Calico House, Newnham - geograph.org.uk - 4992.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
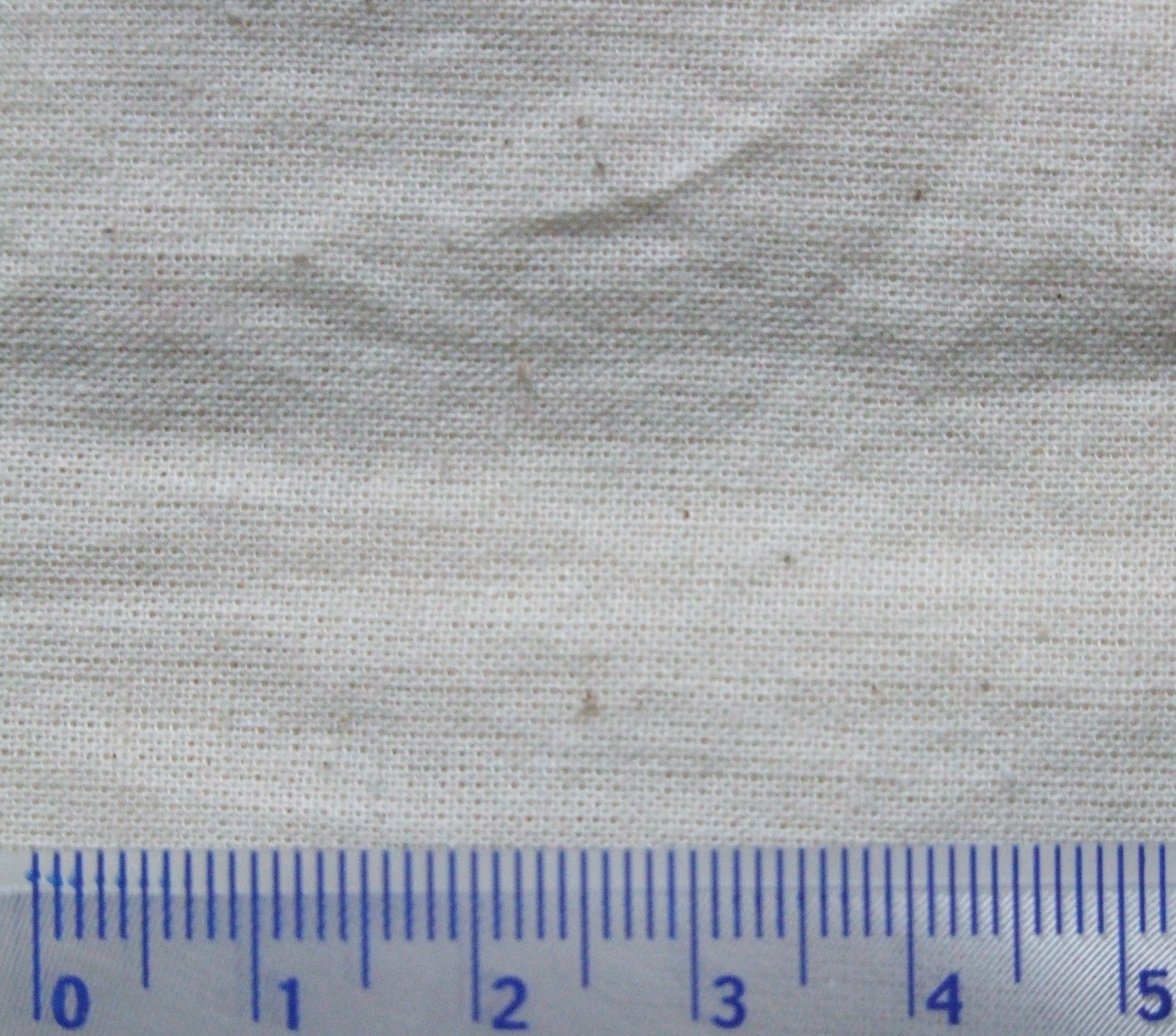 Calico (; in British usage since 1505) is a heavy plain-woven
Calico (; in British usage since 1505) is a heavy plain-woven
"calico"
Calico was woven using Gujarati cotton from Surat for both the warp and weft. By the 15th century, calico from Gujarat made its appearance in Cairo, then capital of the Egypt Eyalet under the Ottoman Empire. Trade with Europe followed from the 17th century onwards.
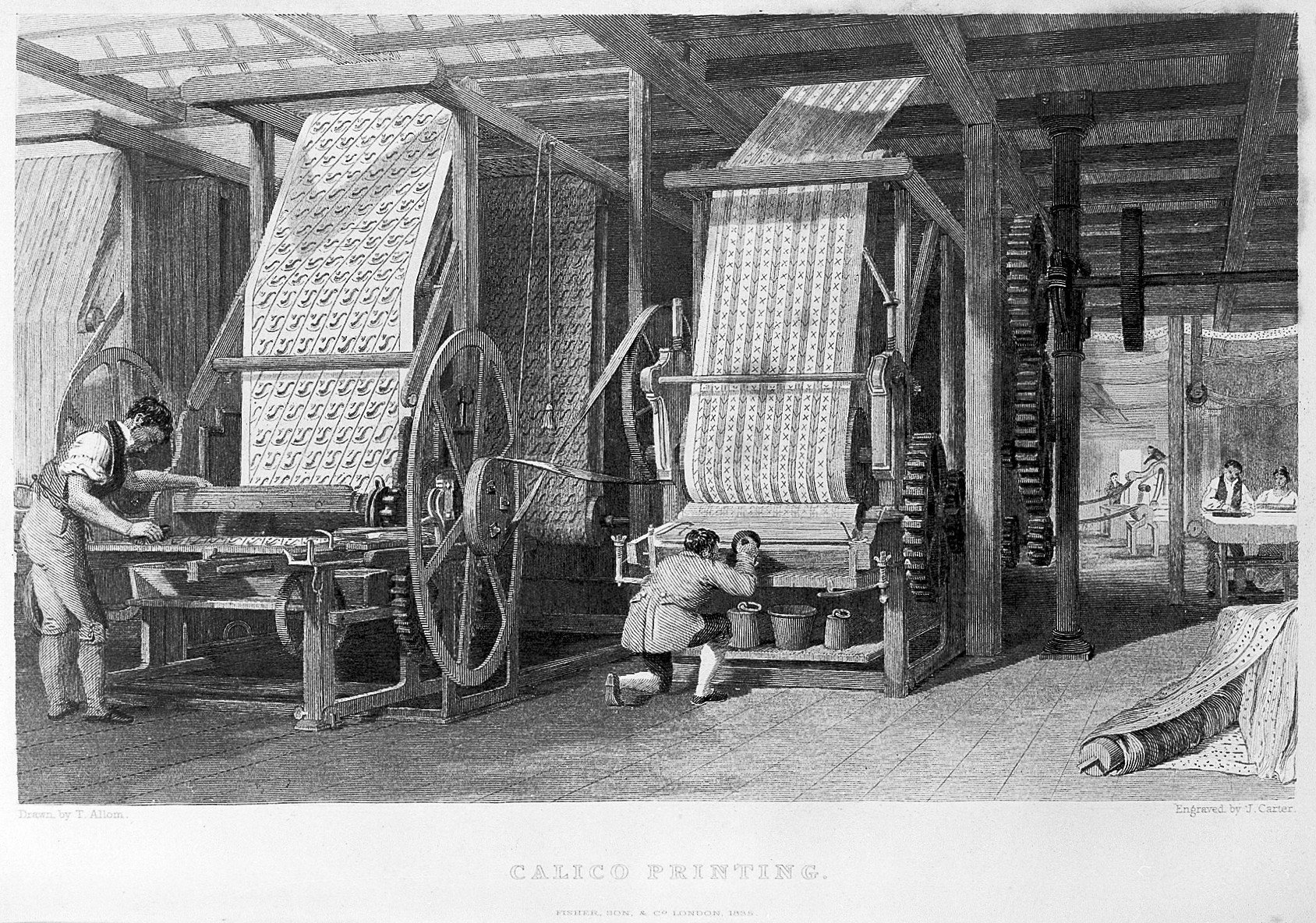
 Early Indian chintz, that is, glazed calico with a large floral pattern, was primarily produced using painting techniques.Turnbull, ''A History of Calico Printing in Great Britain'', 1951. Later, the hues were applied by wooden blocks, and the cloth manufacturers in Britain printed calico using Woodblock printing, wooden block printing. Calico printers at work are depicted in one of the stained glass windows made by Stephen Adam (stained glass designer), Stephen Adam for the Maryhill Burgh Halls, Glasgow. Confusingly, linen and silk printed this way were known as ''linen calicoes'' and ''silk calicoes''. Early European calicoes (1680) were cheap plain weave white cotton fabric, or cream or unbleached cotton, with a design block-printed using a single Rose madder, alizarin dye fixed with two mordants, giving a red and black pattern. Polychromatic prints were possible, using two sets of blocks and an additional blue dye. The Indian taste was for dark printed backgrounds, while the European market preferred a pattern on a cream base. As the century progressed the European preference moved from the large chintz patterns to smaller, tighter patterns.
Thomas Bell (printer), Thomas Bell patented a printing technique in 1783 that used copper rollers. In 1785, Livesey, Hargreaves and Company put the first machine that used this technique into operation in Walton-le-Dale, Lancashire. The production volume for printed cloth in Lancashire in 1750 was estimated at 50,000 pieces of ; in 1850, it was 20,000,000 pieces. The commercial method of calico printing using engraved rollers was invented in 1821 in New Mills, Derbyshire, in the United Kingdom. John Potts (engraver), John Potts of Potts, Oliver and Potts used a copper-engraved master to produce rollers to transfer the inks. After 1888, block printing was only used for short-run specialized jobs. After 1880, profits from printing fell due to overcapacity and the firms started to form Business group, combines. In the first, three Scottish firms formed the United Turkey Red Co. Ltd in 1897, and the second, in 1899, was the much larger Calico Printers' Association 46 printing concerns and 13 merchants combined, representing 85% of the British printing capacity. Some of this capacity was removed and in 1901 Calico had 48% of the printing trade. In 1916, they and the other printers formed and joined a trade association, which then set minimum prices for each 'price section' of the industry.
The trade association remained in operation until 1954, when the arrangement was challenged by the government Monopolies Commission. Over the intervening period much trade had been lost overseas.
Early Indian chintz, that is, glazed calico with a large floral pattern, was primarily produced using painting techniques.Turnbull, ''A History of Calico Printing in Great Britain'', 1951. Later, the hues were applied by wooden blocks, and the cloth manufacturers in Britain printed calico using Woodblock printing, wooden block printing. Calico printers at work are depicted in one of the stained glass windows made by Stephen Adam (stained glass designer), Stephen Adam for the Maryhill Burgh Halls, Glasgow. Confusingly, linen and silk printed this way were known as ''linen calicoes'' and ''silk calicoes''. Early European calicoes (1680) were cheap plain weave white cotton fabric, or cream or unbleached cotton, with a design block-printed using a single Rose madder, alizarin dye fixed with two mordants, giving a red and black pattern. Polychromatic prints were possible, using two sets of blocks and an additional blue dye. The Indian taste was for dark printed backgrounds, while the European market preferred a pattern on a cream base. As the century progressed the European preference moved from the large chintz patterns to smaller, tighter patterns.
Thomas Bell (printer), Thomas Bell patented a printing technique in 1783 that used copper rollers. In 1785, Livesey, Hargreaves and Company put the first machine that used this technique into operation in Walton-le-Dale, Lancashire. The production volume for printed cloth in Lancashire in 1750 was estimated at 50,000 pieces of ; in 1850, it was 20,000,000 pieces. The commercial method of calico printing using engraved rollers was invented in 1821 in New Mills, Derbyshire, in the United Kingdom. John Potts (engraver), John Potts of Potts, Oliver and Potts used a copper-engraved master to produce rollers to transfer the inks. After 1888, block printing was only used for short-run specialized jobs. After 1880, profits from printing fell due to overcapacity and the firms started to form Business group, combines. In the first, three Scottish firms formed the United Turkey Red Co. Ltd in 1897, and the second, in 1899, was the much larger Calico Printers' Association 46 printing concerns and 13 merchants combined, representing 85% of the British printing capacity. Some of this capacity was removed and in 1901 Calico had 48% of the printing trade. In 1916, they and the other printers formed and joined a trade association, which then set minimum prices for each 'price section' of the industry.
The trade association remained in operation until 1954, when the arrangement was challenged by the government Monopolies Commission. Over the intervening period much trade had been lost overseas.
 In the UK, Australia and New Zealand:
*Calico – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton
*Calico bag - a bag made of calico used by banks and other financial institutions
*Muslin – a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – US: muslin – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Gauze – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
*Cheesecloth – US: gauze – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Tote Bag - sometimes made of calico
In the US:
*Calico – cotton fabric with a small, all-over floral printKadolph, Sara J., ed. (2007) ''Textiles'', 10th ed., p. 463, Pearson/Prentice-Hall
*Muslin – UK: muslin gauze – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – the very lightest, most open weave of muslin
*Gauze – UK: cheesecloth – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Cheesecloth – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
Printed calico was imported into the United States from Lancashire in the 1780s, and here a linguistic separation occurred. While Europe maintained the word calico for the fabric, in the States it was used to refer to the printed design.
These colourful, small-patterned printed fabrics gave rise to the use of the word calico to describe a cat coat colour: calico cat. The patterned fabric also gave its name to two species of North American crabs; see Ovalipes ocellatus.
In the UK, Australia and New Zealand:
*Calico – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton
*Calico bag - a bag made of calico used by banks and other financial institutions
*Muslin – a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – US: muslin – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Gauze – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
*Cheesecloth – US: gauze – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Tote Bag - sometimes made of calico
In the US:
*Calico – cotton fabric with a small, all-over floral printKadolph, Sara J., ed. (2007) ''Textiles'', 10th ed., p. 463, Pearson/Prentice-Hall
*Muslin – UK: muslin gauze – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – the very lightest, most open weave of muslin
*Gauze – UK: cheesecloth – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Cheesecloth – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
Printed calico was imported into the United States from Lancashire in the 1780s, and here a linguistic separation occurred. While Europe maintained the word calico for the fabric, in the States it was used to refer to the printed design.
These colourful, small-patterned printed fabrics gave rise to the use of the word calico to describe a cat coat colour: calico cat. The patterned fabric also gave its name to two species of North American crabs; see Ovalipes ocellatus.
''A dictionary of dyeing and calico printing''
- digital facsimile from the Linda Hall Library * William Crookes (1874
''A practical handbook of dyeing and calico-printing''
Illustrated with period fabric swatches. - digital facsimile from the Linda Hall Library * Baba Gee Calico Printin
''A calico Printing store''
where design fabric with calico technique. * Deazley, R. (2008) ‘Commentary on the Calico Printers' Act 1787', in Primary Sources on Copyright (1450-1900), eds L. Bently & M. Kretschme
{{Authority control History of Kerala Woven fabrics Indian inventions History of Kozhikode Economy of Kozhikode Cotton industry in India
textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
made from unbleached, and often not fully processed, cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
. It may also contain unseparated husk parts. The fabric is far coarser than muslin
Muslin () is a cotton fabric of plain weave. It is made in a wide range of weights from delicate sheers to coarse sheeting. It gets its name from the city of Mosul, Iraq, where it was first manufactured.
Muslin of uncommonly delicate hands ...
, but less coarse and thick than canvas or denim
Denim is a sturdy cotton warp-faced textile in which the weft passes under two or more warp threads. This twill weaving produces a diagonal ribbing that distinguishes it from cotton duck. While a denim predecessor known as dungaree has been p ...
. However, it is still very cheap owing to its unfinished and undyed appearance.
The fabric was originally from the city of Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
in southwestern India. It was made by the traditional weavers called Saliya, cāliyans. The raw fabric was dyed and printed in bright hues, and Chintz, calico prints became popular in Europe.
History
Origins
Calico originated in Kozhikode, Calicut, from which the name of the textile came, in South India, now Kerala, during the 11th century, where the cloth was known as "chaliyan". It was mentioned in Indian literature by the 12th century when the polymath and writer Hemachandra described calico fabric prints with a sacred lotus in religious art, lotus design.''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2008)"calico"
Calico was woven using Gujarati cotton from Surat for both the warp and weft. By the 15th century, calico from Gujarat made its appearance in Cairo, then capital of the Egypt Eyalet under the Ottoman Empire. Trade with Europe followed from the 17th century onwards.
Politics of cotton in the British Empire
In the 18th century, England was famous for its woollen and worsted, worsted cloth. That industry, centered in the east and south in towns such as Norwich, jealously protected their product. Cotton processing was tiny: in 1701 only of cottonwool was imported into England, and by 1730 this had fallen to . This was due to commercial legislation to protect the woollen industry. Cheap Chintz, calico prints, imported by the East India Company from Hindustan, Hindustān (India), had become popular. In 1700 an Act of Parliament passed to prevent the importation of dyed or printed calicoes from India, China or Persia. This caused demand to switch to imported Greige goods, grey cloth instead—calico that had not been finished—dyed or printed. These were printed with popular patterns in southern England. Also, Lancashire businessmen produced grey cloth with linen warp and cotton weft, known as fustian, which they sent to London for finishing. Cottonwool imports recovered though, and by 1720 were almost back to their 1701 levels. Coventry woollen manufacturers claimed that the imports were taking jobs away from their workers. The Woollen, etc., Manufactures Act 1720 was passed, enacting fines against anyone caught wearing printed or stained calico muslins. Neckcloths and fustians were exempted. The Lancashire manufacturers exploited this exemption; coloured cotton weft with linen warp were specifically permitted by the Manchester Act 1736, 1736 Manchester Act. In 1764, of cottonwool was imported. This change in consumption patterns, as a result of the restriction on imported finished goods, was a key part of the process that reduced the Indian economy from sophisticated textile production to the mere supply of raw materials. These events occurred under colonial rule, which started after 1757, and were described by Jawaharlal Nehru, Nehru and also some more recent scholars as "de-industrialization".Calico printing
 Early Indian chintz, that is, glazed calico with a large floral pattern, was primarily produced using painting techniques.Turnbull, ''A History of Calico Printing in Great Britain'', 1951. Later, the hues were applied by wooden blocks, and the cloth manufacturers in Britain printed calico using Woodblock printing, wooden block printing. Calico printers at work are depicted in one of the stained glass windows made by Stephen Adam (stained glass designer), Stephen Adam for the Maryhill Burgh Halls, Glasgow. Confusingly, linen and silk printed this way were known as ''linen calicoes'' and ''silk calicoes''. Early European calicoes (1680) were cheap plain weave white cotton fabric, or cream or unbleached cotton, with a design block-printed using a single Rose madder, alizarin dye fixed with two mordants, giving a red and black pattern. Polychromatic prints were possible, using two sets of blocks and an additional blue dye. The Indian taste was for dark printed backgrounds, while the European market preferred a pattern on a cream base. As the century progressed the European preference moved from the large chintz patterns to smaller, tighter patterns.
Thomas Bell (printer), Thomas Bell patented a printing technique in 1783 that used copper rollers. In 1785, Livesey, Hargreaves and Company put the first machine that used this technique into operation in Walton-le-Dale, Lancashire. The production volume for printed cloth in Lancashire in 1750 was estimated at 50,000 pieces of ; in 1850, it was 20,000,000 pieces. The commercial method of calico printing using engraved rollers was invented in 1821 in New Mills, Derbyshire, in the United Kingdom. John Potts (engraver), John Potts of Potts, Oliver and Potts used a copper-engraved master to produce rollers to transfer the inks. After 1888, block printing was only used for short-run specialized jobs. After 1880, profits from printing fell due to overcapacity and the firms started to form Business group, combines. In the first, three Scottish firms formed the United Turkey Red Co. Ltd in 1897, and the second, in 1899, was the much larger Calico Printers' Association 46 printing concerns and 13 merchants combined, representing 85% of the British printing capacity. Some of this capacity was removed and in 1901 Calico had 48% of the printing trade. In 1916, they and the other printers formed and joined a trade association, which then set minimum prices for each 'price section' of the industry.
The trade association remained in operation until 1954, when the arrangement was challenged by the government Monopolies Commission. Over the intervening period much trade had been lost overseas.
Early Indian chintz, that is, glazed calico with a large floral pattern, was primarily produced using painting techniques.Turnbull, ''A History of Calico Printing in Great Britain'', 1951. Later, the hues were applied by wooden blocks, and the cloth manufacturers in Britain printed calico using Woodblock printing, wooden block printing. Calico printers at work are depicted in one of the stained glass windows made by Stephen Adam (stained glass designer), Stephen Adam for the Maryhill Burgh Halls, Glasgow. Confusingly, linen and silk printed this way were known as ''linen calicoes'' and ''silk calicoes''. Early European calicoes (1680) were cheap plain weave white cotton fabric, or cream or unbleached cotton, with a design block-printed using a single Rose madder, alizarin dye fixed with two mordants, giving a red and black pattern. Polychromatic prints were possible, using two sets of blocks and an additional blue dye. The Indian taste was for dark printed backgrounds, while the European market preferred a pattern on a cream base. As the century progressed the European preference moved from the large chintz patterns to smaller, tighter patterns.
Thomas Bell (printer), Thomas Bell patented a printing technique in 1783 that used copper rollers. In 1785, Livesey, Hargreaves and Company put the first machine that used this technique into operation in Walton-le-Dale, Lancashire. The production volume for printed cloth in Lancashire in 1750 was estimated at 50,000 pieces of ; in 1850, it was 20,000,000 pieces. The commercial method of calico printing using engraved rollers was invented in 1821 in New Mills, Derbyshire, in the United Kingdom. John Potts (engraver), John Potts of Potts, Oliver and Potts used a copper-engraved master to produce rollers to transfer the inks. After 1888, block printing was only used for short-run specialized jobs. After 1880, profits from printing fell due to overcapacity and the firms started to form Business group, combines. In the first, three Scottish firms formed the United Turkey Red Co. Ltd in 1897, and the second, in 1899, was the much larger Calico Printers' Association 46 printing concerns and 13 merchants combined, representing 85% of the British printing capacity. Some of this capacity was removed and in 1901 Calico had 48% of the printing trade. In 1916, they and the other printers formed and joined a trade association, which then set minimum prices for each 'price section' of the industry.
The trade association remained in operation until 1954, when the arrangement was challenged by the government Monopolies Commission. Over the intervening period much trade had been lost overseas.
Terminology
 In the UK, Australia and New Zealand:
*Calico – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton
*Calico bag - a bag made of calico used by banks and other financial institutions
*Muslin – a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – US: muslin – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Gauze – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
*Cheesecloth – US: gauze – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Tote Bag - sometimes made of calico
In the US:
*Calico – cotton fabric with a small, all-over floral printKadolph, Sara J., ed. (2007) ''Textiles'', 10th ed., p. 463, Pearson/Prentice-Hall
*Muslin – UK: muslin gauze – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – the very lightest, most open weave of muslin
*Gauze – UK: cheesecloth – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Cheesecloth – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
Printed calico was imported into the United States from Lancashire in the 1780s, and here a linguistic separation occurred. While Europe maintained the word calico for the fabric, in the States it was used to refer to the printed design.
These colourful, small-patterned printed fabrics gave rise to the use of the word calico to describe a cat coat colour: calico cat. The patterned fabric also gave its name to two species of North American crabs; see Ovalipes ocellatus.
In the UK, Australia and New Zealand:
*Calico – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton
*Calico bag - a bag made of calico used by banks and other financial institutions
*Muslin – a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – US: muslin – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Gauze – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
*Cheesecloth – US: gauze – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Tote Bag - sometimes made of calico
In the US:
*Calico – cotton fabric with a small, all-over floral printKadolph, Sara J., ed. (2007) ''Textiles'', 10th ed., p. 463, Pearson/Prentice-Hall
*Muslin – UK: muslin gauze – simple, cheap equal weft and warp plain weave fabric in white, cream or unbleached cotton and/or a very fine, light plain weave cotton fabric
*Muslin gauze – the very lightest, most open weave of muslin
*Gauze – UK: cheesecloth – any very light fabric, generally with a plain weave
*Cheesecloth – extremely soft and fine cotton fabric with a very open plain weave
Printed calico was imported into the United States from Lancashire in the 1780s, and here a linguistic separation occurred. While Europe maintained the word calico for the fabric, in the States it was used to refer to the printed design.
These colourful, small-patterned printed fabrics gave rise to the use of the word calico to describe a cat coat colour: calico cat. The patterned fabric also gave its name to two species of North American crabs; see Ovalipes ocellatus.
See also
*Bafta cloth *Calico Acts *Calico cat *Calico (goldfish) *Calico Jack *PiecegoodsReferences
External links
* * * Charles O'Neill (1869''A dictionary of dyeing and calico printing''
- digital facsimile from the Linda Hall Library * William Crookes (1874
''A practical handbook of dyeing and calico-printing''
Illustrated with period fabric swatches. - digital facsimile from the Linda Hall Library * Baba Gee Calico Printin
''A calico Printing store''
where design fabric with calico technique. * Deazley, R. (2008) ‘Commentary on the Calico Printers' Act 1787', in Primary Sources on Copyright (1450-1900), eds L. Bently & M. Kretschme
{{Authority control History of Kerala Woven fabrics Indian inventions History of Kozhikode Economy of Kozhikode Cotton industry in India