Brampton Bryan castle (geograph 3897894).jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Brampton ( or ) is a city in the Canadian
 Before the arrival of British settlers, the
Before the arrival of British settlers, the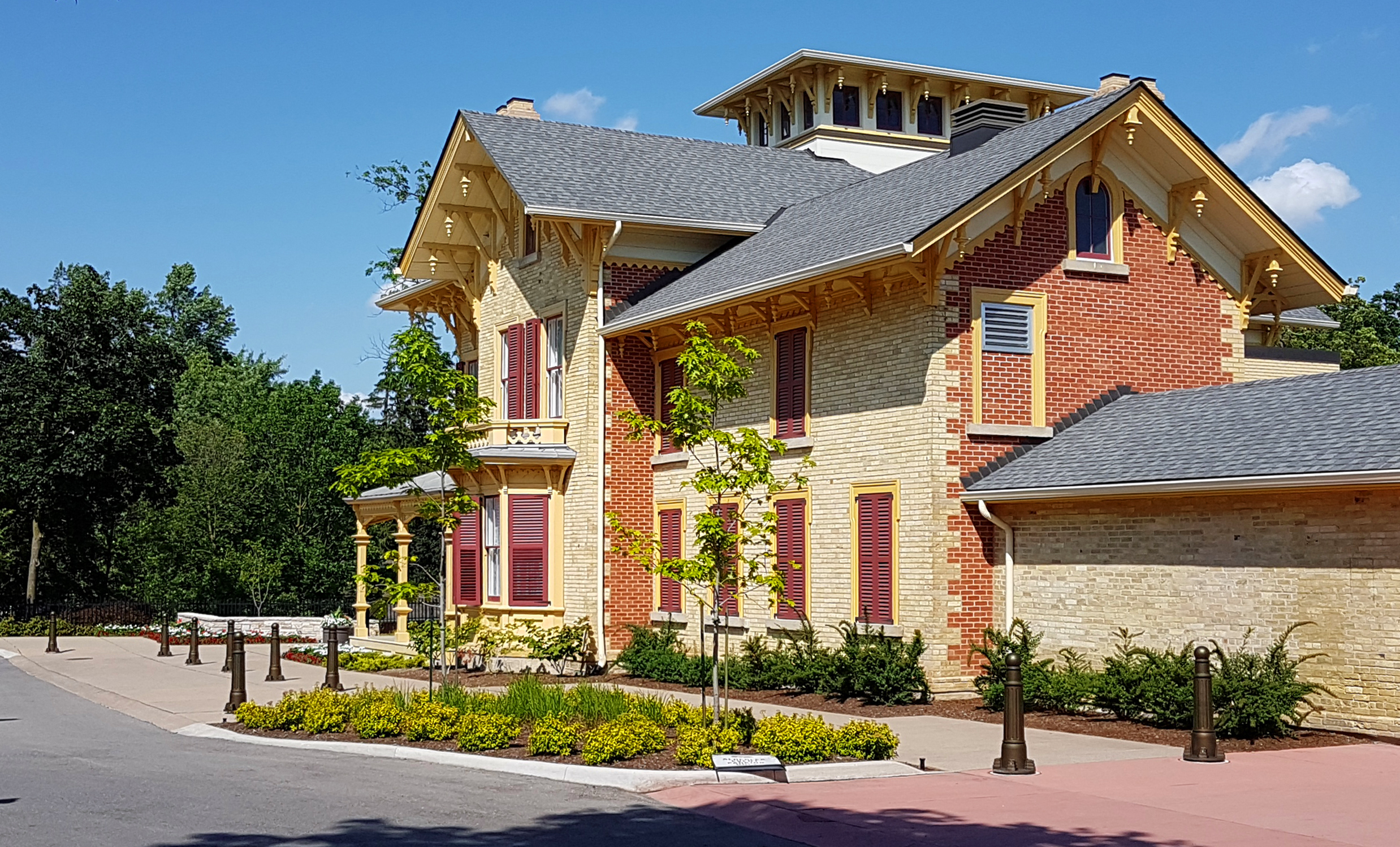  In January 1867, Peel County separated from the County of York, a union which had existed since 1851.
By 1869, Brampton had a population of 1,800. It was incorporated as a town in 1873.
A federal grant had enabled the village to found its first public
In January 1867, Peel County separated from the County of York, a union which had existed since 1851.
By 1869, Brampton had a population of 1,800. It was incorporated as a town in 1873.
A federal grant had enabled the village to found its first public
 Planned as an innovative " new town", Bramalea was developed immediately east of the Town of Brampton in Chinguacousy Township. It was Canada's first satellite community developed by one of the country's largest real estate developers, ''Bramalea Limited.'' The name "Bramalea" was created by the farmer William Sheard, who combined "BRAM" from Brampton, "MAL" from Malton (then a neighbouring town which is now part of the city of Mississauga), and "LEA", an
Planned as an innovative " new town", Bramalea was developed immediately east of the Town of Brampton in Chinguacousy Township. It was Canada's first satellite community developed by one of the country's largest real estate developers, ''Bramalea Limited.'' The name "Bramalea" was created by the farmer William Sheard, who combined "BRAM" from Brampton, "MAL" from Malton (then a neighbouring town which is now part of the city of Mississauga), and "LEA", an
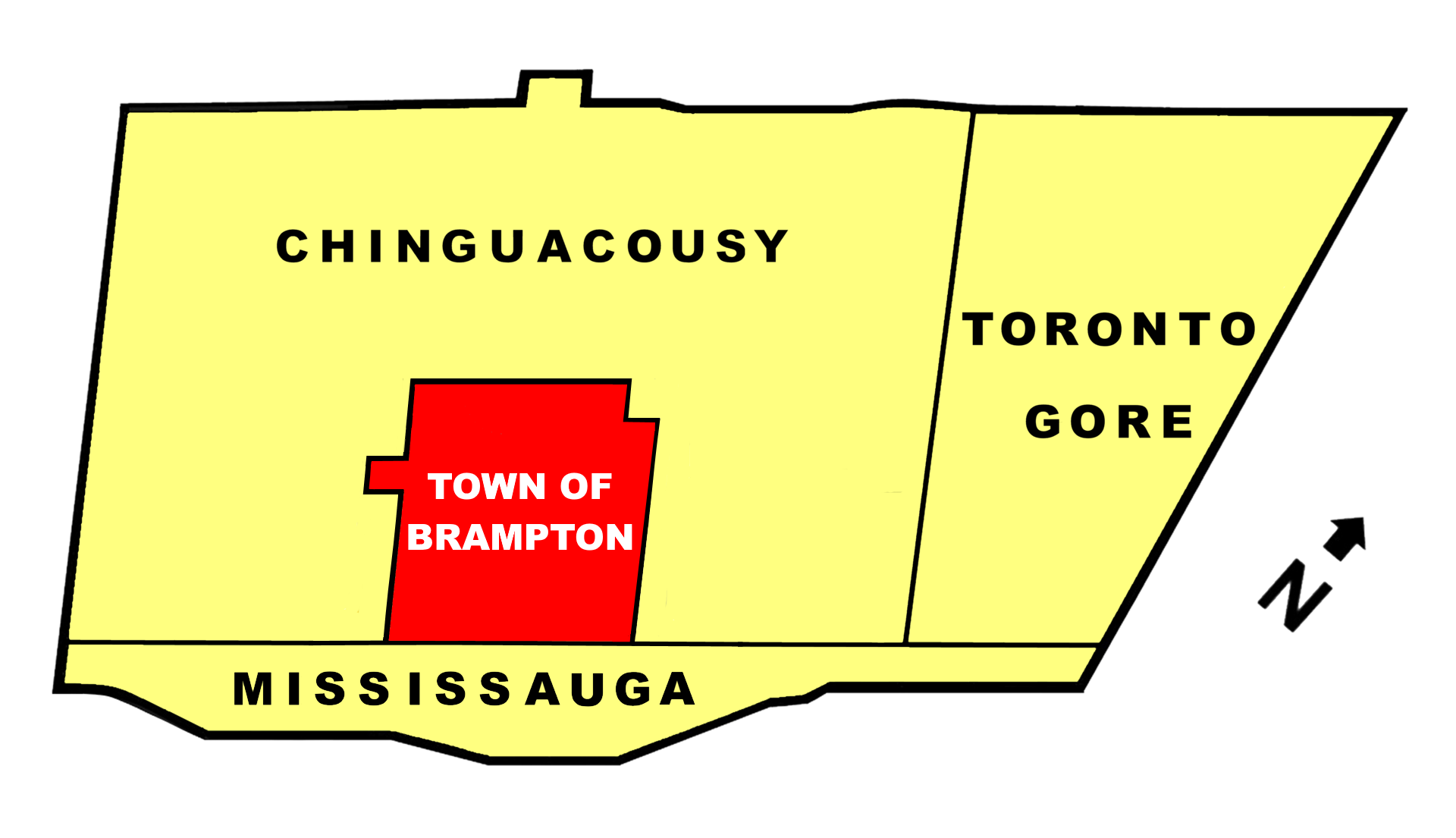 In 1974, the Ontario provincial government decided to update Peel County's structure. It amalgamated several towns and villages into the new City of Mississauga. In addition, it created the present City of Brampton from the town and the greater portion of the Townships of Chinguacousy and
In 1974, the Ontario provincial government decided to update Peel County's structure. It amalgamated several towns and villages into the new City of Mississauga. In addition, it created the present City of Brampton from the town and the greater portion of the Townships of Chinguacousy and


 The late 1970's brought new residential development, as Brampton released large tracts of land to developers. Heart Lake was one of the first major development outside the city's pre-1974 limits or Bramalea.
In the early 1980's, Cineplex Odeon closed the Capitol Theatre in Brampton. The City bought the facility in 1981 under the leadership of councillor Diane Sutter. It adapted the former
The late 1970's brought new residential development, as Brampton released large tracts of land to developers. Heart Lake was one of the first major development outside the city's pre-1974 limits or Bramalea.
In the early 1980's, Cineplex Odeon closed the Capitol Theatre in Brampton. The City bought the facility in 1981 under the leadership of councillor Diane Sutter. It adapted the former


 Several cultural entities in the city operate under the umbrella of the Brampton Arts Council. Located in the city is the
Several cultural entities in the city operate under the umbrella of the Brampton Arts Council. Located in the city is the
 * Gage Park, Brampton, Gage Park
* Artway Gallery
* Beaux Arts Brampton
* CAA Centre
* Camp Naivelt
* Chinguacousy Park-Greenhouse and gardens
* Mount Chinguacousy
* Claireville Conservation Area
* Flower City Theatre Festival
* Great War Flying Museum
* Heart Lake Conservation Area
* Brampton Historical Society
* Historic Bovaird House
* Korean War Memorial Wall (Canada)
* Ontario Field of Honour
*
* Gage Park, Brampton, Gage Park
* Artway Gallery
* Beaux Arts Brampton
* CAA Centre
* Camp Naivelt
* Chinguacousy Park-Greenhouse and gardens
* Mount Chinguacousy
* Claireville Conservation Area
* Flower City Theatre Festival
* Great War Flying Museum
* Heart Lake Conservation Area
* Brampton Historical Society
* Historic Bovaird House
* Korean War Memorial Wall (Canada)
* Ontario Field of Honour
*
 Local transit is provided by Brampton Transit, with connections to other systems such as MiWay, York Region Transit, Go Transit, and Toronto Transit Commission. Brampton Transit also operates a bus rapid transit system, "Züm" (pronounced Zoom), along Hurontario Street, Main/Hurontario Streets,
Local transit is provided by Brampton Transit, with connections to other systems such as MiWay, York Region Transit, Go Transit, and Toronto Transit Commission. Brampton Transit also operates a bus rapid transit system, "Züm" (pronounced Zoom), along Hurontario Street, Main/Hurontario Streets,
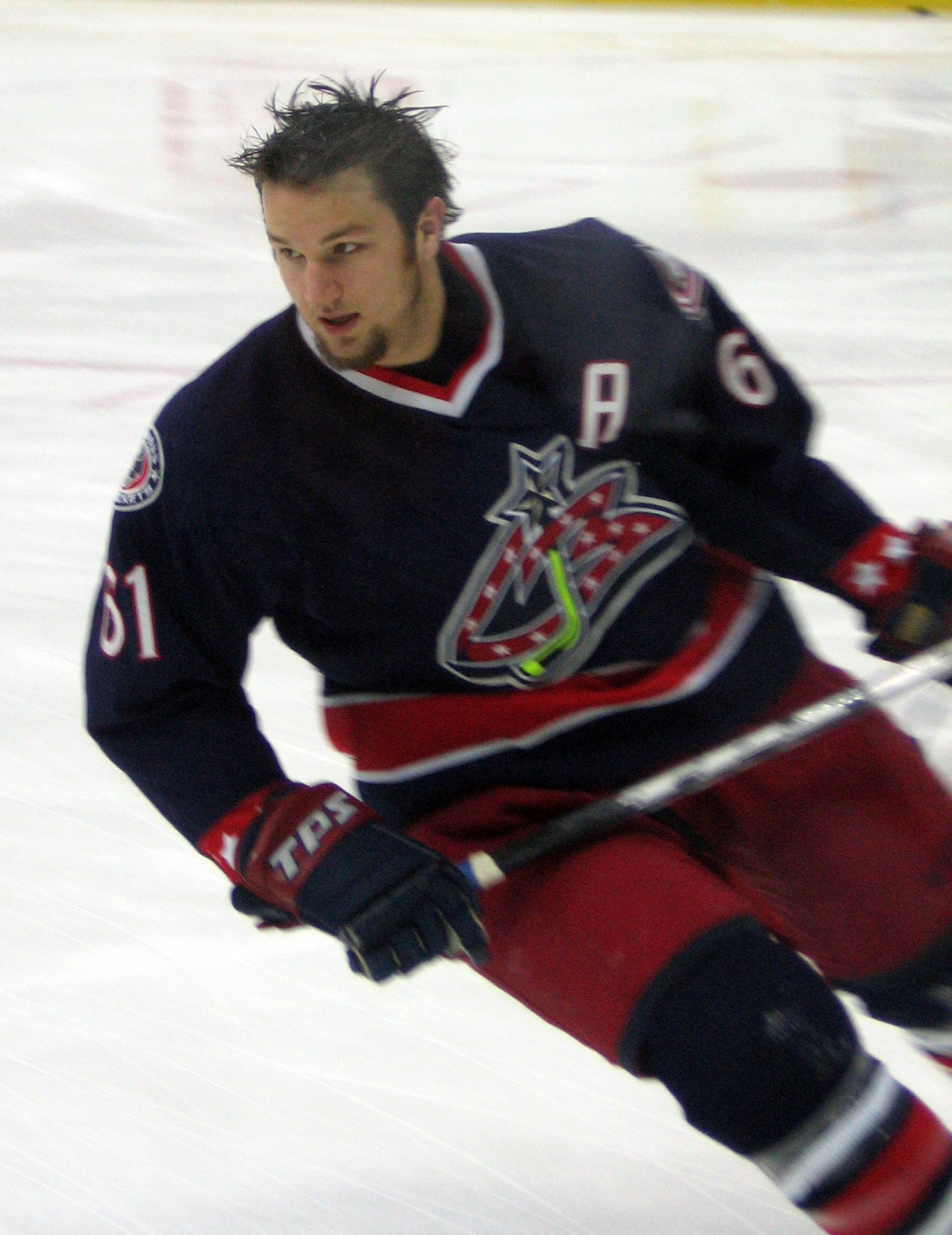 * Baseball: Zach Pop
* Basketball: Michael Meeks (basketball), Michael Meeks (internationally), Tyler Ennis (basketball), Tyler Ennis (NBA), Tristan Thompson (NBA), Anthony Bennett (basketball), Anthony Bennett (NBA)
* Cricket: Saad Bin Zafar, Cecil Pervez,
* Curling: Scott Bailey (curler), Scott Bailey, Peter Corner, Graeme McCarrel, Wayne Middaugh, Allison Pottinger
* Field hockey: Bernadette Bowyer
* Figure skating: Vern Taylor, Mark Janoschak
* Football: Michael Bailey (Canadian football), Michael Bailey (CFL), Fernand Kashama (CFL), Chris Kowalczuk (CFL), Rob Maver (CFL), Jerome Messam (CFL, NFL), Jason Nugent (CFL), Junior Turner (CFL), Steven Turner (CFL), Jabar Westerman (CFL), Jamaal Westerman (NFL), James Yurichuk (CFL) Nakas Onyeka (CFL)
* Golf: David Hearn (golfer), David Hearn; Steve Duplantis (caddy)
* Hockey: Andrew Cassels, Mike Danton, Mike Dwyer (ice hockey), Mike Dwyer, Todd Elik, Chris Felix, Sheldon Keefe, Tom Laidlaw, Kris Newbury, Rick Nash, Tyler Seguin, Jamie Storr, Mike Weaver (ice hockey), Mike Weaver, Mike Wilson (ice hockey), Mike Wilson, Sean Monahan, Tyler Graovac, Cassie Campbell, Mikyla Grant-Mentis
* Horse-racing: Sid C. Attard, Patrick Husbands, Robert P. Tiller, Emma-Jayne Wilson
* Lacrosse: Jim Veltman (NLL)
* Sailing: Kevin Stittle
* Soccer: Gabe Gala (MLS), Atiba Hutchinson (Super Lig), Peter Roe (soccer), Peter Roe (ASL, MISL), Murphy Wiredu, Doneil Henry, Doniel Henry, David Hoilett, David "Junior" Hoilett, Paul Stalteri, Roger Thompson, Cyle Larin, Tajon Buchanan, Jahkeele Marshall-Rutty
* Speed skating: Tyson Heung
* Tennis: Jill Hetherington, Milos Raonic
* Track and field: Charles Allen (athlete), Charles Allen, Mark Boswell (athlete), Mark Boswell, Kate Van Buskirk
* Wrestling: Ohenewa Akuffo
* Baseball: Zach Pop
* Basketball: Michael Meeks (basketball), Michael Meeks (internationally), Tyler Ennis (basketball), Tyler Ennis (NBA), Tristan Thompson (NBA), Anthony Bennett (basketball), Anthony Bennett (NBA)
* Cricket: Saad Bin Zafar, Cecil Pervez,
* Curling: Scott Bailey (curler), Scott Bailey, Peter Corner, Graeme McCarrel, Wayne Middaugh, Allison Pottinger
* Field hockey: Bernadette Bowyer
* Figure skating: Vern Taylor, Mark Janoschak
* Football: Michael Bailey (Canadian football), Michael Bailey (CFL), Fernand Kashama (CFL), Chris Kowalczuk (CFL), Rob Maver (CFL), Jerome Messam (CFL, NFL), Jason Nugent (CFL), Junior Turner (CFL), Steven Turner (CFL), Jabar Westerman (CFL), Jamaal Westerman (NFL), James Yurichuk (CFL) Nakas Onyeka (CFL)
* Golf: David Hearn (golfer), David Hearn; Steve Duplantis (caddy)
* Hockey: Andrew Cassels, Mike Danton, Mike Dwyer (ice hockey), Mike Dwyer, Todd Elik, Chris Felix, Sheldon Keefe, Tom Laidlaw, Kris Newbury, Rick Nash, Tyler Seguin, Jamie Storr, Mike Weaver (ice hockey), Mike Weaver, Mike Wilson (ice hockey), Mike Wilson, Sean Monahan, Tyler Graovac, Cassie Campbell, Mikyla Grant-Mentis
* Horse-racing: Sid C. Attard, Patrick Husbands, Robert P. Tiller, Emma-Jayne Wilson
* Lacrosse: Jim Veltman (NLL)
* Sailing: Kevin Stittle
* Soccer: Gabe Gala (MLS), Atiba Hutchinson (Super Lig), Peter Roe (soccer), Peter Roe (ASL, MISL), Murphy Wiredu, Doneil Henry, Doniel Henry, David Hoilett, David "Junior" Hoilett, Paul Stalteri, Roger Thompson, Cyle Larin, Tajon Buchanan, Jahkeele Marshall-Rutty
* Speed skating: Tyson Heung
* Tennis: Jill Hetherington, Milos Raonic
* Track and field: Charles Allen (athlete), Charles Allen, Mark Boswell (athlete), Mark Boswell, Kate Van Buskirk
* Wrestling: Ohenewa Akuffo
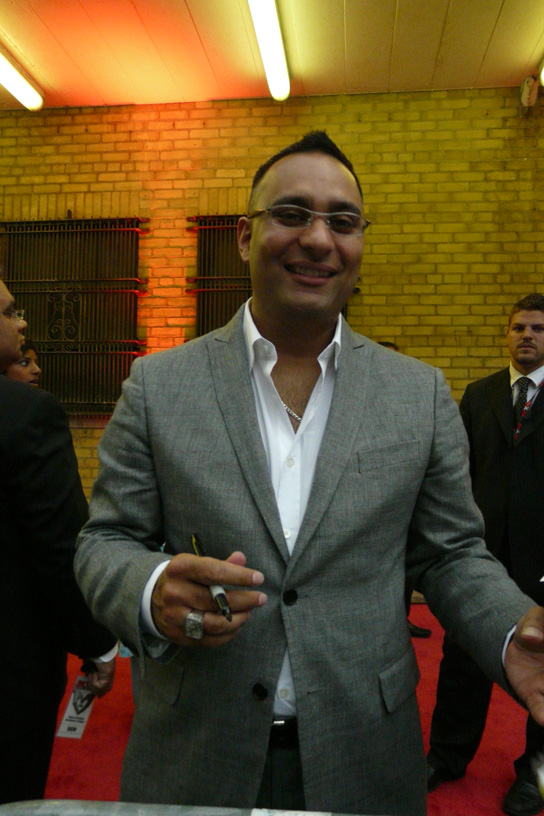 Two notable comedians hail from Brampton: Scott Thompson (comedian), Scott Thompson and Russell Peters.
Comedic actor Michael Cera was born and raised in Brampton. Shawn Ashmore, Aaron Ashmore (''Smallville (TV series), Smallville'') are Brampton-raised. Actor Tyler Labine starred in ''Mad Love (TV series), Mad Love''.
Other Brampton-born or affiliated actors include Paulo Costanzo, Jordan Gavaris, Gemini Award winner Kris Lemche, Lara Jean Chorostecki, Sabrina Grdevich, Nicole Lyn, actor and producer David Phillips (actor, host), David J. Phillips, reality TV star and art dealer Billy Jamieson, performer George R. Robertson, and performer Sidhu Moose Wala.
Others include voice actor Brenna O'Brien, and on-air media personalities Cassie Campbell, Chris Connor, Chris Cuthbert and Scott McGillivray.
Two notable comedians hail from Brampton: Scott Thompson (comedian), Scott Thompson and Russell Peters.
Comedic actor Michael Cera was born and raised in Brampton. Shawn Ashmore, Aaron Ashmore (''Smallville (TV series), Smallville'') are Brampton-raised. Actor Tyler Labine starred in ''Mad Love (TV series), Mad Love''.
Other Brampton-born or affiliated actors include Paulo Costanzo, Jordan Gavaris, Gemini Award winner Kris Lemche, Lara Jean Chorostecki, Sabrina Grdevich, Nicole Lyn, actor and producer David Phillips (actor, host), David J. Phillips, reality TV star and art dealer Billy Jamieson, performer George R. Robertson, and performer Sidhu Moose Wala.
Others include voice actor Brenna O'Brien, and on-air media personalities Cassie Campbell, Chris Connor, Chris Cuthbert and Scott McGillivray.
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
. Brampton is a city in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) and is a lower-tier municipality within Peel Region. The city has a population of 656,480 as of the 2021 Census, making it the ninth most populous municipality in Canada and the third most populous city in the Greater Golden Horseshoe
The Golden Horseshoe is a secondary region of Southern Ontario, Canada, which lies at the western end of Lake Ontario, with outer boundaries stretching south to Lake Erie and north to Lake Scugog, Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay of Lake Huron. The r ...
urban area, behind Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
and Mississauga.
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
have inhabited the Brampton area for thousands of years. Named after the town of Brampton
Brampton ( or ) is a city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Brampton is a city in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) and is a lower-tier municipality within Peel Region. The city has a population of 656,480 as of the 2021 Census, making it ...
in Cumberland, England, Brampton was incorporated as a village in 1853 and as a town in 1873, and became a city in 1974.
The city was once known as "The Flower Town of Canada", a title referring to its large greenhouse industry. Nowadays, Brampton's major economic sectors include advanced manufacturing, retail administration, logistics, information and communication technologies, food and beverage, life sciences, and business services.
History
 Before the arrival of British settlers, the
Before the arrival of British settlers, the Mississaugas of the Credit First Nation
Mississaugas of the Credit First Nation ( oj, Mazina'iga-ziibing Misi-zaagiwininiwag, ''meaning: "Mississauga people at the Credit River"'') is a Mississauga Ojibwa First Nation located near Brantford in south-central Ontario, Canada. In April ...
held of land north of the head of the Lake Purchase lands and extending to the unceded territory of the Chippewa of Lakes Huron and Simcoe. European settlers began to arrive in the area in the 1600s. In October 1818, the chief of the Mississaugas of the Credit First Nation
Mississaugas of the Credit First Nation ( oj, Mazina'iga-ziibing Misi-zaagiwininiwag, ''meaning: "Mississauga people at the Credit River"'') is a Mississauga Ojibwa First Nation located near Brantford in south-central Ontario, Canada. In April ...
signed Treaty 19, also known as the Ajetance Purchase, surrendering the area to the British Crown.
Prior to the 1830s, most business in Chinguacousy Township
Chinguacousy Township is a former municipality and present-day geographic township in the Regional Municipality of Peel, Ontario, Canada. In 1973, when Peel County became the Regional Municipality of Peel, the township was split in half, with t ...
took place at Martin Salisbury's tavern. One mile from the corner of Hurontario Street
Hurontario Street is a roadway running in Ontario, Canada between Lake Ontario at Mississauga and Lake Huron's Georgian Bay at Collingwood. Within Peel Region, it is a major urban thoroughfare within the cities of Mississauga and Brampton, wh ...
and the 5th Sideroad (now Main and Queen Streets in the centre of Brampton), William Buffy's tavern was the only significant building. At the time, the intersection was referred to as "Buffy's Corners". By 1834, John Elliott laid out the area in lots for sale, calling it "Brampton", which was soon adopted by others."Brampton's Beginning" in ''Bramptons's 100th Anniversary as an Incorporated Town: 1873–1973'', Brampton: The Corporation of the Town of Brampton and the Brampton Centennial Committee, 1973, originally published in Ross Cumming, ed., ''Historical Atlas of Peel County'', n.p.: Walker and Miles, 1877.
In 1853, a small agricultural fair was set up by the newly initiated County Agricultural Society of the County of Peel and was held at the corner of Main and Queen streets. Grains, produce, roots, and dairy products were up for sale. Horses and cattle, along with other lesser livestock, were also sold at the market. This agricultural fair eventually became the modern Brampton Fall Fair.
In that same year Brampton was incorporated as a village. In 1866, the town became the county seat and the location of the Peel County Courthouse which was built in 1865–66; a three-storey County jail was added at the rear in 1867.
Edward Dale, an immigrant from Dorking, England, established a flower nursery in Brampton shortly after his arrival in 1863. Dale's Nursery became the town's largest and most prominent employer, developed a flower grading system, and established a global export market for its products. The company chimney was a town landmark, until Brampton Town Council allowed it to be torn down in 1977. At its height, the company had 140 greenhouses, and was the largest cut flower
Cut may refer to:
Common uses
* The act of cutting, the separation of an object into two through acutely-directed force
** A type of wound
** Cut (archaeology), a hole dug in the past
** Cut (clothing), the style or shape of a garment
** Cut ( ...
business in North America, producing 20 million blooms and introducing numerous rose and orchid varietals and species to the market. It also spurred the development of other nurseries in the town. Forty-eight hothouse flower nurseries once did business in the town.
 In January 1867, Peel County separated from the County of York, a union which had existed since 1851.
By 1869, Brampton had a population of 1,800. It was incorporated as a town in 1873.
A federal grant had enabled the village to found its first public
In January 1867, Peel County separated from the County of York, a union which had existed since 1851.
By 1869, Brampton had a population of 1,800. It was incorporated as a town in 1873.
A federal grant had enabled the village to found its first public library
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a vir ...
in 1887, which included 360 volumes from the Mechanic's Institute (established in 1858). In 1907, the library received a grant from the Carnegie Foundation, set up by United States steel magnate and philanthropist Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie (, ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century and became one of the richest Americans i ...
, to build a new, expanded library; it serves several purposes, featuring the Brampton Library. The Carnegie libraries were built on the basis of communities coming up with matching funds and guaranteeing maintenance.
In 1902, Sir William J. Gage (owner of Gage Publishing, a publishing house specializing in school textbooks) purchased a portion of the gardens and lawns of the Alder Lea estate (now called Alderlea) that had been built on Main Street by Kenneth Chisolm in 1867 to 1870. (Chisholm, a merchant and founding father of Brampton, had been the Town reeve, then warden of Peel County, then MPP for Brampton and eventually, Registrar of Peel County.) Gage donated of the property to the town, with a specific condition that it be made into a park. Citizens donated $1,054 and the town used the funds to purchase extra land to ensure a larger park.
A group of regional farmers in Brampton had trouble getting insurance from city-based companies. After several meetings in Clairville Hall, they decided to found the County of Peel Farmers Mutual Fire Insurance Company. In 1955, when the company moved to its third and current location, 103 Queen Street West, it took the new name of Peel Mutual Insurance Company. It reigns as the longest-running company in modern Brampton. Harmsworth Decorating Centre was established in 1890, as Harmsworth and Son, operated out of the family's house on Queen Street West. The current location was purchased on September 1, 1904, after a fire destroyed their original store. Purchased for $1,400, the 24 Main Street South location is the longest-operating retail business in what is now Brampton.
In 1974, the two townships of Chinguacousy and Toronto Gore were incorporated into Brampton. The small pine added to the centre of the shield on the Brampton city flag represents Chinguacousy, honouring the Chippewa chief ''Shinguacose,'' "The Small Pine." After this merger, outlying communities such as Bramalea, Heart Lake and Professor's Lake, Snelgrove, Tullamore
Tullamore (; ) is the county town of County Offaly in Ireland. It is on the Grand Canal, in the middle of the county, and is the fourth most populous town in the midlands region with 14,607 inhabitants at the 2016 census.
The town retained ...
, and Mayfield, were developed.
In 1963, the town established ''The Flower Festival of Brampton'', based on the '' Rose Festival'' of Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
, in the United States. It began to market itself as the ''Flower Town of Canada''.
In a revival of this theme, on 24 June 2002, the City Council established the "Flower City Strategy", to promote a connection to its flower-growing heritage. The intention was to inspire design projects and community landscaping to beautify the city, adopt a sustainable environmental approach, and to protect its natural and cultural heritage. The Rose Theatre was named in keeping with this vision and is to serve as a cultural institution in the city. In addition, the city participates in the national Communities in Bloom
Communities in Bloom is a Canadian non-profit organization
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more peop ...
competition as part of that strategy.
The Old Shoe Factory, located on 57 Mill Street North, once housed the Hewetson Shoe Company. It was listed as a historical property under the Ontario Heritage Act in 2008. Today it is occupied by various small businesses. The lobby and hallways retain details from 1907. Walls are decorated with pictures and artifacts of local Brampton history and old shoemaking equipment.
A self-guided historical walking tour of downtown Brampton called "A Walk Through Time" is available at Brampton City Hall and online at no cost.
Development of Bramalea
 Planned as an innovative " new town", Bramalea was developed immediately east of the Town of Brampton in Chinguacousy Township. It was Canada's first satellite community developed by one of the country's largest real estate developers, ''Bramalea Limited.'' The name "Bramalea" was created by the farmer William Sheard, who combined "BRAM" from Brampton, "MAL" from Malton (then a neighbouring town which is now part of the city of Mississauga), and "LEA", an
Planned as an innovative " new town", Bramalea was developed immediately east of the Town of Brampton in Chinguacousy Township. It was Canada's first satellite community developed by one of the country's largest real estate developers, ''Bramalea Limited.'' The name "Bramalea" was created by the farmer William Sheard, who combined "BRAM" from Brampton, "MAL" from Malton (then a neighbouring town which is now part of the city of Mississauga), and "LEA", an Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
word meaning meadow or grassland. He sold the land to Brampton Leasing (the former name of the developer) and built one of Bramalea's first houses on Dixie Road.
The community was developed according to its detailed master plan, which included provisions for a parkland trail system and a "downtown" to include essential services and a shopping centre
A shopping center (American English) or shopping centre ( Commonwealth English), also called a shopping complex, shopping arcade, shopping plaza or galleria, is a group of shops built together, sometimes under one roof.
The first known colle ...
. The downtown's centrepiece was the Civic Centre, built in 1972 to include the city hall and library. Directly across Team Canada Drive, a shopping centre named Bramalea City Centre
The Bramalea City Centre is a large shopping mall located in the city of Brampton, Ontario, Canada. With over a 1.5 million square feet of retail space and more than 300 outlets, it is one of Canada's largest shopping malls. Regarded as a super r ...
was built. These developments were connected by a long tunnel, planned to provide protection from winter weather. But, the tunnel has long since been closed due to safety issues. Other features included a police station, fire hall, bus terminal, and a collection of seniors' retirement homes.
Each phase of the new city was marked with progressing first letters of street names. Development started with the "A" section, with street names such as Argyle, Avondale, and Aloma. Developers then created a "B" section, "C" section, and so forth. Children on the boundaries of these divisions would regularly compete in street hockey games, pitting, for example, the "D" section versus the "E" section.
The community was initially developed with a large number of recreational facilities, including tennis courts, playgrounds, hockey/lacrosse rinks and swimming pools. An extensive parkland trail and sidewalk system connects the entire community.
Region of Peel
 In 1974, the Ontario provincial government decided to update Peel County's structure. It amalgamated several towns and villages into the new City of Mississauga. In addition, it created the present City of Brampton from the town and the greater portion of the Townships of Chinguacousy and
In 1974, the Ontario provincial government decided to update Peel County's structure. It amalgamated several towns and villages into the new City of Mississauga. In addition, it created the present City of Brampton from the town and the greater portion of the Townships of Chinguacousy and Toronto Gore
Toronto Gore (also the Gore of Toronto) is a former incorporated and now geographic township in Ontario, Canada. It is today split between Mississauga and Brampton.
History
Toronto Gore came into existence as a township in when it was separated ...
, and the northern extremity of Mississauga south of Steeles Avenue
Steeles Avenue is an east–west street that forms the northern city limit of Toronto and the southern limit of York Region in Ontario, Canada. It stretches across the western and central Greater Toronto Area from Appleby Line in Milton in th ...
, including Bramalea and the other communities such as Churchville, Claireville, Ebenezer, Victoria, Springbrook, Coleraine, and Huttonville. While only Huttonville and Churchville still exist as identifiable communities, other names like Claireville are re-emerging as names of new developments.
The province converted Peel County into the Regional Municipality of Peel
The Regional Municipality of Peel (informally Peel Region or Region of Peel, also formerly Peel County) is a regional municipality in the Greater Toronto Area, Southern Ontario, Canada. It consists of three municipalities to the west and northwe ...
. Brampton retained its role as the administrative centre of Peel Region, which it already had as county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US st ...
. The regional council chamber, the Peel Regional Police
The Peel Regional Police (PRP) provide policing services for Peel Region (excluding Caledon) in Ontario, Canada. It is the second largest municipal police service in Ontario after the Toronto Police Service and third largest municipal force in C ...
force, the public health department, and the region's only major museum, the Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives
The Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives (PAMA) is a museum, art gallery, and archives for the Regional Municipality of Peel and are located in Brampton, Ontario, Canada. Previously, it was the Peel Heritage Complex. Its facilities were originally ...
, are all located in Brampton.
This change had its critics among those with a strong sense of local identities. Bramptonians feared urban sprawl would dissolve their town's personality. Bramalea residents took pride in the built-from-scratch and organised structure that had come with their new satellite city and did not want to give it up. Others in Bramalea accept they are part of Brampton, and they make up a "tri-city" area: the original Brampton, Heart Lake, Bramalea.
In 1972, Chinguacousy built a new civic centre in Bramalea. Two years later, when Brampton and Chinguacousy merged, the new city's council was moved from its modest downtown Brampton locale to the Bramalea building. The library systems of Brampton and Chinguacousy were merged, resulting in a system of four locations.
Some have questioned the future of Peel Region as encompassing all of Brampton, Mississauga, and Caledon. The Mississauga council, led by Mayor Hazel McCallion
Hazel McCallion, (; born February 14, 1921) is a Canadian businesswoman and retired politician who served as the fifth mayor of Mississauga, Ontario, from 1978 until 2014. She is the first and current chancellor of Sheridan College.
McCalli ...
, voted to become a single-tier municipality and asked the provincial government to be separated from Peel Region. They argued the city has outgrown the need for a regional layer of government, and that Mississauga is being held back by supporting Brampton and Caledon with its municipal taxes.
Development as a city


 The late 1970's brought new residential development, as Brampton released large tracts of land to developers. Heart Lake was one of the first major development outside the city's pre-1974 limits or Bramalea.
In the early 1980's, Cineplex Odeon closed the Capitol Theatre in Brampton. The City bought the facility in 1981 under the leadership of councillor Diane Sutter. It adapted the former
The late 1970's brought new residential development, as Brampton released large tracts of land to developers. Heart Lake was one of the first major development outside the city's pre-1974 limits or Bramalea.
In the early 1980's, Cineplex Odeon closed the Capitol Theatre in Brampton. The City bought the facility in 1981 under the leadership of councillor Diane Sutter. It adapted the former vaudeville
Vaudeville (; ) is a theatrical genre of variety entertainment born in France at the end of the 19th century. A vaudeville was originally a comedy without psychological or moral intentions, based on a comical situation: a dramatic composition ...
venue and movie house as a performing arts theatre, to be used also as a live music venue. It was renamed the Heritage Theatre. Renovations and maintenance were expensive. In 1983, Toronto consultants Woods Gordon reported to the City that, rather than continue "pouring money" into the Heritage, they should construct a new 750-seat facility with up-to-date features. This recommendation was adopted, and the city designated the 2005–06 season as the Heritage Theatre's "grand finale" season. The city funded construction of the new Rose Theatre, which opened in September 2006.
Carabram was founded in 1982, the result of volunteers from different ethnic communities wanting to organize a festival celebrating diversity and cross-cultural friendship. The name was loosely related to Toronto's Caravan Festival of Cultures. Carabram's first event featured Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Scots, Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
, and West Indian
A West Indian is a native or inhabitant of the West Indies (the Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago). For more than 100 years the words ''West Indian'' specifically described natives of the West Indies, but by 1661 Europeans had begun to use it ...
pavilions. By 2003, the fair had 18 pavilions attracting 45,000 visitors. The national government of Canada had an anchor pavilion in the late 1980s and early 1990s, and for Carabram's 25th Anniversary in 2009.
Brampton has grown to become one of the most diverse cities in Canada. In 1996, the city was 13% South Asian and 8.2% Black. By 2016, the South Asian community grew exponentially to represent 44.3% of the city's population, while the Black population grew to 14%.Census Profile, 2016 Census
Brampton, Ontario, and Peel, Regional Municipality, Ontario Responding to a growing multi-cultural population, the Peel Board of Education introduced evening English as a Second Language
English as a second or foreign language is the use of English by speakers with different native languages. Language education for people learning English may be known as English as a second language (ESL), English as a foreign language (EFL ...
(ESL) classes at high schools. Originally taught by volunteers, the classes eventually were scheduled as daytime courses taught by paid instructors. In the 1980s, the public and Catholic board expanded its language programs, offering night classes in 23 languages. These were introduced due to requests by parents, who wanted their children to learn their ancestral languages and heritage.
In the late 1980s, Mayor Ken Whillans
Kenneth Gilmour 'Ken' Whillans (8 August 1927 – 24 August 1990) served as Mayor#Canada, Mayor of the Brampton, Ontario, City of Brampton from 1982 to 1990.
Personal life and family
Whillans was born in Ottawa. He had a twin brother, Don. Son D ...
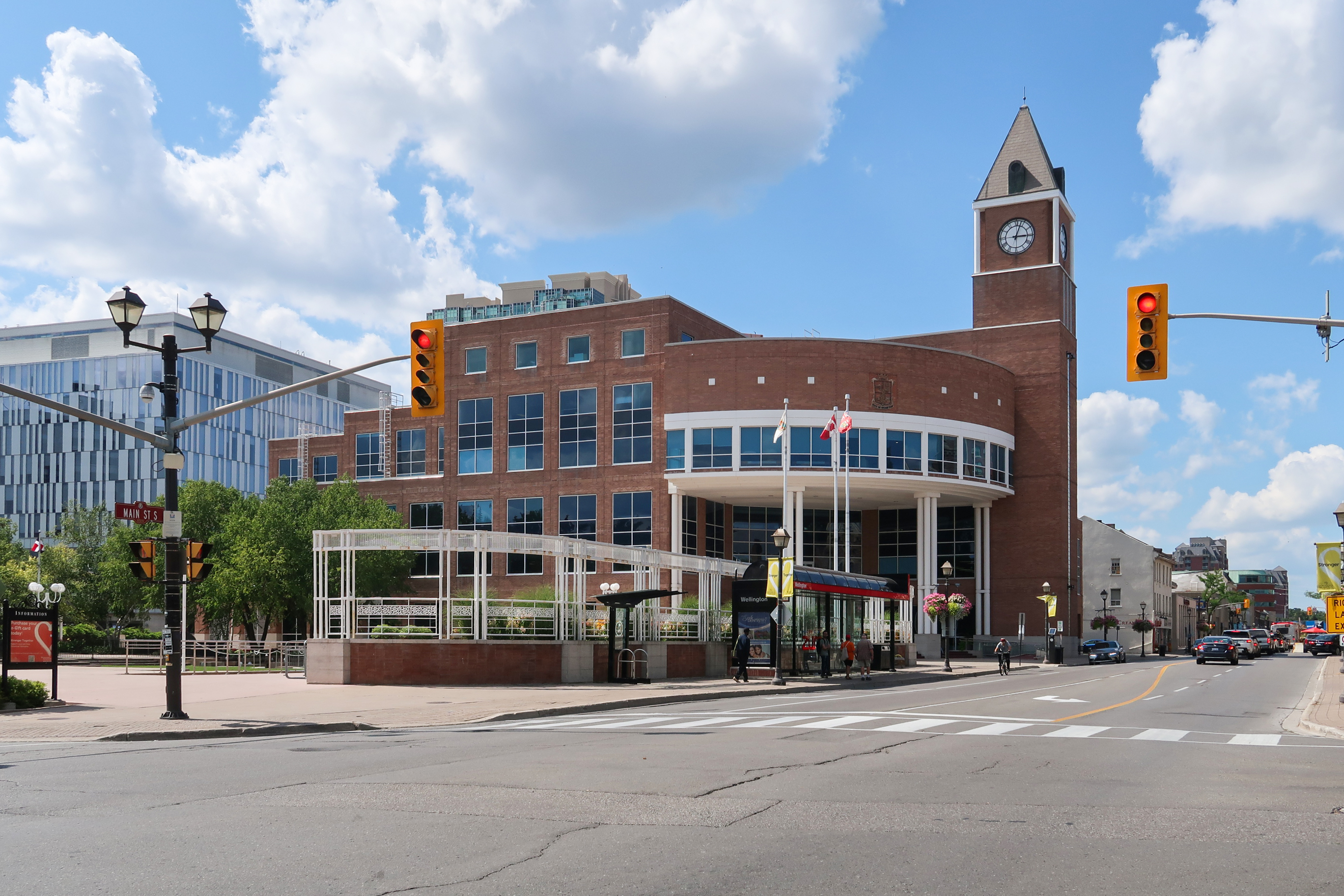
gained approval and funding for the construction of a new city hall in Brampton's downtown. The facility was designed by local architects and constructed by Inzola Construction and built on the site of a former bus terminal. Whillians did not get to see the opening of the new hall in 1991 because of his death in August 1990. With the return of the city government to downtown Brampton, politicians and businesses allied to revitalize the core.
In 1991, development of another new town, Springdale, began. In 1999, development started to appear as far north as the city's border with Caledon along Mayfield Road. The Region designated this border as the line of demarcation for urban development until 2021, although development already began spilling north of Mayfield in the late 2010s. Part of the boundary between Brampton and Vaughan
Vaughan () (2021 population 323,103) is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is located in the Regional Municipality of York, just north of Toronto. Vaughan was the fastest-growing municipality in Canada between 1996 and 2006 with its population increas ...
is also nearly completely urbanized.
Changes continue to reflect the growth of the city. In 1992 the City purchased the Brampton Fairgrounds, to be used for other development. The Agricultural Society relocated in 1997 outside the boundaries of the city to Heart Lake and Old School roads. In 1997 the Health Services Restructuring Commission (HSRC) decided to amalgamate Georgetown and District Memorial Hospital, Etobicoke General Hospital
The Etobicoke General Hospital is a community hospital located at 101 Humber College Boulevard in the Etobicoke district of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Etobicoke General Hospital serves the communities of Etobicoke, Brampton, Mississauga, Caledon, an ...
, and Peel Memorial Hospital as the William Osler Health Centre
William Osler Health System, formerly William Osler Health Centre, is a hospital network in Ontario, Canada that serves the city of Brampton and the northern portion of the western Toronto district of Etobicoke. The network is named for Canadia ...
. It became what is now the province's 6th-largest hospital corporation.
Brampton's 2003 Sesquicentennial celebrations boosted community spirit, reviving the tradition of a summer parade (with 100 floats), and creating other initiatives. To commemorate the town's history, the city under Mayor Fennell reintroduced floral projects to the community. These have included more plantings around town, the revival in 2005 of the city Parade, and participation in the Canada Communities in Bloom
Communities in Bloom is a Canadian non-profit organization
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more peop ...
project.
Geography
Brampton has a total land area of . The City of Brampton is bordered by Highway 50 (Vaughan
Vaughan () (2021 population 323,103) is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is located in the Regional Municipality of York, just north of Toronto. Vaughan was the fastest-growing municipality in Canada between 1996 and 2006 with its population increas ...
) to the East, Winston Churchill Boulevard (Halton Hills
)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 200px
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = CAN ON Halton#Canada Southern Ontario
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, subdivision_type ...
) to the West, Mayfield Road ( Caledon) to the north (except for a small neighbourhood, Snelgrove, which is part of Brampton despite extending somewhat north of Mayfield Road) and the hydro corridor
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This is ...
( Mississauga) to the south as far east as Torbram Road, where the border between the two cities follows the CN Halton Subdivision.
Climate
Brampton features a continental climate (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfb'') which is typical of the rest of the Greater Toronto Area.
Demographics
In the2021 Census of Population
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, which is sli ...
conducted by Statistics Canada, Brampton had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021. At its growth rate of 10.6% since the 2016 census, Brampton was the fastest-growing of Canada's largest 25 municipalities.
In the 2021 census, the largest ethnocultural background in Brampton was South Asian, accounting for 52.4% of the population. Other backgrounds included European (18.9%), Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...
(13.1%), Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
(3.2%), Latin American
Latin Americans ( es, Latinoamericanos; pt, Latino-americanos; ) are the citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America). Latin American countries and their diasporas are multi-eth ...
(2.1%), Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
n (1.4%), Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
(1.1%), West Asian
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes An ...
(1.1%), and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
(1%).
In 2021, the most reported religion among the population was Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
(35.7%), with Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
(17.3%) making up the largest denomination. This was followed by Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fro ...
(25.1%), Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
(18.1%), Islam (9.1%), and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
(1.1%). 10.3% of the population did not identify with a particular religion. Proportionally, Brampton has one of the largest Sikh and Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
populations among all Canadian cities. The Toronto Ontario Temple for the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ch ...
(LDS Church) is located in Brampton.
The 2021 census found that English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
was the mother tongue of 42.9% of the population. The next most common mother tongues were Punjabi (21.7%), Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
* Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub ...
(3.4%), Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Hindi Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
(3%), and '' Hindi Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
(2.2%). The most commonly known languages were English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(95.1%), Punjabi (29.1%), Hindi
Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
(17.5%), Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Gujarati Gujarati may refer to: * something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India * Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat * Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them * Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub ...
(4.7%), and French (4.6%).
'' Gujarati Gujarati may refer to: * something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India * Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat * Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them * Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub ...
Economy
Companies with headquarters in Brampton include MDA Space Missions, which will be building the CanadaArm 3. Loblaw Companies Ltd., Chrysler Canada Brampton Assembly Plant,Gamma-Dynacare Medical Laboratories
Gamma-Dynacare Medical Laboratories is a Canadian medical laboratory services company based in Brampton, Ontario, Canada. Dynacare operates laboratories in Brampton, Bowmanville, London, Ottawa, Thunder Bay, Pointe-Claire, Laval, and Winnipeg. ...
, Mandarin Restaurant
Mandarin Restaurant Franchise Corporation is a chain of all-you-can-eat Chinese-Canadian buffet restaurants. It was founded in 1979 and currently has its headquarters in Brampton, Ontario. The chain consists of licensed restaurants across Sout ...
, Brita, and Clorox
The Clorox Company (formerly Clorox Chemical Company) is an American global manufacturer and marketer of consumer and professional products. As of 2020 the Oakland, California based company had approximately 8,800 employees worldwide. Net sales ...
.
Other major companies operating in Brampton include CN Rail Brampton Intermodal Terminal, Best Buy, Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
which has four production facilities in the city, Ford
Ford commonly refers to:
* Ford Motor Company, an automobile manufacturer founded by Henry Ford
* Ford (crossing), a shallow crossing on a river
Ford may also refer to:
Ford Motor Company
* Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company
* Ford F ...
Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. (; ; ) is a Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Vaud, Switzerland. It is the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other metrics, since ...
, Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
(HBC), Frito Lay Canada, and Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, or Coke, is a carbonated soft drink manufactured by the Coca-Cola Company. Originally marketed as a temperance drink and intended as a patent medicine, it was invented in the late 19th century by John Stith Pemberton in Atlant ...
,
Additional companies in Brampton include Canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western ca ...
, Canadian Tire which has three distribution facilities, Canadian Blood Services
Canadian Blood Services ( French: ''Société canadienne du sang'') is a non-profit charitable organization that is independent from the Canadian government. The Canadian Blood Services was established as Canada's blood authority in all provinces ...
, Boston Scientific
Boston Scientific Corporation ("BSC"), incorporated in Delaware, is a biomedical/biotechnology engineering firm and multinational manufacturer of medical devices used in interventional medical specialties, including interventional radiology, i ...
, Air Canada
Air Canada is the flag carrier and the largest airline of Canada by the size and passengers carried. Air Canada maintains its headquarters in the borough of Saint-Laurent, Montreal, Quebec. The airline, founded in 1937, provides scheduled an ...
, Sleep Country Canada head office, Rogers Communications
Rogers Communications Inc. is a Canadian communications and media company operating primarily in the fields of wireless communications, cable television, telephony and Internet, with significant additional telecommunications and mass media ass ...
, Magna International
Magna International Inc. is a Canadian parts manufacturer for automakers. It is one of the largest companies in Canada and was recognized on the 2020 ''Forbes'' Global 2000. The company is the largest automobile parts manufacturer in North Americ ...
.
Alstom has an assembly plant in Brampton to fulfil their contract with Metrolinx to build Alstom Citadis Spirit LRV cars for the TTC Finch West (ordered 2017 with delivery began 2021 and completed by 2023), Hurontario and Eglinton LRT lines. The Hurontario LRT maintenance facility is currently being built in Brampton.
William Osler Health System
William Osler Health System, formerly William Osler Health Centre, is a hospital network in Ontario, Canada that serves the city of Brampton and the northern portion of the western Toronto district of Etobicoke. The network is named for Canadia ...
operates two health facilities in the city (Peel Memorial and Brampton Civic Hospital).
It is also the location of the Canadian Forces Military reserve force, Army Reserve unit The Lorne Scots (Peel, Dufferin and Halton Regiment).
An automobile manufacturing facility was opened by American Motors (AMC) in 1960 as the Brampton Assembly Plant. In 1986, AMC developed a new, state-of-the-art operation at Bramalea. After AMC was acquired by Chrysler in 1987, AMC's Canadian division and its plants were absorbed; the older facility in Brampton closed in 1992. The newest factory was renamed Brampton Assembly; it is one of the city's largest employers, with almost 4,000 workers when running at capacity.
Education
The Algoma University#Algoma @ Brampton, Algoma University @ Brampton School of Business & Economics offers courses at Market Square Business Centre, 24 Queen Street East. The closest universities to Brampton (offering a wider range of programs) include York University in north Toronto and University of Toronto Mississauga. Along with that, Sheridan College, Davis campus is another major public higher education institution serving Brampton which also has campuses in Oakville, Ontario, Oakville and Mississauga. In 2017, Davis added the Skilled Trades Centre, for training in skilled trades and apprenticeship programs, previously offered in Oakville. A plan by Toronto Metropolitan University, Ryerson University, in partnership with Sheridan College was to establish a new campus in Brampton with a goal of opening in 2022 with $90 million in funding offered by the provincial government in April 2018. On 23 October 2018 however, the new Provincial government (elected in June) withdrew the funding for plans such as this, effectively cancelling the project. Brampton also has many private post-secondary institutions offering vocational training including Springfield College Brampton, CDI College, TriOS College, Academy of Learning, Evergreen Evergreen College (Canada), College, Westervelt College, Medix College, CIMT College, Torbram College, Bitts International Career College, Canadian College of Business, Science & Technology, Hanson College, Queenswood College B, H & T, Flair College of Management and Technology, Sunview College, and College Of Health Studies. Two main school boards operate in Brampton: the Peel District School Board, which operates secular English language, anglophone public schools, and Dufferin-Peel Catholic District School Board, which operates Catholic anglophone public schools. Under the Peel District School Board, the secondary schools are Bramalea Secondary School, Bramalea, Brampton Centennial Secondary School, Brampton Centennial, Central Peel Secondary School, Central Peel, Chinguacousy Secondary School, Chinguacousy, Fletcher's Meadow Secondary School, Fletcher's Meadow, Harold M. Brathwaite Secondary School, Harold M. Brathwaite, Heart Lake Secondary School, Heart Lake, Louise Arbour Secondary School, Louise Arbour, Mayfield Secondary School, Mayfield, North Park Secondary School, North Park, Judith Nyman Secondary School, Judith Nyman, Sandalwood Heights Secondary School, Sandalwood Heights, Turner Fenton Secondary School, Turner Fenton, David Suzuki Secondary School, David Suzuki, Castlebrooke Secondary School, and Jean Augustine, one of the newest. A total of 85 elementary and middle schools feed these high schools in the city. Under the Dufferin-Peel Catholic District School Board, the secondary schools are Cardinal Leger Secondary School, Cardinal Leger, Holy Name of Mary Secondary School, Holy Name of Mary, Notre Dame Catholic Secondary School (Brampton), Notre Dame, St. Augustine Catholic Secondary School, St. Augustine, St. Edmund Campion Secondary School, St. Edmund Campion, St. Roch, St. Marguerite d'Youville Secondary School, St. Marguerite d'Youville, St. Thomas Aquinas Secondary School (Brampton), St. Thomas Aquinas, and Cardinal Ambrozic Secondary School, Cardinal Ambrozic. A total of 44 Catholic elementary and middle schools feed these high schools in the city. The ''Conseil scolaire Viamonde'' operates secular Francophone schools serving the area. The ''Conseil scolaire catholique MonAvenir'' operates Catholic Francophone schools serving the area.Culture


 Several cultural entities in the city operate under the umbrella of the Brampton Arts Council. Located in the city is the
Several cultural entities in the city operate under the umbrella of the Brampton Arts Council. Located in the city is the Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives
The Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives (PAMA) is a museum, art gallery, and archives for the Regional Municipality of Peel and are located in Brampton, Ontario, Canada. Previously, it was the Peel Heritage Complex. Its facilities were originally ...
(PAMA, formerly the Peel Heritage Complex), which is run by the Region of Peel.
The Rose Theatre (originally the Brampton Performing Arts Centre), opened in September 2006. The city had expected the facility to generate $2.7 million in economic activity the first year, growing to $19.8 million by the fifth year. The Rose Theatre far surpassed projections, attracting more than 137,000 patrons in its inaugural year, which exceeded its five-year goal. The arrival of so many new patrons downtown has stimulated the development of numerous new businesses nearby. A new Fountain Stage was unveiled in June 2008 at the nearby Garden Square.
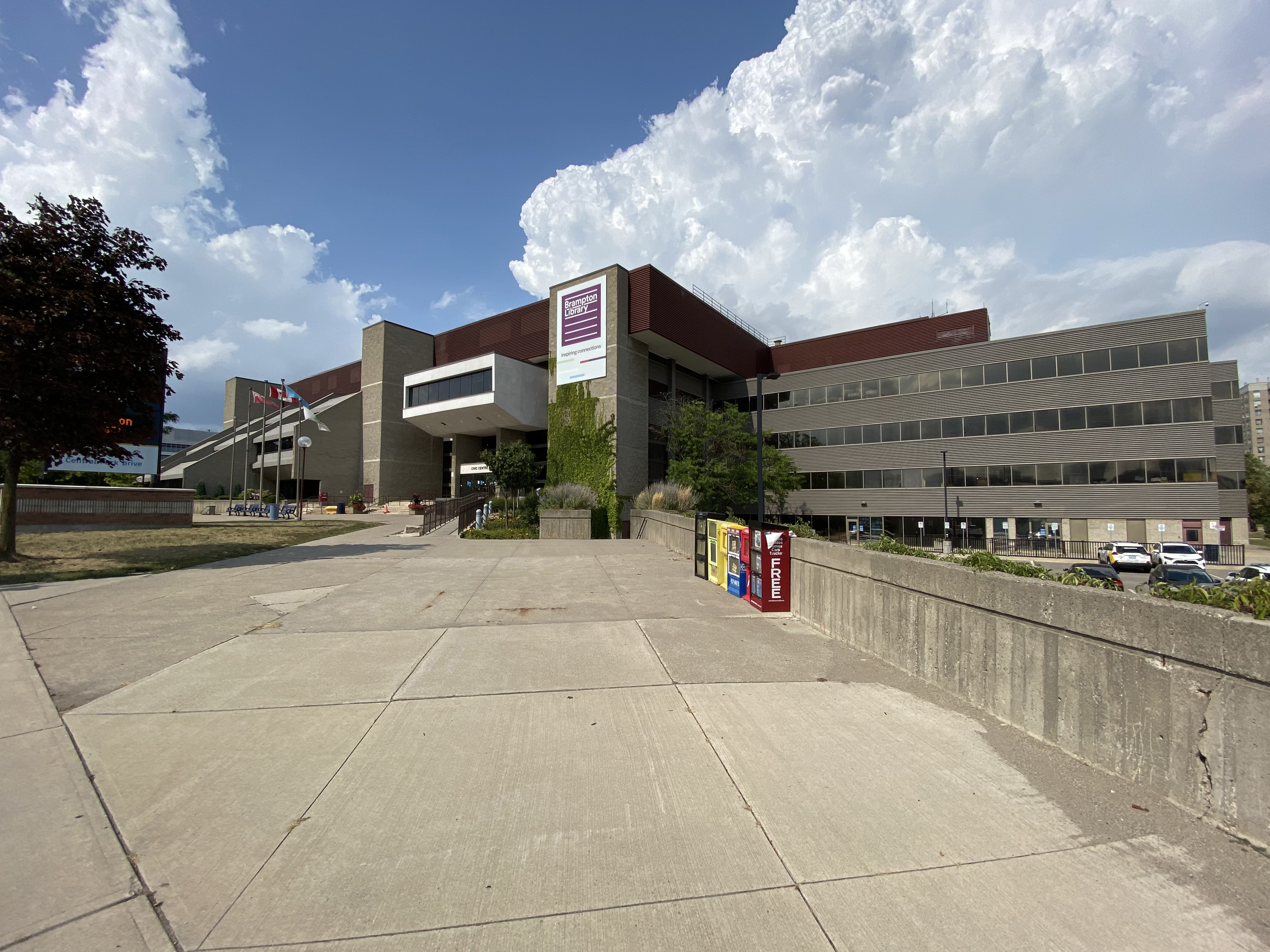
Brampton has six library locations to serve its half-million residents. With a ratio of one library per more than 80,000 residents, it has the lowest library ratio among major Canadian cities.
Festivals in the city include the annual Festival of Literary Diversity, a literary festival devoted to writers from underrepresented groups such as people of colour and LGBTQ writers.
The Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives
The Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives (PAMA) is a museum, art gallery, and archives for the Regional Municipality of Peel and are located in Brampton, Ontario, Canada. Previously, it was the Peel Heritage Complex. Its facilities were originally ...
(PAMA) in Brampton includes a museum, art gallery, and archives. Since opening in 1968, the art gallery section (previously known as the Art Gallery of Peel) has exhibited local, national, and international artists, both contemporary and historical from their permanent collection.
The City of Brampton's long-standing heritage conservation program was recognised with the 2011 Lieutenant Governor's Ontario Heritage Award for Community Leadership. In 2010 the city received an 'honourable mention' under the same provincial awards program.
Sites of interest
 * Gage Park, Brampton, Gage Park
* Artway Gallery
* Beaux Arts Brampton
* CAA Centre
* Camp Naivelt
* Chinguacousy Park-Greenhouse and gardens
* Mount Chinguacousy
* Claireville Conservation Area
* Flower City Theatre Festival
* Great War Flying Museum
* Heart Lake Conservation Area
* Brampton Historical Society
* Historic Bovaird House
* Korean War Memorial Wall (Canada)
* Ontario Field of Honour
*
* Gage Park, Brampton, Gage Park
* Artway Gallery
* Beaux Arts Brampton
* CAA Centre
* Camp Naivelt
* Chinguacousy Park-Greenhouse and gardens
* Mount Chinguacousy
* Claireville Conservation Area
* Flower City Theatre Festival
* Great War Flying Museum
* Heart Lake Conservation Area
* Brampton Historical Society
* Historic Bovaird House
* Korean War Memorial Wall (Canada)
* Ontario Field of Honour
* Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives
The Peel Art Gallery, Museum and Archives (PAMA) is a museum, art gallery, and archives for the Regional Municipality of Peel and are located in Brampton, Ontario, Canada. Previously, it was the Peel Heritage Complex. Its facilities were originally ...
* Professor's Lake
* Rose Theatre
* Lester B. Pearson Theatre
* South Fletchers Sportsplex
* St. Elias Ukrainian Catholic Church
* Wet'n'Wild Toronto
Major shopping areas include Bramalea City Centre
The Bramalea City Centre is a large shopping mall located in the city of Brampton, Ontario, Canada. With over a 1.5 million square feet of retail space and more than 300 outlets, it is one of Canada's largest shopping malls. Regarded as a super r ...
, Shoppers World, Brampton, Shoppers World, and "big box centre" Trinity Commons. The downtown area has some retail; the Centennial Mall and the Brampton Mall are also of note.
Media
Brampton was one of the first areas where Rogers Cable offered its service. The city started a community access channel in the 1970s, which still operates. While some programs on the channel are produced in its Brampton studios, most are based in its Mississauga location. Christian specialty channel Vertical TV is based in Brampton. ''The Brampton Guardian'' is the community's only newspaper, starting as the Bramalea Guardian in 1964. The city's first newspaper, ''The Daily Times'', stopped circulation in the early 1980s. For a little over a year, ''The Brampton Bulletin'' attempted to challenge the ''Guardian'', but it was dismantled after a series of editor changes. Brampton is the official city of license for two radio stations, CIAO (AM), CIAO and CFNY-FM, CFNY. Both stations address their programming toward the entire Greater Toronto Area rather than exclusively to Brampton. CFNY was located upstairs at 83 Kennedy Road until moving to Toronto in 1996.Sports and recreation
Brampton has been home minor professional sports franchises at the CAA Centre, formerly the Powerade Centre. From 2013 to 2015, the Brampton A's played in the National Basketball League of Canada, but relocated to Orangeville, Ontario, to decrease costs of operations of switching the arena floor from ice hockey to basketball. From 2013 to 2020, the Brampton Beast played in the Central Hockey League and ECHL, but ceased operations during the COVID-19 pandemic in February 2021 after having not been able to play since March 2020. The numerous sporting venues and activities includes the outdoor ice path for ice skating, skating through Gage Park, Brampton, Gage Park. Chinguacousy Park includes a ski lift, a curling club, and Tennis Centre for multi-season activities. In the summer, amateur softball leagues abound. Crowds line the beaches at Professor's Lake for the annual outdoor "shagging" display. Since 1967, the Brampton Canadettes have hosted the annual Brampton Canadettes Easter Tournament in hockey. Brampton also held the U-18 Women's Softball World Cup, 2013 Junior Women's Softball World Championship.Infrastructure
Health and medicine
Courts
A. Grenville and William Davis Courthouse, Grenville & William Davis Courthouse, Ontario Court of Justice, is located in Brampton at 7755 Hurontario Street (Hurontario Street at County Court).Transportation
Public transit
 Local transit is provided by Brampton Transit, with connections to other systems such as MiWay, York Region Transit, Go Transit, and Toronto Transit Commission. Brampton Transit also operates a bus rapid transit system, "Züm" (pronounced Zoom), along Hurontario Street, Main/Hurontario Streets,
Local transit is provided by Brampton Transit, with connections to other systems such as MiWay, York Region Transit, Go Transit, and Toronto Transit Commission. Brampton Transit also operates a bus rapid transit system, "Züm" (pronounced Zoom), along Hurontario Street, Main/Hurontario Streets, Steeles Avenue
Steeles Avenue is an east–west street that forms the northern city limit of Toronto and the southern limit of York Region in Ontario, Canada. It stretches across the western and central Greater Toronto Area from Appleby Line in Milton in th ...
, Queen Street/List of numbered roads in York Region, Highway 7, Bovaird Drive–Airport Road, and Queen Street West–Mississauga Road, which form the backbone to its bus network.
There is GO Bus service to York University and subway stations at Yorkdale Mall and York Mills in Toronto. There are three GO Train stations in Brampton along the Kitchener line: Bramalea, Brampton and Mount Pleasant.
Rail
Both Canadian National Railway (CN) and the Orangeville-Brampton Railway Shortline railroad, short line (formerly part of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) line) run through the city. CN's Intermodal Yards are located east of Airport Road, Ontario, Airport Road between Steeles and Queen Street East. The CN Track from Toronto's Union Station, Toronto, Union Station is used by the Kitchener line, Kitchener GO Transit Rail Corridor providing commuter rail to and from Toronto with rail station stops at Bramalea GO Station, Bramalea, Brampton GO Station, Downtown Brampton, and Mount Pleasant GO Station, Mount Pleasant. Via Rail connects through Brampton as part of the Quebec City-Windsor Corridor.Air
Canada's busiest airport, Toronto Pearson International Airport (CYYZ), is located near Brampton, in Mississauga. For general aviation, the city is served by the privately owned Brampton Airport (CNC3), located to the north of the city in neighbouring Caledon.Road
Brampton is served by several major transportation routes: Ontario Highway 401, Highway 401 from Toronto is a short distance south in Mississauga, and can be reached by Ontario Highway 410, Highway 410, which runs north–south through the middle of the city. Ontario Highway 407, Highway 407 runs along the southern portion of the city, just north of the boundary with Mississauga. Steeles Avenue, which runs north of the 407, is a thoroughfare continuing from Toronto. Queen Street is the city's main east–west street. Farther north, Bovaird Drive is another main artery. Sections of both Queen (eastern portion) and Bovaird (western portion) were part the former Highway 7 (Ontario), Highway 7, (now List of numbered roads in Peel Region, Regional Road 107), with Highway 410 being the route followed between the two streets. Main Street, part of the historic road,Hurontario Street
Hurontario Street is a roadway running in Ontario, Canada between Lake Ontario at Mississauga and Lake Huron's Georgian Bay at Collingwood. Within Peel Region, it is a major urban thoroughfare within the cities of Mississauga and Brampton, wh ...
(as well as Hurontario proper in the northern and southern parts of the city), and formerly Ontario Highway 10, Highway 10, is the city's main north–south artery. In the east end, Airport Road is a busy artery that is used as a route north to Wasaga Beach, a popular beach resort town.
Representation in other media
*Deepa Mehta's 2008 film ''Heaven on Earth (2008 film), Heaven on Earth'' is set in Brampton.Notable people
Four people from Brampton have received the Order of Canada: Robert William Bradford, former Director of the National Aviation Museum; Michael F. Clarke, director at Evergreen, the Yonge Street Mission for street youth in Toronto; Howard Pawley, professor and former Premier of Manitoba; and William G. Davis, former Premier of Ontario.Sports
 * Baseball: Zach Pop
* Basketball: Michael Meeks (basketball), Michael Meeks (internationally), Tyler Ennis (basketball), Tyler Ennis (NBA), Tristan Thompson (NBA), Anthony Bennett (basketball), Anthony Bennett (NBA)
* Cricket: Saad Bin Zafar, Cecil Pervez,
* Curling: Scott Bailey (curler), Scott Bailey, Peter Corner, Graeme McCarrel, Wayne Middaugh, Allison Pottinger
* Field hockey: Bernadette Bowyer
* Figure skating: Vern Taylor, Mark Janoschak
* Football: Michael Bailey (Canadian football), Michael Bailey (CFL), Fernand Kashama (CFL), Chris Kowalczuk (CFL), Rob Maver (CFL), Jerome Messam (CFL, NFL), Jason Nugent (CFL), Junior Turner (CFL), Steven Turner (CFL), Jabar Westerman (CFL), Jamaal Westerman (NFL), James Yurichuk (CFL) Nakas Onyeka (CFL)
* Golf: David Hearn (golfer), David Hearn; Steve Duplantis (caddy)
* Hockey: Andrew Cassels, Mike Danton, Mike Dwyer (ice hockey), Mike Dwyer, Todd Elik, Chris Felix, Sheldon Keefe, Tom Laidlaw, Kris Newbury, Rick Nash, Tyler Seguin, Jamie Storr, Mike Weaver (ice hockey), Mike Weaver, Mike Wilson (ice hockey), Mike Wilson, Sean Monahan, Tyler Graovac, Cassie Campbell, Mikyla Grant-Mentis
* Horse-racing: Sid C. Attard, Patrick Husbands, Robert P. Tiller, Emma-Jayne Wilson
* Lacrosse: Jim Veltman (NLL)
* Sailing: Kevin Stittle
* Soccer: Gabe Gala (MLS), Atiba Hutchinson (Super Lig), Peter Roe (soccer), Peter Roe (ASL, MISL), Murphy Wiredu, Doneil Henry, Doniel Henry, David Hoilett, David "Junior" Hoilett, Paul Stalteri, Roger Thompson, Cyle Larin, Tajon Buchanan, Jahkeele Marshall-Rutty
* Speed skating: Tyson Heung
* Tennis: Jill Hetherington, Milos Raonic
* Track and field: Charles Allen (athlete), Charles Allen, Mark Boswell (athlete), Mark Boswell, Kate Van Buskirk
* Wrestling: Ohenewa Akuffo
* Baseball: Zach Pop
* Basketball: Michael Meeks (basketball), Michael Meeks (internationally), Tyler Ennis (basketball), Tyler Ennis (NBA), Tristan Thompson (NBA), Anthony Bennett (basketball), Anthony Bennett (NBA)
* Cricket: Saad Bin Zafar, Cecil Pervez,
* Curling: Scott Bailey (curler), Scott Bailey, Peter Corner, Graeme McCarrel, Wayne Middaugh, Allison Pottinger
* Field hockey: Bernadette Bowyer
* Figure skating: Vern Taylor, Mark Janoschak
* Football: Michael Bailey (Canadian football), Michael Bailey (CFL), Fernand Kashama (CFL), Chris Kowalczuk (CFL), Rob Maver (CFL), Jerome Messam (CFL, NFL), Jason Nugent (CFL), Junior Turner (CFL), Steven Turner (CFL), Jabar Westerman (CFL), Jamaal Westerman (NFL), James Yurichuk (CFL) Nakas Onyeka (CFL)
* Golf: David Hearn (golfer), David Hearn; Steve Duplantis (caddy)
* Hockey: Andrew Cassels, Mike Danton, Mike Dwyer (ice hockey), Mike Dwyer, Todd Elik, Chris Felix, Sheldon Keefe, Tom Laidlaw, Kris Newbury, Rick Nash, Tyler Seguin, Jamie Storr, Mike Weaver (ice hockey), Mike Weaver, Mike Wilson (ice hockey), Mike Wilson, Sean Monahan, Tyler Graovac, Cassie Campbell, Mikyla Grant-Mentis
* Horse-racing: Sid C. Attard, Patrick Husbands, Robert P. Tiller, Emma-Jayne Wilson
* Lacrosse: Jim Veltman (NLL)
* Sailing: Kevin Stittle
* Soccer: Gabe Gala (MLS), Atiba Hutchinson (Super Lig), Peter Roe (soccer), Peter Roe (ASL, MISL), Murphy Wiredu, Doneil Henry, Doniel Henry, David Hoilett, David "Junior" Hoilett, Paul Stalteri, Roger Thompson, Cyle Larin, Tajon Buchanan, Jahkeele Marshall-Rutty
* Speed skating: Tyson Heung
* Tennis: Jill Hetherington, Milos Raonic
* Track and field: Charles Allen (athlete), Charles Allen, Mark Boswell (athlete), Mark Boswell, Kate Van Buskirk
* Wrestling: Ohenewa Akuffo
Politics
Three Canadian premiers got their start in Brampton; Premiers Tobias Norris and Howard Pawley OC of Manitoba, and "Brampton Billy", Ontario premier William Grenville Davis CC. Other notable politicians include John Coyne (politician), John Coyne, and Conservative opposition leader Gordon Graydon. Alberta politician and businessman James Alexander Lougheed, Sir James A. Lougheed was born in Brampton, and served 30 years in Senate; Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina mayor David Lynch Scott was born here. President of the Treasury Board Tony Clement spent time as a Brampton MPP. John McDermid held various cabinet positions under Brian Mulroney, Bal Gosal Minister of State-Sport, and former Mayor Linda Jeffrey held cabinet positions at the provincial level. Ruby Dhalla represented the riding of Brampton—Springdale in the Canadian House of Commons from 2004 to 2011 as a member of the Liberal Party. Dhalla and British Columbia Conservative MP Nina Grewal were the first Sikh women to serve in the Canadian House of Commons. Parm Gill was elected as the member of parliament from the Conservative Party of Canada for the riding of Brampton-Springdale in 2011, who was also appointed as the Parliamentary Secretary to the Minister of Veteran Affairs in 2013. Jagmeet Singh began his political career in Brampton running in two elections in 2011, defeated in the federal election in May but elected Member of Provincial Parliament for Bramalea—Gore—Malton in October. In 2015 he became deputy leader of the Ontario New Democratic Party. In 2017 he became party leader, leader of the New Democratic Party (Canada), federal NDP, the first member of a visible minority to become permanent leader of a major federal party in Canada.Arts
Authors born in or living in Brampton include Rohinton Mistry, Jesse Thistle, Edo Van Belkom and Rupi Kaur (poet). Visual arts notables from Brampton include etcher Caroline Helena Armington, Ronald Bloore, Member of the Order of Canada; Organiser and member of the "Regina Five",(1960) watercolourist Jack Reid, and William Ronald, who was raised in town. Norman Mills Price. Animators David Feiss and Jay Stephens grew up here. Music acts from Brampton include Punk band The Flatliners, Indie Rock band Moneen, R&B singer Keshia Chanté, country singer Johnny Reid, "Metal Queen" Lee Aaron and pop singer Alyssa Reid. Country singer and "World Champion Yodeller" Donn Reynolds lived here from 1969 to 1997. Barry Stock, guitarist from Three Days Grace was raised in Brampton, and currently resides in Caledon. Singer Alessia Cara, hip-hop artist Roy Woods, and hip-hop artist Tory Lanez were also born in Brampton. Hip-hop record producer WondaGurl was also born in Brampton.Film, television and comedy
 Two notable comedians hail from Brampton: Scott Thompson (comedian), Scott Thompson and Russell Peters.
Comedic actor Michael Cera was born and raised in Brampton. Shawn Ashmore, Aaron Ashmore (''Smallville (TV series), Smallville'') are Brampton-raised. Actor Tyler Labine starred in ''Mad Love (TV series), Mad Love''.
Other Brampton-born or affiliated actors include Paulo Costanzo, Jordan Gavaris, Gemini Award winner Kris Lemche, Lara Jean Chorostecki, Sabrina Grdevich, Nicole Lyn, actor and producer David Phillips (actor, host), David J. Phillips, reality TV star and art dealer Billy Jamieson, performer George R. Robertson, and performer Sidhu Moose Wala.
Others include voice actor Brenna O'Brien, and on-air media personalities Cassie Campbell, Chris Connor, Chris Cuthbert and Scott McGillivray.
Two notable comedians hail from Brampton: Scott Thompson (comedian), Scott Thompson and Russell Peters.
Comedic actor Michael Cera was born and raised in Brampton. Shawn Ashmore, Aaron Ashmore (''Smallville (TV series), Smallville'') are Brampton-raised. Actor Tyler Labine starred in ''Mad Love (TV series), Mad Love''.
Other Brampton-born or affiliated actors include Paulo Costanzo, Jordan Gavaris, Gemini Award winner Kris Lemche, Lara Jean Chorostecki, Sabrina Grdevich, Nicole Lyn, actor and producer David Phillips (actor, host), David J. Phillips, reality TV star and art dealer Billy Jamieson, performer George R. Robertson, and performer Sidhu Moose Wala.
Others include voice actor Brenna O'Brien, and on-air media personalities Cassie Campbell, Chris Connor, Chris Cuthbert and Scott McGillivray.
Sister cities
Brampton has two sister cities as well as active economic, historic, and cultural relationships with others. Sister cities: * Miami Beach, Florida * Plano, Texas Friendship relationships: * Ribeira Grande, Azores, Ribeira Grande, Azores, Portugal * Xuzhou, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China * Brampton, Eden, Brampton, Eden, Cumbria, England * Marikina, Marikina, Philippines * Gapyeong County, Gapyeong, South Korea * Fangshan District, Fangshan District (Funhill), Beijing, ChinaSee also
* Brampton Board of Trade * Brampton municipal election, 2006 * City of Brampton Arts Person of the Year * List of airports in the Greater Toronto Area * List of historic places in BramptonReferences
*Notes
External links
* * {{Authority control Brampton, Cities in Ontario Lower-tier municipalities in Ontario Populated places established in 1853 1853 establishments in Ontario Ethnic enclaves in Canada Little Indias Sikh enclaves