Croydon clocktower.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Croydon is a large town in south
 As the vast majority of place names in the area are of Anglo-Saxon origin, the theory accepted by most
As the vast majority of place names in the area are of Anglo-Saxon origin, the theory accepted by most
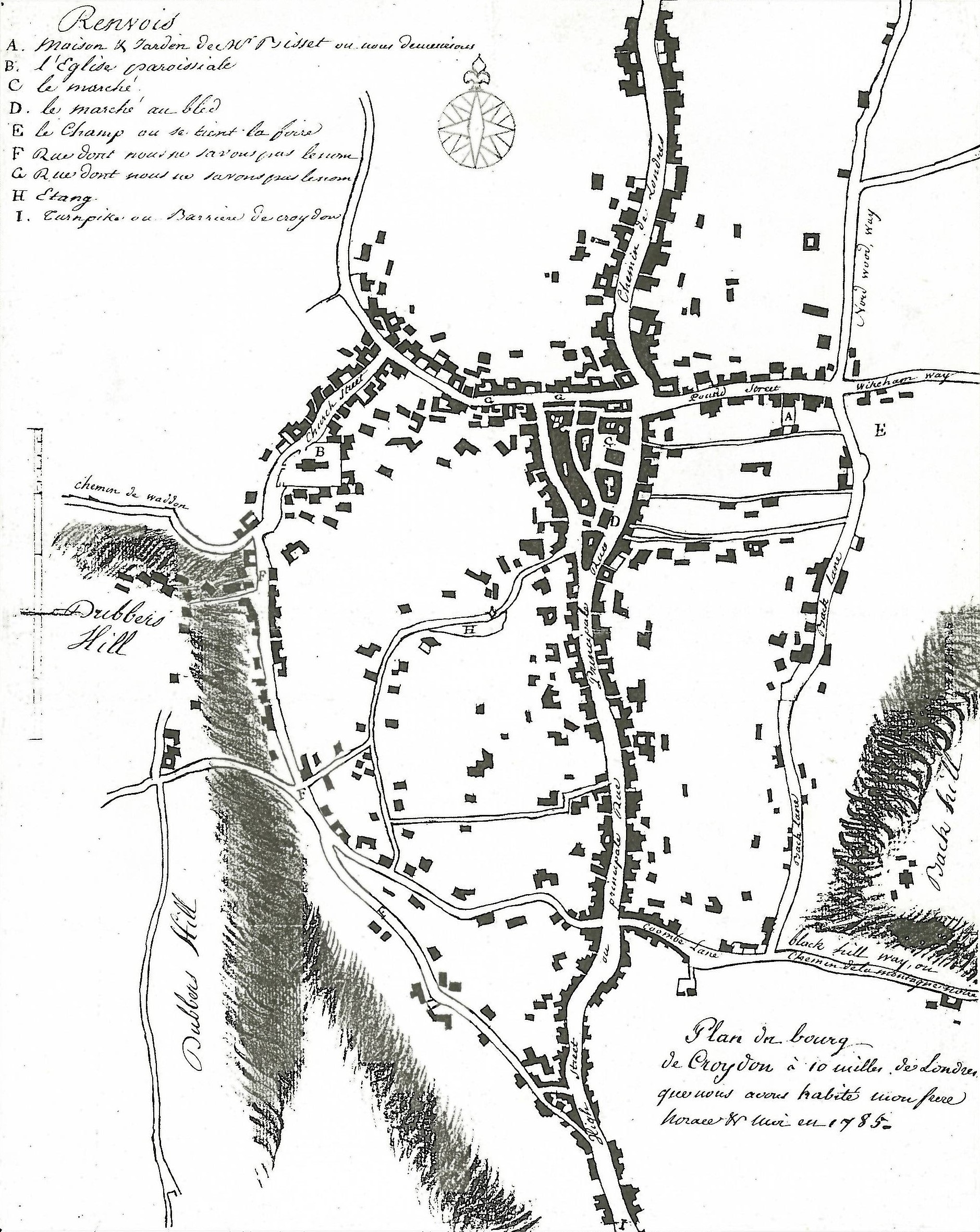
 The church had been established in the middle Saxon period, and was probably a
The church had been established in the middle Saxon period, and was probably a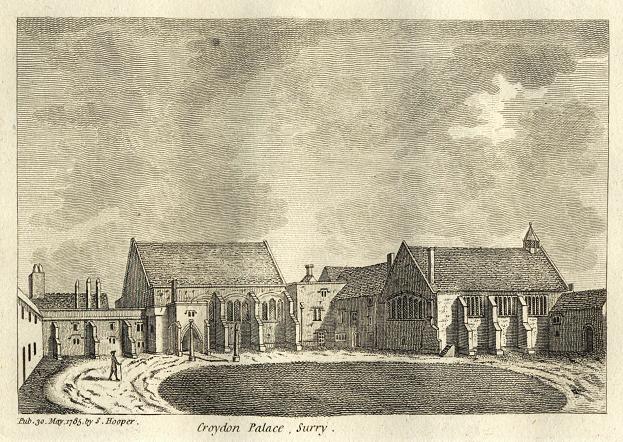  In 1276 Archbishop
In 1276 Archbishop  The Parish Church (now
The Parish Church (now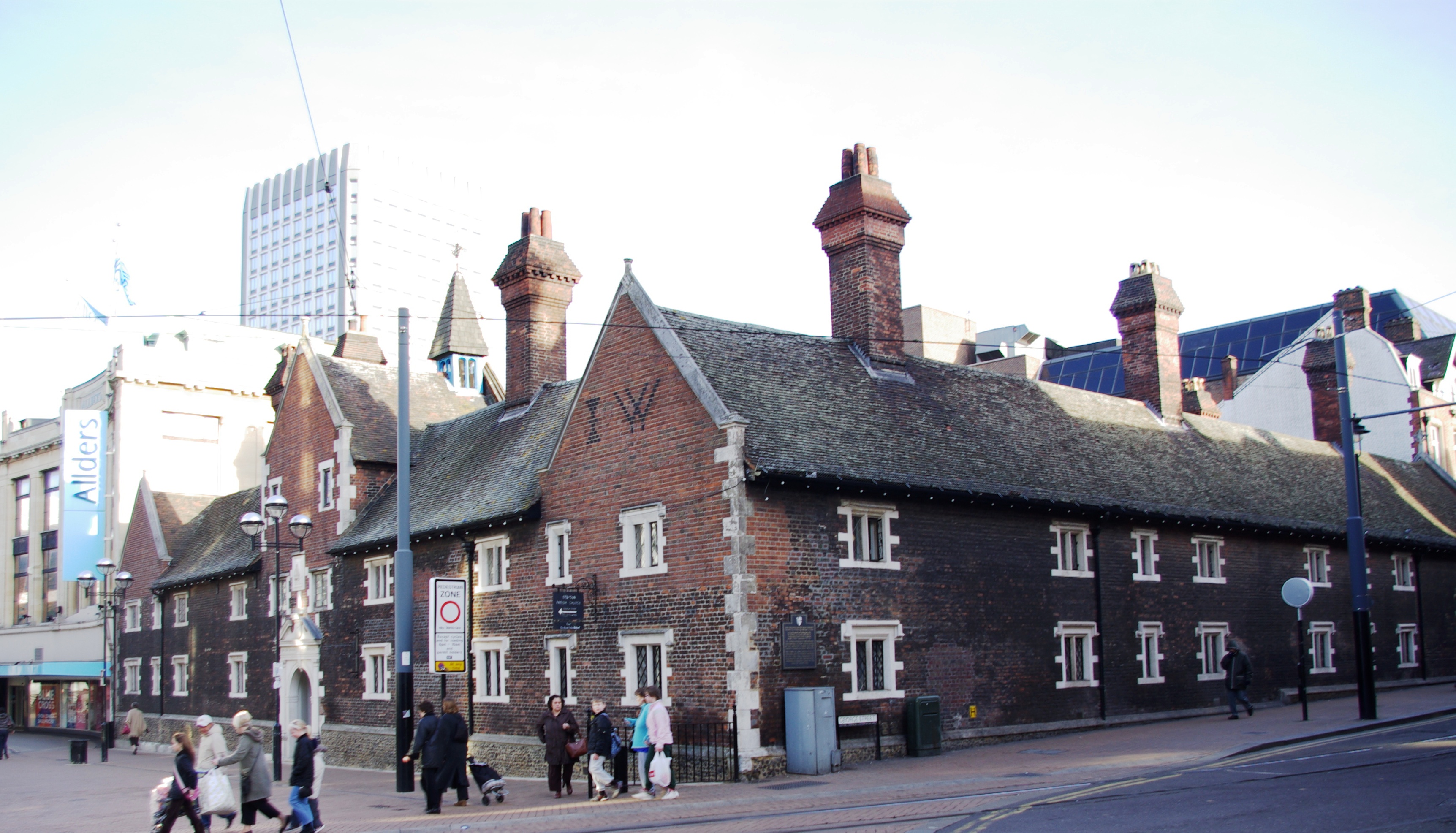 


 The development of Brighton as a fashionable resort in the 1780s increased Croydon's importance as a halt for stage coaches on the road south of London. At the beginning of the 19th century, Croydon became the terminus of two pioneering commercial transport links with London. The first, opened in 1803, was the horse-drawn
The development of Brighton as a fashionable resort in the 1780s increased Croydon's importance as a halt for stage coaches on the road south of London. At the beginning of the 19th century, Croydon became the terminus of two pioneering commercial transport links with London. The first, opened in 1803, was the horse-drawn
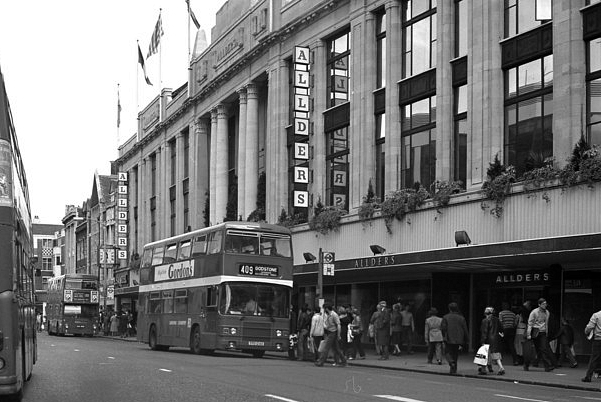

 In 1883 Croydon was incorporated as a borough. In 1889 it became a county borough, with a greater degree of autonomy. The new county borough council implemented the Croydon Improvement scheme in the early 1890s, which widened the High Street and cleared much of the "Middle Row" slum area. The remaining slums were gentrification, cleared shortly after Second World War, with much of the population relocated to the isolated new settlement of New Addington. New stores opened and expanded in central Croydon, including Allders, Kennards and Grade II listed Grants of Croydon, Grants, as well as the first Sainsbury's self-service shop in the country. There was a market on Surrey Street Market, Surrey Street.
Croydon was the location of London's main airport until the Second World War. During the war, much of central Croydon was devastated by German V-1 flying bombs and V-2 rocket, V-2 rockets, and for many years the town bore the scars of the destruction. After the war, Heathrow Airport superseded Croydon Airport as London's main airport, and Croydon Airport quickly went into a decline, finally closing in 1959.
By the 1950s, with its continuing growth, the town was becoming traffic congestion, congested, and the Council decided on another major redevelopment scheme. The Croydon Corporation Act was passed in 1956. This, coupled with national government incentives for office relocation out of Central London, led to the building of new offices and accompanying road schemes through the late 1950s and 1960s, and the town boomed as a business centre in the 1960s, with many multi-storey office blocks, an underpass, a Overpass, flyover and multi-storey car parks. The redeveloped town centre has since been identified as an "edge city" – a significant urban and commercial centre in its own right, located on the outskirts of a larger metropolitan area (in this case, London).
In 1960 Croydon celebrated its millennium with a pageant held at Lloyd Park and an exhibition held at the old Croydon Aerodrome.
In 1883 Croydon was incorporated as a borough. In 1889 it became a county borough, with a greater degree of autonomy. The new county borough council implemented the Croydon Improvement scheme in the early 1890s, which widened the High Street and cleared much of the "Middle Row" slum area. The remaining slums were gentrification, cleared shortly after Second World War, with much of the population relocated to the isolated new settlement of New Addington. New stores opened and expanded in central Croydon, including Allders, Kennards and Grade II listed Grants of Croydon, Grants, as well as the first Sainsbury's self-service shop in the country. There was a market on Surrey Street Market, Surrey Street.
Croydon was the location of London's main airport until the Second World War. During the war, much of central Croydon was devastated by German V-1 flying bombs and V-2 rocket, V-2 rockets, and for many years the town bore the scars of the destruction. After the war, Heathrow Airport superseded Croydon Airport as London's main airport, and Croydon Airport quickly went into a decline, finally closing in 1959.
By the 1950s, with its continuing growth, the town was becoming traffic congestion, congested, and the Council decided on another major redevelopment scheme. The Croydon Corporation Act was passed in 1956. This, coupled with national government incentives for office relocation out of Central London, led to the building of new offices and accompanying road schemes through the late 1950s and 1960s, and the town boomed as a business centre in the 1960s, with many multi-storey office blocks, an underpass, a Overpass, flyover and multi-storey car parks. The redeveloped town centre has since been identified as an "edge city" – a significant urban and commercial centre in its own right, located on the outskirts of a larger metropolitan area (in this case, London).
In 1960 Croydon celebrated its millennium with a pageant held at Lloyd Park and an exhibition held at the old Croydon Aerodrome.
 The growing town attracted many new buildings. The Fairfield Halls arts centre and event venue opened in 1962. Croydon developed as an important centre for shopping, with the construction of the
The growing town attracted many new buildings. The Fairfield Halls arts centre and event venue opened in 1962. Croydon developed as an important centre for shopping, with the construction of the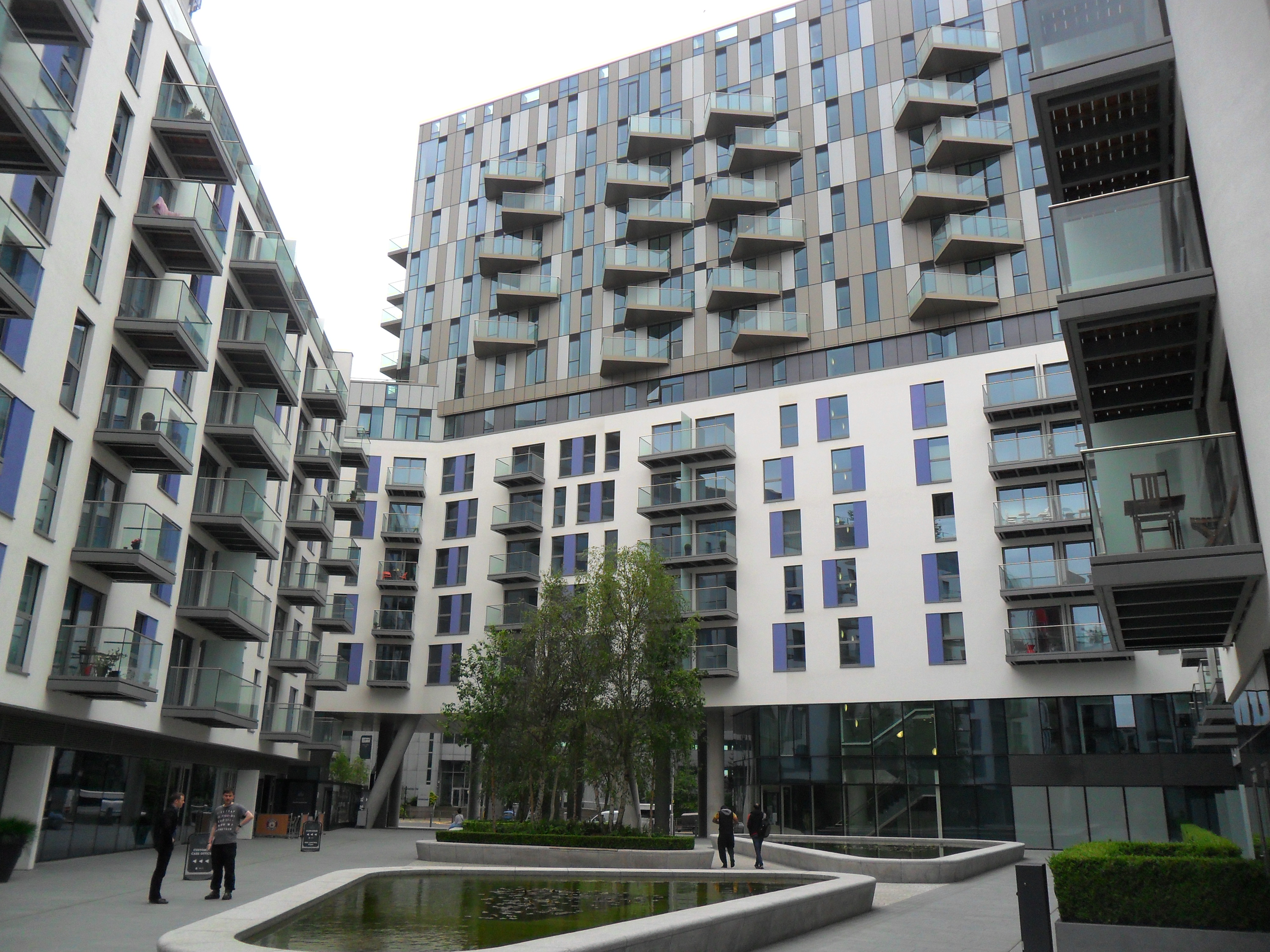  Croydon has many tall buildings such as the former Nestlé Tower (St George's House). The London Borough of Croydon's strategic planning committee in February 2013 gave the go-ahead to property fund manager Legal and General Property's plans to convert the empty 24-storey St George's House office building, occupied by Nestlé until September 2012, into 288 flats.
In 2007, events were held under the label of Croydon Exp07 to promote billions of pounds of promised projects, including swimming pools and a library. However, plans for a new shopping centre, to be called Park Place (Croydon), Park Place, had already been abandoned amid a scandal about 2006-2007 Life Peerages scandal, cash for peerages. Also abandoned were plans for an arena near the East Croydon station, after a compulsory purchase order was rejected in 2008 at Cabinet level.
On 22 November 2011, then Mayor of London Boris Johnson announced £23m of additional funding to help redevelop the town at the Develop Croydon Conference.
Several apartment developments, for instance Altitude 25 (completed 2010), have been built in recent years, and several more are being built or planned. The construction of Saffron Square, which includes a 43-storey tower, began on Wellesley Road in 2011 and was completed in 2016. Other developments with towers over 50 floors high have been given planning approval. These include the 54-storey "Menta Tower" in Cherry Orchard Road near East Croydon station, and a 55-storey tower at One Lansdowne Road, on which construction was set to begin in early 2013. The latter is set to be Britain's tallest block of flats, including office space, a four-star hotel and a health club.
In May 2012 it was announced that Croydon had been successful in its bid to become one of twelve "Portas Pilot Areas, Portas Pilot" towns, and would receive a share of £1.2m funding to help rejuvenate its central shopping areas.
Croydon has many tall buildings such as the former Nestlé Tower (St George's House). The London Borough of Croydon's strategic planning committee in February 2013 gave the go-ahead to property fund manager Legal and General Property's plans to convert the empty 24-storey St George's House office building, occupied by Nestlé until September 2012, into 288 flats.
In 2007, events were held under the label of Croydon Exp07 to promote billions of pounds of promised projects, including swimming pools and a library. However, plans for a new shopping centre, to be called Park Place (Croydon), Park Place, had already been abandoned amid a scandal about 2006-2007 Life Peerages scandal, cash for peerages. Also abandoned were plans for an arena near the East Croydon station, after a compulsory purchase order was rejected in 2008 at Cabinet level.
On 22 November 2011, then Mayor of London Boris Johnson announced £23m of additional funding to help redevelop the town at the Develop Croydon Conference.
Several apartment developments, for instance Altitude 25 (completed 2010), have been built in recent years, and several more are being built or planned. The construction of Saffron Square, which includes a 43-storey tower, began on Wellesley Road in 2011 and was completed in 2016. Other developments with towers over 50 floors high have been given planning approval. These include the 54-storey "Menta Tower" in Cherry Orchard Road near East Croydon station, and a 55-storey tower at One Lansdowne Road, on which construction was set to begin in early 2013. The latter is set to be Britain's tallest block of flats, including office space, a four-star hotel and a health club.
In May 2012 it was announced that Croydon had been successful in its bid to become one of twelve "Portas Pilot Areas, Portas Pilot" towns, and would receive a share of £1.2m funding to help rejuvenate its central shopping areas.
 In November 2013, Central Croydon MP Gavin Barwell gave a presentation at a public meeting on the Croydon regeneration project, detailing various developments underway due to be completed in coming years.
On 26 November 2013, Croydon Council approved a redevelopment of the Town Centre by The Croydon Partnership, a joint venture by The Westfield Group and Hammerson. London Mayor Boris Johnson approved the plan the following day. The Croydon Advertiser listed the approval as an "Historic Night for Croydon".
At Ruskin Square, a Boxpark made of sea containers opened in 2016 as a temporary measure until new buildings are constructed for shops, offices and housing. The ''London Evening Standard'' said that this and other developments were reviving the town which was in the process of gentrification.
In November 2013, Central Croydon MP Gavin Barwell gave a presentation at a public meeting on the Croydon regeneration project, detailing various developments underway due to be completed in coming years.
On 26 November 2013, Croydon Council approved a redevelopment of the Town Centre by The Croydon Partnership, a joint venture by The Westfield Group and Hammerson. London Mayor Boris Johnson approved the plan the following day. The Croydon Advertiser listed the approval as an "Historic Night for Croydon".
At Ruskin Square, a Boxpark made of sea containers opened in 2016 as a temporary measure until new buildings are constructed for shops, offices and housing. The ''London Evening Standard'' said that this and other developments were reviving the town which was in the process of gentrification.



 Croydon town centre is near the centre of the borough of Croydon, to the north of the
Croydon town centre is near the centre of the borough of Croydon, to the north of the
 There are several arts venues. Foremost is the Fairfield Halls, opened in 1962, which consists of a large concert hall frequently used for BBC recordings, the Ashcroft Theatre and the Arnhem Gallery. Fairfield is the home of the London Mozart Players. Many famous faces have appeared at the Fairfield Halls, including
There are several arts venues. Foremost is the Fairfield Halls, opened in 1962, which consists of a large concert hall frequently used for BBC recordings, the Ashcroft Theatre and the Arnhem Gallery. Fairfield is the home of the London Mozart Players. Many famous faces have appeared at the Fairfield Halls, including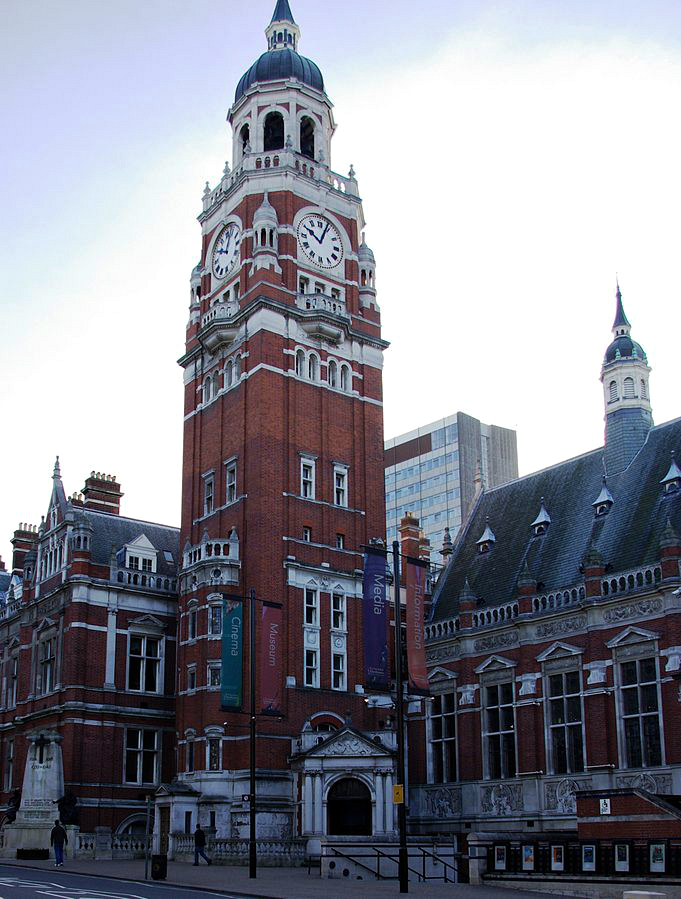  Croydon Clocktower, developed by the London Borough of Croydon in the mid-1990s, houses a state-of-the-art library, a performance venue in the old reference library, the David Lean Cinema (a small, independent, art-house cinema) and the Museum of Croydon, which details Croydon's history. The building links into Croydon Town Hall and some areas of the building, most notably the Braithwaite Hall, are part of the original town hall and library complex, built in 1892–1896 to a design by Charles Henman. A bronze statue of Queen Victoria was erected outside the buildings in 1903.
The Warehouse Theatre (which closed in 2012), was a studio theatre known for promoting new writing, comedy and youth theatre. It had to close because of the major Ruskin Square redevelopment, but will re-open in the future in a new larger theatre building within the new development.
The Pembroke Theatre had many productions with well-known actors before its closure in about 1962.
There are several local and small venues for comedy and community events dotted around Croydon and its districts. Croydon Youth Theatre Organisation celebrated its 40th birthday in 2005. There are several community arts groups, particularly in the large British Asian, Asian community.
The Spread Eagle Theatre is a new 50-seat studio theatre. Opened in October 2013, it is situated in the town centre, 10 minutes' walk from East Croydon Station. The Spread Eagle works closely with its sister venue, the Old Joint Stock Theatre in Birmingham. Both venues champion 'big plays for small spaces' with an emphasis on new writing, supporting emerging artists and theatre companies.
A calendar titled "Rare Roundabouts of Croydon", with a picture of a different Croydon roundabout each month, has enjoyed some success.
Croydon Clocktower, developed by the London Borough of Croydon in the mid-1990s, houses a state-of-the-art library, a performance venue in the old reference library, the David Lean Cinema (a small, independent, art-house cinema) and the Museum of Croydon, which details Croydon's history. The building links into Croydon Town Hall and some areas of the building, most notably the Braithwaite Hall, are part of the original town hall and library complex, built in 1892–1896 to a design by Charles Henman. A bronze statue of Queen Victoria was erected outside the buildings in 1903.
The Warehouse Theatre (which closed in 2012), was a studio theatre known for promoting new writing, comedy and youth theatre. It had to close because of the major Ruskin Square redevelopment, but will re-open in the future in a new larger theatre building within the new development.
The Pembroke Theatre had many productions with well-known actors before its closure in about 1962.
There are several local and small venues for comedy and community events dotted around Croydon and its districts. Croydon Youth Theatre Organisation celebrated its 40th birthday in 2005. There are several community arts groups, particularly in the large British Asian, Asian community.
The Spread Eagle Theatre is a new 50-seat studio theatre. Opened in October 2013, it is situated in the town centre, 10 minutes' walk from East Croydon Station. The Spread Eagle works closely with its sister venue, the Old Joint Stock Theatre in Birmingham. Both venues champion 'big plays for small spaces' with an emphasis on new writing, supporting emerging artists and theatre companies.
A calendar titled "Rare Roundabouts of Croydon", with a picture of a different Croydon roundabout each month, has enjoyed some success.
 About 60 murals were added to Croydon town centre in 2018, as part of the Rise street art festival coordinated by the Rise art gallery in Croydon.
About 60 murals were added to Croydon town centre in 2018, as part of the Rise street art festival coordinated by the Rise art gallery in Croydon.
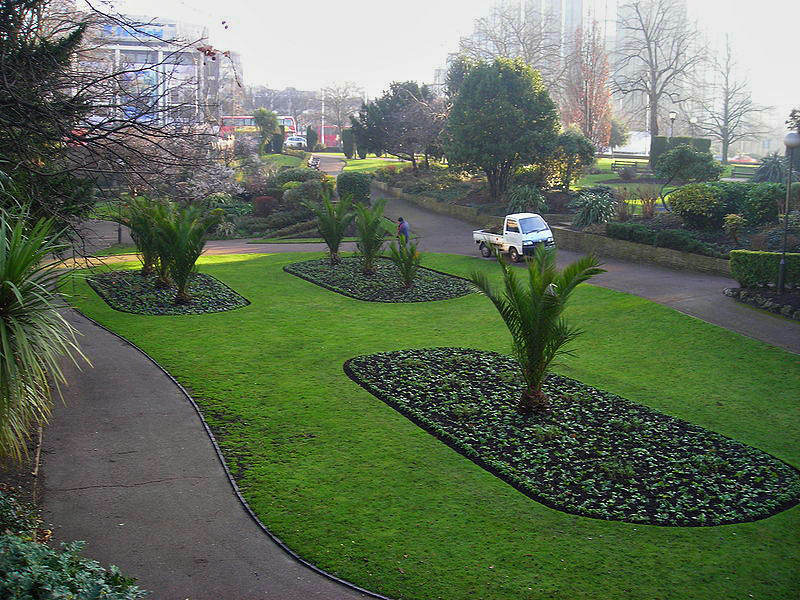 The borough has many woods for walking in, which together account for 8.5% of Greater London's woodland resource (626.46 hectares). These include Lloyd Park (Croydon), Lloyd Park and Croham Hurst.
Among several other parks and open spaces around Croydon, there is an area of landscaped green space in the town centre called Queens Gardens; it is adjacent to the town hall and Clocktower art centre.
The borough has many woods for walking in, which together account for 8.5% of Greater London's woodland resource (626.46 hectares). These include Lloyd Park (Croydon), Lloyd Park and Croham Hurst.
Among several other parks and open spaces around Croydon, there is an area of landscaped green space in the town centre called Queens Gardens; it is adjacent to the town hall and Clocktower art centre.



 * Peggy Ashcroft (1907–1991), actress, was born in Croydon, lived in George Street as a child and attended Croydon High School; honoured in the name of the Ashcroft Theatre, part of the Fairfield Halls
* Robert Barclay (historiographer), Robert Barclay (1833–1876), an English Quaker historiographer
* Jon Benjamin (Jewish leader), Jon Benjamin (1964–), Chief Executive of the Board of Deputies of British Jews, born and grew up in Croydon
* Alex Brooker (1984–), Journalist, born in Croydon
* Raymond Chandler (1888–1959), American detective fiction writer, lived in Upper Norwood as a schoolboy
* Anne Clark (poet), Anne Clark (1960–), electronic music artist and poet, was born in Croydon
* Carlton Cole (1983–), English footballer, born in Croydon
* Kit Connor (2004–), Actor known for Rocketman (film) and Heartstopper (TV series) on Netflix, born and raised in Croydon
* Roger Ward Crosskey (1930–2017), entomologist, born in Croydon
* Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (1859–1930), Scottish-born fiction writer, lived at No. 12 Tennison Road, South Norwood and featured the area in some of his Sherlock Holmes detective stories
* Jane Drew (1911–1996), modernist architect, born in Thornton Heath and head girl at Croydon High School
* Havelock Ellis (1859–1939), sexologist, born in Croydon
* Paul Garelli (1924–2006), French Assyriologist, born in Croydon
* Ben Haenow (1985–), pop singer, winner of The X Factor (UK series 11), ''The X Factor'' (UK series 11), born in Croydon
* Roy Hodgson (1947–), Crystal Palace F.C., Crystal Palace and former England manager, born and grew up in Croydon
* Tom Holland (actor), Tom Holland (1996–), actor in five Marvel Cinematic Universe films, educated at the BRIT School
* William Forster Lanchester, FRSE (1875–1953), zoologist, born and raised in Croydon
* Eden Kane (born Richard Graham Sarstedt) (1940–), singer and older brother of Peter and Robin Sarstedt
* Rachel Khoo (1980–), cook, editor-in-chief of online lifestyle magazine ''Khoollect'', with her own BBC series
* George Arthur Knowland, George Knowland (1922–1945), Victoria Cross recipient, went to Elmwood Junior School
* Nish Kumar (1985–), comedian, born in
* Peggy Ashcroft (1907–1991), actress, was born in Croydon, lived in George Street as a child and attended Croydon High School; honoured in the name of the Ashcroft Theatre, part of the Fairfield Halls
* Robert Barclay (historiographer), Robert Barclay (1833–1876), an English Quaker historiographer
* Jon Benjamin (Jewish leader), Jon Benjamin (1964–), Chief Executive of the Board of Deputies of British Jews, born and grew up in Croydon
* Alex Brooker (1984–), Journalist, born in Croydon
* Raymond Chandler (1888–1959), American detective fiction writer, lived in Upper Norwood as a schoolboy
* Anne Clark (poet), Anne Clark (1960–), electronic music artist and poet, was born in Croydon
* Carlton Cole (1983–), English footballer, born in Croydon
* Kit Connor (2004–), Actor known for Rocketman (film) and Heartstopper (TV series) on Netflix, born and raised in Croydon
* Roger Ward Crosskey (1930–2017), entomologist, born in Croydon
* Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (1859–1930), Scottish-born fiction writer, lived at No. 12 Tennison Road, South Norwood and featured the area in some of his Sherlock Holmes detective stories
* Jane Drew (1911–1996), modernist architect, born in Thornton Heath and head girl at Croydon High School
* Havelock Ellis (1859–1939), sexologist, born in Croydon
* Paul Garelli (1924–2006), French Assyriologist, born in Croydon
* Ben Haenow (1985–), pop singer, winner of The X Factor (UK series 11), ''The X Factor'' (UK series 11), born in Croydon
* Roy Hodgson (1947–), Crystal Palace F.C., Crystal Palace and former England manager, born and grew up in Croydon
* Tom Holland (actor), Tom Holland (1996–), actor in five Marvel Cinematic Universe films, educated at the BRIT School
* William Forster Lanchester, FRSE (1875–1953), zoologist, born and raised in Croydon
* Eden Kane (born Richard Graham Sarstedt) (1940–), singer and older brother of Peter and Robin Sarstedt
* Rachel Khoo (1980–), cook, editor-in-chief of online lifestyle magazine ''Khoollect'', with her own BBC series
* George Arthur Knowland, George Knowland (1922–1945), Victoria Cross recipient, went to Elmwood Junior School
* Nish Kumar (1985–), comedian, born in
<学校紹介>
. The Japanese Saturday School of London. Retrieved on 5 April 2015. – See "9.校舎 "
Royal Russell School is a co-educational independent boarding and day school in South Croydon and is a member of the Headmasters' Conference.
File:Old Palace School (Croydon Palace).JPG, The Old Palace School
File:Croydon College.JPG, Croydon College's main buildings in Central Croydon
London Borough of CroydonOpen directory project
{{Authority control Areas of London Districts of the London Borough of Croydon History of the London Borough of Croydon Metropolitan centres of London Market towns in London
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon
The London Borough of Croydon () is a London borough in south London, part of Outer London. It covers an area of . It is the southernmost borough of London. At its centre is the historic town of Croydon from which the borough takes its name; ...
, a local government district
The districts of England (also known as local authority districts or local government districts to distinguish from unofficial city districts) are a level of subnational division of England used for the purposes of local government. As the st ...
of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensive shopping district and night-time economy. The entire town had a population of 192,064 as of 2011, whilst the wider borough had a population of 384,837.
Historically an ancient parish in the Wallington hundred of Surrey, at the time of the Norman conquest of England Croydon had a church, a mill, and around 365 inhabitants, as recorded in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
of 1086. Croydon expanded in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
as a market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
and a centre for charcoal production, leather tanning and brewing. The Surrey Iron Railway
The Surrey Iron Railway (SIR) was a horse-drawn plateway that linked Wandsworth and Croydon via Mitcham, all then in Surrey but now suburbs of south London, in England. It was established by Act of Parliament in 1801, and opened partly in 1802 ...
from Croydon to Wandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
Toponymy
Wandsworth takes its nam ...
opened in 1803 and was an early public railway. Later 19th century railway building facilitated Croydon's growth as a commuter town
A commuter town is a populated area that is primarily residential rather than commercial or industrial. Routine travel from home to work and back is called commuting, which is where the term comes from. A commuter town may be called by many ...
for London. By the early 20th century, Croydon was an important industrial area, known for car manufacture, metal working and Croydon Airport. In the mid 20th century these sectors were replaced by retailing and the service economy
Service economy can refer to one or both of two recent economic developments:
* The increased importance of the service sector in industrialized economies. The current list of Fortune 500 companies contains more service companies and fewer manu ...
, brought about by massive redevelopment which saw the rise of office blocks and the Whitgift Centre
The Whitgift Centre is a large shopping centre in the town centre of Croydon, opening in stages between 1968 and 1970. The centre comprises of retail space, and was the largest covered shopping development in Greater London until the opening of ...
, the largest shopping centre in Greater London until 2008. Historically, the town formed part of the County
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
of Surrey but was amalgamated into Greater London in 1965.
Croydon lies on a transport corridor between central London and the south coast of England, to the north of two high gaps in the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills a ...
, one taken by the A23 Brighton Road and the main railway line through Purley and Merstham
Merstham is a town in the borough of Reigate and Banstead in Surrey, England. It lies 25 miles south of Charing Cross and 2 miles south of the Greater London border. Part of the North Downs Way runs along the northern boundary of the town. Mers ...
and the other by the A22 from Purley to the M25 Godstone
Godstone is a village and civil parish in Surrey, England, east of Reigate at the junction of the A22 and A25 roads, near the M25 motorway and the North Downs. Godstone railway station is separated from it by agricultural land. Blindley H ...
interchange. Road traffic is diverted away from a largely pedestrianised town centre, mostly consisting of North End. East Croydon is a major hub of the national railway transport system, with frequent fast services to central London, Brighton and the south coast. The town is also at the centre of the only tramway system in southern England.
History
Toponymy
 As the vast majority of place names in the area are of Anglo-Saxon origin, the theory accepted by most
As the vast majority of place names in the area are of Anglo-Saxon origin, the theory accepted by most philologists
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources; it is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics (with especially strong ties to etymology). Philology is also defined ...
is that the name Croydon derives originally from the Anglo-Saxon ''croh'', meaning "crocus
''Crocus'' (; plural: crocuses or croci) is a genus of seasonal flowering plants in the family Iridaceae (iris family) comprising about 100 species of perennials growing from corms. They are low growing plants, whose flower stems remain under ...
", and ''denu'', "valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ove ...
", indicating that, like Saffron Walden
Saffron Walden is a market town in the Uttlesford district of Essex, England, north of Bishop's Stortford, south of Cambridge and north of London. It retains a rural appearance and some buildings of the medieval period. The population was 15, ...
in Essex, it was a centre for the cultivation of saffron
Saffron () is a spice derived from the flower of ''Crocus sativus'', commonly known as the "saffron crocus". The vivid crimson stigma and styles, called threads, are collected and dried for use mainly as a seasoning and colouring agent in ...
. It has been argued that this cultivation is likely to have taken place in the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
period, when the saffron crocus would have been grown to supply the London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
market, most probably for medicinal
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
purposes, and particularly for the treatment of granulation of the eyelids.
There is also a plausible Brittonic origin for Croydon in the form "Crai-din" meaning "settlement near fresh water" (cf Creuddyn, Ceredigion
250px, Llanfihangel-y-Creuddyn viewed from the north.
Creuddyn was a medieval commote (Welsh: ''cwmwd'') and, later, a lordship in Ceredigion, Wales. It was located between the rivers Ystwyth and Rheidol,''The Vaughans of Trawsgoed'', p. 22 an ...
), the name Crai (variously spelled) being found in Kent at various places even as late as the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
.
Alternative, although less probable, theories of the name's origin have been proposed. According to John Corbet Anderson: "The earliest mention of Croydon is in the joint will of Beorhtric and Aelfswth, dated about the year 962. In this Anglo-Saxon document the name is spelt Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
characters] ''Crogdaene''. Crog was, and still is, the Norse or Danish word for crooked, which is expressed in Anglo-Saxon by ''crumb'', a totally different word. From the Danish came our ''crook'' and ''crooked''. This term accurately describes the locality; it is a ''crooked'' or ''winding valley'', in reference to the valley that runs in an oblique and serpentine course from Godstone
Godstone is a village and civil parish in Surrey, England, east of Reigate at the junction of the A22 and A25 roads, near the M25 motorway and the North Downs. Godstone railway station is separated from it by agricultural land. Blindley H ...
to Croydon." Anderson challenged a claim, originally made by Andrew Coltee Ducarel, that the name came from the Old French for "chalk hill", because it was in use at least a century before the French language would have been commonly used following the Norman conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
. However, there was no long-term Danish occupation (see Danelaw
The Danelaw (, also known as the Danelagh; ang, Dena lagu; da, Danelagen) was the part of England in which the laws of the Danes held sway and dominated those of the Anglo-Saxons. The Danelaw contrasts with the West Saxon law and the Mercian ...
) in Surrey, which was part of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
, and Danish-derived nomenclature is also highly unlikely. More recently, David Bird has speculated that the name might derive from a personal name, ''Crocus'': he suggests a family connection with the documented Chrocus, king of the Alemanni, who allegedly played a part in the proclamation of Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
as emperor at York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
in AD 306.
Early history
The town lies on the line of the Roman road from London to Portslade, and there is some archaeological evidence for small-scaleRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
settlement in the area: there may have been a '' mansio'' (staging-post) here. Later, in the 5th to 7th centuries, a large pagan Saxon cemetery was situated on what is now Park Lane, although the extent of any associated settlement is unknown.
By the late Saxon period Croydon was the hub of an estate belonging to the Archbishops of Canterbury. The church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* C ...
and the archbishops' manor house
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals w ...
occupied the area still known as "Old Town". The archbishops used the manor house as an occasional place of residence: as lords of the manor
Lord of the Manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England, referred to the landholder of a rural estate. The lord enjoyed manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seigno ...
they dominated the life of the town well into the early modern period, and as local patrons they continue to have an influence. Croydon appears in Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
(1086) as ''Croindene'', held by Archbishop Lanfranc. Its Domesday assets included 16 hides and 1 virgate
The virgate, yardland, or yard of land ( la, virgāta was an English unit of land. Primarily a measure of tax assessment rather than area, the virgate was usually (but not always) reckoned as hide and notionally (but seldom exactly) equa ...
of land; a church; a mill
Mill may refer to:
Science and technology
*
* Mill (grinding)
* Milling (machining)
* Millwork
* Textile mill
* Steel mill, a factory for the manufacture of steel
* List of types of mill
* Mill, the arithmetic unit of the Analytical Engine early ...
worth 5s; 38 plough-teams; of meadow
A meadow ( ) is an open habitat, or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non- woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows may be naturally occurring or arti ...
; and woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (se ...
for 200 hogs. It had a recorded population of 73 households (representing roughly 365 individuals); and its value in terms of taxes rendered was £37 10s 0d..
 The church had been established in the middle Saxon period, and was probably a
The church had been established in the middle Saxon period, and was probably a minster church
Minster is an honorific title given to particular churches in England, most notably York Minster in Yorkshire, Westminster Abbey in London and Southwell Minster in Nottinghamshire.
The term ''minster'' is first found in royal foundation charte ...
, a base for a group of clergy living a communal life. A charter issued by King Coenwulf of Mercia
Coenwulf (; also spelled Cenwulf, Kenulf, or Kenwulph; la, Coenulfus) was the King of Mercia from December 796 until his death in 821. He was a descendant of King Pybba, who ruled Mercia in the early 7th century. He succeeded Ecgfrith, the son ...
refers to a council that had taken place close to the ''monasterium'' (meaning minster) of Croydon. An Anglo-Saxon will made in about 960 is witnessed by Elfsies, priest of Croydon; and the church is also mentioned in Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
. The will of John de Croydon, fishmonger, dated 6 December 1347, includes a bequest to "the church of S John de Croydon", the earliest clear record of its dedication. The church still bears the arms of Archbishop Courtenay and Archbishop Chichele, believed to have been its benefactors.
 In 1276 Archbishop
In 1276 Archbishop Robert Kilwardby
Robert Kilwardby ( c. 1215 – 11 September 1279) was an Archbishop of Canterbury in England and a cardinal. Kilwardby was the first member of a mendicant order to attain a high ecclesiastical office in the English Church.
Life
Kilwardby s ...
acquired a charter for a weekly market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
Geography
*Märket, an ...
, and this probably marks the foundation of Croydon as an urban centre. Croydon developed into one of the main market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
s of north east Surrey. The market place
A marketplace or market place is a location where people regularly gather for the purchase and sale of provisions, livestock, and other goods. In different parts of the world, a marketplace may be described as a ''souk'' (from the Arabic), '' ...
was laid out on the higher ground to the east of the manor house in the triangle now bounded by High Street, Surrey Street and Crown Hill. By the 16th century the manor house had become a substantial palace, used as the main summer home of the archbishops and visited by monarchs and other dignitaries. However, the palace gradually became dilapidated and surrounded by slums and stagnant ponds, and in 1781 the archbishops sold it, and in its place purchased a new residence at nearby Addington. Nevertheless, many of the buildings of the original Croydon Palace
Croydon Palace, in Croydon, now part of south London, was the summer residence of the Archbishop of Canterbury for over 500 years. Regular visitors included Henry III and Queen Elizabeth I. Now known as "Old Palace", the buildings are still in us ...
survive, and are in use today as Old Palace School
The Old Palace of John Whitgift School is a selective independent school for girls in Croydon, London. The Old Palace is protected as a Grade I listed building.
It consists of a pre-school for the ages of 3-4, a preparatory department for the a ...
.
 The Parish Church (now
The Parish Church (now Croydon Minster
Croydon Minster is the parish and civic church of the London Borough of Croydon. There are currently more than 35 churches in the borough, with Croydon Minster being the most prominent. It is Grade I listed.
Six Archbishops of Canterbury are b ...
) is a Perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It ca ...
-style church, which was remodelled in 1849 but destroyed in a great fire in 1867, after which only the tower, south porch, and outer walls remained. A new church was designed by Sir George Gilbert Scott, one of the greatest architects of the Victorian age
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edward ...
, and opened in 1870. His design loosely followed the previous layout, with knapped flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
facing and many of the original features, including several tombs. Croydon Parish Church is the burial place of six Archbishops of Canterbury: John Whitgift, Edmund Grindal
Edmund Grindal ( 15196 July 1583) was Bishop of London, Archbishop of York, and Archbishop of Canterbury during the reign of Elizabeth I. Though born far from the centres of political and religious power, he had risen rapidly in the church durin ...
, Gilbert Sheldon
Gilbert Sheldon (19 June 1598 – 9 November 1677) was an English religious leader who served as the Archbishop of Canterbury from 1663 until his death.
Early life
Sheldon was born in Stanton, Staffordshire in the parish of Ellastone, on 19 J ...
, William Wake
William Wake (26 January 165724 January 1737) was a priest in the Church of England and Archbishop of Canterbury from 1716 until his death in 1737.
Life
Wake was born in Blandford Forum, Dorset, and educated at Christ Church, Oxford. He took ...
, John Potter and Thomas Herring
Thomas Herring (169323 March 1757) was Archbishop of Canterbury from 1747 to 1757.
Early life and education
He was the son of John Herring, rector of Walsoken in Norfolk, who had previously been vicar of Foxton, near Cambridge, and his wife, ...
. Historically part of the Diocese of Canterbury
The Diocese of Canterbury is a Church of England diocese covering East Kent, eastern Kent which was founded by St. Augustine of Canterbury in 597. The diocese is centred on Canterbury Cathedral and is the oldest episcopal see, see of the Church o ...
, Croydon is now in the Diocese of Southwark
The Diocese of Southwark is one of the 42 dioceses of the Church of England, part of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The diocese forms part of the Province of Canterbury in England. It was created on 1 May 1905 from part of the ancient Dio ...
. In addition to the suffragan Bishop of Croydon
The Bishop of Croydon is an episcopal title used by an area bishop of the Church of England Diocese of Southwark, in the Province of Canterbury, England. The Croydon Archdeaconry was transferred from Canterbury Diocese to Southwark in 1984.
...
, the Vicar of Croydon is a preferment
A ferment (also known as bread starter) is a fermentation starter used in ''indirect'' methods of bread making. It may also be called mother dough.
A ferment and a longer fermentation in the bread making, bread-making process have several benefi ...
.



Addington Palace
Addington Palace is an 18th-century mansion in Addington located within the London Borough of Croydon. It was built on the site of a 16th-century manor house. It is particularly known for having been, between 1807 and 1897, the summer resid ...
is a Palladian-style mansion between Addington Village and Shirley
Shirley may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Shirley'' (novel), an 1849 novel by Charlotte Brontë
* ''Shirley'' (1922 film), a British silent film
* ''Shirley'' (2020 film), an American film
* ''Shirley'' (album), a 1961 album by Shirley Bas ...
, in the London Borough of Croydon
The London Borough of Croydon () is a London borough in south London, part of Outer London. It covers an area of . It is the southernmost borough of London. At its centre is the historic town of Croydon from which the borough takes its name; ...
. Six archbishops lived there between 1807 and 1898, when it was sold. Between 1953 and 1996 it was the home of the Royal School of Church Music
The Royal School of Church Music (RSCM) is a Christian music education organisation dedicated to the promotion of music in Christian worship, in particular the repertoire and traditions of Anglican church music, largely through publications, tr ...
. It is now a conference and banqueting venue.
Croydon was a leisure destination in the mid 19th century. In 1831, one of England's most prominent architects, Decimus Burton, designed a spa and pleasure gardens below Beulah Hill
The A215 is an A road in south London, starting at Elephant and Castle and finishing around Shirley. It runs through the London Boroughs of Lambeth, Southwark and Croydon.
Beginning as Walworth Road, the A215 becomes Camberwell Road—much of ...
and off what is now Spa Hill in a bowl of land on the south-facing side of the hill around a spring of chalybeate water. Burton was responsible for the Beulah Spa Hotel (demolished around 1935) and the layout of the grounds. Its official title was The Royal Beulah Spa and Gardens. It became a popular society venue attracting crowds to its ''fêtes''. One widely publicised event was a "Grand Scottish Fete" on 16 September 1834 "with a tightrope performance by Pablo Fanque
Pablo Fanque (born William Darby; 30 March 1810 – 4 May 1871) was a British equestrian performer and circus proprietor, becoming the first recorded Black circus owner in Britain. His circus was popular in Victorian Britain for 30 years, a p ...
, the black circus performer who would later dominate the Victorian circus and achieve immortality in The Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the most influential band of all time and were integral to the developmen ...
song, ''Being for the Benefit of Mr. Kite!''" The spa closed in 1856 soon after the opening nearby of the Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. The exhibition took place from 1 May to 15 October 1851, and more than 14,000 exhibitors from around th ...
which had been rebuilt on Sydenham Hill
Sydenham Hill forms part of a longer ridge and is an affluent locality in southeast London. It is also the name of a road which runs along the northeastern part of the ridge, demarcating the London Boroughs of Southwark, Bromley, and Lewisham ...
in 1854, following its success at the Great Exhibition in Hyde Park. It was destroyed in a spectacular fire in 1936.
Horse racing in the area took place occasionally, notably during visits of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
to the archbishop. Regular meetings became established first on a course at Park Hill in 1860 and from 1866 at Woodside, where particularly good prizes were offered for the races run under National Hunt
In horse racing in the United Kingdom, France and Republic of Ireland, National Hunt racing requires horses to jump fences and ditches. National Hunt racing in the UK is informally known as "jumps" and is divided into two major distinct branches: ...
rules. In that sphere its prestige was second only to Aintree, home of the Grand National. Increasing local opposition to the presence of allegedly unruly racegoers coupled with the need to obtain a licence from the local authority led to it being closed down in 1890.
The Elizabethan Whitgift Foundation, Whitgift Almshouses, the "Hospital of the Holy Trinity", in the centre of Croydon at the corner of North End and George Street, were erected by Archbishop John Whitgift. He petitioned for and received permission from Queen Elizabeth I of England, Elizabeth I to establish a hospital and school in Croydon for the "poor, needy and impotent people" from the parishes of Croydon and Lambeth. The foundation stone was laid in 1596 and the building was completed in 1599.
The premises included the Hospital or Almshouses, providing accommodation for between 28 and 40 people, and a nearby schoolhouse and schoolmaster's house. There was a Warden in charge of the well-being of the almoners. The building takes the form of a courtyard surrounded by the chambers of the almoners and various offices.
Threatened by various reconstruction plans and road-widening schemes, the Almshouses were saved in 1923 by intervention of the House of Lords. On 21 June 1983 Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, Elizabeth II visited the Almshouses and unveiled a plaque celebrating the recently completed reconstruction of the building. On 22 March each year the laying of the foundation stone is commemorated as Founder's Day.
The Grade II listed West Croydon Baptist Church was built in 1873 by J. Theodore Barker. It is a red brick building with stone dressings. Its three bays are divided by paired Doric pilasters supporting a triglyph frieze and panelled parapet.
The Parish Church of St Michael and All Angels by John Loughborough Pearson in West Croydon was built between 1880 and 1885, and is Grade I listed.
Industrial Revolution and the railway
 The development of Brighton as a fashionable resort in the 1780s increased Croydon's importance as a halt for stage coaches on the road south of London. At the beginning of the 19th century, Croydon became the terminus of two pioneering commercial transport links with London. The first, opened in 1803, was the horse-drawn
The development of Brighton as a fashionable resort in the 1780s increased Croydon's importance as a halt for stage coaches on the road south of London. At the beginning of the 19th century, Croydon became the terminus of two pioneering commercial transport links with London. The first, opened in 1803, was the horse-drawn Surrey Iron Railway
The Surrey Iron Railway (SIR) was a horse-drawn plateway that linked Wandsworth and Croydon via Mitcham, all then in Surrey but now suburbs of south London, in England. It was established by Act of Parliament in 1801, and opened partly in 1802 ...
from Wandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
Toponymy
Wandsworth takes its nam ...
, which in 1805 was extended to Merstham
Merstham is a town in the borough of Reigate and Banstead in Surrey, England. It lies 25 miles south of Charing Cross and 2 miles south of the Greater London border. Part of the North Downs Way runs along the northern boundary of the town. Mers ...
, as the Croydon, Merstham and Godstone Railway. The second, opened in 1809, was the Croydon Canal, which branched off the Grand Surrey Canal at Deptford. The London and Croydon Railway (an Atmospheric railway, atmospheric and steam-powered railway) opened between London Bridge station, London Bridge and West Croydon station, West Croydon in 1839, using much of the route of the canal (which had closed in 1836). Other connections to London and the south followed.
The arrival of the railways and other communications advances in the 19th century led to a 23-fold increase in Croydon's population between 1801 and 1901. This rapid expansion of the town led to considerable health problems, especially in the damp and overcrowded working class district of Old Town. In response to this, in 1849 Croydon became one of the first towns in the country to acquire a local board of health. The Board constructed public health infrastructure including a lake, reservoir, water supply network, sanitary sewer, sewers, a pumping station and sewage collection and disposal, sewage disposal works.
The Surrey Street Pumping Station is Grade II listed; it was built in four phases. starting with the engine house in 1851, with a further engine house in 1862, a further extension in 1876–7 to house a compound horizontal engine and a further extension in 1912.
A growing town

 In 1883 Croydon was incorporated as a borough. In 1889 it became a county borough, with a greater degree of autonomy. The new county borough council implemented the Croydon Improvement scheme in the early 1890s, which widened the High Street and cleared much of the "Middle Row" slum area. The remaining slums were gentrification, cleared shortly after Second World War, with much of the population relocated to the isolated new settlement of New Addington. New stores opened and expanded in central Croydon, including Allders, Kennards and Grade II listed Grants of Croydon, Grants, as well as the first Sainsbury's self-service shop in the country. There was a market on Surrey Street Market, Surrey Street.
Croydon was the location of London's main airport until the Second World War. During the war, much of central Croydon was devastated by German V-1 flying bombs and V-2 rocket, V-2 rockets, and for many years the town bore the scars of the destruction. After the war, Heathrow Airport superseded Croydon Airport as London's main airport, and Croydon Airport quickly went into a decline, finally closing in 1959.
By the 1950s, with its continuing growth, the town was becoming traffic congestion, congested, and the Council decided on another major redevelopment scheme. The Croydon Corporation Act was passed in 1956. This, coupled with national government incentives for office relocation out of Central London, led to the building of new offices and accompanying road schemes through the late 1950s and 1960s, and the town boomed as a business centre in the 1960s, with many multi-storey office blocks, an underpass, a Overpass, flyover and multi-storey car parks. The redeveloped town centre has since been identified as an "edge city" – a significant urban and commercial centre in its own right, located on the outskirts of a larger metropolitan area (in this case, London).
In 1960 Croydon celebrated its millennium with a pageant held at Lloyd Park and an exhibition held at the old Croydon Aerodrome.
In 1883 Croydon was incorporated as a borough. In 1889 it became a county borough, with a greater degree of autonomy. The new county borough council implemented the Croydon Improvement scheme in the early 1890s, which widened the High Street and cleared much of the "Middle Row" slum area. The remaining slums were gentrification, cleared shortly after Second World War, with much of the population relocated to the isolated new settlement of New Addington. New stores opened and expanded in central Croydon, including Allders, Kennards and Grade II listed Grants of Croydon, Grants, as well as the first Sainsbury's self-service shop in the country. There was a market on Surrey Street Market, Surrey Street.
Croydon was the location of London's main airport until the Second World War. During the war, much of central Croydon was devastated by German V-1 flying bombs and V-2 rocket, V-2 rockets, and for many years the town bore the scars of the destruction. After the war, Heathrow Airport superseded Croydon Airport as London's main airport, and Croydon Airport quickly went into a decline, finally closing in 1959.
By the 1950s, with its continuing growth, the town was becoming traffic congestion, congested, and the Council decided on another major redevelopment scheme. The Croydon Corporation Act was passed in 1956. This, coupled with national government incentives for office relocation out of Central London, led to the building of new offices and accompanying road schemes through the late 1950s and 1960s, and the town boomed as a business centre in the 1960s, with many multi-storey office blocks, an underpass, a Overpass, flyover and multi-storey car parks. The redeveloped town centre has since been identified as an "edge city" – a significant urban and commercial centre in its own right, located on the outskirts of a larger metropolitan area (in this case, London).
In 1960 Croydon celebrated its millennium with a pageant held at Lloyd Park and an exhibition held at the old Croydon Aerodrome.
Modern Croydon
 The growing town attracted many new buildings. The Fairfield Halls arts centre and event venue opened in 1962. Croydon developed as an important centre for shopping, with the construction of the
The growing town attracted many new buildings. The Fairfield Halls arts centre and event venue opened in 1962. Croydon developed as an important centre for shopping, with the construction of the Whitgift Centre
The Whitgift Centre is a large shopping centre in the town centre of Croydon, opening in stages between 1968 and 1970. The centre comprises of retail space, and was the largest covered shopping development in Greater London until the opening of ...
in 1969. No. 1 Croydon (formerly the NLA Tower) designed by Richard Seifert, Richard Seifert & Partners was completed in 1970. The Warehouse Theatre opened in 1977.
The 1990s saw further changes intended to give the town a more attractive image. These included the closure of North End to vehicles in 1989 and the opening of the Croydon Clocktower arts centre in 1994. An early success of the centre was the "Picasso's Croydon Period" exhibition of March–May 1995.
The Croydon Tramlink began operation in May 2000 (see Transport section below).
The Prospect West office development was built in 1991 to 1992, and its remodelling planned in 2012 has now been completed. Renamed Interchange Croydon when it was reopened in 2014, the 180,000 square foot office development was the first new grade A office development of its size to open in Croydon for more than 20 years.
Another large shopping centre, Centrale (shopping centre), Centrale, opened in 2004 opposite the Whitgift Centre, and adjoining the smaller Drummond Centre. House of Fraser and Debenhams are the anchor stores in the combined centre. In addition, there are plans for a large, new one billion pound shopping centre, in the form of a new Westfield Group, Westfield shopping mall to add to the two which the company currently has in Greater London; Westfield plans to work jointly with Hammersons and to incorporate the best aspects of the two companies' designs. In November 2017, Croydon Council gave permission for the new Westfield shopping centre to be built and in January 2018, the Mayor of London, Sadiq Khan, approved the regeneration scheme. Work to demolish the existing Whitgift Centre was due to begin in 2018 and Westfield Croydon was initially to open by 2022. The Westfield plans were delayed and the planning permission elapsed: however, in 2021, Croydon Council confirmed they were committed to see the Westfield Centre proceed. There are several other major plans for the town including the redevelopment of the Croydon Gateway site; and extensions of Tramlink to Purley Way, Streatham, Lewisham and Crystal Palace, London, Crystal Palace.
 In November 2013, Central Croydon MP Gavin Barwell gave a presentation at a public meeting on the Croydon regeneration project, detailing various developments underway due to be completed in coming years.
On 26 November 2013, Croydon Council approved a redevelopment of the Town Centre by The Croydon Partnership, a joint venture by The Westfield Group and Hammerson. London Mayor Boris Johnson approved the plan the following day. The Croydon Advertiser listed the approval as an "Historic Night for Croydon".
At Ruskin Square, a Boxpark made of sea containers opened in 2016 as a temporary measure until new buildings are constructed for shops, offices and housing. The ''London Evening Standard'' said that this and other developments were reviving the town which was in the process of gentrification.
In November 2013, Central Croydon MP Gavin Barwell gave a presentation at a public meeting on the Croydon regeneration project, detailing various developments underway due to be completed in coming years.
On 26 November 2013, Croydon Council approved a redevelopment of the Town Centre by The Croydon Partnership, a joint venture by The Westfield Group and Hammerson. London Mayor Boris Johnson approved the plan the following day. The Croydon Advertiser listed the approval as an "Historic Night for Croydon".
At Ruskin Square, a Boxpark made of sea containers opened in 2016 as a temporary measure until new buildings are constructed for shops, offices and housing. The ''London Evening Standard'' said that this and other developments were reviving the town which was in the process of gentrification.
Future
A Croydon Vision 2020 plan was drawn up by the borough after a 1999 study by town planning consultants EDAW. The plan includes new office blocks, apartment buildings, shopping centres and other developments, some of which have already been built. More than 2,000 new homes are planned. A redeveloped Fairfield Halls has been planned to be the linchpin of a cultural quarter encompassing nearby College Green. Plans include an art gallery, a Croydon College, new college, shops and offices, with a multi-storey car park set for demolition to make space for 218 homes.Economy
As of 2011, Croydon's annual retail turnover from comparison goods was £353 million, the fifth-highest in Greater London behind the West End of London, West End, Shepherd's Bush, Stratford, London, Stratford and Kingston upon Thames. Croydon had as of 2012 of total town centre floorspace, the second highest in Greater London only behind the West End. Apart from its large central shopping district, Croydon has a number of smaller shopping areas, especially towards the southern end of the town in which are many restaurants. As of 2011, two of Croydon's restaurants were listed in ''The Good Food Guide''. In a 2015 study by CACI, Croydon was ranked 12th in the "Hot 100 UK retail locations" with a score of 90%. The Zotefoams company is headquartered in Croydon.Government

Status
For centuries the area lay within the Wallington (hundred), Wallington hundred, an ancient Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon administrative division of the county of Surrey. In the laterMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
– probably from the late 13th century onwards – residents of the town of Croydon, as defined by boundary markers known as the "four crosses", enjoyed a degree of Self-governance, self-government through a town court or ''portmote'', and a form of free Land tenure, tenure of property. These privileges set the area of the town apart from its rural hinterland, where the more usual and more restrictive rules of Manorialism, manorial tenure applied. However, Croydon did not hold any kind of formal Ancient borough, borough status.
In 1690, the leading inhabitants petitioned William III of England, William III and Mary II of England, Mary for Croydon to be Ancient borough#Charters of incorporation, incorporated as a borough. The application was initially approved, the king authorising the drafting of a charter, but the process was then abruptly halted, apparently through the intervention of Archbishop John Tillotson, who probably feared a threat to his own authority over the town. The application was revived the following year, when Queen Mary again authorised a charter, but once again it was abandoned. A second petition in 1707 was effectively ignored.
Croydon's growth in the 19th century brought the issue of incorporation back on to the political agenda, and in 1883 the ancient parish of Croydon, apart from its exclave of Croydon Crook or Selsdon, was created a municipal borough within Surrey. In 1889, because the population was high enough, it was made a county borough, exempt from county administration.
In 1965 (under the terms of the London Government Act 1963) the County Borough of Croydon was abolished and the area was transferred to Greater London and combined with the Coulsdon and Purley Urban District to form the London Borough of Croydon
The London Borough of Croydon () is a London borough in south London, part of Outer London. It covers an area of . It is the southernmost borough of London. At its centre is the historic town of Croydon from which the borough takes its name; ...
.
The borough has on several occasions sought City status in the United Kingdom, city status. (This would be a purely honorific change of title, making no practical difference to the borough's governance.) A draft petition was submitted by the County Borough of Croydon, County Borough to the Home Office in 1951, a more formal petition in 1954, and two more applications in 1955 and 1958. When the London Borough of Croydon, London Borough was created in 1965, the Council endeavoured to have it styled a City, as was the City of Westminster. Further bids for city status were made in 1977, 1992, 2000, 2002, and 2012. All have failed. The borough's predominant argument has always been its size: in 2000 it pointed out that it was "the largest town which does not have the title of City in the whole of Western Europe". The grounds on which it has been turned down have invariably been that it is (as was stated in 1992) merely "part of the London conurbation, rather than a place with a character and identity of its own". Undeterred, council representatives have more than once described Croydon as "a city in all but name". In 2008, Boris Johnson, then Mayor of London, said he would support Croydon being awarded city status.
Modern governance
The London Borough of Croydon has a Labour-controlled council with 41 Labour councillors and 29 Conservative councillors elected on 3 May 2018. Most of the town centre lies within the Addiscombe (ward), Addiscombe and Fairfield (Croydon ward), Fairfield wards, which form part of the Croydon Central (UK Parliament constituency), Croydon Central constituency. The rest of the town centre is in the Croham (ward), Croham ward, which is part of the Croydon South (UK Parliament constituency), Croydon South constituency. These wards are all in the London Borough of Croydon, which is responsible for services along with other agencies such as education, refuse collection, road maintenance, local planning and social care. The Addiscombe ward is currently represented by Labour Councillors . The Fairfield and Croham wards have, by contrast, habitually elected Conservative members. The sitting Member of Parliament for Croydon Central (UK Parliament constituency), Croydon Central is Sarah Jones (politician), Sarah Jones, a member of the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party. The sitting Member of Parliament for Croydon South is Chris Philp, a member of the Conservatives. The Member of Parliament for Croydon North is Steve Reed (politician), Steve Reed, for the Labour Party.Public services
The Territorial police force#United Kingdom, territorial police force is the Metropolitan Police. Their Croydon Police Station is on Park Lane opposite the Croydon Flyover . The statute, statutory Fire department, fire and rescue service in Croydon is the London Fire Brigade (LFB) who have a fire station in Old Town, with two pumping appliances. The nearest hospital is Croydon University Hospital (known from 1923 to 2010 as Mayday Hospital) in nearby Thornton Heath, which is part of Croydon Health Services NHS Trust. The London Ambulance Service provides the ambulance service.Demography and population
The town of Croydon includes its neighbourhoods Addiscombe, Addington, Broad Green, London, Broad Green, Coombe, Croydon, Coombe, Forestdale, London, Forestdale, New Addington, Sanderstead, Selsdon,Shirley
Shirley may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Shirley'' (novel), an 1849 novel by Charlotte Brontë
* ''Shirley'' (1922 film), a British silent film
* ''Shirley'' (2020 film), an American film
* ''Shirley'' (album), a 1961 album by Shirley Bas ...
, and Waddon. The 13 electoral wards that make it up together counted a population of 192,064 in the 2011 census, forming the majority of the borough overall (pop. 384,837).
Croydon is ethnically diverse. Those who are from Black, Asian and minority ethnic, BAME minority background range from 19.5% in Sanderstead ward to 68.6% in Broad Green. West Thornton ward (part of Thornton Heath) is one of the most ethnically diverse areas of England.
Fairfield ward, which is the major ward covering the central town, was ethnically 40% White British, 16% Indian, and 10% Other White in the 2011 UK Census. Religiously, 46% was Christian, 21% irreligious, 13% Hindu and 8% Muslim. The most common household tenure type was either owned or privately rented. The median age was 33. In addition, the Broad Green ward was ethnically 23% White British, 13% Indian, 13% Other Asian, and 11% Black African. About 41% of household tenures were owned, while privately and socially rented each made up 29% each. The median age was 31. The Addiscombe ward was ethnically 45% White British and 10% Other White. Religiously, 52% of the population was Christian, 24% irreligious, 7% Muslim and 6% Hindu. 52% of house tenures were owned. There are 10 other wards that cover Croydon's neighbourhoods.
The median house price as of 2014 was £212,998 in Selhurst ward, one of London's lowest. The highest in the town was in Sanderstead ward, £392,500. The mean age in 2013 ranged from 32 years in Broad Green and Fieldway wards, to 43.2 years in Selsdon and Ballards ward.
Geography



 Croydon town centre is near the centre of the borough of Croydon, to the north of the
Croydon town centre is near the centre of the borough of Croydon, to the north of the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills a ...
and the Pilgrims' Way path. To the north of Croydon are typical London districts, whereas a short distance southeast (such as Coombe, Croydon, Coombe and Selsdon) is green, hilly and rural land. To the west are industrial areas, part of which are in the London Borough of Sutton. The southern suburbs are mainly affluent and also hilly.
The town centre is bordered by Waddon immediately southwest of central Croydon. To the west, inside the London Borough of Sutton lies Beddington. To the north are Broad Green, London, Broad Green, Thornton Heath and Selhurst. To the south lies South Croydon, and going further south are Purley and Sanderstead. To the east lie Addiscombe and Shirley
Shirley may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Shirley'' (novel), an 1849 novel by Charlotte Brontë
* ''Shirley'' (1922 film), a British silent film
* ''Shirley'' (2020 film), an American film
* ''Shirley'' (album), a 1961 album by Shirley Bas ...
.
Croydon High Street runs from South Croydon up to the point where it meets the street called North End. North End is the main shopping street, while Croydon High Street is the main restaurant quarter.
The High Street is also home to Wrencote House, a Listed building, Grade II* listed building. Dating from the late 17th or early 18th centuries, and probably built as a merchant's house, it has a distinctive "H" plan form over its four floors (including basement and attic storey). External features include a rich red brick facade with black Brickwork#Orientation, headers, and a heavily carved and enriched wooden eaves cornice.
Wellesley Road on the A212 road forms a north–south axis through the town centre. In line with London Plan policy, there have been a number of proposals to create greater integration between East Croydon station, which lies on one side of the A212, and the town centre of Croydon, which lies on the other side of it. Croydon Vision 2020 aims to tackle this though such solutions as making the road easier for pedestrians to cross by creating a centre island pathway.
Topographically, central Croydon generally lies between (in the north) and (in the south) above sea level. Elevation significantly climbs towards the east of the town – Coombe Park peaks at about above sea level, whereas the Addington Hills, Coombe Wood and Addington Golf Course are as high as , with the southern end of New Addington having an elevation of over . To the south, Croham Hurst has a hill of , and the highest area of Croydon is the Sanderstead Plantation at . The lowest elevation is around Broad Green, London, Broad Green, about above sea level.
River Wandle
The River Wandle is a tributary of the River Thames, flowing some 9 miles (14 km) toWandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
Toponymy
Wandsworth takes its nam ...
and Putney from its source in Croydon. It roughly forms the borough's western boundary with the London Borough of Sutton, and for part of its length also forms the boundary between the London Boroughs of Croydon and London Borough of Lambeth, Lambeth. One of its tributaries rises in Selhurst.
Culture
Arts

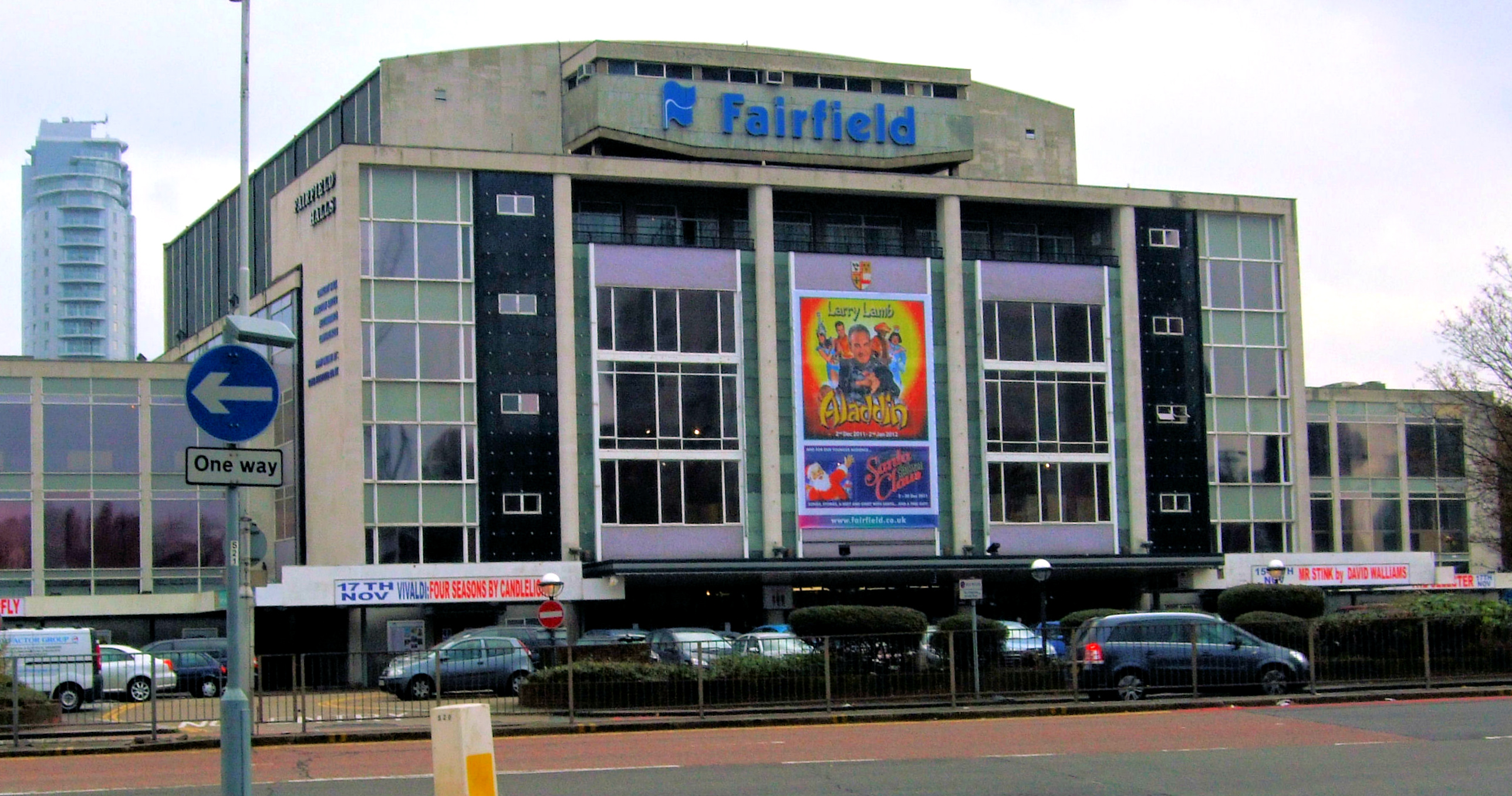
 There are several arts venues. Foremost is the Fairfield Halls, opened in 1962, which consists of a large concert hall frequently used for BBC recordings, the Ashcroft Theatre and the Arnhem Gallery. Fairfield is the home of the London Mozart Players. Many famous faces have appeared at the Fairfield Halls, including
There are several arts venues. Foremost is the Fairfield Halls, opened in 1962, which consists of a large concert hall frequently used for BBC recordings, the Ashcroft Theatre and the Arnhem Gallery. Fairfield is the home of the London Mozart Players. Many famous faces have appeared at the Fairfield Halls, including The Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the most influential band of all time and were integral to the developmen ...
, Bucks Fizz (band), Bucks Fizz, Omid Djalili, Robert Cray, JLS, Chuck Berry, BB King, Don McLean, The Monkees, Johnny Cash, Dionne Warwick, Gladys Knight, Morecambe and Wise, Tom Jones (singer), Tom Jones, The Stylistics, Status Quo (band), Status Quo, Level 42, A-HA, John Mayall, Jools Holland, Kenny Rogers, James Last, and Coolio. The main concert hall was used for the conference scene in the Ron Howard film ''The Da Vinci Code (film), The Da Vinci Code'' (2006). The Fairfield Halls reopened in 2019, following a programme of modernisation and refurbishment.
 Croydon Clocktower, developed by the London Borough of Croydon in the mid-1990s, houses a state-of-the-art library, a performance venue in the old reference library, the David Lean Cinema (a small, independent, art-house cinema) and the Museum of Croydon, which details Croydon's history. The building links into Croydon Town Hall and some areas of the building, most notably the Braithwaite Hall, are part of the original town hall and library complex, built in 1892–1896 to a design by Charles Henman. A bronze statue of Queen Victoria was erected outside the buildings in 1903.
The Warehouse Theatre (which closed in 2012), was a studio theatre known for promoting new writing, comedy and youth theatre. It had to close because of the major Ruskin Square redevelopment, but will re-open in the future in a new larger theatre building within the new development.
The Pembroke Theatre had many productions with well-known actors before its closure in about 1962.
There are several local and small venues for comedy and community events dotted around Croydon and its districts. Croydon Youth Theatre Organisation celebrated its 40th birthday in 2005. There are several community arts groups, particularly in the large British Asian, Asian community.
The Spread Eagle Theatre is a new 50-seat studio theatre. Opened in October 2013, it is situated in the town centre, 10 minutes' walk from East Croydon Station. The Spread Eagle works closely with its sister venue, the Old Joint Stock Theatre in Birmingham. Both venues champion 'big plays for small spaces' with an emphasis on new writing, supporting emerging artists and theatre companies.
A calendar titled "Rare Roundabouts of Croydon", with a picture of a different Croydon roundabout each month, has enjoyed some success.
Croydon Clocktower, developed by the London Borough of Croydon in the mid-1990s, houses a state-of-the-art library, a performance venue in the old reference library, the David Lean Cinema (a small, independent, art-house cinema) and the Museum of Croydon, which details Croydon's history. The building links into Croydon Town Hall and some areas of the building, most notably the Braithwaite Hall, are part of the original town hall and library complex, built in 1892–1896 to a design by Charles Henman. A bronze statue of Queen Victoria was erected outside the buildings in 1903.
The Warehouse Theatre (which closed in 2012), was a studio theatre known for promoting new writing, comedy and youth theatre. It had to close because of the major Ruskin Square redevelopment, but will re-open in the future in a new larger theatre building within the new development.
The Pembroke Theatre had many productions with well-known actors before its closure in about 1962.
There are several local and small venues for comedy and community events dotted around Croydon and its districts. Croydon Youth Theatre Organisation celebrated its 40th birthday in 2005. There are several community arts groups, particularly in the large British Asian, Asian community.
The Spread Eagle Theatre is a new 50-seat studio theatre. Opened in October 2013, it is situated in the town centre, 10 minutes' walk from East Croydon Station. The Spread Eagle works closely with its sister venue, the Old Joint Stock Theatre in Birmingham. Both venues champion 'big plays for small spaces' with an emphasis on new writing, supporting emerging artists and theatre companies.
A calendar titled "Rare Roundabouts of Croydon", with a picture of a different Croydon roundabout each month, has enjoyed some success.
Public art
 About 60 murals were added to Croydon town centre in 2018, as part of the Rise street art festival coordinated by the Rise art gallery in Croydon.
About 60 murals were added to Croydon town centre in 2018, as part of the Rise street art festival coordinated by the Rise art gallery in Croydon.
Literature
Croydon is the setting of two poems by British Poet Laureate Sir John Betjeman, "Croydon" and "Love in a Valley". The borough has been the residence of many renowned authors and novelists, including Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, who set up house in Norwood, D.H. Lawrence, and French novelist Émile Zola, who lived for a time in the Queen's Hotel, Upper Norwood. Cicely Mary Barker, author and illustrator of the Flower Fairies series of books, was born in Croydon. Croydon is the setting of novels. The now defunct airport lent itself to the mysteries ''The 12.30 from Croydon'' and ''Death in the Clouds'', and the town is mentioned in some Sherlock Holmes mysteries. Croydon is referred to in a rhyme dating back to the 18th century, revised in the Victorian era to: In Jane Austen's unfinished novel ''The Watsons'' (written ''c''.1803–1805), the heroine, Emma Watson, has a brother and sister-in-law who live in Croydon, and who urge her to join them for an extended visit. Another sister, Elizabeth, encourages the idea, commenting "there is always something lively going on at Croydon". It would appear that the plot was intended to continue with Emma moving to Croydon.Music
The composer Samuel Coleridge-Taylor (1875–1912) lived at 30 Dagnall Park, Selhurst, until his death. He grew up in Croydon and sang in the church choir at St George's and taught at the Crystal Palace School, Crystal Palace School of Music and many other schools of music. He died from pneumonia after collapsing at West Croydon station. There is an impressive grave with a poem at Bandon Hill Cemetery, and exhibits about him in the Museum of Croydon. In addition to the Fairfield Halls, several venues in Croydon have hosted rock acts. Established in 1976, the Cartoon was a popular live music venue that closed in 2006. The Greyhound in Park Lane played host to acts such as Led Zeppelin, Jimi Hendrix, The Who, David Bowie, Queen (band), Queen, Siouxsie and the Banshees, The Damned (band), The Damned, The Boomtown Rats, A-ha in (1987) and others during the 1960s and '70s. Mott The Hoople paid tribute to the town's music scene in the song Saturday Gigs. The Greyhound also saw the debut of the Electric Light Orchestra in 1972. Captain Sensible released the song "Croydon" in 1982 in tribute to his home town. In 1993, ''Music Week'' reported that Croydon's record shops were thriving. The town centre was for 30 years home to Europe's largest second-hand record store, Beano's, offering rare vinyl, CDs and books. In November 2008, it was announced that Beano's would close. The premises, off Church Street near the Grant's cinema complex, became a "market place" with stalls for rent by small business and individuals. Croydon has a rock scene producing such local talent as Frankmusik, Noisettes, and Saint Etienne (band), Saint Etienne. Croydon has been at the centre of the development of the dubstep genre, a relatively recent musical development that traces its roots from Jamaican dub music, UK Garage and drum and bass. Artists such as Benga (musician), Benga and Skream, who honed their production and DJing skills whilst working at the now defunct ''Big Apple Records'' on Surrey Street Market, Surrey Street, along with Norwood's Digital Mystikz, DJ Chef, Timi Korus and Thornton Heath's Plastician, form the core roster of dubstep DJs and producers. Moreover, UK rappers and grime artists Stormzy, Krept and Konan, Nadia Rose and Section Boyz all hail from or can trace their roots to the London Borough of Croydon. The oldest currently surviving shop in Croydon is 46 South End. Dating back to the 16th century, this Grade II listed building still retains all its original Tudor features. Records show that the premises has been a shop for at least 163 years, where street directories from 1851 give the names of E. C. Johnson & Thorpe. The building is currently in use as a music shop. Croydon is home to the BRIT School for performing arts and technology, based in Selhurst, which has produced stars such as Adele, Jessie J, Amy Winehouse, Leona Lewis, Katie Melua, Katy B, Kate Nash, Imogen Heap, Rizzle Kicks, Dane Bowers and members of the Feeling & the Kooks. Independent of such institutions, Croydon is also the home of artists such as Nosferatu D2.Media
Croydon plays host to the popular Channel 4 show ''Peep Show (British TV series), Peep Show''. The ITV police drama ''The Bill'', although set in East London, was filmed in Croydon and many of the town centre locations were filmed around Surrey Street and St George's House (the Nestle building). Sun Hill Police Station is in nearby Mitcham. The opening credit sequence for the sitcom ''Terry and June'' featured the eponymous stars walking around the Whitgift Centre and the Fairfield Halls. In 2007, the music video for pop star Mika (singer), Mika's single "Big Girl (You Are Beautiful)" was shot in various locations around the town, including High Street and Surrey Street Market. The Delta Point building, close to West Croydon station appeared in the film ''The Dark Knight Rises'' as Gotham City, Gotham General Hospital. The 2018 interactive film, Black Mirror: Bandersnatch featured several scenes shot in Croydon, such as St George's Walk and No.1 Croydon. Croydon has its own fully independent television station: it does not receive any government or local authority grant or funding and is supported by donations, sponsorship and by commercial advertising. In 2012, Croydon Radio, an internet radio station, began in the area.Sport and leisure
Parks and open spaces
Clubs and teams
The most prominent sports club in the borough is Crystal Palace F.C., Crystal Palace Football Club, based in the north of the borough since 1918. Palace play at the purpose-built stadium of Selhurst Park, which the club moved to in 1924 from Croydon Common Athletic Ground, the Nest, its first Croydon-based stadium. The Nest had previously been the home of the defunct Croydon Common, Croydon Common Football Club and sat next to Selhurst railway station, Selhurst station. Palace won promotion to the Premier League (the top tier of football in England) at the end of the 2012–13 season. Croydon has a Non-League football club, Croydon F.C. who play at South Norwood#Croydon Sports Arena, Croydon Sports Arena. Sunday League team Purley Saint Germain also play at Croydon Sports Arena. Streatham-Croydon RFC, founded in 1871, is one of Greater London's oldest extant rugby union clubs, playing just north of the town centre at Frant Road in Thornton Heath. Croydon Amphibians SC plays in Division 2 British Waterpolo League. In 2008, the team won the National League Division 3. The borough also has a women's roller derby team called Croydon Roller Derby, which trains in Carshalton. The team was established in the early part of this decade and has played both national and international teams including Roller Derby Madrid, Stuttgart Valley Rollergirlz and Oxford Roller Derby. The sport is full-contact and played on quad skates with players skating round an elliptical track.Transport



Rail
Croydon is served by East Croydon, South Croydon railway station, South Croydon and West Croydon railway station, West Croydon. East Croydon and South Croydon are served by Govia Thameslink Railway, operating under the Southern (train operating company), Southern and Thameslink brands via the Brighton Main Line. West Croydon is served by London Overground and Southern services. The largest and busiest of the three stations is East Croydon, although West Croydon is located closer to Croydon's main shopping district.Tramlink
The Tramlink tram system opened in 2000; Croydon is its hub. Its network consists of two main lines, from Elmers End tram stop, Elmers End or Beckenham Junction tram stop, Beckenham to Wimbledon tram stop, Wimbledon, and from New Addington tram stop, New Addington to West Croydon, with all trams running via a loop in central Croydon. It is the only tram system in Greater London. It serves Mitcham, Woodside, Addiscombe and the Purley Way retail and industrial area. The system was previously known as the "Croydon Tramlink", having been established under the Croydon Tramlink Act 1994.Road
A few miles to the south of Croydon is a small gap (landform), gap in theNorth Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills a ...
, a route for transport from London to the south coast. The London to Brighton road used to pass through the town on North End before the A23 road, A23 Purley Way was built to the west. Transport for London operates many bus routes in and around Croydon. Most buses serve West Croydon bus station, next to the railway station and tram stop.
Croydon's early transport links
The horse-drawnSurrey Iron Railway
The Surrey Iron Railway (SIR) was a horse-drawn plateway that linked Wandsworth and Croydon via Mitcham, all then in Surrey but now suburbs of south London, in England. It was established by Act of Parliament in 1801, and opened partly in 1802 ...
was an early public railway. It was opened in 1803, had double track, was some long and ran from Wandsworth to Croydon, at what is now Reeves Corner. In 1805 it was extended to Merstham as the Croydon, Merstham, and Godstone Railway. The railway boom of the 1840s brought superior and faster steam lines and it closed in 1846. The route is followed in part by the modern Tramlink. The last remaining sections of rail can be seen behind railings in a corner of Rotary Field in Purley.
With the opening of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway line to London Victoria railway station, London Victoria in 1860 extra platforms were provided at East Croydon, which the LBSCR treated as a separate station named ''New Croydon''. The South Eastern Railway, UK, South Eastern Railway (SER) was excluded from this station, which ran exclusively LBSCR services to London at fares cheaper than those the SER offered from the original station.White, H.P., op. cit. p. 79. In 1864, the LBSCR obtained authorisation to construct a -mile long branch line into the heart of the town centre near Katharine Street, where Croydon Central railway station, Croydon Central station was built. The line opened in 1868 but enjoyed little success and closed in 1871, only to reopen in 1886 under pressure from the Town Council before finally closing in 1890. The station was subsequently demolished and replaced by the Town Hall. In 1897–98, East Croydon and New Croydon were merged into a single station with three island platforms, which remain today, but the two stations kept separate booking accounts until 1924.
The Croydon Canal ran for from what is now West Croydon station. It travelled north largely along the course of the present railway line to New Cross Gate, where it joined the Grand Surrey Canal and went on into the River Thames. It opened in 1809 and had 28 canal lock, locks. It had a strong competitor in the Surrey Iron Railway and was never a financial success. It sold out to the London & Croydon Railway in 1836. The lake at South Norwood is the former reservoir for the canal.
Croydon Airport on Purley Way was the main airport for London until it was superseded by Heathrow Airport and Gatwick Airport. It opened on 29 March 1920 by combining two smaller airfields used for defence in World War I. It developed into one of the great airports of the world during the 1920s and 1930s. It welcomed the world's pioneer aviators in its heyday. As aviation technology progressed and aircraft became larger and more numerous, it was recognised in 1952 that the airport would be too small to cope with increasing air traffic and its role was decreased.. The last scheduled flight departed on 30 September 1959. The air terminal, now known as Airport House adjoining Purley Way to the west of the town, has been restored and has a museum open one day a month. The name "Croydon Airport" is still used as a landmark and as a bus stop designation.
Notable people
 * Peggy Ashcroft (1907–1991), actress, was born in Croydon, lived in George Street as a child and attended Croydon High School; honoured in the name of the Ashcroft Theatre, part of the Fairfield Halls
* Robert Barclay (historiographer), Robert Barclay (1833–1876), an English Quaker historiographer
* Jon Benjamin (Jewish leader), Jon Benjamin (1964–), Chief Executive of the Board of Deputies of British Jews, born and grew up in Croydon
* Alex Brooker (1984–), Journalist, born in Croydon
* Raymond Chandler (1888–1959), American detective fiction writer, lived in Upper Norwood as a schoolboy
* Anne Clark (poet), Anne Clark (1960–), electronic music artist and poet, was born in Croydon
* Carlton Cole (1983–), English footballer, born in Croydon
* Kit Connor (2004–), Actor known for Rocketman (film) and Heartstopper (TV series) on Netflix, born and raised in Croydon
* Roger Ward Crosskey (1930–2017), entomologist, born in Croydon
* Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (1859–1930), Scottish-born fiction writer, lived at No. 12 Tennison Road, South Norwood and featured the area in some of his Sherlock Holmes detective stories
* Jane Drew (1911–1996), modernist architect, born in Thornton Heath and head girl at Croydon High School
* Havelock Ellis (1859–1939), sexologist, born in Croydon
* Paul Garelli (1924–2006), French Assyriologist, born in Croydon
* Ben Haenow (1985–), pop singer, winner of The X Factor (UK series 11), ''The X Factor'' (UK series 11), born in Croydon
* Roy Hodgson (1947–), Crystal Palace F.C., Crystal Palace and former England manager, born and grew up in Croydon
* Tom Holland (actor), Tom Holland (1996–), actor in five Marvel Cinematic Universe films, educated at the BRIT School
* William Forster Lanchester, FRSE (1875–1953), zoologist, born and raised in Croydon
* Eden Kane (born Richard Graham Sarstedt) (1940–), singer and older brother of Peter and Robin Sarstedt
* Rachel Khoo (1980–), cook, editor-in-chief of online lifestyle magazine ''Khoollect'', with her own BBC series
* George Arthur Knowland, George Knowland (1922–1945), Victoria Cross recipient, went to Elmwood Junior School
* Nish Kumar (1985–), comedian, born in
* Peggy Ashcroft (1907–1991), actress, was born in Croydon, lived in George Street as a child and attended Croydon High School; honoured in the name of the Ashcroft Theatre, part of the Fairfield Halls
* Robert Barclay (historiographer), Robert Barclay (1833–1876), an English Quaker historiographer
* Jon Benjamin (Jewish leader), Jon Benjamin (1964–), Chief Executive of the Board of Deputies of British Jews, born and grew up in Croydon
* Alex Brooker (1984–), Journalist, born in Croydon
* Raymond Chandler (1888–1959), American detective fiction writer, lived in Upper Norwood as a schoolboy
* Anne Clark (poet), Anne Clark (1960–), electronic music artist and poet, was born in Croydon
* Carlton Cole (1983–), English footballer, born in Croydon
* Kit Connor (2004–), Actor known for Rocketman (film) and Heartstopper (TV series) on Netflix, born and raised in Croydon
* Roger Ward Crosskey (1930–2017), entomologist, born in Croydon
* Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (1859–1930), Scottish-born fiction writer, lived at No. 12 Tennison Road, South Norwood and featured the area in some of his Sherlock Holmes detective stories
* Jane Drew (1911–1996), modernist architect, born in Thornton Heath and head girl at Croydon High School
* Havelock Ellis (1859–1939), sexologist, born in Croydon
* Paul Garelli (1924–2006), French Assyriologist, born in Croydon
* Ben Haenow (1985–), pop singer, winner of The X Factor (UK series 11), ''The X Factor'' (UK series 11), born in Croydon
* Roy Hodgson (1947–), Crystal Palace F.C., Crystal Palace and former England manager, born and grew up in Croydon
* Tom Holland (actor), Tom Holland (1996–), actor in five Marvel Cinematic Universe films, educated at the BRIT School
* William Forster Lanchester, FRSE (1875–1953), zoologist, born and raised in Croydon
* Eden Kane (born Richard Graham Sarstedt) (1940–), singer and older brother of Peter and Robin Sarstedt
* Rachel Khoo (1980–), cook, editor-in-chief of online lifestyle magazine ''Khoollect'', with her own BBC series
* George Arthur Knowland, George Knowland (1922–1945), Victoria Cross recipient, went to Elmwood Junior School
* Nish Kumar (1985–), comedian, born in Wandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
Toponymy
Wandsworth takes its nam ...
and raised in Croydon
* D. H. Lawrence (1885–1930), novelist, lived at 12 Colworth Road, Addiscombe, 1908–1912 whilst a teacher at Davidson Road School
* David Lean (1908–1991), film director, born in Croydon
* Kirsty MacColl (1959–2000), singer and songwriter, born and grew up in Croydon
* David McAlmont (1967–), singer, songwriter, writer, historian; born at St Mary's Maternity Hospital, attended Broadmead Primary.
* Ralph McTell (1944–), musician, composer of "Streets of London (song), Streets of London", was brought up in Croydon
* Katie Melua (1984–), musician, singer and songwriter, attended the BRIT School
* Kate Moss (1974–), model, attended Riddlesdown High School
* Malcolm Muggeridge (1903–1990), author and media personality, the son of H. T. Muggeridge, a prominent Croydon Labour councillor, and taught at John Ruskin College, John Ruskin Central School in the 1920s
* Lucy Porter (1973–), comedian, born in Croydon
* Jason Puncheon (1986–), professional footballer playing in midfield for Pafos FC (Cyprus)
* Peter Sarstedt (1941–2017), singer, winner of Ivor Novello Award, lived in Croydon as a teenager
* Robin Sarstedt (1944–), singer and younger brother of Peter
* Captain Sensible (born Raymond Burns) (1954–), guitarist with The Damned, attended school in South Norwood
* Ashraf Sinclair (1979–2020), Malaysian actor, born in Croydon
* Emile Smith Rowe (2000–), professional football player, born in Thornton Heath before relocating to North London
* Dan Stevens (1982–), actor, born in Croydon
* Stormzy (1993–) UK grime rapper, born in Croydon
* Aaron Wan-Bissaka (1997–), English footballer, born in Croydon
* Algy Ward (born Alaisdair Terry Mackie Ward) (1959–), bass guitarist and musician with The Saints, The Damned, and Tank, born in Croydon
* Amy Winehouse (1983–2011), singer, attended the BRIT School
* Edward Woodward (1930–2009), actor, born and for many years lived in Croydon
* Wilfried Zaha (1992–), professional football player, grew up in Thornton Heath and attended Selsdon High School
Education
The town is home to Croydon College, with its main site on Park Lane and College Road near East Croydon station. It has over 13,000 students attending one of its three sub-colleges. The sub-colleges were created in 2007. The three sub-colleges are the Croydon Sixth Form College, Croydon Skills and Enterprise College and the Croydon Higher Education College. The Higher Education College offers university-level education in a range of subjects from Law through to Fine Art. Croydon Skills and Enterprise College delivers training and education opportunities. The town has five fee-paying schools, three of which are part of the Whitgift Foundation. Two are boys' schools (though Trinity School has a co-educational sixth form): Whitgift School was situated near the Almshouses until 1931 when it moved to its current site in Haling Park in South Croydon, the Middle School (renamed Trinity School of John Whitgift in 1954) remained on the site until 1965 when it moved to Shirley Park. A direct grant grammar school until 1968, it is now a member of the Headmasters' Conference.Old Palace School
The Old Palace of John Whitgift School is a selective independent school for girls in Croydon, London. The Old Palace is protected as a Grade I listed building.
It consists of a pre-school for the ages of 3-4, a preparatory department for the a ...
, an independent girls' school situated in the old Summer Palace of the Archbishops of Canterbury, joined the Whitgift Foundation group of schools in 1993. Croham Hurst School, an independent girls' school in South Croydon, became part of Old Palace in 2007 and its old buildings are now used as the Old Palace junior school. The site of the old Whitgift grammar school is now the Whitgift shopping centre whose freehold is owned by the Whitgift Foundation.
Croydon is also home to three single-sex Catholic state schools. The formerly independent The John Fisher School, John Fisher School in Purley has not charged fees since the late 1970s, but during the 1990s was selective, choosing boys via exams, interviews, tests, previous school reports and written statements. The school ended its selection policy in 1999, and now accepts pupils under a Catholic points-based admission school, points system, which favours those who have high mass attendance and whose families are most involved in the Catholic Church. Coloma Convent Girls' School is one of England's Catholic girls' schools: formerly a grammar school, it has now, like John Fisher, adopted points-based admission criteria. St. Joseph's College, Upper Norwood, St. Joseph's College, on Beulah Hill
The A215 is an A road in south London, starting at Elephant and Castle and finishing around Shirley. It runs through the London Boroughs of Lambeth, Southwark and Croydon.
Beginning as Walworth Road, the A215 becomes Camberwell Road—much of ...
in Upper Norwood, is a boys' school with a mixed sixth form.
Croydon High School, Croydon High School for Girls is an independent girls' school in Selsdon, and a member of the Girls' Day School Trust. The Japanese Saturday School of London, a Hoshuko, weekend Japanese programme, uses Croydon High School as its Croydon Campus (クロイドン校舎 ''Kuroidon Kōsha'').. The Japanese Saturday School of London. Retrieved on 5 April 2015. – See "9.校舎 "
References
Further reading
* * *External links
*London Borough of Croydon
{{Authority control Areas of London Districts of the London Borough of Croydon History of the London Borough of Croydon Metropolitan centres of London Market towns in London