is popular and the best university teams compete in the annual NCAA Men's Ice Hockey Championship. The American Collegiate Hockey Association is composed of college teams at the club level.
In Canada, the Canadian Hockey League is an umbrella organization comprising three major junior leagues: the Ontario Hockey League, the Western Hockey League, and the Quebec Major Junior Hockey League. It attracts players from Canada, the United States and Europe. The major junior players are considered amateurs as they are under 21-years-old and not paid a salary, however, they do get a stipend and play a schedule similar to a professional league. Typically, the NHL drafts many players directly from the major junior leagues.
In the United States, the United States Hockey League (USHL) is the highest junior league. Players in this league are also amateur with players required to be under 21-years old, but do not get a stipend, which allows players to retain their eligibility for participation in College ice hockey#NCAA, NCAA ice hockey.
 The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) is the largest and most popular ice hockey league in Eurasia. The league is the direct successor to the Russian Super League, which in turn was the successor to the Soviet Championship League, Soviet League, the history of which dates back to the Soviet adoption of ice hockey in the 1940s. The KHL was 2008ŌĆō09 KHL season, launched in 2008 with clubs predominantly from Russia, but featuring teams from other post-Soviet states. The league expanded beyond the former Soviet countries beginning in the 2011ŌĆō12 KHL season, 2011ŌĆō12 season, with clubs in Croatia and Slovakia. The KHL currently comprises member clubs based in Belarus (1), China (1), Finland (1), Latvia (1), Kazakhstan (1) and Russia (19) for a total of 24.
The second division of hockey in Eurasia is the Supreme Hockey League (VHL). This league features 24 teams from Russia and 2 from Kazakhstan. This league is currently being converted to a farm league for the KHL, similarly to the AHL's function in relation to the NHL. The third division is the Russian Hockey League, which features only teams from Russia. The Asia League Ice Hockey, Asia League, an international ice hockey league featuring clubs from China, Japan, South Korea, and the Russian Far East, is the successor to the Japan Ice Hockey League.
The highest junior league in Eurasia is the Junior Hockey League (Russia), Junior Hockey League (MHL). It features 32 teams from post-Soviet states, predominantly Russia. The second tier to this league is the Junior Hockey League Championships (MHL-B).
The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) is the largest and most popular ice hockey league in Eurasia. The league is the direct successor to the Russian Super League, which in turn was the successor to the Soviet Championship League, Soviet League, the history of which dates back to the Soviet adoption of ice hockey in the 1940s. The KHL was 2008ŌĆō09 KHL season, launched in 2008 with clubs predominantly from Russia, but featuring teams from other post-Soviet states. The league expanded beyond the former Soviet countries beginning in the 2011ŌĆō12 KHL season, 2011ŌĆō12 season, with clubs in Croatia and Slovakia. The KHL currently comprises member clubs based in Belarus (1), China (1), Finland (1), Latvia (1), Kazakhstan (1) and Russia (19) for a total of 24.
The second division of hockey in Eurasia is the Supreme Hockey League (VHL). This league features 24 teams from Russia and 2 from Kazakhstan. This league is currently being converted to a farm league for the KHL, similarly to the AHL's function in relation to the NHL. The third division is the Russian Hockey League, which features only teams from Russia. The Asia League Ice Hockey, Asia League, an international ice hockey league featuring clubs from China, Japan, South Korea, and the Russian Far East, is the successor to the Japan Ice Hockey League.
The highest junior league in Eurasia is the Junior Hockey League (Russia), Junior Hockey League (MHL). It features 32 teams from post-Soviet states, predominantly Russia. The second tier to this league is the Junior Hockey League Championships (MHL-B).
 Several countries in Europe have their own top professional senior leagues. Many future KHL and NHL players start or end their professional careers in these leagues. The National League A in Switzerland, Swedish Hockey League in Sweden, Liiga in Finland, and Czech Extraliga in the Czech Republic are all very popular in their respective countries.
Beginning in the 2014ŌĆō15 season, the Champions Hockey League was launched, a league consisting of first-tier teams from several European countries, running parallel to the teams' domestic leagues. The competition is meant to serve as a Europe-wide ice hockey club championship. The competition is a direct successor to the European Trophy and is related to the 2008ŌĆō09 Champions Hockey League (2008ŌĆō09), tournament of the same name.
There are also several annual tournaments for clubs, held outside of league play. Season (sports), Pre-season tournaments include the European Trophy, Tampere Cup and the Pajulahti Cup. One of the oldest international ice hockey competition for clubs is the Spengler Cup, held every year in Davos, Switzerland, between Christmas and New Year's Day. It was first awarded in 1923 to the Oxford University Ice Hockey Club. The Memorial Cup, a competition for junior-level (age 20 and under) clubs is held annually from a pool of junior championship teams in Canada and the United States.
International club competitions organized by the IIHF include the IIHF Continental Cup, Continental Cup, the Victoria Cup (ice hockey), Victoria Cup and the European Women's Champions Cup. The World Junior Club Cup is an annual tournament of junior ice hockey clubs representing each of the top junior leagues.
Several countries in Europe have their own top professional senior leagues. Many future KHL and NHL players start or end their professional careers in these leagues. The National League A in Switzerland, Swedish Hockey League in Sweden, Liiga in Finland, and Czech Extraliga in the Czech Republic are all very popular in their respective countries.
Beginning in the 2014ŌĆō15 season, the Champions Hockey League was launched, a league consisting of first-tier teams from several European countries, running parallel to the teams' domestic leagues. The competition is meant to serve as a Europe-wide ice hockey club championship. The competition is a direct successor to the European Trophy and is related to the 2008ŌĆō09 Champions Hockey League (2008ŌĆō09), tournament of the same name.
There are also several annual tournaments for clubs, held outside of league play. Season (sports), Pre-season tournaments include the European Trophy, Tampere Cup and the Pajulahti Cup. One of the oldest international ice hockey competition for clubs is the Spengler Cup, held every year in Davos, Switzerland, between Christmas and New Year's Day. It was first awarded in 1923 to the Oxford University Ice Hockey Club. The Memorial Cup, a competition for junior-level (age 20 and under) clubs is held annually from a pool of junior championship teams in Canada and the United States.
International club competitions organized by the IIHF include the IIHF Continental Cup, Continental Cup, the Victoria Cup (ice hockey), Victoria Cup and the European Women's Champions Cup. The World Junior Club Cup is an annual tournament of junior ice hockey clubs representing each of the top junior leagues.
 Ice hockey has been played at the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics since 1924 (and was played at the Ice hockey at the 1920 Summer Olympics, summer games in 1920). Hockey is Canada's national winter sport, and Canadians are extremely passionate about the game. The nation has traditionally done very well at the Olympic games, winning six of the first seven gold medals. However, by 1956, its amateur club teams and national teams could not compete with the teams of government-supported players from the Soviet Union. The USSR won all but two gold medals from Ice hockey at the 1956 Winter Olympics, 1956 to Ice hockey at the 1988 Winter Olympics, 1988. The United States won its first gold medal in Ice hockey at the 1960 Winter Olympics, 1960. On the way to winning the gold medal at the 1980 Winter Olympics, 1980 Lake Placid Olympics, amateur US college players defeated the heavily favoured Soviet squadŌĆöan event known as the "Miracle on Ice" in the United States. Restrictions on professional players were fully dropped at the 1988 games in Calgary. NHL agreed to participate ten years later. The 1998 Games saw the full participation of players from the NHL, which suspended operations during the Games and has done so in subsequent Games up until 2018. The 2010 Winter Olympics, 2010 games in Vancouver were the first played in an NHL city since the inclusion of NHL players. The 2010 games were the first played on NHL-sized ice rinks, which are narrower than the IIHF standard.
National teams representing the member federations of the IIHF compete annually in the IIHF Ice Hockey World Championships. Teams are selected from the available players by the individual federations, without restriction on amateur or professional status. Since it is held in the spring, the tournament coincides with the annual NHL Stanley Cup playoffs and many of the top players are hence not available to participate in the tournament. Many of the NHL players who do play in the IIHF tournament come from teams eliminated before the playoffs or in the first round, and federations often hold open spots until the tournament to allow for players to join the tournament after their club team is eliminated. For many years, the tournament was an amateur-only tournament, but this restriction was removed, beginning in 1977.
Ice hockey has been played at the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics since 1924 (and was played at the Ice hockey at the 1920 Summer Olympics, summer games in 1920). Hockey is Canada's national winter sport, and Canadians are extremely passionate about the game. The nation has traditionally done very well at the Olympic games, winning six of the first seven gold medals. However, by 1956, its amateur club teams and national teams could not compete with the teams of government-supported players from the Soviet Union. The USSR won all but two gold medals from Ice hockey at the 1956 Winter Olympics, 1956 to Ice hockey at the 1988 Winter Olympics, 1988. The United States won its first gold medal in Ice hockey at the 1960 Winter Olympics, 1960. On the way to winning the gold medal at the 1980 Winter Olympics, 1980 Lake Placid Olympics, amateur US college players defeated the heavily favoured Soviet squadŌĆöan event known as the "Miracle on Ice" in the United States. Restrictions on professional players were fully dropped at the 1988 games in Calgary. NHL agreed to participate ten years later. The 1998 Games saw the full participation of players from the NHL, which suspended operations during the Games and has done so in subsequent Games up until 2018. The 2010 Winter Olympics, 2010 games in Vancouver were the first played in an NHL city since the inclusion of NHL players. The 2010 games were the first played on NHL-sized ice rinks, which are narrower than the IIHF standard.
National teams representing the member federations of the IIHF compete annually in the IIHF Ice Hockey World Championships. Teams are selected from the available players by the individual federations, without restriction on amateur or professional status. Since it is held in the spring, the tournament coincides with the annual NHL Stanley Cup playoffs and many of the top players are hence not available to participate in the tournament. Many of the NHL players who do play in the IIHF tournament come from teams eliminated before the playoffs or in the first round, and federations often hold open spots until the tournament to allow for players to join the tournament after their club team is eliminated. For many years, the tournament was an amateur-only tournament, but this restriction was removed, beginning in 1977.
 The Summit Series, 1972 Summit Series and 1974 Summit Series, two series pitting the best Canadian and Soviet players without IIHF restrictions were major successes, and established a rivalry between Canada and the USSR. In the spirit of best-versus-best without restrictions on amateur or professional status, the series were followed by five Canada Cup (ice hockey), Canada Cup tournaments, played in North America. Two NHL versus USSR series were also held: the 1979 Challenge Cup and Rendez-vous '87. The Canada Cup tournament later became the World Cup of Hockey, played in 1996, 2004 and 2016. The United States won in 1996 and Canada won in 2004 and 2016.
Since the initial women's world championships in 1990, there have been fifteen tournaments. Women's hockey has been played at the Olympics since 1998. The only finals in the women's world championship or Olympics that did not involve both Canada and the United States were the Ice hockey at the 2006 Winter Olympics ŌĆō Women's tournament, 2006 Winter Olympic final between Canada and Sweden and 2019 IIHF Women's World Championship Final, 2019 World Championship final between the US and Finland.
Other ice hockey tournaments featuring national teams include the IIHF World Junior Championship, World Junior Championship, the IIHF World U18 Championships, World U18 Championships, the World U-17 Hockey Challenge, the World Junior A Challenge, the Ivan Hlinka Memorial Tournament, the IIHF World Women's U18 Championships, World Women's U18 Championships and the 4 Nations Cup. The annual Euro Hockey Tour, an unofficial European championship between the national men's teams of the Czech Republic, Finland, Russia and Sweden have been played since 1996ŌĆō97.
The Summit Series, 1972 Summit Series and 1974 Summit Series, two series pitting the best Canadian and Soviet players without IIHF restrictions were major successes, and established a rivalry between Canada and the USSR. In the spirit of best-versus-best without restrictions on amateur or professional status, the series were followed by five Canada Cup (ice hockey), Canada Cup tournaments, played in North America. Two NHL versus USSR series were also held: the 1979 Challenge Cup and Rendez-vous '87. The Canada Cup tournament later became the World Cup of Hockey, played in 1996, 2004 and 2016. The United States won in 1996 and Canada won in 2004 and 2016.
Since the initial women's world championships in 1990, there have been fifteen tournaments. Women's hockey has been played at the Olympics since 1998. The only finals in the women's world championship or Olympics that did not involve both Canada and the United States were the Ice hockey at the 2006 Winter Olympics ŌĆō Women's tournament, 2006 Winter Olympic final between Canada and Sweden and 2019 IIHF Women's World Championship Final, 2019 World Championship final between the US and Finland.
Other ice hockey tournaments featuring national teams include the IIHF World Junior Championship, World Junior Championship, the IIHF World U18 Championships, World U18 Championships, the World U-17 Hockey Challenge, the World Junior A Challenge, the Ivan Hlinka Memorial Tournament, the IIHF World Women's U18 Championships, World Women's U18 Championships and the 4 Nations Cup. The annual Euro Hockey Tour, an unofficial European championship between the national men's teams of the Czech Republic, Finland, Russia and Sweden have been played since 1996ŌĆō97.
 The attendance record for an ice hockey game was set on December 11, 2010, when the University of Michigan's Michigan Wolverines men's ice hockey, men's ice hockey team faced cross-state rival Michigan State Spartans men's ice hockey, Michigan State in an event billed as "The Big Chill at the Big House". The game was played at Michigan Wolverines football, Michigan's (American) football venue, Michigan Stadium in Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor, with a capacity of 109,901 as of the 2010 Michigan Wolverines football team, 2010 football season. When UM stopped sales to the public on May 6, 2010, with plans to reserve remaining tickets for students, over 100,000 tickets had been sold for the event. Ultimately, a crowd announced by UM as 113,411, the largest in the stadium's history (including football), saw the homestanding Wolverines win 5ŌĆō0. ''Guinness World Records'', using a count of ticketed fans who actually entered the stadium instead of UM's figure of tickets sold, announced a final figure of 104,173.
The record was approached but not broken at the 2014 NHL Winter Classic, which also held at Michigan Stadium, with the Detroit Red Wings as the home team and the Toronto Maple Leafs as the opposing team with an announced crowd of 105,491. The record for a NHL Stanley Cup playoff game is 28,183, set on April 23, 1996, at the Tropicana Field, Thunderdome during a Tampa Bay Lightning ŌĆō Philadelphia Flyers game.
The attendance record for an ice hockey game was set on December 11, 2010, when the University of Michigan's Michigan Wolverines men's ice hockey, men's ice hockey team faced cross-state rival Michigan State Spartans men's ice hockey, Michigan State in an event billed as "The Big Chill at the Big House". The game was played at Michigan Wolverines football, Michigan's (American) football venue, Michigan Stadium in Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor, with a capacity of 109,901 as of the 2010 Michigan Wolverines football team, 2010 football season. When UM stopped sales to the public on May 6, 2010, with plans to reserve remaining tickets for students, over 100,000 tickets had been sold for the event. Ultimately, a crowd announced by UM as 113,411, the largest in the stadium's history (including football), saw the homestanding Wolverines win 5ŌĆō0. ''Guinness World Records'', using a count of ticketed fans who actually entered the stadium instead of UM's figure of tickets sold, announced a final figure of 104,173.
The record was approached but not broken at the 2014 NHL Winter Classic, which also held at Michigan Stadium, with the Detroit Red Wings as the home team and the Toronto Maple Leafs as the opposing team with an announced crowd of 105,491. The record for a NHL Stanley Cup playoff game is 28,183, set on April 23, 1996, at the Tropicana Field, Thunderdome during a Tampa Bay Lightning ŌĆō Philadelphia Flyers game.
 Ice hockey is most popular in Ice hockey in Canada, Canada, Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, and the Ice hockey in the United States, United States. Ice hockey is the official National sport, national winter sport of Canada. In addition, ice hockey is the most popular winter sport in Belarus, Sport in Croatia, Croatia, the Sport in the Czech Republic, Czech Republic, Sport in Finland, Finland, Sport in Latvia, Latvia, Sport in Russia, Russia, Sport in Slovakia, Slovakia, Sport in Sweden, Sweden, and Sport in Switzerland, Switzerland. North America's
Ice hockey is most popular in Ice hockey in Canada, Canada, Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, and the Ice hockey in the United States, United States. Ice hockey is the official National sport, national winter sport of Canada. In addition, ice hockey is the most popular winter sport in Belarus, Sport in Croatia, Croatia, the Sport in the Czech Republic, Czech Republic, Sport in Finland, Finland, Sport in Latvia, Latvia, Sport in Russia, Russia, Sport in Slovakia, Slovakia, Sport in Sweden, Sweden, and Sport in Switzerland, Switzerland. North America's
 Pond hockey is a form of ice hockey played generally as pick-up hockey on lakes, ponds and artificial outdoor rinks during the winter. Pond hockey is commonly referred to in hockey circles as shinny. Its rules differ from traditional hockey because there is no hitting and very little shooting, placing a greater emphasis on skating, stickhandling and passing abilities. Since 2002, the World Pond Hockey Championship has been played on Roulston Lake in Plaster Rock, New Brunswick, Canada. Since 2006, the US Pond Hockey Championships have been played in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and the Canadian National Pond Hockey Championships have been played in Huntsville, Ontario.
Pond hockey is a form of ice hockey played generally as pick-up hockey on lakes, ponds and artificial outdoor rinks during the winter. Pond hockey is commonly referred to in hockey circles as shinny. Its rules differ from traditional hockey because there is no hitting and very little shooting, placing a greater emphasis on skating, stickhandling and passing abilities. Since 2002, the World Pond Hockey Championship has been played on Roulston Lake in Plaster Rock, New Brunswick, Canada. Since 2006, the US Pond Hockey Championships have been played in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and the Canadian National Pond Hockey Championships have been played in Huntsville, Ontario.
Mandatory Equipment
ĆöCanadian Tire Hockey School
The Origins of Hockey
an
Hockey Origins Reference Database
ĆöSociety for International Hockey Research
History of ice hockey
Map of College & Pro Ice Hockey Teams in Canada and USA
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ice Hockey Ice hockey, Ice hockey Ice skating sports Stick sports Ice hockey terminology, Ice hockey terminology Athletic sports National symbols of Canada Sports originating in Canada Canadian culture Team sports Winter Olympic sports Indoor sports 19th century in Canada Games and sports introduced in the 19th century
team sport
A team sport includes any sport where individuals are organized into opposing teams which compete to win or cooperate to entertain their audience. Team members act together towards a shared objective. This can be done in a number of ways s ...
played on ice skates
Ice skates are metal blades attached underfoot and used to propel the bearer across a sheet of ice while ice skating.
The first ice skates were made from leg bones of horse, ox or deer, and were attached to feet with leather straps. These skate ...
, usually on an ice skating rink
An ice rink (or ice skating rink) is a frozen body of water and/or an artificial sheet of ice created using hardened chemicals where people can ice skate or play winter sports. Ice rinks are also used for exhibitions, contests and ice shows. The ...
with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey
Hockey is a term used to denote a family of various types of both summer and winter team sports which originated on either an outdoor field, sheet of ice, or dry floor such as in a gymnasium. While these sports vary in specific rules, numbers o ...
. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hockey stick
An ice hockey stick is a piece of equipment used in ice hockey to shoot, pass, and carry the puck across the ice. Ice hockey sticks are approximately 150ŌĆō200 cm long, composed of a long, slender shaft with a flat extension at one end c ...
s to control, advance and shoot
In botany, a plant shoot consists of any plant stem together with its appendages, leaves and lateral buds, flowering stems, and flower buds. The new growth from seed germination that grows upward is a shoot where leaves will develop. In the sp ...
a closed, vulcanized
Vulcanization (British: Vulcanisation) is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to inclu ...
, rubber disc called a " puck" into the other team's goal. Each goal is worth one point. The team which scores the most goals
A goal is an objective that a person or a system plans or intends to achieve.
Goal may also refer to:
Sport
* Goal (sports), a method of scoring in many sports, or the physical structure or area where scoring occurs
** Goals, the goal frame in ...
is declared the winner. In a formal game, each team has six skaters
Skater may refer to:
Sports
*Someone who practices skateboarding
*Someone who practices roller skating
*Someone who practices inline skating
* Someone who practices ice skating
*An ice hockey player who is not a goaltender
*Skater (subculture), ...
on the ice at a time, barring any penalties, one of whom is the goaltender
In ice hockey, the goaltender (commonly referred to as the goalie) is the player responsible for preventing the hockey puck from entering their team's net, thus preventing the opposing team from scoring. The goaltender mostly plays in or near t ...
. Ice hockey is a full contact
''Full Contact'' () is a 1992 Hong Kong action film produced and directed by Ringo Lam, and starring Chow Yun-fat, Simon Yam, and Anthony Wong.
Plot
The first part of the movie takes place in Bangkok, Thailand. Gou Fei's (Chow Yun-fat) frie ...
sport.
Ice hockey is one of the sports featured in the Winter Olympics
The Winter Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'hiver) is a major international multi-sport event held once every four years for sports practiced on snow and ice. The first Winter Olympic Games, the 1924 Winter Olympics, were h ...
while its premiere international amateur competition, the IIHF World Championships
The Ice Hockey World Championships are an annual international men's ice hockey tournament organized by the International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). First officially held at the 1920 Summer Olympics, it is the sport's highest profile annual ...
, are governed by the International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: F├®d├®ration internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-F├Čderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
(IIHF) for both men's and women's competitions. Ice hockey is also played as a professional sport.
In North America as well as many European countries, the sport is known simply as hockey. However, in other countries, "hockey" usually refers to field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ...
. In 1994 hockey was officially recognized as Canada's national winter sport.
The modern sport of ice hockey was developed in Canada, most notably in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montr├®al, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, where the first indoor game was played on March 3, 1875. Some characteristics of that game, such as the length of the ice rink and the use of a puck, have been retained to this day. Amateur ice hockey leagues began in the 1880s, and professional ice hockey
Professional ice hockey (hockey) is the competition of ice hockey in which participants are paid to play. Professional competition began in North America in the United States in Pennsylvania and Michigan and in Canada around 1900. Professional ice ...
originated around 1900. The Stanley Cup, emblematic of ice hockey club supremacy, was initially commissioned in 1892 as the "Dominion Hockey Challenge Cup" and was first awarded in 1893 to recognize the Canadian amateur champion and later became the championship trophy of the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockeyŌĆöLNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teamsŌĆö25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
(NHL). In the early 1900s, the Canadian rules were adopted by the Ligue Internationale de Hockey Sur Glace, in Paris, France
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km┬▓ (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
, the precursor of the International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: F├®d├®ration internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-F├Čderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
. The sport was played for the first time at the Olympics during the 1920 Summer Olympics.
While women also played during the game's early formative years, it was not until organizers began to officially remove body checking from female ice hockey beginning in the mid-1980s that it began to gain greater popularity, which by then had spread to Europe and a variety of other countries. The first IIHF Women's World Championship was held in 1990, and women's play was introduced into the Olympics in 1998
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''.
Events January
* January 6 ŌĆō The ''Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently s ...
.
History
Ice hockey is believed to have evolved from simple stick and ball games played in the 18th and 19th centuries in Britain, Ireland, and elsewhere, primarily bandy, hurling, and shinty. The North American sport oflacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensiv ...
was also influential. Arguably the games most influential to the early design of ice hockey were early forms of an organized sport today known as bandy, a sport distinctly separate from ice hockey. These games were brought to North America and several similar winter games using informal rules developed, such as shinny
Shinny (also shinney, pick-up hockey, pond hockey, or "outdoor puck") is an informal type of hockey played on ice. It is also used as another term for street hockey. There are no formal rules or specific positions, and often, there are no goa ...
and ice polo, but would later be absorbed into a new organized game with codified rules which today is ice hockey.
Name
In England,field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ...
has historically been called simply ''hockey'' and was what was referenced by first appearances in print. The first known mention spelled as ''hockey'' occurred in the 1772 book ''Juvenile Sports and Pastimes, to Which Are Prefixed, Memoirs of the Author: Including a New Mode of Infant Education'', by Richard Johnson (Pseud. Master Michel Angelo), whose chapter XI was titled "New Improvements on the Game of Hockey". The 1527 Statute of Galway banned a sport called hokie'ŌĆöthe hurling of a little ball with sticks or staves". A form of this word was thus being used in the 16th century, though much removed from its current usage.
The belief that hockey was mentioned in a 1363 proclamation by King Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 ŌĆō 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ro ...
is based on modern translations of the proclamation, which was originally in Latin and explicitly forbade the games .
According to the Austin Hockey Association, the word ''puck'' derives from the Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, G├Āidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well ...
or the Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***├ēire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
('to poke, punch or deliver a blow'). "...The blow given by a hurler to the ball with his or hurley is always called a puck."
Precursors

 Stick-and-ball games date go back to the pre-Christian era in
Stick-and-ball games date go back to the pre-Christian era in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The game of polo is very similar to many group games such as ice hockey, and probably the main idea of the game of hockey was taken from polo. In Europe, these games included the Irish game of hurling, the closely related Scottish game of shinty and versions of field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ...
(including bandy ball, played in England). IJscolf
IJscolf was a sport played on ice, popular in the Low Countries between the Middle Ages and the Dutch Golden Age. It was similar to ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skati ...
, a game resembling colf on an ice-covered surface, was popular in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, d├®i Niddereg L├żnnereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
between the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and the Dutch Golden Age. It was played with a wooden curved bat (called a ''colf'' or ''kolf''), a wooden or leather ball and two poles (or nearby landmarks), with the objective to hit the chosen point using the fewest strokes. A similar game (') had been played for a thousand years or more by the Scandinavian peoples, as documented in the Icelandic sagas
The sagas of Icelanders ( is, ├Źslendingas├Čgur, ), also known as family sagas, are one genre of Icelandic sagas. They are prose narratives mostly based on historical events that mostly took place in Iceland in the ninth, tenth, and early el ...
. Polo has been referred to as "hockey on horseback". In England, field hockey developed in the late 17th century, and there is evidence that some games of field hockey took place on the ice. These games of "hockey on ice" were sometimes played with a bung
A stopper or cork is a cylindrical or conical closure used to seal a container, such as a bottle, tube or barrel. Unlike a lid or bottle cap, which encloses a container from the outside without displacing the inner volume, a bung is partially ...
(a plug of cork or oak used as a stopper on a barrel). William Pierre Le Cocq stated, in a 1799 letter written in Chesham
Chesham (, , or ) is a market town and civil parish in Buckinghamshire, England, south-east of the county town of Aylesbury, north-west of central London, and part of the London commuter belt. It is in the Chess Valley, surrounded by farmla ...
, England:A 1797 engraving unearthed by Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
sport historians Carl Gid├®n and Patrick Houda shows a person on skates with a stick and bung on the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
, probably in December 1796.
British soldiers and immigrants to Canada and the United States brought their stick-and-ball games with them and played them on the ice and snow of winter.
In 1825, John Franklin
Sir John Franklin (16 April 1786 ŌĆō 11 June 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. After serving in wars against Napoleonic France and the United States, he led two expeditions into the Canadian Arctic and through t ...
wrote "The game of hockey played on the ice was the morning sport" on Great Bear Lake
Great Bear Lake ( den, Saht├║; french: Grand lac de l'Ours) is a lake in the boreal forest of Canada. It is the largest lake entirely in Canada (Lake Superior and Lake Huron are larger but straddle the CanadaŌĆōUS border), the fourth-largest ...
near the town of D├®l─▒╠©n─Ö
The Charter Community of D├®l─▒╠©n─Ö (North Slavey: ) is located in the Sahtu Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada, on the western shore of Great Bear Lake and is northwest of Yellowknife. D├®l─▒╠©n─Ö means "where the waters flow", a ref ...
during one of his Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
expeditions. A mid-1830s watercolour portrays New Brunswick lieutenant-governor Archibald Campbell and his family with British soldiers on skates playing a stick-on-ice sport. Captain R.G.A. Levinge, a British Army officer in New Brunswick during Campbell's time, wrote about "hockey on ice" on Chippewa Creek (a tributary of the Niagara River) in 1839. In 1843 another British Army officer in Kingston, Ontario
Kingston is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the north-eastern end of Lake Ontario, at the beginning of the St. Lawrence River and at the mouth of the Cataraqui River (south end of the Rideau Canal). The city is midway between To ...
, wrote, "Began to skate this year, improved quickly and had great fun at hockey on the ice." An 1859 ''Boston Evening Gazette'' article referred to an early game of hockey on ice in Halifax that year. An 1835 painting by John O'Toole depicts skaters with sticks and bung on a frozen stream in the American state of West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
, at that time still part of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
.
In the same era, the Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''MiĻ×īkmaw'' or ''MiĻ×īgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gasp├® Peninsula of Quebec as well as the nort ...
, a First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
people of the Canadian Maritimes, also had a stick-and-ball game. Canadian oral histories
Oral history is the collection and study of historical information about individuals, families, important events, or everyday life using audiotapes, videotapes, or transcriptions of planned interviews. These interviews are conducted with people wh ...
describe a traditional stick-and-ball game played by the Mi'kmaq, and Silas Tertius Rand
Silas Tertius Rand (May 18, 1810 ŌĆō October 4, 1889) was a Canadian Baptist clergyman, missionary, ethnologist, linguist and translator. His work centred on the Mi'kmaq people of Maritime Canada and he was the first to record the legend of Gloos ...
(in his 1894 ''Legends of the Micmacs'') describes a Mi'kmaq ball game known as ''tooadijik''. Rand also describes a game played (probably after European contact) with hurleys, known as ''wolchamaadijik''.Dalhousie University (2000)Thomas Raddall Selected Correspondence: An Electronic Edition
. From Thomas Raddall to Douglas M. Fisher, January 25, 1954. MS-2-202 41.14. ''Oochamkunutk'' was the name used by the Mi'kmaq to describe their own stick and ball game which they played on the ice while "Alchamadyk" was what the Mi'kmaq called the new the game of "Hurley on Ice" which was played by others around the province during the same period. Of particular note among influential Micmacs is Joe Cope ("Old Joe"), a Mi'kmaq elder known for his talent for carving what became one of the earliest types of ice hockey sticks used. Cope once stated, "Long before the pale faces strayed to this country, the Micmacs were playing two ball games, a field game and an ice game." Sticks made by the Mi'kmaq were used by the British for their games.
 Early 19th-century paintings depict
Early 19th-century paintings depict shinny
Shinny (also shinney, pick-up hockey, pond hockey, or "outdoor puck") is an informal type of hockey played on ice. It is also used as another term for street hockey. There are no formal rules or specific positions, and often, there are no goa ...
, an early form of hockey with no standard rules which was played in Nova Scotia. Many of these early games absorbed the physical aggression of what the Onondaga Onondaga may refer to:
Native American/First Nations
* Onondaga people, a Native American/First Nations people and one of the five founding nations of the Iroquois League
* Onondaga (village), Onondaga settlement and traditional Iroquois capita ...
called ' (lacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensiv ...
). Shinny was played on the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
at Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montr├®al, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
and Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Qu├®bec), officially Qu├®bec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
, and in Kingston and Ottawa. The number of players was often large. To this day, shinny (derived from the Scottish game of shinty) is a popular Canadian term for an informal type of hockey, either ice or street hockey
Street hockey (also known as shinny, dek hockey, ball hockey, road hockey) is a collection of team sport variants played outdoors either on foot or with wheeled skates, using a either a ball or puck designed for play on flat, dry surfaces. The ...
.
Thomas Chandler Haliburton
Thomas Chandler Haliburton (17 December 1796 ŌĆō 27 August 1865) was a Nova Scotian politician, judge, and author. He made an important political contribution to the state of Nova Scotia before its entry into Confederation of Canada. He was the ...
, in ''The Attache: Second Series'' (published in 1844) imagined a dialogue, between two of the novel's characters, which mentions playing "hurly on the long pond on the ice". This has been interpreted by some historians from Windsor, Nova Scotia
Windsor is a community located in Hants County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is a service centre for the western part of the county and is situated on Highway 101.
The community has a history dating back to its use by the Mi'kmaq Nation for sev ...
as reminiscent of the days when the author was a student at King's College School
King's College School, also known as Wimbledon, KCS, King's and KCS Wimbledon, is a public school in Wimbledon, southwest London, England. The school was founded in 1829 by King George IV, as the junior department of King's College London an ...
in that town in 1810 and earlier. Based on Haliburton's quote, claims were made that modern hockey was invented in Windsor, Nova Scotia, by King's College students and perhaps named after an individual ("Colonel Hockey's game"). Others claim that the origins of hockey come from games played in the area of Dartmouth and Halifax in Nova Scotia. However, several references have been found to hurling and shinty being played on the ice long before the earliest references from both Windsor and Dartmouth/Halifax, and the word "hockey" was used to designate a stick-and-ball game at least as far back as 1773, as it was mentioned in the book ''Juvenile Sports and Pastimes, to Which Are Prefixed, Memoirs of the Author: Including a New Mode of Infant Education'' by Richard Johnson (Pseud. Master Michel Angelo), whose chapter XI was titled "New Improvements on the Game of Hockey".
Initial development
 The Canadian city of
The Canadian city of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montr├®al, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Qu├®bec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, became the centre of the development of contemporary ice hockey, and is recognized as the birthplace of organized ice hockey. On March 3, 1875, the first organized indoor game was played at Montreal's Victoria Skating Rink
The Victoria Skating Rink was an indoor ice skating rink located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Opened in 1862, it was described at the start of the twentieth century to be "one of the finest covered rinks in the world". The building was used dur ...
between two nine-player teams, including James Creighton and several McGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Universit├® McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec
Montreal ( ; officially Montr├®al, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous ...
students. Instead of a ball or bung, the game featured a "flat circular piece of wood" (to keep it in the rink and to protect spectators). The goal posts were apart (today's goals are wide). Some observers of the game at McGill made quick note of its surprisingly aggressive and violent nature.
In 1876, games played in Montreal were "conducted under the 'Hockey Association' rules"; the Hockey Association was England's field hockey organization. In 1877, '' The Gazette'' (Montreal) published a list of seven rules, six of which were largely based on six of the Hockey Association's twelve rules, with only minor differences (even the word "ball" was kept); the one added rule explained how disputes should be settled. The McGill University Hockey Club, the first ice hockey club, was founded in 1877 (followed by the Quebec Hockey Club
The Quebec Bulldogs (french: Bulldogs de Qu├®bec) were a men's senior-level ice hockey team based in Quebec City. The team was officially known as the Quebec Hockey Club (french: Club de hockey de Qu├®bec), and later as the Quebec Athletic Club ...
in 1878 and the Montreal Victorias
The Victoria Hockey Club of Montreal, Quebec, Canada was an early men's amateur ice hockey club. Its date of origin is ascribed to either 1874, 1877 or 1881, making it either the first or second organized ice hockey club after McGill University. ...
in 1881). In 1880, the number of players per side was reduced from nine to seven.
 The number of teams grew, enough to hold the first "world championship" of ice hockey at Montreal's annual
The number of teams grew, enough to hold the first "world championship" of ice hockey at Montreal's annual Winter Carnival
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures d ...
in 1883. The McGill team won the tournament and was awarded the Carnival Cup. The game was divided into thirty-minute halves. The positions were now named: left and right wing, centre
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
* Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentri ...
, rover
Rover may refer to:
People
* Constance Rover (1910ŌĆō2005), English historian
* Jolanda de Rover (born 1963), Dutch swimmer
* Rover Thomas (c. 1920ŌĆō1998), Indigenous Australian artist
Places
* Rover, Arkansas, US
* Rover, Missouri, US
...
, point and cover-point, and goaltender
In ice hockey, the goaltender (commonly referred to as the goalie) is the player responsible for preventing the hockey puck from entering their team's net, thus preventing the opposing team from scoring. The goaltender mostly plays in or near t ...
. In 1886, the teams competing at the Winter Carnival organized the Amateur Hockey Association of Canada (AHAC), and played a season comprising "challenges" to the existing champion.
In Europe, it was previously believed that in 1885 the Oxford University Ice Hockey Club
The Oxford University Ice Hockey Club (OUIHC) is home to the MenŌĆÖs and WomenŌĆÖs Blues ice hockey teams of the University of Oxford, England. The Men's Blues, also known as Oxford University Blues,BUIHA Website Listin"Oxford University Blues" ...
was formed to play the first Ice Hockey Varsity Match
The Ice Hockey Varsity Match is a longstanding competition between the Cambridge and Oxford University Ice Hockey Clubs.
Tradition places the origin of the match in 1885, when a game is said to have been played in St Moritz. This date is recogni ...
against traditional rival Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
in St. Moritz, Switzerland; however, this is now considered to have been a game of bandy. A similar claim which turned out to be accurate is that the oldest rivalry in ice hockey history is between Queen's University at Kingston and Royal Military College of Kingston, Ontario, with the first known match taking place in 1886.
In 1888, the Governor General of Canada
The governor general of Canada (french: gouverneure g├®n├®rale du Canada) is the federal viceregal representative of the . The is head of state of Canada and the 14 other Commonwealth realms, but resides in oldest and most populous realm, ...
, The Lord Stanley of Preston, first attended the Montreal Winter Carnival tournament and was impressed with the game.
His sons and his daughter, Isobel Stanley
{{Infobox noble
, honorific_prefix = Lady
, name = Isobel Constance Mary {{no-wrap, Gathorne-Hardy
, honorific_suffix = {{post-nominals, country=GBR, size=100%, DCVO
, title =
, image = File:Lady Isobel ...
, were hockey enthusiasts. In 1892, realizing that there was no recognition for the best team in Canada (although a number of leagues had championship trophies), he purchased a silver bowl for use as a trophy. The Dominion Hockey Challenge Cup (which later became known as the Stanley Cup) was first awarded in 1893 to the Montreal Hockey Club
The Montreal Hockey Club of Montreal, Quebec, Canada was a senior-level men's amateur ice hockey club, organized in 1884. They were affiliated with Montreal Amateur Athletic Association (MAAA) and used the MAAA 'winged wheel' logo. The team was ...
, champions of the AHAC; it continues to be awarded annually to the National Hockey League's championship team. Stanley's son Arthur
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning ŌĆ£BearŌĆØ. Another theory, more wi ...
helped organize the Ontario Hockey Association, and Stanley's daughter Isobel Isobel, is the Scottish form of the female given name Isabel. It originates from the medieval form of the name Elisabeth (Hebrew Elisheba).
Isobel is a feminine given name. People named Isobel include:
* Isobel of Huntingdon (1199-1251), Scottish ...
was one of the first women to play ice hockey.
 By 1893, there were almost a hundred teams in Montreal alone; in addition, there were leagues throughout Canada.
By 1893, there were almost a hundred teams in Montreal alone; in addition, there were leagues throughout Canada. Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
hockey players used cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
pads to better protect the goaltender's legs; they also introduced the "scoop" shot, or what is now known as the wrist shot
A wrist shot is a type of hockey shot that involves using arm muscles (especially those in the wrist and forearm) to propel a puck forward from the concave side of the blade of a hockey stick. Generally, when the puck is shot in a similar manne ...
. William Fairbrother William Fairbrother was a Canadian ice hockey player who is credited with inventing the ice hockey net in the 1890s. During the 1880s, Fairbrother played for Beamsville, Ontario's Men's Hockey team. At first, two poles or two rocks served as goals ...
, from Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, Canada, is credited with inventing the ice hockey net in the 1890s. Goal nets became a standard feature of the Canadian Amateur Hockey League
The Canadian Amateur Hockey League (CAHL) was an early men's amateur hockey league founded in 1898, replacing the organization that was formerly the Amateur Hockey Association of Canada (AHAC) before the 1898ŌĆō99 season. The league existed for s ...
in 1900. Left and right defence began to replace the point and cover-point positions in the OHA in 1906.
American financier Malcolm Greene Chace
Malcolm Greene Chace (March 12, 1875 ŌĆō July 16, 1955) was an American financier and textile industrialist who was instrumental in bringing electric power to New England. He was a pioneer of the sport of ice hockey in the United States, and was ...
is credited with being the father of hockey in the United States. In 1892, Chace put together a team of men from Yale
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wor ...
, Brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
, and Harvard, and toured across Canada as captain of this team. The first collegiate hockey match in the United States was played between Yale and Johns Hopkins in Baltimore in 1893. In 1896, the first ice hockey league in the US was formed. The US Amateur Hockey League was founded in New York City, shortly after the opening of the artificial-ice St. Nicholas Rink.
 By 1898 the following leagues had already formed: the Amateur Hockey League of New York, the Amateur Hockey Association of Canada, and the Ontario Hockey Association. The 1898
By 1898 the following leagues had already formed: the Amateur Hockey League of New York, the Amateur Hockey Association of Canada, and the Ontario Hockey Association. The 1898 Spalding Athletic Library
Spalding Athletic Library sold sports and exercise books through American Sports Publishing Company from 1892 to 1941. Both companies were owned and founded by Spalding. Books cover over 30 different sports and exercises, and over 20 different o ...
book includes rules and results for each league.
Stanley's five sons were instrumental in bringing ice hockey to Europe, defeating a court team (which included the future Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 ŌĆō 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria and ...
and George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 ŌĆō 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother Qu ...
) at Buckingham Palace in 1895. By 1903, a five-team league had been founded. The ''Ligue Internationale de Hockey sur Glace'' was founded in 1908 to govern international competition, and the first European championship was won by Great Britain in 1910. The sport grew further in Europe in the 1920s, after ice hockey became an Olympic sport. Many bandy players switched to hockey to be able to compete in the Olympics. In the mid-20th century, the ''Ligue'' became the International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: F├®d├®ration internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-F├Čderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
.
As the popularity of ice hockey as a spectator sport grew, earlier rinks were replaced by larger rinks. Most of the early indoor ice rinks have been demolished; Montreal's Victoria Rink, built in 1862, was demolished in 1925. Many older rinks succumbed to fire, such as Denman Arena
Denman Arena was an indoor arena located in downtown Vancouver, British Columbia. The arena was located at 1805 West Georgia Street at the northwest corner with Denman Street. It opened in December 1911 and was destroyed by fire in 1936. Its pri ...
, Dey's Arena Dey's Arena, also known as Dey Brothers Rink, Dey's Skating Rink and The Arena, were a series of ice rinks and arenas located in Ottawa, Ontario, that hold importance in the early development of the organized sport of ice hockey in Canada. It was t ...
, Quebec Skating Rink and Montreal Arena
The Montreal Arena, also known as Westmount Arena, was an indoor arena located in Westmount, Quebec, Canada on the corner of St. Catherine Street and Wood Avenue. It was likely one of the first arenas designed expressly for hockey, opening in 1 ...
, a hazard of the buildings' wood construction. The Stannus Street Rink in Windsor, Nova Scotia (built in 1897) may be the oldest still in existence; however, it is no longer used for hockey. The Aberdeen Pavilion (built in 1898) in Ottawa was used for hockey in 1904 and is the oldest existing facility that has hosted Stanley Cup games.
The oldest indoor ice hockey arena still in use today for hockey is Boston's Matthews Arena, which was built in 1910. It has been modified extensively several times in its history and is used today by Northeastern University for hockey and other sports. It was the original home rink of the Boston Bruins professional team, itself the oldest United States-based team in the NHL, starting play in the league in what was then called Boston Arena on December 1, 1924. Madison Square Garden in New York City, built in 1968, is the oldest continuously-operating arena in the NHL.
Professional era
 While scattered incidents of players taking pay to play hockey occurred as early as the 1890s, those found to have done so were banned from playing in the amateur leagues which dominated the sport. By 1902, the Western Pennsylvania Hockey League (WPHL) was the first to employ professionals. The league joined with teams in Michigan and Ontario to form the first fully professional leagueŌĆöthe International Professional Hockey League (IPHL)ŌĆöin 1904. The WPHL and IPHL hired players from Canada; in response, Canadian leagues began to pay players (who played with amateur sports, amateurs). The IPHL, cut off from its largest source of players, disbanded in 1907. By then, several professional hockey leagues were operating in Canada (with leagues in Manitoba, Ontario and Quebec).
In 1910, the National Hockey Association (NHA) was formed in Montreal. The NHA would further refine the rules: dropping the rover position, dividing the game into three 20-minute periods and introducing minor and major penalties. After re-organizing as the National Hockey League in 1917, the league expanded into the United States, starting with the Boston Bruins in 1924.
Professional hockey leagues developed later in Europe, but amateur leagues leading to national championships were in place. One of the first was the Swiss National League A, founded in 1916. Today, professional leagues have been introduced in most countries of Europe. Top European leagues include the Kontinental Hockey League, the Czech Extraliga, the Finnish Liiga and the Swedish Hockey League.
While scattered incidents of players taking pay to play hockey occurred as early as the 1890s, those found to have done so were banned from playing in the amateur leagues which dominated the sport. By 1902, the Western Pennsylvania Hockey League (WPHL) was the first to employ professionals. The league joined with teams in Michigan and Ontario to form the first fully professional leagueŌĆöthe International Professional Hockey League (IPHL)ŌĆöin 1904. The WPHL and IPHL hired players from Canada; in response, Canadian leagues began to pay players (who played with amateur sports, amateurs). The IPHL, cut off from its largest source of players, disbanded in 1907. By then, several professional hockey leagues were operating in Canada (with leagues in Manitoba, Ontario and Quebec).
In 1910, the National Hockey Association (NHA) was formed in Montreal. The NHA would further refine the rules: dropping the rover position, dividing the game into three 20-minute periods and introducing minor and major penalties. After re-organizing as the National Hockey League in 1917, the league expanded into the United States, starting with the Boston Bruins in 1924.
Professional hockey leagues developed later in Europe, but amateur leagues leading to national championships were in place. One of the first was the Swiss National League A, founded in 1916. Today, professional leagues have been introduced in most countries of Europe. Top European leagues include the Kontinental Hockey League, the Czech Extraliga, the Finnish Liiga and the Swedish Hockey League.
Game
 Hockey is an Offside (ice hockey), off-side game, meaning that forward passes are allowed, unlike in rugby. Before the 1930s, hockey was an on-side game, meaning that only backward passes were allowed. Those rules emphasized individual stick-handling to drive the puck forward. With the arrival of offside rules, the forward pass transformed hockey into a true team sport, where individual performance diminished in importance relative to team play, which could now be coordinated over the entire surface of the ice as opposed to merely rearward players.
The six players on each team are typically divided into three forwards, two defencemen, and a goaltender. The term ''skaters'' typically applies to all players except goaltenders. The ''Forward (ice hockey), forward'' positions consist of a ''Center (ice hockey), centre'' and two ''Winger (ice hockey), wingers'': a ''left wing'' and a ''right wing''. Forwards often play together as units or ''lines'', with the same three forwards always playing together. The ''Defenceman (ice hockey), defencemen'' usually stay together as a pair generally divided between left and right. Left and right side wingers or defencemen are generally positioned on the side on which they carry their stick. A substitution (sport), substitution of an entire unit at once is called a ''line change''. Teams typically employ alternate sets of forward lines and defensive pairings when ''short-handed'' or on a ''Power play (sporting term), power play''. The goaltender stands in a, usually blue, semi-circle called the ''crease'' in the defensive zone keeping pucks out of the goal. Substitutions are permitted at any time during the game, although during a stoppage of play the home team is permitted the final change. When players are substituted during play, it is called changing ''on the fly''. An NHL rule added in the 2005ŌĆō06 season prevents a team from changing their line after they ''Icing (ice hockey), ice'' the puck.
Hockey is an Offside (ice hockey), off-side game, meaning that forward passes are allowed, unlike in rugby. Before the 1930s, hockey was an on-side game, meaning that only backward passes were allowed. Those rules emphasized individual stick-handling to drive the puck forward. With the arrival of offside rules, the forward pass transformed hockey into a true team sport, where individual performance diminished in importance relative to team play, which could now be coordinated over the entire surface of the ice as opposed to merely rearward players.
The six players on each team are typically divided into three forwards, two defencemen, and a goaltender. The term ''skaters'' typically applies to all players except goaltenders. The ''Forward (ice hockey), forward'' positions consist of a ''Center (ice hockey), centre'' and two ''Winger (ice hockey), wingers'': a ''left wing'' and a ''right wing''. Forwards often play together as units or ''lines'', with the same three forwards always playing together. The ''Defenceman (ice hockey), defencemen'' usually stay together as a pair generally divided between left and right. Left and right side wingers or defencemen are generally positioned on the side on which they carry their stick. A substitution (sport), substitution of an entire unit at once is called a ''line change''. Teams typically employ alternate sets of forward lines and defensive pairings when ''short-handed'' or on a ''Power play (sporting term), power play''. The goaltender stands in a, usually blue, semi-circle called the ''crease'' in the defensive zone keeping pucks out of the goal. Substitutions are permitted at any time during the game, although during a stoppage of play the home team is permitted the final change. When players are substituted during play, it is called changing ''on the fly''. An NHL rule added in the 2005ŌĆō06 season prevents a team from changing their line after they ''Icing (ice hockey), ice'' the puck.
 The boards surrounding the ice help keep the puck in play and they can also be used as tools to play the puck. Players are permitted to bodycheck opponents into the boards to stop progress. The referees, linesmen and the outsides of the goal are "in play" and do not stop the game when the puck or players either bounce into or collide with them. Play can be stopped if the goal is knocked out of position. Play often proceeds for minutes without interruption. After a stoppage, play is restarted with a faceoff. Two players face each other and an official drops the puck to the ice, where the two players attempt to gain control of the puck. Markings (circles) on the ice indicate the locations for the faceoff and guide the positioning of players.
Three major rules of play in ice hockey limit the movement of the puck: ''offside'', ''icing'', and the puck going out of play.
*A player is offside if he enters his Hockey rink#Zones, opponent's zone before the puck itself.
*Under many situations, a player may not "ice the puck", which means shooting the puck all the way across both the centre line and the opponent's goal line.
*The puck goes out of play whenever it goes past the perimeter of the ice rink (onto the player benches, over the Plexiglas, glass, or onto the protective netting above the glass) and a stoppage of play is called by the officials using whistles. It does not matter if the puck comes back onto the ice surface from outside of the rink, because the puck is considered dead once it leaves the perimeter of the rink. The referee may also blow the whistle for a stoppage in play if the puck is jammed along the boards when 2 or more players are battling for the puck for a long time, or if the puck is stuck on the back of any of the two nets for a period of time.
Under IIHF rules, each team may carry a maximum of 20 players and two goaltenders on their roster. NHL rules restrict the total number of players per game to 18, plus two goaltenders. In the NHL, the players are usually divided into four lines of three forwards, and into three pairs of defencemen. On occasion, teams may elect to substitute an extra defenceman for a forward. The seventh defenceman may play as a substitute defenceman, spend the game on the bench, or if a team chooses to play four lines then this seventh defenceman may see ice-time on the fourth line as a forward.
The boards surrounding the ice help keep the puck in play and they can also be used as tools to play the puck. Players are permitted to bodycheck opponents into the boards to stop progress. The referees, linesmen and the outsides of the goal are "in play" and do not stop the game when the puck or players either bounce into or collide with them. Play can be stopped if the goal is knocked out of position. Play often proceeds for minutes without interruption. After a stoppage, play is restarted with a faceoff. Two players face each other and an official drops the puck to the ice, where the two players attempt to gain control of the puck. Markings (circles) on the ice indicate the locations for the faceoff and guide the positioning of players.
Three major rules of play in ice hockey limit the movement of the puck: ''offside'', ''icing'', and the puck going out of play.
*A player is offside if he enters his Hockey rink#Zones, opponent's zone before the puck itself.
*Under many situations, a player may not "ice the puck", which means shooting the puck all the way across both the centre line and the opponent's goal line.
*The puck goes out of play whenever it goes past the perimeter of the ice rink (onto the player benches, over the Plexiglas, glass, or onto the protective netting above the glass) and a stoppage of play is called by the officials using whistles. It does not matter if the puck comes back onto the ice surface from outside of the rink, because the puck is considered dead once it leaves the perimeter of the rink. The referee may also blow the whistle for a stoppage in play if the puck is jammed along the boards when 2 or more players are battling for the puck for a long time, or if the puck is stuck on the back of any of the two nets for a period of time.
Under IIHF rules, each team may carry a maximum of 20 players and two goaltenders on their roster. NHL rules restrict the total number of players per game to 18, plus two goaltenders. In the NHL, the players are usually divided into four lines of three forwards, and into three pairs of defencemen. On occasion, teams may elect to substitute an extra defenceman for a forward. The seventh defenceman may play as a substitute defenceman, spend the game on the bench, or if a team chooses to play four lines then this seventh defenceman may see ice-time on the fourth line as a forward.
Periods and overtime
A professional game consists of three periods of twenty minutes, the clock running only when the puck is in play. The teams change ends after each period of play, including overtime. Recreational leagues and children's leagues often play shorter games, generally with three shorter periods of play. If a tie occurs in tournament play, as well as in the NHL playoffs, North Americans favour ''sudden death Overtime (ice hockey), overtime'', in which the teams continue to play twenty-minute periods until a goal is scored. Up until the 1999ŌĆō2000 season, regular-season NHL games were settled with a single five-minute sudden death period with five players (plus a goalie) per side, with both teams awarded one point in the standings in the event of a tie. With a goal, the winning team would be awarded two points and the losing team none (just as if they had lost in regulation). The total elapsed time from when the puck first drops, is about 2 hours and 20 minutes for a 60-minute game.
From the 1999ŌĆō2000 until the 2003ŌĆō04 seasons, the National Hockey League decided ties by playing a single five-minute sudden-death overtime period with each team having four skaters per side (plus the goalie). In the event of a tie, each team would still receive one point in the standings but in the event of a victory the winning team would be awarded two points in the standings and the losing team one point. The idea was to discourage teams from playing for a tie, since previously some teams might have preferred a tie and 1 point to risking a loss and zero points. The exception to this rule is if a team opts to pull their goalie in exchange for an extra skater during overtime and is subsequently scored upon (an ''empty net'' goal), in which case the losing team receives no points for the overtime loss. Since the 2015ŌĆō16 season, the single five-minute sudden-death overtime session involves three skaters on each side. Since three skaters must always be on the ice in an NHL game, the consequences of penalties are slightly different from those during regulation play; any penalty during overtime that would result in a team losing a skater during regulation instead causes the other side to add a skater. Once the penalized team's penalty ends, the penalized skater exits the penalty box and the teams continue at 4-on-4 until the next stoppage of play, at which point the teams return to three skaters per side.
If a tie occurs in tournament play, as well as in the NHL playoffs, North Americans favour ''sudden death Overtime (ice hockey), overtime'', in which the teams continue to play twenty-minute periods until a goal is scored. Up until the 1999ŌĆō2000 season, regular-season NHL games were settled with a single five-minute sudden death period with five players (plus a goalie) per side, with both teams awarded one point in the standings in the event of a tie. With a goal, the winning team would be awarded two points and the losing team none (just as if they had lost in regulation). The total elapsed time from when the puck first drops, is about 2 hours and 20 minutes for a 60-minute game.
From the 1999ŌĆō2000 until the 2003ŌĆō04 seasons, the National Hockey League decided ties by playing a single five-minute sudden-death overtime period with each team having four skaters per side (plus the goalie). In the event of a tie, each team would still receive one point in the standings but in the event of a victory the winning team would be awarded two points in the standings and the losing team one point. The idea was to discourage teams from playing for a tie, since previously some teams might have preferred a tie and 1 point to risking a loss and zero points. The exception to this rule is if a team opts to pull their goalie in exchange for an extra skater during overtime and is subsequently scored upon (an ''empty net'' goal), in which case the losing team receives no points for the overtime loss. Since the 2015ŌĆō16 season, the single five-minute sudden-death overtime session involves three skaters on each side. Since three skaters must always be on the ice in an NHL game, the consequences of penalties are slightly different from those during regulation play; any penalty during overtime that would result in a team losing a skater during regulation instead causes the other side to add a skater. Once the penalized team's penalty ends, the penalized skater exits the penalty box and the teams continue at 4-on-4 until the next stoppage of play, at which point the teams return to three skaters per side.
 International play and several North American professional leagues, including the NHL (in the regular season), now use an overtime period identical to that from 1999ŌĆō2000 to 2003ŌĆō04 followed by a Shootout (hockey), penalty shootout. If the score remains tied after an extra overtime period, the subsequent shootout consists of three players from each team taking penalty shots. After these six total shots, the team with the most goals is awarded the victory. If the score is still tied, the shootout then proceeds to ''Sudden death (sport), sudden death''. Regardless of the number of goals scored by either team during the shootout, the final score recorded will award the winning team one more goal than the score at the end of regulation time. In the NHL if a game is decided in overtime or by a shootout the winning team is awarded two points in the standings and the losing team is awarded one point. Ties no longer occur in the NHL.
Overtime in the NHL playoffs differs from the regular season. In the playoffs there are no shootouts. If a game is tied after regulation, then a 20-minute period of 5-on-5 sudden-death overtime will be added. If the game is still tied after the overtime, another period is added until a team scores, which wins the match. Since 2019, the IIHF World Championships and the gold medal game in the Olympics use the same format, but in a 3-on-3 format.
International play and several North American professional leagues, including the NHL (in the regular season), now use an overtime period identical to that from 1999ŌĆō2000 to 2003ŌĆō04 followed by a Shootout (hockey), penalty shootout. If the score remains tied after an extra overtime period, the subsequent shootout consists of three players from each team taking penalty shots. After these six total shots, the team with the most goals is awarded the victory. If the score is still tied, the shootout then proceeds to ''Sudden death (sport), sudden death''. Regardless of the number of goals scored by either team during the shootout, the final score recorded will award the winning team one more goal than the score at the end of regulation time. In the NHL if a game is decided in overtime or by a shootout the winning team is awarded two points in the standings and the losing team is awarded one point. Ties no longer occur in the NHL.
Overtime in the NHL playoffs differs from the regular season. In the playoffs there are no shootouts. If a game is tied after regulation, then a 20-minute period of 5-on-5 sudden-death overtime will be added. If the game is still tied after the overtime, another period is added until a team scores, which wins the match. Since 2019, the IIHF World Championships and the gold medal game in the Olympics use the same format, but in a 3-on-3 format.
Penalties
 In ice hockey, infractions of the rules lead to a play stoppage whereby the play is restarted at a faceoff. Some infractions result in a ''penalty'' on a player or team. In the simplest case, the offending player is sent to the ''penalty box'' and their team must play with one less player on the ice for a designated time. ''Minor'' penalties last for two minutes, ''major'' penalties last for five minutes, and a ''double minor'' penalty is two ''consecutive'' penalties of two minutes duration. A single minor penalty may be extended by two minutes for causing visible injury to the victimized player. This is usually when blood is drawn during high sticking. Players may be also assessed personal extended penalties or game expulsions for misconduct in addition to the penalty or penalties their team must serve. The team that has been given a penalty is said to be playing ''short-handed'' while the opposing team is on a ''power play (sport), power play''.
A two-minute minor penalty is often charged for lesser infractions such as tripping (ice hockey), tripping, elbow (strike), elbowing, roughing, high-sticking, delay of game, delay of the game, too many men, too many players on the ice, boarding (ice hockey), boarding, illegal equipment, charging (ice hockey), charging (leaping into an opponent or body-checking him after taking more than two strides), holding, holding the stick (grabbing an opponent's stick), interference, hooking (ice hockey), hooking, slashing (ice hockey), slashing, kneeing, unsportsmanlike conduct (arguing a penalty call with referee, extremely vulgar or inappropriate verbal comments), "butt-ending" (striking an opponent with the knob of the stick), "spearing" (jabbing an opponent with the blade of the stick), or cross-checking. As of the 2005ŌĆō2006 season, a minor penalty is also assessed for diving (ice hockey), diving, where a player embellishes or simulates an offence. More egregious fouls may be penalized by a four-minute double-minor penalty, particularly those that injure the victimized player. These penalties end either when the time runs out or when the other team scores during the power play. In the case of a goal scored during the first two minutes of a double-minor, the penalty clock is set down to two minutes upon a score, effectively expiring the first minor penalty.
Five-minute major penalties are called for especially violent instances of most minor infractions that result in intentional injury to an opponent, or when a minor penalty results in visible injury (such as bleeding), as well as for fighting. Major penalties are always served in full; they do not terminate on a goal scored by the other team. Major penalties assessed for fighting are typically offsetting, meaning neither team is short-handed and the players exit the penalty box upon a stoppage of play following the expiration of their respective penalties. The foul of boarding (defined as "check[ing] an opponent in such a manner that causes the opponent to be thrown violently in the boards") is penalized either by a minor or major penalty at the discretion of the referee, based on the violent state of the hit. A minor or major penalty for boarding is often assessed when a player checks an opponent from behind and into the boards.
Some varieties of penalty do not require the offending team to play a man short. Concurrent five-minute major penalties in the NHL usually result from fighting. In the case of two players being assessed five-minute fighting majors, both the players serve five minutes without their team incurring a loss of player (both teams still have a full complement of players on the ice). This differs with two players from opposing sides getting minor penalties, at the same time or at any intersecting moment, resulting from more common infractions. In this case, both teams will have only four skating players (not counting the goaltender) until one or both penalties expire (if one penalty expires before the other, the opposing team gets a power play for the remainder of the time); this applies regardless of current pending penalties. However, in the NHL, a team always has at least three skaters on the ice. Thus, ten-minute ''misconduct'' penalties are served in full by the penalized player, but his team may immediately substitute another player on the ice ''unless'' a minor or major penalty is assessed in conjunction with the misconduct (a ''two-and-ten'' or ''five-and-ten''). In this case, the team designates another player to serve the minor or major; both players go to the penalty box, but only the designee may not be replaced, and he is released upon the expiration of the two or five minutes, at which point the ten-minute misconduct begins. In addition, ''game misconducts'' are assessed for deliberate intent to inflict severe injury on an opponent (at the officials' discretion), or for a major penalty for a stick infraction or repeated major penalties. The offending player is ejected from the game and must immediately leave the playing surface (he does not sit in the penalty box); meanwhile, if an additional minor or major penalty is assessed, a designated player must serve out of that segment of the penalty in the box (similar to the above-mentioned "two-and-ten"). In some rare cases, a player may receive up to nineteen minutes in penalties for one string of plays. This could involve receiving a four-minute double-minor penalty, getting in a fight with an opposing player who retaliates, and then receiving a game misconduct after the fight. In this case, the player is ejected and two teammates must serve the double-minor and major penalties.
In ice hockey, infractions of the rules lead to a play stoppage whereby the play is restarted at a faceoff. Some infractions result in a ''penalty'' on a player or team. In the simplest case, the offending player is sent to the ''penalty box'' and their team must play with one less player on the ice for a designated time. ''Minor'' penalties last for two minutes, ''major'' penalties last for five minutes, and a ''double minor'' penalty is two ''consecutive'' penalties of two minutes duration. A single minor penalty may be extended by two minutes for causing visible injury to the victimized player. This is usually when blood is drawn during high sticking. Players may be also assessed personal extended penalties or game expulsions for misconduct in addition to the penalty or penalties their team must serve. The team that has been given a penalty is said to be playing ''short-handed'' while the opposing team is on a ''power play (sport), power play''.
A two-minute minor penalty is often charged for lesser infractions such as tripping (ice hockey), tripping, elbow (strike), elbowing, roughing, high-sticking, delay of game, delay of the game, too many men, too many players on the ice, boarding (ice hockey), boarding, illegal equipment, charging (ice hockey), charging (leaping into an opponent or body-checking him after taking more than two strides), holding, holding the stick (grabbing an opponent's stick), interference, hooking (ice hockey), hooking, slashing (ice hockey), slashing, kneeing, unsportsmanlike conduct (arguing a penalty call with referee, extremely vulgar or inappropriate verbal comments), "butt-ending" (striking an opponent with the knob of the stick), "spearing" (jabbing an opponent with the blade of the stick), or cross-checking. As of the 2005ŌĆō2006 season, a minor penalty is also assessed for diving (ice hockey), diving, where a player embellishes or simulates an offence. More egregious fouls may be penalized by a four-minute double-minor penalty, particularly those that injure the victimized player. These penalties end either when the time runs out or when the other team scores during the power play. In the case of a goal scored during the first two minutes of a double-minor, the penalty clock is set down to two minutes upon a score, effectively expiring the first minor penalty.
Five-minute major penalties are called for especially violent instances of most minor infractions that result in intentional injury to an opponent, or when a minor penalty results in visible injury (such as bleeding), as well as for fighting. Major penalties are always served in full; they do not terminate on a goal scored by the other team. Major penalties assessed for fighting are typically offsetting, meaning neither team is short-handed and the players exit the penalty box upon a stoppage of play following the expiration of their respective penalties. The foul of boarding (defined as "check[ing] an opponent in such a manner that causes the opponent to be thrown violently in the boards") is penalized either by a minor or major penalty at the discretion of the referee, based on the violent state of the hit. A minor or major penalty for boarding is often assessed when a player checks an opponent from behind and into the boards.
Some varieties of penalty do not require the offending team to play a man short. Concurrent five-minute major penalties in the NHL usually result from fighting. In the case of two players being assessed five-minute fighting majors, both the players serve five minutes without their team incurring a loss of player (both teams still have a full complement of players on the ice). This differs with two players from opposing sides getting minor penalties, at the same time or at any intersecting moment, resulting from more common infractions. In this case, both teams will have only four skating players (not counting the goaltender) until one or both penalties expire (if one penalty expires before the other, the opposing team gets a power play for the remainder of the time); this applies regardless of current pending penalties. However, in the NHL, a team always has at least three skaters on the ice. Thus, ten-minute ''misconduct'' penalties are served in full by the penalized player, but his team may immediately substitute another player on the ice ''unless'' a minor or major penalty is assessed in conjunction with the misconduct (a ''two-and-ten'' or ''five-and-ten''). In this case, the team designates another player to serve the minor or major; both players go to the penalty box, but only the designee may not be replaced, and he is released upon the expiration of the two or five minutes, at which point the ten-minute misconduct begins. In addition, ''game misconducts'' are assessed for deliberate intent to inflict severe injury on an opponent (at the officials' discretion), or for a major penalty for a stick infraction or repeated major penalties. The offending player is ejected from the game and must immediately leave the playing surface (he does not sit in the penalty box); meanwhile, if an additional minor or major penalty is assessed, a designated player must serve out of that segment of the penalty in the box (similar to the above-mentioned "two-and-ten"). In some rare cases, a player may receive up to nineteen minutes in penalties for one string of plays. This could involve receiving a four-minute double-minor penalty, getting in a fight with an opposing player who retaliates, and then receiving a game misconduct after the fight. In this case, the player is ejected and two teammates must serve the double-minor and major penalties.
 A Penalty shot (ice hockey), penalty shot is awarded to a player when the illegal actions of another player stop a clear scoring opportunity, most commonly when the player is on a Breakaway (ice hockey), breakaway. A penalty shot allows the obstructed player to pick up the puck on the centre red-line and attempt to score on the goalie with no other players on the ice, to compensate for the earlier missed scoring opportunity. A penalty shot is also awarded for a defender other than the goaltender covering the puck in the goal crease, a goaltender intentionally displacing his own goal posts during a breakaway to avoid a goal, a defender intentionally displacing his own goal posts when there is less than two minutes to play in regulation time or at any point during overtime, or a player or coach intentionally throwing a stick or other object at the puck or the puck carrier and the throwing action disrupts a shot or pass play.
Officials also stop play for puck movement violations, such as using one's hands to pass the puck in the offensive end, but no players are penalized for these offences. The sole exceptions are deliberately falling on or gathering the puck to the body, carrying the puck in the hand, and shooting the puck out of play in one's defensive zone (all penalized two minutes for delay of game).
In the NHL, a unique penalty applies to the goalies. The goalies now are forbidden to play the puck in the "corners" of the rink near their own net. This will result in a two-minute penalty against the goalie's team. Only in the area in front of the goal line and immediately behind the net (marked by two red lines on either side of the net) can the goalie play the puck.
An additional rule that has never been a penalty, but was an infraction in the NHL before recent rules changes, is the Two-line pass, two-line offside pass. Prior to the 2005ŌĆō06 NHL season, play was stopped when a pass from inside a team's defending zone crossed the centre line, with a face-off held in the defending zone of the offending team. Now, the centre line is no longer used in the NHL to determine a two-line pass infraction, a change that the IIHF had adopted in 1998. Players are now able to pass to teammates who are more than the blue and centre ice red line away.
The NHL has taken steps to speed up the game of hockey and create a game of finesse, by reducing the number of illegal hits, fights, and "clutching and grabbing" that occurred in the past. Rules are now more strictly enforced, resulting in more penalties, which provides more protection to the players and facilitates more goals being scored. The governing body for United States' amateur hockey has implemented many new rules to reduce the number of stick-on-body occurrences, as well as other detrimental and illegal facets of the game ("zero tolerance").
In men's hockey, but not in women's, a player may use his hip or shoulder to hit another player if the player has the puck or is the last to have touched it. This use of the hip and shoulder is called '' body checking''. Not all physical contact is legalŌĆöin particular, hits from behind, hits to the head and most types of forceful stick-on-body contact are illegal.
A Penalty shot (ice hockey), penalty shot is awarded to a player when the illegal actions of another player stop a clear scoring opportunity, most commonly when the player is on a Breakaway (ice hockey), breakaway. A penalty shot allows the obstructed player to pick up the puck on the centre red-line and attempt to score on the goalie with no other players on the ice, to compensate for the earlier missed scoring opportunity. A penalty shot is also awarded for a defender other than the goaltender covering the puck in the goal crease, a goaltender intentionally displacing his own goal posts during a breakaway to avoid a goal, a defender intentionally displacing his own goal posts when there is less than two minutes to play in regulation time or at any point during overtime, or a player or coach intentionally throwing a stick or other object at the puck or the puck carrier and the throwing action disrupts a shot or pass play.
Officials also stop play for puck movement violations, such as using one's hands to pass the puck in the offensive end, but no players are penalized for these offences. The sole exceptions are deliberately falling on or gathering the puck to the body, carrying the puck in the hand, and shooting the puck out of play in one's defensive zone (all penalized two minutes for delay of game).
In the NHL, a unique penalty applies to the goalies. The goalies now are forbidden to play the puck in the "corners" of the rink near their own net. This will result in a two-minute penalty against the goalie's team. Only in the area in front of the goal line and immediately behind the net (marked by two red lines on either side of the net) can the goalie play the puck.
An additional rule that has never been a penalty, but was an infraction in the NHL before recent rules changes, is the Two-line pass, two-line offside pass. Prior to the 2005ŌĆō06 NHL season, play was stopped when a pass from inside a team's defending zone crossed the centre line, with a face-off held in the defending zone of the offending team. Now, the centre line is no longer used in the NHL to determine a two-line pass infraction, a change that the IIHF had adopted in 1998. Players are now able to pass to teammates who are more than the blue and centre ice red line away.
The NHL has taken steps to speed up the game of hockey and create a game of finesse, by reducing the number of illegal hits, fights, and "clutching and grabbing" that occurred in the past. Rules are now more strictly enforced, resulting in more penalties, which provides more protection to the players and facilitates more goals being scored. The governing body for United States' amateur hockey has implemented many new rules to reduce the number of stick-on-body occurrences, as well as other detrimental and illegal facets of the game ("zero tolerance").
In men's hockey, but not in women's, a player may use his hip or shoulder to hit another player if the player has the puck or is the last to have touched it. This use of the hip and shoulder is called '' body checking''. Not all physical contact is legalŌĆöin particular, hits from behind, hits to the head and most types of forceful stick-on-body contact are illegal.
 A ''delayed penalty call'' occurs when an offence is committed by the team that does not have possession of the puck. In this circumstance the team with possession of the puck is allowed to complete the play; that is, play continues until a goal is scored, a player on the opposing team gains control of the puck, or the team in possession commits an infraction or penalty of their own. Because the team on which the penalty was called cannot control the puck without stopping play, it is impossible for them to score a goal. In these cases, the team in possession of the puck can pull the goalie for an extra attacker without fear of being scored on. However, it is possible for the controlling team to mishandle the puck into their own net. If a delayed penalty is signalled and the team in possession scores, the penalty is still assessed to the offending player, but not served. In 2012, this rule was changed by the United States' National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) for college ice hockey, college level hockey. In college games, the penalty is still enforced even if the team in possession scores.
A ''delayed penalty call'' occurs when an offence is committed by the team that does not have possession of the puck. In this circumstance the team with possession of the puck is allowed to complete the play; that is, play continues until a goal is scored, a player on the opposing team gains control of the puck, or the team in possession commits an infraction or penalty of their own. Because the team on which the penalty was called cannot control the puck without stopping play, it is impossible for them to score a goal. In these cases, the team in possession of the puck can pull the goalie for an extra attacker without fear of being scored on. However, it is possible for the controlling team to mishandle the puck into their own net. If a delayed penalty is signalled and the team in possession scores, the penalty is still assessed to the offending player, but not served. In 2012, this rule was changed by the United States' National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) for college ice hockey, college level hockey. In college games, the penalty is still enforced even if the team in possession scores.
Officials
A typical game of hockey is governed by two to four ''Official (ice hockey), officials'' on the ice, charged with enforcing the rules of the game. There are typically two ''linesmen'' who are mainly responsible for calling "offside" and "Icing (ice hockey), icing" violations, breaking up fights, and conducting faceoffs, and one or two ''referees'', who call goals and all other penalties. Linesmen can, however, report to the referee(s) that a penalty should be assessed against an offending player in some situations. The restrictions on this practice vary depending on the governing rules. On-ice officials are assisted by off-ice officials who act as goal judges, time keepers, and official scorers. The most widespread system is the "three-man system", which uses one referee and two linesmen. A less commonly used system is the two referee and one linesman system. This system is close to the regular three-man system except for a few procedure changes. Beginning with the National Hockey League, a number of leagues have implemented the "four-official system", where an additional referee is added to aid in the calling of penalties normally difficult to assess by one referee. The system is used in every NHL game since 2001, at
The most widespread system is the "three-man system", which uses one referee and two linesmen. A less commonly used system is the two referee and one linesman system. This system is close to the regular three-man system except for a few procedure changes. Beginning with the National Hockey League, a number of leagues have implemented the "four-official system", where an additional referee is added to aid in the calling of penalties normally difficult to assess by one referee. The system is used in every NHL game since 2001, at IIHF World Championships
The Ice Hockey World Championships are an annual international men's ice hockey tournament organized by the International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). First officially held at the 1920 Summer Olympics, it is the sport's highest profile annual ...
, the Olympics and in many professional and high-level amateur leagues in North America and Europe.
Officials are selected by the league they work for. Amateur hockey leagues use guidelines established by national organizing bodies as a basis for choosing their officiating staffs. In North America, the national organizing bodies Hockey Canada and USA Hockey approve officials according to their experience level as well as their ability to pass rules knowledge and skating ability tests. Hockey Canada has officiating levels I through VI. USA Hockey has officiating levels 1 through 4.
Equipment
Protective gear
 Since men's ice hockey is a full-contact sport, body checks are allowed so injuries are a common occurrence. Protective equipment is mandatory and is enforced in all competitive situations. This includes a helmet with either a visor or a full face mask, shoulder pads, elbow pads, mouth guard, protective gloves, heavily padded shorts (also known as hockey pants) or a girdle, athletic cup (also known as a jock, for males; and jill, for females), shin pads, skates, and (optionally) a neck protector.
Since men's ice hockey is a full-contact sport, body checks are allowed so injuries are a common occurrence. Protective equipment is mandatory and is enforced in all competitive situations. This includes a helmet with either a visor or a full face mask, shoulder pads, elbow pads, mouth guard, protective gloves, heavily padded shorts (also known as hockey pants) or a girdle, athletic cup (also known as a jock, for males; and jill, for females), shin pads, skates, and (optionally) a neck protector.
Goaltenders
Ice hockey goaltending equipment, Goaltenders use different equipment. With hockey pucks approaching them at speeds of up to 100 mph (160 km/h) they must wear equipment with more protection. Goaltenders wear specialized goalie skates (these skates are built more for movement side to side rather than forwards and backwards), a jock or jill, large leg pads (there are size restrictions in certain leagues), blocking glove, catching glove, a chest protector, a goalie mask, and a large jersey. Goaltenders' equipment has continually become larger and larger, leading to fewer goals in each game and many official rule changes.Ice skates
Ice skates#Ice hockey skates, Ice hockey skates are optimized for physical acceleration, speed and manoeuvrability. This includes rapid starts, stops, turns, and changes in skating direction. In addition, they must be rigid and tough to protect the skater's feet from contact with other skaters, sticks, pucks, the boards, and the ice itself. Rigidity also improves the overall manoeuvrability of the skate. Blade length, thickness (width), and curvature (rocker/radius (front to back) and radius of hollow (across the blade width) are quite different from speed or figure skates. Hockey players usually adjust these parameters based on their skill level, position, and body type. The blade width of most skates are about thick.Ice hockey stick
The hockey stick consists of a long, relatively wide, and slightly curved flat blade, attached to a shaft. The curve itself has a big impact on its performance. A deep curve allows for lifting the puck easier while a shallow curve allows for easier backhand shots. The flex of the stick also impacts the performance. Typically, a less flexible stick is meant for a stronger player since the player is looking for the right balanced flex that allows the stick to flex easily while still having a strong "whip-back" which sends the puck flying at high speeds. It is quite distinct from sticks in other sports games and most suited to hitting and controlling the flat puck. Its unique shape contributed to the early development of the game.Injury
Ice hockey is a full-contact sport and carries a high risk of injury. Players are moving at speeds around approximately and much of the game revolves around the physical contact between the players. Skate blades, hockey sticks, shoulder contact, hip contact, and hockey pucks can all potentially cause injuries. Lace bite, an irritation felt on the front of the foot or ankle, is a common ice hockey injury. Compared to athletes who play other sports, ice hockey players are at higher risk of overuse injuries and injuries caused by early sports specialization by teenagers. According to the Hughston Health Alert, "Lacerations to the head, scalp, and face are the most frequent types of injury [in hockey]." One of the leading causes of head injury is body checking from behind. Due to the danger of delivering a check from behind, many leagues ŌĆō including the NHL ŌĆō have made this a major and game misconduct penalty. Another type of check that accounts for many of the player-to-player contact concussions is a check to the head resulting in a misconduct penalty (called "head contact"). In recent years, the NHL has implemented new rules which penalize and suspend players for illegal checks to the heads, as well as checks to unsuspecting players. Studies show that ice hockey causes 44.3% of all sports-related traumatic brain injuries among Canadian children.Tactics
Checking
 An important defensive tactic is checkingŌĆöattempting to take the puck from an opponent or to remove the opponent from play. ''Stick checking'', ''sweep checking'', and ''poke checking'' are legal uses of the stick to obtain possession of the puck. The ''neutral zone trap'' is designed to isolate the puck carrier in the neutral zone preventing him from entering the offensive zone. ''Body checking'' is using one's shoulder or hip to strike an opponent who has the puck or who is the last to have touched it (the last person to have touched the puck is still legally "in possession" of it, although a penalty is generally called if he is checked more than two seconds after his last touch). Body checking is also a penalty in certain leagues in order to reduce the chance of injury to players. Often the term checking is used to refer to body checking, with its true definition generally only propagated among fans of the game.
An important defensive tactic is checkingŌĆöattempting to take the puck from an opponent or to remove the opponent from play. ''Stick checking'', ''sweep checking'', and ''poke checking'' are legal uses of the stick to obtain possession of the puck. The ''neutral zone trap'' is designed to isolate the puck carrier in the neutral zone preventing him from entering the offensive zone. ''Body checking'' is using one's shoulder or hip to strike an opponent who has the puck or who is the last to have touched it (the last person to have touched the puck is still legally "in possession" of it, although a penalty is generally called if he is checked more than two seconds after his last touch). Body checking is also a penalty in certain leagues in order to reduce the chance of injury to players. Often the term checking is used to refer to body checking, with its true definition generally only propagated among fans of the game.
Offensive tactics
Offensive tactics include improving a team's position on the ice by advancing the puck out of one's zone towards the opponent's zone, progressively by gaining lines, first your own blue line, then the red line and finally the opponent's blue line. National Hockey League rules, NHL rules instated for the 2006 season redefined the offside rule to make the two-line pass legal; a player may pass the puck from behind his own blue line, past both that blue line and the centre red line, to a player on the near side of the opponents' blue line. Offensive tactics are designed ultimately to score a goal by taking a shot. When a player purposely directs the puck towards the opponent's goal, he or she is said to "shoot" the puck. A ''deflection'' is a shot that redirects a shot or a pass towards the goal from another player, by allowing the puck to strike the stick and carom towards the goal. A ''one-timer'' is a shot struck directly off a pass, without receiving the pass and shooting in two separate actions. ''Headmanning the puck'', also known as ''breaking out'', is the tactic of rapidly passing to the player farthest down the ice. ''Loafing (ice hockey), Loafing'', also known as ''cherry picking (basketball), cherry-picking'', is when a player, usually a forward, skates behind an attacking team, instead of playing defence, in an attempt to create an easy scoring chance.
A team that is losing by one or two goals in the last few minutes of play will often elect to ''pull the goalie''; that is, remove the goaltender and replace him or her with an ''extra attacker'' on the ice in the hope of gaining enough advantage to score a goal. However, it is an act of desperation, as it sometimes leads to the opposing team extending their lead by scoring a goal in the empty net.
One of the most important strategies for a team is their ''forecheck''. Forechecking is the act of attacking the opposition in their defensive zone. Forechecking is an important part of the ''dump and chase'' strategy (i.e. shooting the puck into the offensive zone and then chasing after it). Each team will use their own unique system but the main ones are: 2-1-2 Forecheck, 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2, 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2, and 1ŌĆō4. The 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2 is the most basic forecheck system where two forwards will go in deep and pressure the opposition's defencemen, the third forward stays high and the two defencemen stay at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2 is a bit more conservative system where one forward pressures the puck carrier and the other two forwards cover the oppositions' wingers, with the two defencemen staying at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō4 is the most defensive forecheck system, referred to as the neutral zone trap, where one forward will apply pressure to the puck carrier around the oppositions' blueline and the other 4 players stand basically in a line by their blueline in hopes the opposition will skate into one of them. Another strategy is the left wing lock, which has two forwards pressure the puck and the left wing and the two defencemen stay at the blueline.
A ''deflection'' is a shot that redirects a shot or a pass towards the goal from another player, by allowing the puck to strike the stick and carom towards the goal. A ''one-timer'' is a shot struck directly off a pass, without receiving the pass and shooting in two separate actions. ''Headmanning the puck'', also known as ''breaking out'', is the tactic of rapidly passing to the player farthest down the ice. ''Loafing (ice hockey), Loafing'', also known as ''cherry picking (basketball), cherry-picking'', is when a player, usually a forward, skates behind an attacking team, instead of playing defence, in an attempt to create an easy scoring chance.
A team that is losing by one or two goals in the last few minutes of play will often elect to ''pull the goalie''; that is, remove the goaltender and replace him or her with an ''extra attacker'' on the ice in the hope of gaining enough advantage to score a goal. However, it is an act of desperation, as it sometimes leads to the opposing team extending their lead by scoring a goal in the empty net.
One of the most important strategies for a team is their ''forecheck''. Forechecking is the act of attacking the opposition in their defensive zone. Forechecking is an important part of the ''dump and chase'' strategy (i.e. shooting the puck into the offensive zone and then chasing after it). Each team will use their own unique system but the main ones are: 2-1-2 Forecheck, 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2, 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2, and 1ŌĆō4. The 2ŌĆō1ŌĆō2 is the most basic forecheck system where two forwards will go in deep and pressure the opposition's defencemen, the third forward stays high and the two defencemen stay at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō2ŌĆō2 is a bit more conservative system where one forward pressures the puck carrier and the other two forwards cover the oppositions' wingers, with the two defencemen staying at the blueline. The 1ŌĆō4 is the most defensive forecheck system, referred to as the neutral zone trap, where one forward will apply pressure to the puck carrier around the oppositions' blueline and the other 4 players stand basically in a line by their blueline in hopes the opposition will skate into one of them. Another strategy is the left wing lock, which has two forwards pressure the puck and the left wing and the two defencemen stay at the blueline.
 There are many other little tactics used in the game of hockey. ''Cycling (ice hockey), Cycling'' moves the puck along the boards in the offensive zone to create a scoring chance by making defenders tired or moving them out of position. ''Pinching'' is when a defenceman pressures the opposition's winger in the offensive zone when they are breaking out, attempting to stop their attack and keep the puck in the offensive zone. A ''saucer pass'' is a pass used when an opposition's stick or body is in the passing lane. It is the act of raising the puck over the obstruction and having it land on a teammate's stick.
A deke (ice hockey), deke, short for "decoy", is a feint with the body or stick to fool a defender or the goalie. Many modern players, such as Pavel Datsyuk, Sidney Crosby and Patrick Kane, have picked up the skill of "dangling", which is fancier deking and requires more stick handling skills.
There are many other little tactics used in the game of hockey. ''Cycling (ice hockey), Cycling'' moves the puck along the boards in the offensive zone to create a scoring chance by making defenders tired or moving them out of position. ''Pinching'' is when a defenceman pressures the opposition's winger in the offensive zone when they are breaking out, attempting to stop their attack and keep the puck in the offensive zone. A ''saucer pass'' is a pass used when an opposition's stick or body is in the passing lane. It is the act of raising the puck over the obstruction and having it land on a teammate's stick.
A deke (ice hockey), deke, short for "decoy", is a feint with the body or stick to fool a defender or the goalie. Many modern players, such as Pavel Datsyuk, Sidney Crosby and Patrick Kane, have picked up the skill of "dangling", which is fancier deking and requires more stick handling skills.
Fights
Women's ice hockey
TheInternational Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: F├®d├®ration internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-F├Čderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
(IIHF) holds the IIHF World Women's Championships tournaments in several divisions; championships are held annually, except that the top flight does not play in Winter Olympics, Olympic years.
Body checking
Checking (ice hockey), Body checking has been prohibited in women's ice hockey since the mid-1980s in Canada, and spreading from there internationally. Canada's Rhonda Leeman Taylor was responsible for banning body contact from all national women's ice hockey tournaments in Canada in 1983. Body checking in some of the women's hockey leagues in Canada were completely removed in 1986 resulting in a substantial increase in female participation in ice hockey in Canada. Prior to this point, bodychecking had been a part of the women's game in most cases, including in Europe. It wasn't until after the 1990 IIHF Women's World Championship, 1990 Women's World Championship (sanctioned by theInternational Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: F├®d├®ration internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-F├Čderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
) that body checking was eliminated from the women's ice hockey format internationally. In addition, until the mid 2000s, obstruction and interference were allowed, including pushing players around in front of the net, minor hooking, and "setting picks". When the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockeyŌĆöLNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teamsŌĆö25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
in North America removed obstruction and interference in the mid 2000s, minor hockey leagues and female leagues followed suit.
In women's IIHF ice hockey today, body checking is considered an "illegal hit" and is punishable by a minor penalty, major penalty and game misconduct, or match penalty. In current IIHF women's competition, body checking is either a minor or major penalty (ice hockey), penalty, decided at the referee's discretion.
Controversy
The idea of reintroducing bodychecking to the female game after its removal in the 1990s remains controversial. Some of those opposed to the idea of its reintroduction maintain it would lead to a loss of female participants, as once stated by Arto Sieppi, Finland's director of women's hockey. Sieppi made the statement in response to claims made by the then head coach of Sweden's women's national ice hockey team, Peter Elander, who had claimed its absence was due to patriarchal sexism. The Swedish Women's Hockey League, Svenska damhockeyligan (SDHL), known as the Swedish Women's Hockey League in English, announced in 2022 that it would include body checking during its 2022ŌĆō23 season, but would maintain a prohibition on the, "..."north-south" open-ice hit". The new program will also be extended to the Damettan, SwedenŌĆÖs second-tier womenŌĆÖs league.Equipment
Players in women's competition are required to wear protective full-hockey mask, face masks. At all levels, players must wear a Jockstrap#Jockstraps for females, pelvic protector, essentially the female equivalent of a jockstrap, known colloquially as a "jill" or "jillstrap". Other protective equipment for girls and women in ice hockey is sometimes specifically designed for the female body, such as shoulder pads designed to protect a women's breast area without reducing mobility.History
 Women began playing the game of ice hockey in the late 19th century. Several games were recorded in the 1890s in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The women of Lord Stanley's family were known to participate in the game of ice hockey on the outdoor ice rink at Rideau Hall, the residence of Canada's Governor-General.
The earliest available records of women's ice hockey were in the late 19th-century in Canada. Much like the men's game, women had previously been playing a conglomeration of stick-and-ball ice games. As with men's hockey, the women's game developed at first without an organizing body. A tournament in 1902 between
Women began playing the game of ice hockey in the late 19th century. Several games were recorded in the 1890s in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The women of Lord Stanley's family were known to participate in the game of ice hockey on the outdoor ice rink at Rideau Hall, the residence of Canada's Governor-General.
The earliest available records of women's ice hockey were in the late 19th-century in Canada. Much like the men's game, women had previously been playing a conglomeration of stick-and-ball ice games. As with men's hockey, the women's game developed at first without an organizing body. A tournament in 1902 between Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montr├®al, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
and Trois-Rivieres was billed as the first women's ice hockey championship tournament. Several tournaments, such as at the Banff Winter Carnival, were held in the early 20th century with numerous women's teams such as the Seattle Vamps and Vancouver Amazons. Organizations started to develop in the 1920s, such as the Ladies Ontario Hockey Association in Canada, and later, the Dominion Women's Amateur Hockey Association.
Starting in Canada in 1961, the women's game spread to more universities after the Fitness and Amateur Sport Act came into force in whereby the Canadian Government of Canada made an official commitment to "encourage, promote and develop fitness and amateur sport in Canada."
 Today, the women's game is played from youth through adult leagues, and the university level in North America and internationally. There are major professional women's hockey leagues: the Premier Hockey Federation, (formerly the National Women's Hockey League) with teams in the United States, Canada, and the Zhenskaya Hockey League with teams in Russia and China. In 2019, the Professional Women's Hockey Players Association was formed by over 150 players with the goal of creating a sustainable professional league for women's ice hockey in North America.
Between 1995 and 2005 the number of participants increased by 400 percent. In 2011, Canada had 85,827 women players, United States had 65,609, Finland 4,760, Sweden 3,075 and Switzerland 1,172.
Women's ice hockey was added as a medal sport eight years after the 1990 IIHF World Women's Championship, first world women's ice hockey championship in 1990 at the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Nagano, Nagano, Japan.
Today, the women's game is played from youth through adult leagues, and the university level in North America and internationally. There are major professional women's hockey leagues: the Premier Hockey Federation, (formerly the National Women's Hockey League) with teams in the United States, Canada, and the Zhenskaya Hockey League with teams in Russia and China. In 2019, the Professional Women's Hockey Players Association was formed by over 150 players with the goal of creating a sustainable professional league for women's ice hockey in North America.
Between 1995 and 2005 the number of participants increased by 400 percent. In 2011, Canada had 85,827 women players, United States had 65,609, Finland 4,760, Sweden 3,075 and Switzerland 1,172.
Women's ice hockey was added as a medal sport eight years after the 1990 IIHF World Women's Championship, first world women's ice hockey championship in 1990 at the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Nagano, Nagano, Japan.
 Prior to the professionalization of women's ice hockey in the 21st century, almost all professional women hockey players who played against men were goaltenders. No woman has ever played a full season in top tier men's professional ice hockey. The United States Hockey League (USHL) welcomed the first female professional ice hockey player in 1969ŌĆō70, when the Marquette Iron Rangers signed 18 yearŌĆōold, Karen Koch, a goaltender. Only one woman has ever played in the
Prior to the professionalization of women's ice hockey in the 21st century, almost all professional women hockey players who played against men were goaltenders. No woman has ever played a full season in top tier men's professional ice hockey. The United States Hockey League (USHL) welcomed the first female professional ice hockey player in 1969ŌĆō70, when the Marquette Iron Rangers signed 18 yearŌĆōold, Karen Koch, a goaltender. Only one woman has ever played in the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockeyŌĆöLNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teamsŌĆö25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
(NHL), goaltender Manon Rh├®aume. Rh├®aume played in NHL pre-season games as a goaltender for the Tampa Bay Lightning against the St. Louis Blues and the Boston Bruins. In 2003, Hayley Wickenheiser played with the Kirkkonummi HC Salamat, Salamat in the Finnish men's Suomi-sarja league.
Women have occasionally competed in North American minor leagues: among them Rh├®aume, and fellow goaltenders Kelly Dyer and Erin Whitten. Defenseman Angela Ruggiero became the first woman to actively play in a regular season professional hockey game in North America at a position other than goalie, playing in a single game for the Tulsa Oilers of the Central Hockey League.
Women's World Championship
The 1989 IIHF European Women Championships in West Germany was the first European Championship held in women's ice hockey and preceded the eventualInternational Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: F├®d├®ration internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-F├Čderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
-sanctioned Women's World Championship for ice hockey. The first world ice hockey championship for women was the 1990 IIHF World Women's Championship.
Leagues and championships
The following is a list of professional ice hockey leagues by attendance:Club competition
North America
 The NHL is the best attended and most popular ice hockey league in the world, and is among the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada. The league's history began after Canada's National Hockey Association decided to disband in 1917; the result was the creation of the National Hockey League with four teams. The league expanded to the United States beginning in 1924 and had as many as 10 teams before contracting to six teams by 1942ŌĆō43. In 1967, the NHL doubled in size to 12 teams, undertaking one of the greatest expansions in professional sports history. A few years later, in 1972, a new 12-team league, the World Hockey Association (WHA) was formed and due to its ensuing rivalry with the NHL, it caused an escalation in players' salaries. In 1979, the 17-team NHL merged with the WHA creating a 21-team league. By 2017, the NHL had expanded to 31 teams, and after a realignment in 2013, these teams were divided into two conferences and four divisions. The league expanded to 32 teams in 2021.
The American Hockey League (AHL) is the primary developmental professional league for players aspiring to enter the NHL. It comprises 31 teams from the United States and Canada. It is run as a Farm team, farm league to the NHL, with the vast majority of AHL players under contract to an NHL team. The ECHL (called the East Coast Hockey League before the 2003ŌĆō04 season) is a mid-level minor league in the United States with a few players under contract to NHL or AHL teams.
As of 2019, there are three minor professional leagues with no NHL affiliations: the Federal Prospects Hockey League (FPHL), Ligue Nord-Am├®ricaine de Hockey (LNAH), and the Southern Professional Hockey League (SPHL).
The NHL is the best attended and most popular ice hockey league in the world, and is among the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada. The league's history began after Canada's National Hockey Association decided to disband in 1917; the result was the creation of the National Hockey League with four teams. The league expanded to the United States beginning in 1924 and had as many as 10 teams before contracting to six teams by 1942ŌĆō43. In 1967, the NHL doubled in size to 12 teams, undertaking one of the greatest expansions in professional sports history. A few years later, in 1972, a new 12-team league, the World Hockey Association (WHA) was formed and due to its ensuing rivalry with the NHL, it caused an escalation in players' salaries. In 1979, the 17-team NHL merged with the WHA creating a 21-team league. By 2017, the NHL had expanded to 31 teams, and after a realignment in 2013, these teams were divided into two conferences and four divisions. The league expanded to 32 teams in 2021.
The American Hockey League (AHL) is the primary developmental professional league for players aspiring to enter the NHL. It comprises 31 teams from the United States and Canada. It is run as a Farm team, farm league to the NHL, with the vast majority of AHL players under contract to an NHL team. The ECHL (called the East Coast Hockey League before the 2003ŌĆō04 season) is a mid-level minor league in the United States with a few players under contract to NHL or AHL teams.
As of 2019, there are three minor professional leagues with no NHL affiliations: the Federal Prospects Hockey League (FPHL), Ligue Nord-Am├®ricaine de Hockey (LNAH), and the Southern Professional Hockey League (SPHL).
Eurasia
 The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) is the largest and most popular ice hockey league in Eurasia. The league is the direct successor to the Russian Super League, which in turn was the successor to the Soviet Championship League, Soviet League, the history of which dates back to the Soviet adoption of ice hockey in the 1940s. The KHL was 2008ŌĆō09 KHL season, launched in 2008 with clubs predominantly from Russia, but featuring teams from other post-Soviet states. The league expanded beyond the former Soviet countries beginning in the 2011ŌĆō12 KHL season, 2011ŌĆō12 season, with clubs in Croatia and Slovakia. The KHL currently comprises member clubs based in Belarus (1), China (1), Finland (1), Latvia (1), Kazakhstan (1) and Russia (19) for a total of 24.
The second division of hockey in Eurasia is the Supreme Hockey League (VHL). This league features 24 teams from Russia and 2 from Kazakhstan. This league is currently being converted to a farm league for the KHL, similarly to the AHL's function in relation to the NHL. The third division is the Russian Hockey League, which features only teams from Russia. The Asia League Ice Hockey, Asia League, an international ice hockey league featuring clubs from China, Japan, South Korea, and the Russian Far East, is the successor to the Japan Ice Hockey League.
The highest junior league in Eurasia is the Junior Hockey League (Russia), Junior Hockey League (MHL). It features 32 teams from post-Soviet states, predominantly Russia. The second tier to this league is the Junior Hockey League Championships (MHL-B).
The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) is the largest and most popular ice hockey league in Eurasia. The league is the direct successor to the Russian Super League, which in turn was the successor to the Soviet Championship League, Soviet League, the history of which dates back to the Soviet adoption of ice hockey in the 1940s. The KHL was 2008ŌĆō09 KHL season, launched in 2008 with clubs predominantly from Russia, but featuring teams from other post-Soviet states. The league expanded beyond the former Soviet countries beginning in the 2011ŌĆō12 KHL season, 2011ŌĆō12 season, with clubs in Croatia and Slovakia. The KHL currently comprises member clubs based in Belarus (1), China (1), Finland (1), Latvia (1), Kazakhstan (1) and Russia (19) for a total of 24.
The second division of hockey in Eurasia is the Supreme Hockey League (VHL). This league features 24 teams from Russia and 2 from Kazakhstan. This league is currently being converted to a farm league for the KHL, similarly to the AHL's function in relation to the NHL. The third division is the Russian Hockey League, which features only teams from Russia. The Asia League Ice Hockey, Asia League, an international ice hockey league featuring clubs from China, Japan, South Korea, and the Russian Far East, is the successor to the Japan Ice Hockey League.
The highest junior league in Eurasia is the Junior Hockey League (Russia), Junior Hockey League (MHL). It features 32 teams from post-Soviet states, predominantly Russia. The second tier to this league is the Junior Hockey League Championships (MHL-B).
Europe
 Several countries in Europe have their own top professional senior leagues. Many future KHL and NHL players start or end their professional careers in these leagues. The National League A in Switzerland, Swedish Hockey League in Sweden, Liiga in Finland, and Czech Extraliga in the Czech Republic are all very popular in their respective countries.
Beginning in the 2014ŌĆō15 season, the Champions Hockey League was launched, a league consisting of first-tier teams from several European countries, running parallel to the teams' domestic leagues. The competition is meant to serve as a Europe-wide ice hockey club championship. The competition is a direct successor to the European Trophy and is related to the 2008ŌĆō09 Champions Hockey League (2008ŌĆō09), tournament of the same name.
There are also several annual tournaments for clubs, held outside of league play. Season (sports), Pre-season tournaments include the European Trophy, Tampere Cup and the Pajulahti Cup. One of the oldest international ice hockey competition for clubs is the Spengler Cup, held every year in Davos, Switzerland, between Christmas and New Year's Day. It was first awarded in 1923 to the Oxford University Ice Hockey Club. The Memorial Cup, a competition for junior-level (age 20 and under) clubs is held annually from a pool of junior championship teams in Canada and the United States.
International club competitions organized by the IIHF include the IIHF Continental Cup, Continental Cup, the Victoria Cup (ice hockey), Victoria Cup and the European Women's Champions Cup. The World Junior Club Cup is an annual tournament of junior ice hockey clubs representing each of the top junior leagues.
Several countries in Europe have their own top professional senior leagues. Many future KHL and NHL players start or end their professional careers in these leagues. The National League A in Switzerland, Swedish Hockey League in Sweden, Liiga in Finland, and Czech Extraliga in the Czech Republic are all very popular in their respective countries.
Beginning in the 2014ŌĆō15 season, the Champions Hockey League was launched, a league consisting of first-tier teams from several European countries, running parallel to the teams' domestic leagues. The competition is meant to serve as a Europe-wide ice hockey club championship. The competition is a direct successor to the European Trophy and is related to the 2008ŌĆō09 Champions Hockey League (2008ŌĆō09), tournament of the same name.
There are also several annual tournaments for clubs, held outside of league play. Season (sports), Pre-season tournaments include the European Trophy, Tampere Cup and the Pajulahti Cup. One of the oldest international ice hockey competition for clubs is the Spengler Cup, held every year in Davos, Switzerland, between Christmas and New Year's Day. It was first awarded in 1923 to the Oxford University Ice Hockey Club. The Memorial Cup, a competition for junior-level (age 20 and under) clubs is held annually from a pool of junior championship teams in Canada and the United States.
International club competitions organized by the IIHF include the IIHF Continental Cup, Continental Cup, the Victoria Cup (ice hockey), Victoria Cup and the European Women's Champions Cup. The World Junior Club Cup is an annual tournament of junior ice hockey clubs representing each of the top junior leagues.
Other regions
The Australian Ice Hockey League and New Zealand Ice Hockey League are represented by nine and five teams respectively. As of 2012, the two top teams of the previous season from each league compete in the Trans-Tasman Champions League. Ice hockey in Africa is a small but growing sport; while no African ice hockey playing nation has a domestic national league, there are several regional leagues in South Africa.National team competitions
 Ice hockey has been played at the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics since 1924 (and was played at the Ice hockey at the 1920 Summer Olympics, summer games in 1920). Hockey is Canada's national winter sport, and Canadians are extremely passionate about the game. The nation has traditionally done very well at the Olympic games, winning six of the first seven gold medals. However, by 1956, its amateur club teams and national teams could not compete with the teams of government-supported players from the Soviet Union. The USSR won all but two gold medals from Ice hockey at the 1956 Winter Olympics, 1956 to Ice hockey at the 1988 Winter Olympics, 1988. The United States won its first gold medal in Ice hockey at the 1960 Winter Olympics, 1960. On the way to winning the gold medal at the 1980 Winter Olympics, 1980 Lake Placid Olympics, amateur US college players defeated the heavily favoured Soviet squadŌĆöan event known as the "Miracle on Ice" in the United States. Restrictions on professional players were fully dropped at the 1988 games in Calgary. NHL agreed to participate ten years later. The 1998 Games saw the full participation of players from the NHL, which suspended operations during the Games and has done so in subsequent Games up until 2018. The 2010 Winter Olympics, 2010 games in Vancouver were the first played in an NHL city since the inclusion of NHL players. The 2010 games were the first played on NHL-sized ice rinks, which are narrower than the IIHF standard.
National teams representing the member federations of the IIHF compete annually in the IIHF Ice Hockey World Championships. Teams are selected from the available players by the individual federations, without restriction on amateur or professional status. Since it is held in the spring, the tournament coincides with the annual NHL Stanley Cup playoffs and many of the top players are hence not available to participate in the tournament. Many of the NHL players who do play in the IIHF tournament come from teams eliminated before the playoffs or in the first round, and federations often hold open spots until the tournament to allow for players to join the tournament after their club team is eliminated. For many years, the tournament was an amateur-only tournament, but this restriction was removed, beginning in 1977.
Ice hockey has been played at the Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics since 1924 (and was played at the Ice hockey at the 1920 Summer Olympics, summer games in 1920). Hockey is Canada's national winter sport, and Canadians are extremely passionate about the game. The nation has traditionally done very well at the Olympic games, winning six of the first seven gold medals. However, by 1956, its amateur club teams and national teams could not compete with the teams of government-supported players from the Soviet Union. The USSR won all but two gold medals from Ice hockey at the 1956 Winter Olympics, 1956 to Ice hockey at the 1988 Winter Olympics, 1988. The United States won its first gold medal in Ice hockey at the 1960 Winter Olympics, 1960. On the way to winning the gold medal at the 1980 Winter Olympics, 1980 Lake Placid Olympics, amateur US college players defeated the heavily favoured Soviet squadŌĆöan event known as the "Miracle on Ice" in the United States. Restrictions on professional players were fully dropped at the 1988 games in Calgary. NHL agreed to participate ten years later. The 1998 Games saw the full participation of players from the NHL, which suspended operations during the Games and has done so in subsequent Games up until 2018. The 2010 Winter Olympics, 2010 games in Vancouver were the first played in an NHL city since the inclusion of NHL players. The 2010 games were the first played on NHL-sized ice rinks, which are narrower than the IIHF standard.
National teams representing the member federations of the IIHF compete annually in the IIHF Ice Hockey World Championships. Teams are selected from the available players by the individual federations, without restriction on amateur or professional status. Since it is held in the spring, the tournament coincides with the annual NHL Stanley Cup playoffs and many of the top players are hence not available to participate in the tournament. Many of the NHL players who do play in the IIHF tournament come from teams eliminated before the playoffs or in the first round, and federations often hold open spots until the tournament to allow for players to join the tournament after their club team is eliminated. For many years, the tournament was an amateur-only tournament, but this restriction was removed, beginning in 1977.
 The Summit Series, 1972 Summit Series and 1974 Summit Series, two series pitting the best Canadian and Soviet players without IIHF restrictions were major successes, and established a rivalry between Canada and the USSR. In the spirit of best-versus-best without restrictions on amateur or professional status, the series were followed by five Canada Cup (ice hockey), Canada Cup tournaments, played in North America. Two NHL versus USSR series were also held: the 1979 Challenge Cup and Rendez-vous '87. The Canada Cup tournament later became the World Cup of Hockey, played in 1996, 2004 and 2016. The United States won in 1996 and Canada won in 2004 and 2016.
Since the initial women's world championships in 1990, there have been fifteen tournaments. Women's hockey has been played at the Olympics since 1998. The only finals in the women's world championship or Olympics that did not involve both Canada and the United States were the Ice hockey at the 2006 Winter Olympics ŌĆō Women's tournament, 2006 Winter Olympic final between Canada and Sweden and 2019 IIHF Women's World Championship Final, 2019 World Championship final between the US and Finland.
Other ice hockey tournaments featuring national teams include the IIHF World Junior Championship, World Junior Championship, the IIHF World U18 Championships, World U18 Championships, the World U-17 Hockey Challenge, the World Junior A Challenge, the Ivan Hlinka Memorial Tournament, the IIHF World Women's U18 Championships, World Women's U18 Championships and the 4 Nations Cup. The annual Euro Hockey Tour, an unofficial European championship between the national men's teams of the Czech Republic, Finland, Russia and Sweden have been played since 1996ŌĆō97.
The Summit Series, 1972 Summit Series and 1974 Summit Series, two series pitting the best Canadian and Soviet players without IIHF restrictions were major successes, and established a rivalry between Canada and the USSR. In the spirit of best-versus-best without restrictions on amateur or professional status, the series were followed by five Canada Cup (ice hockey), Canada Cup tournaments, played in North America. Two NHL versus USSR series were also held: the 1979 Challenge Cup and Rendez-vous '87. The Canada Cup tournament later became the World Cup of Hockey, played in 1996, 2004 and 2016. The United States won in 1996 and Canada won in 2004 and 2016.
Since the initial women's world championships in 1990, there have been fifteen tournaments. Women's hockey has been played at the Olympics since 1998. The only finals in the women's world championship or Olympics that did not involve both Canada and the United States were the Ice hockey at the 2006 Winter Olympics ŌĆō Women's tournament, 2006 Winter Olympic final between Canada and Sweden and 2019 IIHF Women's World Championship Final, 2019 World Championship final between the US and Finland.
Other ice hockey tournaments featuring national teams include the IIHF World Junior Championship, World Junior Championship, the IIHF World U18 Championships, World U18 Championships, the World U-17 Hockey Challenge, the World Junior A Challenge, the Ivan Hlinka Memorial Tournament, the IIHF World Women's U18 Championships, World Women's U18 Championships and the 4 Nations Cup. The annual Euro Hockey Tour, an unofficial European championship between the national men's teams of the Czech Republic, Finland, Russia and Sweden have been played since 1996ŌĆō97.
Attendance records
International Status
 Ice hockey is most popular in Ice hockey in Canada, Canada, Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, and the Ice hockey in the United States, United States. Ice hockey is the official National sport, national winter sport of Canada. In addition, ice hockey is the most popular winter sport in Belarus, Sport in Croatia, Croatia, the Sport in the Czech Republic, Czech Republic, Sport in Finland, Finland, Sport in Latvia, Latvia, Sport in Russia, Russia, Sport in Slovakia, Slovakia, Sport in Sweden, Sweden, and Sport in Switzerland, Switzerland. North America's
Ice hockey is most popular in Ice hockey in Canada, Canada, Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, and the Ice hockey in the United States, United States. Ice hockey is the official National sport, national winter sport of Canada. In addition, ice hockey is the most popular winter sport in Belarus, Sport in Croatia, Croatia, the Sport in the Czech Republic, Czech Republic, Sport in Finland, Finland, Sport in Latvia, Latvia, Sport in Russia, Russia, Sport in Slovakia, Slovakia, Sport in Sweden, Sweden, and Sport in Switzerland, Switzerland. North America's National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockeyŌĆöLNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teamsŌĆö25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
(NHL) is the highest level for men's ice hockey and the strongest professional ice hockey league in the world. The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) is the highest league in Russia and much of Eastern Europe. The International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: F├®d├®ration internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-F├Čderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
(IIHF) is the formal governing body for international ice hockey, with the IIHF managing international tournaments and maintaining the IIHF World Ranking. Worldwide, the International Ice Hockey Federation has 83 member national associations, comprising 60 full members, 22 associate members, and one affiliate member.
In international competitions, the national teams of six countries (the Big Six (ice hockey), Big Six) predominate: Canada men's national ice hockey team, Canada, Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech Republic, Finland men's national ice hockey team, Finland, Russia men's national ice hockey team, Russia, Sweden men's national ice hockey team, Sweden and United States men's national ice hockey team, the United States. Of the 69 medals awarded all-time in men's competition at the Olympics, only seven medals were not awarded to one of those countries (or two of their precursors, the Soviet Union for Russia, and Czechoslovakia for the Czech Republic). In the annual Ice Hockey World Championships, 177 of 201 medals have been awarded to the six nations; Canada has won the most gold medals. Teams outside the Big Six have won only nine medals in either competition since 1953. The World Cup of Hockey is organized by the National Hockey League and the National Hockey League Players' Association (NHLPA), unlike the annual World Championships and quadrennial Olympic tournament, both run by the International Ice Hockey Federation. World Cup games are played under NHL rules and not those of the IIHF, and the tournament occurs prior to the NHL pre-season, allowing for all NHL players to be available, unlike the World Championships, which overlaps with the NHL's Stanley Cup playoffs. Furthermore, all 12 Women's Olympic and 36 IIHF World Women's Championship medals were awarded to one of the Big Six. The Canada women's national ice hockey team, Canadian national team or the United States women's national ice hockey team, United States national team have between them won every gold medal of either series.
Number of registered players by country
Number of registered hockey players, including male, female and junior, provided by the respective countries' federations. Note that this list only includes the 36 of 83 IIHF member countries with more than 1,000 registered players as of November 2022.Variants
Pond hockey
Sledge hockey
Sledge hockey is an adaption of ice hockey designed for players who have a physical disability. Players are seated in sleds and use a specialized hockey stick that also helps the player navigate on the ice. The sport was created in Sweden in the early 1960s and is played under similar rules to ice hockey.In popular culture
Ice hockey is the Sports in Canada#Official sports, official winter sport of Canada. Ice hockey, partially because of its popularity as a major professional sport, has been a source of inspiration for numerous films, television episodes and songs in North American popular culture.See also
* College ice hockey * Glossary of ice hockey * Ice hockey by country * Minor ice hockeyReferences
Citations
Works cited
* * * *Further reading
* * * * * *External links
Mandatory Equipment
ĆöCanadian Tire Hockey School
The Origins of Hockey
an
Hockey Origins Reference Database
ĆöSociety for International Hockey Research
History of ice hockey
Map of College & Pro Ice Hockey Teams in Canada and USA
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ice Hockey Ice hockey, Ice hockey Ice skating sports Stick sports Ice hockey terminology, Ice hockey terminology Athletic sports National symbols of Canada Sports originating in Canada Canadian culture Team sports Winter Olympic sports Indoor sports 19th century in Canada Games and sports introduced in the 19th century