Corticogenesis in a wild-type mouse with captions in english copy.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Corticogenesis is the process during which the
 The preplate also contains the predecessor to the subplate, which is sometimes referred to as a layer. As the cortical plate appears, the preplate separates into two components. The Cajal-Retzius cells go into the marginal zone, above the cortical plate, while the subplate moves inferior to the 6 cortical layers.
Appropriate functioning and development of the subplate is highly dependent upon organization and connectivity. Disruptions during the transition from preplate to cortical plate can lead to significant malformation and disruption in function of the thalamus, inhibitory neuron activity, and maturation of cortical response. Injuries during the second trimester of human development have been associated with disorders such as
The preplate also contains the predecessor to the subplate, which is sometimes referred to as a layer. As the cortical plate appears, the preplate separates into two components. The Cajal-Retzius cells go into the marginal zone, above the cortical plate, while the subplate moves inferior to the 6 cortical layers.
Appropriate functioning and development of the subplate is highly dependent upon organization and connectivity. Disruptions during the transition from preplate to cortical plate can lead to significant malformation and disruption in function of the thalamus, inhibitory neuron activity, and maturation of cortical response. Injuries during the second trimester of human development have been associated with disorders such as
cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consistin ...
of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
is formed as part of the development of the nervous system
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The fiel ...
of mammals including its development in humans. The cortex is the outer layer of the brain and is composed of up to six layers. Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
s formed in the ventricular zone
In vertebrates, the ventricular zone (VZ) is a transient embryonic layer of tissue containing neural stem cells, principally radial glial cells, of the central nervous system (CNS). The VZ is so named because it lines the ventricular system, whi ...
migrate to their final locations in one of the six layers of the cortex. The process occurs from embryonic day 10 to 17 in mice and between gestational weeks seven to 18 in humans.
The cortex is the outermost layer of the brain and consists primarily of gray matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distingui ...
, or neuronal cell bodies. Interior areas of the brain consist of myelinated
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be l ...
axons and appear as white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distributi ...
.Cortical plates
Preplate
The preplate is the first stage in corticogenesis prior to the development of the cortical plate. The preplate is located between thepia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
pioneer neuron A pioneer neuron is a cell that is a derivative of the preplate in the early stages of corticogenesis of the brain. Pioneer neurons settle in the marginal zone of the cortex and project to sub-cortical levels. In the rat, pioneer neurons are only ...
s. These neurons are mainly thought to be Cajal-Retzius cells, a transient cell type that signals for in
pioneer neuron A pioneer neuron is a cell that is a derivative of the preplate in the early stages of corticogenesis of the brain. Pioneer neurons settle in the marginal zone of the cortex and project to sub-cortical levels. In the rat, pioneer neurons are only ...
cell migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing and immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular dire ...
and organization.
Subplate
 The preplate also contains the predecessor to the subplate, which is sometimes referred to as a layer. As the cortical plate appears, the preplate separates into two components. The Cajal-Retzius cells go into the marginal zone, above the cortical plate, while the subplate moves inferior to the 6 cortical layers.
Appropriate functioning and development of the subplate is highly dependent upon organization and connectivity. Disruptions during the transition from preplate to cortical plate can lead to significant malformation and disruption in function of the thalamus, inhibitory neuron activity, and maturation of cortical response. Injuries during the second trimester of human development have been associated with disorders such as
The preplate also contains the predecessor to the subplate, which is sometimes referred to as a layer. As the cortical plate appears, the preplate separates into two components. The Cajal-Retzius cells go into the marginal zone, above the cortical plate, while the subplate moves inferior to the 6 cortical layers.
Appropriate functioning and development of the subplate is highly dependent upon organization and connectivity. Disruptions during the transition from preplate to cortical plate can lead to significant malformation and disruption in function of the thalamus, inhibitory neuron activity, and maturation of cortical response. Injuries during the second trimester of human development have been associated with disorders such as cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sens ...
and epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
.
The cortical plate is the final plate formed in corticogenesis. It includes cortical layers two through six.
The subplate is located beneath the cortical plate. It is named for both its location relative to the cortical plate and for the time frame in which it is created. While the cortical plate matures, the cells located in the subplate establish connections with neurons that have not yet moved to their destination layer within the cortical plate.
Pioneer cells are also present in the subplate and work to create neuronal synapses within the plate. In early development, synaptic connections and circuits continue to proliferate at an exponential rate.
Cortical zones
In humans the intermediate zone is located between the ventricular zone and the cortical plate. The intermediate zone containsbipolar cells
A bipolar neuron, or bipolar cell, is a type of neuron that has two extensions (one axon and one dendrite). Many bipolar cells are specialized sensory neurons for the transmission of sense. As such, they are part of the sensory pathways for smell ...
and multipolar cells
A multipolar neuron is a type of neuron that possesses a single axon and many dendrites (and dendritic branches), allowing for the integration of a great deal of information from other neurons. These processes are projections from the neuron cell ...
. The multipolar cells have a special type of migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
known as multipolar migration, they do not resemble the cells migrating by locomotion or somal translocation. Instead these multipolar cells express neuronal markers and extend multiple thin processes in various directions independently of the radial glial fibers. This zone is only present during corticogenesis and eventually transforms into adult white matter.
The ventricular and subventricular zones exist inferior to the intermediate zone and communicate with other zones through cell signalling. These zones additionally create neurons destined to migrate to other areas in the cortex.Antypa, M., Faux, C., Eichele, G., Parnavelas, J. G., & Andrews, W. D. (2011). Differential gene expression in migratory streams of cortical interneurons. European Journal of Neuroscience, 34(10), 1584-1594. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07896.x
The marginal zone, along with the cortical zone, make up the 6 layers that form the cortex. This zone is the predecessor for layer I of the cortex. Astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
form an outer limiting membrane to interact with the pia. In humans it has been found that the cells here also form a subpial layer. Cajal-Retzius cells are also present in this zone and release reelin
Reelin, encoded by the ''RELN'' gene, is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this impor ...
along the radial axis, a key signaling molecule in neuronal migration during corticogenesis.Kwon, H. J., Ma, S., & Huang, Z. (2011). Radial glia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myel ...
regulate Cajal-Retzius cell positioning in the early embryonic cerebral cortex. Developmental Biology, 351(1), 25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.12.026
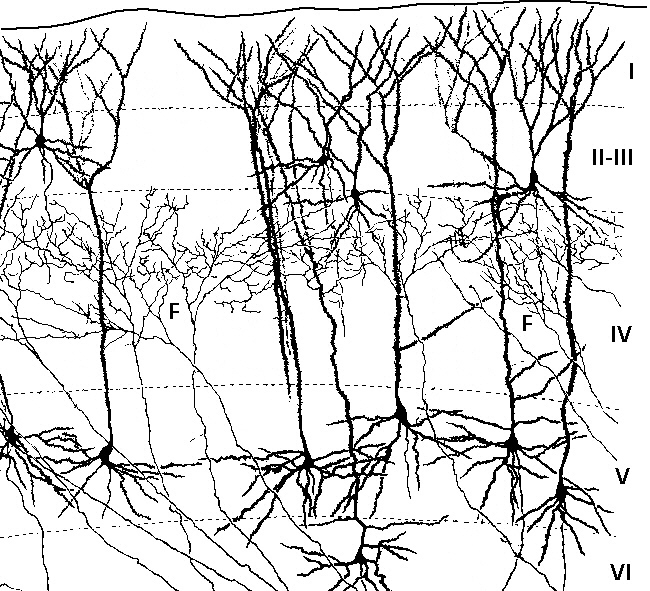
Formation of layers
The cerebral cortex is divided into layers. Each layer is formed byradial glial cell
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including astrocytes and ...
s located in the ventricular zone or subventricular zone, and then migrate to their final destination.

Layer I
Layer I, the molecular layer, is the first cortical layer produced during neurogenesis at mice at embryonal days 10.5 to 12.5 (E10.5 to E12.5). Of the six layers found within the neocortex, layer I is the most superficial and is composed ofCajal–Retzius cell
Cajal–Retzius cells (CR cells) (also known as Horizontal cells of Cajal) are a heterogeneous population of morphologically and molecularly distinct reelin-producing cell types in the marginal zone/layer I of the developmental cerebral cortex an ...
s and pyramidal cells.Germain, N., Banda, E., & Grabel, L. (2010). Embryonic Stem Cell Neurogenesis and Neural Specification. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 111(3), 535-542. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22747 This layer is unique in the aspect that these cells migrate to the outer edge of the cortex opposed to the migration experienced by the other 5 layers. Layer I is also characterized by expression of reelin
Reelin, encoded by the ''RELN'' gene, is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this impor ...
, transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
T-box brain 1, and cortical migratory neuronal marker.Meyer, G. (2007). Genetic Control of Neuronal Migrations in Human Cortical Development(Advances in Anatomy, Embryology and Cell Biology). F. F. Beck, Melbourne, F. Clascá, Madrid, M. Frotscher, Freiburg, D. E. Haines, Jackson, H-W. Korf, Frankfurt, E.Marani, Enschede, R. Putz, München, Y. Sano, Kyoto, T. H. Schiebler, Würzburg & K. Zilles, Düsseldorf (Eds). New York, NY:Springer.
Layers II and III
The second and third layers, or the external granular layer and external pyramidal layer respectively, are formed around mouse embryonal ages 13.5 to 16 days (E13.5 to E16). These layers are the last to form during corticogenesis and includepyramidal neurons
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cor ...
, astrocytes, Stellates, and radial glial cells.
In humans the pyramidal and stellate neurons express ''SATB2
SATB is an initialism that describes the scoring of compositions for choirs, and also choirs (or consorts) of instruments. The initials are for the voice types: S for soprano, A for alto, T for tenor and B for bass.
Choral music
Four-part harmo ...
'' and ''CUX1''. SATB2 and CUX1 are DNA binding proteins involved in determining the fate of cortical cells.
Layers IV, V, and VI
The fourth, fifth and sixth layers, or the internal granular layer, internal pyramidal layer, andmultiform layer
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of ...
, respectively, are formed during mouse E11.5 to E14.5. Included in these layers are stellates, radial glia, and pyramidal neurons. Layer VIis adjacent to the ventricular zone. During the production of these layers, transcription factors ''TBR1
T-box, brain, 1 is a transcription factor protein important in vertebrate embryo development. It is encoded by the ''TBR1'' gene. This gene is also known by several other names: ''T-Brain 1'', ''TBR-1'', ''TES-56'', and ''MGC141978''. TBR1 is ...
'' and ''OTX1
Homeobox protein OTX1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OTX1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''b ...
'' are expressed along with ''CTIP2'', or corticoneuronal zinc finger protein.
Neuronal migration
Neuronal migration
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The fiel ...
plays significant role in corticogenesis. Throughout the process of creating the six cortical layers, all the neurons and cells migrate from the ventricular zone, through the subplate, and come to rest at their appropriate layer of the cortex. Neuronal migration is generally subdivided into radial migration, tangential migration and multipolar migration. The migration of subcortical brain functions to the cortex is known as corticalization.
Cell signaling
Appropriate formation of the cerebral cortex relies heavily on a densely intertwined network of multiple signaling pathways and distinct signaling molecules. While the majority of the process remains to be understood, some signals and pathways have been carefully unraveled in an effort to gain full knowledge of the mechanisms that control corticogenesis.Reelin-DAB1 pathway
TheReelin
Reelin, encoded by the ''RELN'' gene, is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this impor ...
-DAB1
The Disabled-1 (Dab1) gene encodes a key regulator of Reelin signaling. Reelin is a large glycoprotein secreted by neurons of the developing brain, particularly Cajal-Retzius cells. DAB1 functions downstream of Reln in a signaling pathway
that ...
pathway is a well-defined pathway involved in corticogenesis. Cajal-Retzius cells located in the marginal zone secrete reelin to start the cascade. Reelin is able to interact with specific neurons in the cortical plate and direct these neurons to their proper locations. It is thought that the result downstream from this signalling could influence the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is com ...
. Reelin is secreted only by the Cajal-Retzius cells located in the marginal zone, and its receptors are confined to the cortical plate. This segregation could be used to understand the actions of Reelin.
DAB1 is a regulator protein downstream of the reelin receptors. This protein is located inside cells residing in the ventricular zone, displaying highest concentrations in migrating pyramidal cells. When either reelin or DAB1 are inactivated in mice, the resulting phenotypes are the same. In this case, the neurons are unable to migrate properly through the cortical plate. It does not affect the proliferation of neurons and in the wild does not seem to have detrimental effects on memory or learning.
Sonic hedgehog
Knocking out the Sonic hedgehog, or ''Shh'', has been shown to severely affect corticogenesis in the genetically modified mice. Theventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
and dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal c ...
sides of the cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb ...
are affected as ''Shh'' expresses the transcription factors to Nkx2 which is important in patterning the cortex. ''Shh'' is also important to corticogenesis as it affects cell proliferation and differentiation, helping neuronal progenitor cell
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that can differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only differ ...
s in fate determination.Komada, M. (2012). Sonic hedgehog signaling coordinates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells by regulating cell cycle kinetics during development of the neocortex. Congenital Anomalies, 52(2), 72-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-4520.2012.00368.x
Bmp-7
In mice, bone morphogenetic protein 7 (Bmp-7), is an important regulator in corticogenesis, though it is not understood whether it promotes or inhibits neurogenesis. Bmp-7 can be detected in the ventricular zone and is secreted intocerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
(CSF). The CSF is an area to promote neurogenesis and it is believed that the synergy between Bmp-7 and other regulators promote cell division along with homeostasis.Segklia, A., Seuntjens, E., Elkouris, M., Tsalavos, S., Stappers, E., Mitsiadis, T. A., . . . Graf, D. (2012). Bmp7 Regulates the Survival, Proliferation, and Neurogenic Properties of Neural Progenitor Cells during Corticogenesis in the Mouse. PLoS ONE, 7(3). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034088
Other bone morphogenetic proteins are also known to impact corticogenesis in the mouse. Bmp2, 4, 5, and 6 are expressed during the process and can compensate for one another. For example, if Bmp-4 was absent from corticogenesis, very little would change in the cortex phenotype, due to the other Bmps helping accomplish the tasks of Bmp-4. However, Bmp-7 is the only Bmp that promotes radial glia survival and therefore considered more important.
Cdk5-p35 pathway
Cdk5
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a protein, and more specifically an enzyme, that is encoded by the Cdk5 gene. It was discovered 15 years ago, and it is saliently expressed in post-mitotic central nervous system neurons (CNS).
The molecule belongs ...
has a pathway parallel to the Reelin-DAB1. This pathway affects the neuronal positioning, and results in similar malformations when absent as the Reelin or DAB1 malformations except that migration is affected at an earlier stage on the cortical plate. Cdk5/p35 pathway is also responsible for actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
and microtubule dynamics involved in neuronal migration.
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (p57, Kip2), also known as CDKN1C, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CDKN1C'' imprinted gene.
Function
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C is a tight-binding inhibitor of several G1 cyclin/ ...
, or p57, also affects corticogenesis. It has been shown the p57 induces cells to exit from the cell cycle and begin differentiation, but it is dependent on Cdks. p57 is able to induce neuronal progenitor cells to start differentiating into highly specialized neurons in the cortex. However, the mechanism by which p57 is able to affect such control is not yet known.Tury, A., Mairet-Coello, G., & DiCicco-Bloom, E. (2011). The Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p57(Kip2) Regulates Cell Cycle Exit, Differentiation, and Migration of Embryonic Cerebral Cortical Precursors. Cerebral Cortex, 21(8), 1840-1856. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq254
Other signals
Besides the ones listed above, there are several more signals that affect corticogenesis. Cnr1 is aG protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
that is widely expressed throughout the brain and in interneurons. In knockout mice, the cortex exhibited decreased immunoreactivity. Nrp1
Neuropilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NRP1'' gene. In humans, the neuropilin 1 gene is located at 10p11.22. This is one of two human neuropilins.
Function
NRP1 is a membrane-bound coreceptor to a tyrosine kinase rece ...
, Robo1
Roundabout homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ROBO1'' gene.
Function
Bilateral symmetric nervous systems have special midline structures that establish a partition between the two mirror image halves. Some axons project t ...
, and Robo2 have also been shown to be present and important in the development of interneurons. Cdh8 is known to be expressed in the intermediate and subventricular zone, though not in specific neurons in that area, and it is suggested to regulate fiber releasing.
Disorders of cortical development
Lissencephaly
Lissencephaly
Lissencephaly (, meaning "smooth brain") is a set of rare brain disorders whereby the whole or parts of the surface of the brain appear smooth. It is caused by defective neuronal migration during the 12th to 24th weeks of gestation resulting in ...
, or 'smooth brain', is a disorder in which the brain does not properly form the gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other m ...
and sulci
Sulci or Sulki (in Greek , Steph. B., Ptol.; , Strabo; , Paus.), was one of the most considerable cities of ancient Sardinia, situated in the southwest corner of the island, on a small island, now called Isola di Sant'Antioco, which is, how ...
as a result from neuronal migration and cortical folding. This disorder can also result in epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
and cognitive impairment.Toba, S., & Hirotsune, S. (2012). A unique role of dynein and nud family proteins in corticogenesis. Neuropathology, 32(4), 432-439. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2012.01301.x Type 1 lissencephaly is due to an error in migration. LIS1, also known as PAFAH1B, is a gene that is expressed in both dividing and migrating cells found in the brain. When LIS1 is deleted, lissencephaly occurs.
LIS1 is thought to have several important roles in the creation of the cortex. Since LIS1 is similar to the nuclear distribution protein F (''nudF''), they are thought to work similarly. The nud family is known to be a factor in nuclear translocation, or moving the nuclei of daughter cells after cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
has occurred. By relation, it is thought that LIS1 is a factor in neuronal migration. LIS1 is also considered to be a factor in controlling dynein, a motor protein that affects intercellular movement such as protein sorting and the process of cell division.
Another protein that contributes to a lissencephaly disorder is DCX, or Doublecortin
Neuronal migration protein doublecortin, also known as doublin or lissencephalin-X is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCX gene.
Function
Doublecortin (DCX) is a microtubule-associated protein expressed by neuronal precursor cells an ...
. DCX is a microtubule associated protein that is responsible for double cortex malformations. DCX is found in the second layer of the cortex, and in fact is still present in immature neurons of an adult cortex.Zhang, M. Q., Wang, H., & Xiong, K. (2011). Is the neocortex a novel reservoir for adult mammalian neurogenesis? Neural Regeneration Research, 6(17), 1334-1341. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2011.17.009 It is thought that DCX affects neuronal migration through affecting the microtubule dynamics. Since DCX malformations results as a similar phenotype as with LIS1 malformations, it is thought they interact with one another on a cellular level. However, it is not yet known how this occurs.
Tsc1 knockout
TSC, or tuberous sclerosis, is an autosomal dominant disorder that results in formation of tumors along neuroectodermally-derived tissue.TSC1
Tuberous sclerosis 1 (TSC1), also known as hamartin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TSC1'' gene.
Function
TSC1 functions as a co-chaperone which inhibits the ATPase activity of the chaperone Hsp90 (heat shock protein-90) and de ...
or TSC2
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2 (TSC2), also known as Tuberin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TSC2'' gene.
Function
Mutations in this gene lead to tuberous sclerosis. Its gene product is believed to be a tumor suppressor and is a ...
inactivation can cause TSC and the associated tumors in the brain. When inactivation of TSC1 is present during corticogenesis, malformations of cortical tubers, or abnormal benign tissue growth, along with white matter nodes would form in mice. This replicates the effect TSC is found to have in humans afflicted with TSC. In the mice there would be a lack of GFAP in astrocytes however astrogliosis
Astrogliosis (also known as astrocytosis or referred to as reactive astrogliosis) is an abnormal increase in the number of astrocytes due to the destruction of nearby neurons from central nervous system (CNS) trauma, infection, ischemia, stroke, a ...
would not occur like in the human TSC.Feliciano, D. M., Su, T., Lopez, J., Platel, J. C., & Bordey, A. (2011). Single-cell Tsc1 knockout during corticogenesis generates tuber-like lesions and reduces seizure threshold in mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 121(4), 1596-1607. doi: 10.1172/jci44909
Human cortex alformation (overfolding)
Variations within the sodium channel SCN3A, and Na+/K+,ATPase (ATP1A3), has been implicated in cortical malformations. {{cite journal , last1=Smith , first1=Richard S. , last2=Florio , first2=Marta , last3=Akula , first3=Shyam K. , last4=Neil , first4=Jennifer E. , last5=Wang , first5=Yidi , last6=Hill , first6=R. Sean , last7=Goldman , first7=Melissa , last8=Mullally , first8=Christopher D. , last9=Reed , first9=Nora , last10=Bello-Espinosa , first10=Luis , last11=Flores-Sarnat , first11=Laura , last12=Monteiro , first12=Fabiola Paoli , last13=Erasmo , first13=Casella B. , last14=Pinto e Vairo , first14=Filippo , last15=Morava , first15=Eva , last16=Barkovich , first16=A. James , last17=Gonzalez-Heydrich , first17=Joseph , last18=Brownstein , first18=Catherine A. , last19=McCarroll , first19=Steven A. , last20=Walsh , first20=Christopher A. , title=Early role for a Na + ,K + -ATPase ( ATP1A3 ) in brain development , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , date=22 June 2021 , volume=118 , issue=25 , pages=e2023333118 , doi=10.1073/pnas.2023333118 , pmid=34161264 , pmc=8237684 , doi-access=freeRecapitulation
Recapitulation of corticogenesis in both human and mouse embryos has been accomplished with a three dimensional culture using embryonic stem cells (ESC). By carefully using embryo body intermediates and cultured in a serum free environment cortical progenitors form in a space and time related pattern similar to ''in vivo'' corticogenesis. Using immunocytochemical analysis on mouse neural stem cells derived from ESCs, after 6 days there was evidence of neuronal differentiation. The recapitulation ability only follows after the knowledge of spatial and temporal patterns have been identified, along with giving the knowledge that corticogenesis can occur without input from the brain.Gaspard N, Bouschet T, Hourex R, Dimidschstein J, Naeije G, van den Ameele J, Espuny-Camacho I, Herpoel A, Passante L, Schiffmann SN, Gaillard A, Vanderhargen P. (2008). An Intrinsic mechanism of corticogenesis from embryonic stem cells. Nature, 455:351-357.References