Anubis Mask from Harrogate - rotating animation - HARGM10686.gif on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Anubis (; grc, Ἄνουβις), also known as Inpu, Inpw, Jnpw, or Anpu in Ancient Egyptian () is the god of death, mummification, embalming, the afterlife, cemeteries, tombs, and the
"
 In Egypt's Early Dynastic period (c. 3100 – c. 2686 BC), Anubis was portrayed in full animal form, with a "
In Egypt's Early Dynastic period (c. 3100 – c. 2686 BC), Anubis was portrayed in full animal form, with a "
 Anubis was a protector of
Anubis was a protector of
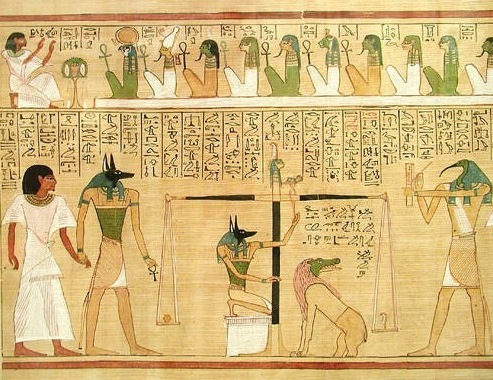 One of the roles of Anubis was as the "Guardian of the Scales." The critical scene depicting the weighing of the heart, in the '' Book of the Dead'', shows Anubis performing a measurement that determined whether the person was worthy of entering the realm of the dead (the
One of the roles of Anubis was as the "Guardian of the Scales." The critical scene depicting the weighing of the heart, in the '' Book of the Dead'', shows Anubis performing a measurement that determined whether the person was worthy of entering the realm of the dead (the
File:Lintel of Amenemhat I and Deities MET DP322051.jpg, Lintel of
Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwor ...
, in ancient Egyptian religion, usually depicted as a canine or a man with a canine head.
Like many ancient Egyptian deities
Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural f ...
, Anubis assumed different roles in various contexts. Depicted as a protector of graves as early as the First Dynasty (c. 3100 – c. 2890 BC), Anubis was also an embalmer. By the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BC) he was replaced by Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He wa ...
in his role as lord of the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwor ...
. One of his prominent roles was as a god who ushered souls into the afterlife. He attended the weighing scale
A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, and weight balances.
The traditional scale consists of two plates or bowls suspended at equal distances from a ...
during the "Weighing of the Heart", in which it was determined whether a soul would be allowed to enter the realm of the dead. Anubis is one of the most frequently depicted and mentioned gods in the Egyptian pantheon
Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural f ...
, however, no relevant myth involved him.
Anubis was depicted in black, a color that symbolized regeneration, life, the soil of the Nile River, and the discoloration of the corpse after embalming. Anubis is associated with his brother Wepwawet
In late Egyptian mythology, Wepwawet ( hieroglyphic ''wp-w3w.t''; also rendered Upuaut, Wep-wawet, Wepawet, and Ophois) was originally a war deity, whose cult centre was Asyut in Upper Egypt (Lycopolis in the Greco-Roman period). His name means ...
, another Egyptian god portrayed with a dog's head or in canine form, but with grey or white fur. Historians assume that the two figures were eventually combined. Anubis' female counterpart is Anput
Anput is a goddess in ancient Egyptian religion. Her name is written in hieroglyphs as ''jnpwt'' (reconstructed in Middle Egyptian as /ʔan.ˈpa.wat/ or /jan.ˈpa.wat/). In English, her name also is rendered as Anupet, Input, Inpewt, and Yinep ...
. His daughter is the serpent goddess Kebechet
In Egyptian mythology, Kebechet (spelt in hieroglyphs as Qeb-Hwt, and also transliterated as Khebhut, Kebehut, Qébéhout, Kabehchet and Kebehwet) is a goddess, a deification of embalming liquid. Her name means ''cooling water''.
Myths
Kebechet ...
.
Name
"Anubis" is a Greek rendering of this god's i-n:p-w-C6 A new form with the jackal on a tall stand appeared in the late Old Kingdom and became common thereafter: i-n:p-w-E16
Anubis' name ''jnpw'' was possibly pronounced .ˈna.pʰa(w) based on Coptic ''Anoup'' and the Akkadian transcription in the name Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
name. Before the Greeks arrived in Egypt, around the 7th century BC, the god was known as ''Anpu'' or ''Inpu.'' The root of the name in ancient Egyptian language means "a royal child." ''Inpu'' has a root to "inp," which means "to decay." The god was also known as "First of the Westerners," "Lord of the Sacred Land," "He Who is Upon his Sacred Mountain," "Ruler of the Nine Bows," "The Dog who Swallows Millions," "Master of Secrets," "He Who is in the Place of Embalming," and "Foremost of the Divine Booth." The positions that he had were also reflected in the titles he held such as "He Who Is upon His Mountain," "Lord of the Sacred Land," "Foremost of the Westerners," and "He Who Is in the Place of Embalming."
In the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth ...
(c. 2686 BC – c. 2181 BC), the standard way of writing his name in hieroglyphs
A hieroglyph (Greek for "sacred carvings") was a character of the ancient Egyptian writing system. Logographic scripts that are pictographic in form in a way reminiscent of ancient Egyptian are also sometimes called "hieroglyphs". In Neoplatonis ...
was composed of the sound signs ''inpw'' followed by a jackal over a ''ḥtp
Hotep (; also rendered ''hetep'') is an Egyptian word that roughly translates as "to be satisfied, at peace". The word also refers to an "offering" ritually presented to a deity or a dead person, hence "be pleased, be gracious, be at peace". ...
'' sign: Reanap Reanap, also Reanapa (cuneiform: ''ri-a-na-pa'') was an ancient Egyptian commissioner, of the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters, written from a 15–20 year time period. Of the 382 El-Amarna letters correspondence, Reanapa is referenced in three:
:* ...
a" that appears in Amarna letter
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between ...
EA 315. However, this transcription may also be interpreted as ''rˁ-nfr'', a name similar to that of Prince Ranefer of the Fourth Dynasty
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other ...
.
History
 In Egypt's Early Dynastic period (c. 3100 – c. 2686 BC), Anubis was portrayed in full animal form, with a "
In Egypt's Early Dynastic period (c. 3100 – c. 2686 BC), Anubis was portrayed in full animal form, with a "jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
" head and body. A jackal god, probably Anubis, is depicted in stone inscriptions from the reigns of Hor-Aha, Djer, and other pharaohs of the First Dynasty. Since Predynastic Egypt
Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt span the period from the earliest human settlement to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period around 3100 BC, starting with the first Pharaoh, Narmer for some Egyptologists, Hor-Aha for others, with ...
, when the dead were buried in shallow graves, jackals had been strongly associated with cemeteries because they were scavengers which uncovered human bodies and ate their flesh. In the spirit of "fighting like with like," a jackal was chosen to protect the dead, because "a common problem (and cause of concern) must have been the digging up of bodies, shortly after burial, by jackals and other wild dogs which lived on the margins of the cultivation."
In the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth ...
, Anubis was the most important god of the dead. He was replaced in that role by Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He wa ...
during the Middle Kingdom (2000–1700 BC). In the Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
, which started in 30 BC, tomb paintings depict him holding the hand of deceased persons to guide them to Osiris.
The parentage of Anubis varied between myths, times and sources. In early mythology, he was portrayed as a son of Ra. In the Coffin Texts, which were written in the First Intermediate Period (c. 2181–2055 BC), Anubis is the son of either the cow goddess Hesat or the cat-headed Bastet
Bastet or Bast ( egy, bꜣstjt, cop, Ⲟⲩⲃⲁⲥⲧⲉ, Oubaste , Phoenician: 𐤀𐤁𐤎𐤕, romanized: ’bst, or 𐤁𐤎𐤕, romanized: bst) was a goddess of ancient Egyptian religion, worshipped as early as the Second Dynasty (2 ...
. Another tradition depicted him as the son of Ra and Nephthys. The Greek Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
(c. 40–120 AD) reported a tradition that Anubis was the illegitimate son of Nephthys and Osiris, but that he was adopted by Osiris's wife Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kin ...
:
George Hart sees this story as an "attempt to incorporate the independent deity Anubis into the Osirian pantheon." An Egyptian papyrus from the Roman period (30–380 AD) simply called Anubis the "son of Isis."
In Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or ...
, Anubis was seen as the husband of his mother Nephthys.
In the Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
period (350–30 BC), when Egypt became a Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
kingdom ruled by Greek pharaohs, Anubis was merged with the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
god Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
, becoming Hermanubis
Hermanubis ( grc, Ἑρμανοῦβις, translit=Hermanoubis) is a Graeco-Egyptian god who conducts the souls of the dead to the underworld. He is a syncretism of Hermes from Greek mythology and Anubis from Egyptian mythology.
Description
Her ...
. The two gods were considered similar because they both guided souls to the afterlife. The center of this cult was in ''uten-ha''/''Sa-ka''/ Cynopolis
Cynopolis ( gr, Κυνόπολις for "city of the dog") was the Hellenistic toponym for two cities in ancient Egypt. Both Cynopolis superior and Cynopolis inferior were bishoprics in Christian times.
Cynopolis superior
Cynopolis was the Gre ...
, a place whose Greek name means "city of dogs." In Book XI of ''The Golden Ass
The ''Metamorphoses'' of Apuleius, which Augustine of Hippo referred to as ''The Golden Ass'' (''Asinus aureus''), is the only ancient Roman novel in Latin to survive in its entirety.
The protagonist of the novel is Lucius. At the end of the no ...
'' by Apuleius
Apuleius (; also called Lucius Apuleius Madaurensis; c. 124 – after 170) was a Numidian Latin-language prose writer, Platonist philosopher and rhetorician. He lived in the Roman province of Numidia, in the Berber city of Madauros, modern- ...
, there is evidence that the worship of this god was continued in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
through at least the 2nd century. Indeed, Hermanubis also appears in the alchemical
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
and hermetical literature of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
.
Although the Greeks and Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
typically scorned Egyptian animal-headed gods as bizarre and primitive (Anubis was mockingly called "Barker" by the Greeks), Anubis was sometimes associated with Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CM ...
in the heavens and Cerberus
In Greek mythology, Cerberus (; grc-gre, Κέρβερος ''Kérberos'' ), often referred to as the hound of Hades, is a multi-headed dog that guards the gates of the Underworld to prevent the dead from leaving. He was the offspring of the ...
and Hades in the underworld. In his dialogues, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
often has Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no te ...
utter oaths "by the dog" (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: ''kai me ton kuna''), "by the dog of Egypt", and "by the dog, the god of the Egyptians", both for emphasis and to appeal to Anubis as an arbiter of truth in the underworld.
Roles
Embalmer
As ''jmy-wt'' (Imiut or theImiut fetish
The Imiut fetish (''jmy-wt'') is a religious object that has been documented throughout the history of ancient Egypt. It was a stuffed, headless animal skin, often of a feline or bull. This fetish was tied by the tail to a pole, terminating in a ...
) "He who is in the place of embalming
Embalming is the art and science of preserving human remains by treating them (in its modern form with chemicals) to forestall decomposition. This is usually done to make the deceased suitable for public or private viewing as part of the funeral ...
", Anubis was associated with mummification
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
. He was also called ''ḫnty zḥ-nṯr'' "He who presides over the god's booth", in which "booth" could refer either to the place where embalming was carried out or the pharaoh's burial chamber.
In the Osiris myth, Anubis helped Isis to embalm Osiris. Indeed, when the Osiris myth emerged, it was said that after Osiris had been killed by Set, Osiris's organs were given to Anubis as a gift. With this connection, Anubis became the patron god of embalmers; during the rites of mummification, illustrations from the '' Book of the Dead'' often show a wolf-mask-wearing priest supporting the upright mummy.
Protector of tombs
 Anubis was a protector of
Anubis was a protector of grave
A grave is a location where a dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as grav ...
s and cemeteries. Several epithets attached to his name in Egyptian texts and inscriptions referred to that role. '' Khenty-Amentiu'', which means "foremost of the westerners" and was also the name of a different canine funerary god, alluded to his protecting function because the dead were usually buried on the west bank of the Nile. He took other names in connection with his funerary role, such as ''tpy-ḏw.f'' (Tepy-djuef) "He who is upon his mountain" (i.e. keeping guard over tombs from above) and ''nb-t3-ḏsr'' (Neb-ta-djeser) "Lord of the sacred land", which designates him as a god of the desert necropolis.
The Jumilhac papyrus recounts another tale where Anubis protected the body of Osiris from Set. Set attempted to attack the body of Osiris by transforming himself into a leopard. Anubis stopped and subdued Set, however, and he branded Set's skin with a hot iron rod. Anubis then flayed
Flaying, also known colloquially as skinning, is a method of slow and painful execution in which skin is removed from the body. Generally, an attempt is made to keep the removed portion of skin intact.
Scope
A dead animal may be flayed when pr ...
Set and wore his skin as a warning against evil-doers who would desecrate the tombs of the dead. Priests who attended to the dead wore leopard skin in order to commemorate Anubis' victory over Set. The legend of Anubis branding the hide of Set in leopard form was used to explain how the leopard got its spots.
Most ancient tombs had prayers to Anubis carved on them.
Guide of souls
By the late pharaonic era (664–332 BC), Anubis was often depicted as guiding individuals across the threshold from the world of the living to the afterlife. Though a similar role was sometimes performed by the cow-headedHathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sk ...
, Anubis was more commonly chosen to fulfill that function. Greek writers from the Roman period of Egyptian history designated that role as that of "psychopomp
Psychopomps (from the Greek word , , literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are supernatural creatures, spirits, entities, angels, demons or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly deceased souls from Earth to the afte ...
", a Greek term meaning "guide of souls" that they used to refer to their own god Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
, who also played that role in Greek religion. Funerary art
Funerary art is any work of art forming, or placed in, a repository for the remains of the dead. The term encompasses a wide variety of forms, including cenotaphs ("empty tombs"), tomb-like monuments which do not contain human remains, and comm ...
from that period represents Anubis guiding either men or women dressed in Greek clothes into the presence of Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He wa ...
, who by then had long replaced Anubis as ruler of the underworld.
Weigher of hearts
 One of the roles of Anubis was as the "Guardian of the Scales." The critical scene depicting the weighing of the heart, in the '' Book of the Dead'', shows Anubis performing a measurement that determined whether the person was worthy of entering the realm of the dead (the
One of the roles of Anubis was as the "Guardian of the Scales." The critical scene depicting the weighing of the heart, in the '' Book of the Dead'', shows Anubis performing a measurement that determined whether the person was worthy of entering the realm of the dead (the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwor ...
, known as ''Duat
The Duat ( egy, dwꜣt, Egyptological pronunciation "do-aht", cop, ⲧⲏ, also appearing as ''Tuat'', ''Tuaut'' or ''Akert'', ''Amenthes'', ''Amenti'', or ''Neter-khertet'') is the realm of the dead in ancient Egyptian mythology. It has been ...
''). By weighing the heart of a deceased person against Ma'at
Maat or Maʽat ( Egyptian:
mꜣꜥt /ˈmuʀʕat/, Coptic: ⲙⲉⲓ) refers to the ancient Egyptian concepts of truth, balance, order, harmony, law, morality, and justice. Ma'at was also the goddess who personified these concepts, and regul ...
(or "truth"), who was often represented as an ostrich feather, Anubis dictated the fate of souls. Souls heavier than a feather would be devoured by Ammit
Ammit (; egy, ꜥm-mwt, "devourer of the dead";Erman, Adolf; Grapow, Hermann (1926-1961) ''Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache'', Berlin: Akademie-Verlag, volume 1, page 184.9 also rendered Ammut or Ahemait) was a goddess in ancient Egyptian ...
, and souls lighter than a feather would ascend to a heavenly existence.
Portrayal in art
Anubis was one of the most frequently represented deities inancient Egyptian art
Ancient Egyptian art refers to art produced in ancient Egypt between the 6th millennium BC and the 4th century AD, spanning from Prehistoric Egypt until the Christianization of Roman Egypt. It includes paintings, sculptu ...
. He is depicted in royal tombs as early as the First Dynasty. The god is typically treating a king's corpse, providing sovereign to mummification rituals and funerals, or standing with fellow gods at the Weighing of the Heart of the Soul in the Hall of Two Truths. One of his most popular representations is of him, with the body of a man and the head of a jackal with pointed ears, standing or kneeling, holding a gold scale while a heart of the soul is being weighed against Ma'at
Maat or Maʽat ( Egyptian:
mꜣꜥt /ˈmuʀʕat/, Coptic: ⲙⲉⲓ) refers to the ancient Egyptian concepts of truth, balance, order, harmony, law, morality, and justice. Ma'at was also the goddess who personified these concepts, and regul ...
's white truth feather.
In the early dynastic period, he was depicted in animal form, as a black canine. Anubis's distinctive black color did not represent the animal, rather it had several symbolic meanings. It represented "the discolouration of the corpse after its treatment with natron
Natron is a naturally occurring mixture of sodium carbonate decahydrate ( Na2CO3·10H2O, a kind of soda ash) and around 17% sodium bicarbonate (also called baking soda, NaHCO3) along with small quantities of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate. ...
and the smearing of the wrappings with a resinous substance during mummification." Being the color of the fertile silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
of the River Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
, to Egyptians, black also symbolized fertility and the possibility of rebirth in the afterlife. In the Middle Kingdom, Anubis was often portrayed as a man with the head of a jackal. An extremely rare depiction of him in fully human form was found in a chapel of Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded as ...
in Abydos.
Anubis is often depicted wearing a ribbon and holding a ''nḫ3ḫ3'' "flail
A flail is an agriculture, agricultural tool used for threshing, the process of separating cereal, grains from their husks.
It is usually made from two or more large sticks attached by a short chain; one stick is held and swung, causing the othe ...
" in the crook of his arm. Another of Anubis's attributes was the ''jmy-wt'' or imiut fetish
The Imiut fetish (''jmy-wt'') is a religious object that has been documented throughout the history of ancient Egypt. It was a stuffed, headless animal skin, often of a feline or bull. This fetish was tied by the tail to a pole, terminating in a ...
, named for his role in embalming.
In funerary contexts, Anubis is shown either attending to a deceased person's mummy or sitting atop a tomb protecting it. New Kingdom tomb-seals also depict Anubis sitting atop the nine bows
The Nine Bows is a visual representation in Ancient Egyptian art of foreigners or others. Besides the nine bows, there were no other generic representations of foreigners. Due to its ability to stand in for any nine enemies to Ancient Egypt, the ...
that symbolize his domination over the enemies of Egypt.
Gallery
Amenemhat I
:''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.''
Amenemhat I ( Ancient Egyptian: ''Ỉmn-m-hꜣt'' meaning 'Amun is at the forefront'), also known as Amenemhet I, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the first king of the Twelfth Dynas ...
and deities; 1981–1952 BC; painted limestone; 36.8 × 172 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
(New York City)
File:Tutankhamun jackal.jpg, The ''Anubis Shrine
The Anubis Shrine was part of the burial equipment of the 18th Dynasty pharaoh Tutankhamun, whose tomb in the Valley of the Kings was discovered almost intact in 1922 by Egyptologists led by Howard Carter. Today the object, with the find ...
''; 1336–1327 BC; painted wood and gold; 1.1 × 2.7 × 0.52 m; from the Valley of the Kings
The Valley of the Kings ( ar, وادي الملوك ; Late Coptic: ), also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings ( ar, وادي أبوا الملوك ), is a valley in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the 16th to 11th ...
; Egyptian Museum (Cairo)
File:Hermitage hall 100 - Egyptian hall 46.jpg, Stela depicting Anubis receiving offerings from king Tutankhamun's fanbearer Ipy; 14th century BC; painted limestone; from Saqqara
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis ...
(Egypt); Hermitage (Sankt Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, Russia)
File:The King with Anubis, Tomb of Haremhab MET DP234736.jpg, The king with Anubis, from the tomb of Horemheb; 1323-1295 BC; tempera on paper; Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:Anubis Amulet MET DP109371.jpg, Anubis amulet; 664–30 BC; faience; height: 4.7 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:Recumbent Anubis MET DP228716.jpg, Recumbent Anubis; 664–30 BC; limestone, originally painted black; height: 38.1 cm, length: 64 cm, width: 16.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:Statuette of Anubis MET 38.5 EGDP022863.jpg, Statuette of Anubis; 332–30 BC; plastered and painted wood; 42.3 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:Casa degli Amorini Dorati. Fresco. 09.JPG, Anubis, Harpocrates
Harpocrates ( grc, Ἁρποκράτης, Phoenician: 𐤇𐤓𐤐𐤊𐤓𐤈, romanized: ḥrpkrṭ, ''harpokrates'') was the god of silence, secrets and confidentiality in the Hellenistic religion developed in Ptolemaic Alexandria (and also ...
, Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kin ...
and Serapis
Serapis or Sarapis is a Graeco-Egyptian deity. The cult of Serapis was promoted during the third century BC on the orders of Greek Pharaoh Ptolemy I Soter of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt as a means to unify the Greeks and Egyptians in his r ...
, antique fresco in Pompeii, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
Worship
Although he does not appear in many myths, he was extremely popular with Egyptians and those of other cultures. TheGreeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
linked him to their god Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
, the god who guided the dead to the afterlife. The pairing was later known as Hermanubis
Hermanubis ( grc, Ἑρμανοῦβις, translit=Hermanoubis) is a Graeco-Egyptian god who conducts the souls of the dead to the underworld. He is a syncretism of Hermes from Greek mythology and Anubis from Egyptian mythology.
Description
Her ...
. Anubis was heavily worshipped because, despite modern beliefs, he gave the people hope. People marveled in the guarantee that their body would be respected at death, their soul would be protected and justly judged.
Anubis had male priests who sported wood masks with the god's likeness when performing rituals. His cult center was at Cynopolis
Cynopolis ( gr, Κυνόπολις for "city of the dog") was the Hellenistic toponym for two cities in ancient Egypt. Both Cynopolis superior and Cynopolis inferior were bishoprics in Christian times.
Cynopolis superior
Cynopolis was the Gre ...
in Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient E ...
but memorials were built everywhere and he was universally revered in every part of the nation.
In popular culture
In popular and media culture, Anubis is often falsely portrayed as the sinister god of the dead. He gained popularity during the 20th and 21st centuries through books, video games, and movies where artists would give him evil powers and a dangerous army. Despite his nefarious reputation, his image is still the most recognizable of the Egyptian gods and replicas of his statues and paintings remain popular.See also
* ''Anubias
''Anubias'' is a genus of aquatic and semi-aquatic flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to tropical central and western Africa. They primarily grow in rivers and streams, but can also be found in marshes. They are characterized by broad ...
''
* Egyptian mythology in popular culture
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
* Animal mummy#Miscellaneous animals
* Abatur
Abatur ( myz, ࡀࡁࡀࡕࡅࡓ, sometimes called Abathur; Yawar, myz, ࡉࡀࡅࡀࡓ; and the Ancient of Days) is an Uthra and the second of three subservient emanations created by the Mandaean God '' Hayyi Rabbi'' ( myz, ࡄࡉࡉࡀ ࡓࡁ ...
, Mandaean uthra
An uthra or ʿutra ( myz, ࡏࡅࡕࡓࡀ; plural: ʿutri) is a "divine messenger of the light" in Mandaeism. Charles G. Häberl and James F. McGrath translate it as "excellency". Jorunn J. Buckley defines them as "Lightworld beings, called 'u ...
who weighs the souls of the dead to determine their fate
* Hades
* Anput
Anput is a goddess in ancient Egyptian religion. Her name is written in hieroglyphs as ''jnpwt'' (reconstructed in Middle Egyptian as /ʔan.ˈpa.wat/ or /jan.ˈpa.wat/). In English, her name also is rendered as Anupet, Input, Inpewt, and Yinep ...
* Bhairava
Bhairava (Sanskrit: भैरव ) or Kala Bhairava is a Shaivite and Vajrayāna deity worshiped by Hindus and Buddhists. In Shaivism, he is a powerful manifestation, or avatar, of Shiva associated with annihilation. In Trika system ''Bhaira ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
{{Portal bar, Ancient Egypt, Mythology, Religion Animal gods Canines in religion Death gods Egyptian death gods Egyptian gods Egyptian underworld Mythological canines Mythological human hybrids Psychopomps Underworld gods Wolves in folklore, religion and mythology