Borneo Topography.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Borneo (; id,
 Borneo was formed through Mesozoic accretion of microcontinental fragments, ophiolite terranes and island arc crust onto a Paleozoic continental core. At the beginning of the
Borneo was formed through Mesozoic accretion of microcontinental fragments, ophiolite terranes and island arc crust onto a Paleozoic continental core. At the beginning of the  Before sea levels rose at the end of the last ice age, Borneo was part of the mainland of Asia, forming, with Java and
Before sea levels rose at the end of the last ice age, Borneo was part of the mainland of Asia, forming, with Java and  The largest river system is the Kapuas in West Kalimantan, with a length of . Other major rivers include the Mahakam in East Kalimantan ( long), the Barito, Kahayan, and Mendawai in
The largest river system is the Kapuas in West Kalimantan, with a length of . Other major rivers include the Mahakam in East Kalimantan ( long), the Barito, Kahayan, and Mendawai in
 The Borneo
The Borneo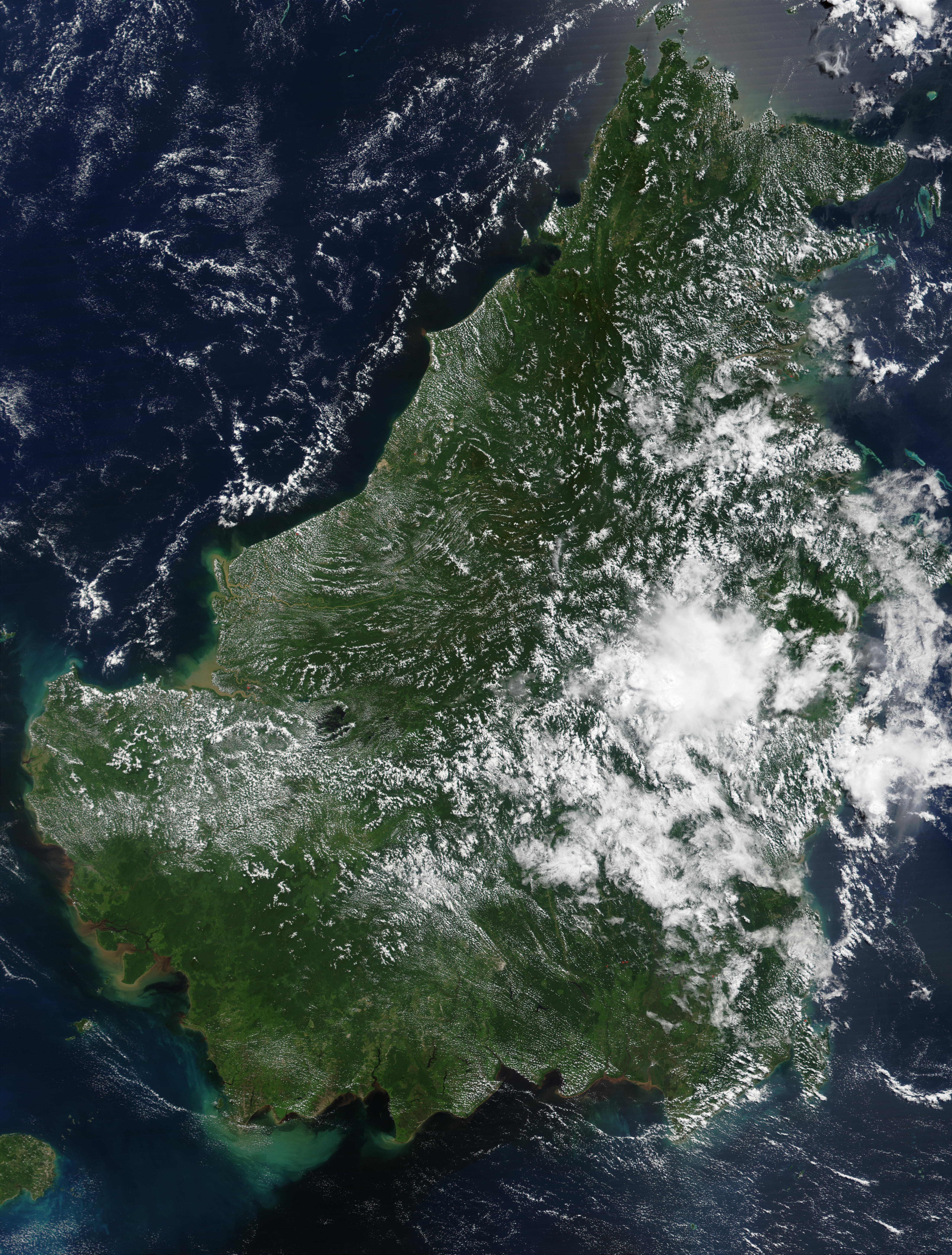 
 The island historically had extensive rainforest cover, but the area was reduced due to heavy
The island historically had extensive rainforest cover, but the area was reduced due to heavy
 In November 2018, scientists reported the discovery of the oldest known figurative art painting, over 40,000 (perhaps as old as 52,000) years old, of an unknown animal, in the cave of
In November 2018, scientists reported the discovery of the oldest known figurative art painting, over 40,000 (perhaps as old as 52,000) years old, of an unknown animal, in the cave of 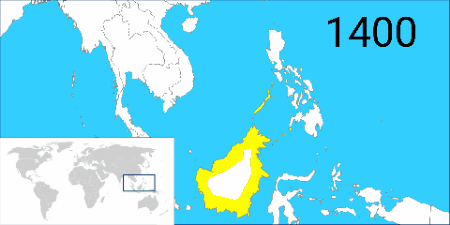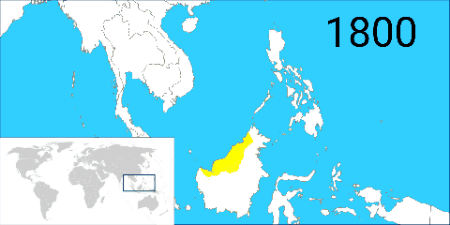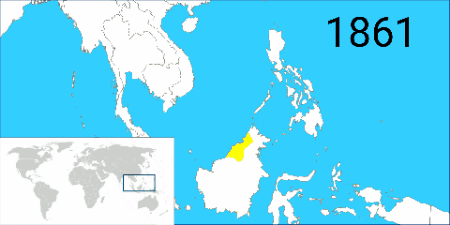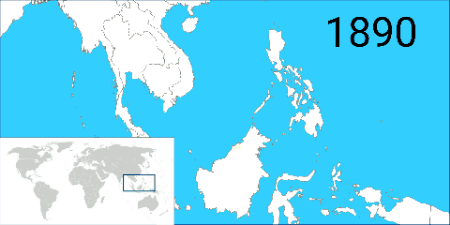 Stone pillars bearing inscriptions in the
Stone pillars bearing inscriptions in the
 Since the fall of Malacca in 1511, Portuguese merchants traded regularly with Borneo, and especially with Brunei from 1530. Having visited Brunei's capital, the Portuguese described the place as surrounded by a stone wall. While Borneo was seen as rich, the Portuguese did not make any attempts to conquer it. The Spanish had sailed from Latin America and conquered the Brunei's provinces in the Philippines and incorporated it into the Mexico-Centered Viceroyalty of New Spain. The Spanish visit to Brunei led to the
Since the fall of Malacca in 1511, Portuguese merchants traded regularly with Borneo, and especially with Brunei from 1530. Having visited Brunei's capital, the Portuguese described the place as surrounded by a stone wall. While Borneo was seen as rich, the Portuguese did not make any attempts to conquer it. The Spanish had sailed from Latin America and conquered the Brunei's provinces in the Philippines and incorporated it into the Mexico-Centered Viceroyalty of New Spain. The Spanish visit to Brunei led to the  The Dutch began to intervene in the southern part of the island upon resuming contact in 1815, posting '' residents'' to Banjarmasin, Pontianak and Sambas and ''assistant-residents'' to Landak and Mampawa. The Sultanate of Brunei in 1842 granted large parts of land in Sarawak to the English adventurer James Brooke, as a reward for his help in quelling a local rebellion. Brooke established the Raj of Sarawak and was recognised as its rajah after paying a fee to the sultanate. He established a monarchy, and the Brooke dynasty (through his nephew and great-nephew) ruled Sarawak for 100 years; the leaders were known as the White Rajahs. Brooke also acquired the island of Labuan for Great Britain in 1846 through the
The Dutch began to intervene in the southern part of the island upon resuming contact in 1815, posting '' residents'' to Banjarmasin, Pontianak and Sambas and ''assistant-residents'' to Landak and Mampawa. The Sultanate of Brunei in 1842 granted large parts of land in Sarawak to the English adventurer James Brooke, as a reward for his help in quelling a local rebellion. Brooke established the Raj of Sarawak and was recognised as its rajah after paying a fee to the sultanate. He established a monarchy, and the Brooke dynasty (through his nephew and great-nephew) ruled Sarawak for 100 years; the leaders were known as the White Rajahs. Brooke also acquired the island of Labuan for Great Britain in 1846 through the  Prior to the recognition of Spanish presence in the Philippine archipelago, a protocol known as the Madrid Protocol of 1885 was signed between the governments of the United Kingdom, Germany and Spain in Madrid to cement Spanish influence and recognise their sovereignty over the Sultanate of Sulu—in return for Spain's relinquishing its claim to the former possessions of the sultanate in northern Borneo. The British administration then established the first railway network in northern Borneo, known as the
Prior to the recognition of Spanish presence in the Philippine archipelago, a protocol known as the Madrid Protocol of 1885 was signed between the governments of the United Kingdom, Germany and Spain in Madrid to cement Spanish influence and recognise their sovereignty over the Sultanate of Sulu—in return for Spain's relinquishing its claim to the former possessions of the sultanate in northern Borneo. The British administration then established the first railway network in northern Borneo, known as the
 During World War II, Japanese forces gained control and occupied most areas of Borneo from 1941 to 1945. In the first stage of the war, the British saw the Japanese advance to Borneo as motivated by political and territorial ambitions rather than economic factors. The occupation drove many people in the coastal towns to the interior, searching for food and escaping the Japanese. The Chinese residents in Borneo, especially with the Sino-Japanese War in Mainland China mostly resisted the Japanese occupation. Following the formation of resistance movements in northern Borneo such as the Jesselton Revolt, many innocent indigenous and Chinese people were executed by the Japanese for their alleged involvement.
In Kalimantan, the Japanese also killed many Malay intellectuals, executing all the Malay sultans of West Kalimantan in the
During World War II, Japanese forces gained control and occupied most areas of Borneo from 1941 to 1945. In the first stage of the war, the British saw the Japanese advance to Borneo as motivated by political and territorial ambitions rather than economic factors. The occupation drove many people in the coastal towns to the interior, searching for food and escaping the Japanese. The Chinese residents in Borneo, especially with the Sino-Japanese War in Mainland China mostly resisted the Japanese occupation. Following the formation of resistance movements in northern Borneo such as the Jesselton Revolt, many innocent indigenous and Chinese people were executed by the Japanese for their alleged involvement.
In Kalimantan, the Japanese also killed many Malay intellectuals, executing all the Malay sultans of West Kalimantan in the
 The Philippines opposed the newly proposed federation, claiming the eastern part of North Borneo (today the Malaysian state of Sabah) as part of its territory as a former possession of the Sultanate of Sulu. The Philippine government mostly based their claim on the Sultanate of Sulu's cession agreement with the British North Borneo Company, as by now the sultanate had come under the jurisdiction of the Philippine republican administration, which therefore should inherit the Sulu former territories. The Philippine government also claimed that the heirs of the sultanate had ceded all their territorial rights to the republic.
The Sultanate of Brunei at the first welcomed the proposal of a new larger federation. Meanwhile, the Brunei People's Party led by
The Philippines opposed the newly proposed federation, claiming the eastern part of North Borneo (today the Malaysian state of Sabah) as part of its territory as a former possession of the Sultanate of Sulu. The Philippine government mostly based their claim on the Sultanate of Sulu's cession agreement with the British North Borneo Company, as by now the sultanate had come under the jurisdiction of the Philippine republican administration, which therefore should inherit the Sulu former territories. The Philippine government also claimed that the heirs of the sultanate had ceded all their territorial rights to the republic.
The Sultanate of Brunei at the first welcomed the proposal of a new larger federation. Meanwhile, the Brunei People's Party led by
 In Kalimantan, since the 1990s, the Indonesian government has undertaken an intense transmigration program; to that end it has financed the relocation of poor, landless families from Java, Madura, and Bali. By 2001, transmigrants made up 21% of the population in Central Kalimantan. Since the 1990s, the indigenous Dayak and Malays have resisted encroachment by these migrants, and violent conflict has occurred between some transmigrant and indigenous populations. In the 1999 Sambas riots, Dayaks and
In Kalimantan, since the 1990s, the Indonesian government has undertaken an intense transmigration program; to that end it has financed the relocation of poor, landless families from Java, Madura, and Bali. By 2001, transmigrants made up 21% of the population in Central Kalimantan. Since the 1990s, the indigenous Dayak and Malays have resisted encroachment by these migrants, and violent conflict has occurred between some transmigrant and indigenous populations. In the 1999 Sambas riots, Dayaks and
 The island of Borneo is divided administratively by three countries.
* The independent sultanate of Brunei (main part and eastern exclave of
The island of Borneo is divided administratively by three countries.
* The independent sultanate of Brunei (main part and eastern exclave of
Environmental Profile of Borneo
– Background on Borneo, including natural and social history, deforestation statistics, and conservation news. {{Authority control Greater Sunda Islands International islands Islands of Brunei Islands of Indonesia Islands of Malaysia Kalimantan Maritime Southeast Asia Regions of Eurasia
Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo.
In 2019, ...
) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
, and east of Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
.
The island is politically divided among three countries: Malaysia and Brunei in the north, and Indonesia to the south. Approximately 73% of the island is Indonesian territory. In the north, the East Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak make up about 26% of the island. The population in Borneo is 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Additionally, the Malaysian federal territory of Labuan is situated on a small island just off the coast of Borneo. The sovereign state of Brunei, located on the north coast, comprises about 1% of Borneo's land area. A little more than half of the island is in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, including Brunei and the Malaysian portion, while the Indonesian portion spans the Northern and Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
hemispheres.
Etymology
The island is known by many names. Internationally it is known as ''Borneo'', derived from European contact with theBrunei kingdom
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by the ...
in the 16th century during the Age of Exploration. On a map from around 1601, Brunei city is referred to as Borneo, and the whole island is also labelled Borneo. The name ''Borneo'' may derive from the Sanskrit word ' (), meaning either "water" or Varuna, the Hindu god of rain.
The local population called it ''Klemantan'' or ''Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo.
In 2019, ...
,'' which was derived from the Sanskrit word ''Kalamanthana,'' meaning "burning weather" possibly to describe its hot and humid tropical weather. Indonesian historian Slamet Muljana suggests that the name ''Kalamanthana'' was derived from Sanskrit terms ''kala
Kala or Kalah may refer to:
Religion Hinduism
*Kāla, a Sanskrit word meaning ''time''
*Kāla, a Hindu deity of time, destiny, death and destruction closely related to Yama and Shiva.
*Kalā, a Sanskrit word meaning ''performing arts''
* Kala Bo, ...
'' (time or season) and ''manthana'' (churning, kindling or creating fire by friction), which possibly describes the heat of the weather.
In earlier times, the island was known by other names. In 977, Chinese records
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of v ...
began to use the term ''Bo-ni'' to refer to Borneo. In 1225, it was also mentioned by the Chinese official Chau Ju-Kua Zhao Rukuo (; 1170–1231), also read as Zhao Rugua, or misread as Zhao Rushi, was a Chinese historian and politician during the Song dynasty. He wrote a two-volume book titled '' Zhu Fan Zhi''. The book deals with the world known to the Chinese in ...
(趙汝适). The Javanese manuscript Nagarakretagama, written by Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
court poet Mpu Prapanca in 1365, mentioned the island as ''Nusa Tanjungnagara'', which means the island of the Tanjungpura Kingdom. Nevertheless, the same manuscript also mentioned ''Barune'' (Brunei) and other polities on the island.
Geography
Geology
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
Borneo formed a promontory
A promontory is a raised mass of land that projects into a lowland or a body of water (in which case it is a peninsula). Most promontories either are formed from a hard ridge of rock that has resisted the erosive forces that have removed the so ...
of Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
which partly separated from Asian mainland by the proto-South China Sea. The oceanic part of the proto-South China Sea was subducted
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
during the Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
period and a large accretionary complex formed along the northwestern of the island of Borneo. In the early Miocene uplift of the accretionary complex occurred as a result of underthrusting of thinned continental crust in northwest. The uplift may have also resulted from shortening due to the counter-clockwise rotation of Borneo between 20 and 10 mega-annum (Ma) as a consequence of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
-Southeast Asia collision. Large volumes of sediment were shed into basins, which scattered offshore to the west, north and east of Borneo as well into a Neogene
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. ...
basin which is currently exposed in large areas of eastern and southern Sabah. In southeast Sabah, the Miocene to recent island arc terranes of the Sulu Archipelago extend onshore into Borneo with the older volcanic arc was the result of southeast dipping subduction while the younger volcanics are likely resulted from northwest dipping subduction the Celebes Sea.
 Before sea levels rose at the end of the last ice age, Borneo was part of the mainland of Asia, forming, with Java and
Before sea levels rose at the end of the last ice age, Borneo was part of the mainland of Asia, forming, with Java and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, the upland regions of a peninsula that extended east from present day Indochina. The South China Sea and Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand, also known as the Gulf of Siam, is a shallow inlet in the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around in l ...
now submerge the former low-lying areas of the peninsula. Deeper waters separating Borneo from neighbouring Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
prevented a land connection to that island, creating the divide known as Wallace's Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a tran ...
between Asian and Australia- New Guinea biological regions. The island today is surrounded by the South China Sea to the north and northwest, the Sulu Sea
The Sulu Sea ( fil, Dagat Sulu; Tausug: ''Dagat sin Sūg''; Chavacano: ''Mar de Sulu''; Cebuano: ''Dagat sa Sulu''; Hiligaynon: ''Dagat sang Sulu''; Karay-a: ''Dagat kang Sulu''; Cuyonon: ''Dagat i'ang Sulu''; ms, Laut Sulu) is a body o ...
to the northeast, the Celebes Sea and the Makassar Strait
Makassar Strait is a strait between the islands of Borneo and Sulawesi in Indonesia. To the north it joins the Celebes Sea, while to the south it meets the Java Sea. To the northeast, it forms the Sangkulirang Bay south of the Mangkalihat Pe ...
to the east, and the Java Sea
The Java Sea ( id, Laut Jawa, jv, Segara Jawa) is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its nort ...
and Karimata Strait to the south. To the west of Borneo are the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
. To the south and east are islands of Indonesia: Java and Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
, respectively. To the northeast are the Philippine Islands. With an area of , it is the third-largest island in the world, and is the largest island of Asia (the largest continent). Its highest point is Mount Kinabalu in Sabah, Malaysia, with an elevation of .
 The largest river system is the Kapuas in West Kalimantan, with a length of . Other major rivers include the Mahakam in East Kalimantan ( long), the Barito, Kahayan, and Mendawai in
The largest river system is the Kapuas in West Kalimantan, with a length of . Other major rivers include the Mahakam in East Kalimantan ( long), the Barito, Kahayan, and Mendawai in South Kalimantan
South Kalimantan ( id, Kalimantan Selatan) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is the smallest province in Kalimantan, the Indonesian territory of Borneo. The provincial capital was Banjarmasin until 15 February 2022 when it wa ...
(, , and long respectively), Rajang in Sarawak ( long) and Kinabatangan
Kinabatangan ( ms, Pekan Kinabatangan) is the capital of the Kinabatangan District in the Sandakan Division of Sabah, Malaysia. Its population was estimated to be around 10,256 in 2010. Kinabatangan is mostly populated with the Orang Sungai
...
in Sabah ( long). Borneo has significant cave systems. In Sarawak, the Clearwater Cave has one of the world's longest underground rivers while Deer Cave
Deer Cave ( ms, Gua Rusa), located near Miri, Sarawak, Malaysia, is a show cave attraction of Gunung Mulu National Park. It was surveyed in 1961 by G. E. Wilford of the British Borneo Geological Survey, who predicted that Mulu would yield many ...
is home to over three million bats, with guano
Guano (Spanish from qu, wanu) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. G ...
accumulated to over deep. The Gomantong Caves
The Gomantong Caves are an intricate cave system inside Gomantong Hill in Sandakan Division, Sabah, Malaysia. The hill is the largest limestone outcrop in the Lower Kinabatangan area.
Description
Situated in the Gomantong Forest Reserve, the c ...
in Sabah has been dubbed as the "Cockroach Cave" due to the presence of millions of cockroaches inside the cave. The Gunung Mulu National Park in Sarawak and Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat Karst
The Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat Karst is a karstique area in Sub Kelay, Biatan, Talisayan, Batu Putih, and Biduk-biduk Berau districts of East Kalimantan province on the island of Borneo in Indonesia. It covers an area of 105,000 hectares, includin ...
in East Kalimantan which particularly a karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
areas contains thousands of smaller caves.
Ecology
 The Borneo
The Borneo rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
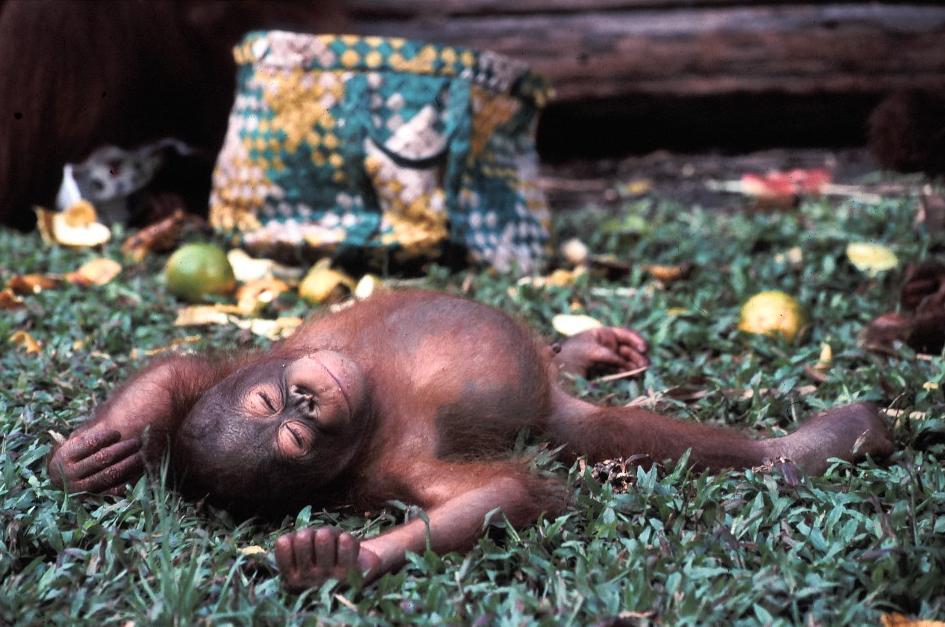
is estimated to be around 140 million years old, making it one of the oldest rainforests in the world. It is the centre of the evolution and distribution of many endemic species of plants and animals, and the rainforest is one of the few remaining natural habitats for the endangered Bornean orangutan
The Bornean orangutan (''Pongo pygmaeus'') is a species of orangutan endemic to the island of Borneo. Together with the Sumatran orangutan (''Pongo abelii'') and Tapanuli orangutan (''Pongo tapanuliensis''), it belongs to the only genus of great ...
. It is an important refuge for many endemic forest species, including the Borneo elephant
The Borneo elephant, also called the Bornean elephant or the Borneo pygmy elephant, is a subspecies of Asian elephant ''(Elephas maximus)'' that inhabits northeastern Borneo, in Indonesia and Malaysia. Its origin remains the subject of debate. A d ...
, the eastern Sumatran rhinoceros
The Bornean rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis harrissoni''), also known as the eastern Sumatran rhinoceros or eastern hairy rhinoceros, is one of three subspecies of Sumatran rhinoceros. The subspecies may be functionally extinct, with only ...
, the Bornean clouded leopard
The Bornean clouded leopard (''Neofelis diardi borneensis'') is a subspecies of the Sunda clouded leopard. It is native to the island of Borneo, and differs from the Batu- Sumatran clouded leopard in the shape and frequency of spots, as well as ...
, the Bornean rock frog, the hose's palm civet and the dayak fruit bat
The dayak fruit bat or dyak fruit bat (''Dyacopterus spadiceus'') is a relatively rare frugivorous megabat species found only on the Sunda Shelf of southeast Asia, specifically the Malay Peninsula south of the Isthmus of Kra, and the islands of ...
.

Peat swamp forests
Peat swamp forests are tropical moist forests where waterlogged soil prevents dead leaves and wood from fully decomposing. Over time, this creates a thick layer of acidic peat. Large areas of these forests are being logged at high rates.
Peat ...
occupy the entire coastline of Borneo. The soil of the peat swamp is comparatively infertile, while it is known to be the home of various bird species such as the hook-billed bulbul
The hook-billed bulbul (''Setornis criniger'') is a species of songbird in the bulbul family, Pycnonotidae. It is found in eastern Sumatra and Borneo, where its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or ...
, helmeted hornbill and rhinoceros hornbill. There are about 15,000 species of flowering plants with 3,000 species of trees (267 species are dipterocarps), 221 species of terrestrial mammals and 420 species of resident birds in Borneo. There are about 440 freshwater fish species in Borneo (about the same as Sumatra and Java combined). The Borneo river shark is known only from the Kinabatangan River
The Kinabatangan River ( ms, Sungai Kinabatangan) is a river in Sandakan Division, in northeastern Sabah, Malaysia. It is the second longest river in Malaysia, with a length of from its headwaters in the mountains of southwest Sabah, to its ou ...
. In 2010, the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) stated that 123 species have been discovered in Borneo since the "Heart of Borneo
The Heart of Borneo is a conservation agreement initiated by the World Wide Fund for Nature to protect a 220,000 km² forested region on Borneo island. The agreement was signed by the governments of Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia in Bali on 1 ...
" agreement was signed in 2007.
The WWF has classified the island into seven distinct ecoregions. Most are lowland regions:
* Borneo lowland rain forests cover most of the island, with an area of ;
* Borneo peat swamp forests
The Borneo peat swamp forests ecoregion, within the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, are on the island of Borneo, which is divided between Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia.
Location and description
Peat swamp forests occur ...
;
* ''Kerangas
The Sundaland heath forest, also known as ''Kerangas'' forest, is a type of tropical moist forest found on the island of Borneo, which is divided between Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia, as well as on the Indonesian islands of Belitung and Bangk ...
'' or Sundaland heath forests;
* Southwest Borneo freshwater swamp forests; and
* Sunda Shelf mangroves
The Sunda Shelf mangroves ecoregion, in the mangrove biome, are on the coasts of the islands of Borneo and eastern Sumatra in Malaysia and Indonesia. They are home to the proboscis monkey.
As well as being an important habitat for terrestrial ...
.
* The Borneo montane rain forests
The Borneo montane rain forests are an ecoregion, of cloud forest, within the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia.
Location and description
This ecoregion consists of tropical moun ...
lie in the central highlands of the island, above the elevation.
*The Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands on South Kalimantan.
The highest elevations of Mount Kinabalu are home to the Kinabalu mountain alpine meadow
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets ...
, an alpine shrubland notable for its numerous endemic species, including many orchids.
According to analysis of data from Global Forest Watch, the Indonesian portion of Borneo lost 10.7 million hectares of tree cover between 2002 and 2019, of which 4 million hectares was primary forest, compared with Malaysian Borneo's 4.4 million hectares of tree cover loss and 1.9 million hectares of primary forest cover loss. As of 2020, Indonesian Borneo accounts for 72% of the island's tree cover, Malaysian Borneo 27%, and Brunei 1%. Primary forest in Indonesia accounts for 44% of Borneo's overall tree cover.
Conservation issues
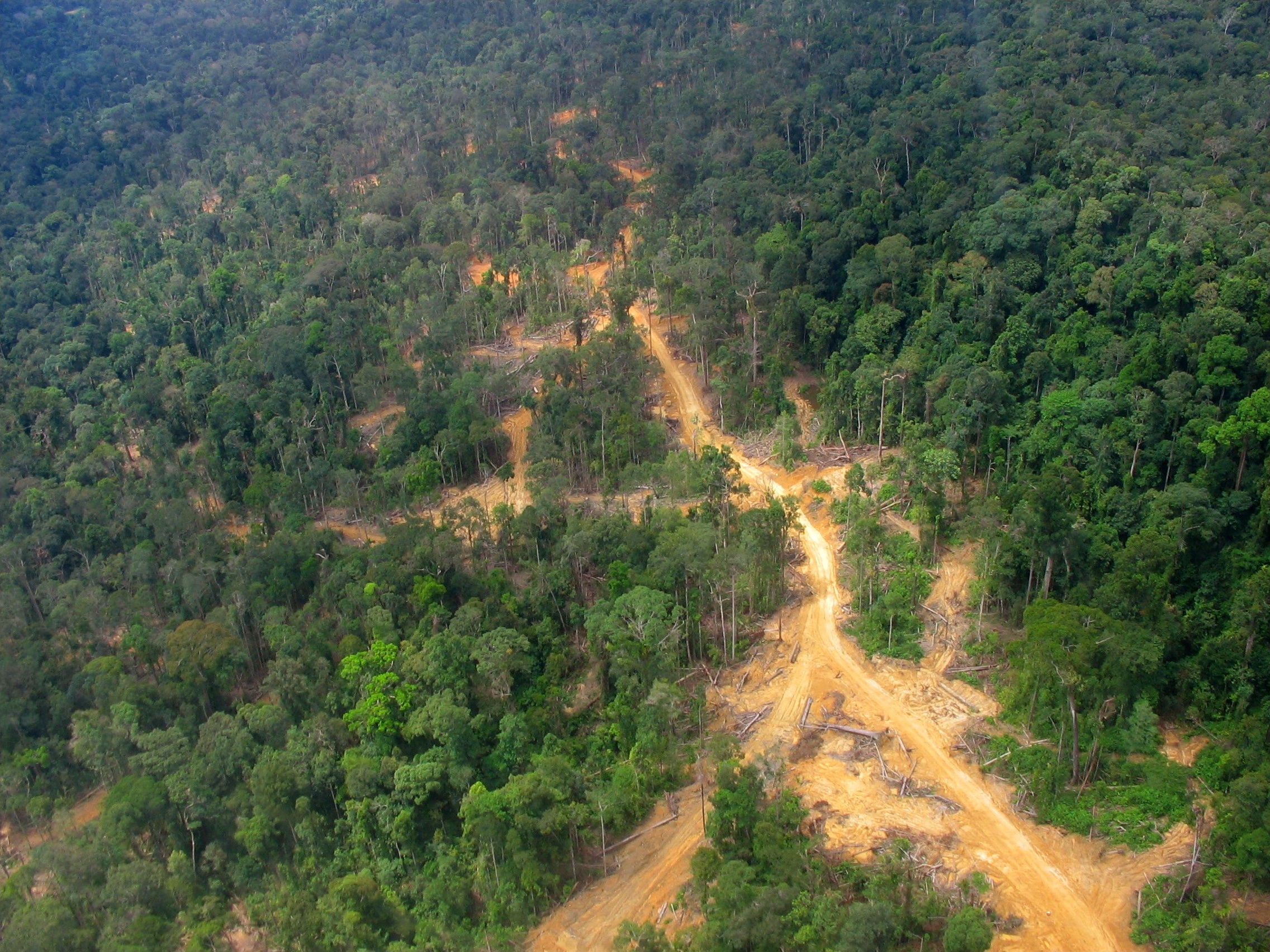
 The island historically had extensive rainforest cover, but the area was reduced due to heavy
The island historically had extensive rainforest cover, but the area was reduced due to heavy logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.
Logging is the beginning of a supply chain ...
by the Indonesian and Malaysian wood industry, especially with the large demands of raw materials from industrial countries along with the conversion of forest lands for large-scale agricultural purposes. Half of the annual global tropical timber acquisition comes from Borneo. Palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 33% of global oils produced from ...
plantations have been widely developed and are rapidly encroaching on the last remnants of primary rainforest. Forest fires since 1997, started by the locals to clear the forests for plantations were exacerbated by an exceptionally dry El Niño season, worsening the annual shrinkage of the rainforest. During these fires, hotspots were visible on satellite images and the resulting haze frequently affected Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia. The haze could also reach southern Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam and the Philippines as evidenced on the 2015 Southeast Asian haze
The 2015 Southeast Asian haze was an air pollution crisis affecting several countries in Southeast Asia, including Brunei, Indonesia (especially its islands of Sumatra and Borneo), Malaysia, Singapore, southern Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia and t ...
.
The orchid Mycaranthes farinosa
''Mycaranthes'' is a genus of orchids. It was previously considered as a synonym of the genus ''Eria'', but eventually it has become an accepted name. Its species are native to Southeast Asia, China, the Himalayas and New Guinea.
Species
# '' ...
is specific to this island
Topography
List of highest peaks in Borneo by elevation. * Mount Kinabalu * Mount Trusmadi * Bukit Raya *Muruk Miau
Muruk ( fa, موروك, also Romanized as Mūrūk; also known as Marūk, Merūk, Morūk, Mowrak, and Mūrak) is a village in Vardasht Rural District, in the Central District (Semirom County), Central District of Semirom County, Isfahan Province, Ir ...
* Mount Wakid
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest.
Mount or Mounts may also refer to:
Places
* Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England
* Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, C ...
* Monkobo Hill
* Mount Lotung
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest.
Mount or Mounts may also refer to:
Places
* Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England
* Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, C ...
* Mount Magdalena
Mount Magdalena ( ms, Gunung Magdalena) is a volcanic cone mountain located at the Tawau Division of Sabah, Malaysia. It reaches a height of approximately .
History
Since 1979, it has been a part of the Tawau Hills Park. backpacking (wildern ...
* Talibu Hill
River systems
List of longest river in Borneo by length. * Kapuas River * Barito River *Mahakam River
The Mahakam River (Indonesian: ''Sungai Mahakam'') is third longest and volume discharge river in Borneo after Kapuas River and Barito River, it is located in Kalimantan, Indonesia. It flows from the district of Long Apari in the highlands of ...
* Rajang River
*Kahayan River
The Kahayan river, or Great Dayak River, is the second largest river after Barito River in Central Kalimantan, a province of Indonesia in Kalimantan – the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo. With a total length of and with a drainage bas ...
* Mendawai River
Mendawai River or Katingan River is a river of Borneo, it is located in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. With a total length of . The longhouses of the Pendahara are located along the river in its upper course. The river has its source in the Schw ...
* Kayan River
The Kayan River is a river of Borneo island, flowing in the North Kalimantan province of Indonesia, about 1600 km northeast of the capital Jakarta. Tributaries include the Bahau River.
Hydrology
The Kayan River rises on Mount Ukeng, pa ...
* Kinabatangan River
The Kinabatangan River ( ms, Sungai Kinabatangan) is a river in Sandakan Division, in northeastern Sabah, Malaysia. It is the second longest river in Malaysia, with a length of from its headwaters in the mountains of southwest Sabah, to its ou ...
* Baram River
* Sembakung River
The Sembakung River is a river of Borneo, in the province of North Kalimantan, Indonesia, about 1600 km northeast of the capital Jakarta.Sesayap River
Sesayap River is a river in Borneo island, flowing in North Kalimantan Province, Indonesia.Sungai Sesayap
at G ...
* at G ...
Pawan River
Pawan River is a major river of West Kalimantan, Indonesia. It has a length of . Tributaries include the Keriau River.
Hydrology
In its mid course Pawan River passes through the little town of Tandjoengpoera (Tanjungpura). Pawan River passes th ...
History
Early history
 In November 2018, scientists reported the discovery of the oldest known figurative art painting, over 40,000 (perhaps as old as 52,000) years old, of an unknown animal, in the cave of
In November 2018, scientists reported the discovery of the oldest known figurative art painting, over 40,000 (perhaps as old as 52,000) years old, of an unknown animal, in the cave of Lubang Jeriji Saléh
Lubang Jeriji Saleh is a limestone cave complex in Indonesia in the Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat Karst located in the remote jungle of Bengalon district in East Kutai, East Kalimantan province on Borneo island. In a 2018 publication a team of resear ...
on the island of Borneo.
According to ancient Chinese (977), Indian and Japanese manuscripts, western coastal cities of Borneo had become trading ports by the first millennium AD. In Chinese manuscripts, gold, camphor
Camphor () is a waxy, colorless solid with a strong aroma. It is classified as a terpenoid and a cyclic ketone. It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel ('' Cinnamomum camphora''), a large evergreen tree found in East Asia; and in the k ...
, tortoise shells, hornbill ivory, rhinoceros horn, crane crest, beeswax, lakawood (a scented heartwood and root wood of a thick liana
A liana is a long- stemmed, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and uses trees, as well as other means of vertical support, to climb up to the canopy in search of direct sunlight. The word ''liana'' does not refer to a ta ...
, ''Dalbergia parviflora''), dragon's blood
Dragon's blood is a bright red resin which is obtained from different species of a number of distinct plant genera: ''Calamus'' spp. (previously ''Daemonorops'') also including ''Calamus rotang'', '' Croton'', '' Dracaena'' and ''Pterocarpus''. ...
, rattan, edible bird's nests and various spices were described as among the most valuable items from Borneo. The Indians
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
named Borneo ''Suvarnabhumi'' (the land of gold) and also ''Karpuradvipa'' (Camphor Island). The Javanese named Borneo ''Puradvipa'', or Diamond Island. Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
findings in the Sarawak river delta reveal that the area was a thriving centre of trade between India and China from the 6th century until about 1300.
 Stone pillars bearing inscriptions in the
Stone pillars bearing inscriptions in the Pallava script
The Pallava script or Pallava Grantha, is a Brahmic scripts, Brahmic script, named after the Pallava dynasty of South India, attested since the 4th century AD. As epigrapher Arlo Griffiths makes clear, however, the term is misleading as not all o ...
, found in Kutai along the Mahakam River
The Mahakam River (Indonesian: ''Sungai Mahakam'') is third longest and volume discharge river in Borneo after Kapuas River and Barito River, it is located in Kalimantan, Indonesia. It flows from the district of Long Apari in the highlands of ...
in East Kalimantan and dating to around the second half of the 4th century, constitute some of the oldest evidence of Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
influence in Southeast Asia. By the 14th century, Borneo became a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
of Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
(in present-day Indonesia), later changing its allegiance to the Ming dynasty of China. Pre-Islamic Sulu, then known locally as Lupah Sug, stretched from Palawan and the Sulu archipelago at the Philippines; to Sabah, Eastern, and Northern Kalimantan in Borneo. The Sulu empire rose as a rebellion and reaction against former Majapahit Imperialism against Sulu which Majapahit briefly occupied. The religion of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
entered the island in the 10th century, following the arrival of Muslim traders who later converted many indigenous peoples in the coastal areas.
The Sultanate of Brunei declared independence from Majapahit following the death of the Majapahit emperor in the mid-14th century. During its golden age under Bolkiah
Bolkiah, also known as Nakhoda Ragam, was the 5th Sultan of Brunei. He ascended the throne upon the abdication of his father, Sultan Sulaiman, and ruled Brunei from 1485 to 1524. His reign marked the Golden Age of Brunei and saw the Sultanat ...
from the 15th to the 17th century, the Bruneian sultanate ruled almost the entire coastal area of Borneo (lending its name to the island due to its influence in the region) and several islands in the Philippines. During the 1450s, Shari'ful Hashem Syed Abu Bakr, an Arab born in Johor, arrived in Sulu from Malacca. In 1457, he founded the Sultanate of Sulu; he titled himself as "Paduka Maulana Mahasari Sharif Sultan Hashem Abu Bakr". Following its independence in 1578 from Brunei's influence, Sulu began to expand its thalassocracy to parts of the northern Borneo. Both the sultanates who ruled northern Borneo had traditionally engaged in trade with China by means of the frequently-arriving Chinese junks. Despite the thalassocracy of the sultanates, Borneo's interior region remained free from the rule of any kingdoms.
British and Dutch control
 Since the fall of Malacca in 1511, Portuguese merchants traded regularly with Borneo, and especially with Brunei from 1530. Having visited Brunei's capital, the Portuguese described the place as surrounded by a stone wall. While Borneo was seen as rich, the Portuguese did not make any attempts to conquer it. The Spanish had sailed from Latin America and conquered the Brunei's provinces in the Philippines and incorporated it into the Mexico-Centered Viceroyalty of New Spain. The Spanish visit to Brunei led to the
Since the fall of Malacca in 1511, Portuguese merchants traded regularly with Borneo, and especially with Brunei from 1530. Having visited Brunei's capital, the Portuguese described the place as surrounded by a stone wall. While Borneo was seen as rich, the Portuguese did not make any attempts to conquer it. The Spanish had sailed from Latin America and conquered the Brunei's provinces in the Philippines and incorporated it into the Mexico-Centered Viceroyalty of New Spain. The Spanish visit to Brunei led to the Castilian War
The Castilian War took place in 1570-1578 and represented the last crusade in Islamic history between the Spanish Empire and the Sultanate of Brunei; the Sultanate of Sulu, the Sultanate of Maguindanao, and the Ottoman Caliphate.
Sultan Saiful ...
in 1578. The English began to trade with Sambas of southern Borneo in 1609, while the Dutch only began their trade in 1644: to Banjar and Martapura, also in the southern Borneo. The Dutch tried to settle the island of Balambangan, north of Borneo, in the second half of the 18th century, but withdrew by 1797. In 1812, the sultan in southern Borneo ceded his forts to the English East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southe ...
. The English, led by Stamford Raffles, then tried to establish an intervention in Sambas but failed. Although they managed to defeat the sultanate the next year and declared a blockade on all ports in Borneo except Brunei, Banjarmasin and Pontianak, the project was cancelled by the British governor-general Lord Minto in India as it was too expensive. At the beginning of British and Dutch exploration on the island, they described the island of Borneo as full of head hunters
''Head Hunters'' is the twelfth studio album by American pianist and composer Herbie Hancock, released October 26, 1973, on Columbia Records. Recording sessions for the album took place in the evening at Wally Heider Studios and Different Fur T ...
, with the indigenous in the interior practising cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
, and the waters around the island infested with pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
, especially between the north eastern Borneo and the southern Philippines. The Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
and Sea Dayak
The Ibans or Sea Dayaks are a branch of the Dayak peoples on the island of Borneo in South East Asia. Dayak is a title given by the westerners to the local people of Borneo island. It is believed that the term "Iban" was originally an exonym ...
pirates preyed on maritime shipping in the waters between Singapore and Hong Kong from their haven in Borneo, along with the attacks by Illanun
The Iranun are a Moro ethnic group native to Mindanao, Philippines (in Maguindanao del Norte: Barira, Buldon, Parang, Matanog, Sultan Mastura, and Sultan Kudarat; North Cotabato: Alamada, Banisilan, Carmen, Libungan, and Pigcawayan; Lan ...
s of the Moro pirates
The Sulu and Celebes Seas, a semi- enclosed sea area and porous region that covers an area of space around 1 million square kilometres, have been subject to illegal maritime activities since the pre-colonial era and continue to pose a maritim ...
from the southern Philippines, such as in the Battle off Mukah
The Battle off Mukah was a naval engagement fought in May 1862 between boats of the Sarawak and pirates. After the kidnapping of Sarawakian citizens some time before, two small gunboats encountered the pirates off Mukah on the northern coast ...
.
 The Dutch began to intervene in the southern part of the island upon resuming contact in 1815, posting '' residents'' to Banjarmasin, Pontianak and Sambas and ''assistant-residents'' to Landak and Mampawa. The Sultanate of Brunei in 1842 granted large parts of land in Sarawak to the English adventurer James Brooke, as a reward for his help in quelling a local rebellion. Brooke established the Raj of Sarawak and was recognised as its rajah after paying a fee to the sultanate. He established a monarchy, and the Brooke dynasty (through his nephew and great-nephew) ruled Sarawak for 100 years; the leaders were known as the White Rajahs. Brooke also acquired the island of Labuan for Great Britain in 1846 through the
The Dutch began to intervene in the southern part of the island upon resuming contact in 1815, posting '' residents'' to Banjarmasin, Pontianak and Sambas and ''assistant-residents'' to Landak and Mampawa. The Sultanate of Brunei in 1842 granted large parts of land in Sarawak to the English adventurer James Brooke, as a reward for his help in quelling a local rebellion. Brooke established the Raj of Sarawak and was recognised as its rajah after paying a fee to the sultanate. He established a monarchy, and the Brooke dynasty (through his nephew and great-nephew) ruled Sarawak for 100 years; the leaders were known as the White Rajahs. Brooke also acquired the island of Labuan for Great Britain in 1846 through the Treaty of Labuan
The Treaty of Labuan was signed between Great Britain and the Bruneian Sultanate (1368–1888), Brunei Sultanate on 18 December 1846. Under this treaty, the Sultan of Brunei ceded the island of Labuan to Great Britain.
Background
Labuan had ...
with the sultan of Brunei, Omar Ali Saifuddin II on 18 December 1846. The region of northern Borneo came under the administration of North Borneo Chartered Company following the acquisition of territory from the Sultanates of Brunei and Sulu by a German businessman and adventurer named Baron von Overbeck
Gustav Overbeck (from 1867 von Overbeck, in 1873 Baron von Overbeck, in 1877 Maharaja of Sabah and Rajah of Gaya and Sandakan; born 4 March 1830 in Lemgo; died 8 April 1894 in London) was a German businessman, adventurer and diplomat.
Biograph ...
, before it was passed to the British Dent brothers (comprising Alfred Dent and Edward Dent). Further expansion by the British continued into the Borneo interior. This led the 26th sultan of Brunei, Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin to appeal the British to halt such efforts, and as a result a Treaty of Protection was signed in 1888, rendering Brunei a British protectorate.
Before the acquisition by the British, the Americans also managed to establish their temporary presence in northwestern Borneo after acquiring a parcel of land from the Sultanate of Brunei. A company known as American Trading Company of Borneo was formed by Joseph William Torrey, Thomas Bradley Harris and several Chinese investors, establishing a colony named "Ellena" in the Kimanis area. The colony failed and was abandoned, due to denials of financial backing, especially by the US government, and to diseases and riots among the workers. Before Torrey left, he managed to sell the land to the German businessman, Overbeck. Meanwhile, the Germans under William Frederick Schuck were awarded a parcel of land in northeastern Borneo of the Sandakan Bay from the Sultanate of Sulu where he conducted business and exported large quantities of arms, opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
, textiles and tobacco to Sulu before the land was also passed to Overbeck by the sultanate.
 Prior to the recognition of Spanish presence in the Philippine archipelago, a protocol known as the Madrid Protocol of 1885 was signed between the governments of the United Kingdom, Germany and Spain in Madrid to cement Spanish influence and recognise their sovereignty over the Sultanate of Sulu—in return for Spain's relinquishing its claim to the former possessions of the sultanate in northern Borneo. The British administration then established the first railway network in northern Borneo, known as the
Prior to the recognition of Spanish presence in the Philippine archipelago, a protocol known as the Madrid Protocol of 1885 was signed between the governments of the United Kingdom, Germany and Spain in Madrid to cement Spanish influence and recognise their sovereignty over the Sultanate of Sulu—in return for Spain's relinquishing its claim to the former possessions of the sultanate in northern Borneo. The British administration then established the first railway network in northern Borneo, known as the North Borneo Railway
Sabah State Railway (SSR) is a railway system and operator in the state of Sabah in Malaysia. It is the only rail transport system operating on the island of Borneo. The railway consists of a single 134-kilometre line from Tanjung Aru, Kota Kina ...
. During this time, the British sponsored a large number of Chinese workers to migrate to northern Borneo to work in European plantation and mines, and the Dutch followed suit to increase their economic production. By 1888, North Borneo, Sarawak and Brunei in northern Borneo had become British protectorate. The area in southern Borneo was made Dutch protectorate in 1891. The Dutch who already claimed the whole Borneo were asked by Britain to delimit their boundaries between the two colonial territories to avoid further conflicts. The British and Dutch governments had signed the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, also known as the Treaty of London, was a treaty signed between the United Kingdom and the Netherlands in London on 17 March 1824. The treaty was to resolve disputes arising from the execution of the Anglo-D ...
to exchange trading ports in Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
that were under their controls and assert spheres of influence. This resulted in indirectly establishing British- and Dutch-controlled areas in the north (Malay Peninsula) and south (Sumatra and Riau Islands) respectively.
In 1895, Marcus Samuel received a concession in the Kutei area of east Borneo, and based on oil seepages in the Mahakam River
The Mahakam River (Indonesian: ''Sungai Mahakam'') is third longest and volume discharge river in Borneo after Kapuas River and Barito River, it is located in Kalimantan, Indonesia. It flows from the district of Long Apari in the highlands of ...
delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also re ...
, Mark Abrahams struck oil in February 1897. This was the discovery of the Sanga Sanga Oil Field, a refinery was built in Balikpapan, and discovery of the Samboja Oil Field followed in 1909. In 1901, the Pamusian Oil Field was discovered on Tarakan, and the Bunyu
Bunyu is an oil-rich Indonesian island situated to the north of Tarakan City, in the eastern Celebes Sea off the north-eastern coast of Borneo in North Kalimantan province. The administrative area comprising Bunyu District is composed of eleven ...
Oil Field in 1929. Royal Dutch Shell discovered the Miri Oil Field in 1910, and the Seria oil field in 1929.
World War II
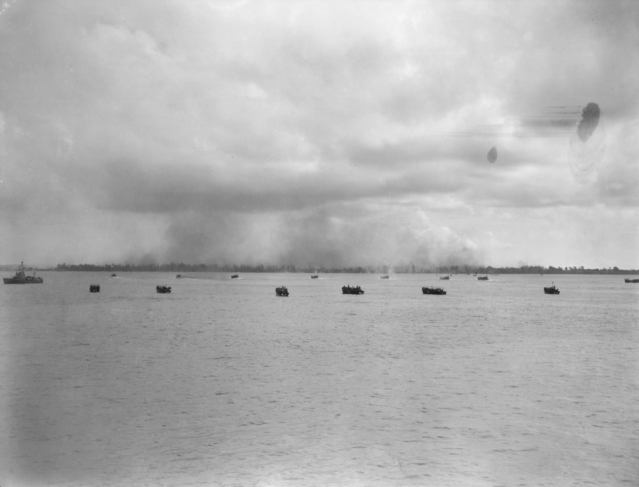
 During World War II, Japanese forces gained control and occupied most areas of Borneo from 1941 to 1945. In the first stage of the war, the British saw the Japanese advance to Borneo as motivated by political and territorial ambitions rather than economic factors. The occupation drove many people in the coastal towns to the interior, searching for food and escaping the Japanese. The Chinese residents in Borneo, especially with the Sino-Japanese War in Mainland China mostly resisted the Japanese occupation. Following the formation of resistance movements in northern Borneo such as the Jesselton Revolt, many innocent indigenous and Chinese people were executed by the Japanese for their alleged involvement.
In Kalimantan, the Japanese also killed many Malay intellectuals, executing all the Malay sultans of West Kalimantan in the
During World War II, Japanese forces gained control and occupied most areas of Borneo from 1941 to 1945. In the first stage of the war, the British saw the Japanese advance to Borneo as motivated by political and territorial ambitions rather than economic factors. The occupation drove many people in the coastal towns to the interior, searching for food and escaping the Japanese. The Chinese residents in Borneo, especially with the Sino-Japanese War in Mainland China mostly resisted the Japanese occupation. Following the formation of resistance movements in northern Borneo such as the Jesselton Revolt, many innocent indigenous and Chinese people were executed by the Japanese for their alleged involvement.
In Kalimantan, the Japanese also killed many Malay intellectuals, executing all the Malay sultans of West Kalimantan in the Pontianak incidents
The Pontianak incident consisted of two massacres which took place in Kalimantan during the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies. One of them is also known as the Mandor Affair. The victims were from a wide variety of ethnic groups, and ...
, together with Chinese people who were already against the Japanese for suspecting them to be threats. Sultan Muhammad Ibrahim Shafi ud-din II of Sambas was executed in 1944. The sultanate was thereafter suspended and replaced by a Japanese council. The Japanese also set-up ''Pusat Tenaga Rakjat'' (PUTERA) in the Indonesian archipelago in 1943, although it was abolished the following year when it became too nationalistic. Some of the Indonesian nationalist like Sukarno
Sukarno). (; born Koesno Sosrodihardjo, ; 6 June 1901 – 21 June 1970) was an Indonesian statesman, orator, revolutionary, and nationalist who was the first president of Indonesia, serving from 1945 to 1967.
Sukarno was the leader of ...
and Hatta who had returned from Dutch exile began to co-operate with the Japanese. Shortly after his release, Sukarno became president of the Central Advisory Council, an advisory council for south Borneo, Celebes, and Lesser Sunda
The Lesser Sunda Islands or nowadays known as Nusa Tenggara Islands ( id, Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, formerly ) are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up ...
, set up in February 1945.
Since the fall of Singapore, the Japanese sent several thousand of British and Australian prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
to camps in Borneo such as Batu Lintang camp. From the Sandakan camp
The Sandakan camp, also known as Sandakan POW Camp ( Malay: Kem Tawanan Perang Sandakan), was a prisoner-of-war camp established during World War II by the Japanese in Sandakan in the Malaysian state of Sabah. This site has gained notoriety as t ...
site, only six of some 2,500 prisoners survived after they were forced to march in an event known as the Sandakan Death March
The Sandakan Death Marches were a series of forced marches in Borneo from Sandakan to Ranau which resulted in the deaths of 2,434 Allied prisoners of war held captive by the Empire of Japan during the Pacific campaign of World War II at the ...
. In addition, of the total of 17,488 Javanese labourers brought in by the Japanese during the occupation, only 1,500 survived mainly due to starvation, harsh working conditions and maltreatment. The Dayak and other indigenous people played a role in guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or Irregular military, irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, Raid (military), raids ...
against the occupying forces, particularly in the Kapit Division. They temporarily revived headhunting of Japanese toward the end of the war, with Allied Z Special Unit provided assistance to them. Australia contributed significantly to the liberation of Borneo. The Australian Imperial Force was sent to Borneo to fight off the Japanese. Together with other Allies, the island was completely liberated in 1945.
Recent history
In May 1945, officials in Tokyo suggested that whether northern Borneo should be included in the proposed new country of Indonesia should be separately determined based on the desires of its indigenous people and following the disposition ofMalaya
Malaya refers to a number of historical and current political entities related to what is currently Peninsular Malaysia in Southeast Asia:
Political entities
* British Malaya (1826–1957), a loose collection of the British colony of the Straits ...
. Sukarno and Mohammad Yamin
Mohammad Yamin (24 August 1903 – 17 October 1962) was an Indonesians, Indonesian poet, politician and National Hero of Indonesia, national hero who played a key role in the writing of the draft preamble to the Constitution of Indonesia, 1945 c ...
meanwhile continuously advocated for a Greater Indonesian republic. Towards the end of the war, Japan decided to give an early independence to a new proposed country of Indonesia on 17 July 1945, with an Independence Committee meeting scheduled for 19 August 1945. However, following the surrender of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy ...
to the Allied forces, the meeting was shelved. Sukarno and Hatta continued the plan by unilaterally declaring independence, although the Dutch tried to retake their colonial possession in Borneo. The southern part of the island achieved its independence through the Proclamation of Indonesian Independence
The Proclamation of Indonesian Independence ( id, Proklamasi Kemerdekaan Indonesia, or simply ''Proklamasi'') was read at 10:00 on Friday, 17 August 1945 in Jakarta. The declaration marked the start of the diplomatic and armed resistance of th ...
on 17 August 1945. The southern part saw guerilla conflicts followed by Dutch blockade to cut supplies for nationalist within the region. While nationalist guerrillas supporting the inclusion of southern Borneo in the new Indonesian republic were active in Ketapang, and to lesser extent in Sambas where they rallied with the red-white flag which became the flag of Indonesia, most of the Chinese residents in southern Borneo expected to be liberated by Chinese Nationalist troops from mainland China and to integrate their districts as an overseas province of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Meanwhile, Sarawak and Sabah in northern Borneo became separate British crown colonies in 1946.
In 1961, Prime Minister Tunku Abdul Rahman of the independent Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya ( ms, Persekutuan Tanah Melayu; Jawi script, Jawi: ) was a federation of what previously had been British Malaya comprising eleven states (nine Malay states and two of the British Empire, British Straits Settlements, P ...
desired to unite Malaya, the British colonies of Sarawak, North Borneo
North Borneo (usually known as British North Borneo, also known as the State of North Borneo) was a British Protectorate, British protectorate in the northern part of the island of Borneo, which is present day Sabah. The territory of North Borneo ...
, Singapore and the protectorate of Brunei under the proposed Federation of Malaysia. The idea was heavily opposed by the governments in both Indonesia and the Philippines as well from communist sympathisers and nationalists in Borneo. Sukarno, as the president of the new republic, perceiving the British trying to maintain their presence in northern Borneo and the Malay Peninsula, decided to launch a military infiltration, later known as the ''confrontation
Confrontation is an element of conflict wherein parties confront one another, directly engaging one another in the course of a dispute between them. A confrontation can be at any scale, between any number of people, between entire nations or cult ...
'', from 1962 to 1969. As a response to the growing opposition, the British deployed their armed forces to guard their colonies against Indonesian and communist revolts, which was also participated by Australia and New Zealand.
 The Philippines opposed the newly proposed federation, claiming the eastern part of North Borneo (today the Malaysian state of Sabah) as part of its territory as a former possession of the Sultanate of Sulu. The Philippine government mostly based their claim on the Sultanate of Sulu's cession agreement with the British North Borneo Company, as by now the sultanate had come under the jurisdiction of the Philippine republican administration, which therefore should inherit the Sulu former territories. The Philippine government also claimed that the heirs of the sultanate had ceded all their territorial rights to the republic.
The Sultanate of Brunei at the first welcomed the proposal of a new larger federation. Meanwhile, the Brunei People's Party led by
The Philippines opposed the newly proposed federation, claiming the eastern part of North Borneo (today the Malaysian state of Sabah) as part of its territory as a former possession of the Sultanate of Sulu. The Philippine government mostly based their claim on the Sultanate of Sulu's cession agreement with the British North Borneo Company, as by now the sultanate had come under the jurisdiction of the Philippine republican administration, which therefore should inherit the Sulu former territories. The Philippine government also claimed that the heirs of the sultanate had ceded all their territorial rights to the republic.
The Sultanate of Brunei at the first welcomed the proposal of a new larger federation. Meanwhile, the Brunei People's Party led by A.M. Azahari
Sheikh Azahari bin Sheikh Mahmud (3 September 1928 – 20 April 2002), better known as A.M. Azahari, was a Brunei politician. According to historian Hussaymiya, it is not possible to verify the truth about his 'Brunei birth'. Many people claime ...
desired to reunify Brunei, Sarawak and North Borneo into one federation known as the North Borneo Federation ( ms, Kesatuan Negara Kalimantan Utara), where the sultan of Brunei
The sultan of Brunei is the monarchical head of state of Brunei and head of government in his capacity as prime minister of Brunei. Since independence from the British in 1984, only one sultan has reigned, though the royal institution dates bac ...
would be the head of state for the federation—though Azahari had his own intention to abolish the Brunei monarchy, to make Brunei more democratic, and to integrate the territory and other former British colonies in Borneo into Indonesia, with the support from the latter government. This directly led to the Brunei Revolt, which thwarted Azahari's attempt and forced him to escape to Indonesia. Brunei withdrew from being part of the new Federation of Malaysia due to some disagreements on other issues while political leaders in Sarawak and North Borneo continued to favour inclusion in a larger federation.
With the continuous opposition from Indonesia and the Philippines, the Cobbold Commission
The Cobbold Commission, was a Commission of Enquiry set up to determine whether the people of Crown Colony of North Borneo, North Borneo (now Sabah) and Crown Colony of Sarawak, Sarawak supported the proposal to create the Federation of Malaysia ...
was established to discover the feeling of the native populations in northern Borneo; it found the people greatly in favour of federation, with various stipulations. The federation was successfully achieved with the inclusion of northern Borneo through the Malaysia Agreement on 16 September 1963. To this day, the area in northern Borneo is still subjected to attacks by Moro pirates since the 18th century and militant from groups such as Abu Sayyaf since 2000 in the frequent cross border attacks. During the administration of Philippine president Ferdinand Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. ( , , ; September 11, 1917 – September 28, 1989) was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial ...
, Marcos made some attempts to destabilise the state of Sabah, although his plan failed and resulted in the Jabidah massacre
The Jabidah massacre on March 18, 1968 was the purported assassinations or executions of Moro people, Moro army recruits who allegedly mutiny, mutinied upon learning the true nature of their mission. It is acknowledged as a major flashpoint tha ...
and later the insurgency in the southern Philippines.
In August 2019, Indonesian president Joko Widodo
Joko Widodo (; born 21 June 1961), popularly known as Jokowi, is an Indonesian politician and businessman who is the 7th and current president of Indonesia. Elected in July 2014, he was the first Indonesian president not to come from an elite ...
announced a plan to move the capital of Indonesia from Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
to a newly established location in the East Kalimantan province in Borneo.
Demographics
Thedemonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
for Borneo is Bornean.
Borneo had 23,053,723 inhabitants (in 2020 Censuses), a population density of . Most of the population lives in coastal cities, although the hinterland has small towns and villages along the rivers. The population consists mainly of Dayak ethnic groups, Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, Banjar, Ida'an, Bajau, Suluk, Orang Ulu
Orang Ulu ("people of the interior" in Malay) is an ethnic designation politically coined to group together roughly 27 very small but ethnically diverse tribal groups in northeastern Sarawak, Malaysia with populations ranging from less than 300 p ...
, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
and Kadazan-Dusun. The Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, who make up 29% of the population of Sarawak and 17% of total population in West Kalimantan, Indonesia are descendants of immigrants primarily from southeastern China.
In Sabah, during the administration of Mustapha Harun
Datu Mustapha bin Datu Harun, or Tun Mustapha for short (31 July 1918 – 2 January 1995), was a Malaysian people, Malaysian politician who served as the 3rd Chief Minister of Sabah from May 1967 to November 1975 and the 1st Yang di-Pertua Neg ...
of the United Sabah National Organisation (USNO) in the 1970s, thousands of Muslim immigrants and refugees from the southern Philippines island of Mindanao and the island of Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
in Indonesia were given sanctuary and later identity cards in a bid to increase the Muslim population of the state: a policy later known as Project IC. Due to the high number of crimes attributed to the new migrant populations, ethnic tension
An ethnic conflict is a conflict between two or more contending ethnic groups. While the source of the conflict may be political, social, economic or religious, the individuals in conflict must expressly fight for their ethnic group's positio ...
between the indigenous and migrant populations has risen up to the present.
 In Kalimantan, since the 1990s, the Indonesian government has undertaken an intense transmigration program; to that end it has financed the relocation of poor, landless families from Java, Madura, and Bali. By 2001, transmigrants made up 21% of the population in Central Kalimantan. Since the 1990s, the indigenous Dayak and Malays have resisted encroachment by these migrants, and violent conflict has occurred between some transmigrant and indigenous populations. In the 1999 Sambas riots, Dayaks and
In Kalimantan, since the 1990s, the Indonesian government has undertaken an intense transmigration program; to that end it has financed the relocation of poor, landless families from Java, Madura, and Bali. By 2001, transmigrants made up 21% of the population in Central Kalimantan. Since the 1990s, the indigenous Dayak and Malays have resisted encroachment by these migrants, and violent conflict has occurred between some transmigrant and indigenous populations. In the 1999 Sambas riots, Dayaks and Malays
Malays may refer to:
* Malay race, a racial category encompassing peoples of Southeast Asia and sometimes the Pacific Islands
** Overseas Malays, people of Malay race ancestry living outside Malay archipelago home areas
** Cape Malays, a communit ...
joined to massacre thousands of the Madurese migrants. In Kalimantan, thousands were killed in 2001 fighting between Madurese transmigrant
id, Orang Madura
, image =
, image_caption = A portrait of Madurese village head.
, population = 7,179,356
, popplace = :
, region1 = East Java
, pop1 = 6,520,403
, region2 = West Kalimantan
, pop2 ...
s and the Dayak people in the Sampit conflict.
Religion
Administration
Temburong
Temburong District ( ms, Daerah Temburong; Jawi: دائيره تمبوروڠ) or simply Temburong () is the easternmost district in Brunei. It is an exclave — the land is separated from the rest of the country by Malaysia and Brunei Bay, and ...
)
* The Indonesian provinces of East, South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
, West, North and Central Kalimantan, in Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo.
In 2019, ...
* The East Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak, as well as the Federal Territory
A federal territory is an administrative division under the direct and usually exclusive jurisdiction of a federation's national government. A federal territory is a part of a federation, but not a part of any federated state. The states constit ...
of Labuan (on offshore islands nearby)
Economy
Borneo's economy depends mainly on agriculture, logging and mining, oil and gas, and ecotourism. Brunei's economy is highly dependent on the oil and gas production sector, and the country has become one of the largest oil producers in Southeast Asia. The Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak are both top exporters of timber. Sabah is also known as the agricultural producer of rubber,cacao
Cacao is the seed from which cocoa and chocolate are made, from Spanish cacao, an adaptation of Nahuatl cacaua, the root form of cacahuatl ("bean of the cocoa-tree"). It may also refer to:
Plants
*''Theobroma cacao'', a tropical evergreen tree
** ...
, and vegetables, and for its fisheries, while Sabah, Sarawak and Labuan export liquefied natural gas (LNG) and petroleum. The Indonesian provinces of Kalimantan are mostly dependent on mining sectors despite also being involved in logging and oil and gas explorations.
See also
* Hikayat Banjar * Kutai basin *List of islands of Indonesia
The islands of Indonesia, also known as the Indonesian Archipelago ( id, Kepulauan Indonesia) or Nusantara, may refer either to the islands comprising the country of Indonesia or to the geographical groups which include its islands.
History ...
* List of islands of Malaysia
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
* Maphilindo
Maphilindo (for Malaya, the Philippines, and Indonesia), is a proposed, nonpolitical confederation of the three Southeast Asian countries in the Malay Archipelago.
Background
The original plan for a united state based on the concept of t ...
* List of bats of Borneo This is a list of the bats of Borneo.
Bats of Sarawak
*''Rousettus amplexicaudatus'': Baram, Niah
*'' Rousettus spinalatus'': Niah, Bintulu, Lambir NP, Simulajau NP
*''Pteropus vampyrus'': coastal, interior
*'' Pteropus hypomelanus'': off coast isl ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* *Environmental Profile of Borneo
– Background on Borneo, including natural and social history, deforestation statistics, and conservation news. {{Authority control Greater Sunda Islands International islands Islands of Brunei Islands of Indonesia Islands of Malaysia Kalimantan Maritime Southeast Asia Regions of Eurasia