Cantabria prerromana.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an
 Numerous authors, including Isidore of Seville,
Numerous authors, including Isidore of Seville,
During the Spanish liberal regimes of the 19th century, the term came to be increasingly associated to the province of Santander. However, during the late medieval and Modern Period literature, ''Cantabria'' and ''Cantabrians'' refer to the Basque Country, especially the lordship of Biscay, and the Basques.


 Due to the gulf stream, Cantabria, as well as the rest of "Green Spain", has a much more
Due to the gulf stream, Cantabria, as well as the rest of "Green Spain", has a much more
 The main rivers of the region, sorted by
The main rivers of the region, sorted by
 The variation in the altitude of the region, which in a short distance ranges from sea level to 2,600 meters in the mountains, leads to a great deal of diversity in vegetation and a large number of
The variation in the altitude of the region, which in a short distance ranges from sea level to 2,600 meters in the mountains, leads to a great deal of diversity in vegetation and a large number of  *The maritime region, near the coast and including altitudes up to 500 metres. Originally it had mixed deciduous forests containing
*The maritime region, near the coast and including altitudes up to 500 metres. Originally it had mixed deciduous forests containing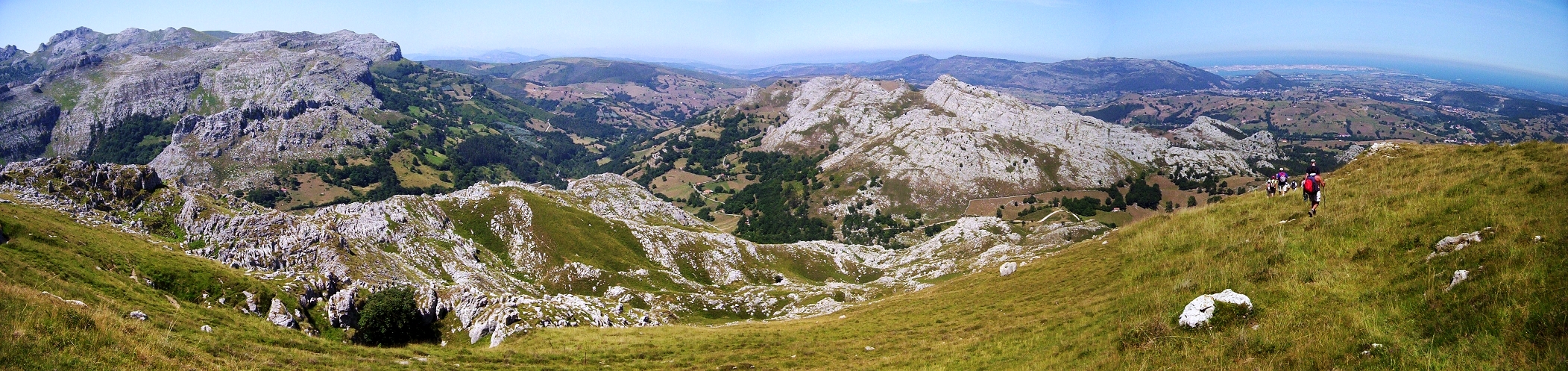  The plantation of pines has given way in the last decades to that of eucalyptus because this
The plantation of pines has given way in the last decades to that of eucalyptus because this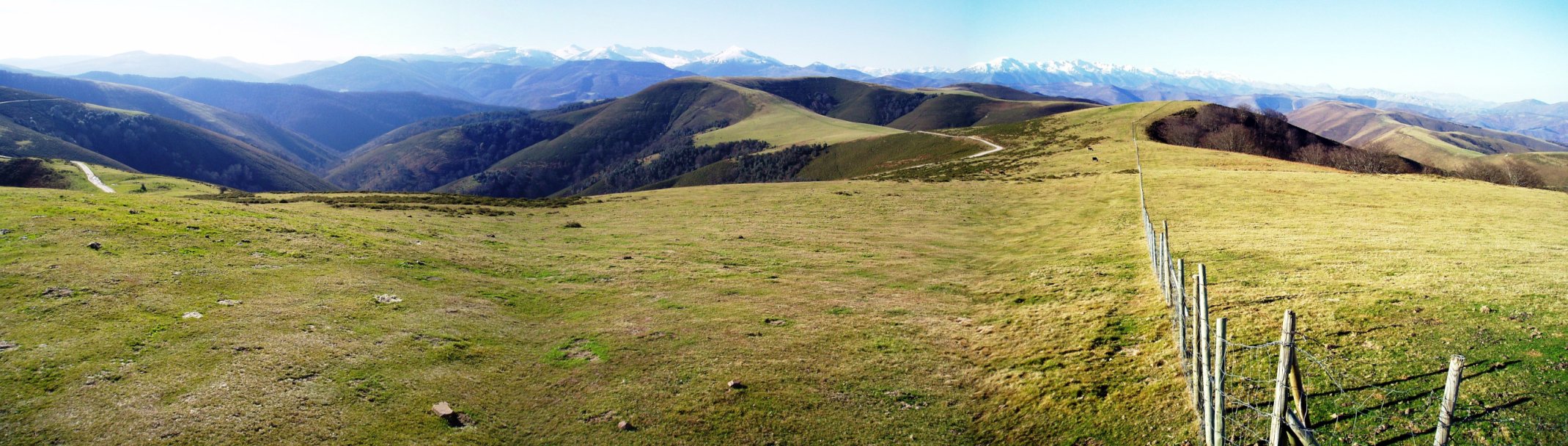  * The subalpine plane, in this high country, the plant life is composed of birch, scrub, and
* The subalpine plane, in this high country, the plant life is composed of birch, scrub, and
 There are seven natural areas in this autonomous community designated as
There are seven natural areas in this autonomous community designated as

 According to the 2009 census, the region has a population of 591,886 which constitutes 1.29% of the population of Spain, with the population density numbering 106.8 people per kilometer. The average life expectancy for male inhabitants is 75 years; for female inhabitants, it is 83 years. Eight years later in 2017 the population has fallen to 581,477 according to INE.
In relative contrast to other regions of Spain, Cantabria has not experienced much immigration. In 2007, only 4.7% of the population were immigrants. The predominant countries of origin for immigrants to Cantabria are Colombia,
According to the 2009 census, the region has a population of 591,886 which constitutes 1.29% of the population of Spain, with the population density numbering 106.8 people per kilometer. The average life expectancy for male inhabitants is 75 years; for female inhabitants, it is 83 years. Eight years later in 2017 the population has fallen to 581,477 according to INE.
In relative contrast to other regions of Spain, Cantabria has not experienced much immigration. In 2007, only 4.7% of the population were immigrants. The predominant countries of origin for immigrants to Cantabria are Colombia,

 The first written reference to the name Cantabria emerges around 195 BC, in which the historian
The first written reference to the name Cantabria emerges around 195 BC, in which the historian
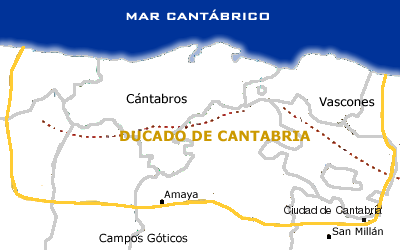 Following the collapse of the Roman Empire, Cantabria regained its independence from the rule of the Visigoths. In 574, King Liuvigild attacked Cantabria and managed to capture the south of the country, including the city of Amaya (Burgos), Amaya, where he established a Visigothic province called the Duchy of Cantabria (see picture), which would serve as a Limes (Roman Empire), limes or frontier zone to contain the Cantabri as well as their neighbors the Vascones. To the north of this cordon, however, the Cantabri continued to live independently until the Arab invasion. In 714, a mixed Arab/Berber people, Berber army of Muslim Moors invaded the upper valleys of the Ebro and succeeded in capturing Amaya, the Cantabrian capital, forcing the Cantabrians back to their traditional frontiers, where they joined forces with the Kingdom of Asturias.
In the first chronicles of the Reconquista, Cantabria still appears to be acknowledged as a region. In the ''Albendense Chronicle'', when speaking of Alfonso I of Asturias, Alfonso I, it says, "This was the son of Peter of Cantabria, Peter, the duke of Cantabria".
During the 9th century, on mentioning the monastery of Saint Zacharias, Eulogius pinpoints it in ''Seburim'' (maybe Zubiri) on the river Arga, "waters all of Cantabria", in a letter sent to the bishop of Pamplona Williesind, suggesting a region stretching out far into the east. From this period on, source documents barely reference Cantabria by name, with ''Asturias'' featuring in names of the ''comarcas'' called ''Asturias de Santillana'', ''Asturias de Trasmiera'' and ''Asturias de Laredo''.
Following the collapse of the Roman Empire, Cantabria regained its independence from the rule of the Visigoths. In 574, King Liuvigild attacked Cantabria and managed to capture the south of the country, including the city of Amaya (Burgos), Amaya, where he established a Visigothic province called the Duchy of Cantabria (see picture), which would serve as a Limes (Roman Empire), limes or frontier zone to contain the Cantabri as well as their neighbors the Vascones. To the north of this cordon, however, the Cantabri continued to live independently until the Arab invasion. In 714, a mixed Arab/Berber people, Berber army of Muslim Moors invaded the upper valleys of the Ebro and succeeded in capturing Amaya, the Cantabrian capital, forcing the Cantabrians back to their traditional frontiers, where they joined forces with the Kingdom of Asturias.
In the first chronicles of the Reconquista, Cantabria still appears to be acknowledged as a region. In the ''Albendense Chronicle'', when speaking of Alfonso I of Asturias, Alfonso I, it says, "This was the son of Peter of Cantabria, Peter, the duke of Cantabria".
During the 9th century, on mentioning the monastery of Saint Zacharias, Eulogius pinpoints it in ''Seburim'' (maybe Zubiri) on the river Arga, "waters all of Cantabria", in a letter sent to the bishop of Pamplona Williesind, suggesting a region stretching out far into the east. From this period on, source documents barely reference Cantabria by name, with ''Asturias'' featuring in names of the ''comarcas'' called ''Asturias de Santillana'', ''Asturias de Trasmiera'' and ''Asturias de Laredo''.
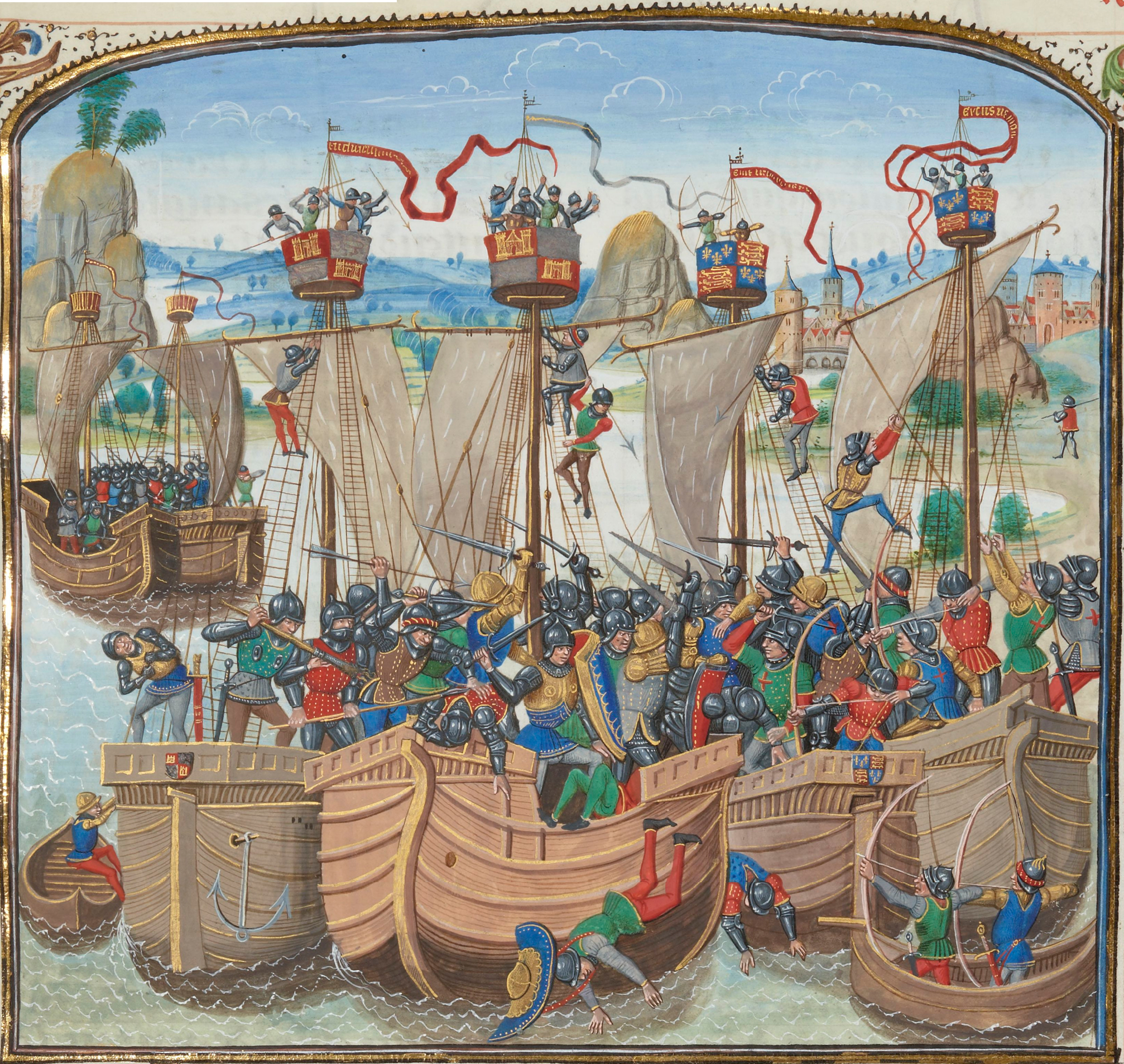 From a central core formed by the ''Hermandad de las Cuatro Villas'' (''Brotherhood of the Four Cities'') (Santander, Laredo, Castro Urdiales and San Vicente de la Barquera), the ''Hermandad de las Marismas'' (''Brotherhood of the Marshes'') was created, thereby uniting all the important seaports to the East of Asturias. During the period of the Reconquista, the Four Cities actively participated in the re-settling of Andalusia, dispatching men and ships. The coastal port cities of Cádiz and El Puerto de Santa María were settled by families from the Cantabrian Sea ports. Ships from the Four Cities took part in the taking of Seville, destroying the ship bridge linking Triana (Seville), Triana and Sevilla, a victory that is represented by the Carrack and the Torre del Oro of Sevilla in the coat of arms of Coat of arms of Santander, Santander, Coat of arms of Cantabria and Avilés (Asturias).
From a central core formed by the ''Hermandad de las Cuatro Villas'' (''Brotherhood of the Four Cities'') (Santander, Laredo, Castro Urdiales and San Vicente de la Barquera), the ''Hermandad de las Marismas'' (''Brotherhood of the Marshes'') was created, thereby uniting all the important seaports to the East of Asturias. During the period of the Reconquista, the Four Cities actively participated in the re-settling of Andalusia, dispatching men and ships. The coastal port cities of Cádiz and El Puerto de Santa María were settled by families from the Cantabrian Sea ports. Ships from the Four Cities took part in the taking of Seville, destroying the ship bridge linking Triana (Seville), Triana and Sevilla, a victory that is represented by the Carrack and the Torre del Oro of Sevilla in the coat of arms of Coat of arms of Santander, Santander, Coat of arms of Cantabria and Avilés (Asturias).
 With the rise of the Catholic Monarchs, the Brethren of the Marshes disappeared, leaving the Coregiment of the Four Villas, which included the whole area of influence of the old Brethren of the Four Villas (almost all of Cantabria). During the ''Ancien Régime, ancien régime'', the greatest jurisdictional lordships of Cantabria were mainly under the control of three of the Grandee, Grandee families of Spain: that of Mendoza (Dukedom of Infantado, Dukes of Infantado, Marquises of Santillana), of Manrique de Lara (Marquises of Aguilar de Campoo, Counts of Castañeda), and to a lesser extent that of Velasco (Dukedom of Frías, Dukes of Frías, Constable of Castile, Constables of Castile).
From the 16th century on, there was renewed interest in studying Cantabria and the Cantabri, particularly concerning the precise location of the territory that this people had occupied. It was not until the 18th century that the debate about the location and size of Ancient Cantabria was settled in a series of works which described the history of the history of the region such as ''La Cantabria'' by the Augustinian father and historian Enrique Flórez de Setién. Concurrent with the resurgence of this interest in the Cantabrians and the clarification of the aforementioned polemic, many institutions, organizations and jurisdictions in the mountainous territory received the name of "Cantabrian" or "of Cantabria".
In 1727, the first attempt to unify what would later become the Province of Cantabria occurred. Despite this, the high level of autonomy that the small entities of the fractured estate of Cantabria enjoyed, combined with a lack of resources, continued to be the main reason for Cantabria's weakness, aggravated by the progressive advance of the House of Bourbon, Bourbonic Unitary state, centralism and its administrative efficiency. The latter continually emphasised the impossibility of the smaller territories facing a multitude of problems on their own: from communications to the exercise of justice, from putting aside adequate reserves for hard times to the indiscriminate levée en masse, levees for soldiers, and above all the progression of fiscal impositions. All of this led to an acceleration of contact between villas, valleys and jurisdictions, which tended to focus on the Assemblies of the Provinces of the Nine Valleys, led by the deputies elected by the traditional entities of self-government.
There were two events that triggered the culmination of the integration process in this second attempt:
*On the one hand, the collective interest in avoiding making contributions to the reconstruction of the bridge of Miranda de Ebro, imposed by order of the Intendant of Burgos on 11 July 1775, the same year that Cantabria suffered two tremendous floods, on 20 June and on 3 November. There was a need to face as the banditry that operated with impunity in Cantabria as a result of a lack of local juridical resources. After the General Deputy of Nine Valleys gathered the affected jurisdictions to the assembly that was to take place in Puente San Miguel on 21 March 1777, they sent their respective deputies with sufficient authority to join with the Nine Valleys.
In this General Assembly a framework was established and formal steps began to be taken, leading to administrative and legal unity in 1778. This all culminated in the success of the Assembly held in the Assembly House of ''Puente San Miguel'' on July 28, 1778, where the Province of Cantabria was constituted. It was achieved by passing the common ordinances which had been developed to that end, and which had been discussed and approved previously in councils of all the villas, valleys and subscribed jurisdictions. They were, in addition to the Nine Valleys: Rivadedeva, Peñamellera, the Province of Liébana, Peñarrubia, Lamasón, Rionansa, the Villa of San Vicente de la Barquera, Coto de Estrada, Valdáliga, the Villa of Santillana del Mar, Lugar de Viérnoles, the Villa of Cartes and environs, the Valley of Buelna, the Valley of Cieza, the Valley of Iguña with the Villas of San Vicente and Los Llares, the Villa of Pujayo, the Villa of Pie de Concha y Bárcena, the Valley of Anievas, and the Valley of Toranzo.
With the rise of the Catholic Monarchs, the Brethren of the Marshes disappeared, leaving the Coregiment of the Four Villas, which included the whole area of influence of the old Brethren of the Four Villas (almost all of Cantabria). During the ''Ancien Régime, ancien régime'', the greatest jurisdictional lordships of Cantabria were mainly under the control of three of the Grandee, Grandee families of Spain: that of Mendoza (Dukedom of Infantado, Dukes of Infantado, Marquises of Santillana), of Manrique de Lara (Marquises of Aguilar de Campoo, Counts of Castañeda), and to a lesser extent that of Velasco (Dukedom of Frías, Dukes of Frías, Constable of Castile, Constables of Castile).
From the 16th century on, there was renewed interest in studying Cantabria and the Cantabri, particularly concerning the precise location of the territory that this people had occupied. It was not until the 18th century that the debate about the location and size of Ancient Cantabria was settled in a series of works which described the history of the history of the region such as ''La Cantabria'' by the Augustinian father and historian Enrique Flórez de Setién. Concurrent with the resurgence of this interest in the Cantabrians and the clarification of the aforementioned polemic, many institutions, organizations and jurisdictions in the mountainous territory received the name of "Cantabrian" or "of Cantabria".
In 1727, the first attempt to unify what would later become the Province of Cantabria occurred. Despite this, the high level of autonomy that the small entities of the fractured estate of Cantabria enjoyed, combined with a lack of resources, continued to be the main reason for Cantabria's weakness, aggravated by the progressive advance of the House of Bourbon, Bourbonic Unitary state, centralism and its administrative efficiency. The latter continually emphasised the impossibility of the smaller territories facing a multitude of problems on their own: from communications to the exercise of justice, from putting aside adequate reserves for hard times to the indiscriminate levée en masse, levees for soldiers, and above all the progression of fiscal impositions. All of this led to an acceleration of contact between villas, valleys and jurisdictions, which tended to focus on the Assemblies of the Provinces of the Nine Valleys, led by the deputies elected by the traditional entities of self-government.
There were two events that triggered the culmination of the integration process in this second attempt:
*On the one hand, the collective interest in avoiding making contributions to the reconstruction of the bridge of Miranda de Ebro, imposed by order of the Intendant of Burgos on 11 July 1775, the same year that Cantabria suffered two tremendous floods, on 20 June and on 3 November. There was a need to face as the banditry that operated with impunity in Cantabria as a result of a lack of local juridical resources. After the General Deputy of Nine Valleys gathered the affected jurisdictions to the assembly that was to take place in Puente San Miguel on 21 March 1777, they sent their respective deputies with sufficient authority to join with the Nine Valleys.
In this General Assembly a framework was established and formal steps began to be taken, leading to administrative and legal unity in 1778. This all culminated in the success of the Assembly held in the Assembly House of ''Puente San Miguel'' on July 28, 1778, where the Province of Cantabria was constituted. It was achieved by passing the common ordinances which had been developed to that end, and which had been discussed and approved previously in councils of all the villas, valleys and subscribed jurisdictions. They were, in addition to the Nine Valleys: Rivadedeva, Peñamellera, the Province of Liébana, Peñarrubia, Lamasón, Rionansa, the Villa of San Vicente de la Barquera, Coto de Estrada, Valdáliga, the Villa of Santillana del Mar, Lugar de Viérnoles, the Villa of Cartes and environs, the Valley of Buelna, the Valley of Cieza, the Valley of Iguña with the Villas of San Vicente and Los Llares, the Villa of Pujayo, the Villa of Pie de Concha y Bárcena, the Valley of Anievas, and the Valley of Toranzo.
 Having learned lessons from the failed attempt of 1727, the first objective of the new entity was to obtain approval from King Charles III of Spain, Charles III for the union of all the Cantabrian jurisdictions into one province. The royal ratification was granted on 22 November 1779.
The 28 jurisdictions that initially comprised the Province of Cantabria were clear in their intention that all the other jurisdictions that formed the ''Party and Baton of the Four Villas of the Coast'' should be included in the new province. To this end they set out the steps needed for this to happen as soon as those jurisdictions should request it. They would have to abide by the ordinances, having the same rights and duties as the founders, all on an equal footing. Thus, the following joined in quick succession: the Abbey of Santillana del Mar, Santillana, the Valleys of Tudanca, Polaciones, Herrerías, Castañeda, the Villa of
Having learned lessons from the failed attempt of 1727, the first objective of the new entity was to obtain approval from King Charles III of Spain, Charles III for the union of all the Cantabrian jurisdictions into one province. The royal ratification was granted on 22 November 1779.
The 28 jurisdictions that initially comprised the Province of Cantabria were clear in their intention that all the other jurisdictions that formed the ''Party and Baton of the Four Villas of the Coast'' should be included in the new province. To this end they set out the steps needed for this to happen as soon as those jurisdictions should request it. They would have to abide by the ordinances, having the same rights and duties as the founders, all on an equal footing. Thus, the following joined in quick succession: the Abbey of Santillana del Mar, Santillana, the Valleys of Tudanca, Polaciones, Herrerías, Castañeda, the Villa of
 During the Peninsular War, War of Independence (1808–1814), Bishop Rafael Tomás Menéndez de Luarca, a strong defender of absolutism, promoted himself as the "Regent of Cantabria" and established the ''Cantabrian Armaments'' in Santander, a section of the army whose purpose was to travel to all the mountain passes from the Central Plateau to detain any French troop.
Although defeated, he managed later to regroup in Liébana under the command of General Juan Díaz Porlier, calling his forces the ''Cantabrian Division'', in which there were various regiments and battalions, such as the ''Hussars of Cantabria'' (cavalry) or the ''Shooters of Cantabria'' (infantry). During the First Carlist War, Carlist wars they formed a unit called the ''Cantabrian Brigade''.
During the Peninsular War, War of Independence (1808–1814), Bishop Rafael Tomás Menéndez de Luarca, a strong defender of absolutism, promoted himself as the "Regent of Cantabria" and established the ''Cantabrian Armaments'' in Santander, a section of the army whose purpose was to travel to all the mountain passes from the Central Plateau to detain any French troop.
Although defeated, he managed later to regroup in Liébana under the command of General Juan Díaz Porlier, calling his forces the ''Cantabrian Division'', in which there were various regiments and battalions, such as the ''Hussars of Cantabria'' (cavalry) or the ''Shooters of Cantabria'' (infantry). During the First Carlist War, Carlist wars they formed a unit called the ''Cantabrian Brigade''.
 There are 102 municipalities in Cantabria generally comprising several townships, and from these, several districts. A number of municipalities bear the name of one of their townships (be it its capital or not), but not all them do. Each municipality is governed by its own city council, city or municipal council, and two of them, Tresviso, Cantabria, Tresviso and Pesquera, Cantabria, Pesquera, do it by ''concejo abierto'' (''open council''), having fewer than 250 inhabitants.
The Mancomunidad Campoo-Cabuérniga is not a municipality, but a communal property, singular for its size and characteristics, of shared management between the municipalities of Hermandad de Campoo de Suso, Cabuérniga, Los Tojos and Ruente. This mountain estate is used as a grazing ground for Tudanca cattle and also for horses in less amount, in its ''brañas'' or grass prairies, and even nowadays transhumant cattle farming traditions survive in this region.
See also:
*List of municipalities in Cantabria
There are 102 municipalities in Cantabria generally comprising several townships, and from these, several districts. A number of municipalities bear the name of one of their townships (be it its capital or not), but not all them do. Each municipality is governed by its own city council, city or municipal council, and two of them, Tresviso, Cantabria, Tresviso and Pesquera, Cantabria, Pesquera, do it by ''concejo abierto'' (''open council''), having fewer than 250 inhabitants.
The Mancomunidad Campoo-Cabuérniga is not a municipality, but a communal property, singular for its size and characteristics, of shared management between the municipalities of Hermandad de Campoo de Suso, Cabuérniga, Los Tojos and Ruente. This mountain estate is used as a grazing ground for Tudanca cattle and also for horses in less amount, in its ''brañas'' or grass prairies, and even nowadays transhumant cattle farming traditions survive in this region.
See also:
*List of municipalities in Cantabria
 The economy of Cantabria has a primary sector, now in decline, employing 5.8% of the active population in the industry (economics), industries of cattle farming, traditional dairy farming, and meat production; agriculture, especially corn, potatoes, vegetables, and roughage; maritime fishing; and the mining of zinc and quarry, quarries.
The secondary sector which employs 30.3% of the active population is the sector with the most productivity in recent years due to construction; that of ironworking (Reinosa being the most important city), food service (milk, meat, vegetables and seafood), chemical industry, chemistry (Solvay, Sniace), paper production (Sinace, Papelera del Besaya), textile fabrication (Textil Santanderina in Cabezón de la Sal), pharmacy (Moehs in Requejada), industrial groups and transport, etc. The service sector employs 63.8% of the active population and is increasing, given that large concentrations of the population live in the urban centers and the importance that tourism has acquired in the recent years. As of July 2014, the unemployment rate in Cantabria is 19.3%, compared to 24.47% in Spain; while as of April 2010 its purchasing power parity was €25,326, compared to €26,100 in Spain and €25,100 in the European Union, EU25. In 2007, Cantabria's growth of real GDP was 4.1%, compared to a 3.9% average for Spain. The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was 13.8 billion € in 2018. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 25,500 € or 84% of the EU27 average in the same year.
The economy of Cantabria has a primary sector, now in decline, employing 5.8% of the active population in the industry (economics), industries of cattle farming, traditional dairy farming, and meat production; agriculture, especially corn, potatoes, vegetables, and roughage; maritime fishing; and the mining of zinc and quarry, quarries.
The secondary sector which employs 30.3% of the active population is the sector with the most productivity in recent years due to construction; that of ironworking (Reinosa being the most important city), food service (milk, meat, vegetables and seafood), chemical industry, chemistry (Solvay, Sniace), paper production (Sinace, Papelera del Besaya), textile fabrication (Textil Santanderina in Cabezón de la Sal), pharmacy (Moehs in Requejada), industrial groups and transport, etc. The service sector employs 63.8% of the active population and is increasing, given that large concentrations of the population live in the urban centers and the importance that tourism has acquired in the recent years. As of July 2014, the unemployment rate in Cantabria is 19.3%, compared to 24.47% in Spain; while as of April 2010 its purchasing power parity was €25,326, compared to €26,100 in Spain and €25,100 in the European Union, EU25. In 2007, Cantabria's growth of real GDP was 4.1%, compared to a 3.9% average for Spain. The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was 13.8 billion € in 2018. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 25,500 € or 84% of the EU27 average in the same year.
 The most significant consequence of the strong relief of the Cantabrian territory is the existence of topographic barriers that condition decisively the courses of the linking infrastructures, as much in the north–south orientation in the accesses to the Geography of Spain#The Inner Plateau and associated mountains, Castilian Mesa, as in the east–west in the communication between valleys. Moreover, the cost of their construction and maintenance is much higher than average.
The main communications infrastructures of the region are:
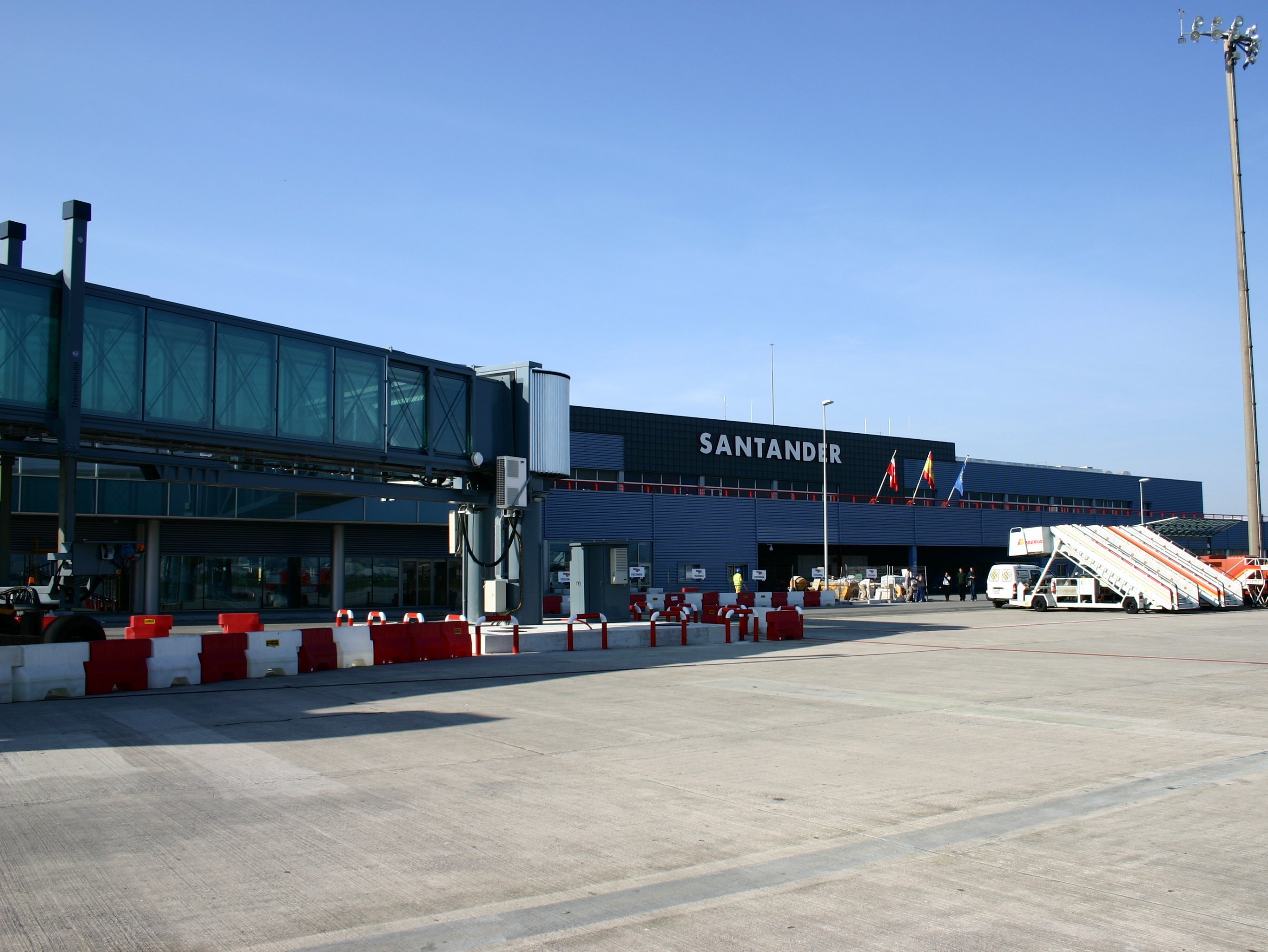
* Santander Airport
* Cantabrian Motorway (Autovía A-8, European route E-70)
* Cantabria-Meseta Motorway (Autovía A-67)
* Narrow-gauge railway
The most significant consequence of the strong relief of the Cantabrian territory is the existence of topographic barriers that condition decisively the courses of the linking infrastructures, as much in the north–south orientation in the accesses to the Geography of Spain#The Inner Plateau and associated mountains, Castilian Mesa, as in the east–west in the communication between valleys. Moreover, the cost of their construction and maintenance is much higher than average.
The main communications infrastructures of the region are:
* Santander Airport
* Cantabrian Motorway (Autovía A-8, European route E-70)
* Cantabria-Meseta Motorway (Autovía A-67)
* Narrow-gauge railway

 *Caves: Altamira (cave), Altamira Cave, Cave of El Soplao, El Soplao, Cave del Valle (Cantabria), Del Valle, El Pendo, Cueva de La Pasiega, La Pasiega Cave, Las Monedas, El Castillo, Morín, and others.
*Civil architecture: Palacio de la Magdalena, Magdalena palace in Santander; Capricho de Gaudí, Comillas Pontifical University, Pontifical University of Comillas and Sobrellano palace in Comillas; Bárcena palace in Ampuero; Castle of Argüeso in Campoo; Hornillos palace in Las Fraguas del Besaya; etc.
*Religious architecture: Collegiate of Santillana del Mar, Collegiate of Santa Cruz de Castañeda, Santo Toribio de Liébana, Santo Toribio de Liébana Monastery, Santa María de Lebeña, Santa María de Piasca, Santa María del Puerto, San Román del Moroso, Santa Catalina del Cintul, Santuario de Virgen de la Peña, ermita de San Cipriano, ermita de Monte Corona, etc.
*Museums: Cantabrian Sea Maritime Museum, Ethnographic Museum of Cantabria, Santander Museum of Fine Arts, Regional Museum of Prehistory and Arqueology of Cantabria, Cantabrian Museum of Nature, Altamira National Museum and Investigation Centre, and others.
*Caves: Altamira (cave), Altamira Cave, Cave of El Soplao, El Soplao, Cave del Valle (Cantabria), Del Valle, El Pendo, Cueva de La Pasiega, La Pasiega Cave, Las Monedas, El Castillo, Morín, and others.
*Civil architecture: Palacio de la Magdalena, Magdalena palace in Santander; Capricho de Gaudí, Comillas Pontifical University, Pontifical University of Comillas and Sobrellano palace in Comillas; Bárcena palace in Ampuero; Castle of Argüeso in Campoo; Hornillos palace in Las Fraguas del Besaya; etc.
*Religious architecture: Collegiate of Santillana del Mar, Collegiate of Santa Cruz de Castañeda, Santo Toribio de Liébana, Santo Toribio de Liébana Monastery, Santa María de Lebeña, Santa María de Piasca, Santa María del Puerto, San Román del Moroso, Santa Catalina del Cintul, Santuario de Virgen de la Peña, ermita de San Cipriano, ermita de Monte Corona, etc.
*Museums: Cantabrian Sea Maritime Museum, Ethnographic Museum of Cantabria, Santander Museum of Fine Arts, Regional Museum of Prehistory and Arqueology of Cantabria, Cantabrian Museum of Nature, Altamira National Museum and Investigation Centre, and others.
 *University of Cantabria
*International University Menéndez Pelayo
*Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia
*Campus Comillas
*CESINE
*European University of the Atlantic, Universidad Europea del Atlántico
*University of Cantabria
*International University Menéndez Pelayo
*Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia
*Campus Comillas
*CESINE
*European University of the Atlantic, Universidad Europea del Atlántico
 Regarding the fairs, understood as big markets of products periodically celebrated, it is remarkable the ''Livestock Fair of Torrelavega'' taking place in the National Livestock Market "Jesús Collado Soto", the third biggest of Spain, that groups the buy and sell of all kinds of cattle in the region itself and the adjacent ones, being the bovine the main product. All over the region cattle and typical products fairs are celebrated weekly, monthly, or annually to gather the neighbours of the land. There are many different festivities in Cantabria, some of them limited just to small villages, but there are also festivals that attract tourism from all over the country. The most important are the following:
*''La Vijanera'' (Winter Carnival), celebrated during the first Sunday of the year in Silió. It celebrates the end of the short winter days and the arrival of the sun. The representation of a white bear hunt takes place all over this little village. The traditional dressing of the characters in the play, the trapajones and the zarramacos, is one of its main features.
*''Carnaval marinero'' (Sailor Carnival), in February in
Regarding the fairs, understood as big markets of products periodically celebrated, it is remarkable the ''Livestock Fair of Torrelavega'' taking place in the National Livestock Market "Jesús Collado Soto", the third biggest of Spain, that groups the buy and sell of all kinds of cattle in the region itself and the adjacent ones, being the bovine the main product. All over the region cattle and typical products fairs are celebrated weekly, monthly, or annually to gather the neighbours of the land. There are many different festivities in Cantabria, some of them limited just to small villages, but there are also festivals that attract tourism from all over the country. The most important are the following:
*''La Vijanera'' (Winter Carnival), celebrated during the first Sunday of the year in Silió. It celebrates the end of the short winter days and the arrival of the sun. The representation of a white bear hunt takes place all over this little village. The traditional dressing of the characters in the play, the trapajones and the zarramacos, is one of its main features.
*''Carnaval marinero'' (Sailor Carnival), in February in
 The traditional sport of Cantabria is the game of ''bolos''
The traditional sport of Cantabria is the game of ''bolos''History of the ''Bolos'' in Cantabria.
Selaya Township website. Retrieved on 5 August 2007. (skittles (sport), skittles) in its four forms: ''bolo palma'', ''pasabolo tablón'', ''pasabolo losa'' and ''bolo pasiego''. The first one is the most widespread, exceeding regional nature and reaching the eastern zone of Asturias and also being the most complex in its game rules. The existence of ''boleras'' or skittle rings is important in every Cantabrian township, often being near the church or the village pub. Since the late 1980s, skittle play has consolidated with the reinforcement of skittle schools, revamped by different town councils and Cantabrian institutions, various competitions, and media coverage. The remo (rowing (sport), rowing) is a very traditional sport in the coastal towns. The origins of rowing in Cantabria go back many centuries, when several ''traineras'' (traditional fishing longboats) competed for the selling of the caught fish, which was reserved for the first ship to arrive to the fish market. At the end of the 19th century, work became sport and people started to celebrate regattas between Cantabrian townships. The sport clubs of Cantabria, especially the Sociedad Deportiva de Remo Astillero, Astillero, Sociedad Deportiva de Remo Castro Urdiales, Castro Urdiales, and the Sociedad Deportiva de Remo Pedreña, Pedreña belong to the most prize-winning teams of the history of this sport, and nowadays they are having one of the best moments after a decades-long period of trophy drought. The Pasiegan jump is another of the outstanding rural sports of the region and a clear example of how the use of a work skill that disappears with the pass of time, gives rise to games and competition. Similar to other forms, like the Salto del pastor, Canarian shepherd jump, in the beginning this technique was used in the Pasiegan valleys to cross the stone walls, the fences, the creeks or the ravines that bordered the fields and obstructed the pass in the abrupt geography of the highland areas of Cantabria.
Referring to mass sports, Cantabria is present in national and international competitions through teams such as the ''Racing de Santander'', the ''RS Gimnástica de Torrelavega'' and the Cantabria autonomous football team in Football in Spain, football or the ''Independiente RC'' in División de Honor de Rugby, rugby union. The ''CB Cantabria, Club Balonmano Cantabria'' that won Liga ASOBAL, Leagues and Copa del Rey de Balonmano, King's Cups as well as IHF Super Globe, EHF Champions League, EHF Cup Winners' Cup and EHF Cup in team handball, handball or the Cantabria Baloncesto, Cantabria Lobos that played in the Liga ACB, ACB in basketball represented the highest level of the Cantabrian sport in the recent past.
The Pasiegan jump is another of the outstanding rural sports of the region and a clear example of how the use of a work skill that disappears with the pass of time, gives rise to games and competition. Similar to other forms, like the Salto del pastor, Canarian shepherd jump, in the beginning this technique was used in the Pasiegan valleys to cross the stone walls, the fences, the creeks or the ravines that bordered the fields and obstructed the pass in the abrupt geography of the highland areas of Cantabria.
Referring to mass sports, Cantabria is present in national and international competitions through teams such as the ''Racing de Santander'', the ''RS Gimnástica de Torrelavega'' and the Cantabria autonomous football team in Football in Spain, football or the ''Independiente RC'' in División de Honor de Rugby, rugby union. The ''CB Cantabria, Club Balonmano Cantabria'' that won Liga ASOBAL, Leagues and Copa del Rey de Balonmano, King's Cups as well as IHF Super Globe, EHF Champions League, EHF Cup Winners' Cup and EHF Cup in team handball, handball or the Cantabria Baloncesto, Cantabria Lobos that played in the Liga ACB, ACB in basketball represented the highest level of the Cantabrian sport in the recent past.
 Cantabria has been the birthplace of exceptional and notable individuals in fields such as literature, arts, sciences, etc. Many of them have played a decisive role, not only in the history and events of the region, but also on the national and international levels. These include:
*Business: Jesús de Polanco, Emilio Botín, Ana Patricia Botín, Ana Patricia Botin, Vicente Calderón, Vicente Calderon
*Sports: Francisco Gento, Santillana (footballer), "Santillana", José Manuel Abascal, Seve Ballesteros, Óscar Freire, Juan José Cobo, Cecilio Lastra, Francisco Ventoso, Ruth Beitia, Sergio Canales, Athenea del Castillo
*Music: Ataúlfo Argenta, David Bustamante, La Fuga (band), La Fuga
*Film, radio, and TV: Mario Camus, Manuel Gutiérrez Aragón, Eduardo Noriega (Spanish actor), Eduardo Noriega, Antonio Resines, Nacho Vigalondo, Ricardo Palacios.
*Military: Corocotta, Pedro Velarde
*Religion: Emeterius and Celedonius, San Emeterio, San Celedonio, Beatus of Liébana
*Explorers: Juan de la Cosa, Vital Alsar, José de Bustamante y Guerra
*Literature: José María de Pereda, Concha Espina, Gerardo Diego, Álvaro Pombo, Luys Santa Marina.
*Painting: María Blanchard, José de Madrazo, Francisco González Gómez
*Science and technology: Leonardo Torres Quevedo, Juan de Herrera
*Politics: Luis Carrero Blanco, José Luis Zamanillo González-Camino, José Luis Zamanillo, Alfredo Pérez Rubalcaba, Joaquín Leguina, Miguel Ángel Revilla, Antonio Valverde y Cosío
*Sociology: Rosa Cobo Bedía
Cantabria has been the birthplace of exceptional and notable individuals in fields such as literature, arts, sciences, etc. Many of them have played a decisive role, not only in the history and events of the region, but also on the national and international levels. These include:
*Business: Jesús de Polanco, Emilio Botín, Ana Patricia Botín, Ana Patricia Botin, Vicente Calderón, Vicente Calderon
*Sports: Francisco Gento, Santillana (footballer), "Santillana", José Manuel Abascal, Seve Ballesteros, Óscar Freire, Juan José Cobo, Cecilio Lastra, Francisco Ventoso, Ruth Beitia, Sergio Canales, Athenea del Castillo
*Music: Ataúlfo Argenta, David Bustamante, La Fuga (band), La Fuga
*Film, radio, and TV: Mario Camus, Manuel Gutiérrez Aragón, Eduardo Noriega (Spanish actor), Eduardo Noriega, Antonio Resines, Nacho Vigalondo, Ricardo Palacios.
*Military: Corocotta, Pedro Velarde
*Religion: Emeterius and Celedonius, San Emeterio, San Celedonio, Beatus of Liébana
*Explorers: Juan de la Cosa, Vital Alsar, José de Bustamante y Guerra
*Literature: José María de Pereda, Concha Espina, Gerardo Diego, Álvaro Pombo, Luys Santa Marina.
*Painting: María Blanchard, José de Madrazo, Francisco González Gómez
*Science and technology: Leonardo Torres Quevedo, Juan de Herrera
*Politics: Luis Carrero Blanco, José Luis Zamanillo González-Camino, José Luis Zamanillo, Alfredo Pérez Rubalcaba, Joaquín Leguina, Miguel Ángel Revilla, Antonio Valverde y Cosío
*Sociology: Rosa Cobo Bedía
Camara de Comercio de Cantabria
{{Authority control Cantabria, Green Spain NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1982 Autonomous communities of Spain
autonomous community
eu, autonomia erkidegoa
ca, comunitat autònoma
gl, comunidade autónoma
oc, comunautat autonòma
an, comunidat autonoma
ast, comunidá autónoma
, alt_name =
, map =
, category = Autonomous administra ...
in northern Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
with Santander
Santander may refer to:
Places
* Santander, Spain, a port city and capital of the autonomous community of Cantabria, Spain
* Santander Department, a department of Colombia
* Santander State, former state of Colombia
* Santander de Quilichao, a m ...
as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the east by the Basque autonomous community
The Basque Country (; eu, Euskadi ; es, País Vasco ), also called Basque Autonomous Community ( eu, Euskal Autonomia Erkidegoa, links=no, EAE; es, Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco, links=no, CAPV), is an autonomous community of Spain. It ...
(province of Biscay
Biscay (; eu, Bizkaia ; es, Vizcaya ) is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country, heir of the ancient Lordship of Biscay, lying on the south shore of the eponymous bay. The capital and largest city is Bilbao.
...
), on the south by Castile and León ( provinces of León, Palencia
Palencia () is a city of Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the province of Palencia.
Located in the Northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, in the northern half o ...
and Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of ...
), on the west by the Principality of Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea
The Cantabrian Sea; french: Mer Cantabrique, gl, Mar Cantábrico, ast, Mar Cantábricu, eu, Kantauri. is the term used mostly in Spain to describe the coastal sea of the Atlantic Ocean that borders the northern coast of Spain and the southwe ...
(Bay of Biscay).
Cantabria belongs to ''Green Spain
Cantabrian Coast is the name given to a lush natural region in Northern Spain, stretching along the Atlantic coast from the border with Portugal to the border with France. The region includes nearly all of Galicia, Asturias, and Cantabria, in ...
'', the name given to the strip of land between the Bay of Biscay and the Cantabrian Mountains
, etymology=Named after the Cantabri
, photo=Cordillera Cantábrica vista desde el Castro Valnera.jpg
, photo_caption=Cantabrian Mountains parallel to the Cantabrian Sea seen from Castro Valnera in an east-west direction. In the background, ...
, so called because of its particularly lush vegetation, due to the wet and moderate oceanic climate. The climate is strongly influenced by Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
winds trapped by the mountains; the average annual precipitation is about .
Cantabria has archaeological sites from the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
period, although the first signs of human occupation date from the Lower Paleolithic. The most significant site for cave paintings is that in the cave of Altamira
The Cave of Altamira (; es, Cueva de Altamira ) is a cave complex, located near the historic town of Santillana del Mar in Cantabria, Spain. It is renowned for prehistoric cave art featuring charcoal drawings and polychrome paintings of contem ...
, dating from about 37,000 BC and declared, along with nine other Cantabrian caves, as World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
. Historically, the territory sits in the Ancient Period Cantabri
The Cantabri ( grc-gre, Καντάβροι, ''Kantabroi'') or Ancient Cantabrians, were a pre-Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. Thes ...
a, but from the Late Middle Ages to the early 19th century, the name Cantabria usually refers to the territory of the Basques, especially the lordship of Biscay
The Lordship of Biscay ( es, Señorío de Vizcaya, Basque: ''Bizkaiko jaurerria'') was a region under feudal rule in the region of Biscay in the Iberian Peninsula between 1040 and 1876, ruled by a political figure known as the Lord of Biscay. On ...
.
The modern Province of Cantabria was constituted on 28 July 1778 at Puente San Miguel, Reocín
Reocín is a municipality in Cantabria, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, nation ...
. The yearly Day of the Institutions holiday on 28 July celebrates this. The Organic Law of the Autonomy Statute of Cantabria, approved on 30 December 1981, gave the region its own institutions of self-government.
Etymology and usage
 Numerous authors, including Isidore of Seville,
Numerous authors, including Isidore of Seville, Julio Caro Baroja
Julio Caro Baroja (13 November 1914 – 18 August 1995) was a Spanish anthropologist, historian, linguist and essayist. He was known for his special interest in Basque culture, Basque history and Basque society. Of Basque ancestry, he was the ...
, Aureliano Fernández Guerra and Adolf Schulten, have explored the etymology of the name ''Cantabria'', yet its origins remain uncertain. The Online Etymology Dictionary states the root ''cant-'' is said to come from the Celtic for "rock" or "rocky", while ''-abr'' was a common suffix used in Celtic regions. Thus, ''Cantabrian'' could mean "people who live in the rocks" or " highlanders", a reference to the steep and mountainous territory of Cantabria.
The name ''Cantabria'' could also be related to the Celtic root "kant" or "cant" meaning edge or rim thus "coastal district," or "corner-land", "land on the edge" thus having the same probable derivation as the name of the English county of ''Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
'' and Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of ...
, one of its major cities.During the Spanish liberal regimes of the 19th century, the term came to be increasingly associated to the province of Santander. However, during the late medieval and Modern Period literature, ''Cantabria'' and ''Cantabrians'' refer to the Basque Country, especially the lordship of Biscay, and the Basques.
Geography


Relief
Cantabria is a mountainous and coastal region, with important natural resources. It has two distinct areas which are well differentiated morphologically: *Coast. A coastal strip of low, wide and gently rolling valleys some 10 kilometres in width, the altitude of which does not rise above 500 metres, and which meets the ocean in a line of abrupt cliffs broken by river estuaries, formingria
A ria (; gl, ría) is a coastal inlet formed by the partial submergence of an unglaciated river valley. It is a drowned river valley that remains open to the sea.
Definitions
Typically rias have a dendritic, treelike outline although they ca ...
s and beaches. Santander Bay is the most prominent indentation in the coastline. To the south, the coastal strip rises to meet the mountains.
*Mountains. This is a long barrier made up of abruptly rising mountains parallel to the sea, which are part of the Cantabrian Mountains
, etymology=Named after the Cantabri
, photo=Cordillera Cantábrica vista desde el Castro Valnera.jpg
, photo_caption=Cantabrian Mountains parallel to the Cantabrian Sea seen from Castro Valnera in an east-west direction. In the background, ...
. The mountains are mostly made of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
with karst topography, and occupy most of Cantabria's area. They form deep valleys running north–south. The torrential rivers are short, fast flowing and of great eroding power, so the slopes are steep. The valleys define different natural regions, delimited physically by the intervening mountain ranges: Liébana
Liébana is a ''Comarcas of Cantabria, comarca'' of Cantabria (Spain). It covers 575 square kilometres and is located in the far southwest of Cantabria, bordering Asturias, León (province), León and Palencia (province), Palencia. It is made up o ...
, Saja-Nansa
The Valleys of the Saja and Nansa Rivers comprise an administrative ''comarca'' in Cantabria, Spain. It is formed by the valleys of said rivers, each one being a natural ''comarca'' of its own.
Saja valley
The valley of the Saja River, located ...
, Besaya, Pas- Pisueña, Miera, Asón- Gándara, Campoo
Campoo (formally Campoo-Los Valles) is a ''comarca'' of Cantabria ( Spain) located in the High Ebro, with a surface little bigger than 1,000 km2, and including the municipalities of Hermandad de Campoo de Suso, Campoo de Enmedio, Campoo de Yu ...
. To the 'mountain' region belongs the Escudo Range, a mountain range of high that covers in a parallel line to the coast in the West part of Cantabria.
Towards the south are higher mountains, the tops of which form the watershed between the drainage basins of the Rivers Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
, Duero
The Douro (, , ; es, Duero ; la, Durius) is the highest-flow river of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province, central Spain, meanders south briefly then flows generally west through the north-west part of ...
and the rivers that flow into the Bay of Biscay. These peaks generally exceed from the Pass of San Glorio in the west to the Pass of Los Tornos in the eastern part: Peña Labra, Castro Valnera and the mountain passes of Sejos, El Escudo and La Sía. The great limestone masses of Picos de Europa
The Picos de Europa ("Peaks of Europe", also the Picos) are a mountain range extending for about , forming part of the Cantabrian Mountains in northern Spain.
The range is situated in the Autonomous Communities of Asturias, Cantabria and Castil ...
also stand out in the southwest of the region: most of their summits exceed , and their topography is shaped by the former presence of glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s.
Climate
 Due to the gulf stream, Cantabria, as well as the rest of "Green Spain", has a much more
Due to the gulf stream, Cantabria, as well as the rest of "Green Spain", has a much more temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
than might be expected for its latitude, which is comparable to that of Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
. The region has a humid oceanic climate, with warm summers and mild winters. Annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
is around 1,200 mm at the coasts and higher in the mountains. The mean temperature is about . Snow is frequent in the higher zones of Cantabria between the months of October and March. Some zones of Picos de Europa, over 2,500 metres high, have an alpine climate
Alpine climate is the typical weather (climate) for elevations above the tree line, where trees fail to grow due to cold. This climate is also referred to as a mountain climate or highland climate.
Definition
There are multiple definitions o ...
with snow persisting year round. The driest months are July and August. The mountainous relief of Cantabria has a dominant effect on local microclimate in Cantabria. It is the main cause of the peculiar meteorologic situations like the so-called "suradas" ( Ábrego wind), due to the foehn effect: the southerly wind coming down from the mountains blows strongly and dry, increasing the temperature closer to the coast. This causes a decrease in air humidity and rainfall. These conditions are more frequent in autumn and winter, and the temperatures are commonly higher than . Fires are often helped by this type of wind: one example is the fire that destroyed part of the city of Santander in the winter of 1941. In these specific cases in the southern part of the mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
the dry adiabatic gradient produces different conditions to the rest of the region: the wind there is fresher and more humid, and there is more rain.
Hydrology
The rivers of Cantabria are short and rapid, descending steeply because the sea is so close to their source in the Cantabrian Mountains. They flow perpendicular to the coastline, except for theEbro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
. They also generally flow year round due to constant rainfall. Nevertheless, the rate of flow is modest (20 m³/s annual average) compared to the other rivers of the Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
. The rapidness of their waters, caused by their steep descents, gives them great erosive power, creating the narrow V-shaped valleys characteristic of Green Spain. The environmental condition of the rivers is generally good, although increasing human activity due to rising population in the valleys continues to pose a challenge.
drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
, are:
* North Basin (flows into the Cantabrian Sea
The Cantabrian Sea; french: Mer Cantabrique, gl, Mar Cantábrico, ast, Mar Cantábricu, eu, Kantauri. is the term used mostly in Spain to describe the coastal sea of the Atlantic Ocean that borders the northern coast of Spain and the southwe ...
)
** Agüera
** Asón
** Besaya
** Deva
** Miera
** Nansa
** Pas
** Saja
*Ebro Basin The Ebro Basin was a foreland basin that formed to the south of the Pyrenees during the Paleogene. It was also limited to the southeast by the Catalan Coastal Ranges. It began as a fully marine basin with connections to both the Atlantic Ocean and ...
(flows into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
)
** Híjar
**Ebro
* Duero Basin (flows into the Atlantic Ocean)
Cantabria is the only autonomous community whose rivers flow into every one of the seas which surround the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
: The Cantabrian Sea, the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
Vegetation
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s.
Cantabria has vegetation typical of the Atlantic side of the Iberian Peninsula. It is characterized by forests of leafy deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
trees such as oak and European beech
''Fagus sylvatica'', the European beech or common beech is a deciduous tree belonging to the beech family Fagaceae.
Description
''Fagus sylvatica'' is a large tree, capable of reaching heights of up to tall and trunk diameter, though more ...
. Nevertheless, human intervention dating back to ancient times has favored the creation of pastures, allowing the existence of large areas of grassland and prairies suitable for grazing cattle. These grasslands are mingled with plantations of eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as e ...
and native oak. The southern part of Cantabria, including the ''comarca
A ''comarca'' (, or , or ) is a traditional region or local administrative division found in Portugal, Spain and some of their former colonies, like Brazil, Nicaragua, and Panama. The term is derived from the term ''marca'', meaning a "march, ...
'' of Campoo the fringes of the Castilian plateau, is characterized by the transition to drier vegetation. Another diversifying factor which contributes to local variation within the region is the Mediterranean ecotone
An ecotone is a transition area between two biological communities, where two communities meet and integrate. It may be narrow or wide, and it may be local (the zone between a field and forest) or regional (the transition between forest and gras ...
, giving rise to species unique to the region, such as the holm oak and arbutus trees, which are found in poor limestone soils with little moisture.
In Cantabria there are several zones of plant life:
*The coastal strip, including sandy dunes with minimal vegetation. Adjacent to these are steep cliffs with plants unique to that type of terrain.
 *The maritime region, near the coast and including altitudes up to 500 metres. Originally it had mixed deciduous forests containing
*The maritime region, near the coast and including altitudes up to 500 metres. Originally it had mixed deciduous forests containing ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
, linden, bay laurel
''Laurus nobilis'' is an aromatic evergreen tree or large shrub with green, glabrous (smooth) leaves. It is in the flowering plant family Lauraceae. It is native to the Mediterranean region and is used as bay leaf for seasoning in cookin ...
, hazel, maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http ...
, oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
, poplar, birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains ...
, holm oak, and others. The riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks a ...
parts were filled with forests of alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few sp ...
and willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
. Today these native forests have almost completely disappeared, leaving only reserves in area of poor arability. In their place there are grasslands which are quite productive in the temperate climate and which sustain the economy of rural Cantabria. Next to these are very large monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monoculture is widely used in intensive farming and in organic farming: both a 1,000-hectare/acre cornfield and a 10-ha/acre field of organic kale are ...
plantations of eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as e ...
for paper production, of disastrous ecological consequences to the biodiversity and climate of the region.
During the last two decades of the 20th century, and due mainly to European agricultural policies (CAP
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. Caps typically have a visor, or no brim at all. They are popular in casual and informal se ...
), many farmers substituted forestry for livestock farming, so as to avoid unemployment and poverty. This provoked a surge of eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as e ...
– see eucalyptus article on Spanish Wikipedia – plantations (and to a less extent of pines
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
) which often hid the illegal destruction of native forests, just as the spread of livestock farming had done in the past by the endemic conversion of forest into prairie. These acts have been laxly controlled by the local councils or the central governments, in a process that clearly follows the saying: "''Pan para hoy, hambre para mañana''" (which translates as 'Bread for today, hunger for tomorrow'; i.e., "short-term gain, long-term pain").
 The plantation of pines has given way in the last decades to that of eucalyptus because this
The plantation of pines has given way in the last decades to that of eucalyptus because this non-indigenous species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there ...
has no natural attacker within the European ecosystem (while pines are highly vulnerable to the pine processionary).
Both in relative and absolute terms the use of woods for forestry has increased in Cantabria, and is now almost 70% of all woods in the region.
*The foothills, from 500 to 1,100 metres altitude are colonized by monoculture forests of oak (''Quercus robur
''Quercus robur'', commonly known as common oak, pedunculate oak, European oak or English oak, is a species of flowering plant in the beech and oak family, Fagaceae. It is a large tree, native to most of Europe west of the Caucasus. It is widel ...
'' and ''Quercus petraea
''Quercus petraea'', commonly known as the sessile oak, Cornish oak, Irish Oak or durmast oak, is a species of oak tree native to most of Europe and into Anatolia and Iran. The sessile oak is the national tree of Ireland, and an unofficial embl ...
'') on the sunnier slopes. In more shaded areas and especially from about 800 metres there are forests of European beech
''Fagus sylvatica'', the European beech or common beech is a deciduous tree belonging to the beech family Fagaceae.
Description
''Fagus sylvatica'' is a large tree, capable of reaching heights of up to tall and trunk diameter, though more ...
which are the main food source in winter for many animal species.
 * The subalpine plane, in this high country, the plant life is composed of birch, scrub, and
* The subalpine plane, in this high country, the plant life is composed of birch, scrub, and grasses
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns ...
which are especially important for the economy because during the summer they serve as pasture for grazing cattle and horses.
Along with these characteristics it would also be necessary to mention peculiarities of the ''comarca'' of Liébana
Liébana is a ''Comarcas of Cantabria, comarca'' of Cantabria (Spain). It covers 575 square kilometres and is located in the far southwest of Cantabria, bordering Asturias, León (province), León and Palencia (province), Palencia. It is made up o ...
, which has a microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squ ...
very similar to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
, allowing to grow cork oak
''Quercus suber'', commonly called the cork oak, is a medium-sized, evergreen oak tree in the section ''Quercus'' sect. ''Cerris''. It is the primary source of cork for wine bottle stoppers and other uses, such as cork flooring and as the core ...
s, vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themsel ...
s and olives, and which is still very well conserved from human activity.
The other remarkable ''comarca'' is Campoo
Campoo (formally Campoo-Los Valles) is a ''comarca'' of Cantabria ( Spain) located in the High Ebro, with a surface little bigger than 1,000 km2, and including the municipalities of Hermandad de Campoo de Suso, Campoo de Enmedio, Campoo de Yu ...
, in southern Cantabria, with its Pyrenean oak.
Natural parks
 There are seven natural areas in this autonomous community designated as
There are seven natural areas in this autonomous community designated as Natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
or national parks:
* Picos de Europa National Park
*Collados del Asón Natural Park
* Santoña, Victoria and Joyel Marshes Natural Park
*Macizo de Peña Cabarga Natural Park
*Oyambre Natural Park
*Saja-Besaya Natural Park
Saja-Besaya Natural Park is Cantabrias largest natural park on the northern slope of the Cantabrian Mountains in West Central Cantabria, Spain. Its hunting reserve is approximately 1800km², the largest and most important in Spain.
Geography
T ...
*Dunes of Liencres Natural Park
The most important of these is the Picos de Europa National Park, which affects Castile and León and Asturias in addition to Cantabria, the three autonomous communities sharing its management.
Santoña, Victoria and Joyel marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found a ...
es are also Special Protection Area
A Special Protection Area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certa ...
s for the birds (ZEPA).
Furthermore, nine Sites of Community Importance
A Site of Community Importance (SCI) is defined in the European Commission Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC) as a site which, in the biogeographical region or regions to which it belongs, contributes significantly to the maintenance or restoration at ...
(LIC) have been declared: Western Mountain, Eastern Mountain, Western Rias and Oyambre Dunes, Dunes of Liencres and Estuary of the Pas, El Puntal Dunes and Estuary of the Miera, Ria de Ajo, Marshes of Noja-Santoña
Santoña is a town in the eastern coast of the autonomous community of Cantabria, on the north coast of Spain. It is situated by the bay of the same name. It is from the capital Santander. Santoña is divided into two zones, an urban plain, and ...
, Escudo de Cabuérniga Range and several caves with important bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
colonies.
Demographics

 According to the 2009 census, the region has a population of 591,886 which constitutes 1.29% of the population of Spain, with the population density numbering 106.8 people per kilometer. The average life expectancy for male inhabitants is 75 years; for female inhabitants, it is 83 years. Eight years later in 2017 the population has fallen to 581,477 according to INE.
In relative contrast to other regions of Spain, Cantabria has not experienced much immigration. In 2007, only 4.7% of the population were immigrants. The predominant countries of origin for immigrants to Cantabria are Colombia,
According to the 2009 census, the region has a population of 591,886 which constitutes 1.29% of the population of Spain, with the population density numbering 106.8 people per kilometer. The average life expectancy for male inhabitants is 75 years; for female inhabitants, it is 83 years. Eight years later in 2017 the population has fallen to 581,477 according to INE.
In relative contrast to other regions of Spain, Cantabria has not experienced much immigration. In 2007, only 4.7% of the population were immigrants. The predominant countries of origin for immigrants to Cantabria are Colombia, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
, and Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
.
The majority of the population resides in the coastal area, particularly in two cities: Santander
Santander may refer to:
Places
* Santander, Spain, a port city and capital of the autonomous community of Cantabria, Spain
* Santander Department, a department of Colombia
* Santander State, former state of Colombia
* Santander de Quilichao, a m ...
, with 183,000 people, and Torrelavega
Torrelavega ( Cantabrian: ''Torlavega'') is a municipality and important industrial and commercial hub in the single province Autonomous Community of Cantabria, northern Spain.
It is situated roughly 8 kilometres from the Cantabrian Coast and 27.5 ...
, the second largest urban and industrial centre in Cantabria, having a population of around 60,000. These two cities form a conurbation known as the Santander-Torrelavega metropolitan area. Castro Urdiales has an official population of 28,542, making it the fourth largest in the region because of its proximity to the Bilbao
)
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize = 275 px
, map_caption = Interactive map outlining Bilbao
, pushpin_map = Spain Basque Country#Spain#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption ...
metropolitan area, there are a large number of people not registered in Castro Urdiales, and the true count may be double the official figure.
The most populated municipalities of Cantabria as of 2018 are the following:
# Santander
Santander may refer to:
Places
* Santander, Spain, a port city and capital of the autonomous community of Cantabria, Spain
* Santander Department, a department of Colombia
* Santander State, former state of Colombia
* Santander de Quilichao, a m ...
(pop. 172,044)
# Torrelavega
Torrelavega ( Cantabrian: ''Torlavega'') is a municipality and important industrial and commercial hub in the single province Autonomous Community of Cantabria, northern Spain.
It is situated roughly 8 kilometres from the Cantabrian Coast and 27.5 ...
(pop. 51,687)
#Castro-Urdiales
Castro Urdiales is a seaport of northern Spain, in the autonomous community of Cantabria, situated on the Bay of Biscay.
Castro Urdiales is a modern town, although its castle and the Gothic-style parish church of Santa María de la Asunción, date ...
(pop. 31,977)
# Camargo (pop. 30,263)
# Piélagos
Piélagos is a municipality in Cantabria
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its current Stat ...
(pop. 25,223)
# El Astillero (pop. 18,108)
# Santa Cruz de Bezana (pop. 12,964)
# Laredo (pop. 11,148)
#Santoña
Santoña is a town in the eastern coast of the autonomous community of Cantabria, on the north coast of Spain. It is situated by the bay of the same name. It is from the capital Santander. Santoña is divided into two zones, an urban plain, and ...
(pop. 11,050)
# Los Corrales de Buelna
Los Corales de Buelna is a municipality in Cantabria
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its ...
(pop. 10,910)
# Reinosa
Reinosa is a municipality in Cantabria, Spain. , it has 10,307 inhabitants. The municipality, one of the smallest by land area in Cantabria, is notable for being one of the nearest towns to the headwaters of the Ebro River. It is surrounded by th ...
(pop. 9,095)
History
Roman Empire
Cato the Elder
Marcus Porcius Cato (; 234–149 BC), also known as Cato the Censor ( la, Censorius), the Elder and the Wise, was a Roman soldier, senator, and historian known for his conservatism and opposition to Hellenization. He was the first to write his ...
speaks in his book ''Origines
(, "Origins") is the title of a lost work on Roman and Italian history by Cato the Elder, composed in the early-2nd centuryBC.
Contents
According to Cato's biographer Cornelius Nepos, the ''Origins'' consisted of seven books. Book I was the hi ...
'' about the source of the Ebro River in the country of the Cantabri
The Cantabri ( grc-gre, Καντάβροι, ''Kantabroi'') or Ancient Cantabrians, were a pre-Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. Thes ...
:
There are about 150 references to Cantabria or the Cantabri in surviving Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
texts. The Cantabri were used as mercenaries in various conflicts, both within the Iberian Peninsula and elsewhere. It is certain that they participated the Second Punic War, from references by Silius Italicus and Horace. When C. Hostilius Mancinus was besieging Numantia
Numantia ( es, Numancia) is an ancient Celtiberian settlement, whose remains are located on a hill known as Cerro de la Muela in the current municipality of Garray ( Soria), Spain.
Numantia is famous for its role in the Celtiberian Wars. In ...
, he withdrew upon learning that Cantabri and Vaccaei
The Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre-Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania (specifically in Castile and León). Their capital was ''Intercatia'' in P ...
were present among his auxiliaries
Auxiliaries are support personnel that assist the military or police but are organised differently from regular forces. Auxiliary may be military volunteers undertaking support functions or performing certain duties such as garrison troops, ...
. The Cantabrian Wars
The Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC) (''Bellum Cantabricum''), sometimes also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars (''Bellum Cantabricum et Asturicum''), were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what tod ...
began in They were defeated by Agrippa Agrippa may refer to:
People Antiquity
* Agrippa (mythology), semi-mythological king of Alba Longa
* Agrippa (astronomer), Greek astronomer from the late 1st century
* Agrippa the Skeptic, Skeptic philosopher at the end of the 1st century
* Agri ...
with great slaughter in , but they revolted again under Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
and were never entirely subdued.
In older geographers, the term Cantabria referred to an expansive country bounded by the Cantabrian Sea (the Bay of Biscay), the western side of the Sella valley in Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
, the hillfort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
of Peña Amaya in Burgos (province), Burgos, and along the Aguera River almost as far as Castro Urdiales. It thus included areas of Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
, Santander
Santander may refer to:
Places
* Santander, Spain, a port city and capital of the autonomous community of Cantabria, Spain
* Santander Department, a department of Colombia
* Santander State, former state of Colombia
* Santander de Quilichao, a m ...
, Biscay, and Guipuzcoa. Following the Roman conquest of Spain, however, it was restricted to the area of Santander
Santander may refer to:
Places
* Santander, Spain, a port city and capital of the autonomous community of Cantabria, Spain
* Santander Department, a department of Colombia
* Santander State, former state of Colombia
* Santander de Quilichao, a m ...
and eastern Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
, forming a part of Hispania Tarraconensis ("Tarragonan Spain"). The principal tribes of the area were the Pleutauri, the Varduli, the Autrigones, the Tuisi, and the Conisci or Concaui, who were known for blood drinking, feeding on their horses' blood. The area was well settled, with the largest city being Juliobriga, and the local mountains exploited for lead mines.
Middle Ages
 Following the collapse of the Roman Empire, Cantabria regained its independence from the rule of the Visigoths. In 574, King Liuvigild attacked Cantabria and managed to capture the south of the country, including the city of Amaya (Burgos), Amaya, where he established a Visigothic province called the Duchy of Cantabria (see picture), which would serve as a Limes (Roman Empire), limes or frontier zone to contain the Cantabri as well as their neighbors the Vascones. To the north of this cordon, however, the Cantabri continued to live independently until the Arab invasion. In 714, a mixed Arab/Berber people, Berber army of Muslim Moors invaded the upper valleys of the Ebro and succeeded in capturing Amaya, the Cantabrian capital, forcing the Cantabrians back to their traditional frontiers, where they joined forces with the Kingdom of Asturias.
In the first chronicles of the Reconquista, Cantabria still appears to be acknowledged as a region. In the ''Albendense Chronicle'', when speaking of Alfonso I of Asturias, Alfonso I, it says, "This was the son of Peter of Cantabria, Peter, the duke of Cantabria".
During the 9th century, on mentioning the monastery of Saint Zacharias, Eulogius pinpoints it in ''Seburim'' (maybe Zubiri) on the river Arga, "waters all of Cantabria", in a letter sent to the bishop of Pamplona Williesind, suggesting a region stretching out far into the east. From this period on, source documents barely reference Cantabria by name, with ''Asturias'' featuring in names of the ''comarcas'' called ''Asturias de Santillana'', ''Asturias de Trasmiera'' and ''Asturias de Laredo''.
Following the collapse of the Roman Empire, Cantabria regained its independence from the rule of the Visigoths. In 574, King Liuvigild attacked Cantabria and managed to capture the south of the country, including the city of Amaya (Burgos), Amaya, where he established a Visigothic province called the Duchy of Cantabria (see picture), which would serve as a Limes (Roman Empire), limes or frontier zone to contain the Cantabri as well as their neighbors the Vascones. To the north of this cordon, however, the Cantabri continued to live independently until the Arab invasion. In 714, a mixed Arab/Berber people, Berber army of Muslim Moors invaded the upper valleys of the Ebro and succeeded in capturing Amaya, the Cantabrian capital, forcing the Cantabrians back to their traditional frontiers, where they joined forces with the Kingdom of Asturias.
In the first chronicles of the Reconquista, Cantabria still appears to be acknowledged as a region. In the ''Albendense Chronicle'', when speaking of Alfonso I of Asturias, Alfonso I, it says, "This was the son of Peter of Cantabria, Peter, the duke of Cantabria".
During the 9th century, on mentioning the monastery of Saint Zacharias, Eulogius pinpoints it in ''Seburim'' (maybe Zubiri) on the river Arga, "waters all of Cantabria", in a letter sent to the bishop of Pamplona Williesind, suggesting a region stretching out far into the east. From this period on, source documents barely reference Cantabria by name, with ''Asturias'' featuring in names of the ''comarcas'' called ''Asturias de Santillana'', ''Asturias de Trasmiera'' and ''Asturias de Laredo''.
 From a central core formed by the ''Hermandad de las Cuatro Villas'' (''Brotherhood of the Four Cities'') (Santander, Laredo, Castro Urdiales and San Vicente de la Barquera), the ''Hermandad de las Marismas'' (''Brotherhood of the Marshes'') was created, thereby uniting all the important seaports to the East of Asturias. During the period of the Reconquista, the Four Cities actively participated in the re-settling of Andalusia, dispatching men and ships. The coastal port cities of Cádiz and El Puerto de Santa María were settled by families from the Cantabrian Sea ports. Ships from the Four Cities took part in the taking of Seville, destroying the ship bridge linking Triana (Seville), Triana and Sevilla, a victory that is represented by the Carrack and the Torre del Oro of Sevilla in the coat of arms of Coat of arms of Santander, Santander, Coat of arms of Cantabria and Avilés (Asturias).
From a central core formed by the ''Hermandad de las Cuatro Villas'' (''Brotherhood of the Four Cities'') (Santander, Laredo, Castro Urdiales and San Vicente de la Barquera), the ''Hermandad de las Marismas'' (''Brotherhood of the Marshes'') was created, thereby uniting all the important seaports to the East of Asturias. During the period of the Reconquista, the Four Cities actively participated in the re-settling of Andalusia, dispatching men and ships. The coastal port cities of Cádiz and El Puerto de Santa María were settled by families from the Cantabrian Sea ports. Ships from the Four Cities took part in the taking of Seville, destroying the ship bridge linking Triana (Seville), Triana and Sevilla, a victory that is represented by the Carrack and the Torre del Oro of Sevilla in the coat of arms of Coat of arms of Santander, Santander, Coat of arms of Cantabria and Avilés (Asturias).
16th to 18th centuries
In the 16th century, the name ''La Montaña'' (''The Mountain'') was widespread in popular usage and in literature, as a designation of the Ancient Cantabria, as opposed to Castile (historical region), Castile, which referred solely to the Geography of Spain#The Inner Plateau and associated mountains, Central Plateau. This distinction has survived into modern times.Torrelavega
Torrelavega ( Cantabrian: ''Torlavega'') is a municipality and important industrial and commercial hub in the single province Autonomous Community of Cantabria, northern Spain.
It is situated roughly 8 kilometres from the Cantabrian Coast and 27.5 ...
and environs, Val de San Vicente, Valle de Carriedo, Tresviso, and the Pasiegan Villas of La Vega, Cantabria, La Vega, San Roque, Cantabria, San Roque and San Pedro, Cantabria, San Pedro, as well as the city of Santander with its abbey.
Competition between the townships of Laredo and Santander led to the latter, having initially allowed the name of Cantabria for the province created at the beginning of the 19th century, later retracting its consent and demanding that it bear the name of Santander, so there would be no doubt as to which was the capital. When in 1821 the Provincial Council presented before the constitutional Cortes Generales, Courts its definitive plan for the provincial borders and legal entities, it proposed the name of Province of Cantabria, to which the Township of Santander replied that "''this province must retain the name of Santander''". However, many newspapers still showed in their headings the name of Cantabria, or Cantabrian.
19th century
 During the Peninsular War, War of Independence (1808–1814), Bishop Rafael Tomás Menéndez de Luarca, a strong defender of absolutism, promoted himself as the "Regent of Cantabria" and established the ''Cantabrian Armaments'' in Santander, a section of the army whose purpose was to travel to all the mountain passes from the Central Plateau to detain any French troop.
Although defeated, he managed later to regroup in Liébana under the command of General Juan Díaz Porlier, calling his forces the ''Cantabrian Division'', in which there were various regiments and battalions, such as the ''Hussars of Cantabria'' (cavalry) or the ''Shooters of Cantabria'' (infantry). During the First Carlist War, Carlist wars they formed a unit called the ''Cantabrian Brigade''.
During the Peninsular War, War of Independence (1808–1814), Bishop Rafael Tomás Menéndez de Luarca, a strong defender of absolutism, promoted himself as the "Regent of Cantabria" and established the ''Cantabrian Armaments'' in Santander, a section of the army whose purpose was to travel to all the mountain passes from the Central Plateau to detain any French troop.
Although defeated, he managed later to regroup in Liébana under the command of General Juan Díaz Porlier, calling his forces the ''Cantabrian Division'', in which there were various regiments and battalions, such as the ''Hussars of Cantabria'' (cavalry) or the ''Shooters of Cantabria'' (infantry). During the First Carlist War, Carlist wars they formed a unit called the ''Cantabrian Brigade''.
20th century
The use of terms with ancestral resonance through the 18th and 19th centuries continued during the 20th century, taking on a political tone that was distinctly regionalist, until 1936. In fact, the ''Republican Federal Party'' produced an autonomy statute for a Cantabrian-Castilian Federal State that year, which would include present-day Cantabria and any neighbouring areas from Castile (historical region), Castile andAsturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
willing to join it. It could not be passed because of the Spanish Civil War, Civil War. Following the war and the subsequent marginalization of such efforts under the Spain under Franco, Francoists regime, the use of the name of Cantabria decreased, to the point that for official purposes it was relegated to sports associations, the only arena in which Cantabria was noted as a region.
In 1963, the president of the Provincial Council, Pedro Escalante y Huidobro, proposed reapplying the name of Cantabria to the Province of Santander, as suggested in an academic report written by the historian Tomás Maza Solano. Although further steps were taken and many of the townships were in favour of the move, the petition did not succeed, mostly due to the opposition of Santander City Council. On 30 December 1981, a process that had been started in April 1979 by the Council of Cabezón de la Sal, under the presidency of Ambrosio Calzada Hernández, culminated in the granting of self-rule to Cantabria, outlined in Article 143 of the Spanish Constitution.
Cantabria based its claim to autonomy on the constitutional precept that made provision for self-government for "''provinces with a historic regional character''".
A Mixed Assembly formed out of provincial deputies and national members of parliament began the task of drawing up an Statute of Autonomy of Cantabria, Autonomy Statute on 10 September 1979. Following the approval of the General Courts on 15 December 1981, the Juan Carlos I, King of Spain signed the corresponding Organic Law of Autonomy Statute for Cantabria on December 30 of the same year. Thus, the province of Santander broke its link to Castile, and left the former region of Castile and León to which it had belonged up to that time, together with the provinces of province of Ávila, Ávila, province of Burgos, Burgos, province of León, León, La Rioja (Spain), Logroño, province of Palencia, Palencia, province of Salamanca, Salamanca, province of Segovia, Segovia, province of Soria, Soria, province of Valladolid, Valladolid and province of Zamora, Zamora.
On 20 February 1982, the first Regional Assembly (now Parliament) was formed, with provisional status. From this time, the former province of Santander has been known as Cantabria and has thereby regained its historic name. The first home-rule elections were held in May 1983. The 4th Legislature (1995–1999) brought into effect the first great reform of the Autonomy Statute of Cantabria, approved by all the parliamentary groups.
Government and administration
The Autonomy Statute of Cantabria of 30 December 1981, established that Cantabria has in its institutions the desire to respect fundamental rights and public freedom, at the same time as consolidating and stimulating regional development through democratic channels. This document gathers all competences of the Autonomous Community that were transferred from the Government of Spain. As in other Autonomous Communities, some competences were not transferred, for example, Justice. The Statute also defines the symbols that should represent the region: The Flag of Cantabria, flag, the Coat of arms of Cantabria, coat of arms and the Himno de Cantabria, anthem of Cantabria. The Parliament of Cantabria is the principal self-government institution of the Autonomous Community, being the representative body of the Cantabrians. Presently it is constituted by thirty-nine deputies elected by universal, equal, free, direct and secret suffrage. The primary functions of the Parliament are: to exercise the legislation, legislative power, to approve the budgets of the Autonomous Community, to motivate and control the actions of the government, and to develop the rest of the competences that the Spanish Constitution, the Autonomy Statute and the rest of the legal order bestow on it. The President of Cantabria, President of the Autonomous Community holds the highest representation of the Community and ordinary representation of the Country in Cantabria, and presides over the Government, coordinating its activities. The Government of Cantabria is the body in charge of directing the political activities and exercising the executive and regulatory powers according to the Constitution, the Statute and the laws. The Government is made up of the President, the Vicepresident (in which the President can delegate his executive functions and representations) and the Councillors, who are appointed and ceased by the President. After several legislatures presided by the People's Party (Spain), Partido Popular or by Juan Hormaechea's UPCA, the Regional Government of Cantabria was directed by a coalition of the Regionalist Party of Cantabria and Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) from year 2003 until 2011. The President was Miguel Ángel Revilla of Partido Regionalista de Cantabria (PRC), and the Vice President was Dolores Gorostiaga of the PSOE. As a result of the absolute majority of the People's Party (Spain), Partido Popular in the regional elections of 2011, the president from 2011 to 2015 was Ignacio Diego Palacios, and the Vice President was also the healthcare Councillor, Maria José Sáenz de Buruaga. After the 2015 regional elections, Miguel Ángel Revilla of Partido Regionalista de Cantabria (PRC) was invested president for a third tenure with the support of PSOE.Territorial organization
The autonomous community of Cantabria is structured in ''Municipalities of Spain, municipios'' (municipalities) and ''comarca
A ''comarca'' (, or , or ) is a traditional region or local administrative division found in Portugal, Spain and some of their former colonies, like Brazil, Nicaragua, and Panama. The term is derived from the term ''marca'', meaning a "march, ...
s'' (regions).
Municipalities
''Comarcas'' (regions)
The Cantabrian legislation divides the autonomous community in administrative regions called ''comarcas'', but traditionally, other subdivisions of the territory have been used. *Administrative regions ''Law 8/1999 of ''Comarcas'' of the Autonomous Community of Cantabria'' of 28 April 1999 establishes that the comarca is a necessary entity, integral in the territorial organization of the region. This law opens the development of the ''comarcalization'' in Cantabria promoting the creation of ''comarcal'' entities, which have barely begun to appear. The law establishes that the creation of comarcas will not become mandatory for the whole territory until at least the 70% of it had not been ''comarcalized'' by its own will. It also adds that Santander will not ruled by comarcalization and should establish its own metropolitan area instead. ''Comarcas'' in Cantabria have not reached administrative nature and barely have definite borders. Only Liébana for its geographic position in Picos de Europa, Trasmiera and Campoo, in the Ebro basin are established are clearly defined ''comarcas'' in the region. Nevertheless, functional differences in the territory can be distinguished, dividing it in the following areas: Santander Bay, of industrial and urban nature; Besaya, also industrial; Saja and Nansa valleys, Saja-Nansa, eminently rural; Western coast of Cantabria, Western Coast, which has urban character; Eastern coast of Cantabria, Eastern Coast, vacational; the traditionally renowned Trasmiera; rural Valles Pasiegos, Pas-Miera; Asón valley, Asón-Agüera, also mainly rural; the very well definedLiébana
Liébana is a ''Comarcas of Cantabria, comarca'' of Cantabria (Spain). It covers 575 square kilometres and is located in the far southwest of Cantabria, bordering Asturias, León (province), León and Palencia (province), Palencia. It is made up o ...
, and Campoo, Campoo-Los Valles, rural and industrial by regions.
*Natural regions (regarding geographical features)
**Coastal strip
**Central strip (Cantabrian valleys perpendicular to the coast): Liébana, Saja and Nansa, Besaya, Pas and Miera (or Valles Pasiegos), and Asón-Gándara valleys.
**Southern strip (Rivers Ebro and Duero's basins): Campoo and Southern valleys
*Historic regions
Until the 13th century, Cantabria was organized in valleys, as was typical in all of northern Spain. From then on, it was substituted by the organization in cities, towns or historic ''comarcas'' that grouped several valleys.
Economy
 The economy of Cantabria has a primary sector, now in decline, employing 5.8% of the active population in the industry (economics), industries of cattle farming, traditional dairy farming, and meat production; agriculture, especially corn, potatoes, vegetables, and roughage; maritime fishing; and the mining of zinc and quarry, quarries.
The secondary sector which employs 30.3% of the active population is the sector with the most productivity in recent years due to construction; that of ironworking (Reinosa being the most important city), food service (milk, meat, vegetables and seafood), chemical industry, chemistry (Solvay, Sniace), paper production (Sinace, Papelera del Besaya), textile fabrication (Textil Santanderina in Cabezón de la Sal), pharmacy (Moehs in Requejada), industrial groups and transport, etc. The service sector employs 63.8% of the active population and is increasing, given that large concentrations of the population live in the urban centers and the importance that tourism has acquired in the recent years. As of July 2014, the unemployment rate in Cantabria is 19.3%, compared to 24.47% in Spain; while as of April 2010 its purchasing power parity was €25,326, compared to €26,100 in Spain and €25,100 in the European Union, EU25. In 2007, Cantabria's growth of real GDP was 4.1%, compared to a 3.9% average for Spain. The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was 13.8 billion € in 2018. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 25,500 € or 84% of the EU27 average in the same year.
The economy of Cantabria has a primary sector, now in decline, employing 5.8% of the active population in the industry (economics), industries of cattle farming, traditional dairy farming, and meat production; agriculture, especially corn, potatoes, vegetables, and roughage; maritime fishing; and the mining of zinc and quarry, quarries.
The secondary sector which employs 30.3% of the active population is the sector with the most productivity in recent years due to construction; that of ironworking (Reinosa being the most important city), food service (milk, meat, vegetables and seafood), chemical industry, chemistry (Solvay, Sniace), paper production (Sinace, Papelera del Besaya), textile fabrication (Textil Santanderina in Cabezón de la Sal), pharmacy (Moehs in Requejada), industrial groups and transport, etc. The service sector employs 63.8% of the active population and is increasing, given that large concentrations of the population live in the urban centers and the importance that tourism has acquired in the recent years. As of July 2014, the unemployment rate in Cantabria is 19.3%, compared to 24.47% in Spain; while as of April 2010 its purchasing power parity was €25,326, compared to €26,100 in Spain and €25,100 in the European Union, EU25. In 2007, Cantabria's growth of real GDP was 4.1%, compared to a 3.9% average for Spain. The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was 13.8 billion € in 2018. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 25,500 € or 84% of the EU27 average in the same year.
Transportation and communications
 The most significant consequence of the strong relief of the Cantabrian territory is the existence of topographic barriers that condition decisively the courses of the linking infrastructures, as much in the north–south orientation in the accesses to the Geography of Spain#The Inner Plateau and associated mountains, Castilian Mesa, as in the east–west in the communication between valleys. Moreover, the cost of their construction and maintenance is much higher than average.
The main communications infrastructures of the region are:
* Santander Airport
* Cantabrian Motorway (Autovía A-8, European route E-70)
* Cantabria-Meseta Motorway (Autovía A-67)
* Narrow-gauge railway
The most significant consequence of the strong relief of the Cantabrian territory is the existence of topographic barriers that condition decisively the courses of the linking infrastructures, as much in the north–south orientation in the accesses to the Geography of Spain#The Inner Plateau and associated mountains, Castilian Mesa, as in the east–west in the communication between valleys. Moreover, the cost of their construction and maintenance is much higher than average.
The main communications infrastructures of the region are:
* Santander Airport
* Cantabrian Motorway (Autovía A-8, European route E-70)
* Cantabria-Meseta Motorway (Autovía A-67)
* Narrow-gauge railway Santander
Santander may refer to:
Places
* Santander, Spain, a port city and capital of the autonomous community of Cantabria, Spain
* Santander Department, a department of Colombia
* Santander State, former state of Colombia
* Santander de Quilichao, a m ...
-Oviedo (Renfe Feve)
* Narrow-gauge railway Santander-Bilbao
)
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize = 275 px
, map_caption = Interactive map outlining Bilbao
, pushpin_map = Spain Basque Country#Spain#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption ...
(Renfe Feve)
* Broad-gauge railway Santander-Palencia-Valladolid-Ávila, Spain, Ávila-Madrid (Renfe)
* Broad-gauge high-speed railway Santander-Torrelavega
Torrelavega ( Cantabrian: ''Torlavega'') is a municipality and important industrial and commercial hub in the single province Autonomous Community of Cantabria, northern Spain.
It is situated roughly 8 kilometres from the Cantabrian Coast and 27.5 ...
-Valladolid-Segovia-Madrid (Renfe)
* Ferry line Santander-Plymouth
Mass media and public opinion
In Cantabria, there are two daily regional newspapers in addition to the national ones: ''El Diario Montañés'' and ''Alerta'', as well as many weekly, fortnightly and monthly publications. The main national radio stations have transmitter stations in places like Santander, Torrelavega, Castro-Urdiales, or Reinosa. There are also numerous local and regional stations. For the moment, there is no Cantabrian autonomic television with public financing, although some local channels exist (including Canal 8 DM, TeleBahía, Telecabarga, Localia TV Cantabria, etc.). In recent years, the Internet has allowed new informative proposals to emerge in the shape of digital diaries or blogs, which contribute to enrich the mediatic panorama of the region.Culture

Language
Spanish language, Spanish is the official language of Cantabria. The eastern part of Cantabria contributed to the origins of Old Spanish, Medieval Spanish in a significant way. In western areas, there are remnants of the Cantabrian dialect, Cantabrian language, also called ''"montañés"'', and it is also somewhat preserved in parts of the Pas and Soba valleys in its eastern zone. Cantabrian can be viewed as a dialect of the wider Astur-Leonese language continuum, and is mutually intelligible with varieties in neighbouringAsturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
.
Monuments and museums
 *Caves: Altamira (cave), Altamira Cave, Cave of El Soplao, El Soplao, Cave del Valle (Cantabria), Del Valle, El Pendo, Cueva de La Pasiega, La Pasiega Cave, Las Monedas, El Castillo, Morín, and others.
*Civil architecture: Palacio de la Magdalena, Magdalena palace in Santander; Capricho de Gaudí, Comillas Pontifical University, Pontifical University of Comillas and Sobrellano palace in Comillas; Bárcena palace in Ampuero; Castle of Argüeso in Campoo; Hornillos palace in Las Fraguas del Besaya; etc.
*Religious architecture: Collegiate of Santillana del Mar, Collegiate of Santa Cruz de Castañeda, Santo Toribio de Liébana, Santo Toribio de Liébana Monastery, Santa María de Lebeña, Santa María de Piasca, Santa María del Puerto, San Román del Moroso, Santa Catalina del Cintul, Santuario de Virgen de la Peña, ermita de San Cipriano, ermita de Monte Corona, etc.
*Museums: Cantabrian Sea Maritime Museum, Ethnographic Museum of Cantabria, Santander Museum of Fine Arts, Regional Museum of Prehistory and Arqueology of Cantabria, Cantabrian Museum of Nature, Altamira National Museum and Investigation Centre, and others.
*Caves: Altamira (cave), Altamira Cave, Cave of El Soplao, El Soplao, Cave del Valle (Cantabria), Del Valle, El Pendo, Cueva de La Pasiega, La Pasiega Cave, Las Monedas, El Castillo, Morín, and others.
*Civil architecture: Palacio de la Magdalena, Magdalena palace in Santander; Capricho de Gaudí, Comillas Pontifical University, Pontifical University of Comillas and Sobrellano palace in Comillas; Bárcena palace in Ampuero; Castle of Argüeso in Campoo; Hornillos palace in Las Fraguas del Besaya; etc.
*Religious architecture: Collegiate of Santillana del Mar, Collegiate of Santa Cruz de Castañeda, Santo Toribio de Liébana, Santo Toribio de Liébana Monastery, Santa María de Lebeña, Santa María de Piasca, Santa María del Puerto, San Román del Moroso, Santa Catalina del Cintul, Santuario de Virgen de la Peña, ermita de San Cipriano, ermita de Monte Corona, etc.
*Museums: Cantabrian Sea Maritime Museum, Ethnographic Museum of Cantabria, Santander Museum of Fine Arts, Regional Museum of Prehistory and Arqueology of Cantabria, Cantabrian Museum of Nature, Altamira National Museum and Investigation Centre, and others.
Universities
 *University of Cantabria
*International University Menéndez Pelayo
*Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia
*Campus Comillas
*CESINE
*European University of the Atlantic, Universidad Europea del Atlántico
*University of Cantabria
*International University Menéndez Pelayo
*Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia
*Campus Comillas
*CESINE
*European University of the Atlantic, Universidad Europea del Atlántico
Fairs and festivals
 Regarding the fairs, understood as big markets of products periodically celebrated, it is remarkable the ''Livestock Fair of Torrelavega'' taking place in the National Livestock Market "Jesús Collado Soto", the third biggest of Spain, that groups the buy and sell of all kinds of cattle in the region itself and the adjacent ones, being the bovine the main product. All over the region cattle and typical products fairs are celebrated weekly, monthly, or annually to gather the neighbours of the land. There are many different festivities in Cantabria, some of them limited just to small villages, but there are also festivals that attract tourism from all over the country. The most important are the following:
*''La Vijanera'' (Winter Carnival), celebrated during the first Sunday of the year in Silió. It celebrates the end of the short winter days and the arrival of the sun. The representation of a white bear hunt takes place all over this little village. The traditional dressing of the characters in the play, the trapajones and the zarramacos, is one of its main features.
*''Carnaval marinero'' (Sailor Carnival), in February in
Regarding the fairs, understood as big markets of products periodically celebrated, it is remarkable the ''Livestock Fair of Torrelavega'' taking place in the National Livestock Market "Jesús Collado Soto", the third biggest of Spain, that groups the buy and sell of all kinds of cattle in the region itself and the adjacent ones, being the bovine the main product. All over the region cattle and typical products fairs are celebrated weekly, monthly, or annually to gather the neighbours of the land. There are many different festivities in Cantabria, some of them limited just to small villages, but there are also festivals that attract tourism from all over the country. The most important are the following:
*''La Vijanera'' (Winter Carnival), celebrated during the first Sunday of the year in Silió. It celebrates the end of the short winter days and the arrival of the sun. The representation of a white bear hunt takes place all over this little village. The traditional dressing of the characters in the play, the trapajones and the zarramacos, is one of its main features.
*''Carnaval marinero'' (Sailor Carnival), in February in Santoña
Santoña is a town in the eastern coast of the autonomous community of Cantabria, on the north coast of Spain. It is situated by the bay of the same name. It is from the capital Santander. Santoña is divided into two zones, an urban plain, and ...
. Commonly known as "the carnivals of the North", in this carnival, started in 1934, many people of the town participate dressing themselves up as fish. The main event is the "Trial at the bottom of the ocean", where the "''Bream, besugo''" is judged before the last act, "The burning of the ''besugo''". (A ''besugo'' is a foolish person besides a type of fish).
*''La Folía'', April in San Vicente de la Barquera, a parade of local fishing boats following one with a statue of the Virgin.
*''Coso Blanco'', first Friday in July in Castro Urdiales. Colorful parade with carts.
*''Cantabria Day'', second Sunday of August in Cabezón de la Sal. Traditional Cantabrian music, ceramics fair, local foods, bolo palma championships, ox dragging contests and public speeches.
*SAUGA folk music festival, celebrated the third weekend of August in Colindres.
*''Floral Gala'', August en Torrelavega
Torrelavega ( Cantabrian: ''Torlavega'') is a municipality and important industrial and commercial hub in the single province Autonomous Community of Cantabria, northern Spain.
It is situated roughly 8 kilometres from the Cantabrian Coast and 27.5 ...
. A festival of international touristic importance with carts decorated with flowers.
*''Battle of Flowers'', August, in Laredo. Carts decorated with flowers and fruit. Fireworks in the evening.
*''Campoo Day'', September in Reinosa
Reinosa is a municipality in Cantabria, Spain. , it has 10,307 inhabitants. The municipality, one of the smallest by land area in Cantabria, is notable for being one of the nearest towns to the headwaters of the Ebro River. It is surrounded by th ...
. Tourist fair of regional importance since 1977 and celebrated since the 19th century, it shows customs and traditions of the Campoo, Campurrians in their capital. Cattle shows, local products market and regional costumes are the items in this festival.
The following festivals are also remarkable in modern Cantabrian culture: Santander International Festival (Arts festival), Santander Summer Festival (Music festival), Sotocine (Film festival)
Mythology
The north of the Spanish state is a rich area for mythology. From Galicia, Spain, Galicia to the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, passing by Asturias and Cantabria, there are rites, stories and imaginary or impossible beings (or maybe not so). Cantabrian lore turns its forests and mountains into magical places where the myths, beliefs and legends have been present as an essential part of the Cantabrian culture, either because they have been living in the popular heritage through the oral tradition transmitted from father to son, or because they have been recovered by scholars (Manuel Llano (scholar), Manuel Llano and others) who have worried about preserving the cultural heritage. Its mythology and superstitions present a great Celtic influence that has diluted with the pass of time, being Religion in ancient Rome, romanized or Christianity, Christianized in many cases. There is a heavy presence of fabulous beings of giant (mythology), giant proportions and Cyclopean features (the ''ojáncanu, ojáncanos''), fantastic animals (''cuélebre, culebres'', ''caballucos del diablu'' (lit. horses of the devil, damselfly, damselflies), ''ramidrejus'', etc.), Fairy, færies (''anjanas'', ''ijanas'' of Aras), duende (mythology), duendes (''nuberos, ventolines, trentis, trasgus, trastolillos, musgosu, tentiruju''), anthropomorphic characters (the ''sirenuca'' (little mermaid), the fish-man, the cuegle, the wife-bear of Andara, the ''guajona''), etc.Cuisine
*Typical dishes: ''Cocido montañés'' (''Highlander stew'') made with common bean, beans and collard greens; ''cocido lebaniego'' (''Liébana
Liébana is a ''Comarcas of Cantabria, comarca'' of Cantabria (Spain). It covers 575 square kilometres and is located in the far southwest of Cantabria, bordering Asturias, León (province), León and Palencia (province), Palencia. It is made up o ...
n stew'') made from chickpeas and marmita).
*Meat dishes: Beef, ox, deer, roe deer or boar. Cooked on the grill, stewed or with vegetables.
:The livestock farming reputation of the region and its climatological conditions favouring cattle breeding allowed the European Union to pass the "Meats of Cantabria" denomination as a ''Protected geographical indications in the European Union, Protected Geographic Denomination'' for the beef of certain kinds of native races (''Tudanca'', ''Monchina'') and others adapted to the environment or integrated by assimilation (''Brown Alpine'').
*Fish and seafood: anchovy, Anchovies, Lophius piscatorius, angler, hake, European seabass, sea bass, Soleidae, sole, Atlantic horse mackerel, mackerel, sardine, European anchovy, European anchovies, bonito of the North (of Spain), gilt-head bream, sea bream, red mullet, and Scorpaenidae, scorpionfish, as well as some river fish such as trout and salmon. ''Rabas'' (fried calamari) and ''cachón en su tinta'' (cuttlefish cooked in its own ink) are local specialties. Clam, blue mussel, mussel, Ensis, muergos (jackknife), cockle (bivalve), cockle, velvet crab, Maja squinado, spider crab, pollicipes pollicipes, goose barnacle, Common periwinkle, periwinkle, Norway lobster and European lobster are available.
*Desserts: ''Quesada Pasiega, Quesadas'' and ''sobaos'' of the Pas valley; Unquera's Corbatas and Torrelavega
Torrelavega ( Cantabrian: ''Torlavega'') is a municipality and important industrial and commercial hub in the single province Autonomous Community of Cantabria, northern Spain.
It is situated roughly 8 kilometres from the Cantabrian Coast and 27.5 ...
's polkas both basically puff pastry); Palucos de Cabezón de la Sal; and Pantortillas of Reinosa.
*Cheeses: Quesucos de Liébana.
*Drinks: txakoli, Chacolí; apple cider and orujo (liquor made from pomace) from Liébana
Liébana is a ''Comarcas of Cantabria, comarca'' of Cantabria (Spain). It covers 575 square kilometres and is located in the far southwest of Cantabria, bordering Asturias, León (province), León and Palencia (province), Palencia. It is made up o ...
; and tostadillo from Potes.
Sports
Selaya Township website. Retrieved on 5 August 2007. (skittles (sport), skittles) in its four forms: ''bolo palma'', ''pasabolo tablón'', ''pasabolo losa'' and ''bolo pasiego''. The first one is the most widespread, exceeding regional nature and reaching the eastern zone of Asturias and also being the most complex in its game rules. The existence of ''boleras'' or skittle rings is important in every Cantabrian township, often being near the church or the village pub. Since the late 1980s, skittle play has consolidated with the reinforcement of skittle schools, revamped by different town councils and Cantabrian institutions, various competitions, and media coverage. The remo (rowing (sport), rowing) is a very traditional sport in the coastal towns. The origins of rowing in Cantabria go back many centuries, when several ''traineras'' (traditional fishing longboats) competed for the selling of the caught fish, which was reserved for the first ship to arrive to the fish market. At the end of the 19th century, work became sport and people started to celebrate regattas between Cantabrian townships. The sport clubs of Cantabria, especially the Sociedad Deportiva de Remo Astillero, Astillero, Sociedad Deportiva de Remo Castro Urdiales, Castro Urdiales, and the Sociedad Deportiva de Remo Pedreña, Pedreña belong to the most prize-winning teams of the history of this sport, and nowadays they are having one of the best moments after a decades-long period of trophy drought.
 The Pasiegan jump is another of the outstanding rural sports of the region and a clear example of how the use of a work skill that disappears with the pass of time, gives rise to games and competition. Similar to other forms, like the Salto del pastor, Canarian shepherd jump, in the beginning this technique was used in the Pasiegan valleys to cross the stone walls, the fences, the creeks or the ravines that bordered the fields and obstructed the pass in the abrupt geography of the highland areas of Cantabria.
Referring to mass sports, Cantabria is present in national and international competitions through teams such as the ''Racing de Santander'', the ''RS Gimnástica de Torrelavega'' and the Cantabria autonomous football team in Football in Spain, football or the ''Independiente RC'' in División de Honor de Rugby, rugby union. The ''CB Cantabria, Club Balonmano Cantabria'' that won Liga ASOBAL, Leagues and Copa del Rey de Balonmano, King's Cups as well as IHF Super Globe, EHF Champions League, EHF Cup Winners' Cup and EHF Cup in team handball, handball or the Cantabria Baloncesto, Cantabria Lobos that played in the Liga ACB, ACB in basketball represented the highest level of the Cantabrian sport in the recent past.
The Pasiegan jump is another of the outstanding rural sports of the region and a clear example of how the use of a work skill that disappears with the pass of time, gives rise to games and competition. Similar to other forms, like the Salto del pastor, Canarian shepherd jump, in the beginning this technique was used in the Pasiegan valleys to cross the stone walls, the fences, the creeks or the ravines that bordered the fields and obstructed the pass in the abrupt geography of the highland areas of Cantabria.
Referring to mass sports, Cantabria is present in national and international competitions through teams such as the ''Racing de Santander'', the ''RS Gimnástica de Torrelavega'' and the Cantabria autonomous football team in Football in Spain, football or the ''Independiente RC'' in División de Honor de Rugby, rugby union. The ''CB Cantabria, Club Balonmano Cantabria'' that won Liga ASOBAL, Leagues and Copa del Rey de Balonmano, King's Cups as well as IHF Super Globe, EHF Champions League, EHF Cup Winners' Cup and EHF Cup in team handball, handball or the Cantabria Baloncesto, Cantabria Lobos that played in the Liga ACB, ACB in basketball represented the highest level of the Cantabrian sport in the recent past.
Notable Cantabrians
 Cantabria has been the birthplace of exceptional and notable individuals in fields such as literature, arts, sciences, etc. Many of them have played a decisive role, not only in the history and events of the region, but also on the national and international levels. These include:
*Business: Jesús de Polanco, Emilio Botín, Ana Patricia Botín, Ana Patricia Botin, Vicente Calderón, Vicente Calderon
*Sports: Francisco Gento, Santillana (footballer), "Santillana", José Manuel Abascal, Seve Ballesteros, Óscar Freire, Juan José Cobo, Cecilio Lastra, Francisco Ventoso, Ruth Beitia, Sergio Canales, Athenea del Castillo
*Music: Ataúlfo Argenta, David Bustamante, La Fuga (band), La Fuga
*Film, radio, and TV: Mario Camus, Manuel Gutiérrez Aragón, Eduardo Noriega (Spanish actor), Eduardo Noriega, Antonio Resines, Nacho Vigalondo, Ricardo Palacios.
*Military: Corocotta, Pedro Velarde
*Religion: Emeterius and Celedonius, San Emeterio, San Celedonio, Beatus of Liébana
*Explorers: Juan de la Cosa, Vital Alsar, José de Bustamante y Guerra
*Literature: José María de Pereda, Concha Espina, Gerardo Diego, Álvaro Pombo, Luys Santa Marina.
*Painting: María Blanchard, José de Madrazo, Francisco González Gómez
*Science and technology: Leonardo Torres Quevedo, Juan de Herrera
*Politics: Luis Carrero Blanco, José Luis Zamanillo González-Camino, José Luis Zamanillo, Alfredo Pérez Rubalcaba, Joaquín Leguina, Miguel Ángel Revilla, Antonio Valverde y Cosío
*Sociology: Rosa Cobo Bedía
Cantabria has been the birthplace of exceptional and notable individuals in fields such as literature, arts, sciences, etc. Many of them have played a decisive role, not only in the history and events of the region, but also on the national and international levels. These include:
*Business: Jesús de Polanco, Emilio Botín, Ana Patricia Botín, Ana Patricia Botin, Vicente Calderón, Vicente Calderon
*Sports: Francisco Gento, Santillana (footballer), "Santillana", José Manuel Abascal, Seve Ballesteros, Óscar Freire, Juan José Cobo, Cecilio Lastra, Francisco Ventoso, Ruth Beitia, Sergio Canales, Athenea del Castillo
*Music: Ataúlfo Argenta, David Bustamante, La Fuga (band), La Fuga
*Film, radio, and TV: Mario Camus, Manuel Gutiérrez Aragón, Eduardo Noriega (Spanish actor), Eduardo Noriega, Antonio Resines, Nacho Vigalondo, Ricardo Palacios.
*Military: Corocotta, Pedro Velarde
*Religion: Emeterius and Celedonius, San Emeterio, San Celedonio, Beatus of Liébana
*Explorers: Juan de la Cosa, Vital Alsar, José de Bustamante y Guerra
*Literature: José María de Pereda, Concha Espina, Gerardo Diego, Álvaro Pombo, Luys Santa Marina.
*Painting: María Blanchard, José de Madrazo, Francisco González Gómez
*Science and technology: Leonardo Torres Quevedo, Juan de Herrera
*Politics: Luis Carrero Blanco, José Luis Zamanillo González-Camino, José Luis Zamanillo, Alfredo Pérez Rubalcaba, Joaquín Leguina, Miguel Ángel Revilla, Antonio Valverde y Cosío
*Sociology: Rosa Cobo Bedía
See also
*Architecture of Cantabria *Caves in Cantabria *Lábaru *Duchy of Cantabria *List of municipalities in Cantabria *Nine Valleys lawsuitNotes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * *External links
Camara de Comercio de Cantabria
{{Authority control Cantabria, Green Spain NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1982 Autonomous communities of Spain