Barley bug.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major

 The
The
 Spikelets are arranged in triplets which alternate along the
Spikelets are arranged in triplets which alternate along the
File:Barley grains 4.jpg, Non-hulless, alt=Non-hulless grains
File:Barley grains 3.jpg, Hulless, alt=Hulless grains
 In traditional classifications of barley, these morphological differences have led to different forms of barley being classified as different species. Under these classifications, two-row barley with shattering spikes (wild barley) is classified as ''
In traditional classifications of barley, these morphological differences have led to different forms of barley being classified as different species. Under these classifications, two-row barley with shattering spikes (wild barley) is classified as ''
 * 'Compana', an American variety, was developed from a composite cross by the Idaho and Montana Agricultural Experiment Stations in cooperation with the USDA's Plant Science Research Division. It was released by Montana in 1941. 'Compana' is a two-row variety with moderately weak straw, midshort with midseason maturity. The kernels are long and wide with yellow aleurone. This variety is resistant to loose smut and moderately resistant to covered smut.
* 'Conlon', a two-row barley, was released by NDSU in 1996. Test weight and yield are better than 'Bowman'. Yield is equal to 'Stark'. 'Conlon' heads earlier than 'Bowman' and shows good heat tolerance by kernel plumpness. It is resistant to
* 'Compana', an American variety, was developed from a composite cross by the Idaho and Montana Agricultural Experiment Stations in cooperation with the USDA's Plant Science Research Division. It was released by Montana in 1941. 'Compana' is a two-row variety with moderately weak straw, midshort with midseason maturity. The kernels are long and wide with yellow aleurone. This variety is resistant to loose smut and moderately resistant to covered smut.
* 'Conlon', a two-row barley, was released by NDSU in 1996. Test weight and yield are better than 'Bowman'. Yield is equal to 'Stark'. 'Conlon' heads earlier than 'Bowman' and shows good heat tolerance by kernel plumpness. It is resistant to
 Barley was one of the first domesticated grains in the
Barley was one of the first domesticated grains in the
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
 Some scholars suppose domesticated barley (''Hordeum vulgare'') originally spread from
Some scholars suppose domesticated barley (''Hordeum vulgare'') originally spread from
 Barley is a widely adaptable crop. It is currently popular in temperate areas where it is grown as a summer crop and tropical areas where it is sown as a
Barley is a widely adaptable crop. It is currently popular in temperate areas where it is grown as a summer crop and tropical areas where it is sown as a
 Cooked barley is 69% water, 28%
Cooked barley is 69% water, 28%
 Barley is a key ingredient in
Barley is a key ingredient in
 Barley straw, in England, is placed in mesh bags and floated in fish ponds or water gardens to help prevent algal growth without harming pond plants and animals. Barley straw has not been approved by the EPA for use as a pesticide and its effectiveness as an algae regulator in ponds has produced mixed results, with either more efficacy against phytoplankton algae versus mat-forming algae, or no significant change, during university testing in the US and the UK.
Barley straw, in England, is placed in mesh bags and floated in fish ponds or water gardens to help prevent algal growth without harming pond plants and animals. Barley straw has not been approved by the EPA for use as a pesticide and its effectiveness as an algae regulator in ponds has produced mixed results, with either more efficacy against phytoplankton algae versus mat-forming algae, or no significant change, during university testing in the US and the UK.
Barley Information for Growers, eXtension
{{Authority control Barley, Forages Hordeum, vulgare Phytoremediation plants Founder crops
cereal grain
A cereal is any grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food ...
grown in temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
s globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread
Barley bread is a type of bread made from barley flour derived from the grain of the barley plant. In the British Isles it is a bread which dates back to the Iron Age. Today, barley flour is commonly blended (in a smaller proportion) with wheat fl ...
of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation.
In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
and wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
.
Etymology

 The
The Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
and is cognate to the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries'').
The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation of the form ''bærlic'' in the ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a co ...
'' dates to around 966 CE, in the compound word ''bærlic-croft''.
The underived word ''bære'' survives in the north of Scotland as '' bere'', and refers to a specific strain of six-row barley grown there.
The word ''barn
A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes. In North America, a barn refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain.Alle ...
'', which originally meant "barley-house", is also rooted in these words.
The Latin word ' (''see''), used as barley's scientific genus name, is derived from an Indo-European root meaning "bristly" after the long prickly awns of the ear of grain.
Biology
Barley is a member of the grass family. It is aself-pollinating
Self-pollination is a form of pollination in which pollen from the same plant arrives at the stigma of a flower (in flowering plants) or at the ovule (in gymnosperms). There are two types of self-pollination: in autogamy, pollen is transferred t ...
, diploid species with 14 chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
s. The wild ancestor of domesticated barley, ''Hordeum vulgare'' subsp. ''spontaneum'', is abundant in grasslands and woodlands throughout the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
area of Western Asia and northeast Africa, and is abundant in disturbed habitats, roadsides, and orchards. Outside this region, the wild barley is less common and is usually found in disturbed habitats. However, in a study of genome-wide diversity markers, Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
was found to be an additional center of domestication of cultivated barley.
Domestication
Wild barley
''Hordeum spontaneum'', commonly known as wild barley or spontaneous barley, is the wild form of the grass in the family Poaceae that gave rise to the cereal barley (''Hordeum vulgare''). Domestication is thought to have occurred on two occasio ...
(''H. spontaneum'') is the ancestor of domestic barley (''H. vulgare''). Over the course of domestication, barley grain morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
changed substantially, moving from an elongated shape to a more rounded spherical one. Additionally, wild barley has distinctive gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s, allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s, and regulators with potential for resistance to abiotic
In biology and ecology, abiotic components or abiotic factors are non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems. Abiotic factors and the phenomena associated with them under ...
or biotic stress
Biotic stress is stress that occurs as a result of damage done to an organism by other living organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, beneficial and harmful insects, weeds, and cultivated or native plants. It is different from ...
es to cultivated barley and adaptation to climatic changes. Wild barley has a brittle spike
Spike, spikes, or spiking may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Books
* ''The Spike'' (novel), a novel by Arnaud de Borchgrave
* ''The Spike'' (book), a nonfiction book by Damien Broderick
* ''The Spike'', a starship in Peter F. Hamilto ...
; upon maturity, the spikelet
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots.
Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that ...
s separate, facilitating seed dispersal
In Spermatophyte plants, seed dispersal is the movement, spread or transport of seeds away from the parent plant.
Plants have limited mobility and rely upon a variety of dispersal vectors to transport their seeds, including both abiotic vectors ...
. Domesticated barley has nonshattering spikes, making it much easier to harvest the mature ears. The nonshattering condition is caused by a mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
in one of two tightly linked genes known as Bt1 and Bt2; many cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture ...
s possess both mutations. The nonshattering condition is recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
, so varieties of barley that exhibit this condition are homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
for the mutant allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
.
Domestication in barley is followed by the change of key phenotypic traits at the genetic level. Little is known about the genetic variation among domesticated and wild genes in the chromosomal
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
regions.
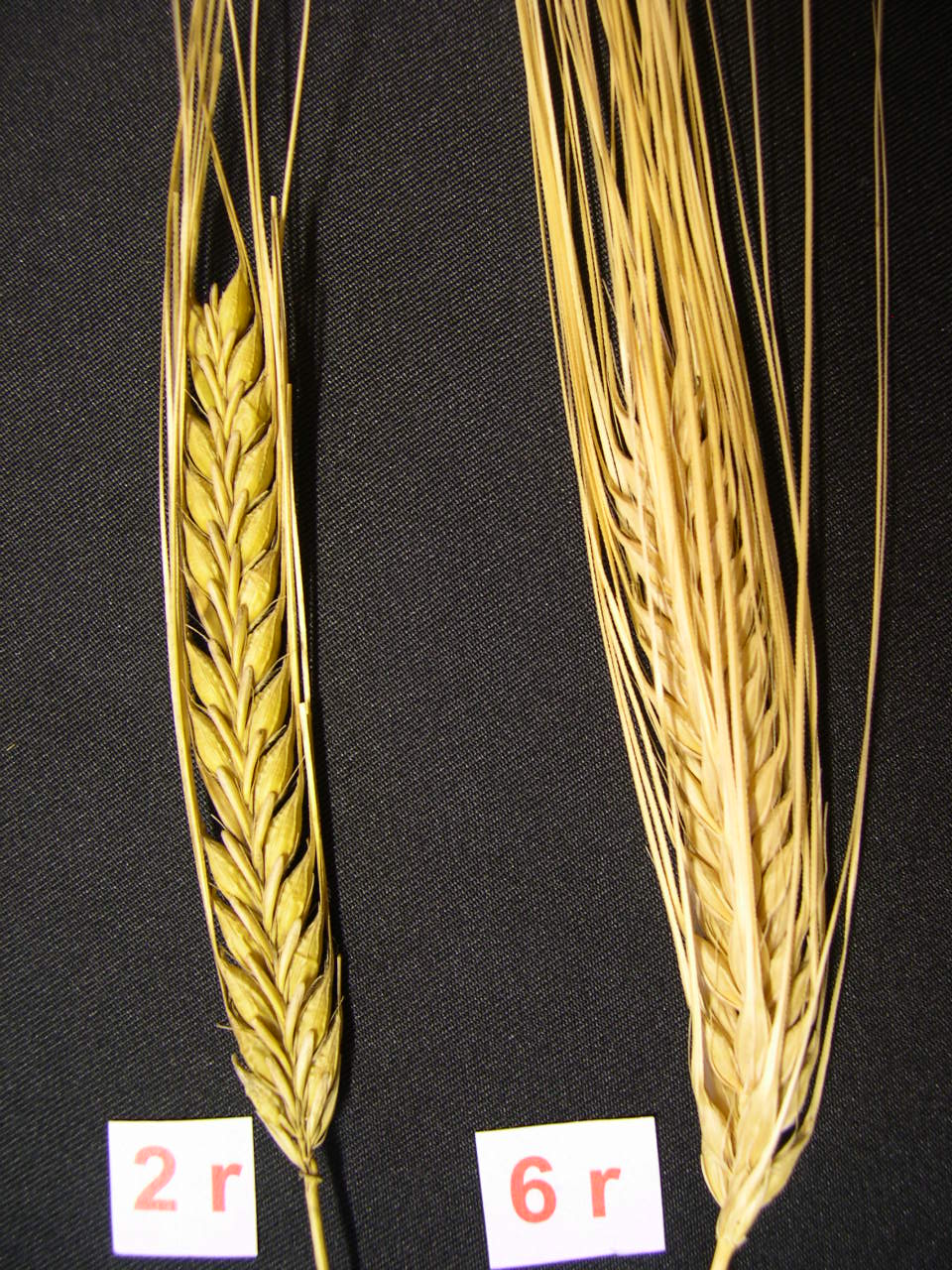
Two-row and six-row barley
rachis
In biology, a rachis (from the grc, ῥάχις [], "backbone, spine") is a main axis or "shaft".
In zoology and microbiology
In vertebrates, ''rachis'' can refer to the series of articulated vertebrae, which encase the spinal cord. In this c ...
. In wild barley (and other Old World species of ''Hordeum''), only the central spikelet is fertile, while the other two are reduced. This condition is retained in certain cultivars known as two-row barleys. A pair of mutations (one dominant, the other recessive) result in fertile lateral spikelets to produce six-row barleys. Recent genetic studies have revealed that a mutation in one gene, ''vrs1'', is responsible for the transition from two-row to six-row barley.
Two-row barley, sometimes considered a separate species, ''Hordeum distichon
''Hordeum distichon'', the common barley or two-rowed barley, is a cultigen of barley, family Poaceae. It is native to Iraq, and is widely grown throughout temperate regions of the world. Some authorities consider it a subspecies of six-rowed bar ...
'', has a lower protein content than six-row barley, thus a more fermentable sugar content. High-protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
barley is best suited for animal feed. Malting barley is usually lower protein ("low grain nitrogen", usually produced without a late fertilizer application) which shows more uniform germination, needs shorter steeping, and has less protein in the extract that can make beer cloudy. Two-row barley is traditionally used in English ale-style beers, with two-row malted summer barley being preferred for traditional German beer
Beer is a major part of German culture. German beer is brewed according to the '' Reinheitsgebot'', which permits only water, hops, and malt as ingredients; and stipulates that beers not exclusively using barley-malt, such as wheat beer, must ...
s.
Amylase-rich six-row barley is common in some American lager
Lager () is beer which has been brewed and conditioned at low temperature. Lagers can be pale, amber, or dark. Pale lager is the most widely consumed and commercially available style of beer. The term "lager" comes from the German for "storag ...
-style beers, especially when adjuncts such as corn and rice are used.
Hulless barley
Hulless or "naked" barley (''Hordeum vulgare ''L. var.'' nudum'' Hook. f.) is a form of domesticated barley with an easier-to-remove hull. Naked barley is an ancient food crop, but a new industry has developed around uses of selected hulless barley to increase the digestible energy of the grain, especially for swine and poultry. Hulless barley has been investigated for several potential new applications as whole grain, and for its value-added products. These include bran and flour for multiple food applications.Classification
 In traditional classifications of barley, these morphological differences have led to different forms of barley being classified as different species. Under these classifications, two-row barley with shattering spikes (wild barley) is classified as ''
In traditional classifications of barley, these morphological differences have led to different forms of barley being classified as different species. Under these classifications, two-row barley with shattering spikes (wild barley) is classified as ''Hordeum spontaneum
''Hordeum spontaneum'', commonly known as wild barley or spontaneous barley, is the wild form of the grass in the Family (biology), family Poaceae that gave rise to the cereal barley (''Hordeum vulgare''). Domestication is thought to have occurr ...
'' (K. Koch
Karl Heinrich Emil Koch (6 June 1809 – 25 May 1879) was a German botanist. He is best known for his botanical explorations in the Caucasus region, including northeast Turkey. Most of his collections have today been lost. He is also known as ...
). Two-row barley with nonshattering spikes is classified as '' H. distichon'' ( L.), six-row barley with nonshattering spikes as ''H. vulgare'' L. (or ''H. hexastichum'' L.), and six-row with shattering spikes as ''H. agriocrithon'' Åberg.
Because these differences were driven by single-gene mutations, coupled with cytological
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
and molecular evidence, most recent classifications treat these forms as a single species, ''H. vulgare'' L.
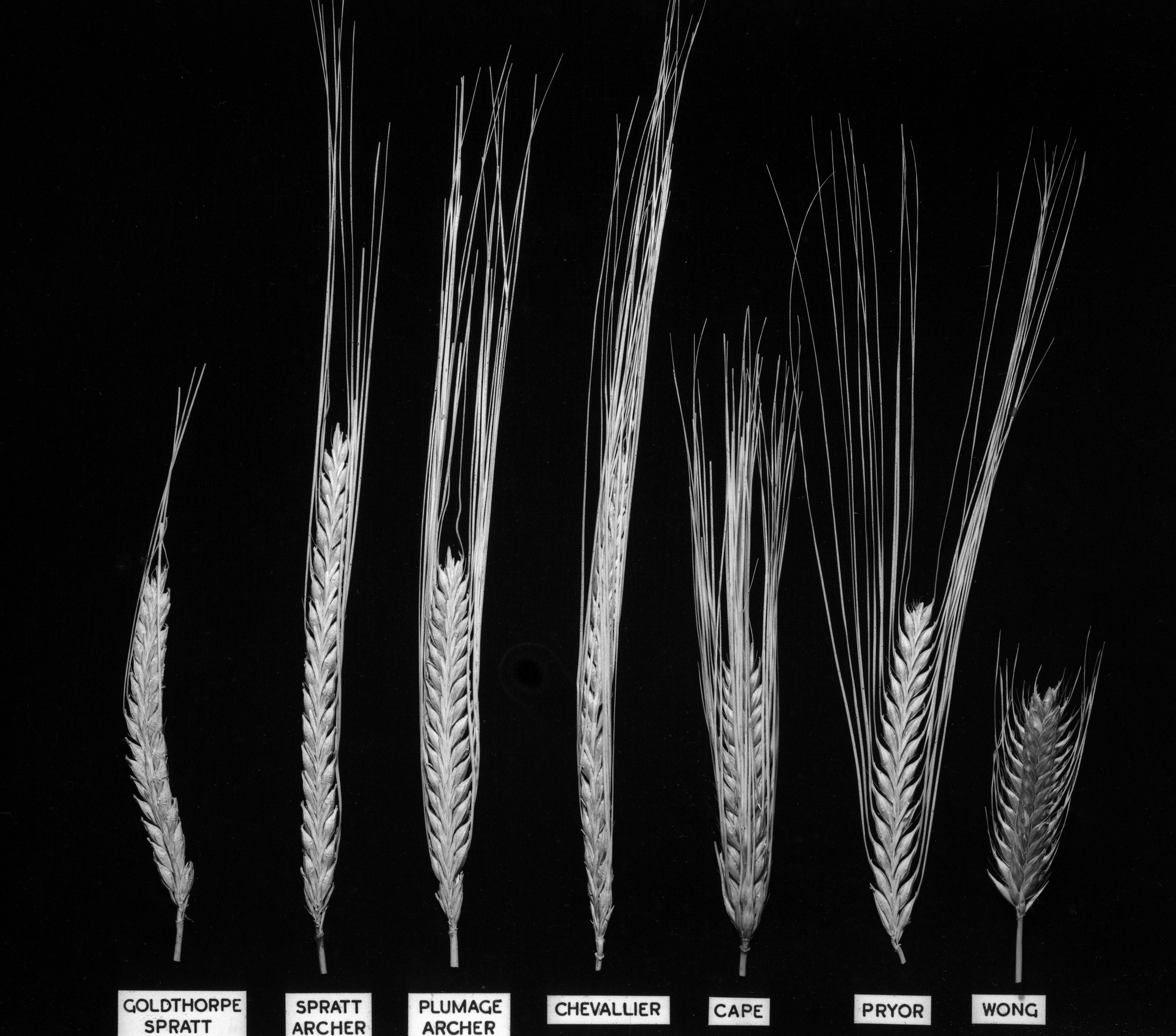
Cultivars
; Vocabulary * DON: Acronym for deoxynivalenol, a toxic byproduct of ''Fusarium'' head blight, also known as vomitoxin * Heading date: A parameter in barley cultivation * Lodging: The bending over of the stems near ground level * ''Nutans'': A designation for a variety with a lax ear, as opposed to 'erectum' (with an erect ear) * QCC: A pathotype ofstem rust
Stem rust, also known as cereal rust, black rust, red rust or red dust, is caused by the fungus ''Puccinia graminis'', which causes significant disease in cereal crops. Crop species that are affected by the disease include bread wheat, durum w ...
(''Puccinia graminis'' f. sp. ''tritici'')
* Rachilla: The part of a spikelet that bears the florets, the length of the rachilla hairs is a characteristic of barley varieties
; Cultivars
* 'Azure', a six-row, blue-aleurone Aleurone (from Greek ''aleuron'', flour) is a protein found in protein granules of maturing seeds and tubers. The term also describes one of the two major cell types of the endosperm, the aleurone layer. The aleurone layer is the outermost layer of ...
malting barley released in 1982, it was high-yielding with strong straw, but was susceptible to loose smut
Loose smut of barley is caused by ''Ustilago nuda''.
It is a disease that can destroy a large proportion of a barley crop. Loose smut replaces grain heads with smut, or masses of spores which infect the open flowers of healthy plants and grow ...
.
* 'Beacon', a six-row malting barley with rough awns, short rachilla hairs and colorless aleurone, it was released in 1973, and was the first North Dakota State University
North Dakota State University (NDSU, formally North Dakota State University of Agriculture and Applied Sciences) is a public land-grant research university in Fargo, North Dakota. It was founded as North Dakota Agricultural College in 1890 as t ...
(NDSU) barley that had resistance to loose smut.
* Bere, a six-row barley, is currently cultivated mainly on 5-15 hectares of land in Orkney, Scotland. Two additional parcels on the island of Islay, Scotland, were planted in 2006 for Bruichladdich Distillery.
* 'Betzes', an old German two-row barley, was introduced into North America from Kraków, Poland, by the United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
(USDA). The Montana and Idaho agricultural experiment stations released Betzes in 1957. It is a midshort, medium strength-strawed, midseason-maturing barley. It has a midsize-to-large kernels with yellow aleurones. Betzes is susceptible to loose and covered smuts, rust
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO( ...
s, and scald The structured computer-aided logic design (SCALD) software was a computer aided design system developed for building the S-1 computer. It used the Stanford University Drawing System (SUDS), and it was developed by Thomas M. McWilliams and Lawrence ...
.
* 'Bowman', a two-rowed, smooth-awned variety, was jointly released by NDSU and USDA in 1984 as a feed barley, spring variety developed in North Dakota. It has good test weight and straw strength. It is resistant to wheat stem rust, but is susceptible to loose smut and barley yellow dwarf virus.
* 'Celebration', a variety developed by the barley breeding program at Busch Agricultural Resources, was released in 2008. Through a collaborative agreement between the NDSU Foundation Seedstocks (NDFSS) project and Busch Agricultural Resources, all foundation seed of 'Celebration' barley will be produced and distributed by the NDFSS. 'Celebration' has excellent agronomic performance and malt quality. It is a Midwestern variety, well-adapted for Minnesota, North Dakota, Idaho, and Montana, with medium-early maturity, medium-early heading, medium-short height, mid-lax head type, rough awns, short rachilla hairs, and colorless aleurone, moderately resistant to ''Septoria
''Septoria'' are ascomycete pycnidia-producing fungi that cause numerous leaf spot diseases on field crops, forages and many vegetables including tomatoes which are known to contract '' Septoria musiva'' from nearby cottonwood trees, and is res ...
'' and net blotch. It has improved reaction to ''Fusarium'' head blight and consistently lower DON content.
* 'Centennial', a Canadian variety, was developed from the cross of 'Lenta' x 'Sanalta' by the University of Alberta
The University of Alberta, also known as U of A or UAlberta, is a Public university, public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford,"A Gentleman of Strathcona – Alexande ...
. It is a two-row, relatively short, stiff-strawed, late-maturing variety. The kernel is midlong with yellow aleurone. It was released as a feed barley.
 * 'Compana', an American variety, was developed from a composite cross by the Idaho and Montana Agricultural Experiment Stations in cooperation with the USDA's Plant Science Research Division. It was released by Montana in 1941. 'Compana' is a two-row variety with moderately weak straw, midshort with midseason maturity. The kernels are long and wide with yellow aleurone. This variety is resistant to loose smut and moderately resistant to covered smut.
* 'Conlon', a two-row barley, was released by NDSU in 1996. Test weight and yield are better than 'Bowman'. Yield is equal to 'Stark'. 'Conlon' heads earlier than 'Bowman' and shows good heat tolerance by kernel plumpness. It is resistant to
* 'Compana', an American variety, was developed from a composite cross by the Idaho and Montana Agricultural Experiment Stations in cooperation with the USDA's Plant Science Research Division. It was released by Montana in 1941. 'Compana' is a two-row variety with moderately weak straw, midshort with midseason maturity. The kernels are long and wide with yellow aleurone. This variety is resistant to loose smut and moderately resistant to covered smut.
* 'Conlon', a two-row barley, was released by NDSU in 1996. Test weight and yield are better than 'Bowman'. Yield is equal to 'Stark'. 'Conlon' heads earlier than 'Bowman' and shows good heat tolerance by kernel plumpness. It is resistant to powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, a ...
and net blotch, but is moderately susceptible to spot blotch. It is prone to lodging under high-yield growing conditions. It appears best adapted to western North Dakota and adjacent western states.
* 'Diamant', a Czech high-yield, is a short-height, mutant variety created with X-rays.
* 'Dickson', a six-row, rough-awned variety, was released by NDSU in 1965. It had good straw strength and was resistant to stem rust, but susceptible to loose smut. 'Dickson' had more resistance to prevalent leaf spot diseases than 'Trophy', 'Larker', and 'Traill'. It was similar to 'Trophy' in heading date, plant height, and straw strength. It had less plumpness than 'Trophy' and 'Larker', but more than 'Traill' and 'Kindred'.
* 'Drummond', a six-row malting variety, was released by NDSU in 2000. It has white aleurone, long rachilla hairs and semismooth awns. 'Drummond' has better straw strength than current six-row varieties. Heading date is similar to Robust and plant height is similar to Stander. It is resistant to spot blotch and moderately susceptible to net blotch. However, its net blotch resistance is better than any current variety. ''Fusarium'' head blight reaction is similar to that of 'Robust'. It is resistant to prevalent races of wheat stem rust, but is susceptible to pathotype Pgt-QCC. 'Drummond' is on the American Malting Barley Association's list of recommended varieties. In two years of plant-scale evaluation, 'Drummond' was found satisfactory by Anheuser-Busch, Inc. and Miller Brewing.
* 'Excel', a six-row, white-aleurone malting barley, was released by Minnesota in 1990. Shorter in height than other six-row barleys grown at that time, it is high-yielding with medium-early maturity, moderately strong straw, smooth awns, and long rachilla hairs. It has high resistance to stem rust and moderate resistance to spot blotch, but is susceptible to loose smut. Malting traits are equal or greater than 'Morex' with plum kernel percentage lower than 'Robust'.
* 'Foster', a six-row, white-aleurone malting barley, was released by NDSU in 1995. About one day earlier and slightly shorter than 'Robust', it is higher-yielding than 'Morex', 'Robust', and 'Hazen'. Straw strength is similar to 'Excel' and 'Stander', but better than 'Robust'. It is moderately susceptible to net blotch, but resistant to spot blotch. Protein is 1.5% lower than 'Robust' and 'Morex'.
* 'Glenn', a six-row, white-aleurone variety, was released by NDSU in 1978. 'Glenn' was resistant to prevalent races of loose and covered smut with better resistance to leaf spot diseases than 'Larker'. It matured about two days earlier than 'Larker' and yielded about 10% more than 'Larker' and 'Beacon'.
* ' Golden Promise', a Scottish semi-dwarf, is a salt-tolerant, mutant
In biology, and especially in genetics, a mutant is an organism or a new genetic character arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is generally an alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome or chromosome of an organism. It ...
variety created with gamma radiation used to make beer and whisky.
* 'Hazen', a six-row, smooth-awn, white-aleurone feed barley, was released by NDSU in 1984. 'Hazen' heads two days later than 'Glenn'. It is susceptible to loose smut.
* Highland barley is a crop cultivated on the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
.
* 'Kindred' was released in 1941 and developed from a selection made by S.T. Lykken, a Kindred, North Dakota
Kindred is a city in Cass County, North Dakota, United States. The population was 889 at the time of the 2020 census. Kindred primarily serves as a bedroom community for Fargo, located about 25 miles to the southwest.
History
Kindred was platt ...
farmer. It was a six-row, rough-awned, medium-early Manchurian-type malting variety that gave good yields. 'Kindred' had stem rust resistance, but was moderately susceptible to spot blotch and ''Septoria
''Septoria'' are ascomycete pycnidia-producing fungi that cause numerous leaf spot diseases on field crops, forages and many vegetables including tomatoes which are known to contract '' Septoria musiva'' from nearby cottonwood trees, and is res ...
''. It was less susceptible to blight and root rot than 'Wisconsin 38'. It was medium-height with weak straw.
* 'Kindred L' is a reselection made to eliminate blue Manchurian types.
* 'Larker', a six-rowed, semi-smooth-awn malting barley, was first released in 1961. It was medium-maturity with moderate straw strength and medium height. 'Larker' was rust-resistant, but susceptible to leaf diseases and loose smut. It was superior to all other malt varieties for kernel plumpness at the time of release.
* 'Logan', released by NDSU in 1995, is classed as a nonmalting barley. It is a white-aleurone, two-row barley similar to 'Bowman' in heading date and plant height and similar to 'Morex' for foliar disease
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomy ...
s. It has better yield, test weight, and lodging score, and lower protein, than 'Bowman' and 'Morex'.
* 'Lux' is a Danish variety.
* 'Manchurian', a blue-aleurone malting variety, was released by NDSU in 1922. It had weak to moderate-stiff straw and was susceptible to stem rust. It was developed from false stripe virus-free stock.
* 'Manscheuri', also designated 'Accession No. 871', is a six-row barley that may have been first released by NDSU before 1904. It outyielded most of the common types being grown in North Dakota at the time. It had stiffer straw than varieties at the time and a longer head filled with large, plump kernels.
* 'Mansury', also designated 'Accession No. 172', is a two-row barley first released by NDSU about 1905.
* 'Maris Otter
Maris Otter is a two-row, autumn sown variety of barley commonly used in the production of malt for the brewing industry. The variety was bred by Dr G D H Bell and his team of plant breeders at the UK's Plant Breeding Institute; the "Maris" ...
' is an English two-row winter variety commonly used in the production of malt for traditional British beers or as a 'maltier' two-row substitute in any style. It remains popular for craft beer and among homebrewers.
* 'Morex', a six-row, white-aleurone, smooth-awn malting variety, was released by Minnesota in 1978. 'Morex', which stands for "more extract", is highly resistant to stem rust, moderate to spot blotch, and susceptible to loose smut.
* 'Nordal', a spring ''nutans'' variety from Carlsberg Sweden, was released in 1971.
* 'Nordic', a six-row, colorless-aleurone feed barley, was released in 1971. It had rough awns and short rachilla hairs. Yield was similar to 'Dickson', but greater than 'Larker'. Kernel plumpness and test weight was superior to 'Dickson', but less than 'Larker'. Lodging, spot, and net blotch resistance was similar to 'Dickson', but it had higher resistance to ''Septoria'' leaf blotch. It showed less leaf rust symptoms compared to other varieties at the time.
* 'Optic'
* 'Pallas'
* 'Park', a six-row, white-aleurone, malting barley, was released in 1978. 'Park' had better resistance to leaf spot diseases, spot blotch, net blotch, and ''Septoria'' leaf blotch than 'Larker'.
* 'Plumage Archer' is an English malt variety.
* 'Pearl'
* 'Pinnacle', a variety released by the North Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station in 2006, has high yield, low protein, long rachilla hairs, smooth awns, white aleurone, medium-late maturity, medium height, and strong straw strength.
* 'Proctor' is a parent cultivar of 'Maris Otter'.
* 'Pioneer' is a parent cultivar of 'Maris Otter'.
* 'Rawson', a variety developed by the NDSU Barley Breeding Program, was released by the North Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station in 2005. 'Rawson's' general characteristics were very large kernels, loose hull, long rachilla hairs, rough awns, white aleurone, medium maturity, medium height, and medium straw strength.
* 'Robust', a six-row, white-aleurone malting variety, was released by Minnesota in 1983. Maturity is two days later than 'Morex'.
* 'Sioux', a selection from Tregal released by NDSU, was a six-row, medium-early variety with white aleurone, rough awns, and long rachilla hairs. It was high-yielding with plump kernels. Its disease reaction was similar to 'Tregal'.
* 'Stark', a two-row nonmalting barley released by NDSU in 1991, has stiff straw and large kernels, and appears best adapted to western North Dakota and adjacent western states. 'Stark' is about one day later and two inches shorter than 'Bowman', with equal or better test weight. 'Stark' yields about 10% better than 'Bowman'. It is moderately resistant to net and spot blotch, but is susceptible to loose smut, leaf rust and the QCC race of wheat stem rust.
* 'Steptoe', a white-kerneled, rough-awned feed variety, was released by Washington State University in 1973. 'Steptoe' is widely adapted and has been one of the highest yielding and most popular six-rowed feed varieties in the inland Pacific northwest for many years.
* 'Tradition', a variety with excellent agronomic performance and malt quality, is well-adapted to Minnesota, North Dakota, Idaho, and Montana. 'Tradition' has medium relative maturity, medium-short height, and very strong straw. It has a nodding head type, semismooth awns, long rachilla hairs. and white aleurone.
* 'Traill', a medium-early, rough-awn, white-aleurone malting variety, was released by NDSU in 1956. It was resistant to stem rust and had the same reaction to spot blotch and ''Septoria'' as 'Kindred'. 'Traill' had greater yield and straw strength than 'Kindred', but had smaller kernel size.
* 'Tregal', a high-yield, smooth-awn, six-row feed barley, was released by NDSU in 1943. It was medium-early with short, stiff straw, erect head, and high resistance to loose smut. 'Tregal' was similar to 'Kindred' for reaction to spot blotch with similar tolerance to ''Septoria''.
* 'Trophy', a six-row, rough-awn malting variety with colorless aleurone, was released by NDSU in 1964. Similar to 'Traill' and 'Kindred' in plant height, heading date, and test weight, it had a higher percentage of plump kernels. Its yield in North Dakota was greater than 'Kindred' and similar to 'Traill'. Similar to 'Kindred' and 'Traill', it was resistant to stem rust, but susceptible to loose smut and ''Septoria'' leaf blotch. It had some field resistance to net blotch. It had greater straw strength than 'Kindred'. 'Trophy' had greater enzymatic activity and quality than 'Traill'.
* 'Windich' is a Western Australian grain cultivar named after Tommy Windich (''circa'' 1840–1876).
* 'Yagan' is a Western Australian grain cultivar named after Yagan
Yagan (; – 11 July 1833) was an Aboriginal Australian warrior from the Noongar people. Yagan was pursued by the local authorities after he killed Erin Entwhistle, a servant of farmer Archibald Butler. It was an act of retaliation after ...
(''circa'' 1795–1833).
Chemistry
''H. vulgare'' contains the phenolicscaffeic acid
Caffeic acid is an organic compound that is classified as a hydroxycinnamic acid. This yellow solid consists of both phenolic and acrylic functional groups. It is found in all plants because it is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, one ...
and p-coumaric acid, the ferulic acid 8,5'-diferulic acid
8,5′-Diferulic acid is a non cyclic type of diferulic acid. It is the predominant diferulic acid in sugar beet pulp. It is also found in barley, in maize bran and rye. 8,5′-Diferulic acid has also been identified to be covalently linked to ...
, the flavonoids catechin-7-O-glucoside
Catechin-7-''O''-glucoside is a flavan-3-ol glycoside formed from catechin.
Natural occurrences
Catechin-7-''O''-glucoside can be isolated from the hemolymph of the European pine sawfly ('' Neodiprion sertifer''). It also occurs in relatively ...
, saponarin
Saponarin is a flavone glucoside. It is found in '' Saponaria officinalis'' and in ''Strongylodon macrobotrys'' where it imparts the characteristic jade color to the flower. This coloration has been shown to be an example of copigmentation, a resu ...
, catechin
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.
The name of the catechin chemical family derives from ''catechu'', which is the tanni ...
, procyanidin B3
Procyanidin B3 is a B type proanthocyanidin. Procyanidin B3 is a catechin dimer (catechin-(4α→8)-catechin).
Natural occurrences
It can be found in red wine, in barley, in beer, in peach or in '' Jatropha macrantha'', the Huanarpo Macho.
H ...
, procyanidin C2
Procyanidin C2 is a B type proanthocyanidin trimer, a type of condensed tannin.
Natural occurrences
Procyanidin C2 is found in grape seeds (''Vitis vinifera'') and wine, in barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), malt and beer, in '' Betula spp.'', in '' ...
, and prodelphinidin B3
Prodelphinidin B3 is a prodelphinidin dimer found in food products such as barley and beer, in fruits and pod vegetables. It can also be found in pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the fami ...
, and the alkaloid hordenine
Hordenine is an alkaloid of the phenethylamine class that occurs naturally in a variety of plants, taking its name from one of the most common, barley (''Hordeum'' species). Chemically, hordenine is the ''N''-methyl derivative of ''N''-methyltyra ...
.
Barley is often assessed by its malting enzyme
Malting is the process of steeping, germinating and drying grain to convert it into malt. The malt is mainly used for brewing or whisky making, but can also be used to make malt vinegar or malt extract. Various grains are used for malting, most o ...
content.
History
Origin
 Barley was one of the first domesticated grains in the
Barley was one of the first domesticated grains in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
, an area of relatively abundant water in Western Asia, and near the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
river of northeast Africa. The grain appeared in the same time as einkorn
Einkorn wheat (from German ''Einkorn'', literally "single grain") can refer either to a wild species of wheat (''Triticum'') or to its domesticated form. The wild form is '' T. boeoticum'' (syn. ''T. m.'' ssp. ''boeoticum''), the domesticated ...
and emmer wheat
Emmer wheat or hulled wheat is a type of awned wheat. Emmer is a tetraploid (4''n'' = 4''x'' = 28 chromosomes). The domesticated types are ''Triticum turgidum'' subsp. ''dicoccum'' and ''Triticum turgidum ''conv.'' durum''. The wild plant is ...
. Wild barley (''H. vulgare'' ssp. ''spontaneum'') ranges from North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
in the west, to Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
in the east. The earliest evidence of the consumption of wild barley in an archaeological context comes from the Epipaleolithic at Ohalo II
Ohalo II is an archaeological site in Northern Israel, near Kinneret, on the southwest shore of the Sea of Galilee. It is one of the best preserved hunter-gatherer archaeological sites of the Last Glacial Maximum, radiocarbon dated to around 23,0 ...
at the southern end of the Sea of Galilee, where grinding stones with traces of starch were found. The remains were dated to about 23,000 BCE. The earliest evidence for the domestication of barley, in the form of cultivars that cannot reproduce without human assistance, comes from Mesopotamia, specifically the Jarmo region of modern-day Iraq, around 9,000-7,000 BCE.
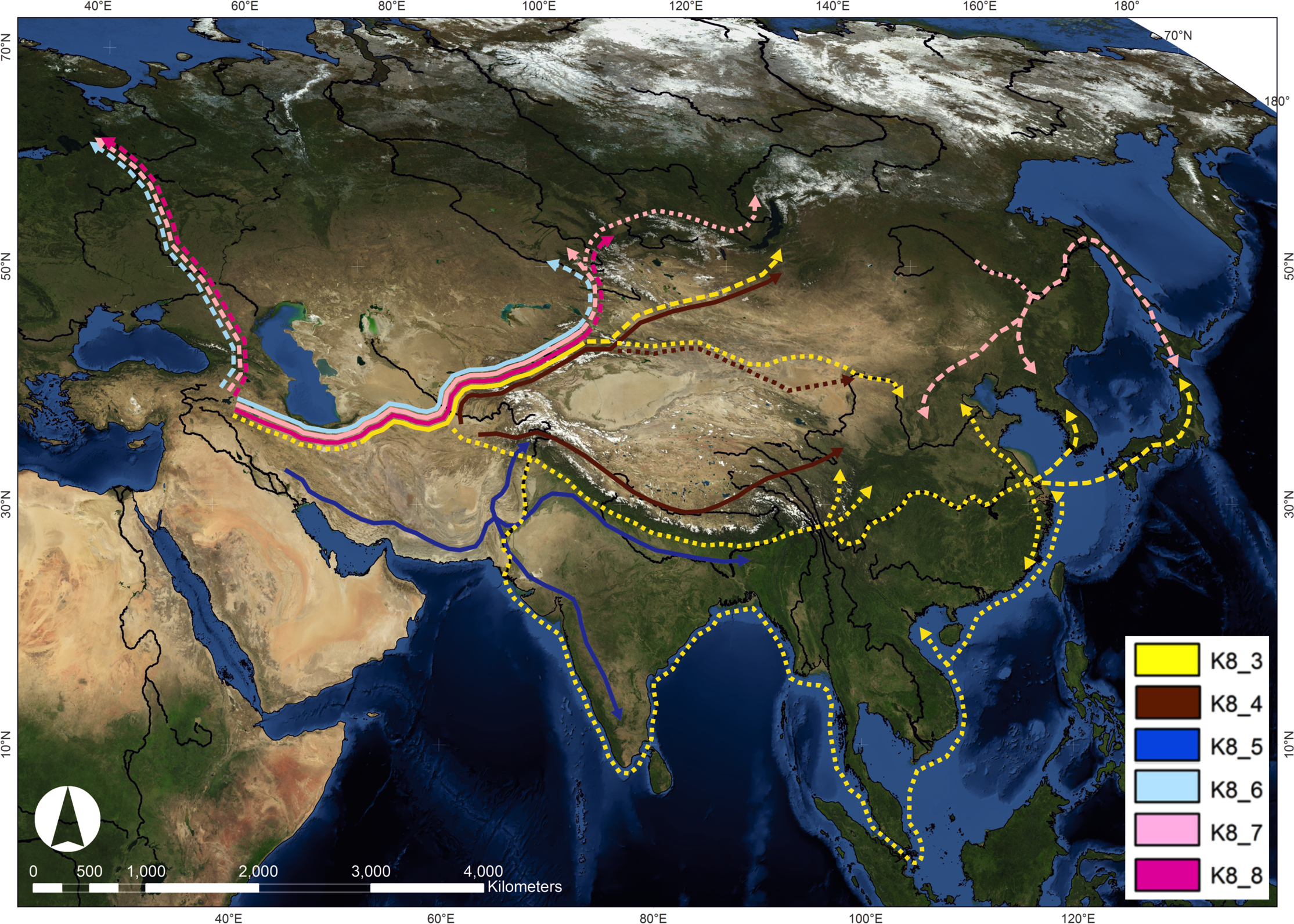
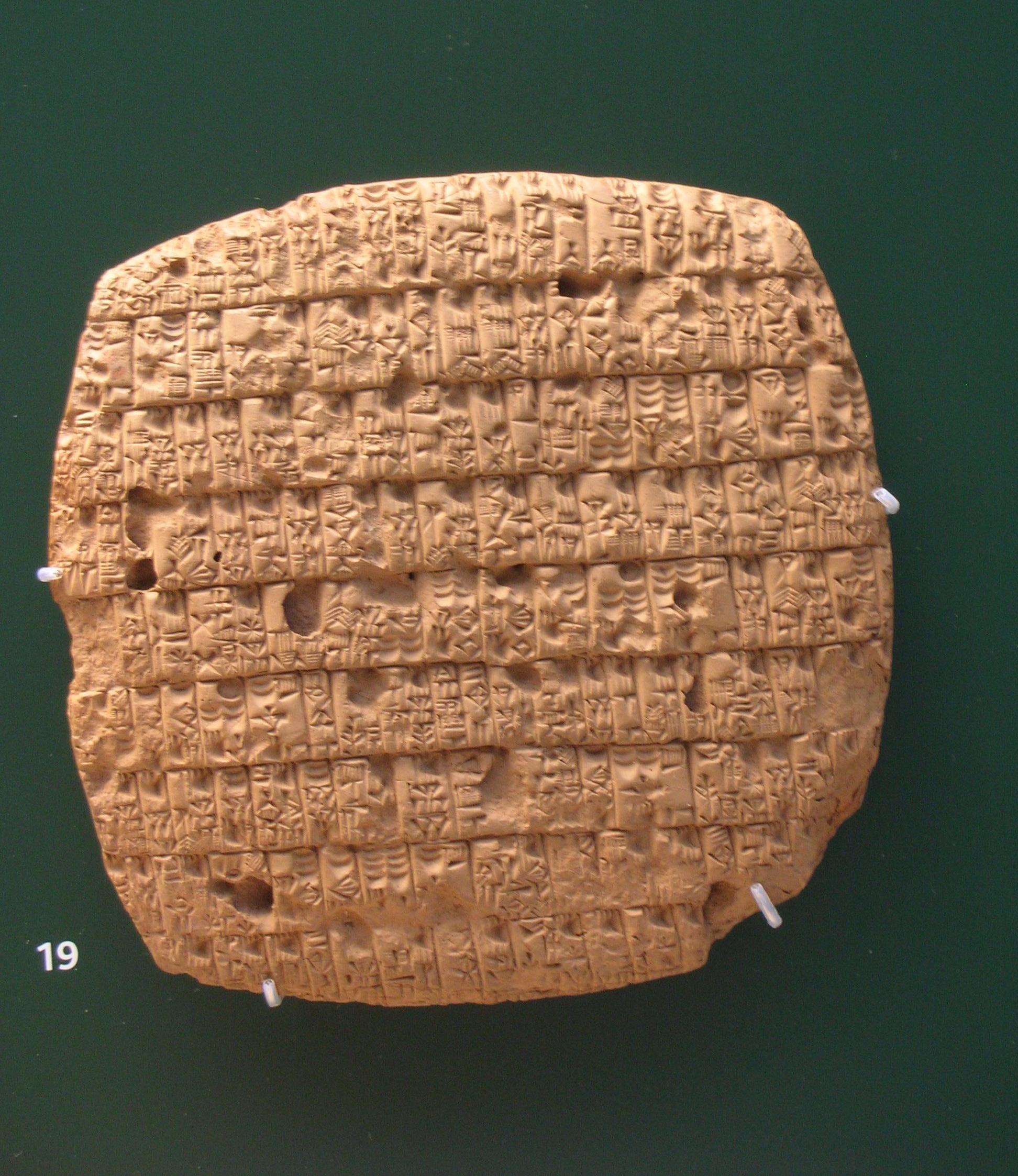
Spread of cultivated barley: genetic analysis
One of the world's most important crops, barley was domesticated in the Near East around 11,000 years ago (circa 9,000 BCE). Barley is a highly resilient crop, able to be grown in varied and marginal environments, such as in regions of high altitude and latitude. Archaeobotanical evidence shows that barley had spread throughout Eurasia by 2,000 BCE. To further elucidate the routes by which barley cultivation was spread through Eurasia, genetic analysis was used to determine genetic diversity and population structure in extant barley taxa. Genetic analysis shows that cultivated barley spread through Eurasia via several different routes, which were most likely separated in both time and space.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Dispersal
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, Syria and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. Some of the earliest domesticated barley occurs at aceramic ("pre-pottery") Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
sites, in the Near East such as the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B
Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to years ago, that is, 8800–6500 BC. It was typed by British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon durin ...
layers of Tell Abu Hureyra, in Syria. By 4200 BCE domesticated barley occurs as far as in Eastern Finland and had reached Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
around the 4th c. BCE. Barley has been grown in the Korean Peninsula since the Early Mumun Pottery Period
The Mumun pottery period is an archaeological era in Korean prehistory that dates to approximately 1500-300 BC. This period is named after the Korean name for undecorated or plain cooking and storage vessels that form a large part of the potter ...
(''circa'' 1500–850 BCE) along with other crops such as millet, wheat, and legumes.
Barley (known as in both Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
and Classical Sanskrit) is only crop which has been mentioned many times in Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
and other Indian scriptures as one of the principal grains in ancient India. Traces of Barley cultivation have also been found in post-Neolithic Bronze Age Harappan civilization 5700–3300 years before present.
In the Pulitzer Prize-winning book ''Guns, Germs, and Steel
''Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies'' (subtitled ''A Short History of Everybody for the Last 13,000 Years'' in Britain) is a 1997 transdisciplinary non-fiction book by Jared Diamond. In 1998, it won the Pulitzer Prize for ge ...
'', Jared Diamond
Jared Mason Diamond (born September 10, 1937) is an American geographer, historian, ornithologist, and author best known for his popular science books '' The Third Chimpanzee'' (1991); ''Guns, Germs, and Steel'' (1997, awarded a Pulitzer Priz ...
proposed that the availability of barley, along with other domesticable crops and animals, in southwestern Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
significantly contributed to the broad historical patterns that human history has followed over approximately the last 13,000 years; ''i.e.'', why Eurasian civilizations, as a whole, have survived and conquered others. Jared Diamond's proposition was criticized, however, for underemphasizing individual and cultural choice and autonomy.
Barley beer was probably one of the first alcoholic drinks developed by Neolithic humans. Barley later on was used as currency. The ancient Sumerian word for barley was ''akiti''. In ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, a stalk of barley was the primary symbol of the goddess Shala
Shala (Šala) was a Mesopotamian goddess of weather and grain and the wife of the weather god Adad. It is assumed that she originated in northern Mesopotamia and that her name might have Hurrian origin. She was worshiped especially in Karkar a ...
. Alongside emmer wheat, barley was a staple cereal of ancient Egypt, where it was used to make bread and beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
. The general name for barley is ''jt'' (hypothetically pronounced "eat"); ''šma'' (hypothetically pronounced "SHE-ma") refers to Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient E ...
ian barley and is a symbol of Upper Egypt. According to Deuteronomy ( 8:8), barley is one of the " Seven Species" of crops that characterize the fertility of the Promised Land
The Promised Land ( he, הארץ המובטחת, translit.: ''ha'aretz hamuvtakhat''; ar, أرض الميعاد, translit.: ''ard al-mi'ad; also known as "The Land of Milk and Honey"'') is the land which, according to the Tanakh (the Hebrew ...
of Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
, and it has a prominent role in the sacrifices
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly exis ...
of the Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
s described in the Five Books of Moses
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the sa ...
(see e.g. 5:15 in the Numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
). It continued to have a religious importance into the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
in Europe, and saw barley's use in justice
Justice, in its broadest sense, is the principle that people receive that which they deserve, with the interpretation of what then constitutes "deserving" being impacted upon by numerous fields, with many differing viewpoints and perspective ...
, via alphitomancy
Alphitomancy (from , and ) is a form of divination involving barley cakes or loaves of barley bread.
When someone in a group was suspected of a crime, the members of the group would be fed barley cakes or slices of barley bread. Supposedly, the ...
and the corsned
In Anglo-Saxon law, corsned ( OE ''cor'', "trial, investigation", + ''snǽd'', "bit, piece"; Latin ''panis conjuratus''), also known as the ''accursed'' or ''sacred'' morsel, or the morsel of execration, was a type of trial by ordeal that consiste ...
.
Rations of barley for workers appear in Linear B tablets in Mycenaean contexts at Knossos
Knossos (also Cnossos, both pronounced ; grc, Κνωσός, Knōsós, ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and has been called Europe's oldest city.
Settled as early as the Neolithic period, the na ...
and at Mycenaean Pylos. In mainland Greece, the ''ritual'' significance of barley possibly dates back to the earliest stages of the Eleusinian Mysteries
The Eleusinian Mysteries ( el, Ἐλευσίνια Μυστήρια, Eleusínia Mystḗria) were initiations held every year for the cult of Demeter and Persephone based at the Panhellenic Sanctuary of Elefsina in ancient Greece. They are th ...
. The preparatory ''kykeon
Kykeon (, ; from , "to stir, to mix") was an Ancient Greek drink of various descriptions. Some were made mainly of water, barley and naturally occurring substances. Others were made with wine and grated cheese. It is widely believed that kykeon us ...
'' or mixed drink of the initiates, prepared from barley and herbs, referred in the Homeric hymn
The ''Homeric Hymns'' () are a collection of thirty-three anonymous ancient Greek hymns celebrating individual gods. The hymns are "Homeric" in the sense that they employ the same epic meter—dactylic hexameter—as the ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'', ...
to Demeter, whose name some scholars believe meant "Barley-mother". The practice was to dry the barley groats
Groats (or in some cases, "berries") are the hulled kernels of various cereal grains, such as oat, wheat, rye, and barley. Groats are whole grains that include the cereal germ and fiber-rich bran portion of the grain, as well as the endospe ...
and roast them before preparing the porridge, according to Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
's '' Natural History'' (xviii.72). This produces malt that soon ferments and becomes slightly alcoholic.
Pliny also noted barley was a special food of gladiators known as ''hordearii'', "barley-eaters". However, by Roman times, he added that wheat had replaced barley as a staple.
Tibetan barley has been a staple food in Tibetan cuisine
Tibetan cuisine includes the culinary traditions and practices and its peoples. The cuisine reflects the Tibetan landscape of mountains and plateaus and includes influences from neighbors (including India and Nepal where many Tibetans abide) ...
since the fifth century CE. This grain, along with a cool climate that permitted storage, produced a civilization that was able to raise great armies. It is made into a flour product called ''tsampa
Tsampa or Tsamba (; ) is a Tibetan and Himalayan staple foodstuff, particularly prominent in the central part of the region. It is glutinous meal made from roasted flour, usually barley flour and sometimes also wheat flour. It is usually mi ...
'' that is still a staple in Tibet. The flour is roasted and mixed with butter and butter tea
Butter tea, also known as ''po cha'' (, "Tibetan tea"), ''cha süma'' (, "churned tea"), Mandarin Chinese: ''sūyóu chá'' ( 酥 油 茶) or ''gur gur cha'' in the Ladakhi language, is a drink of the people in the Himalayan regions of Nepal, Bhut ...
to form a stiff dough that is eaten in small balls.
In medieval Europe, bread made from barley and rye was peasant food, while wheat products were consumed by the upper classes. Potatoes largely replaced barley in Eastern Europe in the 19th century.
Genetics
The genome of barley was sequenced in 2012, due to the efforts of the International Barley Genome Sequencing Consortium and the UK Barley Sequencing Consortium. The genome is composed of seven pairs of nuclear chromosomes (recommended designations: 1H, 2H, 3H, 4H, 5H, 6H and 7H), and one mitochondrial and one chloroplast chromosome, with a total of 5000 Mbp. Abundant biological information is already freely available in several barley databases. The wild barley (''H. vulgare'' ssp.'' spontaneum'') found currently in theFertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
might not be the progenitor of the barley cultivated in Eritrea and Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, indicating that separate domestication may have occurred in eastern Africa.
Being the final end product of food/feed barley and malting barley, both total yield by weight and malting quality are probably influenced by most genes, respectively.
For durable disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
resistance, quantitative resistance is more important than qualitative resistance. The most important foliar disease
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomy ...
s have corresponding resistance gene regions on all chromosomes of barley.
Hybridization
Barley has been crossed with wheat with mixed results that have yet to prove commercially viable. The resulting hybrids have further been crossed with rye, but with even more limited results.Production
In 2020, world production of barley was 157 million tonnes, led byRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
producing 13% of the world total. Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
were major producers.
Cultivation
 Barley is a widely adaptable crop. It is currently popular in temperate areas where it is grown as a summer crop and tropical areas where it is sown as a
Barley is a widely adaptable crop. It is currently popular in temperate areas where it is grown as a summer crop and tropical areas where it is sown as a winter crop
Winter cereals, also called winter grains, fall cereals, fall grains, or autumn-sown grains, are biennial cereal crops sown in the autumn. They germinate before winter comes, may partially grow during mild winters or simply persevere under a suf ...
. Its germination time is one to three days. Barley grows under cool conditions, but is not particularly winter hardy.
Barley is more tolerant of soil salinity than wheat, which might explain the increase of barley cultivation in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
from the second millennium BCE onwards. Barley is not as cold tolerant as the winter wheats (''Triticum aestivum''), fall rye (''Secale cereale'') or winter triticale
Triticale (; × ''Triticosecale'') is a hybrid of wheat (''Triticum'') and rye (''Secale'') first bred in laboratories during the late 19th century in Scotland and Germany. Commercially available triticale is almost always a second-generation ...
(× ''Triticosecale'' Wittm. ex A. Camus.), but may be sown as a winter crop in warmer areas of Australia and Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
.
Barley has a short growing season and is also relatively drought tolerant.
Plant diseases
Stem rust
Stem rust, also known as cereal rust, black rust, red rust or red dust, is caused by the fungus ''Puccinia graminis'', which causes significant disease in cereal crops. Crop species that are affected by the disease include bread wheat, durum w ...
(''Puccinia graminis'' f. sp. ''tritici'', ''Pgt'') affects barley as well as wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
and rye. Stem rust has been absent from Europe for decades, but was detected on wheat and barley in a few areas of Sweden again in 2017. Since then () it has been detected in the same areas every year. Races on this crop in Sweden now include , , , , , , and . Russia now has .
Barley is known or likely to be susceptible to barley mild mosaic bymovirus, as well as bacterial blight
Blight refers to a specific symptom affecting plants in response to infection by a pathogenic organism.
Description
Blight is a rapid and complete chlorosis, browning, then death of plant tissues such as leaves, branches, twigs, or floral org ...
. Barley yellow dwarf virus, vectored by the rice root aphid, can also cause serious crop injury. It can be susceptible to many diseases, but plant breeders have been working hard to incorporate resistance. The devastation caused by any one disease will depend upon the susceptibility of the variety being grown and the environmental conditions during disease development. Serious diseases of barley include powdery mildew caused by ''Blumeria graminis
''Blumeria graminis'' (commonly called barley powdery mildew or corn mildew) is a fungus that causes powdery mildew on grasses, including cereals. It is the only species in the genus ''Blumeria''. It has also been called ''Erysiphe graminis'' and ...
'' f.sp. ''hordei'', leaf scald caused by '' Rhynchosporium secalis'', barley rust caused by '' Puccinia hordei'', crown rust caused by '' P. coronata'', and various diseases caused by ''Cochliobolus sativus
The fungus ''Cochliobolus sativus'' is the teleomorph (sexual stage) of ''Bipolaris sorokiniana'' (anamorph) which is the causal agent of a wide variety of cereal diseases. The pathogen can infect and cause disease on roots (where it is known as ...
''. Barley is also susceptible to head blight.
Food
Nutrition
 Cooked barley is 69% water, 28%
Cooked barley is 69% water, 28% carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or m ...
s, 2% protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
, and 0.4% fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
(table). In a 100-gram (3.5 oz) reference serving, cooked barley provides of food energy
Food energy is chemical energy that animals (including humans) derive from their food to sustain their metabolism, including their muscular activity.
Most animals derive most of their energy from aerobic respiration, namely combining the carbohy ...
and is a good source (10% or more of the Daily Value
The Reference Daily Intake (RDI) used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products in the U.S. and Canada is the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healthy ...
, DV) of essential nutrients, including, dietary fiber, the B vitamin, Niacin (nutrient), niacin (14% DV), and dietary minerals, including iron (10% DV) and manganese (12% DV) (table).
Preparation
Hulled barley (or covered barley) is eaten after removing the inedible, fibrous, outer hull. Once removed, it is called dehulled barley (or pot barley or scotch barley).Simon, André (1963). ''Guide to Good Food and Wines: A Concise Encyclopedia of Gastronomy Complete and Unabridged''. p. 150 Collins, London Considered a whole grain, dehulled barley still has its bran and Cereal germ, germ, making it a commonly consumed food. Pearl barley (or pearled barley) is dehulled barley which has been steam-processed further to remove the bran. It may be polished, a process known as "pearling". Dehulled or pearl barley may be processed into various barley products, including flour, flakes similar to oatmeal, and grits. Barley meal, a wholemeal barley flour lighter than wheat meal but darker in colour, is used in gruel, in contrast to porridge which is made from oats. Barley meal gruel is known as سويق : ''sawīq'' in the Arab world. With a long history of cultivation in the Middle East, barley is used in a wide range of traditional Arab cuisine, Arabic, Assyrian cuisine, Assyrian, Ancient Israelite cuisine, Israelite, Kurdish cuisine, Kurdish, and Persian cuisine, Persian foodstuffs including Keşkek, kashkak, kashk and Murri (condiment), murri. Barley soup is traditionally eaten during Ramadan in Saudi Arabia. Cholent, ''Cholent'' or ''hamin'' (in Hebrew) is a traditional Jewish stew often eaten on Shabbat, Sabbath, in numerous recipes by both Mizrahi Jews, Mizrachi- and Ashkenazi- Jews. In Eastern Europe, Eastern- and Central Europe, Central- Europe, barley is also used in soups and stews such as ričet. In Africa, where it is a traditional food plant, it has the potential to improve nutrition, boost food security, foster rural development, and support sustainable landcare. The six-row variety '' bere'' is cultivated in Orkney, Shetland, Caithness and the Western Isles in the Scottish Highlands and islands. When milled into ''beremeal'', it is used locally in bread, biscuits, and the traditional beremeal Bannock (food), bannock. In Japanese cuisine, Japanese and Korean cuisine, Korean cuisines, barley is steamed like steamed rice. In Japanese, it is mixed withrice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
. Barley rice, called ''mugimeshi'' in Japanese, and ''bori-bap'' (보리밥) in Korean, was long a peasant staple intended to conserve the expensive rice, but the naval surgeon Takaki Kanehiro introduced it into the institutional cooking to combat beriberi, endemic in the armed forces of the time. It remains a staple in the JSDF, but far more publicity it got as a stereotypical prison fare, to the point that "eating ''mugimeshi''" can be heard as a euphemism of "wikt:do time, doing time".
Health implications
According to Health Canada and the US Food and Drug Administration, consuming at least 3 grams per day of barley beta-glucan or 0.75 grams per serving of soluble fiber can lower levels of blood cholesterol, a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Eating whole-grain barley, as well as other high-fiber grains, improves regulation of blood sugar (i.e., reduces blood glucose response to a meal). Consuming breakfast cereals containing barley over weeks to months also improved cholesterol levels and glucose regulation. Likewheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, rye, and their hybrids and derivatives, barley contains gluten, which makes it an unsuitable grain for consumption by people with gluten-related disorders, such as celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity and wheat allergy sufferers, among others. Nevertheless, some wheat allergy patients can tolerate barley or rye.
Beverages
Alcoholic beverages
 Barley is a key ingredient in
Barley is a key ingredient in beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
and whisky production. Two-row barley is traditionally used in German beer, German and Beer in England, English beers. Six-row barley was traditionally used in Beer in the United States, US beers, but both varieties are in common usage now. Distilled from green beer, whisky has been made primarily from barley in Ireland and Scotland, while other countries have used more diverse sources of alcohol, such as the more common corn, rye and wheat in the US. In the US, a grain type may be identified on a whisky label if that type of grain constitutes 51% or more of the ingredients and certain other conditions are satisfied. About 25% of the United States' production of barley is used for malting, for which barley is the best-suited grain.
Barley wine is a style of strong beer from the English brewing tradition. Another alcoholic drink known by the same name, enjoyed in the 18th century, was prepared by boiling barley in water, then mixing the barley water with white wine and other ingredients, such as borage, lemon and sugar. In the 19th century, a different barley wine was made prepared from recipes of ancient Greek origin.
Nonalcoholic beverages
Nonalcoholic drinks such as barley water and roasted barley tea have been made by boiling barley in water. InItaly
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, barley is also sometimes used as coffee substitute, ''caffè d'orzo'' (coffee of barley).
Other uses
Animal feed
Half of the United States' barley production is used as livestock feed. Barley is an important feed grain in many areas of the world not typically suited for maize production, especially in northern climates—for example, northern and eastern Europe. Barley is the principal feed grain inCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, Europe, and in the northern United States. A cattle feeding, finishing diet of barley is one of the defining characteristics of western Canadian beef used in marketing campaigns.
As of 2014, an enzymatic process can be used to make a high-protein fish feed from barley, which is suitable for carnivorous fish such as trout and salmon.
Algistatic
 Barley straw, in England, is placed in mesh bags and floated in fish ponds or water gardens to help prevent algal growth without harming pond plants and animals. Barley straw has not been approved by the EPA for use as a pesticide and its effectiveness as an algae regulator in ponds has produced mixed results, with either more efficacy against phytoplankton algae versus mat-forming algae, or no significant change, during university testing in the US and the UK.
Barley straw, in England, is placed in mesh bags and floated in fish ponds or water gardens to help prevent algal growth without harming pond plants and animals. Barley straw has not been approved by the EPA for use as a pesticide and its effectiveness as an algae regulator in ponds has produced mixed results, with either more efficacy against phytoplankton algae versus mat-forming algae, or no significant change, during university testing in the US and the UK.
Measurement
Barley grains were used for measurement in England, there being three or four Barleycorn (unit), barleycorns to the inch and four or five poppy seeds to the barleycorn. The statute definition of an inch was three barleycorns, although by the 19th century, this had been superseded by standard inch measures. This unit still persists in the shoe sizes used in Britain and the US. As modern studies show, the actual length of a kernel of barley varies from as short as to as long as depending on the cultivar. Older sources stated the average length of a grain of barley to be . The barleycorn was known as ''arpa'' in Turkish, and the feudal system in Ottoman Empire employed the term ''arpalik'', or "barley-money", to refer to a second allowance made to officials to offset the costs of fodder for their horses.Ornamental
A new stabilized variegated variety of ''H. vulgare'', billed as ''H. vulgare'' variegate, has been introduced for cultivation as an ornamental and pot plant for pet cats to nibble.Cultural
In English folklore, the figure of John Barleycorn in the folksong of the same name is a personification of barley, and of the alcoholic beverages made from it: beer and whisky. In the song, John Barleycorn is represented as suffering attacks, death, and indignities that correspond to the various stages of barley cultivation, such as reaping and malting.See also
* Barley wine * Drought tolerance in barley *Hordeum spontaneum
''Hordeum spontaneum'', commonly known as wild barley or spontaneous barley, is the wild form of the grass in the Family (biology), family Poaceae that gave rise to the cereal barley (''Hordeum vulgare''). Domestication is thought to have occurr ...
* Pearl barley
References
Citations
General bibliography
*External links
*Barley Information for Growers, eXtension
{{Authority control Barley, Forages Hordeum, vulgare Phytoremediation plants Founder crops