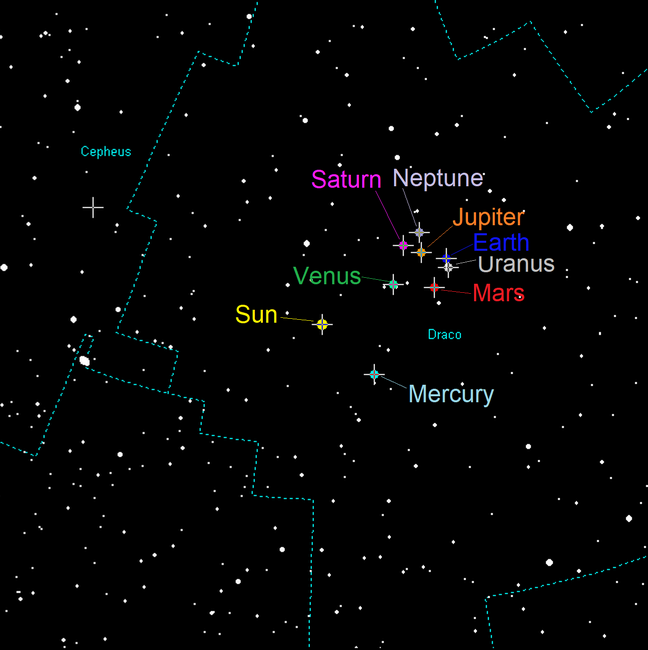
Ecliptic north pole (Běijí 北极) in Tiānlóng 天龙座 (Draco) between the Dippers.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An orbital pole is either point at the ends of an imaginary
An orbital pole is either point at the ends of an imaginary
 An orbital pole is either point at the ends of an imaginary
An orbital pole is either point at the ends of an imaginary line segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a straight line that is bounded by two distinct end points, and contains every point on the line that is between its endpoints. The length of a line segment is given by the Euclidean distance between ...
that runs through the center of an orbit (of a revolving body like a planet, moon or satellite) and is perpendicular to the orbital plane. Projected onto the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
, orbital poles are similar in concept to celestial poles, but are based on the body's orbit instead of its equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
.
The north orbital pole of a revolving body is defined by the right-hand rule
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation of axes in three-dimensional space. It is also a convenient method for quickly finding the direction of a cross-product of 2 vectors.
Most of th ...
. If the fingers of the right hand are curved along the direction of orbital motion, with the thumb extended and oriented to be parallel to the orbital axis, then the direction the thumb points is defined to be the orbital north.
The poles of Earth's orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth ...
are referred to as the ecliptic poles. For the remaining planets, the orbital pole in ecliptic coordinates is given by the longitude of the ascending node
The longitude of the ascending node (☊ or Ω) is one of the orbital elements used to specify the orbit of an object in space. It is the angle from a specified reference direction, called the ''origin of longitude'', to the direction of the asce ...
(☊) and inclination (''i''): ''l'' = ☊ - 90°, ''b'' = 90° - ''i''. In the following table, the planetary orbit poles are given in both celestial coordinates and the ecliptic coordinates for the Earth.
When a satellite orbits close to another large body, it can only maintain continuous observations in areas near its orbital poles. The continuous viewing zone (CVZ) of the Hubble Space Telescope lies inside roughly 24° of Hubble's orbital poles, which precess around the Earth's axis every 56 days.
Ecliptic Pole
The ecliptic is the plane on whichEarth orbits
A geocentric orbit or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA estimated there were approximately 2,465 artificial satellite payloads orbiting Earth and 6,216 pieces of space debris ...
the Sun. The ecliptic poles are the two points where the ecliptic axis, the imaginary line perpendicular to the ecliptic, intersects the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
.
The two ecliptic poles are mapped below.
Due to axial precession, either celestial pole completes a circuit around the nearer ecliptic pole every 25,800 years.
, the positions of the ecliptic poles expressed in equatorial coordinates
The equatorial coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system widely used to specify the positions of celestial objects. It may be implemented in spherical or rectangular coordinates, both defined by an origin at the centre of Earth, a fund ...
, as a consequence of Earth's axial tilt, are the following:
*North: right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
(exact), declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
*South: right ascension (exact), declination
The North Ecliptic Pole is located near the Cat's Eye Nebula and the South Ecliptic Pole is located near the Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), or Nubecula Major, is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around 50 kiloparsecs (≈160,000 light-years), the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the ...
.
It is impossible anywhere on Earth for either ecliptic pole to be at the zenith in the night sky. By definition, the ecliptic poles are located 90° from the Sun's position. Therefore, whenever and wherever either ecliptic pole is directly overhead, the Sun must be on the horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
. The ecliptic poles can contact the zenith only within the Arctic and Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and other ...
circles.
The galactic coordinates of the North ecliptic pole can be calculated as = 96.38°, = 29.81° (see Celestial coordinate system).
See also
* Celestial pole * Polar alignment * Pole star * Poles of astronomical bodiesNotes & References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Orbital Pole Pole Astronomical coordinate systems