Basilica and Dome, from God Quad.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



 In
In
 The Latin word ''
The Latin word ''
 Long, rectangular basilicas with internal
Long, rectangular basilicas with internal 



 * Basilica Porcia: first basilica built in Rome (184 BC), erected on the personal initiative and financing of the censor Marcus Porcius Cato (Cato the Elder) as an official building for the
* Basilica Porcia: first basilica built in Rome (184 BC), erected on the personal initiative and financing of the censor Marcus Porcius Cato (Cato the Elder) as an official building for the
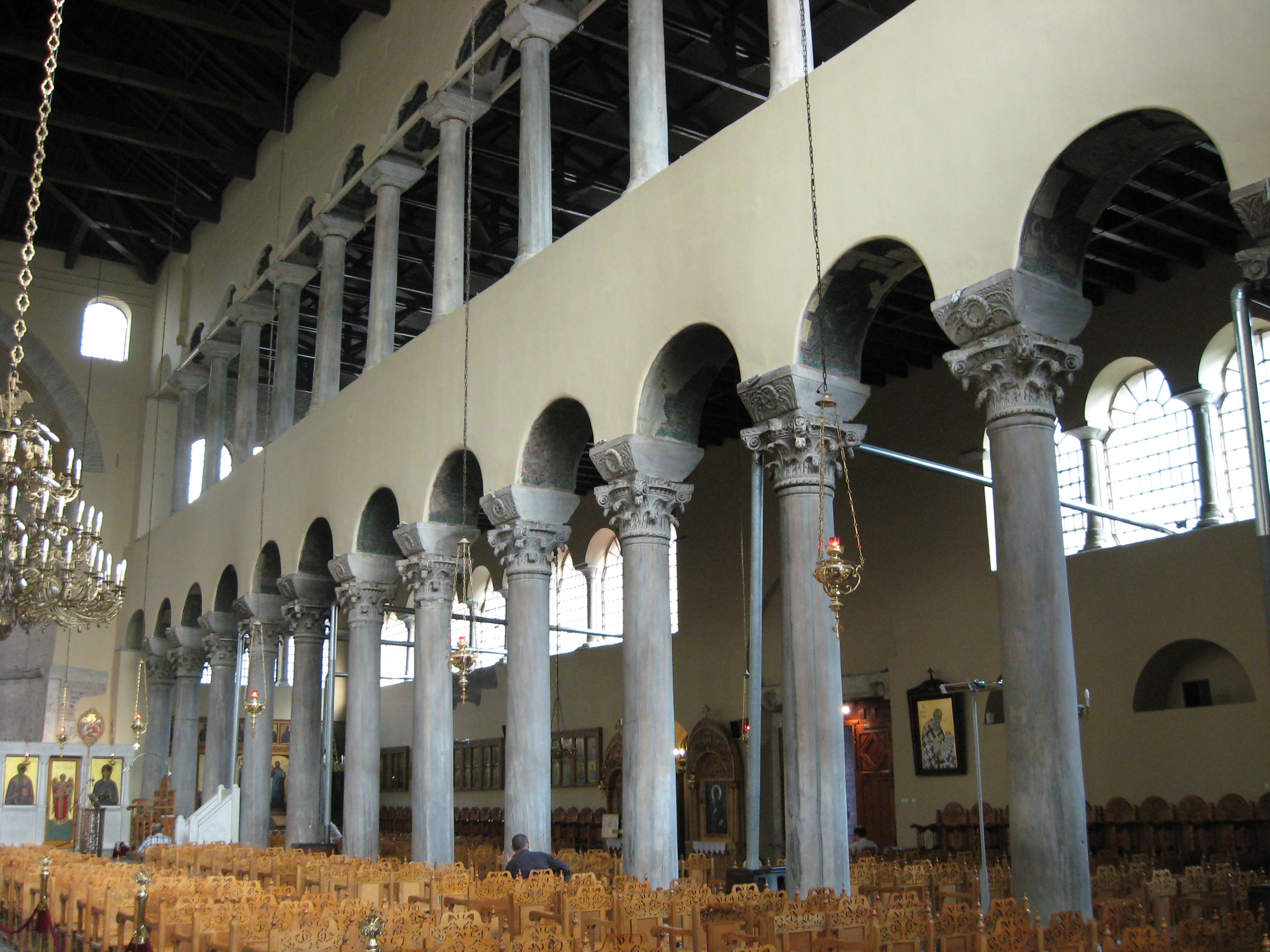



 The aisled-hall plan of the basilica was adopted by a number of religious cults in
The aisled-hall plan of the basilica was adopted by a number of religious cults in
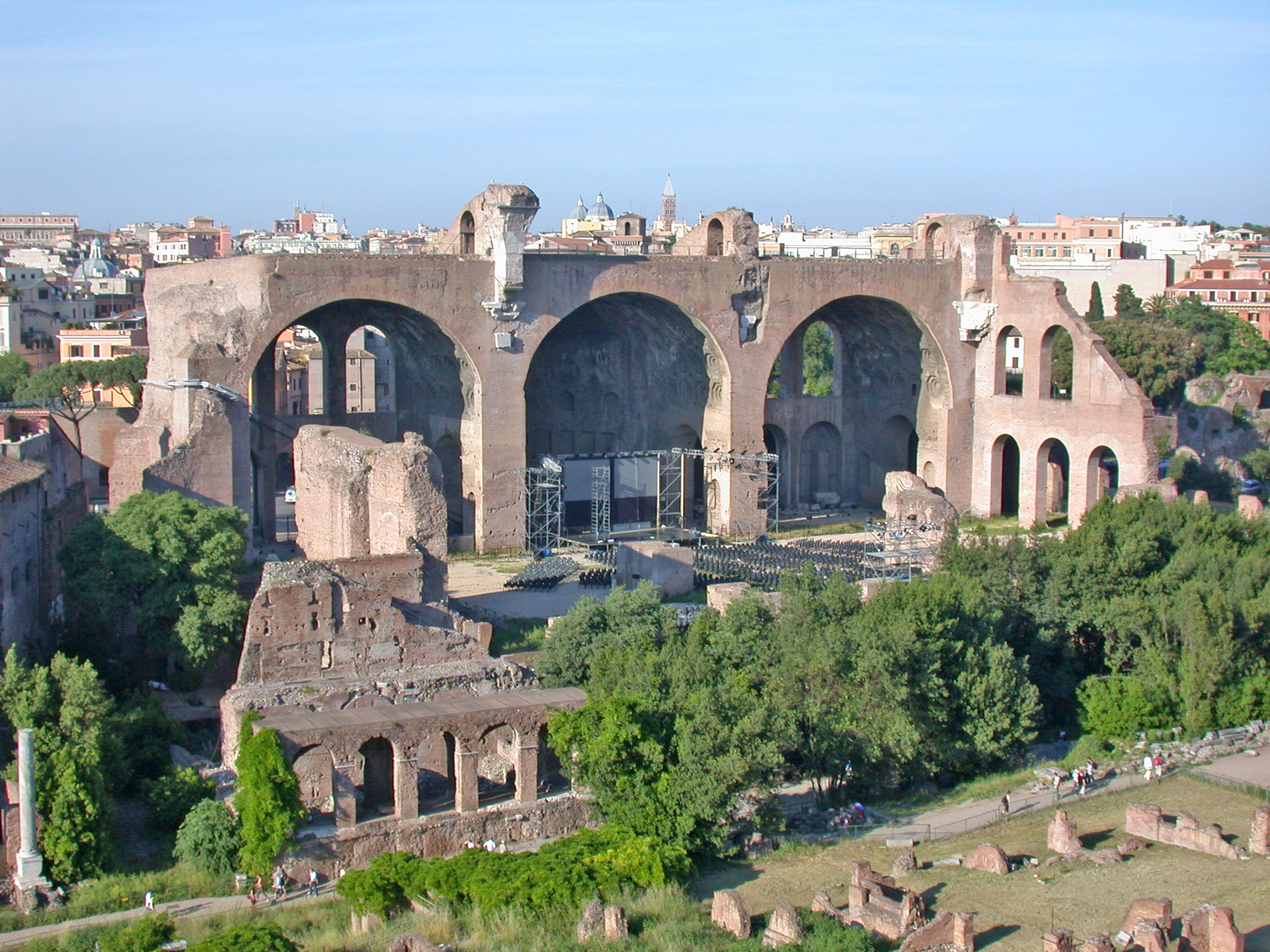


 The 4th century Basilica of Maxentius, begun by Maxentius between 306 and 312 and according to Aurelius Victor's ''De Caesaribus'' completed by Constantine I, was an innovation. Earlier basilicas had mostly had wooden roofs, but this basilica dispensed with timber trusses and used instead cross-vaults made from Roman bricks and Roman concrete, concrete to create one of the ancient world's largest covered spaces: 80 m long, 25 m wide, and 35 m high. The Vertex (geometry), vertices of the cross-vaults, the largest Roman examples, were 35 m. The vault was supported on marble monolithic columns 14.5 m tall. The foundations are as much as 8 m deep. The vault was supported by brick latticework ribs () forming lattice ribbing, an early form of rib vault, and distributing the load evenly across the vault's span. Similar brick ribs were employed at the Baths of Maxentius on the Palatine Hill, where they supported walls on top of the vault. Also known as the or , it chanced to be the last civic basilica built in Rome.
Inside the basilica the central nave was accessed by five doors opening from an entrance hall on the eastern side and terminated in an apse at the western end. Another, shallower apse with niches for statues was added to the centre of the north wall in a second campaign of building, while the western apse housed a colossal acrolithic statue of the emperor Constantine enthroned. Fragments of this statue are now in the courtyard of the Palazzo dei Conservatori on the Capitoline Hill, part of the Capitoline Museums. Opposite the northern apse on the southern wall, another monumental entrance was added and elaborated with a portico of Porphyry (geology), porphyry columns. One of the remaining marble interior columns was removed in 1613 by Pope Paul V and set up as an honorific column outside Santa Maria Maggiore.
The 4th century Basilica of Maxentius, begun by Maxentius between 306 and 312 and according to Aurelius Victor's ''De Caesaribus'' completed by Constantine I, was an innovation. Earlier basilicas had mostly had wooden roofs, but this basilica dispensed with timber trusses and used instead cross-vaults made from Roman bricks and Roman concrete, concrete to create one of the ancient world's largest covered spaces: 80 m long, 25 m wide, and 35 m high. The Vertex (geometry), vertices of the cross-vaults, the largest Roman examples, were 35 m. The vault was supported on marble monolithic columns 14.5 m tall. The foundations are as much as 8 m deep. The vault was supported by brick latticework ribs () forming lattice ribbing, an early form of rib vault, and distributing the load evenly across the vault's span. Similar brick ribs were employed at the Baths of Maxentius on the Palatine Hill, where they supported walls on top of the vault. Also known as the or , it chanced to be the last civic basilica built in Rome.
Inside the basilica the central nave was accessed by five doors opening from an entrance hall on the eastern side and terminated in an apse at the western end. Another, shallower apse with niches for statues was added to the centre of the north wall in a second campaign of building, while the western apse housed a colossal acrolithic statue of the emperor Constantine enthroned. Fragments of this statue are now in the courtyard of the Palazzo dei Conservatori on the Capitoline Hill, part of the Capitoline Museums. Opposite the northern apse on the southern wall, another monumental entrance was added and elaborated with a portico of Porphyry (geology), porphyry columns. One of the remaining marble interior columns was removed in 1613 by Pope Paul V and set up as an honorific column outside Santa Maria Maggiore.
 In the early 4th century Eusebius used the word basilica () to refer to Christian churches; in subsequent centuries as before, the word basilica referred in Greek to the civic, non-ecclesiastical buildings, and only in rare exceptions to churches. Churches were nonetheless basilican in form, with an apse or tribunal at the end of a nave with two or more aisles typical. A narthex (sometimes with an exonarthex) or Vestibule (architecture), vestibule could be added to the entrance, together with an Atrium (architecture), atrium, and the interior might have transepts, a pastophorion, and Gallery (architecture), galleries, but the basic scheme with clerestory windows and a wooden truss roof remained the most typical church type until the 6th century. The nave would be kept clear for liturgical processions by the clergy, with the laity in the galleries and aisles to either side. The function of Christian churches was similar to that of the civic basilicas but very different from temples in contemporary Graeco-Roman polytheism: while pagan temples were entered mainly by priests and thus had their splendour visible from without, within Christian basilicas the main ornamentation was visible to the congregants admitted inside. Christian priests did not interact with attendees during the rituals which took place at determined intervals, whereas pagan priests were required to perform individuals' sacrifices in the more chaotic environment of the temple precinct, with the temple's facade as backdrop. In basilicas constructed for Christian uses, the interior was often decorated with frescoes, but these buildings' wooden roof often decayed and failed to preserve the fragile frescoes within. Thus was lost an important part of the early history of Early Christian art and architecture, Christian art, which would have sought to communicate early Christian ideas to the mainly illiterate Late Antique society. On the exterior, basilica church complexes included cemeteries, baptisteries, and Baptismal font, fonts which "defined ritual and liturgical access to the sacred", elevated the social status of the Church hierarchy, and which complemented the development of a Christian historical landscape; Constantine and his mother Helena (empress), Helena were patrons of basilicas in important Christian sites in the Holy Land and Rome, and at Milan and Constantinople.
Around 310, while still a self-proclaimed ''augustus'' unrecognised at Rome, Constantine began the construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' or , as a reception hall for his imperial seat at Trier (), capital of Belgica Prima. On the exterior, Constantine's palatine basilica was plain and utilitarian, but inside was very grandly decorated.
In the reign of Constantine I, a basilica was constructed for the Pope in the Castra Nova equitum singularium, former barracks of the ''Equites singulares Augusti'', the cavalry arm of the Praetorian Guard. (Constantine had disbanded the Praetorian guard after his defeat of their emperor Maxentius and replaced them with another bodyguard, the ''Scholae Palatinae''.) In 313 Constantine began construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' on the Lateran Hill. This basilica became Rome's cathedral church, known as St John Lateran, and was more richly decorated and larger than any previous Christian structure. However, because of its remote position from the ''Forum Romanum'' on the city's edge, it did not connect with the older imperial basilicas in the fora of Rome. Outside the basilica was the Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius, a rare example of an Antique statue that has never been underground.
According to the ''Liber Pontificalis'', Constantine was also responsible for the rich interior decoration of the Lateran Baptistery constructed under Pope Sylvester I (r. 314–335), sited about . The Lateran Baptistery was the first monumental free-standing baptistery, and in subsequent centuries Christian basilica churches were often endowed with such baptisteries.
At Cirta, a Christian basilica erected by Constantine was taken over by his opponents, the Donatism, Donatists. After Constantine's failure to resolve the Donatist controversy by coercion between 317 and 321, he allowed the Donatists, who dominated Africa (Roman province), Africa, to retain the basilica and constructed a new one for the Catholic Church.
The original titular churches of Rome were those which had been private residences and which were donated to be converted to places of Christian worship. Above an originally 1st century AD villa and its later adjoining Horreum, warehouse and Mithraeum, a large basilica church had been erected by 350, subsuming the earlier structures beneath it as a crypt. The basilica was the first church of San Clemente al Laterano. Similarly, at Santi Giovanni e Paolo al Celio, an entire ancient city block – a 2nd-century Insula (building), ''insula'' on the Caelian Hill – was buried beneath a 4th-century basilica. The site was already venerated as the ''martyrium'' of three early Christian burials beforehand, and part of the ''insula'' had been decorated in the style favoured by Christian communities frequenting the early Catacombs of Rome.
By 350 in History of Sofia, Serdica (Sofia, Bulgaria), a monumental basilica – the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, Church of Saint Sophia – was erected, covering earlier structures including a Christian chapel, an oratory, and a cemetery dated to c. 310. Other major basilica from this period, in this part of Europe, is the Great Basilica, Plovdiv, Great Basilica in Philippopolis (Thrace), Philippopolis (Plovdiv, Bulgaria) from the 4th century AD.
In the early 4th century Eusebius used the word basilica () to refer to Christian churches; in subsequent centuries as before, the word basilica referred in Greek to the civic, non-ecclesiastical buildings, and only in rare exceptions to churches. Churches were nonetheless basilican in form, with an apse or tribunal at the end of a nave with two or more aisles typical. A narthex (sometimes with an exonarthex) or Vestibule (architecture), vestibule could be added to the entrance, together with an Atrium (architecture), atrium, and the interior might have transepts, a pastophorion, and Gallery (architecture), galleries, but the basic scheme with clerestory windows and a wooden truss roof remained the most typical church type until the 6th century. The nave would be kept clear for liturgical processions by the clergy, with the laity in the galleries and aisles to either side. The function of Christian churches was similar to that of the civic basilicas but very different from temples in contemporary Graeco-Roman polytheism: while pagan temples were entered mainly by priests and thus had their splendour visible from without, within Christian basilicas the main ornamentation was visible to the congregants admitted inside. Christian priests did not interact with attendees during the rituals which took place at determined intervals, whereas pagan priests were required to perform individuals' sacrifices in the more chaotic environment of the temple precinct, with the temple's facade as backdrop. In basilicas constructed for Christian uses, the interior was often decorated with frescoes, but these buildings' wooden roof often decayed and failed to preserve the fragile frescoes within. Thus was lost an important part of the early history of Early Christian art and architecture, Christian art, which would have sought to communicate early Christian ideas to the mainly illiterate Late Antique society. On the exterior, basilica church complexes included cemeteries, baptisteries, and Baptismal font, fonts which "defined ritual and liturgical access to the sacred", elevated the social status of the Church hierarchy, and which complemented the development of a Christian historical landscape; Constantine and his mother Helena (empress), Helena were patrons of basilicas in important Christian sites in the Holy Land and Rome, and at Milan and Constantinople.
Around 310, while still a self-proclaimed ''augustus'' unrecognised at Rome, Constantine began the construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' or , as a reception hall for his imperial seat at Trier (), capital of Belgica Prima. On the exterior, Constantine's palatine basilica was plain and utilitarian, but inside was very grandly decorated.
In the reign of Constantine I, a basilica was constructed for the Pope in the Castra Nova equitum singularium, former barracks of the ''Equites singulares Augusti'', the cavalry arm of the Praetorian Guard. (Constantine had disbanded the Praetorian guard after his defeat of their emperor Maxentius and replaced them with another bodyguard, the ''Scholae Palatinae''.) In 313 Constantine began construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' on the Lateran Hill. This basilica became Rome's cathedral church, known as St John Lateran, and was more richly decorated and larger than any previous Christian structure. However, because of its remote position from the ''Forum Romanum'' on the city's edge, it did not connect with the older imperial basilicas in the fora of Rome. Outside the basilica was the Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius, a rare example of an Antique statue that has never been underground.
According to the ''Liber Pontificalis'', Constantine was also responsible for the rich interior decoration of the Lateran Baptistery constructed under Pope Sylvester I (r. 314–335), sited about . The Lateran Baptistery was the first monumental free-standing baptistery, and in subsequent centuries Christian basilica churches were often endowed with such baptisteries.
At Cirta, a Christian basilica erected by Constantine was taken over by his opponents, the Donatism, Donatists. After Constantine's failure to resolve the Donatist controversy by coercion between 317 and 321, he allowed the Donatists, who dominated Africa (Roman province), Africa, to retain the basilica and constructed a new one for the Catholic Church.
The original titular churches of Rome were those which had been private residences and which were donated to be converted to places of Christian worship. Above an originally 1st century AD villa and its later adjoining Horreum, warehouse and Mithraeum, a large basilica church had been erected by 350, subsuming the earlier structures beneath it as a crypt. The basilica was the first church of San Clemente al Laterano. Similarly, at Santi Giovanni e Paolo al Celio, an entire ancient city block – a 2nd-century Insula (building), ''insula'' on the Caelian Hill – was buried beneath a 4th-century basilica. The site was already venerated as the ''martyrium'' of three early Christian burials beforehand, and part of the ''insula'' had been decorated in the style favoured by Christian communities frequenting the early Catacombs of Rome.
By 350 in History of Sofia, Serdica (Sofia, Bulgaria), a monumental basilica – the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, Church of Saint Sophia – was erected, covering earlier structures including a Christian chapel, an oratory, and a cemetery dated to c. 310. Other major basilica from this period, in this part of Europe, is the Great Basilica, Plovdiv, Great Basilica in Philippopolis (Thrace), Philippopolis (Plovdiv, Bulgaria) from the 4th century AD.
File:Rom, Basilika Santa Sabina, Außenansicht.jpg, Santa Sabina, Rome, 422–432.
File:Rom, Basilika Santa Sabina, Innenansicht.jpg, Interior of Santa Sabina, with ''spolia'' Corinthian columns from the Temple of Juno Regina (Aventine), Temple of Juno ''Regina''.
File:Theodore Studite (Menologion of Basil II).jpg, Basilica church of the Monastery of Stoudios, Constantinple, 5th century, as depicted in the Menologion of Basil II, c. 1000.
File:Antioch of Pisidia 2870.jpg, Apse of the ruined ''Great Basilica'', Antioch in Pisidia. The floor dates to late 4th century, and the walls to the 5th or 6th century. The building has a semi-circular interior and a polygonal exterior.
File:Elenska-bazilika-orto.jpg, Bird's eye view of the Elenska Basilica complex, Pirdop, Bulgaria.
File:RedChurchAerial2.jpg, The Red Church (Bulgaria), Red Church, Perushtitsa, Bulgaria.
File:Mosque of Eski Djouma Thessalonica Transversal section Longitudinal section - Texier Charles - 1864.jpg, Drawing of the 5th century Church of the Acheiropoietos by Charles Texier, 1864
File:Church of the Acheiropoietos (Thessaloniki) by Joy of Museums.jpg, House of Leo, Leonid basilica Church of the Acheiropoietos, Thessaloniki, 450–60
File:Basilique à tours - mosaïque Louvre.jpg, 5th-century mosaic of a basilica (Louvre)
File:StSophiaChurch-Sofia-10.jpg, Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, Saint Sophia, Serdica (Sofia), built 4th–8th centuries
File:Nave looking towards the entrance - Sant'Apollinare Nuovo - Ravenna 2016.jpg, Ostrogothic Kingdom, Ostrogothic ''Basilica of Christ the Redeemer'', Ravenna, 504. Basilica of Sant'Apollinare Nuovo, Rededicated 561 to St Apollinaris
File:Basilica di Sant'Apollinare in Classe (interno).JPG, Basilica of Sant'Apollinare in Classe near Ravenna in Italy
File:Church of the Nativity, Bethlehem, Palestine 04155u original.jpg, Justinian I, Justinianic Church of the Nativity, Bethlehem, after 529
File:Ephesos Saint John the Theologian plan rotated.png, Floor plan of the Justinianic Basilica of St. John, Basilica of St John, Ephesus, after 535/6
File:Bosra basilica di BahiraHPIM3296.JPG, Interior of the ruined Basilica of Bahira, Bosra
File:Βασιλική Αγίου Αχιλλείου.jpg, Ruins of the 10th-century Church of Achillius of Larissa, on the eponymous island of Small Prespa Lake, Agios Achilleios, Mikra Prespa, a typical basilica church
File:2011-Belovo Basilica.jpg, Belovo Basilica, Belovo Municipality, Bulgaria
 In the Roman imperial period, Roman Imperial period (after about 27 BC), a basilica for large audiences also became a feature in palaces. In the 3rd century of the Christian era, the governing elite appeared less frequently in the forums.
In the Roman imperial period, Roman Imperial period (after about 27 BC), a basilica for large audiences also became a feature in palaces. In the 3rd century of the Christian era, the governing elite appeared less frequently in the forums.
 In the 4th century, once the Imperial authorities had decriminalised Christianity with the 313 Edict of Milan, and with the activities of Constantine the Great and Christianity, Constantine the Great and his mother Helena (Empress), Helena, Christians were prepared to build larger and more handsome edifices for worship than the furtive meeting-places (such as the Cenacle, cave-churches, house churches such as Santi Giovanni e Paolo al Celio, that of the martyrs John and Paul) they had been using. Architectural formulas for temples were unsuitable due to their pagan associations, and because pagan cult ceremonies and sacrifices occurred outdoors under the open sky in the sight of the gods, with the temple, housing the cult figures and the treasury, as a backdrop. The usable model at hand, when Constantine wanted to memorialise his imperial piety, was the familiar conventional architecture of the basilicas.
There were several variations of the basic plan of the secular basilica, always some kind of rectangular hall, but the one usually followed for churches had a central nave with one aisle at each side and an apse at one end opposite to the main door at the other end. In (and often also in front of) the apse was a raised platform, where the altar was placed, and from where the clergy officiated. In secular building this plan was more typically used for the smaller audience halls of the emperors, governors, and the very rich than for the great public basilicas functioning as law courts and other public purposes. Constantine built a basilica of this type in his palace complex at Trier, later very easily adopted for use as a church. It is a long rectangle two storeys high, with ranks of arch-headed windows one above the other, without aisles (there was no mercantile exchange in this imperial basilica) and, at the far end beyond a huge arch, the apse in which Constantine held state.
In the 4th century, once the Imperial authorities had decriminalised Christianity with the 313 Edict of Milan, and with the activities of Constantine the Great and Christianity, Constantine the Great and his mother Helena (Empress), Helena, Christians were prepared to build larger and more handsome edifices for worship than the furtive meeting-places (such as the Cenacle, cave-churches, house churches such as Santi Giovanni e Paolo al Celio, that of the martyrs John and Paul) they had been using. Architectural formulas for temples were unsuitable due to their pagan associations, and because pagan cult ceremonies and sacrifices occurred outdoors under the open sky in the sight of the gods, with the temple, housing the cult figures and the treasury, as a backdrop. The usable model at hand, when Constantine wanted to memorialise his imperial piety, was the familiar conventional architecture of the basilicas.
There were several variations of the basic plan of the secular basilica, always some kind of rectangular hall, but the one usually followed for churches had a central nave with one aisle at each side and an apse at one end opposite to the main door at the other end. In (and often also in front of) the apse was a raised platform, where the altar was placed, and from where the clergy officiated. In secular building this plan was more typically used for the smaller audience halls of the emperors, governors, and the very rich than for the great public basilicas functioning as law courts and other public purposes. Constantine built a basilica of this type in his palace complex at Trier, later very easily adopted for use as a church. It is a long rectangle two storeys high, with ranks of arch-headed windows one above the other, without aisles (there was no mercantile exchange in this imperial basilica) and, at the far end beyond a huge arch, the apse in which Constantine held state.
File:Basilica, cross-section scheme.png, ''Basilica'': The central nave extends to one or two storeys more than the lateral aisles, and it has upper windows.
File:Pseudobasilica.png, Pseudo-basilica (i. e. ''false basilica''): The central nave extends to an additional storey, but it has no upper windows.
File:Stepped hall church.png, Stepped hall: The vaults of the central nave begin a bit higher than those of the lateral aisles, but there is no additional storey.
File:Hall church central nave wider.png, Hall church: All vaults are almost on the same level.
File:Aisleless church, lateral chapels.png, Aisleless church with wallside pilasters, a barrel-vault and upper windows above lateral chapels
File:Basilica di San Pietro 1450.jpg, Old Saint Peter's Basilica, Old St Peter's, Rome, as the 4th-century basilica had developed by the mid-15th century, in a 19th-century reconstruction
File:Basilica of St. John Lateran (5790154828).jpg, Lateran basilica, St John in the Lateran is both an architectural and an ecclesiastical basilica.
File:Kloster Bursfelde Westkirche.jpg, Romanesque art, Romanesque basilica of nowadays Evangelical Church in Germany, Lutheran Bursfelde Abbey in Germany
File:Chester Cathedral (7251396712).jpg, Chester Cathedral in England, a Gothic style basilica
File:Nuremberg - St. Sebald church.JPG, St. Sebaldus Church, Nuremberg, St. Sebald's in Nuremberg has a basilical nave and a hall choir.
File:14-01-22-palma-de-mallorca-018.jpg, Palma Cathedral on Mallorca in Spain has windows on three levels, one above the aisles, one above the file of chapels and one in the chapels.
File:St Mary's German Church interior December 1987.jpg, A rare American church built imitating the architecture of an Early Christian basilica, St Mary's German Church, St. Mary's (German) Church in Pennsylvania, now demolished
File:Aleksandar-nevski15.jpg, Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Sofia, Alexander Nevsky Cathedral in Sofia
 In the Catholic Church, a basilica is a large and important Church (building), church building. This designation may be made by the Pope or may date from time immemorial.1 CIC 1917, can. 1180 as quoted in ''Basilicas Historical and Canonical Development'', GABRIEL CHOW HOI-YAN, Toronto, Ontario, Canada 13 May 2003 (revised 24 June 2003). "It was not until 1917 that the Code of Canon Law officially recognized de jure churches that had the immemorial custom of using the title of basilica as having such a right to the title.81 We refer to such churches as immemorial."The title of minor basilicas was first attributed to the church of Basilica di San Nicola a Tolentino, San Nicola di Tolentino in 1783. An older minor basilica is referred to as an "immemorial basilica". Basilica churches are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building does not need to be a basilica in the architectural sense. Basilicas are either major basilicas – of which there are four, all in the diocese of Rome—or minor basilicas, of which there were 1,810 worldwide . The Umbraculum is displayed in a basilica to the right side (i.e. the Epistle side) of the altar to indicate that the church has been awarded the rank of a basilica.
In the Catholic Church, a basilica is a large and important Church (building), church building. This designation may be made by the Pope or may date from time immemorial.1 CIC 1917, can. 1180 as quoted in ''Basilicas Historical and Canonical Development'', GABRIEL CHOW HOI-YAN, Toronto, Ontario, Canada 13 May 2003 (revised 24 June 2003). "It was not until 1917 that the Code of Canon Law officially recognized de jure churches that had the immemorial custom of using the title of basilica as having such a right to the title.81 We refer to such churches as immemorial."The title of minor basilicas was first attributed to the church of Basilica di San Nicola a Tolentino, San Nicola di Tolentino in 1783. An older minor basilica is referred to as an "immemorial basilica". Basilica churches are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building does not need to be a basilica in the architectural sense. Basilicas are either major basilicas – of which there are four, all in the diocese of Rome—or minor basilicas, of which there were 1,810 worldwide . The Umbraculum is displayed in a basilica to the right side (i.e. the Epistle side) of the altar to indicate that the church has been awarded the rank of a basilica.
Architecture of the basilica
* Syndicus, Eduard, ''Early Christian Art'', Burns & Oates, London, 1962
from Samuel Ball Platner (as completed and revised by Thomas Ashby), 1929. ''A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome'' (London: Oxford University Press) * Paul Veyne, ed. ''A History of Private Life I: From Pagan Rome to Byzantium,'' 1987
Heritage Foundation of Newfoundland and Labrador
*



 In
In Ancient Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Ancient Greek Architecture, Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architecture, architectural style ...
, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West
Greek East and Latin West are terms used to distinguish between the two parts of the Greco-Roman world and of Medieval Christendom, specifically the eastern regions where Greek was the '' lingua franca'' (Greece, Anatolia, the southern Balkans, t ...
equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the architectural form of the basilica.
Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
flanked by two or more longitudinal aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, certain types of buildings, such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, par ...
s, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an '' exedra''. ...
at one end, or less frequently at both ends or on the side, usually contained the raised tribunal
A tribunal, generally, is any person or institution with authority to judge, adjudicate on, or determine claims or disputes—whether or not it is called a tribunal in its title.
For example, an advocate who appears before a court with a single ...
occupied by the Roman magistrate
The Roman magistrates were elected officials in Ancient Rome.
During the period of the Roman Kingdom, the King of Rome was the principal executive magistrate.Abbott, 8 His power, in practice, was absolute. He was the chief priest, lawgiver, j ...
s. The basilica was centrally located in every Roman town, usually adjacent to the forum and often opposite a temple in imperial-era forums. Basilicas were also built in private residences and imperial palaces and were known as "palace basilicas".
In late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, church buildings were typically constructed either as martyria, or with a basilica's architectural plan. A number of monumental Christian basilicas were constructed during the latter reign of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
. In the post Nicene period, basilicas became a standard model for Christian spaces for congregational worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity. It may involve one or more of activities such as veneration, adoration, praise, and praying. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recogniti ...
throughout the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
. From the early 4th century, Christian basilicas, along with their associated catacombs, were used for burial of the dead.
By extension, the name was applied to Christian churches which adopted the same basic plan and is used as an architectural term to describe such buildings. It continues to be used in an architectural sense to describe rectangular buildings with a central nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
and aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, certain types of buildings, such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, par ...
s, and usually a raised platform at the end opposite the door. In Europe and the Americas, the basilica remained the most common architectural style for churches of all Christian denominations, though this building plan has become less dominant in buildings constructed since the late 20th century.
Origins

 The Latin word ''
The Latin word ''basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's Forum (Roman), forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building ...
'' derives from . The first known basilica—the Basilica Porcia in the Roman Forum—was constructed in 184 BC by Marcus Porcius Cato (the Elder). After the construction of Cato the Elder's basilica, the term came to be applied to any large covered hall, whether it was used for domestic purposes, was a commercial space, a military structure, or religious building.
The plays of Plautus
Titus Maccius Plautus (; c. 254 – 184 BC), commonly known as Plautus, was a Roman playwright of the Old Latin period. His comedies are the earliest Latin literary works to have survived in their entirety. He wrote Palliata comoedia, the ...
suggest that basilica buildings may have existed prior to Cato's building. The plays were composed between 210 and 184 BC and refer to a building that might be identified with the ''Atrium Regium''. Another early example is the basilica at Pompeii (late 2nd century BC). Inspiration may have come from prototypes like Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
's Stoa Basileios
Stoa Basileios ( el, στοά βασίλειος or τοῦ βασιλέως), meaning Royal Stoa, was a stoa constructed in Ancient Athens in the 6th century BC and substantially altered in the 5th century BC. It was located in the northwest corn ...
or the hypostyle hall on Delos, but the architectural form is most derived from the audience halls in the royal palaces of the Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
kingdoms of the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
. These rooms were typically a high nave flanked by colonnades.
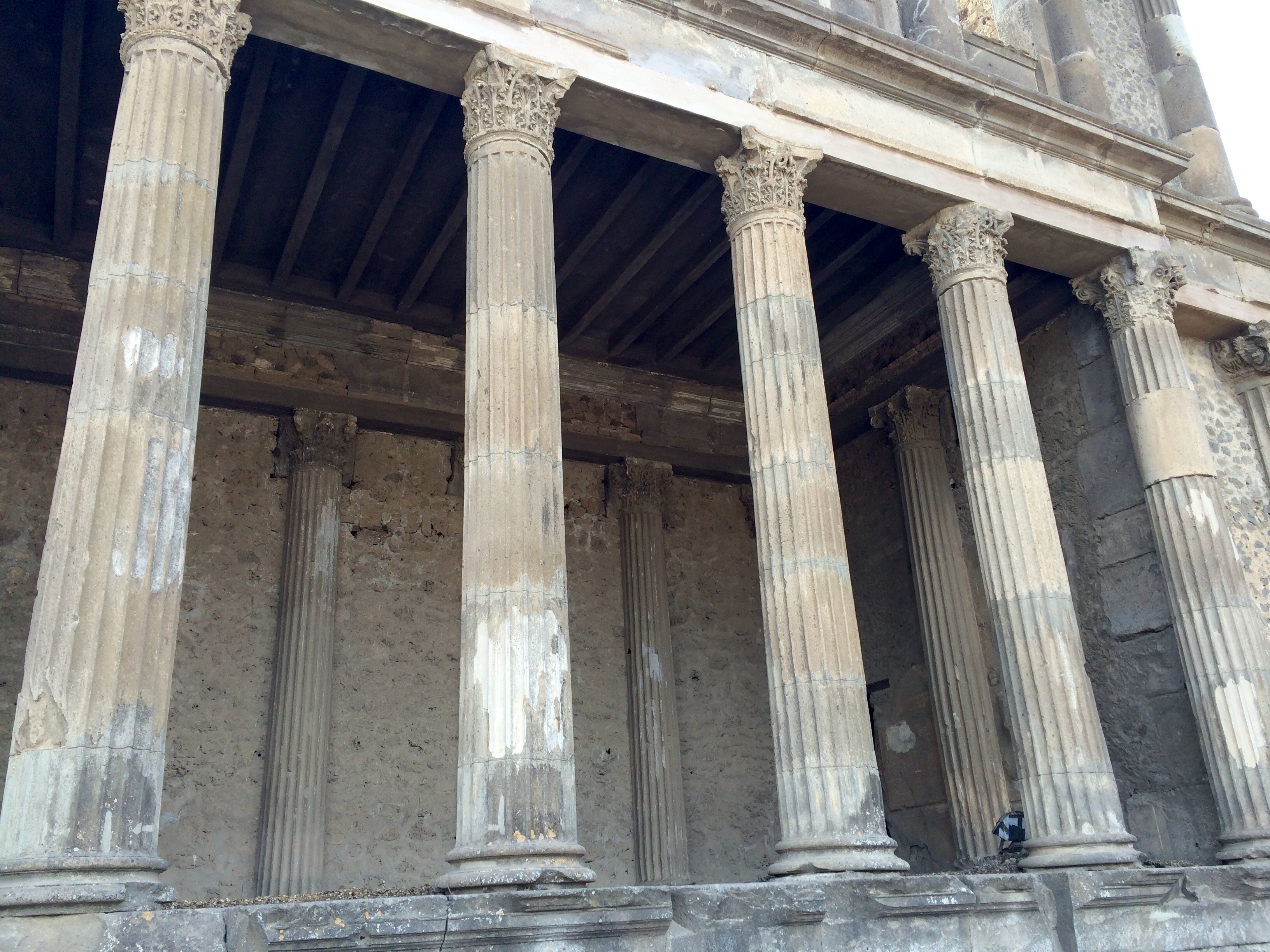
These basilicas were rectangular, typically with central nave and aisles, usually with a slightly raised platform and an apse at each of the two ends, adorned with a statue perhaps of the emperor, while the entrances were from the long sides. The Roman ''basilica'' was a large public building where business or legal matters could be transacted. Although their form was variable, basilicas often contained interior colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or cur ...
s that divided the space, giving aisles or arcaded spaces on one or both sides, with an apse at one end (or less often at each end), where the magistrates sat, often on a slightly raised dais
A dais or daïs ( or , American English also but sometimes considered nonstandard)dais
in the Random House Dictionary< ...
. The central aisle the nave tended to be wider and taller than the flanking aisles, so that light could penetrate through the clerestory windows.
In the late Republican era, basilicas were increasingly monumental; in the Random House Dictionary< ...
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
replaced the Basilica Sempronia with his own Basilica Julia
The Basilica Julia ( it, Basilica Giulia) was a structure that once stood in the Roman Forum. It was a large, ornate, public building used for meetings and other official business during the Roman Empire. Its ruins have been excavated. What is lef ...
, dedicated in 46 BC, while the Basilica Aemilia was rebuilt around 54 BC in so spectacular a fashion that Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
wrote that it was among the most beautiful buildings in the world (it was simultaneously renamed the ''Basilica Paulli''). Thereafter until the 4th century AD, monumental basilicas were routinely constructed at Rome by both private citizens and the emperors. These basilicas were reception halls and grand spaces in which élite persons could impress guests and visitors, and could be attached to a large country ''villa'' or an urban '' domus''. They were simpler and smaller than were civic basilicas, and can be identified by inscriptions or their position in the archaeological context. Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
constructed a basilica on the Palatine Hill for his imperial residential complex around 92 AD, and a palatine basilica was typical in imperial palaces throughout the imperial period.
Roman Republic
 Long, rectangular basilicas with internal
Long, rectangular basilicas with internal peristyle
In ancient Greek and Roman architecture, a peristyle (; from Greek ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. Tetrastoön ( grc, τετράστῳον or τετράστοον, lit=f ...
became a quintessential element of Roman urbanism
Urbanism is the study of how inhabitants of urban areas, such as towns and cities, interact with the built environment. It is a direct component of disciplines such as urban planning, which is the profession focusing on the physical design and ...
, often forming the architectural background to the city forum and used for diverse purposes. Beginning with Cato in the early second century BC, politicians of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
competed with one another by building basilicas bearing their names in the Forum Romanum, the centre of ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
. Outside the city, basilicas symbolised the influence of Rome and became a ubiquitous fixture of Roman ''coloniae'' of the late Republic from c.100 BC. The earliest surviving basilica is the basilica of Pompeii, built 120 BC. Basilicas were the administrative and commercial centres of major Roman settlements: the "quintessential architectural expression of Roman administration". Adjoining it there were normally various offices and rooms housing the ''curia'' and a shrine for the tutela
''Tutela'' was the ancient Roman concept of "guardianship", conceived of as a goddess in the Imperial period, and from the earliest period as a functional role that various tutelary deities might play, particularly Juno. ''Tutela'' had particu ...
. Like Roman public baths, basilicas were commonly used as venues for the display of honorific statues and other sculptures, complementing the outdoor public spaces and thoroughfares.
Beside the Basilica Porcia on the ''Forum Romanum'', the Basilica Aemilia
The Basilica Aemilia ( it, Basilica Emilia, links=no) was a civil basilica in the Roman Forum, in Rome, Italy. Today only the plan and some rebuilt elements can be seen. The Basilica was 100 meters (328 ft) long and about 30 meters (98&nbs ...
was built in 179 BC, and the Basilica Sempronia
The Basilica Sempronia was a structure in the Roman Forum during the Republican period. It was one of four basilicas to make up the original Roman Forum alongside the Basilica Porcia, Basilica Aemilia, and Basilica Opimia, and was the third buil ...
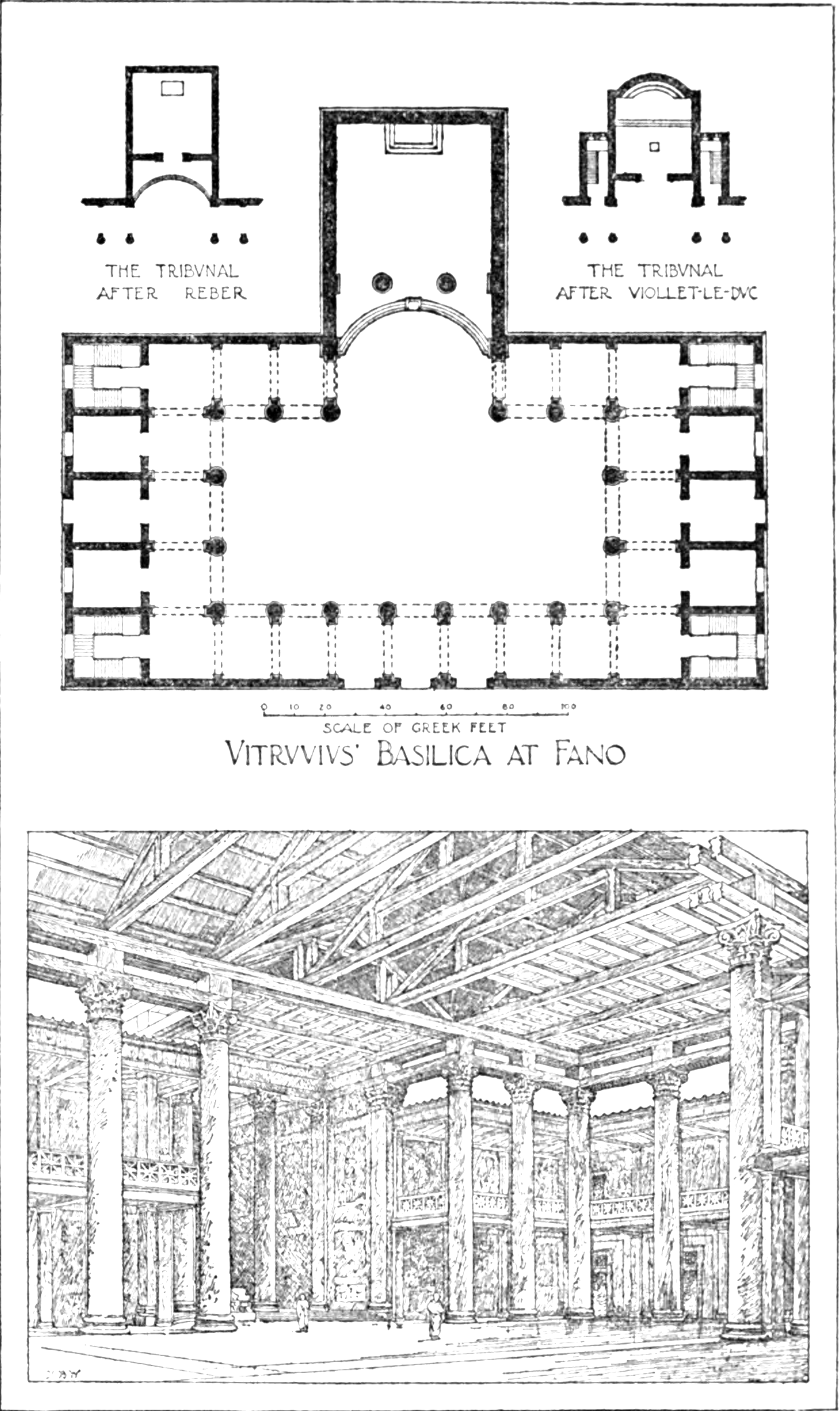
in 169 BC. In the Republic two types of basilica were built across Italy in the mid-2nd to early 1st centuries BC: either they were nearly square as at Fanum Fortunae, designed by Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled '' De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attribut ...
, and Cosa
Cosa was a Latin colony founded in southwestern Tuscany in 273 BC, on land confiscated from the Etruscans, to solidify the control of the Romans and offer the Republic a protected port.
The Etruscan site (called ''Cusi'' or ''Cosia'') may have ...
, with a 3:4 width-length ratio; or else they were more rectangular, as Pompeii's basilica, whose ratio is 3:7.
The basilica at Ephesus is typical of the basilicas in the Roman East, which usually have a very elongated footprint and a ratio between 1:5 and 1:9, with open porticoes facing the '' agora'' (the Hellenic forum); this design was influenced by the existing tradition of long ''stoae'' in Hellenistic Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
. Provinces in the west lacked this tradition, and the basilicas the Romans commissioned there were more typically Italian, with the central nave divided from the side-aisles by an internal colonnade in regular proportions.





Early Empire
Beginning with theForum of Caesar
The Forum of Caesar, also known by the Latin Forum Iulium or Forum Julium, Forum Caesaris,Hornblower, Simon and Antony Spawforth. ''The Oxford Classical Dictionary''. 3d Ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1996. was a forum built by Julius Caes ...
() at the end of the Roman Republic, the centre of Rome was embellished with a series of imperial fora
The Imperial Fora (''Fori Imperiali '' in Italian) are a series of monumental '' fora'' (public squares), constructed in Rome over a period of one and a half centuries, between 46 BC and 113 AD. The fora were the center of the Roman Republic and ...
typified by a large open space surrounded by a peristyle, honorific statues of the imperial family (), and a basilica, often accompanied by other facilities like a temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
, market halls
A market house is a covered space historically used as a marketplace to exchange goods and services such as provisions or livestock, sometimes combined with spaces for public or civic functions on the upper floors and often with a jail or lockup ...
and public libraries. In the imperial period, statues of the emperors with inscribed dedications were often installed near the basilicas' tribunals, as Vitruvius recommended. Examples of such dedicatory inscriptions are known from basilicas at Lucus Feroniae
Lucus Feroniae was an ancient sanctuary or, literally sacred grove (''"lucus"''), dedicated to the Sabine goddess Feronia, protector of freedmen, ex-slaves. It was located near to the ancient town of Feronia in Etruria on the ancient Via Tib ...
and Veleia in Italy and at Cuicul in Africa Proconsolaris
Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, ...
, and inscriptions of all kinds were visible in and around basilicas.
At Ephesus the basilica-''stoa'' had two storeys and three aisles and extended the length of the civic ''agora''Neopythagorean
Neopythagoreanism (or neo-Pythagoreanism) was a school of Hellenistic philosophy which revived Pythagorean doctrines. Neopythagoreanism was influenced by middle Platonism and in turn influenced Neoplatonism. It originated in the 1st century BC ...
basilica dating from the 1st century AD were found near the Porta Maggiore
The Porta Maggiore ("Larger Gate"), or Porta Prenestina, is one of the eastern gates in the ancient but well-preserved 3rd-century Aurelian Walls of Rome. Through the gate ran two ancient roads: the Via Praenestina and the Via Labicana. The Via ...
in Rome in 1917, and is known as the Porta Maggiore Basilica.
After its destruction in 60 AD, Londinium (London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
) was endowed with its first forum and basilica under the Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known ...
. The basilica delimited the northern edge of the forum with typical nave, aisles, and a tribunal, but with an atypical semi-basement at the western side. Unlike in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, basilica-forum complexes in Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
did not usually include a temple; instead a shrine was usually inside the basilica itself. At Londinium however, there was probably no temple at all attached to the original basilica, but instead a contemporary temple was constructed nearby. Later, in 79 AD, an inscription commemorated the completion of the basilica at Verulamium
Verulamium was a town in Roman Britain. It was sited southwest of the modern city of St Albans in Hertfordshire, England. A large portion of the Roman city remains unexcavated, being now park and agricultural land, though much has been built upon ...
( St Albans) under the governor Gnaeus Julius Agricola
Gnaeus Julius Agricola (; 13 June 40 – 23 August 93) was a Roman general and politician responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. Born to a political family of senatorial rank, Agricola began his military career as a military tribu ...
; by contrast the first basilica at Londinium was only . The smallest known basilica in Britain was built by the Silures at Caerwent
Caerwent ( cy, Caer-went) is a village and community in Monmouthshire, Wales. It is located about five miles west of Chepstow and 11 miles east of Newport. It was founded by the Romans as the market town of ''Venta Silurum'', an important sett ...
and measured .
When Londinium became a '' colonia'', the whole city was re-planned and a new great forum-basilica complex erected, larger than any in Britain. Londinium's basilica, more than long, was the largest north of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
and a similar length to the modern St Paul's Cathedral. Only the later basilica-forum complex at Treverorum was larger, while at Rome only the Basilica Ulpia exceeded London's in size. It probably had arcaded, rather than trabeate
In architecture, post and lintel (also called prop and lintel or a trabeated system) is a building system where strong horizontal elements are held up by strong vertical elements with large spaces between them. This is usually used to hold up ...
, aisles, and a double row of square offices on the northern side, serving as the administrative centre of the ''colonia'', and its size and splendour probably indicate an imperial decision to change the administrative capital of Britannia to Londinium from Camulodunum
Camulodunum (; la, ), the Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important castrum and city in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. A temporary "strapline" in the 1960s identifying it as the "oldest re ...
(Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
), as all provincial capitals were designated ''coloniae''. In 300 Londinium's basilica was destroyed as a result of the rebellion led by the ''Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
'' of the break-away Britannic Empire, Carausius. Remains of the great basilica and its arches were discovered during the construction of Leadenhall Market in the 1880s.
At Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government refor ...
in the 1st century AD, a new basilica was constructed in on the east side of the forum. It was possibly inside the basilica that Paul the Apostle, according to the '' Acts of the Apostles'' ( ''Acts'' 18:12–17) was investigated and found innocent by the Suffect Consul Lucius Junius Gallio Annaeanus
Lucius Junius Gallio Annaeanus or Gallio ( el, Γαλλιων, ''Galliōn''; c. 5 BC – c. AD 65) was a Roman senator and brother of the famous writer Seneca. He is best known for dismissing an accusation brought against Paul the Apostle in Cori ...
, the brother of Seneca the Younger
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Younger (; 65 AD), usually known mononymously as Seneca, was a Stoic philosopher of Ancient Rome, a statesman, dramatist, and, in one work, satirist, from the post-Augustan age of Latin literature.
Seneca was born in ...
, after charges were brought against him by members of the local Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
. Modern tradition instead associates the incident with an open-air inscribed '' bema'' in the forum itself.
The emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
constructed his own imperial forum in Rome accompanied by his Basilica Ulpia
The Basilica Ulpia was an ancient Roman civic building located in the Forum of Trajan. The Basilica Ulpia separates the temple from the main courtyard in the Forum of Trajan with the Trajan's Column to the northwest. It was named after Roman emp ...
dedicated in 112. Trajan's Forum
Trajan's Forum ( la, Forum Traiani; it, Foro di Traiano) was the last of the Imperial fora to be constructed in ancient Rome. The architect Apollodorus of Damascus oversaw its construction.
History
This forum was built on the order of the em ...
() was separated from the Temple of Trajan
The Temple of Trajan was a Roman temple dedicated to the emperor Trajan and his wife Plotina after his deification by the Roman Senate. It was built in the Forum of Trajan (Rome), by Trajan's adoptive son and successor Hadrian, between 125 and 13 ...
, the Ulpian Library
The Bibliotheca Ulpia ("Ulpian Library") was a Roman library founded by the Emperor Trajan in AD 114 in his forum, the Forum of Trajan, located in ancient Rome. It was considered one of the most prominent and famous libraries of antiquity and be ...
, and his famous Column depicting the Dacian Wars by the Basilica. It was an especially grand example whose particular symmetrical arrangement with an apse at both ends was repeated in the provinces as a characteristic form. To improve the quality of the Roman concrete
Roman concrete, also called , is a material that was used in construction in ancient Rome. Roman concrete was based on a hydraulic-setting cement. It is durable due to its incorporation of pozzolanic ash, which prevents cracks from spreading. ...
used in the Basilica Ulpia, volcanic scoria
Scoria is a pyroclastic, highly vesicular, dark-colored volcanic rock that was ejected from a volcano as a molten blob and cooled in the air to form discrete grains or clasts.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) '' ...
from the Bay of Naples and Mount Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
were imported which, though heavier, was stronger than the pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular v ...
available closer to Rome. The Bailica Ulpia is probably an early example of tie bars to restrain the lateral thrust of the barrel vault resting on a colonnade; both tie-bars and scoria were used in contemporary work at the Baths of Trajan
The Baths of Trajan ( it, Terme di Traiano) were a massive ''thermae'', a bathing and leisure complex, built in ancient Rome starting from 104 AD and dedicated during the '' kalendae'' of July in 109. Commissioned by Emperor Trajan, the complex of ...
and later the Hadrianic domed vault of the Pantheon
Pantheon may refer to:
* Pantheon (religion), a set of gods belonging to a particular religion or tradition, and a temple or sacred building
Arts and entertainment Comics
*Pantheon (Marvel Comics), a fictional organization
* ''Pantheon'' (Lone S ...
.
In early 123, the ''augusta'' and widow of the emperor Trajan, Pompeia Plotina
Pompeia Plotina (died 121/122) was Roman empress from 98 to 117 as the wife of Trajan. She was renowned for her interest in philosophy, and her virtue, dignity and simplicity. She was particularly devoted to the Epicurean philosophical school in ...
died. Hadrian, successor to Trajan, deified
Apotheosis (, ), also called divinization or deification (), is the glorification of a subject to divine levels and, commonly, the treatment of a human being, any other living thing, or an abstract idea in the likeness of a deity. The term has ...
her and had a basilica constructed in her honour in southern Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.
The Basilica Hilariana
The Basilica Hilariana was a sanctuary dedicated by the cult of Cybele on the Caelian Hill in Rome, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in t ...
(built c.145–155) was designed for the use of the cult of Cybele
Cybele ( ; Phrygian language, Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian language, Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian mother godde ...
.
The largest basilica built outside Rome was that built under the Antonine dynasty on the Byrsa
Byrsa was a walled citadel above the Phoenician harbour in ancient Carthage, Tunisia, as well as the name of the hill it rested on.
Legend
In Virgil's account of Dido's founding of Carthage, when Dido and her party were encamped at Byrsa, the l ...
hill in Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
. The basilica was built together with a forum of enormous size and was contemporary with a great complex of public baths and a new aqueduct system running for , then the longest in the Roman Empire.
The basilica at Leptis Magna
Leptis or Lepcis Magna, also known by other names in antiquity, was a prominent city of the Carthaginian Empire and Roman Libya at the mouth of the Wadi Lebda in the Mediterranean.
Originally a 7th-centuryBC Phoenician foundation, it was great ...
, built by the Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
a century later in about 216 is a notable 3rd century AD example of the traditional type, most notable among the works influenced by the Basilica Ulpia. The basilica at Leptis was built mainly of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
ashlar, but the apses at either end were only limestone in the outer sections and built largely of rubble masonry
Rubble stone is rough, uneven building stone not laid in regular courses. It may fill the core of a wall which is faced with unit masonry such as brick or ashlar. Analogously, some medieval cathedral walls are outer shells of ashlar with an i ...
faced with brick, with a number of decorative panels in ''opus reticulatum
''Opus reticulatum'' (also known as reticulate work) is a facing used for concrete walls in Roman architecture from about the first century BCE to the early first century CE. Facings are a type of polygonal masonry used to apply a smooth finish to ...
''. The basilica stood in a new forum and was accompanied by a programme of Severan works at Leptis including ''thermae'', a new harbour, and a public fountain. At Volubilis
Volubilis (; ar, وليلي, walīlī; ber, ⵡⵍⵉⵍⵉ, wlili) is a partly excavated Berber-Roman city in Morocco situated near the city of Meknes, and may have been the capital of the kingdom of Mauretania, at least from the time of Kin ...
, principal city of Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana (Latin for "Tangerine Mauretania") was a Roman province, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia (or Chella ...
, a basilica modelled on Leptis Magna's was completed during the short reign of Macrinus
Marcus Opellius Macrinus (; – June 218) was Roman emperor from April 217 to June 218, reigning jointly with his young son Diadumenianus. As a member of the equestrian class, he became the first emperor who did not hail from the senatori ...
.
Basilicas in the Roman Forum
 * Basilica Porcia: first basilica built in Rome (184 BC), erected on the personal initiative and financing of the censor Marcus Porcius Cato (Cato the Elder) as an official building for the
* Basilica Porcia: first basilica built in Rome (184 BC), erected on the personal initiative and financing of the censor Marcus Porcius Cato (Cato the Elder) as an official building for the tribunes of the plebs
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune ( la, tribunus plebis) was the first office of the Roman state that was open to the plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power o ...
* Basilica Aemilia
The Basilica Aemilia ( it, Basilica Emilia, links=no) was a civil basilica in the Roman Forum, in Rome, Italy. Today only the plan and some rebuilt elements can be seen. The Basilica was 100 meters (328 ft) long and about 30 meters (98&nbs ...
, built by the censor Marcus Aemilius Lepidus (consul 187 BC), Aemilius Lepidus in 179 BC
* Basilica Sempronia
The Basilica Sempronia was a structure in the Roman Forum during the Republican period. It was one of four basilicas to make up the original Roman Forum alongside the Basilica Porcia, Basilica Aemilia, and Basilica Opimia, and was the third buil ...
, built by the censor Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus (consul 177 BC), Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus in 169 BC
* Basilica Opimia, erected probably by the consul Lucius Opimius in 121 BC, at the same time that he restored the temple of Concord (Platner, Ashby 1929)
* Basilica Julia
The Basilica Julia ( it, Basilica Giulia) was a structure that once stood in the Roman Forum. It was a large, ornate, public building used for meetings and other official business during the Roman Empire. Its ruins have been excavated. What is lef ...
, initially dedicated in 46 BC by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
and completed by Augustus 27 BC to AD 14
* Basilica Argentaria, erected under Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
, emperor from AD 98 to 117
* Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine (built between AD 308 and 312)
Late antiquity



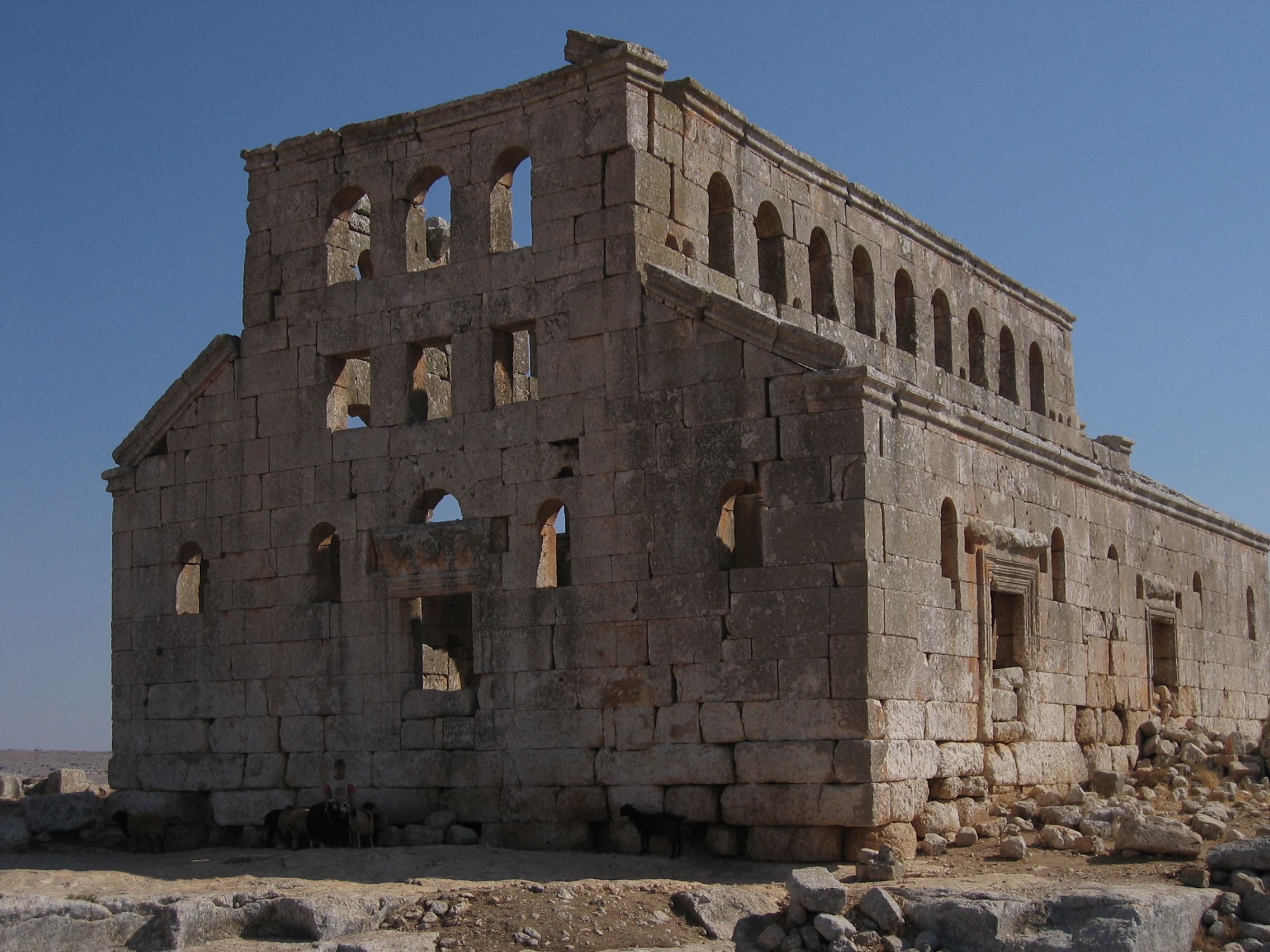
 The aisled-hall plan of the basilica was adopted by a number of religious cults in
The aisled-hall plan of the basilica was adopted by a number of religious cults in late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
. At Sardis, a Sardis Synagogue, monumental basilica housed the city's synagogue, serving the local Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
. New religions like Christianity required space for congregational worship, and the basilica was adapted by the early Church for worship. Because they were able to hold large number of people, basilicas were adopted for Christian liturgical use after Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
. The early churches of Rome were basilicas with an apisidal tribunal and used the same construction techniques of columns and timber roofing.
At the start of the 4th century at Rome there was a change in burial and Funeral, funerary practice, moving away from earlier preferences for inhumation in cemeteries popular from the 2nd and 3rd centuries AD to the newer practice of burial in Catacombs of Rome, catacombs and inhumation inside Christian basilicas themselves. Conversely, new basilicas often were erected on the site of existing early Christian cemeteries and ''martyria'', related to the belief in Resurrection of Jesus, Bodily Resurrection, and the cult of the sacred dead became monumentalised in basilica form. Traditional civic basilicas and ''Bouleuterion, bouleuteria'' declined in use with the weakening of the curial class () in the 4th and 5th centuries, while their structures were well suited to the requirements of congregational liturgies. The conversion of these types of buildings into Christian basilicas was also of symbolic significance, asserting the dominance of Christianity and supplanting the old political function of public space and the city-centre with an emphatic Christian social statement. Traditional monumental civic amenities like Gymnasium (ancient Greece), ''gymnasia'', Palaestra, ''palaestrae'', and ''thermae'' were also falling into disuse, and became favoured sites for the construction of new churches, including basilicas.
Under Constantine, the basilica became the most prestigious style of church building, was "normative" for church buildings by the end of the 4th century, and were ubiquitous in western Asia, North Africa, and most of Europe by the close of the 7th century. Christians also continued to hold services in synagogues, houses, and gardens, and continued practising baptism in rivers, ponds, and Roman bathhouses.
The development of Christian basilicas began even before Constantine's reign: a 3rd-century Mudbrick, mud-brick house at Aqaba had become a Christian church and was rebuilt as a basilica. Within was a rectangular assembly hall with frescoes and at the east end an Ambon (liturgy), ambo, a cathedra, and an altar. Also within the church were a catecumenon (for catechumens), a baptistery, a diaconicon, and a Prothesis (altar), prothesis: all features typical of later 4th century basilica churches. A Christian structure which included the prototype of the triumphal arch at the east end of later Constantinian basilicas. Known as the Megiddo church (Israel), Megiddo church, it was built at Kefar 'Othnay in Palestine (region), Palestine, possibly c. 230, for or by the Roman army stationed at Legio (later Lajjun). Its dedicatory inscriptions include the names of women who contributed to the building and were its major patrons, as well as men's names. A number of buildings previously believed to have been Constantinian or 4th century have been reassessed as dating to later periods, and certain examples of 4th century basilicas are not distributed throughout the Mediterranean world at all evenly. Christian basilicas and ''martyria'' attributable to the 4th century are rare on the Greek mainland and on the Cyclades, while the Christian basilicas of Egypt, Cyprus (island), Cyprus, Syria (region), Syria, Transjordan (region), Transjordan, Hispania, and Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
are nearly all of later date. The basilica at Ephesus's ''Magnesian Gate'', the episcopal church at Laodicea on the Lycus, and two extramural churches at Sardis have all been considered 4th century constructions, but on weak evidence. Development of Pottery#Archaeology, pottery chronologies for Late Antiquity had helped resolve questions of dating basilicas of the period.
Three examples of a ''basilica discoperta'' or "hypaethral basilica" with no roof above the nave are inferred to have existed. The 6th century Anonymous pilgrim of Piacenza described a "a basilica built with a ''quadriporticus'', with the middle atrium uncovered" at Hebron, while at Pécs and near Salona two ruined 5th buildings of debated interpretation might have been either roofless basilica churches or simply courtyards with an exedra at the end. An old theory by Ejnar Dyggve that these were the architectural intermediary between the Christian Martyrium (architecture), ''martyrium'' and the classical Heroon, ''heröon'' is no longer credited.
The magnificence of early Christian basilicas reflected the patronage of the emperor and recalled his imperial palaces and reflected the royal associations of the basilica with the Hellenistic Kingdoms and even earlier monarchies like that of Pharaonic Egypt. Similarly, the name and association resounded with the Christian claims of the royalty of Christ – according to the '' Acts of the Apostles'' the earliest Christians had gathered at the royal ''Stoa'' of Solomon in Jerusalem to assert Jesus's royal heritage. For early Christians, the Bible supplied evidence that the First Temple and Solomon's palace were both hypostyle halls and somewhat resembled basilicas. Hypostyle synagogues, often built with apses in Palestine by the 6th century, share a common origin with the Christian basilicas in the civic basilicas and in the pre-Roman style of hypostyle halls in the Mediterranean Basin, particularly in Egypt, where pre-classical hypostyles continued to be built in the imperial period and were themselves converted into churches in the 6th century. Other influences on the evolution of Christian basilicas may have come from elements of domestic and palatial architecture during the pre-Constantinian period of Christianity, including the reception hall or () and the Atrium (domus), ''atria'' and Triclinium, ''triclinia'' of élite Roman dwellings. The versatility of the basilica form and its variability in size and ornament recommended itself to the early Christian Church: basilicas could be grandiose as the Basilica of Maxentius in the ''Forum Romanum'' or more practical like the so-called Basilica of Bahira in Bosra, while the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' on the Lateran Hill was of intermediate scale. This basilica, begun in 313, was the first imperial Christian basilica. Imperial basilicas were first constructed for the Christian Eucharist liturgy in the reign of Constantine.
Basilica churches were not economically inactive. Like non-Christian or civic basilicas, basilica churches had a commercial function integral to their local trade routes and economies. Amphorae discovered at basilicas attest their economic uses and can reveal their position in wider networks of exchange. At Dion, Pieria, Dion near Mount Olympus in Macedonia (Roman province), Macedonia, now an Archaeological Park of Dion, Archaeological Park, the latter 5th century ''Cemetery Basilica'', a small church, was replete with potsherds from all over the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
, evidencing extensive economic activity took place there. Likewise at Maroni Petrera on Cyprus, the amphorae unearthed by archaeologists in the 5th century basilica church had been imported from North Africa, Egypt, Palestine (region), Palestine, and the Aegean basin, as well as from neighbouring Asia Minor.
According to Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus, Vegetius, writing c. 390, basilicas were convenient for Foot drill, drilling soldiers of the Late Roman army during inclement weather.
Basilica of Maxentius

Constantinian period
 In the early 4th century Eusebius used the word basilica () to refer to Christian churches; in subsequent centuries as before, the word basilica referred in Greek to the civic, non-ecclesiastical buildings, and only in rare exceptions to churches. Churches were nonetheless basilican in form, with an apse or tribunal at the end of a nave with two or more aisles typical. A narthex (sometimes with an exonarthex) or Vestibule (architecture), vestibule could be added to the entrance, together with an Atrium (architecture), atrium, and the interior might have transepts, a pastophorion, and Gallery (architecture), galleries, but the basic scheme with clerestory windows and a wooden truss roof remained the most typical church type until the 6th century. The nave would be kept clear for liturgical processions by the clergy, with the laity in the galleries and aisles to either side. The function of Christian churches was similar to that of the civic basilicas but very different from temples in contemporary Graeco-Roman polytheism: while pagan temples were entered mainly by priests and thus had their splendour visible from without, within Christian basilicas the main ornamentation was visible to the congregants admitted inside. Christian priests did not interact with attendees during the rituals which took place at determined intervals, whereas pagan priests were required to perform individuals' sacrifices in the more chaotic environment of the temple precinct, with the temple's facade as backdrop. In basilicas constructed for Christian uses, the interior was often decorated with frescoes, but these buildings' wooden roof often decayed and failed to preserve the fragile frescoes within. Thus was lost an important part of the early history of Early Christian art and architecture, Christian art, which would have sought to communicate early Christian ideas to the mainly illiterate Late Antique society. On the exterior, basilica church complexes included cemeteries, baptisteries, and Baptismal font, fonts which "defined ritual and liturgical access to the sacred", elevated the social status of the Church hierarchy, and which complemented the development of a Christian historical landscape; Constantine and his mother Helena (empress), Helena were patrons of basilicas in important Christian sites in the Holy Land and Rome, and at Milan and Constantinople.
Around 310, while still a self-proclaimed ''augustus'' unrecognised at Rome, Constantine began the construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' or , as a reception hall for his imperial seat at Trier (), capital of Belgica Prima. On the exterior, Constantine's palatine basilica was plain and utilitarian, but inside was very grandly decorated.
In the reign of Constantine I, a basilica was constructed for the Pope in the Castra Nova equitum singularium, former barracks of the ''Equites singulares Augusti'', the cavalry arm of the Praetorian Guard. (Constantine had disbanded the Praetorian guard after his defeat of their emperor Maxentius and replaced them with another bodyguard, the ''Scholae Palatinae''.) In 313 Constantine began construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' on the Lateran Hill. This basilica became Rome's cathedral church, known as St John Lateran, and was more richly decorated and larger than any previous Christian structure. However, because of its remote position from the ''Forum Romanum'' on the city's edge, it did not connect with the older imperial basilicas in the fora of Rome. Outside the basilica was the Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius, a rare example of an Antique statue that has never been underground.
According to the ''Liber Pontificalis'', Constantine was also responsible for the rich interior decoration of the Lateran Baptistery constructed under Pope Sylvester I (r. 314–335), sited about . The Lateran Baptistery was the first monumental free-standing baptistery, and in subsequent centuries Christian basilica churches were often endowed with such baptisteries.
At Cirta, a Christian basilica erected by Constantine was taken over by his opponents, the Donatism, Donatists. After Constantine's failure to resolve the Donatist controversy by coercion between 317 and 321, he allowed the Donatists, who dominated Africa (Roman province), Africa, to retain the basilica and constructed a new one for the Catholic Church.
The original titular churches of Rome were those which had been private residences and which were donated to be converted to places of Christian worship. Above an originally 1st century AD villa and its later adjoining Horreum, warehouse and Mithraeum, a large basilica church had been erected by 350, subsuming the earlier structures beneath it as a crypt. The basilica was the first church of San Clemente al Laterano. Similarly, at Santi Giovanni e Paolo al Celio, an entire ancient city block – a 2nd-century Insula (building), ''insula'' on the Caelian Hill – was buried beneath a 4th-century basilica. The site was already venerated as the ''martyrium'' of three early Christian burials beforehand, and part of the ''insula'' had been decorated in the style favoured by Christian communities frequenting the early Catacombs of Rome.
By 350 in History of Sofia, Serdica (Sofia, Bulgaria), a monumental basilica – the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, Church of Saint Sophia – was erected, covering earlier structures including a Christian chapel, an oratory, and a cemetery dated to c. 310. Other major basilica from this period, in this part of Europe, is the Great Basilica, Plovdiv, Great Basilica in Philippopolis (Thrace), Philippopolis (Plovdiv, Bulgaria) from the 4th century AD.
In the early 4th century Eusebius used the word basilica () to refer to Christian churches; in subsequent centuries as before, the word basilica referred in Greek to the civic, non-ecclesiastical buildings, and only in rare exceptions to churches. Churches were nonetheless basilican in form, with an apse or tribunal at the end of a nave with two or more aisles typical. A narthex (sometimes with an exonarthex) or Vestibule (architecture), vestibule could be added to the entrance, together with an Atrium (architecture), atrium, and the interior might have transepts, a pastophorion, and Gallery (architecture), galleries, but the basic scheme with clerestory windows and a wooden truss roof remained the most typical church type until the 6th century. The nave would be kept clear for liturgical processions by the clergy, with the laity in the galleries and aisles to either side. The function of Christian churches was similar to that of the civic basilicas but very different from temples in contemporary Graeco-Roman polytheism: while pagan temples were entered mainly by priests and thus had their splendour visible from without, within Christian basilicas the main ornamentation was visible to the congregants admitted inside. Christian priests did not interact with attendees during the rituals which took place at determined intervals, whereas pagan priests were required to perform individuals' sacrifices in the more chaotic environment of the temple precinct, with the temple's facade as backdrop. In basilicas constructed for Christian uses, the interior was often decorated with frescoes, but these buildings' wooden roof often decayed and failed to preserve the fragile frescoes within. Thus was lost an important part of the early history of Early Christian art and architecture, Christian art, which would have sought to communicate early Christian ideas to the mainly illiterate Late Antique society. On the exterior, basilica church complexes included cemeteries, baptisteries, and Baptismal font, fonts which "defined ritual and liturgical access to the sacred", elevated the social status of the Church hierarchy, and which complemented the development of a Christian historical landscape; Constantine and his mother Helena (empress), Helena were patrons of basilicas in important Christian sites in the Holy Land and Rome, and at Milan and Constantinople.
Around 310, while still a self-proclaimed ''augustus'' unrecognised at Rome, Constantine began the construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' or , as a reception hall for his imperial seat at Trier (), capital of Belgica Prima. On the exterior, Constantine's palatine basilica was plain and utilitarian, but inside was very grandly decorated.
In the reign of Constantine I, a basilica was constructed for the Pope in the Castra Nova equitum singularium, former barracks of the ''Equites singulares Augusti'', the cavalry arm of the Praetorian Guard. (Constantine had disbanded the Praetorian guard after his defeat of their emperor Maxentius and replaced them with another bodyguard, the ''Scholae Palatinae''.) In 313 Constantine began construction of the ''Basilica Constantiniana'' on the Lateran Hill. This basilica became Rome's cathedral church, known as St John Lateran, and was more richly decorated and larger than any previous Christian structure. However, because of its remote position from the ''Forum Romanum'' on the city's edge, it did not connect with the older imperial basilicas in the fora of Rome. Outside the basilica was the Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius, a rare example of an Antique statue that has never been underground.
According to the ''Liber Pontificalis'', Constantine was also responsible for the rich interior decoration of the Lateran Baptistery constructed under Pope Sylvester I (r. 314–335), sited about . The Lateran Baptistery was the first monumental free-standing baptistery, and in subsequent centuries Christian basilica churches were often endowed with such baptisteries.
At Cirta, a Christian basilica erected by Constantine was taken over by his opponents, the Donatism, Donatists. After Constantine's failure to resolve the Donatist controversy by coercion between 317 and 321, he allowed the Donatists, who dominated Africa (Roman province), Africa, to retain the basilica and constructed a new one for the Catholic Church.
The original titular churches of Rome were those which had been private residences and which were donated to be converted to places of Christian worship. Above an originally 1st century AD villa and its later adjoining Horreum, warehouse and Mithraeum, a large basilica church had been erected by 350, subsuming the earlier structures beneath it as a crypt. The basilica was the first church of San Clemente al Laterano. Similarly, at Santi Giovanni e Paolo al Celio, an entire ancient city block – a 2nd-century Insula (building), ''insula'' on the Caelian Hill – was buried beneath a 4th-century basilica. The site was already venerated as the ''martyrium'' of three early Christian burials beforehand, and part of the ''insula'' had been decorated in the style favoured by Christian communities frequenting the early Catacombs of Rome.
By 350 in History of Sofia, Serdica (Sofia, Bulgaria), a monumental basilica – the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, Church of Saint Sophia – was erected, covering earlier structures including a Christian chapel, an oratory, and a cemetery dated to c. 310. Other major basilica from this period, in this part of Europe, is the Great Basilica, Plovdiv, Great Basilica in Philippopolis (Thrace), Philippopolis (Plovdiv, Bulgaria) from the 4th century AD.
Valentinianic–Theodosian period
In the late 4th century the dispute between Nicene Christianity, Nicene and Arian Christianity came to head at ''Mediolanum'' (Milan), where Ambrose was bishop. At Easter in 386 the Arianism, Arian party, preferred by the Theodosian dynasty, sought to wrest the use of the basilica from the Nicene partisan Ambrose. According to Augustine of Hippo, the dispute resulted in Ambrose organising an 'orthodox' sit-in at the basilica and arranged the miraculous invention and translation of martyrs, whose hidden remains had been revealed in a Vision (spirituality), vision. During the sit-in, Augustine credits Ambrose with the introduction from the "eastern regions" of antiphonal chanting, to give heart to the orthodox congregation, though in fact music was likely part of Christian ritual since the time of the Pauline epistles. The arrival and reburial of the martyrs' uncorrupted remains in the basilica in time for the Easter celebrations was seen as powerful step towards divine approval. At Philippi, the market adjoining the 1st-century forum was demolished and replaced with a Christian basilica. Civic basilicas throughout Asia Minor became Christian places of worship; examples are known at Ephesus, Aspendos, and at Magnesia on the Maeander. The ''Great Basilica'' in Antioch of Pisidia is a rare securely dated 4th century Christian basilica and was the city's cathedral church. The mosaics of the floor credit Optimus, the bishop, with its dedication. Optimus was a contemporary of Basil of Caesarea and corresponded with him c. 377. Optimus was the city's delegate at the First Council of Constantinople in 381, so the 70 m-long single-apsed basilica near the city walls must have been constructed around that time. Pisidia had a number of Christian basilicas constructed in Late Antiquity, particularly in former ''bouleuteria'', as at Sagalassos, Selge, Pednelissus, while a civic basilica was converted for Christians' use in Cremna. At Chalcedon, opposite Constantinople on the Bosporus, the relics of Euphemia – a supposed Christian martyr of the Diocletianic Persecution – were housed in a ''martyrium'' accompanied by a basilica. The basilica already existed when Egeria (pilgrim), Egeria passed through Chalcedon in 384, and in 436 Melania the Younger visited the church on her own journey to the Holy Land. From the description of Evagrius Scholasticus the church is identifiable as an aisled basilica attached to the ''martyrium'' and preceded by an ''atrium''. The Council of Chalcedon (8–31 October 451) was held in the basilica, which must have been large enough to accommodate the more than two hundred bishops that attneded its third session, together with their translators and servants; around 350 bishops attended the Council in all. In an ekphrasis in his eleventh sermon, Asterius of Amasea described an icon in the church depicting Euphemia's martyrdom. The church was restored under the patronage of the ''patricia'' and daughter of Olybrius'','' Anicia Juliana. Pope Vigilius fled there from Constantinople during the Three-Chapter Controversy. The basilica, which lay outside the walls of Chalcedon, was destroyed by the Persians in the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628 during one of the Sasanian occupations of the city in 615 and 626. The relics of Euphemia were reportedly Translation (relic), translated to a new Palace of Antiochos#Church of Saint Euphemia, Church of St Euphemia in Constantinople in 680, though Cyril Mango argued the translation never took place. Subsequently, Asterius's sermon ''On the Martyrdom of St Euphemia'' was advanced as an argument for iconodulism at the Second Council of Nicaea in 787. In the late 4th century, a large basilica church dedicated to Mary, mother of Jesus was constructed in Ephesus in the former south ''stoa'' (a commercial basilica) of the Temple of Hadrian ''Olympios''. Ephesus was the centre of the Roman province ofAsia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
, and was the site of the city's famed Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It had also been a centre of the Imperial cult of ancient Rome in Asia; Ephesus was three times declared Neocorate () and had constructed a Temple of the Sebastoi to the Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known ...
. The Basilica of the Virgin Mary was probably the venue for the 431 Council of Ephesus and the 449 Second Council of Ephesus, both convened by Theodosius II. At some point during the Christianisation of the Roman world, Christian crosses were cut into the faces of the colossal statues of Augustus and Livia that stood in the basilica-''stoa'' of Ephesus; the crosses were perhaps intended to exorcise demons in a process akin to baptism. In the eastern cemetery of Hierapolis the 5th century domed octagonal ''martyrium'' of Philip the Apostle was built alongside a basilica church, while at Myra the St. Nicholas Church, Demre, Basilica of St Nicholas was constructed at the tomb of Saint Nicholas.
At Constantinople the earliest basilica churches, like the 5th century basilica at the Monastery of Stoudios, were mostly equipped with a small cruciform crypt (), a space under the church floor beneath the altar. Typically, these crypts were accessed from the apse's interior, though not always, as at the 6th century Church of St John at the Hebdomon, where access was from outside the apse. At Thessaloniki, the Roman bath where tradition held Demetrius of Thessaloniki had been martyred was subsumed beneath the 5th century basilica of Hagios Demetrios, forming a crypt.
The largest and oldest basilica churches in Egypt were at Pbow, a coenobitic monastery established by Pachomius the Great in 330. The 4th century basilica was replaced by a large 5th century building (36 × 72 m) with five aisles and internal colonnades of pink granite columns and paved with limestone. This monastery was the administrative centre of the Pachomian order where the monks would gather twice annually and whose library may have produced many surviving manuscripts of biblical, Gnostic, and other texts in Greek and Coptic language, Coptic. In North Africa, late antique basilicas were often built on a doubled plan. In the 5th century, basilicas with two apses, multiple aisles, and doubled churches were common, including examples respectively at Archaeological site of Sbeitla, Sufetula, Tipasa, and Djémila. Generally, North African basilica churches' altars were in the nave and the main building medium was ''opus africanum'' of local stone, and ''spolia'' was infrequently used.
The Church of the East's Council of Seleucia-Ctesiphon was convened by the Sasanian Emperor Yazdegerd I at his capital at Ctesiphon; according to ''Synodicon Orientale'', the emperor ordered that the former churches in the Sasanian Empire to be restored and rebuilt, that such clerics and Asceticism, ascetics as had been imprisoned were to be released, and their Nestorianism, Nestorian Christian communities allowed to circulate freely and practice openly.
In eastern Syria (region), Syria, the Church of the East developed at typical pattern of basilica churches. Separate entrances for men and women were installed in the southern or northern wall; within, the east end of the nave was reserved for men, while women and children were stood behind. In the nave was a ''bema'', from which Scripture could be read, and which were inspired by the equivalent in synagogues and regularised by the Church of Antioch. The Council of 410 stipulated that on Sunday the archdeacon would read the Gospels from the ''bema''. Standing near the ''bema'', the Laity, lay folk could chant responses to the reading and if positioned near the ''šqāqonā'' ("a walled floor-level pathway connecting the ''bema'' to the altar area") could try to kiss or touch the Gospel Book as it was processed from the deacons' room to the ''bema'' and thence to the altar. Some ten Eastern churches in eastern Syria have been investigated by thorough archaeology.
A Christian basilica was constructed in the first half of the 5th century at Olympia, Greece, Olympia, where the Statue of Zeus at Olympia, statue of Zeus by Phidias had been noted as one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World ever since the 2nd century BC list compiled by Antipater of Sidon. Cultural tourism thrived at Olympia and Ancient Greek religion continued to be practised there well into the 4th century. At Nicopolis in Epirus, founded by Augustus to commemorate his victory at the Battle of Actium at the end of the Last war of the Roman Republic, four early Christian basilicas were built during Late Antiquity whose remains survive to the present. In the 4th or 5th century, Nicopolis was surrounded by a new city wall.
In Bulgaria there are major basilicas from that time like Elenska Basilica and the Red Church (Bulgaria), Red Church.
Leonid period
On Crete, the Roman cities suffered from repeated earthquakes in the 4th century, but between c. 450 and c. 550, a large number of Christian basilicas were constructed. Crete was throughout Late Antiquity a Roman province, province of the Diocese of Macedonia, governed from Thessaloniki. Nine basilica churches were built at Nea Anchialos, ancient Phthiotic Thebes (), which was in its heyday the primary port of Thessaly. The episcopal see was the three-aisled ''Basilica A'', the Hagios Demetrios, Church of St Demetrius of Thessaloniki, and similar to the Church of the Acheiropoietos in Thessaloniki. Its atrium perhaps had a pair of towers to either side and its construction dates to the late 5th/early 6th century. The Elpidios Basilica ''Basilica B'' was of similar age, and the city was home to a large complex of ecclesiastical buildings including ''Basilica G'', with its luxurious mosaic floors and a mid-6th century inscription proclaiming the patronage of the bishop Peter. Outside the defensive wall was ''Basilica D'', a 7th-century cemetery church. Stobi, () the capital from the late 4th century of the province of Macedonia Salutaris, Macedonia II Salutaris, had numerous basilicas and six palaces in late antiquity. The ''Old Basilica'' had two phases of geometric pavements, the second phase of which credited the bishop Eustathios as patron of the renovations. A newer episcopal basilica was built by the bishop Philip atop the remains of the earlier structure, and two further basilicas were within the walls. The ''Central Basilica'' replaced a synagogue on a site razed in the late 5th century, and there was also a ''North Basilica'' and further basilicas without the walls. Various mosaics and sculptural decorations have been found there, and while the city suffered from the Ostrogoths in 479 and an earthquake in 518, ceasing to be a major city thereafter, it remained a bishopric until the end of the 7th century and the ''Basilica of Philip'' had its ''templon'' restored in the 8th century. The Small Basilica, Plovdiv, Small Basilica of Philippopolis (Thrace), Philippopolis (Plovdiv, Bulgaria) in Thrace was built in the second half of the 5th century AD.Justinianic period
Justinian I constructed at Ephesus a large basilica church, the Basilica of St. John, Basilica of St John, above the supposed tomb of John the Apostle. The church was a domed cruciform basilica begun in 535/6; enormous and lavishly decorated, it was built in the same style as Justinian's Church of the Holy Apostles in Constantinople. The Justinianic basilica replaced an earlier, smaller structure which Egeria (pilgrim), Egeria had planned to visit in the 4th century, and remains of a aqueduct branch built to supply the complex with water probably dates from Justinian's reign. The Ephesians' basilicas to St Mary and St John were both equipped with Baptistery, baptisteries with filling and draining pipes: both Baptismal font, fonts were flush with the floor and unsuitable for infant baptism. As with most Justinianic baptisteries in the Balkans and Asia Minor, the baptistery at the Basilica of St John was on the northern side of the basilica's nave; the 734 m2 baptistery was separated from the basilica by a 3 m-wide corridor. According to the 6th century Syriac language, Syriac writer John of Ephesus, a Syriac Orthodox Church, Syriac Orthodox Christian, the Heterodoxy, heterodox Miaphysitism, Miaphysites held ordination services in the courtyard of the Basilica of St John under cover of night. Somewhat outside the ancient city on the Ayasuluk Hill, hill of Selçuk, the Justinianic basilica became the centre of the city after the 7th century Arab–Byzantine wars. At Constantinople, Justinian constructed the largest domed basilica: on the site of the 4th century basilica Church of Holy Wisdom, the emperor ordered construction of the huge domed basilica that survives to the present: the Hagia Sophia. This basilica, which "continues to stand as one of the most visually imposing and architecturally daring churches in the Mediterranean", was the cathedral of Constantinople and the patriarchal church of the Patriarch of Constantinople. Hagia Sophia, originally founded by Constantine, was at the social and political heart of Constantinople, near to the Great Palace of Constantinople, Great Palace, the Baths of Zeuxippus, and the Hippodrome of Constantinople, while the headquarters of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarchate was within the basilica's immediate vicinity. The mid-6th century Bishop of Poreč ( la, Parens or ; grc, Πάρενθος, Párenthos, links=no) replaced an earlier 4th century basilica with the magnificent Euphrasian Basilica in the style of contemporary basilicas at Ravenna. Some column Capital (architecture), capitals were of marble from Greece identical to those in Basilica of San Vitale and must have been imported from the Byzantine centre along with the columns and some of the ''opus sectile''. There are Conch (architecture), conch mosaics in the basilica's three apses and the fine ''opus sectile'' on the central apse wall is "exceptionally well preserved". The 4th century basilica of Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, Saint Sophia Church at Serdica (Sofia, Bulgaria) was rebuilt in the 5th century and ultimately replaced by a new monumental basilica in the late 6th century, and some construction phases continued into the 8th century. This basilica was the cathedral of Serdica and was one of three basilicas known to lie outside the walls; three more churches were within the walled city, of which the Church of Saint George, Sofia, Church of Saint George was a former Roman bath built in the 4th century, and another was a former Mithraeum. The basilicas were associated with cemeteries with Christian inscriptions and burials. Another basilica from this period in Bulgaria was the Belovo Basilica (6th century AD). The Miaphysitism, Miaphysite convert from the Church of the East, Ahudemmeh constructed a new basilica c.565 dedicated to Saint Sergius at ''ʿ''Ain Qenoye (or ''ʿ''Ain Qena according to Bar Hebraeus) after being ordained bishop of Dioceses of the Syriac Orthodox Church#Iraq, Beth Arbaye by Jacob Baradaeus and while proselytizing among the Bedouin of Arbayistan in the Sasanian Empire. According to Ahudemmeh's biographer this basilica and its ''martyrium'', in the upper Tigris valley, was supposed to be a copy of the Basilica of St Sergius at Sergiopolis (Resafa), in the middle Euphrates, so that the Arabs would not have to travel so far on pilgrimage. More likely, with the support of Khosrow I for its construction and defence against the Nestorians who were Miaphysites' rivals, the basilica was part of an attempt to control the frontier tribes and limit their contact with the Roman territory of Justinian, who had agreed in the 562 Fifty-Year Peace Treaty to pay 30,000 Solidus (coin), ''nomismata'' annually to Khosrow in return for a demilitarization of the frontier after the latest phase of the Roman–Persian Wars#Byzantine–Sasanian wars, Roman–Persian Wars. After being mentioned in 828 and 936, the basilica at ''ʿ''Ain Qenoye disappeared from recorded history, though it may have remained occupied for centuries, and was rediscovered as a ruin by Carsten Niebuhr in 1766. The name of the modern site Qasr Serīj is derived from the basilica's dedication to St Sergius. Qasr Serīj's construction may have been part of the policy of toleration that Khosrow and his successors had for Miaphysitism a contrast with Justinian's persecution of heterodoxy within the Roman empire. This policy itself encouraged many tribes to favour the Persian cause, especially after the death in 569 of the Ghassanid Kingdom's Miaphysite king al-Harith ibn Jabalah (, ) and the 584 suppression by the Romans of his successors' dynasty.Palace basilicas
They now tended to dominate their cities from opulent palaces and country villas, set a little apart from traditional centers of public life. Rather than retreats from public life, however, these residences were the forum made private. :— Peter Brown, in Paul Veyne, 1987Seated in the tribune (architecture), tribune of his basilica, the great man would meet his dependent ''Patronage in ancient Rome, clientes'' early every morning. Constantine the Great, Constantine's basilica at Trier, the Aula Palatina (AD 306), is still standing. A private basilica excavated at Bulla Regia (Tunisia), in the "House of the Hunt", dates from the first half of the 5th century. Its reception or audience hall is a long rectangular nave-like space, flanked by dependent rooms that mostly also open into one another, ending in a semi-circular apse, with matching transept spaces. Clustered columns emphasised the "crossing" of the two axes.
Christian adoption of the basilica form
Development
Putting an altar instead of the throne, as was done at Trier, made a church. Basilicas of this type were built in western Europe, Greece, Syria, Egypt, and Palestine, that is, at any Early centers of Christianity, early centre of Christianity. Good early examples of the architectural basilica include the Church of the Nativity at Bethlehem (6th century), the church of St Elias at Thessalonica (5th century), and the two great basilicas at Ravenna. The first basilicas with transepts were built under the orders of Emperor Constantine, both in Rome and in his "New Rome", Constantinople:Around 380, Gregory Nazianzen, describing the Constantinian Church of the Holy Apostles at Constantinople, was the first to point out its resemblance to a cross. Because the True Cross, cult of the cross was spreading at about the same time, this comparison met with stunning success. :— Yvon Thébert, in Veyne, 1987Thus, a Christian symbolic theme was applied quite naturally to a form borrowed from civil semi-public precedents. The first great Imperially sponsored Christian basilica is that of Basilica of St. John Lateran, St John Lateran, which was given to the Bishop of Rome by Constantine right before or around the Edict of Milan in 313 and was consecrated in the year 324. In the later 4th century, other Christian basilicas were built in Rome: Santa Sabina, and Basilica of Saint Paul Outside the Walls, St Paul's Outside the Walls (4th century), and later Basilica di San Clemente, St Clement (6th century). A Christian basilica of the 4th or 5th century stood behind its entirely enclosed Courtyard, forecourt ringed with a colonnade or arcade, like the stoa or
peristyle
In ancient Greek and Roman architecture, a peristyle (; from Greek ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. Tetrastoön ( grc, τετράστῳον or τετράστοον, lit=f ...
that was its ancestor or like the cloister that was its descendant. This forecourt was entered from outside through a range of buildings along the public street. This was the architectural ground-plan of Old St. Peter's Basilica, St. Peter's Basilica in Rome, until in the 15th century it was demolished to make way for a modern church built to a new plan.
In most basilicas, the central nave is taller than the aisles, forming a row of windows called a clerestory. Some basilicas in the Caucasus, particularly those of Armenia and Georgia (country), Georgia, have a central nave only slightly higher than the two aisles and a single pitched roof covering all three. The result is a much darker interior. This plan is known as the "oriental basilica", or "pseudobasilica" in central Europe. A peculiar type of basilica, known as three-church basilica, was developed in early medieval Georgia, characterised by the central nave which is completely separated from the aisles with solid walls.
Gradually, in the Early Middle Ages there emerged the massive Romanesque architecture, Romanesque churches, which still kept the fundamental plan of the basilica.
In Bulgarian Empire, Medieval Bulgaria the Great Basilica, Pliska, Great Basilica was finished around 875. The architectural complex in Pliska, the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire, included a cathedral, an archbishop's palace and a monastery. The basilica was one of the greatest Christianity, Christian cathedrals in Europe of the time, with an area of . The still in use Church of Saint Sophia, Ohrid, Church of Saint Sophia in Ohrid is another example from Medieval Bulgaria.
In Romania, the word for church both as a building and as an institution is ''biserică'', derived from the term basilica.
In the United States the style was copied with variances. An American church built imitating the architecture of an Early Christian basilica, St Mary's German Church, St. Mary's (German) Church in Pennsylvania, was demolished in 1997.
Catholic basilicas
 In the Catholic Church, a basilica is a large and important Church (building), church building. This designation may be made by the Pope or may date from time immemorial.1 CIC 1917, can. 1180 as quoted in ''Basilicas Historical and Canonical Development'', GABRIEL CHOW HOI-YAN, Toronto, Ontario, Canada 13 May 2003 (revised 24 June 2003). "It was not until 1917 that the Code of Canon Law officially recognized de jure churches that had the immemorial custom of using the title of basilica as having such a right to the title.81 We refer to such churches as immemorial."The title of minor basilicas was first attributed to the church of Basilica di San Nicola a Tolentino, San Nicola di Tolentino in 1783. An older minor basilica is referred to as an "immemorial basilica". Basilica churches are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building does not need to be a basilica in the architectural sense. Basilicas are either major basilicas – of which there are four, all in the diocese of Rome—or minor basilicas, of which there were 1,810 worldwide . The Umbraculum is displayed in a basilica to the right side (i.e. the Epistle side) of the altar to indicate that the church has been awarded the rank of a basilica.
In the Catholic Church, a basilica is a large and important Church (building), church building. This designation may be made by the Pope or may date from time immemorial.1 CIC 1917, can. 1180 as quoted in ''Basilicas Historical and Canonical Development'', GABRIEL CHOW HOI-YAN, Toronto, Ontario, Canada 13 May 2003 (revised 24 June 2003). "It was not until 1917 that the Code of Canon Law officially recognized de jure churches that had the immemorial custom of using the title of basilica as having such a right to the title.81 We refer to such churches as immemorial."The title of minor basilicas was first attributed to the church of Basilica di San Nicola a Tolentino, San Nicola di Tolentino in 1783. An older minor basilica is referred to as an "immemorial basilica". Basilica churches are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building does not need to be a basilica in the architectural sense. Basilicas are either major basilicas – of which there are four, all in the diocese of Rome—or minor basilicas, of which there were 1,810 worldwide . The Umbraculum is displayed in a basilica to the right side (i.e. the Epistle side) of the altar to indicate that the church has been awarded the rank of a basilica.
See also
* Macellum – Roman covered market * Market hall – modern covered market * Courthouse * Curia * Curia#Municipal curiae, Municipal curiae * Town hallArchitecture
*Architecture of cathedrals and great churches *Byzantine architecture *Church architectureReferences
Citations
General sources
*Architecture of the basilica
* Syndicus, Eduard, ''Early Christian Art'', Burns & Oates, London, 1962
from Samuel Ball Platner (as completed and revised by Thomas Ashby), 1929. ''A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome'' (London: Oxford University Press) * Paul Veyne, ed. ''A History of Private Life I: From Pagan Rome to Byzantium,'' 1987
Heritage Foundation of Newfoundland and Labrador
*
External links
*Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled '' De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attribut ...
, a 1st-century B.C. Roman architect, on :Wikisource:Ten Books on Architecture/Book V, how to design a basilica
{{Authority control
Basilicas,
1st-millennium BC introductions
Ancient Roman architecture
Christian terminology
Roman law
Types of church buildings