Biosphere 2015 01 18 0048.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter, with minimal inputs and outputs. With regard to energy, it is an open system, with photosynthesis capturing solar energy at a rate of around 130 terawatts per year. However it is a self-regulating system close to energetic equilibrium."Biosphere"
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter, with minimal inputs and outputs. With regard to energy, it is an open system, with photosynthesis capturing solar energy at a rate of around 130 terawatts per year. However it is a self-regulating system close to energetic equilibrium."Biosphere"
in ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th ed. (2004) Columbia University Press. By the most general biophysiological definition, the biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all
 The earliest evidence for
The earliest evidence for

 Every part of the planet, from the
Every part of the planet, from the
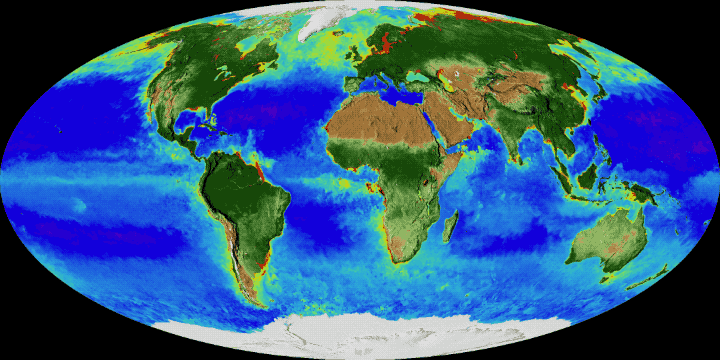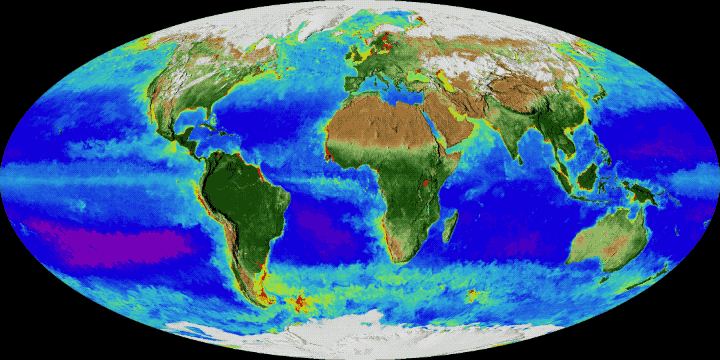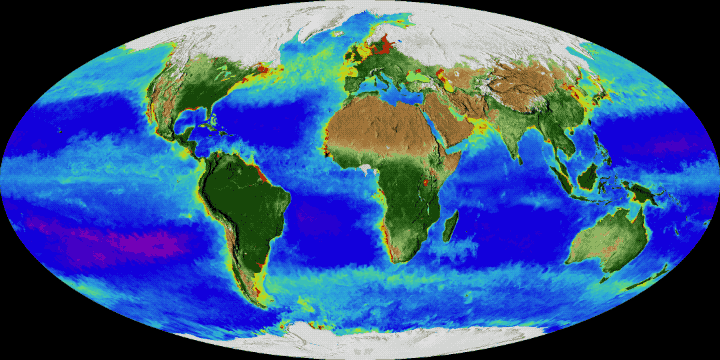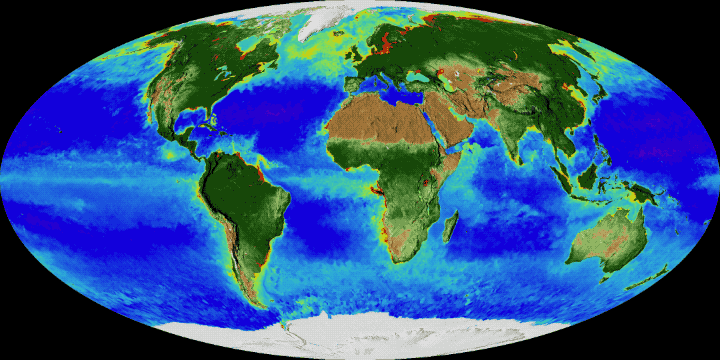
Article on the Biosphere at Encyclopedia of Earth
GLOBIO.info
an ongoing programme to map the past, current and future impacts of human activities on the biosphere
Paul Crutzen Interview
freeview video of
Atlas of the Biosphere
{{Authority control Oceanography Superorganisms Biological systems
 The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter, with minimal inputs and outputs. With regard to energy, it is an open system, with photosynthesis capturing solar energy at a rate of around 130 terawatts per year. However it is a self-regulating system close to energetic equilibrium."Biosphere"
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter, with minimal inputs and outputs. With regard to energy, it is an open system, with photosynthesis capturing solar energy at a rate of around 130 terawatts per year. However it is a self-regulating system close to energetic equilibrium."Biosphere"in ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th ed. (2004) Columbia University Press. By the most general biophysiological definition, the biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all
living beings
Life form (also spelled life-form or lifeform) is an wikt:entity, entity that is Life, living, such as plants (flora) and animals (fauna). It is estimated that more than 99% of all species that ever existed on Earth, amounting to over five billi ...
and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
, cryosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
. The biosphere is postulated to have evolved, beginning with a process of biopoiesis (life created naturally from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds) or biogenesis (life created from living matter), at least some 3.5 billion years ago.
In a general sense, biospheres are any closed, self-regulating systems containing ecosystems. This includes artificial biospheres such as Biosphere 2
Biosphere 2 is an American Earth system science research facility located in Oracle, Arizona. Its mission is to serve as a center for research, outreach, teaching, and lifelong learning about Earth, its living systems, and its place in the univers ...
and BIOS-3
BIOS-3 is an experimental closed ecosystem at the Institute of Biophysics in Krasnoyarsk, Russia.
Its construction began in 1965, and was completed in 1972. BIOS-3 consists of a underground steel structure suitable for up to three persons, and ...
, and potentially ones on other planets or moons.
Origin and use of the term
The term "biosphere" was coined by geologist Eduard Suess in 1875, which he defined as the place on Earth's surface where life dwells. While the concept has a geological origin, it is an indication of the effect of both Charles Darwin andMatthew F. Maury
Matthew Fontaine Maury (January 14, 1806February 1, 1873) was an American oceanographer and naval officer, serving the United States and then joining the Confederacy during the American Civil War.
He was nicknamed "Pathfinder of the Seas" and i ...
on the Earth sciences. The biosphere's ecological context comes from the 1920s (see Vladimir I. Vernadsky
Vladimir Ivanovich Vernadsky (russian: link=no, Влади́мир Ива́нович Верна́дский) or Volodymyr Ivanovych Vernadsky ( uk, Володи́мир Іва́нович Верна́дський; – 6 January 1945) was ...
), preceding the 1935 introduction of the term " ecosystem" by Sir Arthur Tansley
Sir Arthur George Tansley FLS, FRS (15 August 1871 – 25 November 1955) was an English botanist and a pioneer in the science of ecology.
Educated at Highgate School, University College London and Trinity College, Cambridge, Tansley taught a ...
(see ecology history). Vernadsky defined ecology as the science of the biosphere. It is an interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
concept for integrating astronomy, geophysics, meteorology, biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
, evolution, geology, geochemistry, hydrology and, generally speaking, all life and Earth sciences.
Narrow definition
Geochemists define the biosphere as being the total sum of living organisms (the "biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
" or "biota
Biota may refer to:
* Biota (ecology), the plant and animal life of a region
* Biota (plant), common name for a coniferous tree, ''Platycladus orientalis''
* Biota, Cinco Villas, a municipality in Aragon, Spain
* Biota (band), a band from Color ...
" as referred to by biologists and ecologists). In this sense, the biosphere is but one of four separate components of the geochemical model, the other three being '' geosphere'', '' hydrosphere'', and ''atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
''. When these four component spheres are combined into one system, it is known as the Ecosphere. This term was coined during the 1960s and encompasses both biological and physical components of the planet.
The Second International Conference on Closed Life Systems defined ''biospherics'' as the science and technology of analogs and models
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure.
Models c ...
of Earth's biosphere; i.e., artificial Earth-like biospheres. Others may include the creation of artificial non-Earth biospheres—for example, human-centered biospheres or a native Martian biosphere—as part of the topic of biospherics.
Earth's biosphere
Age
 The earliest evidence for
The earliest evidence for life on Earth Life on Earth may refer to:
Science
* Life
* Earliest known life forms
* Evolutionary history of life
** Abiogenesis
Film and television
* ''Life on Earth'' (film) (''La Vie Sur Terre''), a 1998 Malian film
* ''Life on Earth'' (TV series), a 197 ...
includes biogenic
A biogenic substance is a product made by or of life forms. While the term originally was specific to metabolite compounds that had toxic effects on other organisms, it has developed to encompass any constituents, secretions, and metabolites of p ...
graphite found in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks from Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in ...
found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone from Western Australia. More recently, in 2015, "remains of biotic life
Biotic material or biological derived material is any material that originates from living organisms. Most such materials contain carbon and are capable of decay.
The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago.Schopf, JW, Kudrya ...
" were found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. Early edition, published online before print. In 2017, putative fossilized microorganisms (or microfossils) were announced to have been discovered in hydrothermal vent precipitates in the Nuvvuagittuq Belt of Quebec, Canada that were as old as 4.28 billion years, the oldest record of life on earth, suggesting "an almost instantaneous emergence of life" after ocean formation 4.4 billion years ago, and not long after the formation of the Earth 4.54 billion years ago. According to biologist Stephen Blair Hedges, "If life arose relatively quickly on Earth ... then it could be common in the universe."
Extent

 Every part of the planet, from the
Every part of the planet, from the polar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
Polar may refer to:
* Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface of a rotating body or planet, at 90 degrees from the equator, based on the axis around which a body rotates
* Polar climate, the c ...
ice caps to the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
, features life of some kind. Recent advances in microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, prot ...
have demonstrated that microbes live deep beneath the Earth's terrestrial surface, and that the total mass of microbial
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
life in so-called "uninhabitable zones" may, in biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
, exceed all animal and plant life on the surface. The actual thickness of the biosphere on earth is difficult to measure. Birds typically fly at altitudes as high as and fish live as much as underwater in the Puerto Rico Trench.
There are more extreme examples for life on the planet: Rüppell's vulture has been found at altitudes of ; bar-headed geese
The bar-headed goose (''Anser indicus'') is a goose that breeds in Central Asia in colonies of thousands near mountain lakes and winters in South Asia, as far south as peninsular India. It lays three to eight eggs at a time in a ground nest. It ...
migrate at altitudes of at least ; yak
The domestic yak (''Bos grunniens''), also known as the Tartary ox, grunting ox or hairy cattle, is a species of long-haired domesticated cattle found throughout the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, the Tibetan Plateau, Kachin Sta ...
s live at elevations as high as above sea level; mountain goats live up to . Herbivorous animals at these elevations depend on lichens, grasses, and herbs.
Life forms live in every part of the Earth's biosphere, including soil, hot springs, inside rocks at least deep underground, the deepest parts of the ocean, and at least high in the atmosphere. Microorganisms, under certain test conditions, have been observed to survive the vacuum of outer space. The total amount of soil and subsurface bacterial carbon is estimated as 5 × 1017 g, or the "weight of the United Kingdom". The mass of prokaryote microorganisms—which includes bacteria and archaea, but not the nucleated eukaryote microorganisms—may be as much as 0.8 trillion tons of carbon (of the total biosphere mass, estimated at between 1 and 4 trillion tons). Barophilic marine microbes have been found at more than a depth of in the Mariana Trench, the deepest spot in the Earth's oceans. In fact, single-celled life forms have been found in the deepest part of the Mariana Trench, by the Challenger Deep, at depths of . Other researchers reported related studies that microorganisms thrive inside rocks up to below the sea floor under of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States, as well as beneath the seabed off Japan. Culturable thermophilic microbes have been extracted from cores drilled more than into the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
in Sweden, from rocks between . Temperature increases with increasing depth into the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
. The rate at which the temperature increases depends on many factors, including type of crust (continental vs. oceanic), rock type, geographic location, etc. The greatest known temperature at which microbial life can exist is (''Methanopyrus kandleri
In taxonomy, ''Methanopyrus'' is a genus of the Methanopyraceae.
''Methanopyrus'' is a genus of methanogen, with a single described species, ''M. kandleri''. It is a rod-shaped hyperthermophile, discovered on the wall of a black smoker from the ...
'' Strain 116), and it is likely that the limit of life in the " deep biosphere" is defined by temperature rather than absolute depth. On 20 August 2014, scientists confirmed the existence of microorganisms living below the ice of Antarctica. According to one researcher, "You can find microbes everywhere – they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are."
Our biosphere is divided into a number of biomes, inhabited by fairly similar flora and fauna. On land, biomes are separated primarily by latitude. Terrestrial biomes lying within the Arctic and Antarctic Circles are relatively barren of plant and animal life, while most of the more populous biomes lie near the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
.
Annual variation

Artificial biospheres
Experimental biospheres, also calledclosed ecological system
Closed ecological systems (CES) are ecosystems that do not rely on matter exchange with any part outside the system.
The term is most often used to describe small, manmade ecosystems. Such systems are scientifically interesting and can potential ...
s, have been created to study ecosystems and the potential for supporting life outside the Earth. These include spacecraft and the following terrestrial laboratories:
* Biosphere 2
Biosphere 2 is an American Earth system science research facility located in Oracle, Arizona. Its mission is to serve as a center for research, outreach, teaching, and lifelong learning about Earth, its living systems, and its place in the univers ...
in Arizona, United States, 3.15 acres (13,000 m2).
* BIOS-1, BIOS-2 and BIOS-3
BIOS-3 is an experimental closed ecosystem at the Institute of Biophysics in Krasnoyarsk, Russia.
Its construction began in 1965, and was completed in 1972. BIOS-3 consists of a underground steel structure suitable for up to three persons, and ...
at the Institute of Biophysics in Krasnoyarsk, Siberia, in what was then the Soviet Union.
* Biosphere J (CEEF, Closed Ecology Experiment Facilities), an experiment in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
.
* Micro-Ecological Life Support System Alternative ( MELiSSA) at Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
Extraterrestrial biospheres
No biospheres have been detected beyond the Earth; therefore, the existence of extraterrestrial biospheres remains hypothetical. Therare Earth hypothesis
In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligenc ...
suggests they should be very rare, save ones composed of microbial
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
life only. On the other hand, Earth analogs may be quite numerous, at least in the Milky Way galaxy, given the large number of planets. Three of the planets discovered orbiting TRAPPIST-1 could possibly contain biospheres. Given limited understanding of abiogenesis, it is currently unknown what percentage of these planets actually develop biospheres.
Based on observations by the Kepler Space Telescope
The Kepler space telescope is a disused space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orb ...
team, it has been calculated that provided the probability of abiogenesis is higher than 1 to 1000, the closest alien biosphere should be within 100 light-years from the Earth.
It is also possible that artificial biospheres will be created in the future, for example with the terraforming of Mars.
See also
* Climate system * Cryosphere * Thomas Gold * Habitable zone * Homeostasis *Life support system
A life-support system is the combination of equipment that allows survival in an environment or situation that would not support that life in its absence. It is generally applied to systems supporting human life in situations where the outsid ...
* Man and the Biosphere Programme
* Montreal Biosphère
* Noogenesis
* Noosphere
The noosphere (alternate spelling noösphere) is a philosophical concept developed and popularized by the Russian-Ukrainian Soviet biogeochemist Vladimir Vernadsky, and the French philosopher and Jesuit priest Pierre Teilhard de Chardin. Vernads ...
* Rare biosphere
Rare biosphere refers to a large number of rare species of microbial life, i.e. bacteria, archaea and Fungus, fungi, that can be found in very low concentrations in an environment.
Microbial ecosystems
Changes in the biodiversity of an ecosystem, ...
* Shadow biosphere
A shadow biosphere is a hypothetical microbial biosphere of Earth that would use radically different biochemical and molecular processes from that of currently known life. Although life on Earth is relatively well studied, if a shadow biosphere ex ...
* Simple biosphere model In climate science, a biosphere model, is used to model the biosphere of Earth, and can be coupled with atmospheric general circulation models (GCMs) for modelling the entire climate system. It has been suggested that terrestrial biosphere models ( ...
* Soil biomantle
* Wardian case
* Winogradsky column
References
Further reading
* ''The Biosphere'' (A '' Scientific American'' Book), San Francisco, W.H. Freeman and Co., 1970, . This book, originally the December 1970 '' Scientific American'' issue, covers virtually every major concern and concept since debated regarding materials andenergy resource
Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reus ...
s (including solar energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essenti ...
), population trends, and environmental degradation
Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment (biophysical), environment through depletion of resources such as quality of air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; an ...
(including global warming).
External links
Article on the Biosphere at Encyclopedia of Earth
GLOBIO.info
an ongoing programme to map the past, current and future impacts of human activities on the biosphere
Paul Crutzen Interview
freeview video of
Paul Crutzen
Paul Jozef Crutzen (; 3 December 1933 – 28 January 2021) was a Dutch meteorologist and atmospheric chemist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1995 for his work on atmospheric chemistry and specifically for his efforts in studying ...
Nobel Laureate for his work on decomposition of ozone talking to Harry Kroto Nobel Laureate by the Vega Science Trust.
Atlas of the Biosphere
{{Authority control Oceanography Superorganisms Biological systems