Dodecahedron t12 v.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
-shaped "roof" above the faces of that cube with edge length 2.
An important case is ''h'' = (a quarter of the cube edge length) for perfect natural pyrite (also the pyritohedron in the
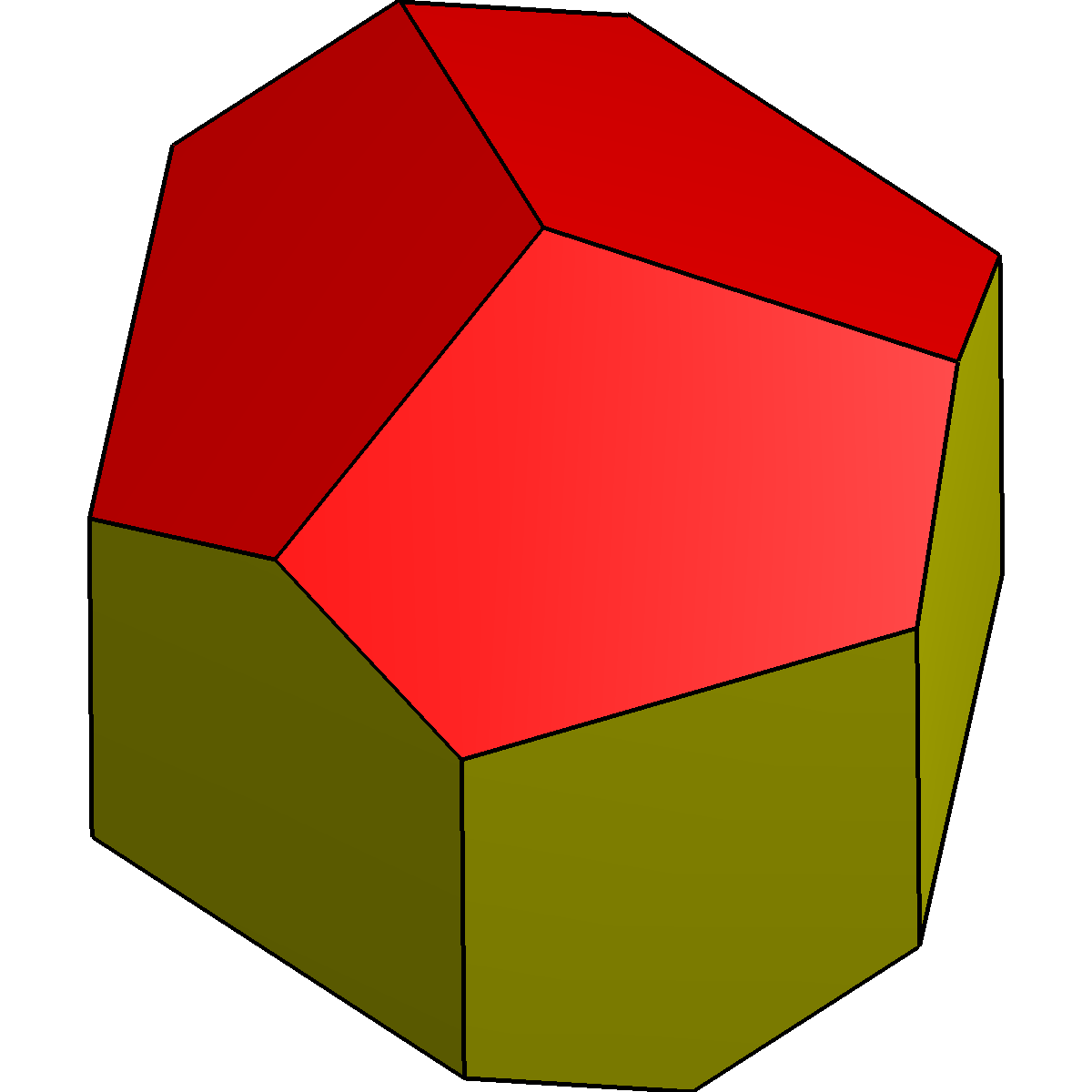
 The ''
The ''
Counting polyhedra
Numericana.com (2001-12-31). Retrieved on 2016-12-02. (Two polyhedra are "topologically distinct" if they have intrinsically different arrangements of faces and vertices, such that it is impossible to distort one into the other simply by changing the lengths of edges or the angles between edges or faces.) Topologically distinct dodecahedra (excluding pentagonal and rhombic forms) *Uniform polyhedra: **
Stellation of Pyritohedron
VRML models and animations of Pyritohedron and its stellations *
Editable printable net of a dodecahedron with interactive 3D viewThe Uniform PolyhedraOrigami Polyhedra
– Models made with Modular Origami
The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
*[http://www.bodurov.com/VectorVisualizer/?vectors=-0.94/-2.885/-3.975/-1.52/-4.67/-0.94v-3.035/0/-3.975/-4.91/0/-0.94v3.975/-2.885/-0.94/1.52/-4.67/0.94v1.52/-4.67/0.94/-1.52/-4.67/-0.94v0.94/-2.885/3.975/1.52/-4.67/0.94v-3.975/-2.885/0.94/-1.52/-4.67/-0.94v-3.975/-2.885/0.94/-4.91/0/-0.94v-3.975/2.885/0.94/-4.91/0/-0.94v-3.975/2.885/0.94/-1.52/4.67/-0.94v-2.455/1.785/3.975/-3.975/2.885/0.94v-2.455/-1.785/3.975/-3.975/-2.885/0.94v-1.52/4.67/-0.94/-0.94/2.885/-3.975v4.91/0/0.94/3.975/-2.885/-0.94v3.975/2.885/-0.94/2.455/1.785/-3.975v2.455/-1.785/-3.975/3.975/-2.885/-0.94v1.52/4.67/0.94/-1.52/4.67/-0.94v3.035/0/3.975/0.94/2.885/3.975v0.94/2.885/3.975/-2.455/1.785/3.975v-2.455/1.785/3.975/-2.455/-1.785/3.975v-2.455/-1.785/3.975/0.94/-2.885/3.975v0.94/-2.885/3.975/3.035/0/3.975v2.455/1.785/-3.975/-0.94/2.885/-3.975v-0.94/2.885/-3.975/-3.035/0/-3.975v-3.035/0/-3.975/-0.94/-2.885/-3.975v-0.94/-2.885/-3.975/2.455/-1.785/-3.975v2.455/-1.785/-3.975/2.455/1.785/-3.97v3.035/0/3.975/4.91/0/0.94v4.91/0/0.94/3.975/2.885/-0.94v3.975/2.885/-0.94/1.52/4.67/0.94v1.52/4.67/0.94/0.94/2.885/3.975 Dodecahedron 3D Visualization]
Stella: Polyhedron Navigator
Software used to create some of the images on this page.
How to make a dodecahedron from a Styrofoam cube
{{Authority control Individual graphs Planar graphs Platonic solids 12 (number)
geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices.
A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on ...
with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron
A regular dodecahedron or pentagonal dodecahedron is a dodecahedron that is regular, which is composed of 12 regular pentagonal faces, three meeting at each vertex. It is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 12 faces, 20 vertices, 30 ed ...
with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all e ...
. There are also three regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry
In mathematics, and especially in geometry, an object has icosahedral symmetry if it has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron. Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual polyhedr ...
, order 120.
Some dodecahedra have the same combinatorial structure as the regular dodecahedron (in terms of the graph formed by its vertices and edges), but their pentagonal faces are not regular:
The pyritohedron
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentago ...
, a common crystal form in pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue giv ...
, has pyritohedral symmetry
image:tetrahedron.jpg, 150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that c ...
, while the tetartoid
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagon ...
has tetrahedral symmetry
150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that combine a reflection ...
.
The rhombic dodecahedron
In geometry, the rhombic dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with 12 congruent rhombic faces. It has 24 edges, and 14 vertices of 2 types. It is a Catalan solid, and the dual polyhedron of the cuboctahedron.
Properties
The rhombic dodecahed ...
can be seen as a limiting case of the pyritohedron, and it has octahedral symmetry
A regular octahedron has 24 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and 48 symmetries altogether. These include transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation. A cube has the same set of symmetries, since it is the polyhedr ...
. The elongated dodecahedron
In geometry, the elongated dodecahedron, extended rhombic dodecahedron, rhombo-hexagonal dodecahedron or hexarhombic dodecahedron is a convex dodecahedron with 8 rhombic and 4 hexagonal faces. The hexagons can be made equilateral, or regular de ...
and trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron
In geometry, the trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron or rhombo-trapezoidal dodecahedron is a convex dodecahedron with 6 rhombic and 6 trapezoidal faces. It has symmetry. A concave form can be constructed with an identical net, seen as excavating tri ...
variations, along with the rhombic dodecahedra, are space-filling. There are numerous other dodecahedra.
While the regular dodecahedron shares many features with other Platonic solids, one unique property of it is that one can start at a corner of the surface and draw an infinite number of straight lines across the figure that return to the original point without crossing over any other corner.
Regular dodecahedron
The convex regular dodecahedron is one of the five regularPlatonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all e ...
s and can be represented by its Schläfli symbol .
The dual polyhedron
In geometry, every polyhedron is associated with a second dual structure, where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other, and the edges between pairs of vertices of one correspond to the edges between pairs of faces of the other. ...
is the regular icosahedron , having five equilateral triangles around each vertex.
The convex regular dodecahedron also has three stellations, all of which are regular star dodecahedra. They form three of the four Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra. They are the small stellated dodecahedron
In geometry, the small stellated dodecahedron is a Kepler-Poinsot polyhedron, named by Arthur Cayley, and with Schläfli symbol . It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra. It is composed of 12 pentagrammic faces, with five pentagrams meeti ...
, the great dodecahedron
In geometry, the great dodecahedron is a Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron, with Schläfli symbol and Coxeter–Dynkin diagram of . It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra. It is composed of 12 pentagonal faces (six pairs of parallel pentagon ...
, and the great stellated dodecahedron
In geometry, the great stellated dodecahedron is a Kepler-Poinsot polyhedron, with Schläfli symbol . It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra.
It is composed of 12 intersecting pentagrammic faces, with three pentagrams meeting at each ve ...
. The small stellated dodecahedron and great dodecahedron are dual to each other; the great stellated dodecahedron is dual to the great icosahedron
In geometry, the great icosahedron is one of four Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra (nonconvex regular polyhedra), with Schläfli symbol and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of . It is composed of 20 intersecting triangular faces, having five triangles meeti ...
. All of these regular star dodecahedra have regular pentagonal or pentagram
A pentagram (sometimes known as a pentalpha, pentangle, or star pentagon) is a regular five-pointed star polygon, formed from the diagonal line segments of a convex (or simple, or non-self-intersecting) regular pentagon. Drawing a circle arou ...
mic faces. The convex regular dodecahedron and great stellated dodecahedron are different realisations of the same abstract regular polyhedron
In mathematics, an abstract polytope is an algebraic partially ordered set which captures the dyadic property of a traditional polytope without specifying purely geometric properties such as points and lines.
A geometric polytope is said to be ...
; the small stellated dodecahedron and great dodecahedron are different realisations of another abstract regular polyhedron.
Other pentagonal dodecahedra
In crystallography, two important dodecahedra can occur as crystal forms in some symmetry classes of the cubic crystal system that are topologically equivalent to the regular dodecahedron but less symmetrical: the pyritohedron withpyritohedral symmetry
image:tetrahedron.jpg, 150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that c ...
, and the tetartoid
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagon ...
with tetrahedral symmetry
150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that combine a reflection ...
:
Pyritohedron
A pyritohedron is a dodecahedron with pyritohedral (Th) symmetry. Like theregular dodecahedron
A regular dodecahedron or pentagonal dodecahedron is a dodecahedron that is regular, which is composed of 12 regular pentagonal faces, three meeting at each vertex. It is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 12 faces, 20 vertices, 30 ed ...
, it has twelve identical pentagonal faces, with three meeting in each of the 20 vertices (see figure). However, the pentagons are not constrained to be regular, and the underlying atomic arrangement has no true fivefold symmetry axis. Its 30 edges are divided into two sets – containing 24 and 6 edges of the same length. The only axes of rotational symmetry
Rotational symmetry, also known as radial symmetry in geometry, is the property a shape has when it looks the same after some rotation by a partial turn. An object's degree of rotational symmetry is the number of distinct orientations in which i ...
are three mutually perpendicular twofold axes and four threefold axes.
Although regular dodecahedra do not exist in crystals, the pyritohedron form occurs in the crystals of the mineral pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue giv ...
, and it may be an inspiration for the discovery of the regular Platonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all e ...
form. The true regular dodecahedron can occur as a shape for quasicrystal
A quasiperiodic crystal, or quasicrystal, is a structure that is ordered but not periodic. A quasicrystalline pattern can continuously fill all available space, but it lacks translational symmetry. While crystals, according to the classical ...
s (such as holmium–magnesium–zinc quasicrystal
A holmium–magnesium–zinc (Ho–Mg–Zn) quasicrystal is a quasicrystal made of an alloy of the three metals holmium, magnesium and zinc that has the shape of a regular dodecahedron, a Platonic solid with 12 five-sided faces. Unlike the simila ...
) with icosahedral symmetry
In mathematics, and especially in geometry, an object has icosahedral symmetry if it has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron. Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual polyhedr ...
, which includes true fivefold rotation axes.
Crystal pyrite
The name ''crystal pyrite'' comes from one of the two common crystal habits shown bypyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue giv ...
(the other one being the cube). In pyritohedral pyrite, the faces have a Miller index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for lattice planes in crystal (Bravais) lattices.
In particular, a family of lattice planes of a given (direct) Bravais lattice is determined by three integers ''h'', ''k'', and ''� ...
of (210), which means that the dihedral angle
A dihedral angle is the angle between two intersecting planes or half-planes. In chemistry, it is the clockwise angle between half-planes through two sets of three atoms, having two atoms in common. In solid geometry, it is defined as the un ...
is 2·arctan(2) ≈ 126.87° and each pentagonal face has one angle of approximately 121.6° in between two angles of approximately 106.6° and opposite two angles of approximately 102.6°. The following formulas show the measurements for the face of a perfect crystal (which is rarely found in nature).
Cartesian coordinates
The eight vertices of a cube have the coordinates (±1, ±1, ±1). The coordinates of the 12 additional vertices are (0, ±(1 + ''h''), ±(1 − ''h''2)), (±(1 + ''h''), ±(1 − ''h''2), 0) and (±(1 − ''h''2), 0, ±(1 + ''h'')). ''h'' is the height of thewedge
A wedge is a triangular shaped tool, and is a portable inclined plane, and one of the six simple machines. It can be used to separate two objects or portions of an object, lift up an object, or hold an object in place. It functions by converti ...
Weaire–Phelan structure
In geometry, the Weaire–Phelan structure is a three-dimensional structure representing an idealised foam of equal-sized bubbles, with two different shapes. In 1993, Denis Weaire and Robert Phelan found that this structure was a better solution ...
).
Another one is ''h'' = = 0.618... for the regular dodecahedron
A regular dodecahedron or pentagonal dodecahedron is a dodecahedron that is regular, which is composed of 12 regular pentagonal faces, three meeting at each vertex. It is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 12 faces, 20 vertices, 30 ed ...
. See section '' Geometric freedom'' for other cases.
Two pyritohedra with swapped nonzero coordinates are in dual positions to each other like the dodecahedra in the compound of two dodecahedra
This uniform polyhedron compound is a composition of 2 icosahedron, icosahedra. It has octahedral symmetry ''Oh''. As a holosnub, it is represented by Schläfli symbol β and Coxeter diagram .
The triangles in this compound decompose into two Or ...
.
Geometric freedom
The pyritohedron has a geometric degree of freedom with limiting cases of a cubic convex hull at one limit of collinear edges, and arhombic dodecahedron
In geometry, the rhombic dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with 12 congruent rhombic faces. It has 24 edges, and 14 vertices of 2 types. It is a Catalan solid, and the dual polyhedron of the cuboctahedron.
Properties
The rhombic dodecahed ...
as the other limit as 6 edges are degenerated to length zero. The regular dodecahedron represents a special intermediate case where all edges and angles are equal.
It is possible to go past these limiting cases, creating concave or nonconvex pyritohedra. The ''endo-dodecahedron'' is concave and equilateral; it can tessellate space with the convex regular dodecahedron. Continuing from there in that direction, we pass through a degenerate case where twelve vertices coincide in the centre, and on to the regular great stellated dodecahedron
In geometry, the great stellated dodecahedron is a Kepler-Poinsot polyhedron, with Schläfli symbol . It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra.
It is composed of 12 intersecting pentagrammic faces, with three pentagrams meeting at each ve ...
where all edges and angles are equal again, and the faces have been distorted into regular pentagrams. On the other side, past the rhombic dodecahedron, we get a nonconvex equilateral dodecahedron with fish-shaped self-intersecting equilateral pentagonal faces.
Tetartoid
A tetartoid (also tetragonal pentagonal dodecahedron, pentagon-tritetrahedron, and tetrahedric pentagon dodecahedron) is a dodecahedron with chiraltetrahedral symmetry
150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that combine a reflection ...
(T). Like the regular dodecahedron
A regular dodecahedron or pentagonal dodecahedron is a dodecahedron that is regular, which is composed of 12 regular pentagonal faces, three meeting at each vertex. It is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 12 faces, 20 vertices, 30 ed ...
, it has twelve identical pentagonal faces, with three meeting in each of the 20 vertices. However, the pentagons are not regular and the figure has no fivefold symmetry axes.
Although regular dodecahedra do not exist in crystals, the tetartoid form does. The name tetartoid comes from the Greek root for one-fourth because it has one fourth of full octahedral symmetry, and half of pyritohedral symmetry. The mineral cobaltite
Cobaltite is a sulfide mineral composed of cobalt, arsenic, and sulfur, Co As S. Its impurities may contain up to 10% iron and variable amounts of nickel.Klein, Cornelus and Cornrlius Hurlbut, 1996, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., Wiley, p. ...
can have this symmetry form.
Abstractions sharing the solid's topology
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing ...
and symmetry can be created from the cube and the tetrahedron. In the cube each face is bisected by a slanted edge. In the tetrahedron each edge is trisected, and each of the new vertices connected to a face center. (In Conway polyhedron notation
In geometry, Conway polyhedron notation, invented by John Horton Conway and promoted by George W. Hart, is used to describe polyhedra based on a seed polyhedron modified by various prefix operations.
Conway and Hart extended the idea of using o ...
this is a gyro tetrahedron.)
Cartesian coordinates
The following points are vertices of a tetartoid pentagon undertetrahedral symmetry
150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that combine a reflection ...
:
:(''a'', ''b'', ''c''); (−''a'', −''b'', ''c''); (−, −, ); (−''c'', −''a'', ''b''); (−, , ),
under the following conditions:
:,
:''n'' = ''a''2''c'' − ''bc''2,
:''d''1 = ''a''2 − ''ab'' + ''b''2 + ''ac'' − 2''bc'',
:''d''2 = ''a''2 + ''ab'' + ''b''2 − ''ac'' − 2''bc'',
:.
Geometric freedom
Theregular dodecahedron
A regular dodecahedron or pentagonal dodecahedron is a dodecahedron that is regular, which is composed of 12 regular pentagonal faces, three meeting at each vertex. It is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 12 faces, 20 vertices, 30 ed ...
is a tetartoid with more than the required symmetry. The triakis tetrahedron
In geometry, a triakis tetrahedron (or kistetrahedron) is a Catalan solid with 12 faces. Each Catalan solid is the dual of an Archimedean solid. The dual of the triakis tetrahedron is the truncated tetrahedron.
The triakis tetrahedron can be se ...
is a degenerate case with 12 zero-length edges. (In terms of the colors used above this means, that the white vertices and green edges are absorbed by the green vertices.)
Dual of triangular gyrobianticupola
A lower symmetry form of the regular dodecahedron can be constructed as the dual of a polyhedron constructed from two triangular anticupola connected base-to-base, called a ''triangular gyrobianticupola.'' It has D3d symmetry, order 12. It has 2 sets of 3 identical pentagons on the top and bottom, connected 6 pentagons around the sides which alternate upwards and downwards. This form has a hexagonal cross-section and identical copies can be connected as a partial hexagonal honeycomb, but all vertices will not match. :
Rhombic dodecahedron
 The ''
The ''rhombic dodecahedron
In geometry, the rhombic dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with 12 congruent rhombic faces. It has 24 edges, and 14 vertices of 2 types. It is a Catalan solid, and the dual polyhedron of the cuboctahedron.
Properties
The rhombic dodecahed ...
'' is a zonohedron
In geometry, a zonohedron is a convex polyhedron that is centrally symmetric, every face of which is a polygon that is centrally symmetric (a zonogon). Any zonohedron may equivalently be described as the Minkowski sum of a set of line segments i ...
with twelve rhombic faces and octahedral symmetry. It is dual to the quasiregular cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
(an Archimedean solid) and occurs in nature as a crystal form. The rhombic dodecahedron packs together to fill space.
The ''rhombic dodecahedron'' can be seen as a degenerate pyritohedron
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentago ...
where the 6 special edges have been reduced to zero length, reducing the pentagons into rhombic faces.
The rhombic dodecahedron has several stellations, the first of which is also a parallelohedral spacefiller.
Another important rhombic dodecahedron, the Bilinski dodecahedron
In geometry, the Bilinski dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with twelve congruent golden rhombus faces. It has the same topology but a different geometry than the face-transitive rhombic dodecahedron. It is a parallelohedron.
History
This s ...
, has twelve faces congruent to those of the rhombic triacontahedron
In geometry, the rhombic triacontahedron, sometimes simply called the triacontahedron as it is the most common thirty-faced polyhedron, is a convex polyhedron with 30 rhombic faces. It has 60 edges and 32 vertices of two types. It is a Ca ...
, i.e. the diagonals are in the ratio of the golden ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0,
where the Greek letter phi ( ...
. It is also a zonohedron
In geometry, a zonohedron is a convex polyhedron that is centrally symmetric, every face of which is a polygon that is centrally symmetric (a zonogon). Any zonohedron may equivalently be described as the Minkowski sum of a set of line segments i ...
and was described by Bilinski in 1960. This figure is another spacefiller, and can also occur in non-periodic spacefillings along with the rhombic triacontahedron, the rhombic icosahedron and rhombic hexahedra.
Other dodecahedra
There are 6,384,634 topologically distinct ''convex'' dodecahedra, excluding mirror images—the number of vertices ranges from 8 to 20.Numericana.com (2001-12-31). Retrieved on 2016-12-02. (Two polyhedra are "topologically distinct" if they have intrinsically different arrangements of faces and vertices, such that it is impossible to distort one into the other simply by changing the lengths of edges or the angles between edges or faces.) Topologically distinct dodecahedra (excluding pentagonal and rhombic forms) *Uniform polyhedra: **
Decagonal prism
In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in the infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra. The decagonal prism has 12 faces, 30 edges, an ...
– 10 squares, 2 decagons, D10h symmetry, order 40.
**Pentagonal antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for ...
– 10 equilateral triangles, 2 pentagons, D5d symmetry, order 20
* Johnson solids (regular faced):
**Pentagonal cupola
In geometry, the pentagonal cupola is one of the Johnson solids (). It can be obtained as a slice of the rhombicosidodecahedron. The pentagonal cupola consists of 5 equilateral triangles, 5 squares, 1 pentagon, and 1 decagon.
Formulae
The ...
– 5 triangles, 5 squares, 1 pentagon, 1 decagon, C5v symmetry, order 10
**Snub disphenoid
In geometry, the snub disphenoid, Siamese dodecahedron, triangular dodecahedron, trigonal dodecahedron, or dodecadeltahedron is a convex polyhedron with twelve equilateral triangles as its faces. It is not a regular polyhedron because some vert ...
– 12 triangles, D2d, order 8
**Elongated square dipyramid
In geometry, the elongated square bipyramid (or elongated octahedron) is one of the Johnson solids (). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by elongating an octahedron by inserting a cube between its congruent halves.
It has been named ...
– 8 triangles and 4 squares, D4h symmetry, order 16
**Metabidiminished icosahedron
In geometry, the metabidiminished icosahedron is one of the Johnson solids (). The name refers to one way of constructing it, by removing two pentagonal pyramids () from a regular icosahedron, replacing two sets of five triangular faces of the ...
– 10 triangles and 2 pentagons, C2v symmetry, order 4
*Congruent irregular faced: (face-transitive
In geometry, a tessellation of dimension (a plane tiling) or higher, or a polytope of dimension (a polyhedron) or higher, is isohedral or face-transitive if all its faces are the same. More specifically, all faces must be not merely congrue ...
)
**Hexagonal bipyramid
A hexagonal bipyramid is a polyhedron formed from two hexagonal pyramids joined at their bases. The resulting solid has 12 triangular faces, 8 vertices and 18 edges. The 12 faces are identical isosceles triangles.
Although it is face-transitiv ...
– 12 isosceles triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- colline ...
s, dual of hexagonal prism
In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. Prisms are polyhedrons; this polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices..
Since it has 8 faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term ''octahedron'' is primarily used ...
, D6h symmetry, order 24
**Hexagonal trapezohedron
In geometry, a hexagonal trapezohedron or deltohedron is the fourth in an infinite series of trapezohedra which are dual polyhedra to the antiprisms. It has twelve faces which are congruence (geometry), congruent kite (geometry), kites. It can be ...
– 12 kites
A kite is a tethered heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create lift and drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. Kites often have a bridle and tail to guide the face ...
, dual of hexagonal antiprism
In geometry, the hexagonal antiprism is the 4th in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps.
Antiprisms are similar to prisms except the bases are twisted relative to each oth ...
, D6d symmetry, order 24
**Triakis tetrahedron
In geometry, a triakis tetrahedron (or kistetrahedron) is a Catalan solid with 12 faces. Each Catalan solid is the dual of an Archimedean solid. The dual of the triakis tetrahedron is the truncated tetrahedron.
The triakis tetrahedron can be se ...
– 12 isosceles triangles, dual of truncated tetrahedron
In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 equilateral triangle faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges (of two types). It can be constructed by truncation (geometry), truncating all 4 vertices of ...
, Td symmetry, order 24
*Other less regular faced:
**Hendecagonal pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilat ...
– 11 isosceles triangles and 1 regular hendecagon
In geometry, a hendecagon (also undecagon or endecagon) or 11-gon is an eleven-sided polygon. (The name ''hendecagon'', from Greek ''hendeka'' "eleven" and ''–gon'' "corner", is often preferred to the hybrid ''undecagon'', whose first part is f ...
, C11v, order 11
**Trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron
In geometry, the trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron or rhombo-trapezoidal dodecahedron is a convex dodecahedron with 6 rhombic and 6 trapezoidal faces. It has symmetry. A concave form can be constructed with an identical net, seen as excavating tri ...
– 6 rhombi, 6 trapezoid
A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezoid () in American and Canadian English. In British and other forms of English, it is called a trapezium ().
A trapezoid is necessarily a convex quadrilateral in Eu ...
s – dual of triangular orthobicupola
In geometry, the triangular orthobicupola is one of the Johnson solids (). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by attaching two triangular cupolas () along their bases. It has an equal number of squares and triangles at each vertex; howev ...
, D3h symmetry, order 12
**Rhombo-hexagonal dodecahedron
In geometry, the elongated dodecahedron, extended rhombic dodecahedron, rhombo-hexagonal dodecahedron or hexarhombic dodecahedron is a convex dodecahedron with 8 rhombic and 4 hexagonal faces. The hexagons can be made equilateral, or regular de ...
or ''elongated Dodecahedron'' – 8 rhombi and 4 equilateral hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A '' regular hexagon'' has ...
s, D4h symmetry, order 16
** Truncated pentagonal trapezohedron, D5d, order 20, topologically equivalent to regular dodecahedron
Practical usage
Armand Spitz
Armand Neustadter Spitz (July 7, 1904 – April 14, 1971) was an American planetarium designer.
Biography
Armand Spitz, the son of Louis Spitz and Rose (Neustadter), was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and was educated at the University of ...
used a dodecahedron as the "globe" equivalent for his Digital Dome planetarium projector. based upon a suggestion from Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
.
See also
*120-cell
In geometry, the 120-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also called a C120, dodecaplex (short for "dodecahedral complex"), hyperdodecahedron, polydodecahedron, hec ...
– a regular polychoron (4D polytope) whose surface consists of 120 dodecahedral cells
* – a dodecahedron shaped coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the king ...
(a unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
phytoplankton algae)
* Pentakis dodecahedron
* Roman dodecahedron
A Roman dodecahedron or Gallo-Roman dodecahedron is a small hollow object made of copper alloy which has been cast into a regular dodecahedral shape: twelve flat pentagonal faces, each face having a circular hole of varying diameter in the midd ...
* Snub dodecahedron
In geometry, the snub dodecahedron, or snub icosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.
The snub dodecahedron has 92 faces (the most ...
* Truncated dodecahedron
In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.
Geometric relations
This polyhedron can be formed from a regular dodecahedron by tr ...
References
External links
*''Plato's Fourth Solid and the "Pyritohedron"'', by Paul Stephenson, 1993, The Mathematical Gazette, Vol. 77, No. 479 (Jul., 1993), pp. 220–22VRML models and animations of Pyritohedron and its stellations *
Editable printable net of a dodecahedron with interactive 3D view
– Models made with Modular Origami
The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
*[http://www.bodurov.com/VectorVisualizer/?vectors=-0.94/-2.885/-3.975/-1.52/-4.67/-0.94v-3.035/0/-3.975/-4.91/0/-0.94v3.975/-2.885/-0.94/1.52/-4.67/0.94v1.52/-4.67/0.94/-1.52/-4.67/-0.94v0.94/-2.885/3.975/1.52/-4.67/0.94v-3.975/-2.885/0.94/-1.52/-4.67/-0.94v-3.975/-2.885/0.94/-4.91/0/-0.94v-3.975/2.885/0.94/-4.91/0/-0.94v-3.975/2.885/0.94/-1.52/4.67/-0.94v-2.455/1.785/3.975/-3.975/2.885/0.94v-2.455/-1.785/3.975/-3.975/-2.885/0.94v-1.52/4.67/-0.94/-0.94/2.885/-3.975v4.91/0/0.94/3.975/-2.885/-0.94v3.975/2.885/-0.94/2.455/1.785/-3.975v2.455/-1.785/-3.975/3.975/-2.885/-0.94v1.52/4.67/0.94/-1.52/4.67/-0.94v3.035/0/3.975/0.94/2.885/3.975v0.94/2.885/3.975/-2.455/1.785/3.975v-2.455/1.785/3.975/-2.455/-1.785/3.975v-2.455/-1.785/3.975/0.94/-2.885/3.975v0.94/-2.885/3.975/3.035/0/3.975v2.455/1.785/-3.975/-0.94/2.885/-3.975v-0.94/2.885/-3.975/-3.035/0/-3.975v-3.035/0/-3.975/-0.94/-2.885/-3.975v-0.94/-2.885/-3.975/2.455/-1.785/-3.975v2.455/-1.785/-3.975/2.455/1.785/-3.97v3.035/0/3.975/4.91/0/0.94v4.91/0/0.94/3.975/2.885/-0.94v3.975/2.885/-0.94/1.52/4.67/0.94v1.52/4.67/0.94/0.94/2.885/3.975 Dodecahedron 3D Visualization]
Stella: Polyhedron Navigator
Software used to create some of the images on this page.
How to make a dodecahedron from a Styrofoam cube
{{Authority control Individual graphs Planar graphs Platonic solids 12 (number)